Assessing Salinity Tolerance in Rice Mutants by Phenotypic Evaluation Alongside Simple Sequence Repeat Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Phenotypic Evaluation
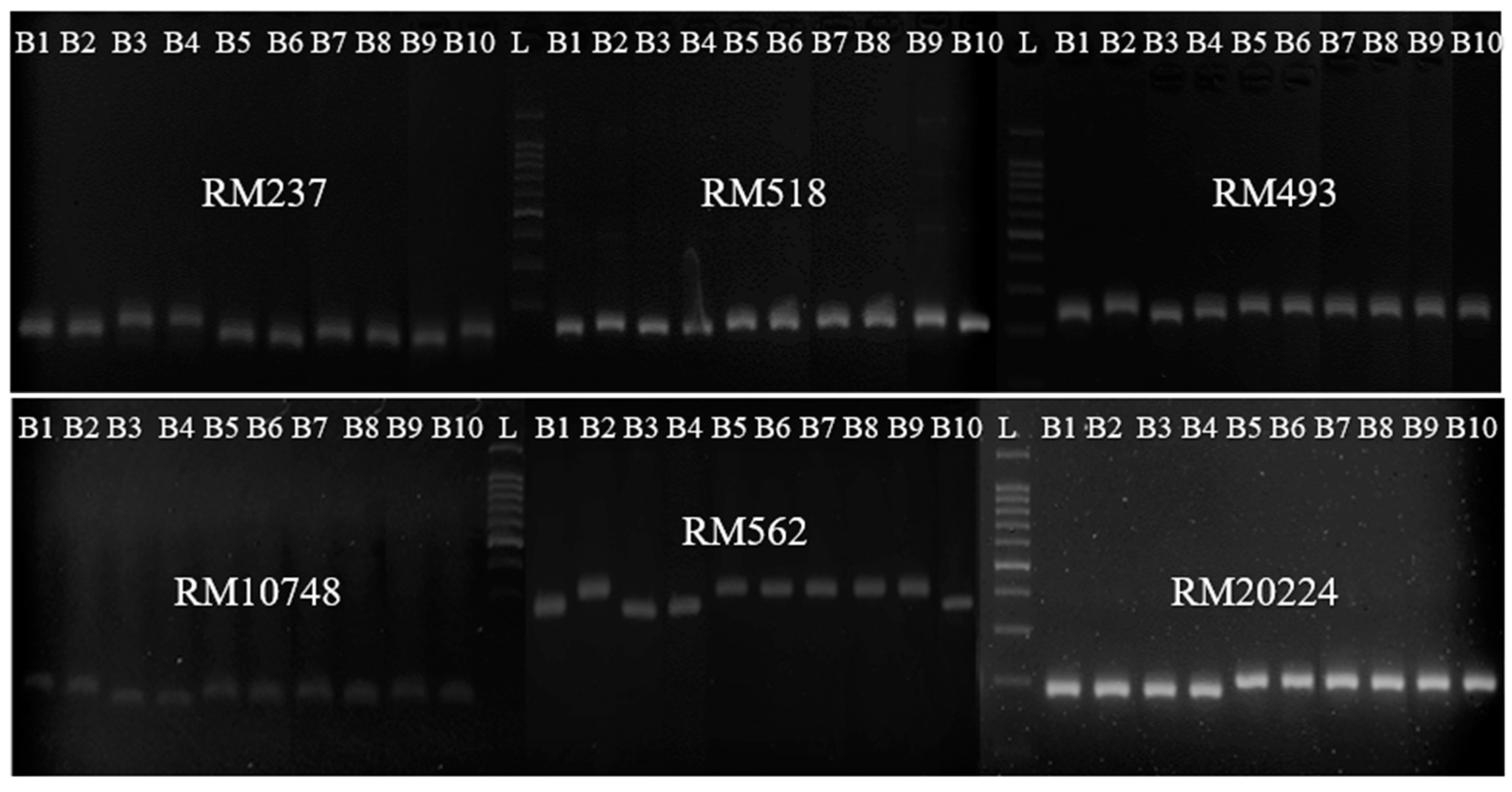
2.3. Genotypic Analysis
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Phenotypic Performance
3.2. Genotypic Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zeng, L.; Shannon, M.C. Salinity effects on seedling growth and yield components of rice. Crop Sci. 2000, 40, 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tester, M.; Davenport, R. Na+ tolerance and Na+ transport in higher plants. Ann. Bot. 2003, 91, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, S.D.; Susan, N.M.; John, J.M. Salinity stress effects on some morpho-physiological traits of selected rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes. Int. J. Dev. Sustain. 2016, 5, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladosu, Y.; Mohd, Y.R.; Norhani, A.; Ghazali, H.; Asfaliza, R.; Harun, A.R.; Gous, M.; Magaji, U. Principle and application of plant mutagenesis in crop improvement: A review. Biotechnol. Biotech. Eq. 2016, 30, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO/IAEA. Available online: http://mvgs.iaea.org/Search.aspx. (accessed on 24 January 2020).
- Sikora, P.; Chawade, A.; Larsson, M.; Olsson, J.; Olsson, O. Mutagenesis as a tool in plant genetics, functional genomics, and breeding. Int. J. Plant. Genom. 2011, 2011, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanyong, Y.; Xinghua, W.; Yiping, W.; Xiaoping, Y.; Shengxiang, T. Study on genetic variation of rice varieties derived from Aizizhan by using morphological traits, allozymes and simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2004, 18, 477–482. [Google Scholar]
- Moradi, F.; Ismail, A.M.; Gregorio, G.B.; Egdane, J.A. Salinity tolerance of rice during reproductive development and association with tolerance at the seedling stage. India J. Plant Physiol. 2003, 8, 105–116. [Google Scholar]
- Maria, L.C.V.; Luciane, S.; Augusto, L.D.; Carla de, F.M. Microsatellite markers: What they mean and why they are so useful. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2016, 3, 312–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.Y.; Guo, Y.; Chen, S.L.; Chen, S.Y. RFLP tagging of a salt tolerance gene in rice. Plant Sci. 1995, 110, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorio, G.B.; Senadhira, D.; Mendoza, R.D. Screening Rice for Salinity Tolerance, 3rd ed.; International Rice Research Institute: Los Baños, The Philippines, 1997; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.L.; Pathan, M.S.; Zhang, J.; Bai, G.; Sarkarung, S.; Nguyun, H.T. Mapping QTLs for root traits in a recombinant inbred population from two indica ecotypes in rice. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2000, 10, 756–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flowers, T.J.; Koyama, M.L.; Flowers, S.A.; Sudhakar, C.; Singh, K.P.; Yeo, A.R. QTL: Their place in engineering tolerance of rice to salinity. J. Exp. Bot. 2000, 51, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.R.; Bagali, P.G.; Hittalmani, S.; Shashidhar, H.E. Molecular mapping of quantitative trait loci associated with seedling tolerance to salt stress in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Curr. Sci. 2000, 78, 162–164. [Google Scholar]
- Koyama, M.L.; Levesley, A.; Koebner, R.M.D.; Flowers, T.J.; Yeo, A.R. Quantitative Trait Loci for component physiological trait determining salt tolerance in rice. Plant Physiol. 2001, 125, 406–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, N.T.; Li, Z.K.; Bui, C.B. Microsatellite markers linked to salt tolerance in rice. Omonrice 2001, 9, 9–21. [Google Scholar]
- Bonilla, P.S.; Dvorak, J.; Mackill, D.; Deal, K.; Gregorio, G. RFLP and SSLP mapping of salinity tolerance genes in chromosome 1 of rice (Oryza sativa L.) using recombinant inbred lines. Phillip. Agric. Sci. 2002, 65, 68–76. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.X.; Zhu, M.Z.; Yano, M.; Gao, J.P.; Liang, Z.W. QTLs for Na and K uptake of the shoots and roots controlling rice salt tolerance. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2004, 103, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niones, J.M. Five Mapping of the Salinity Tolerance Gene on Chromosome 1 of Rice (Oryza Sativa L.) Using Near Isogenic Lines. Master’s Thesis, University of the Philippines Los Banos, Laguna, Philippines, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Z.H.; Gao, J.P.; Li, G.L.; Cai, X.L.; Huang, W.; Chaw, D.Y.; Zhu, M.Z.; Wang, Z.Y.; Luan, S.; Lin, H.Y. A rice quantitative trait locus for salt tolerance encodes a sodium transporter. Nat. Genet. 2005, 37, 1141–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walia, H.; Wilson, C.; Condamine, P.; Liu, X.; Ismail, A.M.; Zeng, L.; Wilson, C.; Condamine, P.; Lile, X.; Zing, L.; et al. Comparative transcriptional profiling of two contrasting rice genotypes under salinity stress during the vegetative growth stage. Plant Physiol. 2005, 139, 822–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabouri, H.; Biabani, A. Toward the mapping of Agronomic characters on a rice genetic map: Quantitative Trait loci analysis under saline conditions. Biotechnology 2009, 8, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, M.J.; de Ocampo, M.; Egdane, J.; Rahman, M.A.; Sajise, A.G.; Adorada, D.L.; Tumimbang-Raiz, A.; Blumwald, E.; Seraj, Z.I.; Singh, R.K.; et al. Characterizing the Saltol quantitative trait locus for salinity tolerance in rice. Rice 2010, 3, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhamad, A.J.; Fahrul, Z.H.; Alina, W.; Faeza, M.S. Identification of QTLs for Morph-Physiological traits related to salinity tolerance at seedling stage in Indica rice. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011, 8, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linh, L.H.; Linh, T.H.; Xuan, T.D.; Ham, L.H.; Ismail, A.M.; Khanh, T.D. Molecular breeding to improve salt tolerance of rice (Oryza sativa L.) in the Red River Delta of Vietnam. Int. J. Plant Genom. 2012, 2012, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.R.; Gregorio, G.B.; Salam, M.A.; Collard, B.C.Y.; Singh, R.K.; Hasan, L. Validation of Saltol linked markers and haplotype diversity on chromosome 1 of rice. Mol. Plant Breed. 2012, 3, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelam, S.; Hemant, R.K.; Praveen, S.; Sneh, L.P.; Ashwani, P. A suite of new genes defining salinity stress tolerance in seedlings of contrasting rice genotypes. Funct. Integr. Genomic. 2013, 13, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, N.N.; Krishnan, S.G.; Bhowmick, P.K.; Vanaja, T.; Krishnamurthy, S.L.; Nagarajan, M.; Singh, N.K.; Prahu, K.V.; Singh, A.K. Maker based haplotype diversity of Satol QTL in relation to seedling stage salinity tolerance in selected genoypes of rice. Indian J. Genet. Plant Br. 2014, 74, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardani, Z.; Rabiei, B.; Sabouri, H.; Sabouri, A. Identification of molecular markers linked to salt-tolerant genes at gemination stage of rice. Plant Breed. 2014, 133, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, A.D.; Haritha, G.; Sunitha, T.; Krishnamurthy, S.L.; Divya, B.; Padmavathi, G.; Ram, T.; Sarla, N. Haplotyping of rice genotypes using simple sequence repeat markers associated with salt tolerance. Rice Sci. 2010, 23, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganie, S.A.; Dey, N.; Mondal, T.K. Differential promoter methylation of salt tolerant and susceptible rice genotypes under salinity stress. Funct. Genomic. 2016, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Camilla, S.C.S.; Flávia, B.S.B.; Cinthia, S.R.; Marcela, P.M.; Amanda, M.M.; Antônio, R.N. Genetic and phenotypic parameters in the selection of upland rice genotypes. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 3450–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Anh, T.T.T.; Xuan, T.D.; Huong, C.T.; Dat, T.D. Phenotypic performance of rice (Oryza sativa L.) populations induced by the MNU mutant on the adaptive characteristics. J. Hort. Plant Res. 2019, 5, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S.; Forno, D.A.; Cock, J.H.; Gomez, K.A. Laboratory Manual for Physiological Studies of Rice, 3rd ed.; International Rice Research Institute: Los Baños, The Philippines, 1976; pp. 1–83. [Google Scholar]
- Anh, T.T.T.; Khanh, T.D.; Dat, T.D.; Xuan, T.D. Identification of phenotypic variation and genetic diversity in rice (Oryza sativa L.) mutants. Agriculture 2018, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramene. Available online: http://www.gramene.org/ (accessed on 14 January 2018).
- PIC Calculator. Available online: https://www.liverpool.ac.uk/~kempsj/pic.html (accessed on 11 March 2018).
- Yeo, A.R.; Flowers, T.J. Mechanisms of salinity resistance in rice and their role as physiological criteria in plant breeding. In Salinity Tolerance in Plants-Strategies for Crop Improvement; Staples, R.C., Toenniessen, G.A., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1984; pp. 151–170. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, S. Gene Tagging for Salt Tolerance in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Ph.D. Thesis, The University of the Philippines, Los Banos, Laguna, Philippines, 1994; 118p. [Google Scholar]
- Makihara, D.; Tsuda, M.; Morita, M.; Hirai, Y.; Kuroda, T. Effect of salinity on the growth and development of rice (Oryza sativa L.) varieties. Jpn. J. Trop. Agri. 1999, 43, 285–294. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.K.; Flowers, T.J. Physiology and Molecular Biology of the Effects of Salinity on Rice, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; pp. 899–939. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.N.; Lucina, Y.; Saikat, G.A.; Rupak, G.; Somsubhra, C. Screening of rice landraces for salinity tolerance at seedling stage through morphological and molecular markers. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2014, 20, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manikanda, B. Genetic Mapping and Marker Assisted Selection: Basics, Practice and Benefits, 3rd ed.; Springers: New Delhi, India, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Collard, B.C.Y.; Mackill, D.J. Marker-assisted selection: An approach for precision plant breeding in the twenty-first century. Phil. Trans. B 2008, 363, 557–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garland, S.H.; Lewin, L.; Abedinia, M.; Henry, R.; Blakeney, A. The use of microsatellite polymorphisms for the identification of Australian breeding lines of rice (Oryza sativa. L). Euphytica 1999, 108, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.K.; Varshney, R.K.; Sharma, P.C.; Ramesh, B. Molecular markers and their applications in wheat breeding. Plant Breed. 1999, 118, 369–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.K.; Varshney, R.K. The development and use of microsatellite markers for genetic analysis and plant breeding with emphasis on bread wheat. Euphytica 2000, 113, 163–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamadi, N.; Arzani, A.; Rezai, A.M.; Singh, R.K.; Gregorio, G.B. Assessment of rice genotypes for salt tolerance using microsatellite markers associated with the Saltol QTL. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 7, 730–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Successful Study: Bright Leaf Tolerant Variety BC15. Available online: http://www.cuctrongtrot.gov.vn/TinTuc/Index/4351 (accessed on 26 June 2019).

| Samples | Origins | Classifications |
|---|---|---|
| B1 | Bao Thai | Cultivar |
| B2 | DT84 | Cultivar |
| B3 | Bao Thai/DT84 | Mutant |
| B4 | DT84DB | Mutant |
| B5 | SKLo | Cultivar |
| B6 | SKLo/BC15 | Mutant |
| B7 | BC15 | Cultivar |
| B8 | Khang dan/Wild rice | Mutant |
| B9 | Bao Thai DB | Mutant |
| B10 | BC15/TBR1 | Mutant |
| Score | Observation | Tolerance |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Normal growth, no leaf symptoms | Highly tolerant |
| 3 | Nearly normal growth, but leaf tips or a few leaves whitish and rolled | Tolerant |
| 5 | Growth severely retarded, most leaves rolled, only a few are elongating | Moderately tolerant |
| 7 | Complete cessation of growth, most leaves dried, some plants are dying | Susceptible |
| 9 | Almost all plants dead or dying | Highly susceptible |
| Samples/ Salinity Levels | Survivability (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 (dS m−1) | 4 (dS m−1) | 8 (dS m−1) | 12 (dS m−1) | |
| B1 | 100 | 100 | 90.00 ± 0.00 ab | 50.00 ± 0.00 bc |
| B2 | 100 | 100 | 86.67 ± 3.33 abc | 46.67 ± 3.33 c |
| B3 | 100 | 100 | 73.33 ± 3.33 c | 16.67 ± 3.33 de |
| B4 | 100 | 100 | 86.67 ± 3.33 abc | 3.33 ± 3.33 e |
| B5 | 100 | 100 | 86.67 ± 3.33 abc | 56.67 ± 3.33 abc |
| B6 | 100 | 100 | 93.33 ± 3.33 ab | 63.33 ± 3.33 ab |
| B7 | 100 | 100 | 96.67 ± 3.33 a | 66.67 ± 3.33 a |
| B8 | 100 | 100 | 83.33 ± 3.33 abc | 46.67 ± 3.33 c |
| B9 | 100 | 100 | 80.00 ± 0.00 bc | 43.33 ± 3.33 c |
| B10 | 100 | 100 | 83.33 ± 3.33 abc | 26.67 ± 3.33 d |
| Samples | Reduction (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Root Length | Plant Height | Dry weight | |
| B1 | −5.88 ± 1.04 cd | 11.15 ± 2.17 ab | 29.66 ± 6.01 ab |
| B2 | −2.21 ± 0.92 c | 13.69 ± 3.68 ab | 24.85 ± 4.18 ab |
| B3 | 2.90 ± 0.93 ab | 20.34 ± 3.80 a | 40.70 ± 4.90 a |
| B4 | 3.17 ± 0.67 a | 16.31 ± 1.82 ab | 29.76 ± 2.78 ab |
| B5 | −5.51 ± 1.19 cd | 10.83 ± 1.76 ab | 17.07 ± 4.34 b |
| B6 | −7.91 ± 1.19 d | 8.57 ± 1.33 b | 15.93 ± 3.56 b |
| B7 | −7.92 ± 1.57 d | 5.65 ± 0.78 b | 14.42 ± 3.19 b |
| B8 | −3.49 ± 0.88 cd | 13.77 ± 1.95 ab | 28.44 ± 5.34 ab |
| B9 | −4.57 ± 1.42 cd | 15.35 ± 1.41 ab | 23.64 ± 3.64 ab |
| B10 | −1.83 ± 0.39 bc | 15.79 ± 2.97 ab | 21.42 ± 2.80 ab |
| Source of Variation | Df | Salt Injury Score | Survivability | Root Length Reduction | Plant Height Reduction | Dry Weight Reduction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sum of Squares | ||||||
| Samples | 9 | 91.93 * | 5298.90 * | 1255.35 * | 1447.31 * | 5155.20 * |
| Salinity levels | 2 | 128.67 * | 47426.00 * | 334.36 * | 2103.27 * | 10942.60 * |
| Interaction | 18 | 7.92 | 4902.20 | 87.12 * | 608.56 * | 1047.80 |
| Error | 60 | 5.16 | 2074.10 | 402.64 | 1254.22 | 723.30 |
| Total | 89 | 233.68 | 59701.20 | 2079.48 | 5413.36 | 17868.80 |
| Parameters | Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TS | SUR (%) | RLR (%) | PHR (%) | DWR (%) | |
| TS | 1 | ||||
| SUR (%) | −0.93 ** | 1 | |||
| RLR (%) | 0.90 ** | −0.95 ** | 1 | ||
| PHR (%) | 0.94 ** | −0.87 ** | 0.89 ** | 1 | |
| DWR (%) | 0.79 ** | −0.70 * | 0.78 ** | 0.82 ** | 1 |
| SSR Markers | Chromosome | Sequences * | Number of Alleles | He | PIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RM 237 | 1 | CAAATCCCGACTGCTGTCC TGGGAAGAGAGCACTACAGC | 3 | 0.65 | 0.58 |
| RM 518 | 4 | CTCTTCACTCACTCACCATGG ATCCATCTGGAGCAAGCAAC | 2 | 0.49 | 0.37 |
| RM 493 | 1 | TAGCTCCAACAGGATCGACC GTACGTAAACGCGGAAGGTG | 2 | 0.41 | 0.33 |
| RM 10748 | 1 | CATCGGTGACCACCTTCTCC CCTGTCATCTATCTCCCTCAAGC | 3 | 0.65 | 0.58 |
| RM 562 | 1 | CACAACCCACAAACAGCAAG CTTCCCCCAAAGTTTTAGCC | 2 | 0.41 | 0.33 |
| RM 20224 | 2 | AGTATGAAAGTCGGTGACGATGG GAGATGTCACGTCTTCACTTAGGG | 3 | 0.65 | 0.58 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huong, C.T.; Anh, T.T.T.; Tran, H.-D.; Duong, V.X.; Trung, N.T.; Dang Khanh, T.; Dang Xuan, T. Assessing Salinity Tolerance in Rice Mutants by Phenotypic Evaluation Alongside Simple Sequence Repeat Analysis. Agriculture 2020, 10, 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10060191
Huong CT, Anh TTT, Tran H-D, Duong VX, Trung NT, Dang Khanh T, Dang Xuan T. Assessing Salinity Tolerance in Rice Mutants by Phenotypic Evaluation Alongside Simple Sequence Repeat Analysis. Agriculture. 2020; 10(6):191. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10060191
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuong, Can Thu, Truong Thi Tu Anh, Hoang-Dung Tran, Vu Xuan Duong, Nguyen Thanh Trung, Tran Dang Khanh, and Tran Dang Xuan. 2020. "Assessing Salinity Tolerance in Rice Mutants by Phenotypic Evaluation Alongside Simple Sequence Repeat Analysis" Agriculture 10, no. 6: 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10060191
APA StyleHuong, C. T., Anh, T. T. T., Tran, H.-D., Duong, V. X., Trung, N. T., Dang Khanh, T., & Dang Xuan, T. (2020). Assessing Salinity Tolerance in Rice Mutants by Phenotypic Evaluation Alongside Simple Sequence Repeat Analysis. Agriculture, 10(6), 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10060191







