Evaluation of Composted Organic Wastes and Farmyard Manure for Improving Fertility of Poor Sandy Soils in Arid Regions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Analytical Methods
2.2.1. Soil Physicochemical Parameters
2.2.2. Plant Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
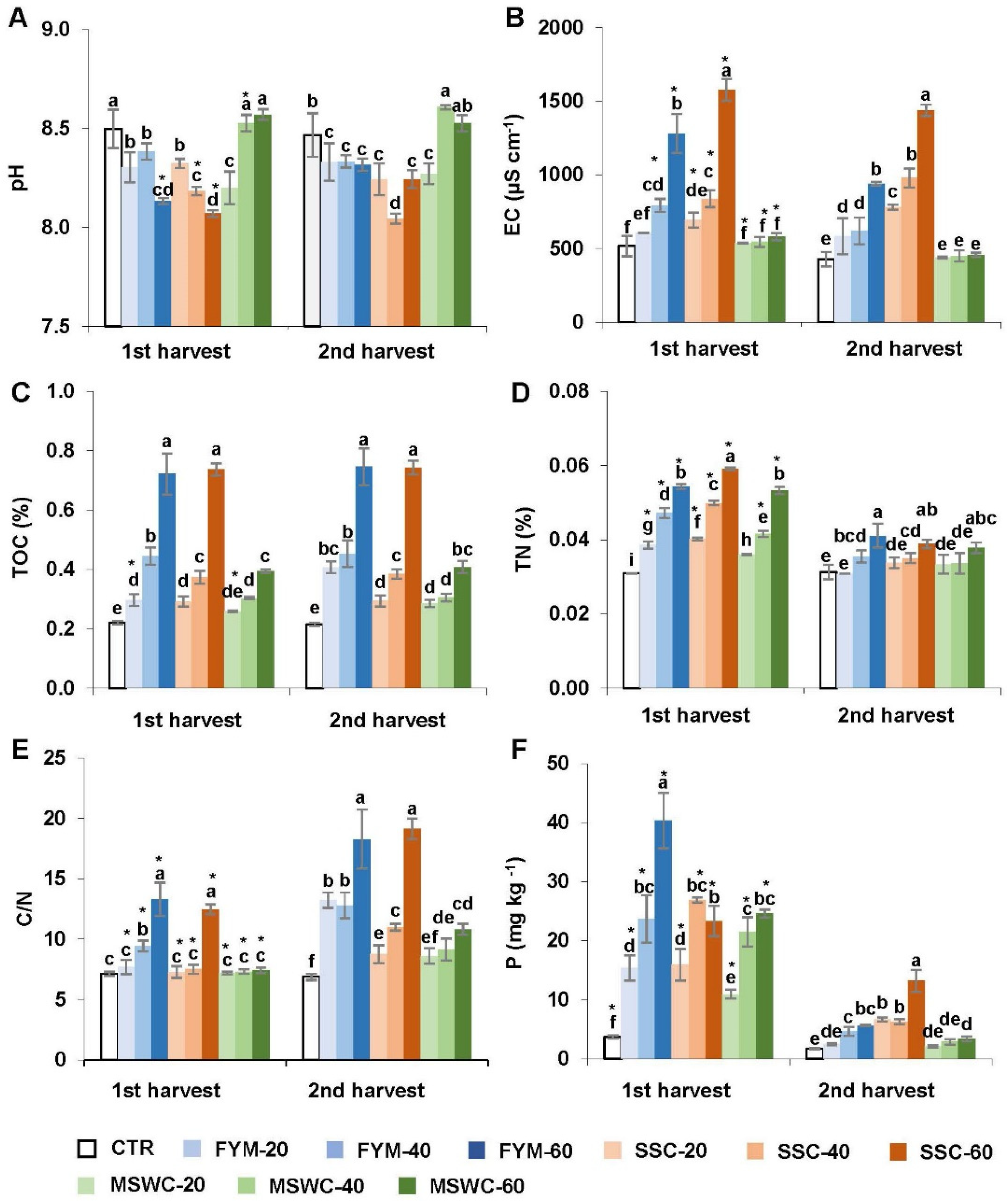
3.1. Soil Physicochemical Properties
3.2. Metal Fractionation
3.3. Effect of Soil Amendments on Grain Yield
3.4. Effect of Soil Amendment on Plant Nutrient Contents
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Soil Amendments on Soil Physicochemical Properties
4.2. Effects of Organic Amendments on Trace Metals Distribution in Soils
4.3. Effect of Organic Amendments on Grain Yield and Plant Nutrient Contents
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brahim, N.; Ibrahim, H.; Hatira, A. Tunisian soil organic carbon stock: Spatial and vertical variation. Procedia. Eng. 2014, 69, 1549–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, C.; Hernandez, T.; Coll, M.; Ondono, S. Organic amendments for soil restoration in arid and semiarid areas: A review. AIMS Environ. Sci. 2017, 4, 640–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Chen, B.; Nie, X.; Shi, Z.; Huang, X.; Li, X. The distribution and partitioning of common antibiotics in water and sediment of the Pearl River Estuary, South china. Chemosphere 2013, 92, 1410–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.H. The combined use of chemical and organic fertilizers and/or biofertilizer for crop growth and soil fertility. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Sustained Management of the Soil-Rhizosphere System for Efficient Crop Production and Fertilizer Use, Bangkok, Thailand, 16–20 October 2006; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Eid, E.M.; Alrumman, S.A.; El-Bebany, A.F.; Hesham, A.E.; Taher, M.A.; Fawy, K.F. The effects of different sewage sludge amendment rates on the heavy metal bioaccumulation, growth and biomass of cucumbers (Cucumis sativus L). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 16371–16382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Camps-Arbestain, M.; Shen, Q.; Singh, B.; Cayuela, M.L. The long-term role of organic amendments in building soil nutrient fertility: A meta-analysis and review. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2018, 111, 103–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakhdar, A.; Scelza, R.; Scotti, R.; Rao, M.A.; Jedidi, N.; Gianfreda, L.; Abdelly, C. The effect of compost and sewage sludge on soil biological activities in salt-affected soil. Rev. Cienc. Suelo Y Nutr. Veg. 2010, 10, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diacono, M.; Montemurro, F. Long-term effects of organic amendments on soil fertility. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2010, 30, 401–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ben Achiba, W.; Gabteni, N.; Lakhdar, A.; Du Laing, G.; Verloo, M.; Jedidi, N.; Gallali, T. Accumulation and fractionation of trace metals in a Tunisian calcareous soil amended with farmyard manure and municipal waste compost. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 176, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamdi, H.; Hechmi, S.; Khelil, M.N.; Zoghlami, I.R.; Benzarti, S.; Mokni-Tlili, S.; Hassen, A.; Jedidi, N. Repetitive land application of urban sewage sludge: Effect of amendment rates and soil texture on fertility and degradation parameters. Catena 2019, 172, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujdeci, M.; Isildar, A.A.; Uygur, V.; Alaboz, P.; Unlu, H.; Senol, H. Cooperative effects of field traffic and organic matter treatments on some compaction-related soil properties. Solid Earth 2017, 8, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aggelides, S.M.; Londra, P.A. Effects of compost produced from town wastes and sewage sludge on the physical properties of a loamy and clay soil. Bioresour. Technol. 2000, 71, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakhdar, A.; Hafsi, C.; Rabhi, M.; Debez, A.; Montemurro, F.; Abdelly, C.; Jedidi, N.; Ouerghi, Z. Application of municipal solid waste compost reduces the negative effects of saline water in Hordeum maritimum L. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 7160–7167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakhdar, A.; Falleh, H.; Ouni, Y.; Oueslati, S.; Debez, A.; Ksouri, R.; Abdelly, C. Municipal solid waste compost application improves productivity, polyphenol content, and antioxidant capacity of Mesembryanthemum edule. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 191, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trivedi, P.; Singh, K.; Pankaj, U.; Verma, S.K.; Verma, R.K.; Patra, D.D. Effect of organic amendments and microbial application on sodic soil properties and growth of an aromatic crop. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 102, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Achiba, W.; Gabteni, N.; Lakhdar, A.; Du Laing, G.; Verloo, M.; Jedidi, N.; Gallali, T. Effects of 5-year application of municipal solid waste compost on the distribution and mobility of heavy metals in a Tunisian calcareous soil. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2009, 130, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roig, N.; Sierra, J.; Martí, E.; Nadal, M.; Schuhmacher, M.; Domingo, J.L. Long-term amendment of Spanish soils with sewage sludge: Effects on soil functioning. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 158, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordao, C.P.; Nascentes, C.C.; Cecon, P.R.; Fontes, R.L.; Pereira, J.L. Heavy metals availability in soil amended with composted urban solid wastes. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2006, 112, 309–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydinalp, C.; Marinova, S. Distribution and forms of heavy metals in some agricultural soils. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2003, 12, 629–633. [Google Scholar]
- Illera, V.; Walker, I.; Souza, P.; Cala, V. Short-term effects of biosolid and municipal solid waste application on heavy metals distribution in a degraded soil under a semi-arid environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 255, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, D.V.; Alcantra, S.; Ribeiro, C.C.; Pereira, R.E.; Fontes, G.C.; Wasserman, M.A.; Venezuela, T.C.; Meneguelli, N.A.; Parradas, C.A.A. Composted municipal waste effects on chemical properties of Brazilian soil. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hueso-González, P.; Muñoz-Rojas, M.; Martínez-Murillo, J.F. The role of organic amendments in drylands restoration. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2017, 5, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scotti, R.; Bonanomi, G.; Scelza, R.; Zoina, A.; Rao, M.A. Organic amendments as sustainable tool to recovery fertility in intensive agricultural systems. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2015, 15, 333–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mtimet, A. Soils of Tunisia. In Soil Resources of Southern and Eastern Mediterranean Countries; Zdruli, P., Steduto, P., Lacirignola, C., Montaranella, L., Eds.; Options Méditerranéennes: Série B. Etudes et Recherches; CIHEAM: Bari, Italy, 2001; Volume 34, pp. 243–268. [Google Scholar]
- Bouzaiane, O.; Cherif, H.; Saidi, N.; Jedidi, N.; Hassen, A. Effects of municipal solid waste compost application on the microbial biomass of cultivated and non-cultivated soil in a semi-arid zone. Waste Manag. Res. 2007, 25, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mbarki, S.; Cerdà, A.; Zivcak, M.; Brestic, M.; Rabhi, M.; Mezni, M.; Abdelly, C.; Pascual, J.A. Alfalfa crops amended with MSW compost can compensate the effect of salty water irrigation depending on the soil texture. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 115, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ben Achiba, W.; Gabteni, N.; Laing, G.D.; Verloo, M.; Jedidi, N.; Tahar, G. Heavy metal availability and uptake by wheat crops cultivated in Tunisian field plots amended during five years with municipal solid waste compost and farmyard manure. J. Res. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 4, 146–154. [Google Scholar]
- Commission Regulation (EEC) No 202/91 of 28 January 1991 Amending Regulation (EEC) No 3885/90 Laying down Detailed Rules for the Application of the Import Arrangements Provided for in Council Regulation (EEC) No 3838/90 for Frozen Meat of Bovine Animals Covered by CN Code 0202 and Products Covered by CN Code 02062991. Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/reg/1991/202/oj (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- Beretta, A.N.; Silbermann, A.V.; Paladino, L.; Torres, D.; Bassahun, D.; Musselli, R.; Garcia-Lamohte, A. Soil texture analyses by hydrometer: Modifications of the Bouyoucos method. Cien. Inv. Agrar. 2014, 41, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walkley, A.; Black, I.A. An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci. 1934, 37, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremner, J.M. Chapter 37−Nitrogen−Total. In Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 3; Sparks, D.L., Page, A.L., Helmke, P.A., Loeppert, R.H., Soltanpour, P.N., Tabatabai, M.A., Johnston, C.T., Sumner, M.E., Eds.; Chemical Methods; SSSA Book Series no. 5; SSSA-ASA: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; pp. 1085–1122. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, J.; Riley, J.P. A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 1962, 27, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauret, G. Extraction procedures for the determination of heavy metals in contaminated soil and sediment. Talanta 1998, 46, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauwels, J.; Van Ranst, E.; Verloo, M.; Mvondo Ze, A. Manuel de Laboratoire de Pédologie-Méthodes d’analyses de sols et de plantes. In Equipment et Gestion des Stocks de Verrerie et de Produits Chimiques; Publications Agricoles nr. 28, A.G.C.D.: Bruxelles, Belgium, 1992; p. 180. [Google Scholar]
- Cantrell, I.C.; Linderman, R.G. 2001. Preinoculation of lettuce and onion with VA mycorrhizal fungi reduces deleterious effects of soil salinity. Plant Soil 2001, 233, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Agrawal, M. Potential benefits and risks of land application of sewage sludge. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattan, R.K.; Datt, S.P.; Chhonkar, P.K.; Suribabu, K.; Singh, A.K. Long-term impact of irrigation with sewage effluents on heavy metal content in soils, crops and groundwater—A case study. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 67, 824–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarenga, P.; Palma, P.; Mourinha, C.; Farto, M.; Dores, J.; Patanita, M.; Cunha-Queda, C.; Natal-da-Luz, T.; Renaud, M.; Sousa, J.P. Recycling organic wastes to agricultural land as a way to improve its quality: A field study to evaluate benefits and risks. Waste Manag. 2017, 61, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yüksel, O.; Kavdır, Y. Improvement of Soil Quality Parameters by Municipal Solid Waste Compost Application in Clay-Loam Soil. Turk. J. Agric.-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 8, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicolardot, B.; Recous, S.; Mary, B. Simulation of C and N mineralization during crop residue decomposition: A simple dynamic model based on the C: N ratio of the residues. Plant Soil 2001, 228, 83–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutser, R.; Ebertseder, T.; Weber, A.; Schraml, M.; Schmidhalter, U. Short-term and residual availability of nitrogen after long-term application of organic amendments on arable land. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2005, 168, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, J.; Ouyang, Y. Controls and adaptive management of nitrification in agricultural soils. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1929–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Demelash, N.; Bayu, W.; Tesfaye, S.; Ziadat, F.; Sommer, R. Current and residual effects of compost and inorganic fertilizer on wheat and soil chemical properties. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2014, 100, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, M.D.; Joshi, P.K.; Jat, H.S.; Chinchmalatpure, A.R.; Narjary, B.; Sheoran, P.; Sharma, D.K. Changes in biological and chemical properties of saline soil amended with municipal solid waste compost and chemical fertilizers in a mustard–pearl millet cropping system. Catena 2016, 140, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hechmi, S.; Hamdi, H.; Mokni-Tlili, S.; Ghorbel, M.; Khelil, M.N.; Zoghlami, I.R.; Benzarti, S.; Jellali, S.; Hassen, A.; Jedidi, N. Impact of urban sewage sludge on soil physico-chemical properties and phytotoxicity as influenced by soil texture and reuse conditions. J. Environ. Qual. 2020, 49, 973–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loveland, P.; Webb, J. Is there a critical level of organic matter in the agricultural soils of temperate regions: A review. Soil Till. Res. 2003, 70, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarenga, P.; Farto, M.; Mourinha, C.; Palma, P. Beneficial Use of Dewatered and Composted Sewage Sludge as Soil Amendments: Behaviour of Metals in Soils and Their Uptake by Plants. Waste Biomass. Valor. 2016, 7, 1189–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, M.; Paradelo Núñez, R.; Piñeiro, J.; Barral, M.T. Physicochemical and biochemical properties of an acid soil under potato culture amended with municipal solid waste compost. Int. J. Recycl. Org. Waste Agric. 2019, 8, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masmoudi, S.; Magdich, S.; Rigane, H.; Medhioub, K.; Rebai, A.; Ammar, E. Effects of Compost and Manure Application Rate on the Soil Physico-Chemical Layers Properties and Plant Productivity. Waste Biomass. Valori. 2018, 11, 1883–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NFU 44-051. French Regulation Established by AFNOR for Organic Amendments.; AFNOR: Paris, France, 2006. (In French) [Google Scholar]
- Kidd, P.S.; Domínguez-Rodríguez, M.J.; Díez, J.; Monterroso, C. Bioavailability and plant accumulation of heavy metals and phosphorus in agricultural soils amended by long-term application of sewage sludge. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 1458–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasheen, M.R.; Ammar, N.S. Assessment of metals speciation in sewage sludge and stabilized sludge from different Wastewater Treatment Plants, Greater Cairo, Egypt. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 740–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadepalle, V.P.; Ouki, S.K.; Van Herwijnen, R.; Hutchings, T. Immobilization of heavy metals in soil using natural and waste materials for vegetation establishment on contaminated sites. Soil Sediment Contam. 2007, 16, 233–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parat, C.; Chaussod, R.; Leveque, J.; Andreux, F. Long-term effects of metal containing farmyard manure and sewage sludge on soil organic matter in a fluvisol. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collivignarelli, M.C.; Abbà, A.; Frattarola, A.; Carnevale Miino, M.; Padovani, S.; Katsoyiannis, I.; Torretta, V. Legislation for the Reuse of Biosolids on Agricultural Land in Europe: Overview. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mbarki, S.; Skalicky, M.; Talbi, O.; Chakraborty, A.; Hnilicka, F.; Hejnak, V.; Zivcak, M.; Brestic, M.; Cerda, A.; Abdelly, C. Performance of Medicago sativa Grown in Clay Soil Favored by Compost or Farmyard Manure to Mitigate Salt Stress. Agronomy 2020, 10, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hammad, H.M.; Khaliq, A.; Abbas, F.; Farhad, W.; Fahad, S.; Aslam, M.; Shah, G.M.; Nasim, W.; Mubeen, M.; Bakhat, H.F. Comparative Effects of Organic and Inorganic Fertilizers on Soil Organic Carbon and Wheat Productivity under Arid Region. Comm. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2020, 10, 1406–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejada, M.; Gonzalez, J.L. Effects of the application of a compost originating from crushed cotton gin residues on wheat yield under dryland conditions. Eur. J. Agron. 2003, 19, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, M.S.; El-Sherbeny, S.E.; Khalil, M.Y.; Naguib, N.Y.; Aly, S.M. Growth characters and chemical constituents of Dracocephalum moldavica L. plants in relation to compost fertilizer and planting distance. Sci. Horticult. 2006, 108, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.A.; Khan, K.S.; Marshchner, P.; Ali, S. Organic amendments differ in their effect on microbial biomass and activity and on P pools in alkaline soils. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2013, 49, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobedo-Monge, M.A.; Aparicio, S.; Escobedo-Monge, M.F.; Marugán-Miguelsanz, J.M. Long-Term Effects of the Application of Urban Waste Compost and Other Organic Amendments on Solanum tuberosum L. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa, R.S.; White, R.E.; Weatherley, A.J. Effect of compost treatment of sewage sludge on nitrogen behavior in two soils. Waste Manag. 2006, 26, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, P.; Chakrabarti, K.; Chakraborty, A.; Nayak, D.C.; Tripathy, S.; Powell, M.A. Municipal waste compost as an alternative to cattle manure for supplying potassium to lowland rice. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 1789–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, M.F.; Thalooth, A.T.; Elewa, T.A.; Ahmed, A.G. Yield and nutrient status of wheat plants (Triticum aestivum L.) as affected by sludge, compost, and biofertilizers under newly reclaimed soil. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2019, 43, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.S.; Joergensen, R.G. Compost and phosphorus amendments for stimulating microorganisms and growth of ryegrass in a Ferralsol and a Luvisol. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2012, 175, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warman, P.R.; Murphy, C.; Burnham, J.; Eaton, L. Soil and plant response to MSW compost applications on lowbush blueberry fields in 2000 and 2001. Small Fruits Rev. 2004, 3, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.L.; Acquah, G.E.; Whitmore, A.P.; McGrath, S.P.; Haefele, S.M. The effect of different organic fertilizers on yield and soil and crop nutrient concentrations. Agronomy 2019, 9, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karthika, K.S.; Parama, V.R.R.; Subbarayappa, C.T.; Hemalatha, B.; Vidya, C.S. Residual effect of enzyme industrial waste-municipal solid waste composts application on growth, yield, content and uptake of nutrients by cowpea. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci. 2018, 7, 1386–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, G.M.; Tufail, N.; Bakhat, H.F.; Ahmad, I.; Shahid, M.; Hammad, H.M.; Nasim, W.; Waqar, A.; Rizwan, M.; Dong, R. Composting of municipal solid waste by different methods improved the growth of vegetables and reduced the health risks of cadmium and lead. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 5463–5474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabata-Pendias, A.; Pendias, H. Trace Elements in Soils and Plants, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]






| Soil | FYM | SSC | MSW | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sand (%) | 89 ± 1 | - | - | - |
| Clay (%) | 9 ± 0 | - | - | - |
| Silt (%) | 2 ± 0 | - | - | - |
| Texture | Sandy | - | - | - |
| pH H2O | 8.3 ± 0.1 | 8.7 ± 0.0 | 6.2 ± 0.0 | 7.6 ± 0.0 |
| EC (µS cm−1) | 525 ± 4.6 | 15.3 ± 0.4 | 15.7 ± 0.0 | 1.6 ± 0.0 |
| P Olsen (mg kg−1) | 3.2 ± 0.09 | 577.7 ± 62.4 | 400.9 ± 26.3 | 181.7 ± 8.1 |
| CEC (cmolc kg−1) | 41.3 ± 2.7 | nd | 128.9 ± 2.3 | 57.6 ± 0.9 |
| Exchangeable Ca (cmolc kg−1) | 39.1 ± 2.6 | nd | 73.8 ± 0.7 | 42.6 ± 0.8 |
| Exchangeable Mg (cmolc kg−1) | 1.5 ± 0.1 | nd | 33.6 ± 1.2 | 4.9 ± 0.0 |
| Exchangeable K (cmolc kg−1) | 0.5 ± 0.0 | nd | 17.3 ± 0.7 | 9.9 ± 0.2 |
| Ca/Mg | 26.3 ± 0.8 | nd | 2.2 ± 0.1 | 8.6 ± 0.1 |
| % C | 0.21 ± 0.0 | 28.9 ± 1.9 | 22.5 ± 1.1 | 7.2 ± 0.0 |
| % N | 0.03 ± 0.0 | 1.2 ± 0.0 | 1.9 ± 0.1 | 0.5 ± 0.0 |
| C/N | 7.2 ± 0.1 | 23.6 ± 2.1 | 11.8 ± 0.1 | 13.8 ± 0.8 |
| Pseudo-total element concentrations | ||||
| g kg−1 | ||||
| P | 0.3 ± 0.0 | 4.0 ± 0.1 | 10.3 ± 0.2 | 4.5 ± 0.1 |
| K | 2.1 ± 0.0 | 13.2 ± 0.3 | 6.2 ± 0.2 | 8.4 ± 0.1 |
| Al | 8.2 ± 0.2 | 5.5 ± 0.0 | 6.4 ± 0.3 | 28.0 ± 0.0 |
| Ca | 32.6 ± 2.1 | 28.5 ± 0.3 | 53.8 ± 1.2 | 138.8 ± 3.3 |
| Mg | 2.9 ± 0.1 | 5.6 ± 0.1 | 6.7 ± 0.2 | 4.7 ± 0.0 |
| Fe | 5.9 ± 0.3 | 3.7 ± 0.1 | 5.4 ± 0.1 | 26.5 ± 1.1 |
| mg kg−1 | ||||
| Cu | 4.4 ± 0.4 | 16.8 ± 0.7 | 97.3 ± 2.9 | 54.9 ± 0.8 |
| Zn | 12.4 ± 1.3 | 87.0 ± 5.8 | 267.2 ± 4.2 | 286.1 ± 3.2 |
| Pb | 3.4 ± 0.1 | 1.4 ± 0.2 | 20.4 ± 1.4 | 76.3 ± 10.6 |
| Cd | 0.2 ± 14.4 | 0.2 ± 0.0 | 0.5 ± 0.0 | 0.6 ± 0.0 |
| Ni | 6.0 ± 0.5 | 6.8 ± 0.3 | 15.3 ± 0.1 | 31.5 ± 0.5 |
| Cr | 13.7 ± 0.3 | 10.3 ± 0.5 | 18.9 ± 0.9 | 28.5 ± 0.3 |
| Co | 1.5 ± 0.2 | 1.2 ± 0.1 | 1.9 ± 0.0 | 5.1 ± 0.4 |
| Mn | 83.4 ± 1.9 | 92.7 ± 1.2 | 95.9 ± 2.4 | 298.9 ± 2.1 |
| Fe (mg kg−1) | Mn (mg kg−1) | Zn (mg kg−1) | Cu (mg kg−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st harvest | |||||
| CTR | 0 | 128.4 ± 4.2 e *** | 6.3 ± 0.1 f | 11.1 ± 0.0 e *** | 4.0 ± 0.5 e ** |
| FYM (t ha−1) | 20 | 158.4 ± 5.5 de ** | 6.5 ± 0.3 f *** | 10.5 ± 0.4 e | 2.6 ± 0.3 f |
| 40 | 130.7 ± 3.1 e *** | 12.2 ± 0.6 d | 12.3 ± 1.0 de | 3.0 ± 0.2 ef | |
| 60 | 242.5 ± 12.9 b | 15.6 ± 0.1 a *** | 15.5 ± 0.0 bc *** | 3.8 ± 0.1 ef ** | |
| SSC (t ha−1) | 20 | 161.0 ± 15.0 de * | 8.2 ± 0.4 e | 13.2 ± 1.4 d * | 5.6 ± 1.0 d ** |
| 40 | 166.8 ± 3.3 d *** | 13.6 ± 0.0 c ** | 15.4 ± 0.3 bc * | 8.2 ± 1.1 bc ** | |
| 60 | 210.2 ± 21.4 bc | 14.7 ± 0.8 b | 17.6 ± 0.8 a * | 10.3 ± 0.9 a *** | |
| MSWC (t ha−1) | 20 | 185.7 ± 29.5 cd | 12.6 ± 0.7 d | 11.2 ± 0.3 e | 7.1 ± 0.6 c *** |
| 40 | 232.8 ± 22.4 b | 13.7 ± 0.1 c ** | 15.1 ± 1.3 c * | 9.1 ± 0.7 ab *** | |
| 60 | 286.9 ± 31.7 a* | 13.9 ± 0.8 bc * | 17.0 ± 1.7 ab | 9.8 ± 0.9 a *** | |
| 2nd harvest | |||||
| CTR | 0 | 94.1 ± 3.0 f *** | 7.2 ± 0.2 d | 10.2 ± 0.1 e *** | 2.1 ± 0.1 d ** |
| FYM (t ha−1) | 20 | 103.7 ± 2.6 f *** | 11.0 ± 0.2 b *** | 10.3 ± 0.2 e | 2.3 ± 0.1 d |
| 40 | 212.7 ± 6.2 c *** | 11.3 ± 0.3 b | 12.3 ± 0.9 d | 3.2 ± 0.1 bc | |
| 60 | 223.8 ± 9.0 abc | 12.9 ± 0.2 a *** | 14.2 ± 0.1 c *** | 3.4 ± 0.1 b ** | |
| SSC (t ha−1) | 20 | 130.9 ± 7.4 e * | 8.7 ± 0.3 c | 10.5 ± 0.4 e * | 2.6 ± 0.4 cd ** |
| 40 | 216.4 ± 5.8 bc *** | 10.9 ± 0.8 b ** | 13.1 ± 0.9 d * | 3.3 ± 0.2 b ** | |
| 60 | 227.2 ± 2.7 ab | 13.1 ± 0.9 a | 18.9 ± 0.1 a * | 4.9 ± 0.5 a *** | |
| MSWC (t ha−1) | 20 | 171.7 ± 11.0 d | 11.3 ± 0.7 b | 10.4 ± 1.1 e | 3.2 ± 0.3 b *** |
| 40 | 221.5 ± 10.2 abc | 11.5 ± 0.6 b ** | 12.5 ± 0.3 d * | 3.5 ± 0.2 b *** | |
| 60 | 231.9 ± 3.5 a * | 11.8 ± 0.8 b * | 16.0 ± 0.2 b | 3.7 ± 0.7 b *** | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oueriemmi, H.; Kidd, P.S.; Trasar-Cepeda, C.; Rodríguez-Garrido, B.; Zoghlami, R.I.; Ardhaoui, K.; Prieto-Fernández, Á.; Moussa, M. Evaluation of Composted Organic Wastes and Farmyard Manure for Improving Fertility of Poor Sandy Soils in Arid Regions. Agriculture 2021, 11, 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11050415
Oueriemmi H, Kidd PS, Trasar-Cepeda C, Rodríguez-Garrido B, Zoghlami RI, Ardhaoui K, Prieto-Fernández Á, Moussa M. Evaluation of Composted Organic Wastes and Farmyard Manure for Improving Fertility of Poor Sandy Soils in Arid Regions. Agriculture. 2021; 11(5):415. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11050415
Chicago/Turabian StyleOueriemmi, Houda, Petra Susan Kidd, Carmen Trasar-Cepeda, Beatriz Rodríguez-Garrido, Rahma Inès Zoghlami, Kaouther Ardhaoui, Ángeles Prieto-Fernández, and Mohamed Moussa. 2021. "Evaluation of Composted Organic Wastes and Farmyard Manure for Improving Fertility of Poor Sandy Soils in Arid Regions" Agriculture 11, no. 5: 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11050415
APA StyleOueriemmi, H., Kidd, P. S., Trasar-Cepeda, C., Rodríguez-Garrido, B., Zoghlami, R. I., Ardhaoui, K., Prieto-Fernández, Á., & Moussa, M. (2021). Evaluation of Composted Organic Wastes and Farmyard Manure for Improving Fertility of Poor Sandy Soils in Arid Regions. Agriculture, 11(5), 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11050415






