Assessment of the Effect of Application of the Herbicide S-Metolachlor on the Activity of Some Enzymes Found in Soil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Herbicide
2.2. Soil Sampling
2.3. Treatment of Soil Samples with Herbicides
2.4. Physicochemical Properties of Soil
2.5. Biochemical Analyses
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.7. Computational Approach
3. Results
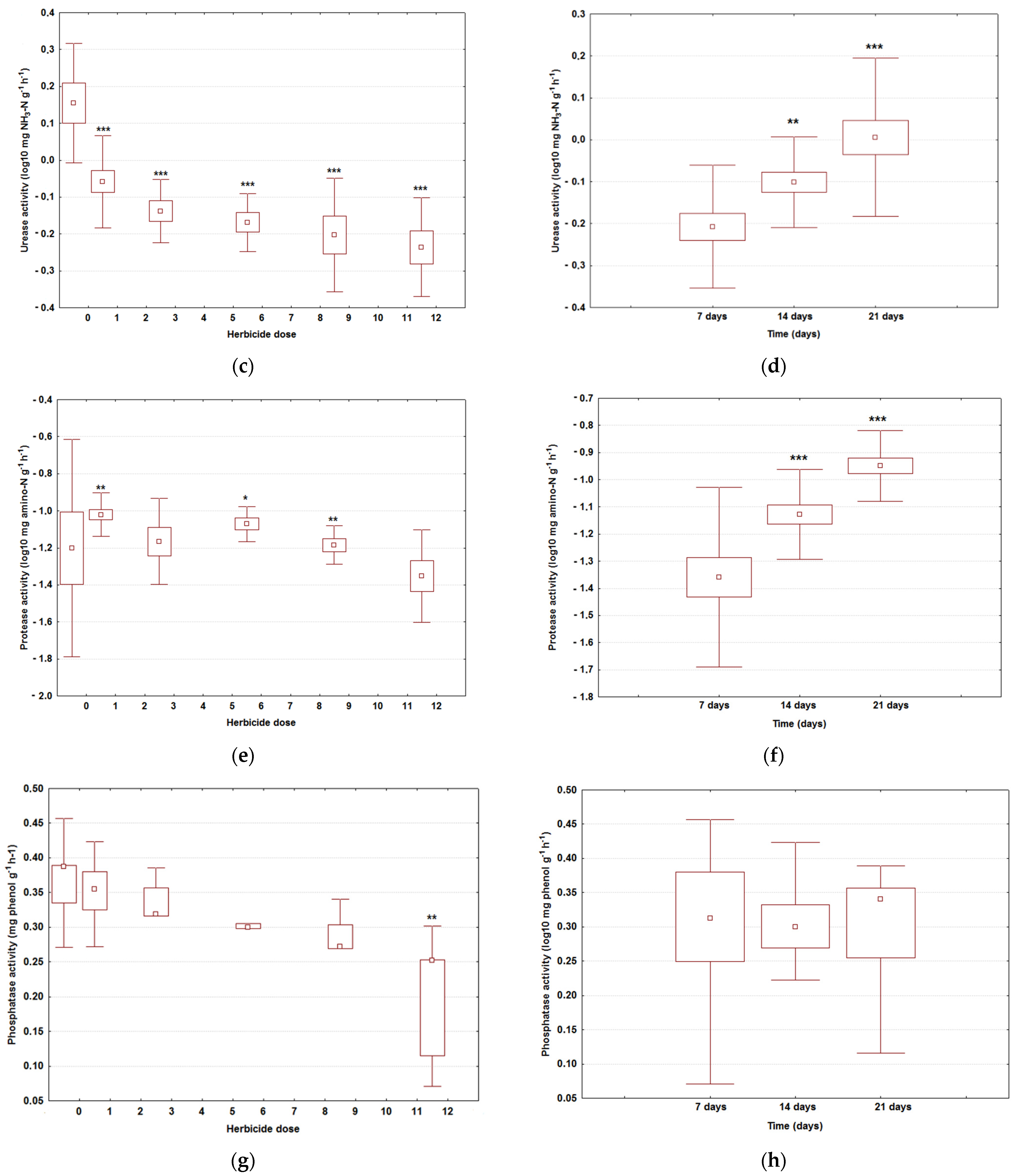
3.1. Assessment of the Enzymatic Activities
3.2. Correlation between the Enzymatic Activities and Physicochemical Properties of the Soil
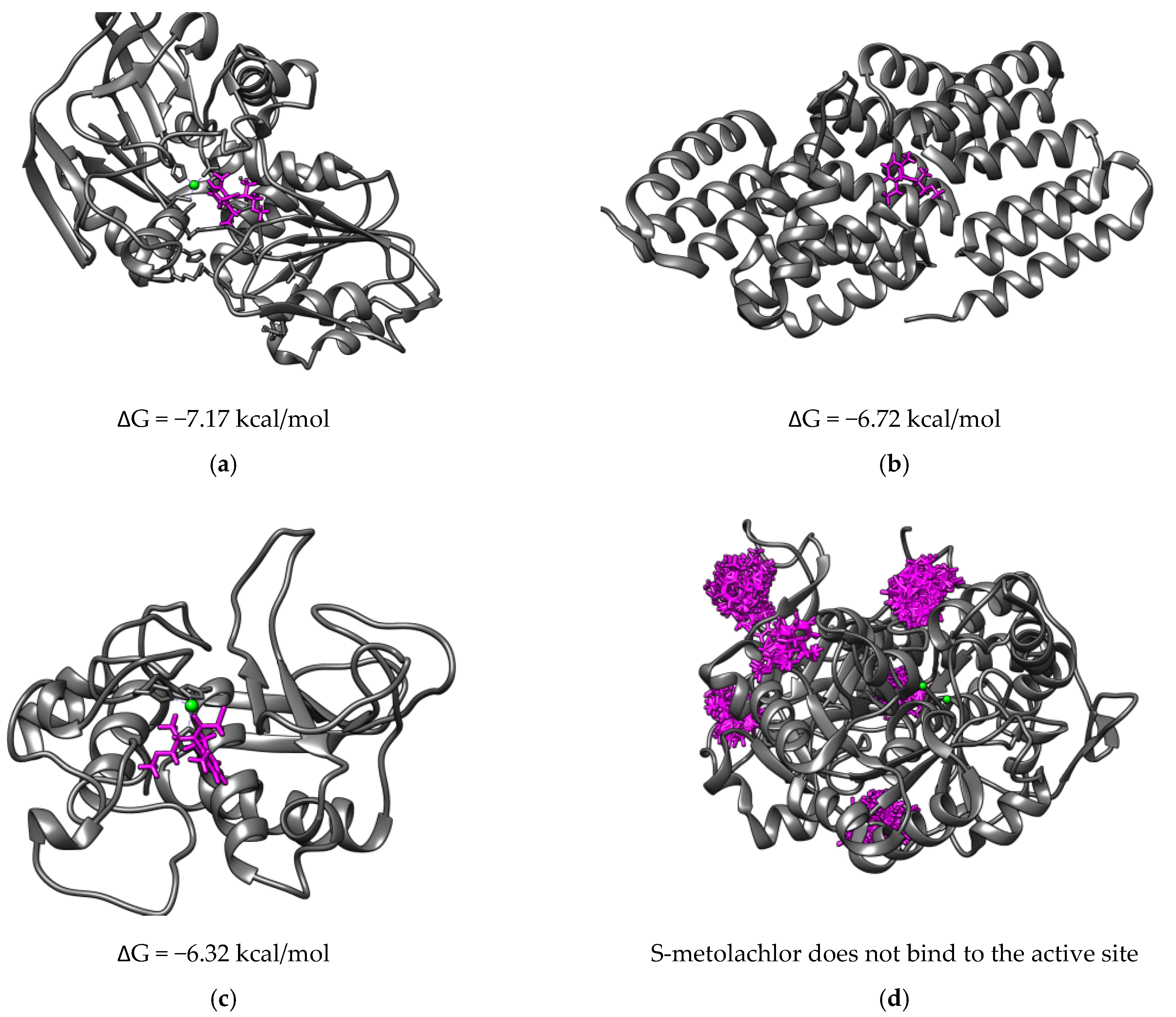
3.3. Computational Approach
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ayansina, A.D.; Amusan, O.A. Effect of Higher Concentrations of Herbicides on Bacterial Populations in Tropical Soil. Unique Res. J. Agric. Sci. 2013, 1, 001–005. Available online: http://www.uniqueresearchjournals.org/URJAS (accessed on 15 January 2021).
- Baćmaga, M.; Kucharski, J.; Wyszkowska, J.; Borowik, A.; Tomkiel, M. Responses of microorganisms and enzymes to soil contamination with metazachlor. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 2251–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzaioli, R.; D’Ascoli, R.; de Pascale, R.A.; Rutigliano, F.A. Soil quality in a Mediterranean area of Southern Italy as related to different land use types. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2010, 44, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Leoz, B.; Garbisu, C.; Charcosset, J.-Y.; Sanchez-Pérez, J.-M.; Antigüedad, I.; Ruiz-Romera, E. Non-target effects of three formulated pesticides on microbially-mediated processes in a clay-loam soil. Sci. Total. Environ. 2013, 449, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baćmaga, M.; Kucharski, J.; Wyszkowska, J.; Borowik, A.; Tomkiel, M. Response of fungi, β-glucosidase and arylsulfatase to soil contamination by Alister Grande 190 OD, Fuego 500 SC and Lumax 357.5 SE herbicides. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2014, 23, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baćmaga, M.; Borowik, A.; Kucharski, J.; Tomkiel, M.; Wyszkowska, J. Microbial and enzymatic activity of soil contaminated with a mixture of diflufenican + mesosulfuron-methyl + iodosulfuron-methyl-sodium. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 643–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, S.; Siddique, T.; Saleem, M.; Arshad, M.; Khalid, A. Chapter 5 Impact of Pesticides on Soil Microbial Diversity, Enzymes, and Biochemical Reactions. Adv. Agron. 2009, 102, 159–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filimon, M.N.; Borozan, A.B.; Bordean, D.M.; Popescu, R.; Gotia, S.R.; Verdes, D.; Sinitean, A. Sulphonylureic herbicidal risk in the detection of soil fungi communities. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2011, 5, 5507–5511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filimon, M.N.; Voia, O.S.; Popescu, R.; Dumitrescu, G.; Petculescu-Ciochina, L.; Mituletu, M.; Vlad, D.C. The effect of some insecticides on soil microorganisms based on enzymatic and bacteriological analyses. Rom. Biotech. Lett. 2015, 20, 10439–10447. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Z.; Li, S.; Zhang, W.; Ma, J.; Wang, J.; Cai, J.; Yang, G. Effects of the novel pyrimidynyloxybenzoic herbicide ZJ0273 on enzyme activities, microorganisms and its degradation in Chinese soils. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 22, 4425–4433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filimon, M.N.; Voia, S.O.; Vladoiu, D.L.; Isvoran, A.; Ostafe, V. Temperature dependent effect of difenoconazole on enzymatic activity from the soil. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 2015, 80, 1127–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharski, J.; Tomkiel, M.; Baćmaga, M.; Borowik, A.; Wyszkowska, J. Enzyme activity and microorganisms diversity in soil contaminated with the Boreal 58 WG herbicide. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2016, 51, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floch, C.; Chevremont, A.-C.; Joanico, K.; Capowiez, Y.; Criquet, S. Indicators of pesticide contamination: Soil enzyme compared to functional diversity of bacterial communities via Biolog® Ecoplates. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2011, 47, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filimon, M.N.; Voia, O.S.; Popescu, R.; Bordean, D.-M.; Vladoiu, D.L.; Mituletu, M.; Ostafe, V. The effect of chlorsulfurone and MCPB-Na on the enzymatic activity of microorganisms. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 2014, 79, 1075–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riah, W.; Laval, K.; Laroche-Ajzenberg, E.; Mougin, C.; Latour, X.; Trinsoutrot-Gattin, I. Effects of pesticides on soil enzymatic activities: General trends. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2014, 12, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, D.; Gao, Z.; Fu, B.; Sun, H.; Tian, S.; Xiao, Y.; Qin, Z. Effect of pyrimorph on soil enzymatic activities and respiration. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2013, 56, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.H.; Li, R.T.; Wu, X.M. Degradation of S-metolachlor in soil as affected by environmental factors. J. Soil Sci. Plant. Nutr. 2014, 14, 189–198. Available online: https://scielo.conicyt.cl/pdf/jsspn/v14n1/aop1514.pdf (accessed on 11 January 2021). [CrossRef]
- Filimon, M.N.; Popescu, R.; Verdes, D.; Dumitrescu, G.; Voia, O.S.; Ahmadi, M.; Dronca, D. The Effects of Difenoconazole Treatment on Microorganism from Soil. Rev. Chim. 2018, 69, 1129–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, X.; Dong, F.; Xu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Li, J. Soil microbial communities response to herbicide 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid butyl ester. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2010, 46, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.M.; Li, M.; Long, Y.H.; Liu, R.X.; Yu, Y.L.; Fang, H.; Li, S.N. Effects of adsorption on degradation and bioavailability of metolachlor in soil. J. Soil. Sci. Plant. Nutr. 2011, 11, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemolin, C.R.; Avila, L.A.; Cassol, G.V.; Massey, J.H.; Camargo, E.R. Environmental fate of S-Metolachlor: A review. Planta Daninha Viçosa-MG 2014, 32, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wołejko, E.; Kaczyński, P.; Łozowicka, B.; Wydro, U.; Borusiewicz, A.; Hrynko, I.; Konecki, R.; Snarska, K.; Dec, D.; Malinowski, P. Dissipation of S-metolachlor in plant and soil and effect on enzymatic activities. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Takagi, K.; Iwasaki, A.; Zhou, D. Adsorption, desorption and dissipation of metolachlor in surface and subsurface soils. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2009, 65, 956–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipşa, F.D.; Ulea, E.; Chiriac, I.P.; Coroi, I.G. Effect of herbicide S-metolachlor on soil microorganisms. Lucr. Stiinţifice Ser. Agron. 2010, 53, 110–113. (In Romanian) [Google Scholar]
- Borowik, A.; Wyszkowska, J.; Kucharski, J.; Baćmaga, M.; Tomkiel, M. Response of microorganisms and enzymes to soil contamination with a mixture of terbuthylazine, mesotrione, and S-metolachlor. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 1910–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Nie, M.; Powell, J.R.; Bissett, A.; Pendall, E. Soil physico-chemical properties are critical for predicting carbon storage and nutrient availability across Australia. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 094088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pub Chem. Data Base. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/S-Metolachlor (accessed on 10 October 2020).
- USEPA. Toxicology Chapter for Metolachlor/S-Metolachlor. 2001. Available online: https://archive.epa.gov/pesticides/chemicalsearch/chemical/foia/web/pdf/108800/108800-2001-12-04a.pdf (accessed on 11 January 2021).
- Bordean, D.M.; Borozan, A.B.; Cojocariu, L.; Moigradean, D.; Cojocariu, A.; Nica, D.; Pirvulescu, L.; Alda, S.; Horablaga, M. Seasonal variation in nutrient content of some leafy vegetables from Banat County, Romania. Rev. Agric. Rural Dev. 2003, 2, 170–174. [Google Scholar]
- Gergen, I. Analiza Produselor Agroalimentare; Editura Eurostampa: Timisoara, Romania, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Baethgen, W.E.; Alley, M.M. A manual colorimetric procedure for measuring ammonium nitrogen in soil and plant Kjeldahl digests. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant. Anal. 1989, 20, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uwah, E.I.; Abah, J.; Ndahi, N.P.; Ogugbuaja, V.O. Concentration levels of nitrate and nitrite in soils and some leafy vegetables obtained in Maiduguri, Nigeria. J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Sanit. 2009, 4, 233–244. [Google Scholar]
- Amponsah, D.; Etsey, G.; Nagai, H. Determination of Amount of Phosphate and Sulphate in Soil Samples from University of Cape Coast Farm. Int. J. Sci. Technol. Res. 2014, 3, 211–215. Available online: http://www.ijstr.org/final-print/july2014/Determination-Of-Amount-Of-Phosphate-And-Sulphate-In-Soil-Samples-From-University-Of-Cape-Coast-Farm.pdf (accessed on 11 January 2021).
- Schinner, F.; Öhlinger, R.; Kandeler, E.; Margesin, R. Methods in Soil Biology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1996; pp. 241–243. [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins, D.W.; Alef, K.; Nannipieri, P. Methods in Applied Soil Microbiology and Biochemistry. J. Appl. Ecol. 1996, 33, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, R.P. Soil enzyme activities as integrative indicators of soil health. In Biological Indicators of Soil Health; Pankhurst, C.E., Doube, B.M., Gupta, V.V.S.R., Eds.; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 1997; pp. 121–156. [Google Scholar]
- Dragan-Bularda, M. Microbiologie Generala-Lucrari Practice; Editura Universitatii Babes-Bolyai: Cluj-Napoca, Romania, 2000; pp. 178–180, 189–191. (In Romanian) [Google Scholar]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Chen, J.; Cheng, T.; Gindulyte, A.; He, J.; He, S.; Li, Q.; Shoemaker, B.A.; Thiessen, P.A.; Yu, B.; et al. PubChem 2019 update: Improved access to chemical data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D1102–D1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosdidier, A.; Zoete, V.; Michielin, O. SwissDock, a protein-small molecule docking web service based on EADock DSS. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W270–W277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosdidier, A.; Zoete, V.; Michielin, O. EADock: Docking of small molecules into protein active sites with a multiobjective evolutionary optimization. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2007, 67, 1010–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schäffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, W.R. An Introduction to Sequence Similarity (“Homology”) Searching. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2013, 42, 3.1.1–3.1.8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, E.; Ferreras, L.; Lovotti, L.; Fernandez, E. Impact of glyphosate application on microbial biomass and metabolic activity in a Vertic Argiudoll from Argentina. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2009, 45, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataikiru, T.L.; Okpokwasili, G.S.C.; Okerentugba, P.O. Impact of Pesticides on Microbial Diversity and Enzymes in Soil. South. Asian J. Res. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swensen, B.; Bakken, L.R. Urease activity and nitrification potential in a mineral subsoil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1998, 30, 1333–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baboo, M.; Pasayat, M.; Samal, A.; Kujur, M.; Maharana, J.K.; Patel, A.K. Effect of Four Herbicides on Soil Organic Car-Bon, Microbial Biomass-c, Enzyme Activity and Microbial Populations in Agricultural Soil. IJEST 2013, 3, 100–112. Available online: http://www.urpjournals.com (accessed on 11 January 2021).
- Richardson, D.M.; Pysek, P.; Rejmanek, M.; Barbour, M.G.; Panetta, F.D.; West, C.J. Naturalization and invasion of alien plants: Concepts and definitions. Divers. Distrib. 2000, 6, 93–107. Available online: http://www.blackwell-science.com/ddi (accessed on 11 January 2021). [CrossRef]
- Pant, H.K.; Warman, P.R. Enzymatic hydrolysis of soil organic phosphorus by immobilized phosphatases. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2000, 30, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, B.; Bolan, N.; Naidu, R.; de la Luz-Mora, M. Phosphorus in organic waste-soil systems. J. Soil Sc. Plant. Nutr. 2006, 6, 64–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martiny, J.B.H.; Bohannan, B.J.M.; Brown, J.H.; Colwell, R.K.; Fuhrman, J.A.; Green, J.L.; Horner-Devine, M.C.; Kane, M.; Krumins, J.A.; Kuske, C.R.; et al. Microbial biogeography: Putting microorganisms on the map. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2006, 4, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Salgado, M.M.; Gutiérrez-Romero, V.; Jannsens, M.; Ortega-Blu, R. Current Research, Technology and Education Topics in Applied Microbiology and Microbial Biotechnology. In Biological Soil Guality Indicators: A Review; Mendez-Vilas, A., Ed.; FORMATEX Microbiology: Badajoz, Spain, 2010; Volume 2, pp. 319–328. [Google Scholar]
- Wyszkowska, J. Effect of soil contamination with Treflan 480 EC on biochemical properties of soil. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2002, 11, 71–77. [Google Scholar]
- Wyszkowska, J.; Kucharski, J. Biochemical and physicochemical properties of soil contaminated with herbicide Triflurotox 250 EC. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2004, 13, 223–231. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, X.-H.; Min, H.; Lü, Z.-H.; Yuan, H.-P. Influence of acetamiprid on soil enzymatic activities and respiration. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2006, 42, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baćmaga, M.; Boros, E.; Kucharski, J.; Wyszkowska, J. Enzymatic activity in soil contaminated with the Aurora 40 WG herbi-cide. Environ. Protect. Eng. 2012, 38, 91–102. [Google Scholar]
- Dhillon, A.; Sharma, K.; Rajulapati, V.; Goyal, A. Proteolytic Enzymes. Curr. Dev. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2017, 149–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subrahmany, G.; Archana, G.; Chamyal, L.S. Soil Microbial Activity and its Relation to Soil Indigenous Properties in Semi-arid Alluvial and Estuarine Soils of Mahi River Basin, Western India. Int. J. Soil Sci. 2011, 6, 224–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kwiatkowski, C.A.; Harasim, E.; Feledyn-Szewczyk, B.; Antonkiewicz, J. Enzymatic Activity of Loess Soil in Organic and Conventional Farming Systems. Agriculture 2020, 10, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kompała-Bąba, A.; Bierza, W.; Sierka, E.; Błońska, A.; Besenyei, L.; Woźniak, G. The role of plants and soil properties in the enzyme activities of substrates on hard coal mine spoil heaps. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
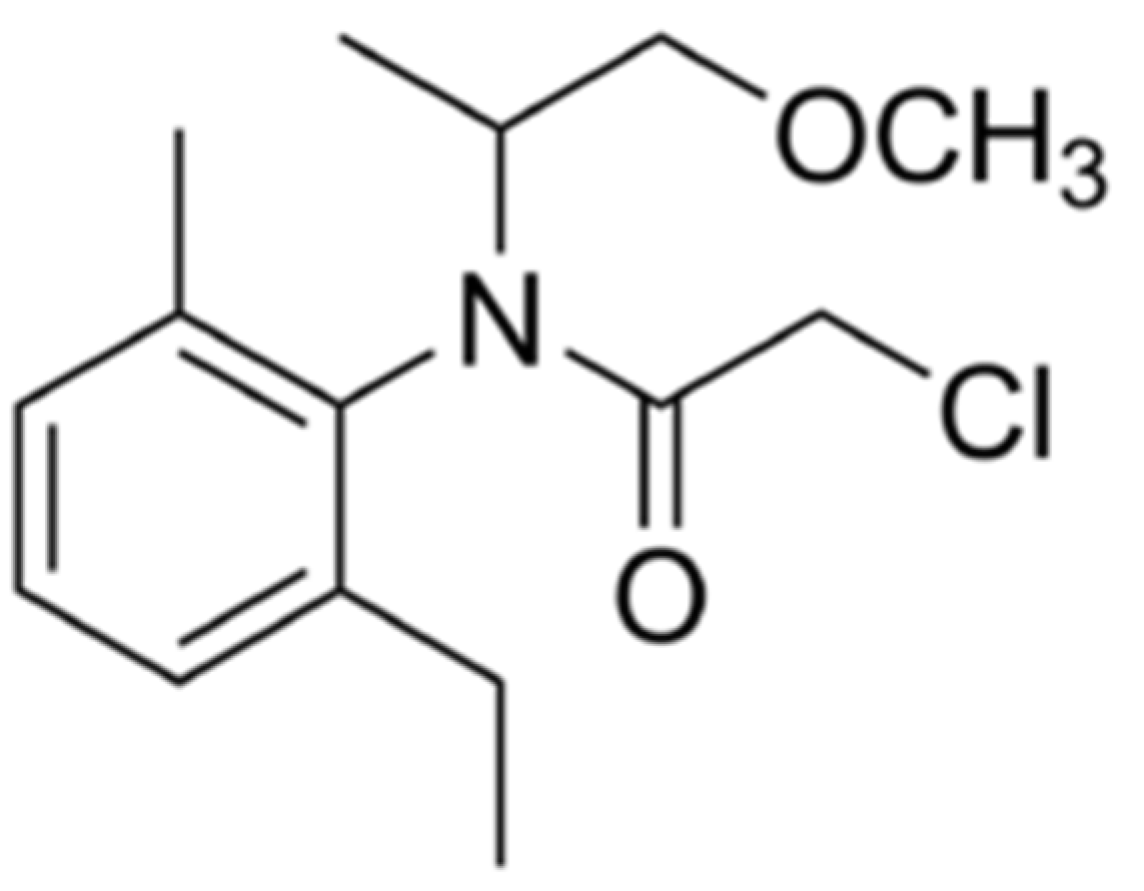

| Experimental Variants | Dose Application in Soil |
|---|---|
| M | control soil (soil untreated with S-metolachlor) |
| V1 | 1 g S-metolachlor/kg of soil |
| V2 | 3 g S-metolachlor/kg of soil |
| V3 | 6 g S-metolachlor/kg of soil |
| V4 | 9 g S-metolachlor/kg of soil |
| V5 | 12 g S-metolachlor/kg of soil |
| Day | Dose (Variant) | DA | UA | PA | PhA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | 0 g (M) | 3.91 ± 0.34 | 1.11 ± 0.22 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 2.56 ± 0.36 |
| 7 | 1 g (V1) | 2.55 ± 0.28 | 0.65 ± 0.11 | 0.07 ± 0.03 *** | 2.27 ± 0.27 |
| 7 | 3 g (V2) | 2.43 ± 0.17 | 0.62 ± 0.11 | 0.04 ± 0.02 *** | 2.16 ± 0.18 |
| 7 | 6 g (V3) | 0.24 ± 0.12 *** | 0.59 ± 0.19 | 0.09 ± 0.01 *** | 1.95 ± 0.25 |
| 7 | 9 g (V4) | 0.21 ± 0.08 *** | 0.49 ± 0.07 | 0.07 ± 0.02 *** | 1.88 ± 0.19 |
| 7 | 12 g (V5) | 0.18 ± 0.05 *** | 0.43 ± 0.16 | 0.03 ± 0.01 *** | 1.38 ± 0.26 |
| 14 | 0 g (M) | 3.07 ± 0.23 | 1.13 ± 0.24 | 0.12 ± 0.03 | 1.90 ± 0.30 |
| 14 | 1 g (V1) | 1.50 ± 0.34 | 0.83 ± 0.19 | 0.08 ± 0.01 *** | 2.04 ± 0.17 |
| 14 | 3 g (V2) | 1.01 ± 0.17 ** | 0.82 ± 0.16 | 0.09 ± 0.02 *** | 2.08 ± 0.14 |
| 14 | 6 g (V3) | 0.21 ± 0.09 *** | 0.71 ± 0.11 | 0.07 ± 0.00 *** | 1.99 ± 0.23 |
| 14 | 9 g (V4) | 0.19 ± 0.10 *** | 0.60 ± 0.18 | 0.05 ± 0.01 *** | 1.86 ± 0.18 |
| 14 | 12 g (V5) | 0.18 ± 0.04 *** | 0.66 ± 0.13 | 0.04 ± 0.01 *** | 1.79 ± 0.26 |
| 21 | 0 g (M) | 2.37 ± 0.23 | 2.33 ± 0.24 | 0.19 ± 0.05 | 2.44 ± 0.19 |
| 21 | 1 g (V1) | 0.44 ± 0.27 *** | 0.96 ± 0.16 | 0.12 ± 0.03 *** | 2.02 ± 0.36 |
| 21 | 3 g (V2) | 0.41 ± 0.13 *** | 0.78 ± 0.11 | 0.10 ± 0.04 *** | 2.11 ± 0.29 |
| 21 | 6 g (V3) | 0.30 ± 0.12 *** | 0.75 ± 0.09 | 0.10 ± 0.01 *** | 1.92 ± 0.32 |
| 21 | 9 g (V4) | 0.18 ± 0.08 *** | 0.90 ± 0.33 | 0.08 ± 0.03 *** | 1.89 ± 0.28 |
| 21 | 12 g (V5) | 0.16 ± 0.11 *** | 0.72 ± 0.17 | 0.09 ± 0.02 *** | 1.70 ± 0.13 |
| Herbicide Dose | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DA | −0.914 * | |||||||||||
| UA | −0.735 * | 0.486 * | ||||||||||
| PA | −0.429 | 0.142 | 0.658 * | |||||||||
| PhA | −0.873 * | 0.897 * | 0.471 * | 0.264 | ||||||||
| pH | −0.863 * | 0.717 * | 0.880 * | 0.552 * | 0.678 * | |||||||
| t (°C) | 0.001 | −0.077 | 0.034 | 0.315 | −0.358 | −0.402 | ||||||
| EC | −0.061 | −0.070 | 0.306 | 0.386 | −0.170 | 0.234 | 0.383 | |||||
| Soil moisture | −0.567 * | 0.442 * | 0.589 * | 0.283 | 0.467 * | 0.539 * | −0.400 | 0.194 | ||||
| OM (mg/g) | −0.624 * | 0.534 * | 0.370 | 0.202 | 0.595 * | 0.514 * | −0.282 | −0.320 | 0.267 | |||
| NO3-N (mg/g) | −0.602 * | 0.509 * | 0.510 * | 0.339 | 0.382 | 0.487 * | 0.298 | 0.262 | 0.283 | 0.146 | ||
| NH4-N (mg/kg) | −0.108 | 0.335 | −0.417 | −0.647 * | 0.217 | −0.153 | −0.376 | −0.294 | −0.100 | 0.217 | −0.051 | |
| Available phosphorus (mg/kg) | −0.806 * | 0.709 * | 0.544 * | 0.386 | 0.706 * | 0.716 * | 0.043 | 0.147 | 0.232 | 0.478 * | 0.666 * | 0.138 |
| Enzyme | Sequences Identity with Other Enzymes |
|---|---|
| alcohol dehydrogenases from Clostridium beijerinckii | 71.2 to 73.4 % with alcohol dehydrogenases from Desulfotomaculum sp. 71.5 to 93.4% alcohol dehydrogenases from Clostridium sp. |
| phosphatase F from Bacillus subtilis | Low sequence identity (up to 57.5 %) with phosphatases F from Bacillus sp. |
| protease from Serratia marcescens | 82.8 to 98.2 % proteases from Seratia sp. |
| urease from Bacillus pasteurii | 70 to 98.2% with ureases from Bacillus sp. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Filimon, M.N.; Roman, D.L.; Caraba, I.V.; Isvoran, A. Assessment of the Effect of Application of the Herbicide S-Metolachlor on the Activity of Some Enzymes Found in Soil. Agriculture 2021, 11, 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11060469
Filimon MN, Roman DL, Caraba IV, Isvoran A. Assessment of the Effect of Application of the Herbicide S-Metolachlor on the Activity of Some Enzymes Found in Soil. Agriculture. 2021; 11(6):469. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11060469
Chicago/Turabian StyleFilimon, Marioara Nicoleta, Diana Larisa Roman, Ion Valeriu Caraba, and Adriana Isvoran. 2021. "Assessment of the Effect of Application of the Herbicide S-Metolachlor on the Activity of Some Enzymes Found in Soil" Agriculture 11, no. 6: 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11060469
APA StyleFilimon, M. N., Roman, D. L., Caraba, I. V., & Isvoran, A. (2021). Assessment of the Effect of Application of the Herbicide S-Metolachlor on the Activity of Some Enzymes Found in Soil. Agriculture, 11(6), 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11060469







