Foliar Application of Zn Agrichemicals Affects the Bioavailability of Arsenic, Cadmium and Micronutrients to Rice (Oryza sativa L.) in Flooded Paddy Soil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Characterization of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles (ZnONPs)
2.2. Soil Preparation
2.3. Experimental Setup
2.4. Total As, Cd, Cu, Fe, and Zn Analysis in Plant Tissues
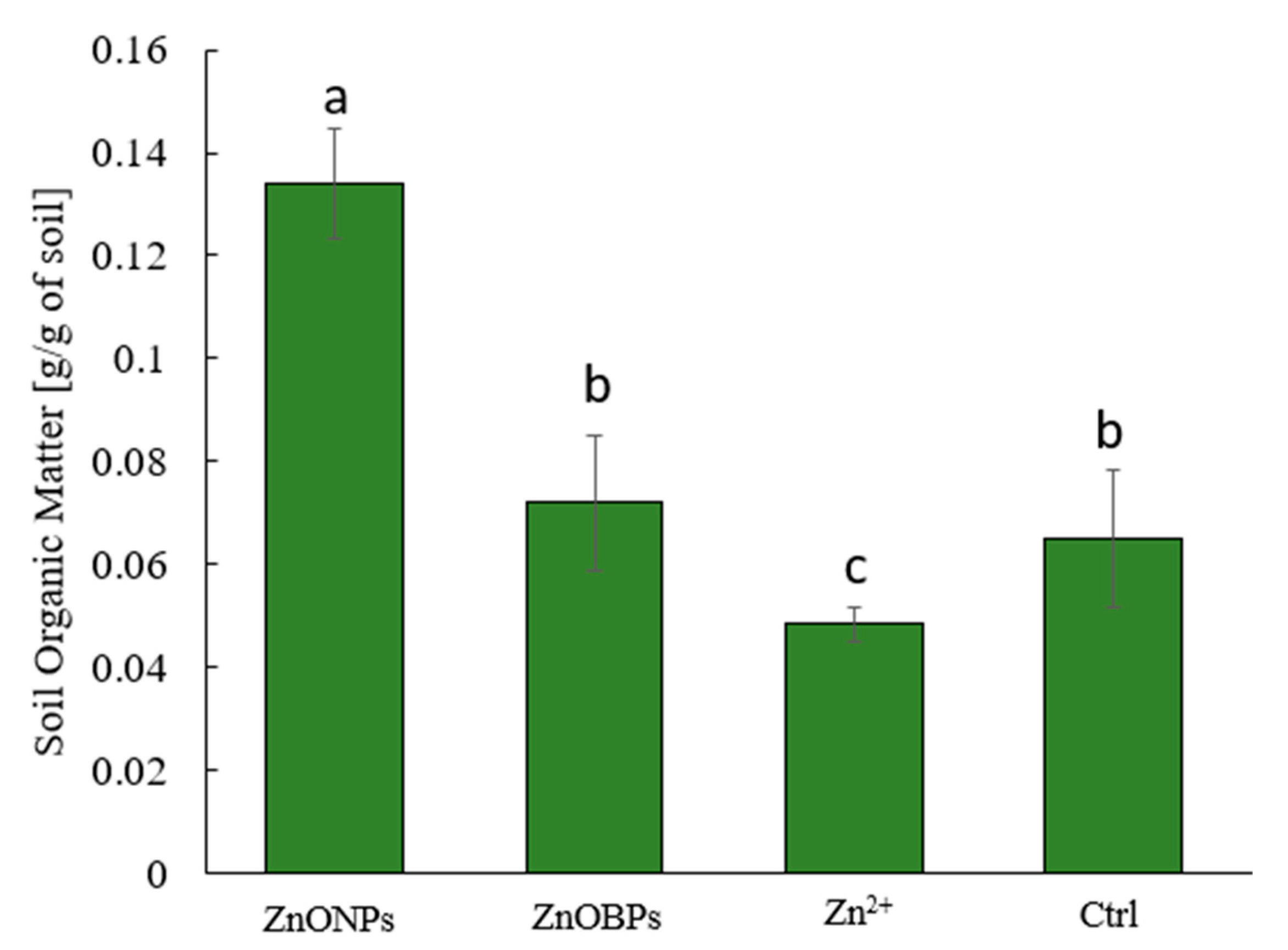
2.5. Soil Organic Content by Loss-on-Ignition (LOI)
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Biomass
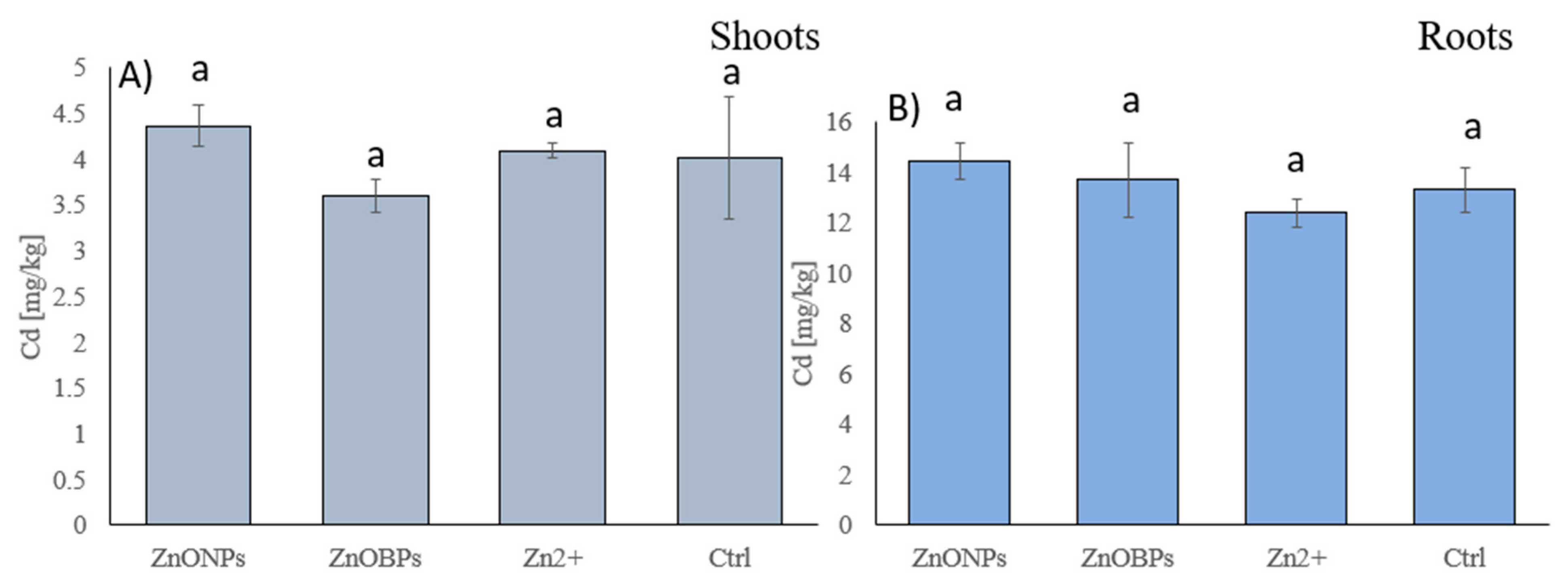
3.2. Arsenic and Cadmium
3.3. Micronutrients
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kah, M.; Tufenkji, N.; White, J.C. Nano-enabled strategies to enhance crop nutrition and protection. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2019, 14, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Wang, S.; Yang, X.; Tufail, S.; Chen, C.; Wang, X.; Shang, J. Green sustainable and highly efficient hematite nanoparticles modified biochar-clay granular composite for Cr(VI) removal and related mechanism. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 123009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, A.; Donnelly, T.; Colbert, J.; Cai, W.; Newman, L.A.; White, J.C. Exposure of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) to silver nanoparticles and silver nitrate: Physiological and molecular response. Int. J. Phytoremed. 2019, 22, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimkpa, C.O.; Singh, U.; Bindraban, P.S.; Elmer, W.H.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.L.; White, J.C. Zinc oxide nanoparticles alleviate drought-induced alterations in sorghum performance, nutrient acquisition, and grain fortification. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 688, 926–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusefi-Tanha, E.; Fallah, S.; Rostamnejadi, A.; Pokhrel, L.R. Zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnONPs) as a novel nanofertilizer: Influence on seed yield and antioxidant defense system in soil grown soybean (Glycine max cv. Kowsar). Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 738, 140240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehata, S.; Tamang, M.K.; Parajuli, K.R.; Rayamajhee, B.; Yadav, U.N.; Mehta, R.K.; Singh, D.R. Prevalence and Predictors of Zinc Deficiency among Children and Non-Pregnant Women in Nepal: Analysis of Nepal Micronutrients Status Survey 2016. Preprints 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, H.; De Diego, N.; Rad, A.C.; Benjamin, J.J.; Trevisan, M.; Lucini, L. Exogenous application of ZnO nanoparticles and ZnSO4 distinctly influence the metabolic response in Phaseolus vulgaris L. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 778, 146331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phattarakul, N.; Rerkasem, B.; Li, L.J.; Wu, L.H.; Zou, C.Q.; Ram, H.; Sohu, V.S.; Kang, B.S.; Surek, H.; Kalayci, M.; et al. Biofortification of rice grain with zinc through zinc fertilization in different countries. Plant Soil 2012, 361, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifan, H.; Moore, J.; Ma, X. Zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles elevated iron and copper contents and mitigated the bioavailability of lead and cadmium in different leafy greens. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 191, 110177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, L.; Fedenia, L.N.; Sharifan, H.; Ma, X.; Lombardini, L. Effects of foliar application of zinc sulfate and zinc nanoparticles in coffee (Coffea arabica L.) plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 135, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Dou, F.; Li, C.; Ma, X.; Ma, L.Q. Impacts of metallic nanoparticles and transformed products on soil health. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 51, 973–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, J.; Slaný, M.; Yan, H.; Li, P.; El-Naggar, A.; Shaheen, S.M.; Rinklebe, J.; Feng, X. Use of biochar to reduce mercury accumulation in Oryza sativa L: A trial for sustainable management of historically polluted farmlands. Environ. Int. 2021, 153, 106527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Shaheen, S.M.; Jiang, Y.; Li, R.; Slaný, M.; Abdelrahman, H.; Kwon, E.; Bolan, N.; Rinklebe, J.; Zhang, Z. Fe/Mn- and P-modified drinking water treatment residuals reduced Cu and Pb phytoavailability and uptake in a mining soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Salem, S.M.; Zeitoun, R.; Dutta, A.; Al-Nasser, A.; Al-Wadi, M.H.; Al-Dhafeeri, A.T.; Karam, H.J.; Asiri, F.; Biswas, A. Baseline soil characterisation of active landfill sites for future restoration and development in the state of Kuwait. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 17, 4407–4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourang, N.; Noori, A. Heavy metals contamination in soil, surface water and groundwater of an agricultural area adjacent to Tehran oil refinery, Iran. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2014, 8, 871–886. [Google Scholar]
- Sharifan, H.; Wang, X.; Guo, B.; Ma, X. Investigation on the Modification of Physicochemical Properties of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles through Adsorption of Cd and As(III)/As(V). ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 13454–13461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawia, A.M.; Hui, S.; Zhou, L.; Li, H.; Tabassum, J.; Lai, C.; Wang, J.; Shao, G.; Wei, X.; Tang, S.; et al. Inorganic arsenic toxicity and alleviation strategies in rice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 408, 124751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Sharifan, H.; Dou, F.; Sun, W. Simultaneous reduction of arsenic (As) and cadmium (Cd) accumulation in rice by zinc oxide nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 384, 123802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifan, H.; Ma, X.; Moore, J.M.; Habib, M.R.; Evans, C. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Alleviated the Bioavailability of Cadmium and Lead and Changed the Uptake of Iron in Hydroponically Grown Lettuce (Lactuca sativa L. var. Longifolia). ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 16401–16409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, L.; Zhang, W.; Schwab, A.P.; Ma, X. Uptake, accumulation, and in planta distribution of coexisting cerium oxide nanoparticles and cadmium in Glycine max (L.) Merr. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 12815–12824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taran, M.; Safaei, M.; Karimi, N.; Almasi, A. Benefits and application of nanotechnology in environmental science: An overview. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2021, 11, 7860–7870. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Sun, W.; Zhang, S.; Sharifan, H.; Ma, X. Elucidating the effects of cerium oxide nanoparticles and zinc oxide nanoparticles on arsenic uptake and speciation in rice (Oryza sativa) in a hydroponic system. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 10040–10047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazdi, M.E.T.; Amiri, M.S.; Nourbakhsh, F.; Rahnama, M.; Forouzanfar, F.; Mousavi, S.H. Bio-indicators in cadmium toxicity: Role of HSP27 and HSP. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 2021, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avellan, A.; Yun, J.; Morais, B.P.; Clement, E.T.; Rodrigues, S.M.; Lowry, G.V. Critical Review: Role of Inorganic Nanoparticle Properties on Their Foliar Uptake and in Planta Translocation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi, H.; Chehregani, A.; Lucini, L.; Majd, A.; Gholami, M. Morphological, proteomic and metabolomic insight into the effect of cerium dioxide nanoparticles to Phaseolus vulgaris L. under soil or foliar application. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 616-617, 1540–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, G.; Vijver, M.G.; Bosker, T.; Peijnenburg, W.J. Foliar versus root exposure of AgNPs to lettuce: Phytotoxicity, antioxidant responses and internal translocation. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 261, 114117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Wang, C.; Wagner, D.C.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.L.; He, F.; Rico, C.M. Foliar application of nanoparticles: Mechanisms of absorption, transfer, and multiple impacts. Environ. Sci: Nano 2021, 8, 1196–1210. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, J.; Xing, G. Comparative physiological and metabolomic analyses revealed that foliar spraying with zinc oxide and silica nanoparticles modulates metabolite profiles in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Food Energy Secur. 2021, 10, e269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Sun, H.; Lv, Z.; Cui, L.; Mao, H.; Kopittke, P.M. Using Synchrotron-Based Approaches To Examine the Foliar Application of ZnSO4and ZnO Nanoparticles for Field-Grown Winter Wheat. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 2572–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, F.; Soriano, J.; Tabien, R.; Chen, K. Soil Texture and Cultivar Effects on Rice (Oryza sativa, L.) Grain Yield, Yield Components and Water Productivity in Three Water Regimes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, J.-T.; Liu, T.-X.; Wang, X.-Q.; Li, F.-B.; Lv, Y.-H.; Cui, J.-H.; Zeng, X.-D.; Yuan, Y.-Z.; Liu, C.-P. Simultaneous alleviation of cadmium and arsenic accumulation in rice by applying zero-valent iron and biochar to contaminated paddy soils. Chemosphere 2018, 195, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Rizwan, M.; Noureen, S.; Anwar, S.; Ali, B.; Naveed, M.; Allah, E.F.A.; A Alqarawi, A.; Ahmad, P. Combined use of biochar and zinc oxide nanoparticle foliar spray improved the plant growth and decreased the cadmium accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) plant. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 11288–11299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Ebbs, S.; Musante, C.; White, J.C.; Gao, C.; Ma, X. Uptake and Accumulation of Bulk and Nanosized Cerium Oxide Particles and Ionic Cerium by Radish (Raphanus sativus L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Dan, Y.; Shi, H.; Ma, X. Elucidating the mechanisms for plant uptake and in-planta speciation of cerium in radish (Raphanus sativus L.) treated with cerium oxide nanoparticles. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez, J.M.; Galantini, J.A.; Duval, M.E.; López, F.M.; Iglesias, J.O. Estimating soil organic carbon in Mollisols and its particle-size fractions by loss-on-ignition in the semiarid and semihumid Argentinean Pampas. Geoderma Reg. 2018, 12, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, C.E.; Grayston, S.J.; Helmisaari, H.-S.; Kaštovská, E.; Körner, C.; Lambers, H.; Meier, I.C.; Millard, P.; Ostonen, I. Surplus Carbon Drives Allocation and Plant–Soil Interactions. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2020, 35, 1110–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, R.; Kalia, A.; Dhaliwal, S.S. Evaluation of Efficacy of ZnO Nanoparticles as Remedial Zinc Nanofertilizer for Rice. J. soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2019, 19, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysargyris, A.; Papakyriakou, E.; Petropoulos, S.A.; Tzortzakis, N. The combined and single effect of salinity and copper stress on growth and quality of Mentha spicata plants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 368, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, G.J.; Carpenter, R.J.; Koutoulis, A.; Price, A.; Brodribb, T. Environmental adaptation in stomatal size independent of the effects of genome size. New Phytol. 2014, 205, 608–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, Y.; He, X.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, G.; Xie, C.; Luo, W.; Zhang, J.; et al. Xylem and Phloem Based Transport of CeO2 Nanoparticles in Hydroponic Cucumber Plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 5215–5221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sharifan, H.; Ma, X. Foliar Application of Zn Agrichemicals Affects the Bioavailability of Arsenic, Cadmium and Micronutrients to Rice (Oryza sativa L.) in Flooded Paddy Soil. Agriculture 2021, 11, 505. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11060505
Sharifan H, Ma X. Foliar Application of Zn Agrichemicals Affects the Bioavailability of Arsenic, Cadmium and Micronutrients to Rice (Oryza sativa L.) in Flooded Paddy Soil. Agriculture. 2021; 11(6):505. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11060505
Chicago/Turabian StyleSharifan, Hamidreza, and Xingmao Ma. 2021. "Foliar Application of Zn Agrichemicals Affects the Bioavailability of Arsenic, Cadmium and Micronutrients to Rice (Oryza sativa L.) in Flooded Paddy Soil" Agriculture 11, no. 6: 505. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11060505
APA StyleSharifan, H., & Ma, X. (2021). Foliar Application of Zn Agrichemicals Affects the Bioavailability of Arsenic, Cadmium and Micronutrients to Rice (Oryza sativa L.) in Flooded Paddy Soil. Agriculture, 11(6), 505. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11060505






