Impact of Packing Density on the Bacterial Community, Fermentation, and In Vitro Digestibility of Whole-Crop Barley Silage
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Barley Silage Preparation
2.2. Silage Extract Preparation
2.3. Microbial Population
2.4. Bacterial Diversity Analysis
2.4.1. DNA Isolation and PCR Amplification
2.4.2. Sequencing and Data Analysis
2.5. Fermentation Quality, Chemical Composition, and In Vitro Digestibility
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Fresh Barley
3.2. Bacterial Community of Fresh Barley and Silages
3.3. Microbial Population, Fermentation Quality, and Chemical Composition of Silage
3.4. Correlation Analysis Heat Map of the Bacterial Community, and Quality Indices, Correlation Networks among Main Bacterial Genera and Density
4. Discussion
4.1. Microbial Composition of Barley before and after Ensiling
4.2. Fermentation Quality, Microbial Counts, DM Recovery, Chemical Composition, and In Vitro Digestibility of Barley Silages
4.3. The Relationship between the Microbial Community and Quality Indices
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, B.; Huan, H.; Gu, H.; Xu, N.; Shen, Q.; Ding, C. Dynamics of a microbial community during ensiling and upon aerobic exposure in lactic acid bacteria inoculation-treated and untreated barley silages. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 273, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikel, D.; Ben-Mair, Y.A.; Yoav, S.; Ran, S.; Idan, R.; Yuri, P.; Shamay, J.; Joshua, M.; Roi, B.D. Nutritive value for high-yielding lactating cows of barley silage and hay as a substitute for wheat silage and hay in low-roughage diets. Anim. Feed Sci. Tech. 2020, 265, 114498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallsten, J.; Hatfield, R. Cell wall chemical characteristics of whole-crop cereal silages harvested at three maturity stages. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 3604–3612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.J.; Kim, D.H.; Amanullah, S.M.; Kim, S.C.; Song, Y.M.; Kim, H.Y. Effects of bacterial inoculants and cutting height on fermentation quality of barley silage. J. Korean Soc. Grassl. Forage Sci. 2014, 34, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nadeau, E. Effects of plant species, stage of maturity and additive on the feeding value of whole-crop cereal silage. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2007, 87, 789–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.P.; Xu, N.X.; Liu, B.Y.; Huan, H.L.; Gu, H.R.; Dong, C.F.; Ding, C.L. Interaction effect of silo density and additives on the fermentation quality, microbial counts, chemical composition and in vitro degradability of rice straw silage. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 297, 122412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sucu, E.; Kalkan, H.; Canbolat, O.; Filya, I. Effects of ensiling density on nutritive value of maize and sorghum silages. R. Bras. Zootec. 2016, 45, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.Z.; Zhang, F.F.; Ma, C.H.; Li, F.F.; Wang, S.L. Effect of compaction on nutritional quality and aerobic stability of silage corn after opening silos. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, T.; Wang, T.; Shimojo, M.; Masuda, Y. Effect of ensiling density on fermentation quality of Guineagrass (Panicum maximum Jacq.) silage during the early stage of ensiling. Asian Austral. J. Anim. 2005, 18, 1273–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driehuis, F.; Oude, E.S. The impact of the quality of silage on animal health and food safety: A review. Vet. Q. 2000, 22, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anésio, A.H.C.; Santos, M.V.; da Silva, L.D.; Silveira, R.R.; Braz, T.G.S.; Pereira, R.C. Effects of ensiling density on chemical and microbiological characteristics of sorghum silage. J. Anim. Feed Sci. 2017, 26, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.M.; Harrison, J.H.; Davidson, D.; Mahanna, W.C.; Shinners, K.; Linder, D. Corn silage management: Effects of maturity, inoculation, and mechanical processing on pack density and aerobic stability. J. Dairy Sci. 2002, 85, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruning, D.; Gerlach, K.; Wei, K.; Sudekum, K.H. Effect of compaction, delayed sealing and aerobic exposure on maize silage quality and on formation of volatile organic compounds. Grass Forage Sci. 2018, 73, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamoto, H.; Yamaguchi, H.; Komatsu, T.; Tanaka, O.; Oshibe, A. Effect of chopping and high-density ensiling on the silage fermentation of forage paddy rice (Oryza sativa L.). Jpn. J. Grassl. Sci. 2009, 54, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungbluth, K.; Trimborn, M.; Maack, G.; Büscher, W.; Li, M.; Cheng, H.; Cheng, Q.; Sun, Y. Effects of three different additives and two different bulk densities on maize silage characteristics, temperature profiles, CO2 and O2–dynamics in small scale silos during aerobic exposure. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, Y.; Benno, Y.; Ogawa, M.; Kumai, S. Effect of applying lactic acid bacteria isolated from forage crops on fermentation characteristics and aerobic deterioration of silage. J. Dairy Sci. 1999, 82, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Yan, Y.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Shuai, Y.; Feng, G.; Ran, Q.; Cai, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X. Microbial communities and natural fermentation of corn silages prepared with farm bunker-silo in Southwest China. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 265, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.M.; Ding, W.R.; Ke, W.C.; Li, F.H.; Zhang, P.; Guo, X.S. Modulation of metabolome and bacterial community in whole crop corn silage by inoculating homofermentative Lactobacillus plantarum and heterofermentative Lactobacillus buchneri. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mu, L.; Xie, Z.; Hu, L.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Z. Cellulase interacts with Lactobacillus plantarum to affect chemical composition, bacterial communities, and aerobic stability in mixed silage of high-moisture amaranth and rice straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 315, 123772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adesogan, A.T.; Krueger, N.; Salawu, M.B.; Dean, D.B.; Staples, C.R. The influence of treatment with dual purpose bacterial inoculants or soluble carbohydrates on the fermentation and aerobic stability of bermudagrass. J. Dairy Sci. 2004, 87, 3407–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Soest, P.J.; Robertson, J.B.; Lewis, B.A. Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and nonstarch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 3583–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Official Methods of Analysis; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Arlington, VA, USA, 1990.
- Contreras-Govea, F.E.; Muck, R.E.; Mertens, D.R.; Weimer, P.J. Microbial inoculant effects on silage and in vitro ruminal fermentation, and microbial biomass estimation for alfalfa, bmr corn, and corn silages. Anim. Feed Sci. Tech. 2011, 163, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, Z.M.; Ludwin, J.; Górka, P.; Rinne, M.; Weisbjerg, M.R.; Jagusiak, W. The use of cellulase and filter bag technique to predict digestibility of forages. Anim. Feed Sci. Tech. 2014, 198, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menke, K.; Raab, L.; Salewski, A.; Steingass, H.; Fritz, D.; Schneider, W. The estimation of the digestibility and metabolizable energy content of ruminant feedingstuffs from the gas production when they are incubated with rumen liquor in vitro. J. Agric. Sci. 1979, 93, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, X.A.; Dong, Z.H.; Li, J.F.; Shao, T.A. Microbial community dynamics and their contributions to organic acid production during the early stage of the ensiling of Napier grass (Pennisetum purpureum). Grass Forage Sci. 2020, 75, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, J.J.; Zhao, Y.; Balseca-Paredes, M.A.; Tiezzi, F.; Gutierrez-Rodriguez, E.; Castillo, M.S. Laboratory silo type and inoculation effects on nutritional composition, fermentation, and bacterial and fungal communities of oat silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 1812–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McGarvey, J.A.; Franco, R.B.; Palumbo, J.D.; Hnasko, R.; Stanker, L.; Mitloehner, F.M. Bacterial population dynamics during the ensiling of Medicago sativa (alfalfa) and subsequent exposure to air. J. Appl. Microbiol 2013, 114, 1661–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, H.; Qin, G.; Tan, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cai, Y. Natural populations of lactic acid bacteria associated with silage fermentation as determined by phenotype, 16S ribosomal RNA and recA gene analysis. Syst. Appl. Microbiol 2011, 34, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Sun, L.; Chen, C.; Lin, J.; Yang, F.; Cai, Y. Exploring microbial community structure and metabolic gene clusters during silage fermentation of paper mulberry, a high-protein woody plant. Anim. Feed Sci. Tech. 2020, 114766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila, C.L.S.; Carvalho, B.F. Silage fermentation-updates focusing on the performance of micro-organisms. J. Appli. Microbiol. 2020, 128, 966–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Braman, W.L.; Bryan, K.A.; Kurtz, J.E. 055 Effect of fermented corn silage density and bacterial inoculants on corn silage pH and fermentation end products. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 94, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Zhao, M.; Yu, Z. Lactic acid bacteria strains for enhancing the fermentation quality and aerobic stability of Leymus chinensis silage. Grass Forage Sci. 2016, 71, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, L.; Shaver, R.D.; Grant, R.J.; Schmidt, R.J. Silage review: Interpretation of chemical, microbial, and organoleptic components of silages. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4020–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlow, G.; Muck, R.E.; Driehuis, F.; Elferink, S.J.W.H.O.; Spoelstra, S.F. Microbiology of ensiling. In Silage Science and Technology; Buxton, D.R., Muck, R.E., Harrison, J.H., Eds.; Agron. Monogr. ASA, CSSA and SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 2003; pp. 31–94. [Google Scholar]
- Ruppel, K.A.; Pitt, R.E.; Chase, L.E.; Galton, D.M. Bunker silo management and its relationship to forage preservation on dairy farms. J. Dairy Sci. 1995, 78, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, A.; Bernardes, T.F.; Copani, G.; Fortunati, P.; Giuberti, G.; Bruschi, S.; Bryan, K.A.; Nielsen, N.G.; Witt, K.L.; Masoero, F. Effect of inoculation with Lactobacillus buchneri LB1819 and Lactococcus lactis O224 on fermentation and mycotoxin production in maize silage compacted at different densities. Anim. Feed Sci. Tech. 2018, 246, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, P.; Henderson, A.R.; Heron, S.J.E. The Biochemistry of Silage, 2nd ed.; Chalcombe Publications: Marlow, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.H.; Amanullah, S.M.; Lee, H.J.; Joo, Y.H.; Han, O.K.; Adesogan, A.T.; Kim, S.C. Effects of different cutting height on nutritional quality of whole crop barley silage and feed value on Hanwoo Heifers. Asian Austral. J. Anim. 2016, 29, 1265–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Dong, Z.H.; Li, J.F.; Chen, L.; Bai, Y.F.; Jia, Y.S.; Shao, T. Effects of lactic acid bacteria and molasses on fermentation dynamics, structural and nonstructural carbohydrate composition and in vitro ruminal fermentation of rice straw silage. Asian Austral. J. Anim. 2019, 32, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lynch, J.P.; Baah, J.; Beauchemin, K.A. Conservation, fiber digestibility, and nutritive value of corn harvested at 2 cutting heights and ensiled with fibrolytic enzymes, either alone or with a ferulic acid esterase-producing inoculant. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 1214–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, L.; Jiang, Y.; Ling, Q.; Na, N.; Xu, H.; Vyas, D.; Adesogan, A.T.; Xue, Y. Effects of adding pre-fermented fluid prepared from lucerne or red clover on fermentation quality and in vitro digestibility of the ensiled wilting-forages. Agriculture 2021, 11, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.; Bai, C.; Sun, J.; Sun, L.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Yu, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhang, K. Fermentation quality and nutritive value of total mixed ration silages based on desert wormwood (Artemisia desertorum Spreng.) combining with early stage corn. Anim. Sci. J. 2017, 88, 1963–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.L.; Yin, G.M.; Zhao, H.P.; Bai, C.S.; Sun, J.J.; Yu, Z.; Sun, Q.Z. Nutritive value of desert wormwood (Artemisia desertorum Spreng.) silage in mixture with high-moisture maize straw. Grass Forage Sci. 2017, 72, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, C.; Zhang, X.; Ingram, L.O.; Preston, J.F. Genetic engineering of Enterobacter asburiae strain JDR-1 for efficient production of ethanol from hemicellulose hydrolysates. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2009, 75, 5743–5749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ogunade, I.M.; Jiang, Y.; Pech Cervantes, A.A.; Kim, D.H.; Oliveira, A.S.; Vyas, D.; Weinberg, Z.G.; Jeong, K.C.; Adesogan, A.T. Bacterial diversity and composition of alfalfa silage as analyzed by Illumina MiSeq sequencing: Effects of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and silage additives. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 101, 2048–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cândido, E.S.; Pereira, J.L.; Quezado-Duval, A.M.; Noronha, E.F.; Krüger, R.H.; Quirino, B.F. Xanthomonas gardneri exoenzymatic activity towards plant tissue. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 24, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
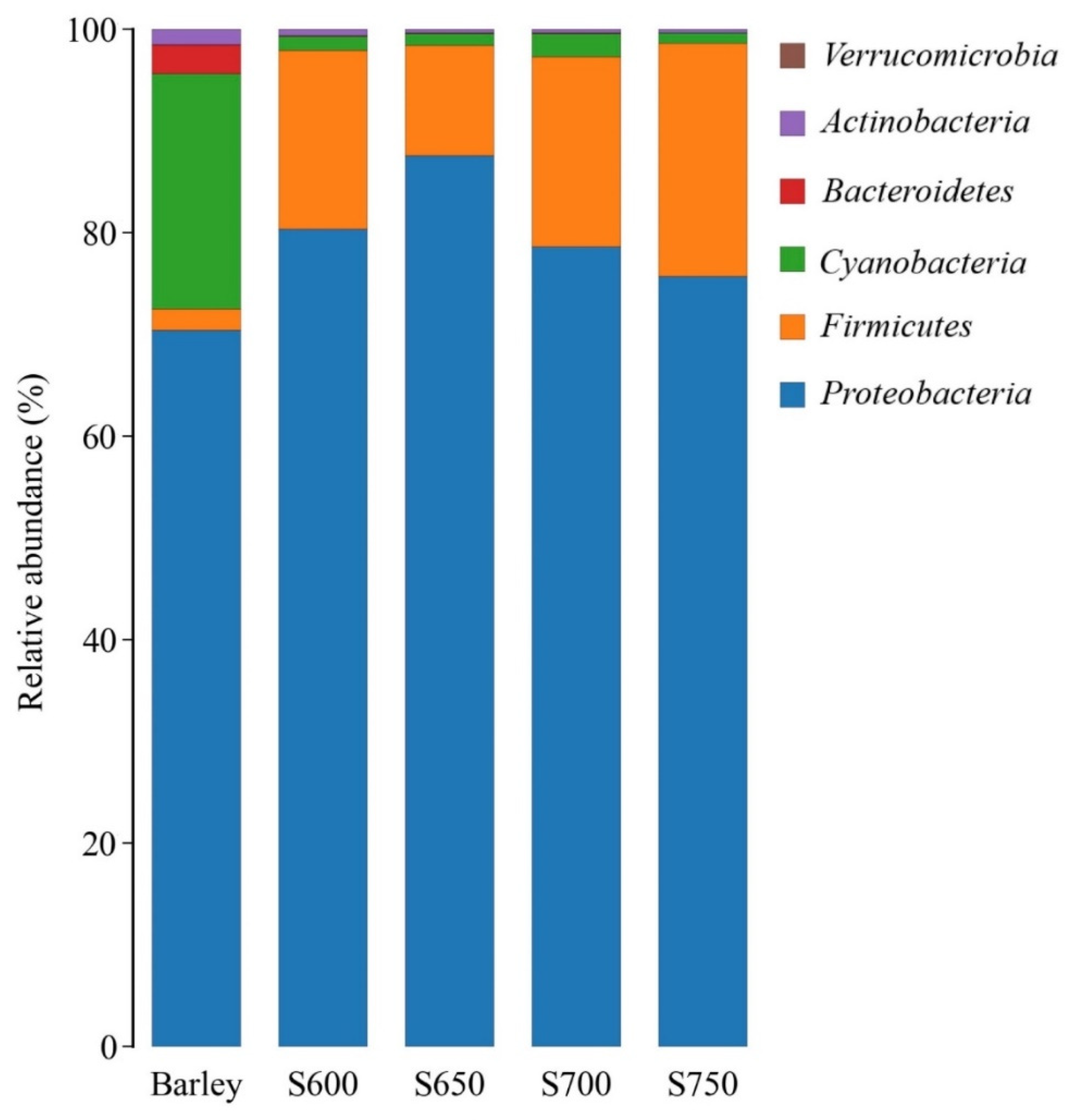

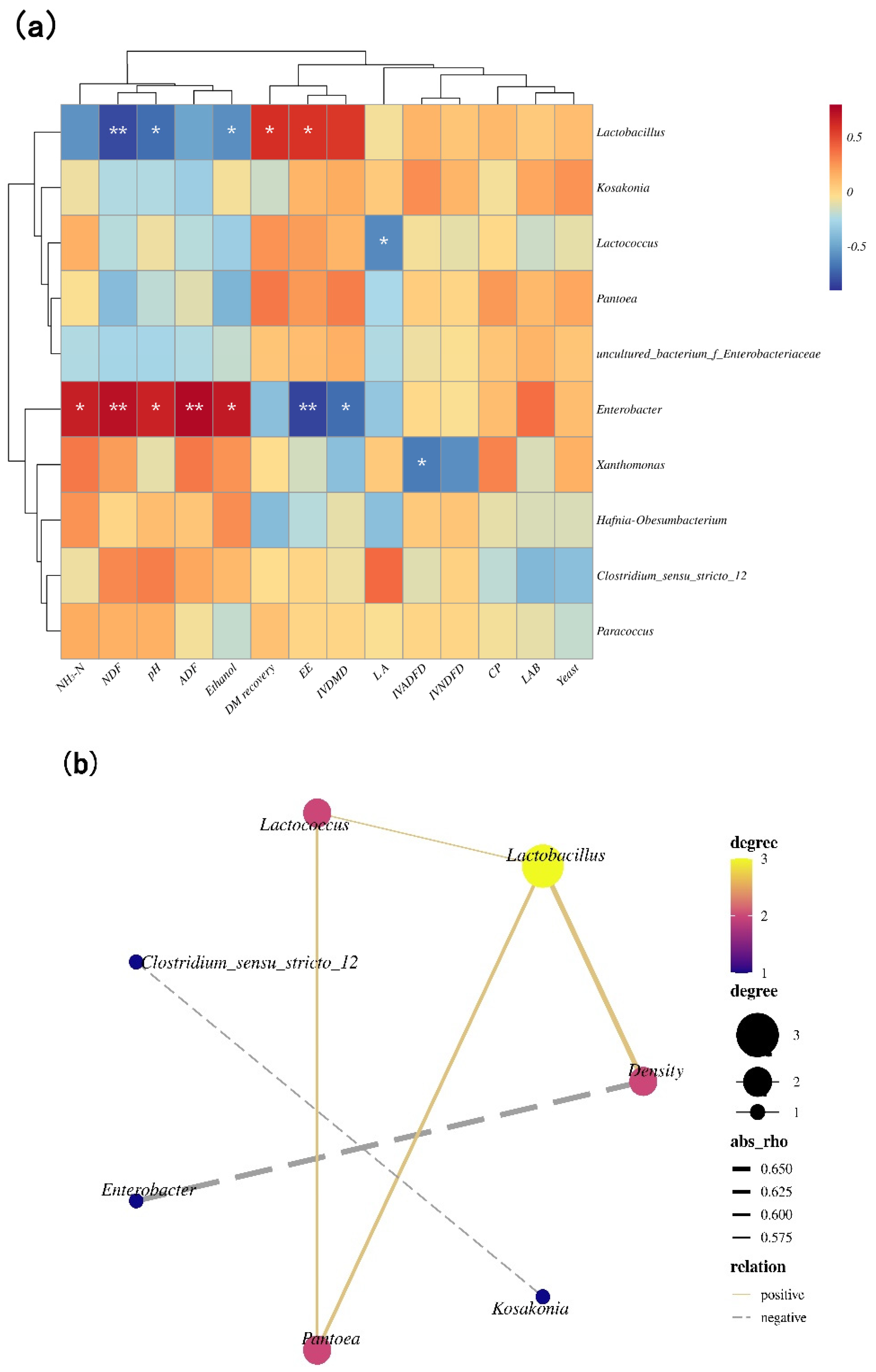
| Item | Fresh Barley | SEM |
|---|---|---|
| pH | 6.15 | 0.018 |
| Microbial Population (Log 10 cfu/g of FM) | ||
| Lactic Acid Bacteria | 4.02 | 0.110 |
| Aerobic Bacteria | 7.25 | 0.042 |
| Yeast | 5.48 | 0.029 |
| Coliform Bacteria | 7.03 | 0.075 |
| Chemical Composition | ||
| DM (g/kg of FM) | 337 | 6.4 |
| OM (g/kg of DM) | 938 | 1.1 |
| CP (g/kg of DM) | 99 | 2.3 |
| EE (g/kg of DM) | 39 | 0.4 |
| NDF (g/kg of DM) | 443 | 15.2 |
| ADF (g/kg of DM) | 236 | 6.7 |
| Sample ID | Number of Reads | Coverage | OTU | ACE | Chao1 Index | Simpson Index | Shannon Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Barley | 70,103 | 0.9999 | 126 (a) | 128.3 | 129.4 | 0.41 (a) | 1.80 |
| Silage | |||||||
| S600 | 78,074 | 0.9998 | 114 (b) | 120.4 | 121.8 | 0.16 (b) | 2.35 |
| S650 | 68,226 | 0.9998 | 108 (b) | 113.7 | 112.2 | 0.21 (b) | 2.20 |
| S700 | 76,433 | 0.9998 | 110 (b) | 118.4 | 118.6 | 0.19 (b) | 2.30 |
| S750 | 76,537 | 0.9999 | 111 (b) | 115.5 | 115.3 | 0.17 (b) | 2.31 |
| SEM | 4,219 | - | 3.8 | 4.66 | 5.06 | 0.064 | 0.223 |
| p-value | 0.535 | - | 0.052 | 0.277 | 0.226 | 0.085 | 0.438 |
| Items | Packing Density (kg/m3) | SEM | p-Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S600 | S650 | S700 | S750 | Linear | Quadratic | Cubic | ||
| Microbial population (log 10 cfu/g of FM) | ||||||||
| Lactic acid bacteria | 7.11 | 6.53 | 6.34 | 6.70 | 0.232 | 0.205 | 0.078 | 0.901 |
| Aerobic bacteria | 6.96 | 6.85 | 6.51 | 6.64 | 0.240 | 0.269 | 0.627 | 0.535 |
| Yeast | 7.17 a | 6.37 ab | 6.35 b | 6.75 ab | 0.227 | 0.241 | 0.030 | 0.739 |
| Coliform bacteria | nd | nd | nd | nd | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Fermentation quality | ||||||||
| pH | 4.42 a | 4.45 a | 4.43 ab | 4.25 b | 0.022 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.265 |
| Lactic acid (g/kg of DM) | 71.3 | 73.6 | 72.8 | 73.7 | 4.27 | 0.747 | 0.867 | 0.803 |
| Acetic acid (g/kg of DM) | 9.5 | 8.9 | 9.7 | 9.7 | 1.08 | 0.773 | 0.774 | 0.639 |
| Propionic acid (g/kg of DM) | 3.2 | 1.9 | 1.7 | nd | 2.04 | 0.317 | 0.924 | 0.777 |
| Butyric acid (g/kg of DM) | nd | nd | nd | nd | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| NH3-N (g/kg of TN) | 90.5 a | 87.4 a | 80.5 ab | 70.9 b | 3.72 | 0.004 | 0.408 | 0.945 |
| Chemical composition | ||||||||
| DM (g/kg of FM) | 312 | 302 | 329 | 323 | 8.6 | 0.157 | 0.860 | 0.105 |
| DM recovery (g/kg of DM) | 907 ab | 878 b | 957 ab | 981 a | 25.4 | 0.028 | 0.323 | 0.189 |
| OM (g/kg of DM) | 932 | 933 | 934 | 933 | 0.8 | 0.276 | 0.122 | 0.818 |
| CP (g/kg of DM) | 109 | 101 | 101 | 107 | 2.8 | 0.642 | 0.034 | 0.823 |
| EE (g/kg of DM) | 28.1 b | 29.5 b | 35.9 a | 37.4 a | 0.9 | <0.001 | 0.930 | 0.038 |
| NDF(g/kg of DM) | 333 a | 328 ab | 309 b | 261 c | 4.8 | <0.001 | 0.002 | 0.488 |
| ADF (g/kg of DM) | 189 a | 178 ab | 158 bc | 146 c | 5.1 | 0.001 | 0.987 | 0.454 |
| Ethanol(g/kg of DM) | 13.8 b | 16.0 a | 8.3 c | 7.6 c | 0.48 | <0.001 | 0.018 | <0.001 |
| In vitro digestibility | ||||||||
| IVDMD (%) | 57.7 c | 61.1 b | 66.3 a | 69.6 a | 0.75 | <0.001 | 0.957 | 0.308 |
| IVNDFD (%) | 54.0 b | 75.5 a | 71.4 a | 72.6 a | 3.30 | 0.008 | 0.015 | 0.069 |
| IVADFD (%) | 50.9 b | 72.4 a | 67.6 a | 69.5 a | 2.56 | 0.002 | 0.005 | 0.020 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, L.; Na, N.; Li, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, C.; Wu, X.; Xiao, Y.; Yin, G.; Liu, S.; Liu, Z.; et al. Impact of Packing Density on the Bacterial Community, Fermentation, and In Vitro Digestibility of Whole-Crop Barley Silage. Agriculture 2021, 11, 672. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11070672
Sun L, Na N, Li X, Li Z, Wang C, Wu X, Xiao Y, Yin G, Liu S, Liu Z, et al. Impact of Packing Density on the Bacterial Community, Fermentation, and In Vitro Digestibility of Whole-Crop Barley Silage. Agriculture. 2021; 11(7):672. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11070672
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Lin, Na Na, Xiaomei Li, Ziqin Li, Chao Wang, Xiaoguang Wu, Yanzi Xiao, Guomei Yin, Sibo Liu, Zhiping Liu, and et al. 2021. "Impact of Packing Density on the Bacterial Community, Fermentation, and In Vitro Digestibility of Whole-Crop Barley Silage" Agriculture 11, no. 7: 672. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11070672
APA StyleSun, L., Na, N., Li, X., Li, Z., Wang, C., Wu, X., Xiao, Y., Yin, G., Liu, S., Liu, Z., Xue, Y., & Yang, F. (2021). Impact of Packing Density on the Bacterial Community, Fermentation, and In Vitro Digestibility of Whole-Crop Barley Silage. Agriculture, 11(7), 672. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11070672






