Comparison of Orchard Target-Oriented Spraying Systems Using Photoelectric or Ultrasonic Sensors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
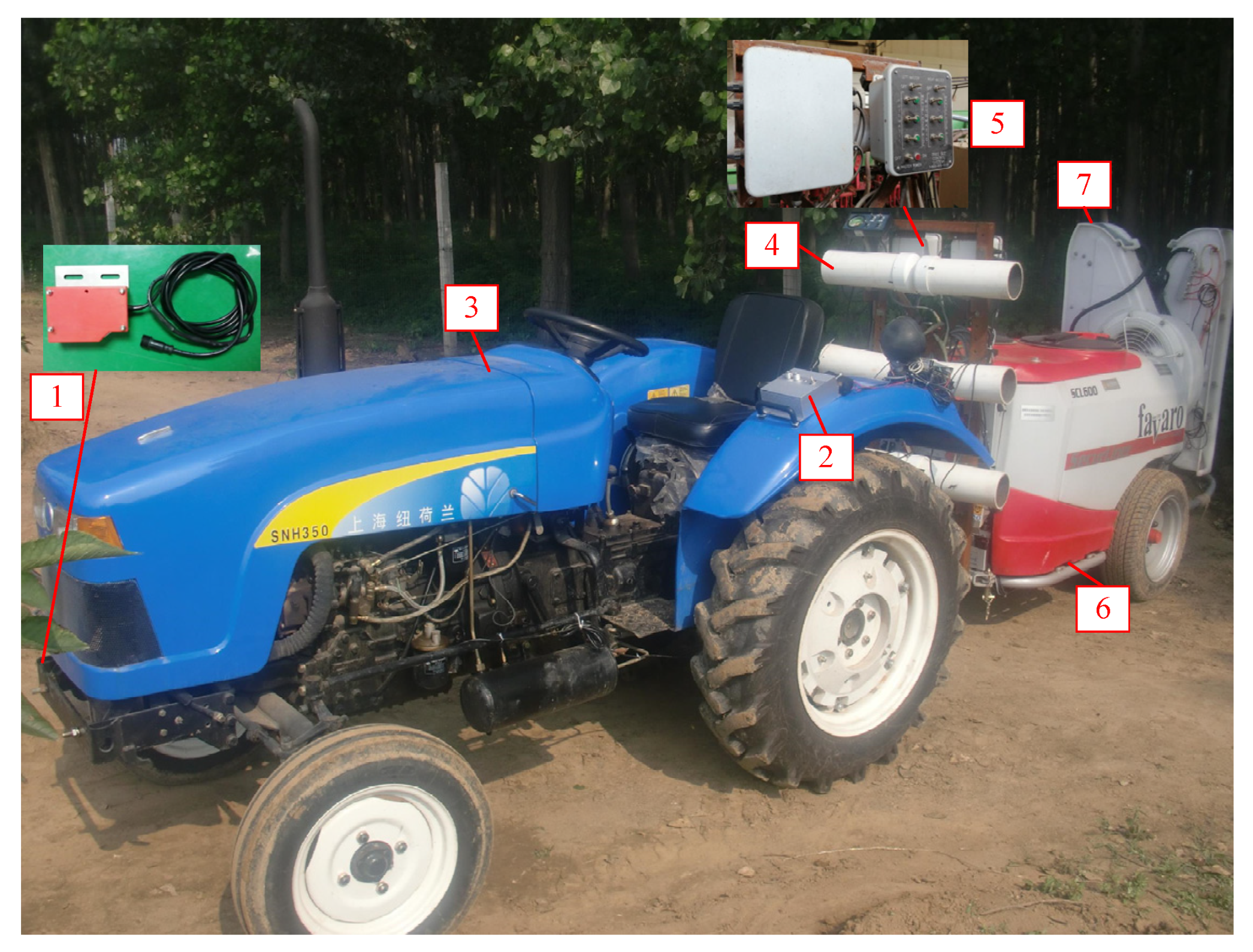
2.1. Orchard Target-Oriented Sprayer
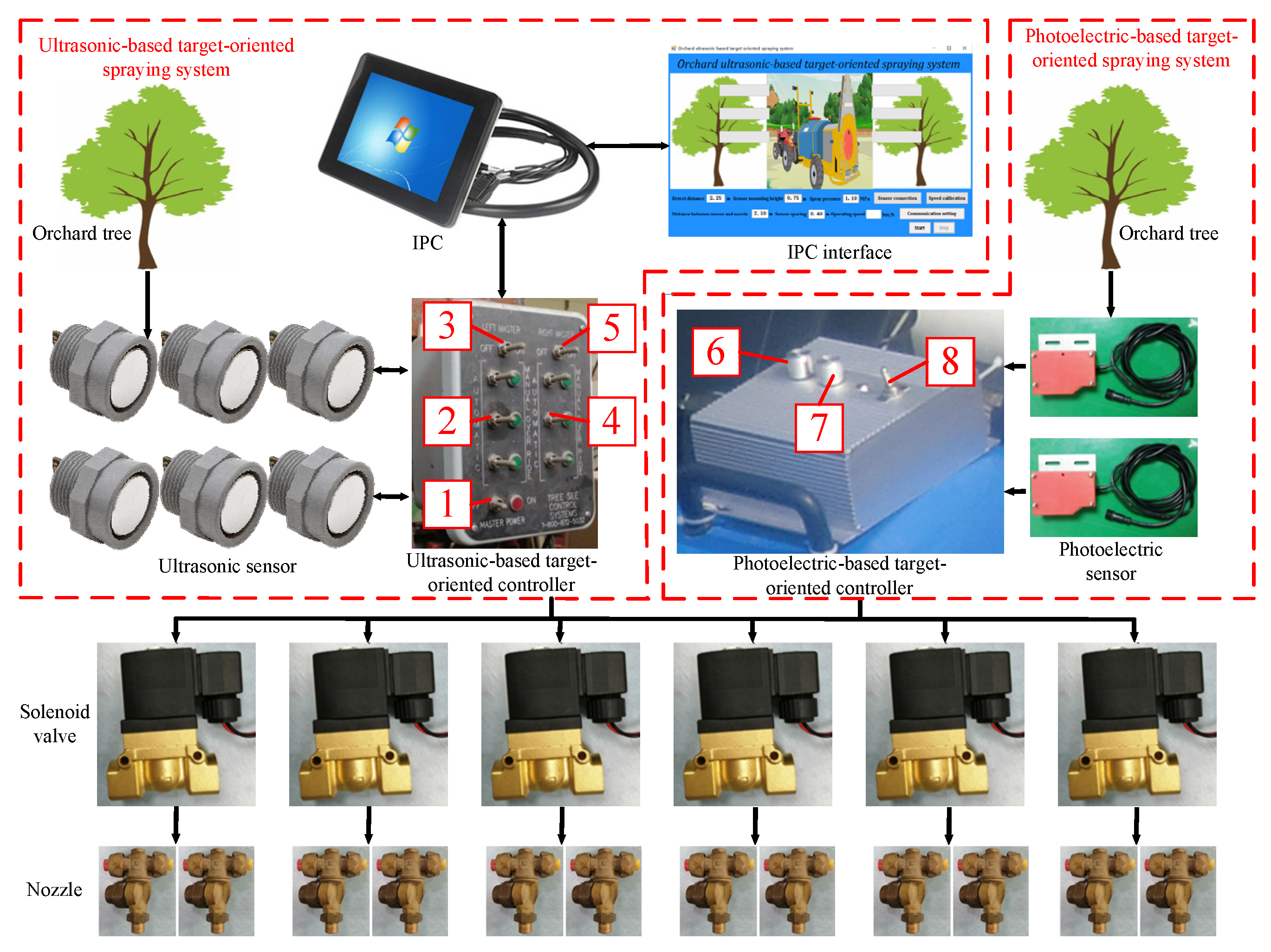
2.2. Photoelectric-Based Target-Oriented Spraying System
2.3. Ultrasonic-Based Target-Oriented Spraying System
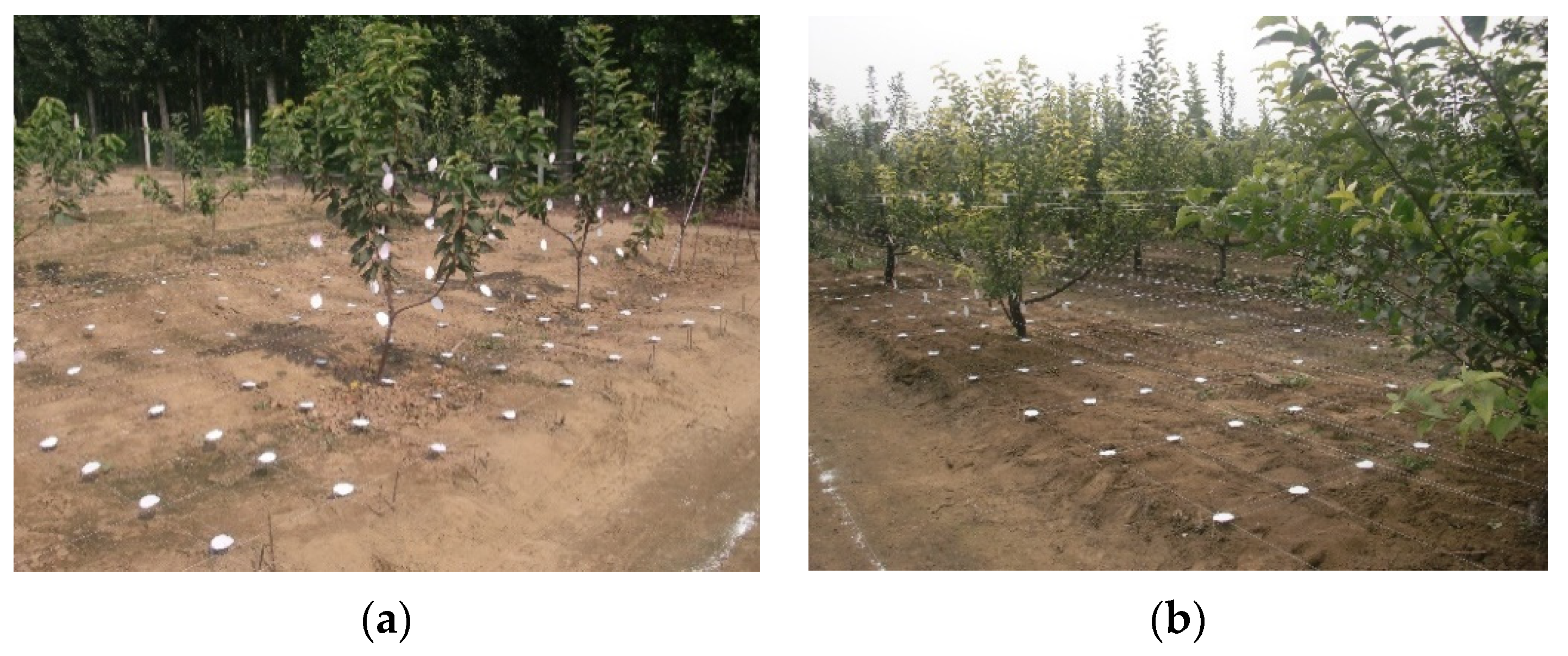
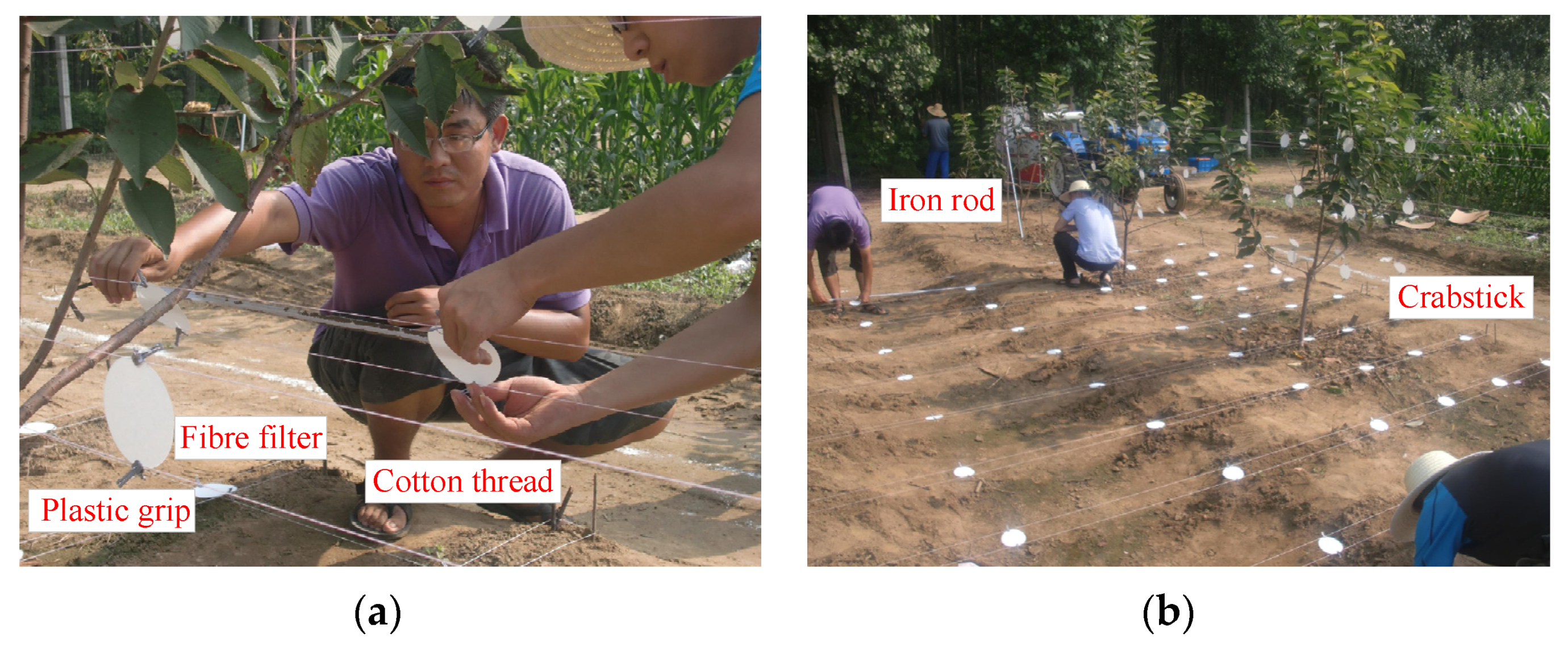
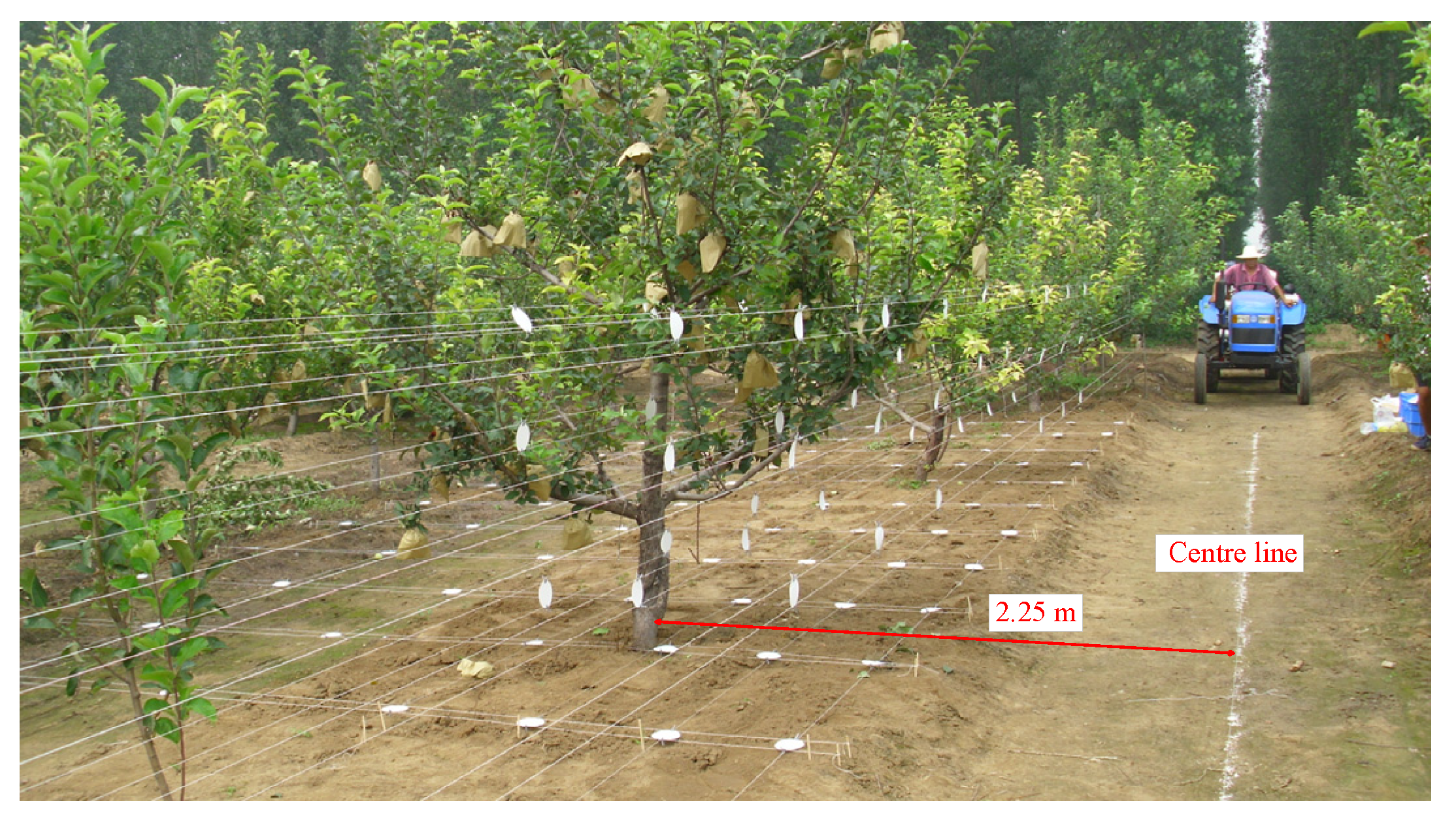
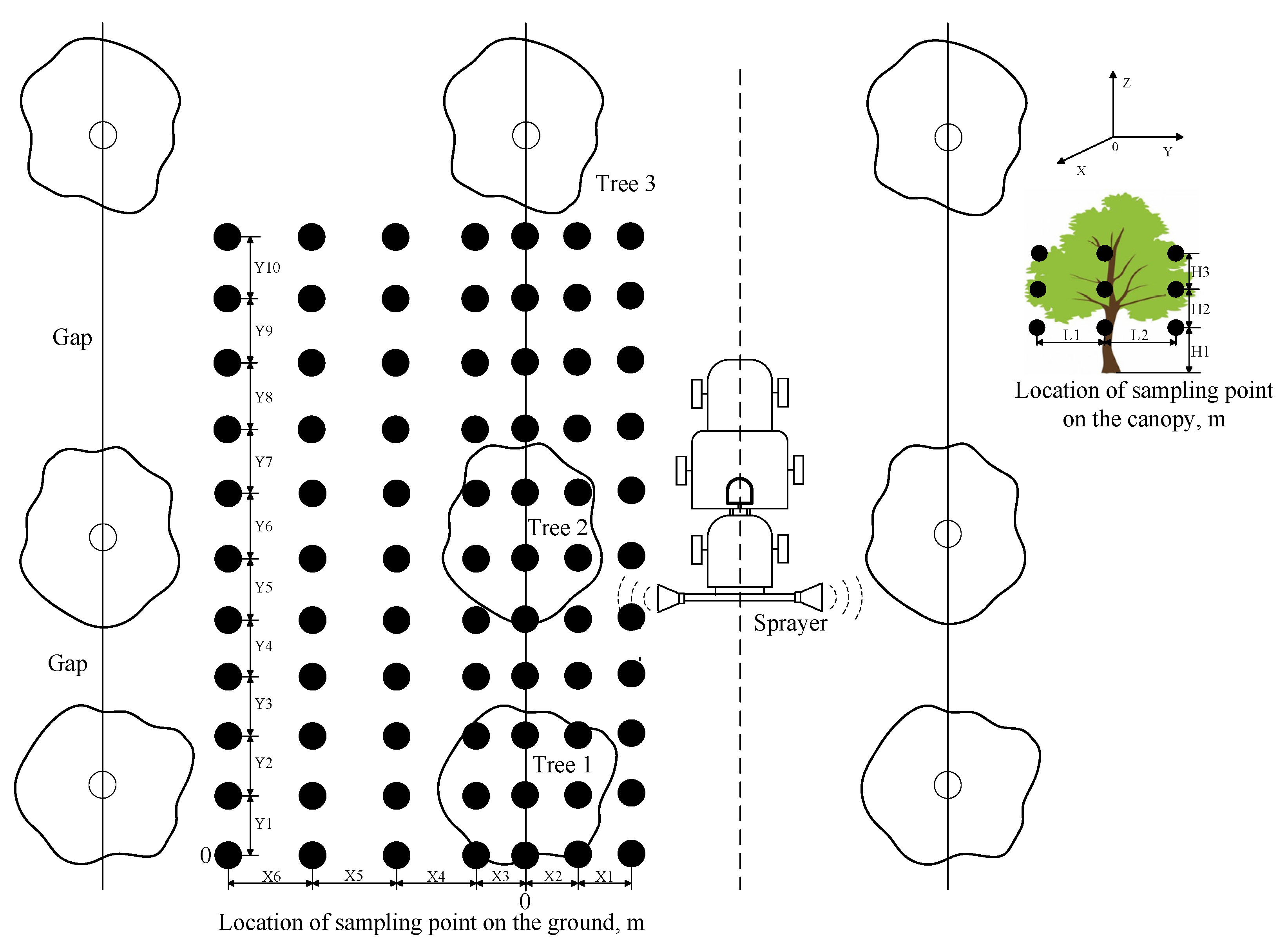
2.4. Experimental Design
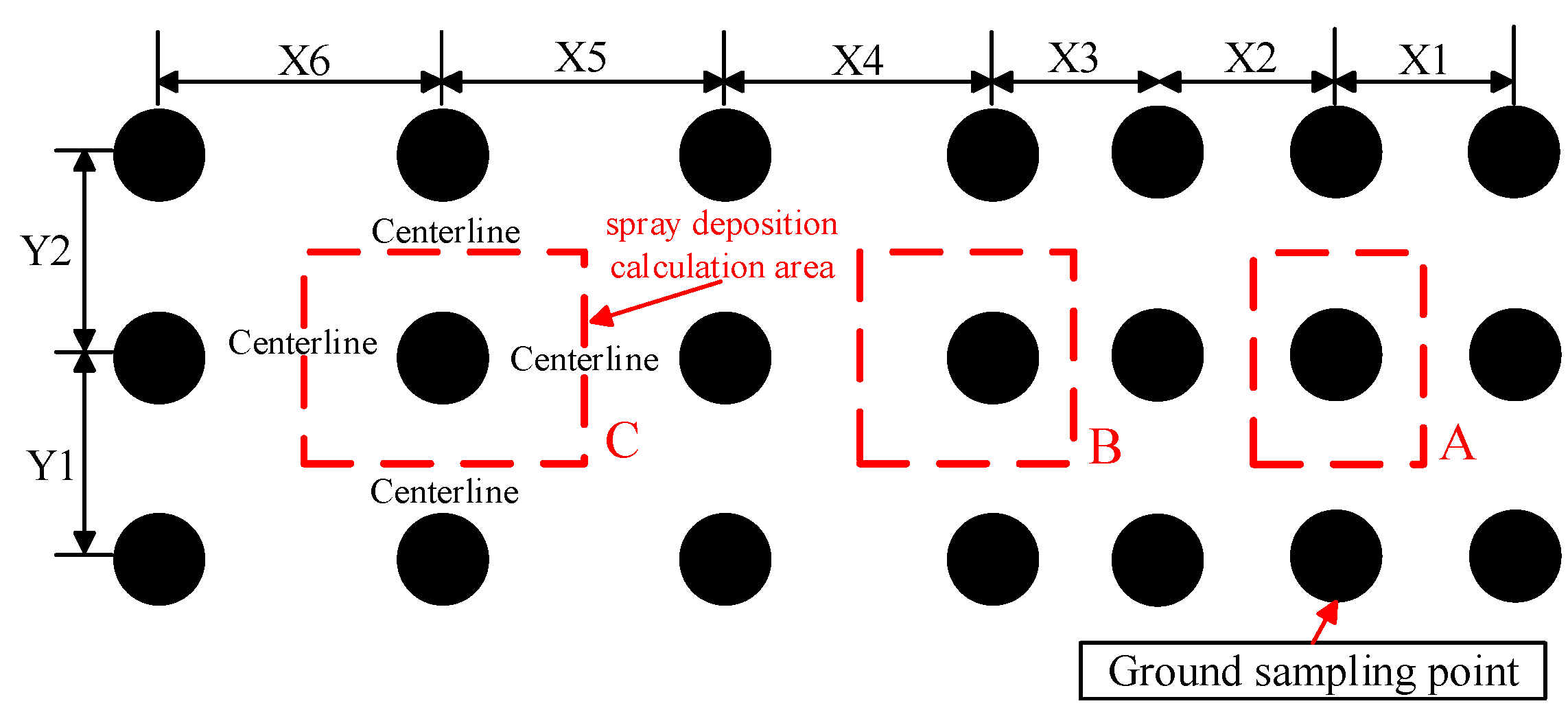
2.5. Data Processing
3. Results
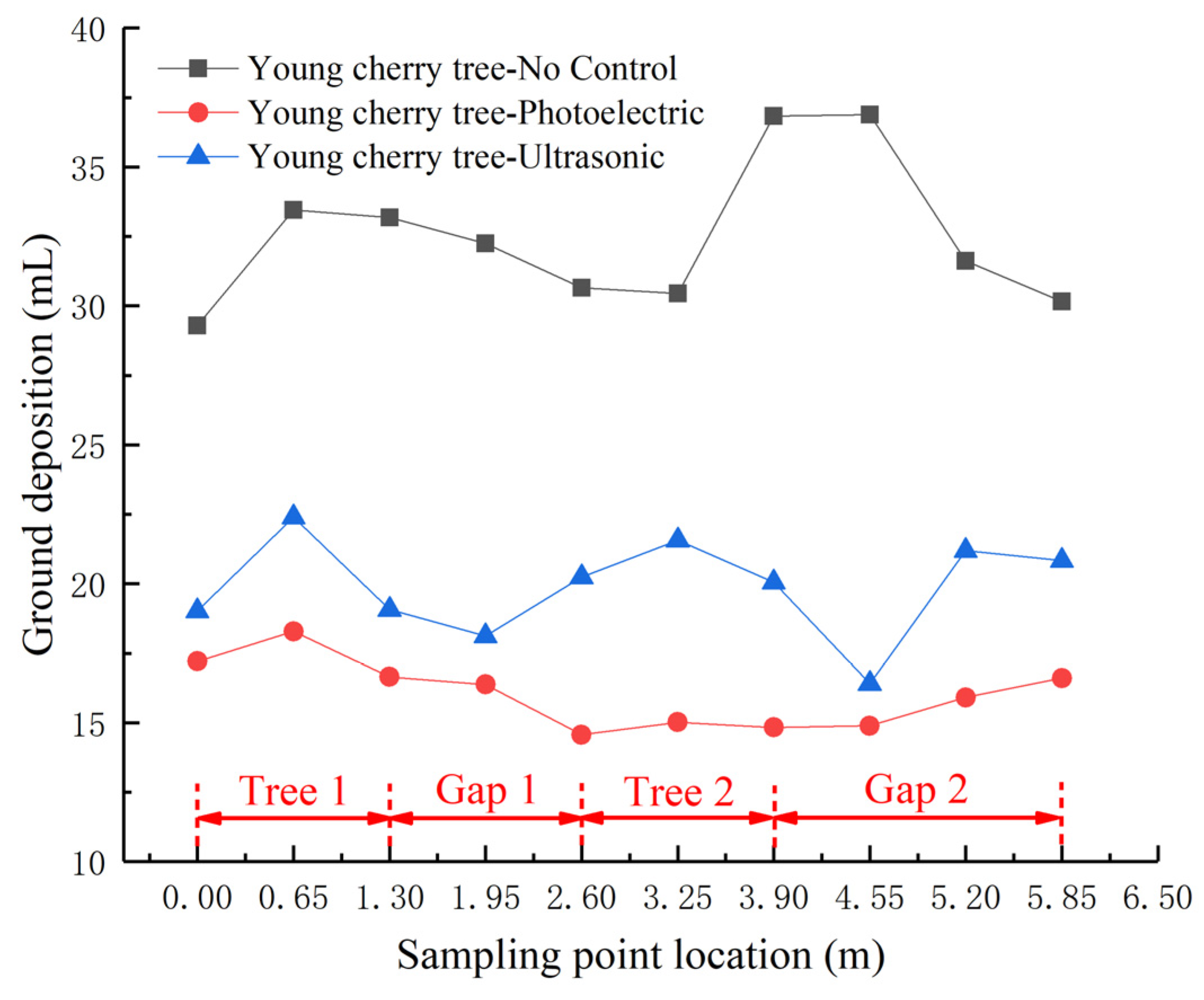
3.1. Ground Deposition
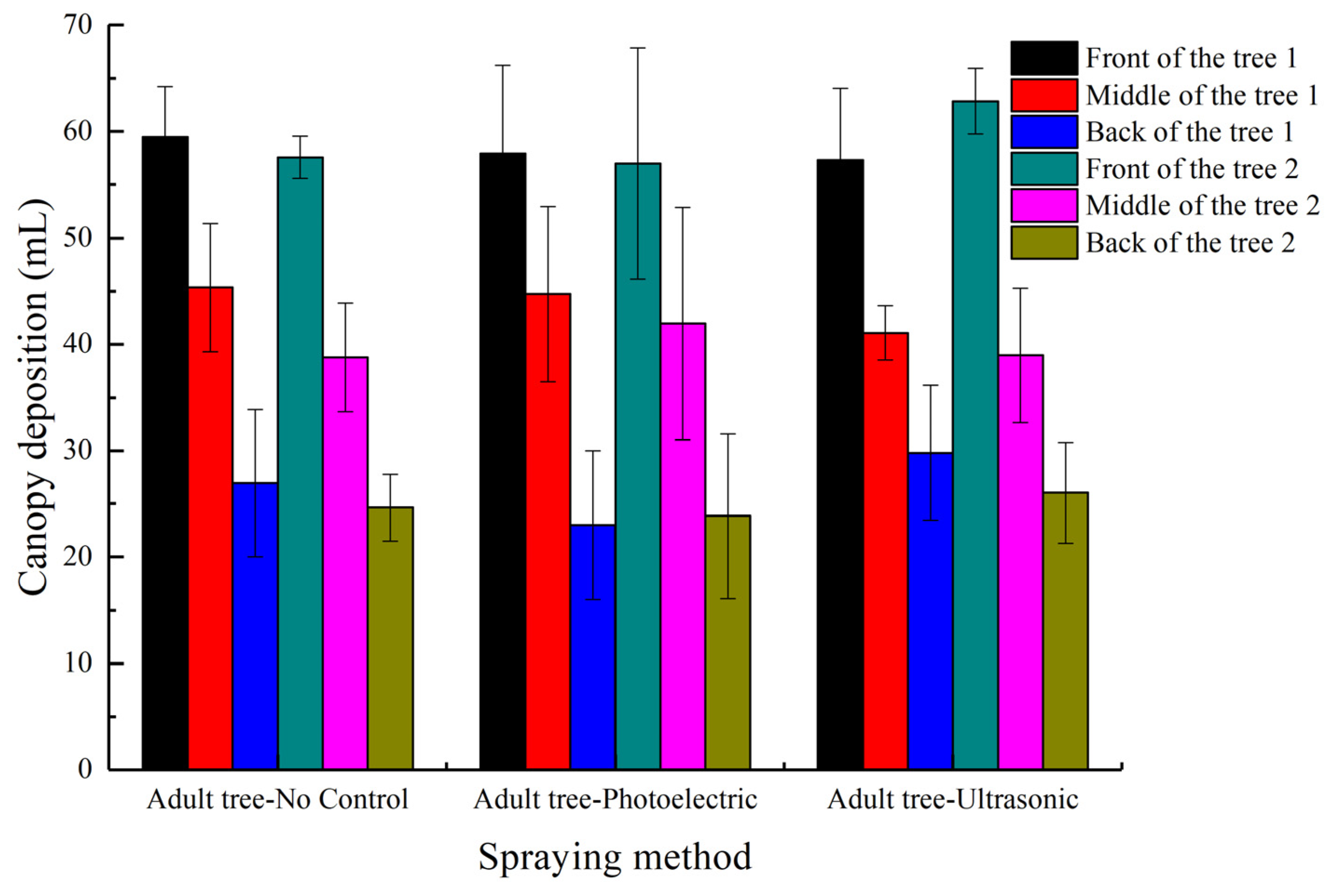
3.2. Fruit Tree Canopy Deposition
4. Discussion
4.1. Ground Deposition
4.2. Fruit Tree Canopy Deposition
5. Future Directions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, X. Research progress and developmental recommendations on precision spraying technology and equipment in China. Smart Agric. 2020, 2, 133–146. [Google Scholar]
- Wandkar, S.V.; Bhatt, Y.C.; Jain, H.K.; Nalawade, S.M.; Pawar, S.G. Real-time variable rate spraying in orchards and vineyards: A review. J. Inst. Eng. Ser. A 2018, 99, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, C.; Zhao, C.; Wang, N.; Long, J.; Zhang, H. Research progress on precision control methods of air-assisted spraying in orchards. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Lai, Q.; Zhang, Z. Review of variable-rate sprayer applications based on real-time sensor technologies. Autom. Agric. Secur. Food Supplies Future Gener. 2018, 4, 53–79. [Google Scholar]
- Hassen, N.S.; Sidik, N.A.C.; Sheriff, J.M. Advanced techniques for reducing spray losses in agrochemical application system. Life Sci. J. 2014, 11, 56–66. [Google Scholar]
- Eugen, M.; Mihai, M.; Mihaela, N.; Gabriel, G. Experimental researches regarding assessment of coverage degree obtained by orchard spraying machine. In Proceedings of the 16th International Scientific Conference: Engineering for Rural Development, Jelgava, Latvia, 24–26 May 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Michael, C.; Gil, E.; Gallart, M.; Stavrinides, M.C. Influence of Spray Technology and Application Rate on Leaf Deposit and Ground Losses in Mountain Viticulture. Agriculture 2020, 10, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, C.; Gil, E.; Gallart, M.; Stavrinides, M.C. Evaluation of the effects of spray technology and volume rate on the control of grape berry moth in mountain viticulture. Agriculture 2021, 11, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.L.; Giles, D.K.; Oliver, M.N.; Klassen, P. Targeted spray technology to reduce pesticide in runoff from dormant orchards. Crop Prot. 2008, 27, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorens, J.; Gil, E.; Llop, J. Ultrasonic and LIDAR sensors for electronic canopy characterization in vineyards: Advances to improve pesticide application methods. Sensors 2011, 11, 2177–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miranda-Fuentes, A.; Rodríguez-Lizana, A.; Cuenca, A.; González-Sánchez, E.J.; Blanco-Roldán, G.L.; Gil-Ribes, J.A. Improving plant protection product applications in traditional and intensive olive orchards through the development of new prototype air-assisted sprayers. Crop Prot. 2017, 94, 44–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, I.; Liu, J.; Faheem, M.; Noor, R.S.; Shaikh, S.A.; Solangi, K.A.; Raza, S.M. Different real-time sensor technologies for the application of variable-rate spraying in agriculture. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 316, 112265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.S.; Alchanatis, V.; Yang, C.; Hirafuji, M.; Moshou, D.; Li, C. Sensing technologies for precision specialty crop production. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2010, 74, 2–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosell, J.R.; Sanz, R. A review of methods and applications of the geometric characterization of tree crops in agricultural activities. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2012, 81, 124–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, L.; Xue, X.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, L.; Ding, S.; Chang, C.; Zhang, X.; Chen, C. Research situation and progress analysis on orchard variable rate spraying technology. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2017, 33, 80–92. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Zeng, A.; Liu, Y.; Song, J. Precision orchard sprayer based on automatically infrared target detecting and electrostatic spraying techniques. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2011, 4, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, C.; Zhao, C.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Xue, W. Design and experiment of young tree target detector. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2012, 28, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, W.; Wang, X.; Deng, W.; Su, S.; Wang, S.; Fan, P. Design and test of automatic toward-target sprayer used in orchard. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Cyber Technology in Automation, Shenyang, China, 8–12 June 2015; pp. 697–702. [Google Scholar]
- Giles, D.K.; Delwiche, M.J.; Dodd, R.B. Sprayer control by sensing orchard crop characteristics: Orchard architecture and spray liquid savings. J. Agric. Eng. Res. 1989, 43, 271–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doruchowski, G.; Swiechowski, W.; Godyn, A.; Holownicki, R. Automatically controlled sprayer to implement spray drift reducing application strategies in orchards. J. Fruit Ornam. Plant Res. 2011, 19, 175–182. [Google Scholar]
- Hołownicki, R.; Doruchowski, G.; Świechowski, W.; Godyń, A.; Konopacki, P.J. Variable air assistance system for orchard sprayers; concept, design and preliminary testing. Biosyst. Eng. 2017, 163, 134–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghsoudi, H.; Minaei, S.; Ghobadian, B.; Masoudi, H. Ultrasonic sensing of pistachio canopy for low-volume precision spraying. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2015, 112, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, E.; Llorens, J.; Llop, J.; Fàbregas, X.; Escolà, A.; Rosell-Polo, J.R. Variable rate sprayer. Part 2-Vineyard prototype: Design, implementation, and validation. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2013, 95, 136–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petrović, D.; Banaj, Đ.; Banaj, A.; Barač, Ž.; Vidaković, I.; Tadić, V. The impact of conventional and Sensor Spraying on Drift and Deposit in Cherry Orchard. Teh. Vjesn. 2019, 26, 1211–1217. [Google Scholar]
- Osterman, A.; Godeša, T.; Hočevar, M.; Širok, B.; Stopar, M. Real-time positioning algorithm for variable-geometry air-assisted orchard sprayer. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2013, 98, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; He, X.; Song, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Jia, X.; Liu, Z. Comparative experiment on profile variable rate spray and conventional air assisted spray in orchards. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2017, 33, 56–63. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Rosetta, R.; Reding, M.E.; Zondag, R.H.; Ranger, C.M.; Canas, L.; Fulcher, A.; Derksen, R.C.; Erdal Ozkan, H.; Krause, C.R. Validation of a laser-guided variable-rate sprayer for managing insects in ornamental nurseries. Trans. ASABE 2017, 60, 337–345. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, C.; Zhao, C.; Wang, X.; Zou, W.; Zhang, R. Probing method of tree spray target profile. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2010, 26, 173–177. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, W.; Wang, X.; Feng, Q.; Fan, P.; Jiang, K. Design of variable spraying control system based on ultrasonic target detection. J. Chin. Agric. Mech. 2020, 43, 58–63. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, H.R.; Chen, J.B.; Lin, Y.H.; Xue, X.Y.; Qiu, B.J. Crop protection equipment–Field measurement of spray distribution in tree and bush crops. In National Agricultural Machinery Standard Technical Committee; GB/T 3244–2015; Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Warneke, B.W.; Zhu, H.; Pscheidt, J.W.; Nackley, L.L. Canopy spray application technology in specialty crops: A slowly evolving landscape. Pest Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 2157–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Attributes | Fruit Tree Types | |
|---|---|---|
| Young Cherry Trees | Adult Apple Trees | |
| Variety | Golden red | Red Fuji |
| Rootstock | Big green leaf | Flowering crabapple |
| Planting system | Artificial planting | Artificial planting |
| Size of the trees | Row spacing of 4.5 m | Row spacing of 4.5 m |
| Plant spacing of 2.7 m | Plant spacing of 5.0 m | |
| Height of 2.7 m (average) | Height of 3.4 m (average) | |
| Canopy width of 1.2 m (average) | Canopy width of 2.8 m (average) | |
| Parameters | Values | Parameters | Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nozzle angle | 80° | Spray unit angle | 0° |
| Spraying pressure | 1.1 MPa | Wind speed | 0.76 m/s (average) |
| Fan speed | 960 r/min | Air temperature | 32.42 °C (average) |
| Travel speed | 1.0 m/s | Relative humidity | 34.36% (average) |
| Left nozzle flow rate (From bottom to top) | 2.25 | Right nozzle flow rate (From bottom to top) | 2.03 |
| 2.09 | 1.97 | ||
| 2.01 | 1.96 | ||
| 2.07 | 1.99 | ||
| 2.10 | 2.01 | ||
| 2.03 | 2.00 |
| Fruit Tree Types | Spraying System | Total Ground Deposition in the Sampling Area (mL) | Spray Volume Savings (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Young cherry trees | Photoelectric-based target-oriented | 160.33 | 50.63 |
| No target-oriented | 324.73 | Compare object | |
| Ultrasonic-based target-oriented | 198.92 | 38.74 | |
| Adult apple trees | Photoelectric-based target-oriented | 319.06 | 21.66 |
| No target-oriented | 407.25 | Compare object | |
| Ultrasonic-based target-oriented | 285.59 | 29.87 |
| Sprayer Types | New Unit Cost (USD) | Approximate Spray Volume Savings (%) | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Photoelectric-based target-oriented spraying system | 2500–5000 | ≤40 | Low cost Little impact of temperature and humidity on sensing accuracy Decreased chemical, water usage and drift | Red light intensity and driving speed can affect sensing ability Narrow field of view Unable to resolve plant structure characteristics or modulate spray output |
| Ultrasonic-based target-oriented spraying system | 15,000 | 15–40 | Easy to implement, flexible crop types Can resolve plant structure Decreased chemical, water usage and drift | Limited resolution of plant structure Need multiple sensors to detect plant structure |
| LiDAR-based target-oriented spraying system | 15,000–30,000 | 25–80 | Automatic modulation of spray to match crop characteristics Fine resolution of crop structure Rapid measurement, rich data acquisition capability Decreased chemical, water usage and drift | High initial purchase cost Limited availability for purchasing and of specialised personnel for repairs Electronics not easily serviceable by the owner |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dou, H.; Zhai, C.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Zou, W. Comparison of Orchard Target-Oriented Spraying Systems Using Photoelectric or Ultrasonic Sensors. Agriculture 2021, 11, 753. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11080753
Dou H, Zhai C, Chen L, Wang X, Zou W. Comparison of Orchard Target-Oriented Spraying Systems Using Photoelectric or Ultrasonic Sensors. Agriculture. 2021; 11(8):753. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11080753
Chicago/Turabian StyleDou, Hanjie, Changyuan Zhai, Liping Chen, Xiu Wang, and Wei Zou. 2021. "Comparison of Orchard Target-Oriented Spraying Systems Using Photoelectric or Ultrasonic Sensors" Agriculture 11, no. 8: 753. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11080753
APA StyleDou, H., Zhai, C., Chen, L., Wang, X., & Zou, W. (2021). Comparison of Orchard Target-Oriented Spraying Systems Using Photoelectric or Ultrasonic Sensors. Agriculture, 11(8), 753. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11080753








