Effects of Water and Nitrogen on Grain Filling Characteristics, Canopy Microclimate with Chalkiness of Directly Seeded Rice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Materials and Experimental Design
- (1)
- Flooding irrigation (W1): from the two-leaf stage of directly seeded rice, with the water layer continuously maintained at 1 to 2 cm, and natural drying was carried out 1 week before maturity;
- (2)
- Dry–wet alternating irrigation (W2): from the two-leaf stage of directly seeded rice, with irrigation at a soil water potential of −25 kPa and establishment of a 1 to 2 cm water layer, and measurement of soil water potential with a vacuum negative soil pressure meter (developed by the Institute of Soil Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences);
- (3)
- Dry alternating irrigation (W3): with irrigation at a soil water potential of −40 kPa, requiring a water-free surface layer.
2.2. Measurement Items and Methods
2.2.1. Measurement and Parameters of Grain Filling
- (1)
- R0 (starting growth potential of grain) = k/N
- (2)
- Wmax (grain weight at maximum filling rate) =
- (3)
- Tmax (time of maximum growth rate) =
- (4)
- GRmean (mean filling rate) =
- (5)
- D (active growth period) =
- (6)
- Samples were divided into early-, middle-, and late-filling stages, which are termed the 0–T1, T1–T2, and T2–T99 stages, respectively.
2.2.2. Canopy Microclimate
- (1)
- Total temperature difference between different filling stages = ∑ (highest temperature of the day–lowest temperature) for each filling stage.
- (2)
- Average daily temperature difference at different filling stages = total temperature difference at each filling stage/number of days.
- (3)
- Effective cumulative temperature at different filling stages = ∑ (average daily temperature of −10) for each filling stage.
- (4)
- Average daily light intensity at different filling stages = total light intensity at each filling stage/number of days.
2.2.3. Chalky Grain Rate and Chalkiness Degree Measurements
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Grain Filling Characteristics
3.1.1. Dynamics of Increasing Grain Weight and Grain Filling Rate
3.1.2. Early-, Middle-, and Late-Stage Grain Filling Characteristics
3.2. Canopy Microclimate during Different Grain Filling Stages
3.3. Grain Chalkiness
3.4. Relationship of Grain Filling Parameters and Canopy Microclimate with Chalkiness under Water–N Interaction
4. Discussion
4.1. Relationship between Grain Filling Characteristics and Rice Chalkiness Traits in Directly Seeded Rice under Water–N Interaction
4.2. Relationship between Canopy Microclimate and Rice Chalkiness Traits at Fruiting Stage under Water–N Interaction
4.3. Physiological and Ecological Basis and Regulatory Pathways for Improving Quality and Yield of Directly Seeded Rice under Water–N Interaction
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Q.H.; Wu, X.; Ma, J.Q.; Xin, C.Y. Effects of cultivars, transplanting patterns, environment, and their interactions on grain quality of japonica rice. Cereal Chem. 2015, 92, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishfaq, M.; Akbar, N.; Zulfiqar, U.; Ali, N.; Jabran, K.; Nawaz, M.; Farooq, M. Influence of nitrogen fertilization pattern on productivity, nitrogen use efficiencies, and profitability in different rice production systems. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 21, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Q.; Peng, S.B.; Liu, H.Y.; Tao, Y.; Huang, J.L.; Cui, K.H.; Nie, L.X. The possibility of replacing puddled transplanted flooded rice with dry seeded rice in central China: A review. Field Crops Res. 2017, 214, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, M.; Guo, P.; Zhang, Z.X. Optimization of water and fertilizer coupling system based on rice grain quality. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 221, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.B.; Fan, C.C.; Xing, Y.Z.; Yun, P.; Luo, L.J.; Yan, B.; Peng, B.; Xie, W.B.; Wang, G.W.; Li, X.H.; et al. Chalk 5 encodes a vacuolar H+-translocating pyrophosphatase influencing grain chalkiness in rice. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.J.; Chen, L.M.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, W.W.; Liu, L.L.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Z.G.; Liu, S.J.; Zhang, L.J.; Wang, J.K.; et al. Fine mapping of the grain chalkiness QTL qPGWC-7 in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2009, 118, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.L.; Guo, T.; Wan, X.Y.; Wang, H.Y.; Zhu, M.Z.; Li, A.L.; Su, N.; Shen, Y.Y.; Mao, B.G.; Zhai, H.Q.; et al. Transcriptome analysis of grain-filling caryopses reveals involvement of multiple regulatory pathways in chalky grain formation in rice. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, N.; Sodhi, N.S.; Kaur, M.; Saxena, S.K. Physico-chemical, morphological, thermal, cooking and textural properties of chalky and translucent rice kernels. Food Chem. 2003, 82, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanche, S.B.; Utomo, H.S.; Wenefrida, I.; Myers, G.O. Genotype × environment interactions of hybrid and varietal rice cultivars for grain yield and milling quality. Crop Sci. 2009, 49, 2011–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.J.; Yan, F.J.; Sun, Y.Y.; Xu, H.; Guo, X.; Yang, Z.Y.; Yin, Y.Z.; Guo, C.C.; Ma, J. Effects of different water regimes and nitrogen application strategies on grain filling characteristics and grain yield in hybrid rice. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2018, 64, 1152–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Zhang, W.; Wu, M.; Liu, G.S.; Zhang, Z.J.; Yang, J.C. Effects of irrigation schedules and phosphorus fertilizer rates on grain yield and quality of upland rice and paddy rice. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2021, 186, 104465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.J.; Ma, J.; Sun, Y.Y.; Xu, H.; Yang, Z.Y.; Liu, S.J.; Jia, X.W.; Zheng, H.Z. The effects of different water and nitrogen managements on yield and nitrogen use efficiency in hybrid rice of China. Field Crops Res. 2012, 127, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.J.; Sun, Y.Y.; Yan, F.J.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.X.; Guo, C.C.; Ma, P.; Yang, G.T.; Yang, Z.Y.; Ma, J. Coordinating postanthesis carbon and nitrogen metabolism of hybrid rice through different irrigation and nitrogen regimes. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.; Zhang, J.H.; Wang, Z.Q.; Liu, L.J.; Zhu, Q.S. Postanthesis water deficits enhance grain filling in two-line hybrid rice. Crop Sci. 2003, 43, 2099–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Du, Y.L.; Tian, X.Y.; Wang, Q.S.; Xiong, R.H.; Xu, G.C.; Yan, C.; Ding, Y.F. Effect of panicle nitrogen on grain filling characteristics of high-yielding rice cultivars. Eur. J. Agron. 2016, 74, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Song, N.Y.; Chen, Q.L.; Sun, H.Z.; Peng, T.; Huang, S.; Zhao, Q.Z. Response of grain-filling rate and grain quality of mid-season indica rice to nitrogen application. J. Integr. Agri. 2021, 20, 1465–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuerz, S.; Sow, A.; Muller, B.; Manneh, B.; Asch, F. Canopy microclimate and gas-exchange in response to irrigation system in lowland rice in the Sahel. Field Crops Res. 2014, 163, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujimoto, Y.; Fuseini, A.; Inusah, B.I.Y.; Dogbe, W.; Yoshimoto, M.; Fukuoka, M. Different effects of water-saving management on canopy microclimate, spikelet sterility, and rice yield in the dry and wet seasons of the sub-humid tropics in northern Ghana. Field Crops Res. 2021, 260, 107978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julia, C.; Dingkuhn, M. Predicting temperature induced sterility of rice spikelets requires simulation of crop-generated microclimate. Eur. J. Agron. 2013, 49, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.T.; Wang, X.C.; Peng, Y.L.; Rasul, F.; Zou, T.; Hu, Y.G. Different micro-climate response of indica rice population to nitrogen fertilizer. Plant Soil Environ. 2018, 64, 407–412. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka, Y.; Iwata, H.; Tabata, M.; Ninomiya, S.; Ohsawa, R. Chalkiness in rice: Potential for evaluation with image analysis. Crop Sci. 2007, 47, 2113–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Huang, J.L.; Zhu, L.Y.; Shah, F.; Nie, L.X.; Cui, K.H.; Peng, S.B. Varietal difference in the response of rice chalkiness to temperature during ripening phase across different sowing dates. Field Crops Res. 2013, 151, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, A.; Song, J.; Kim, K.J.; Lee, H.J. Quality of head and chalky rice and deterioration of eating quality by chalky rice. J. Crop. Sci. Biotech. 2009, 12, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Chen, W.Z.; Liu, W.Z.; Zhou, Q.Y.; Zhang, H.X.; Wang, S.H.; Ding, Y.F. Open-field warming regulates the morphological structure, protein synthesis of grain and affects the appearance quality of rice. J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 84, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.B.; Wei, H.Y.; Zhang, H.C. Response of milling and appearance quality of rice with good eating quality to temperature and solar radiation in lower reaches of huai river. Agronomy 2020, 11, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, F.; Li, Q.P.; Chen, H.; Zeng, Y.L.; Li, B.; Zhong, X.Y.; Wang, L.; Ren, W.J. Relationship between chalkiness and the structural and thermal properties of rice starch after shading during grain-filling stage. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 252, 117212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambardekar, A.A.; Siebenmorgen, T.J.; Counce, P.A.; Lanning, S.B.; Mauromoustakos, A. Impact of field-scale nighttime air temperatures during kernel development on rice milling quality. Field Crops Res. 2011, 122, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanning, S.B.; Siebenmorgen, T.J.; Counce, P.A. Extreme nighttime air temperatures in 2010 impact rice chalkiness and milling quality. Field Crops Res. 2011, 124, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, M.; Sugiura, K.; Kuno, C.; Endo, I.; Tanaka, Y.; Yamauchi, A. Reduction of rice chalky grain by deep and permanent irrigation method; Effect on growth and grain quality of rice. Plant Prod. Sci. 2011, 14, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Q.; Xu, Y.J.; Wang, J.C.; Yang, J.C.; Zhang, J.H. Polyamine and ethylene interactions in grain filling of superior and inferior spikelets of rice. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2012, 66, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.; Zhang, J.H.; Wang, Z.Q.; Liu, K.; Wang, P. Post-anthesis development of inferior and superior spikelets in rice in relation to abscisic acid and ethylene. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bao, J.S.; Ying, Y.N.; Zhou, X.; Xu, Y.J.; Wu, P.; Xu, F.F.; Pang, Y.H. Relationships among starch biosynthesizing protein content, fine structure and functionality in rice. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 237, 116118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.F.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z.K.; Zhou, Q.; Yu, C.; Kong, X.S.; Liu, L.J.; Wang, Z.Q.; Yang, J.C. Canopy light and nitrogen distributions are related to grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency in rice. Field Crops Res. 2017, 206, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Pal, N.; Mahajan, G.; Singh, S.; Shevkani, K. Rice grain and starch properties: Effects of nitrogen fertilizer application. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisle, A.J.; Martin, M.; Fitzgerald, M.A. Chalky and translucent rice grains differ in starch composition and structure and cooking properties. Cereal Chem. 2000, 77, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.J.; Sun, Y.Y.; Yuan, J.; Xing, C.R. Grain quality evaluation of japonica rice effected by cultivars, environment, and their interactions based on appearance and processing characteristics. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 2129–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.S.; Zhang, J.H.; Cao, X.Z. Grain sink strength may be related to the poor grain filling of indica-japonica rice (Oryza sativa) hybrids. Physiol. Plant. 2001, 112, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Tan, G.L.; Wang, Z.Q.; Yang, J.C.; Zhang, J.H. Ethylene and ACC levels in developing grains are related to the poor appearance and milling quality of rice. Plant Growth Regul. 2009, 58, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.F.; Liu, Z.H.; Deng, S.Y.; Ning, H.F.; Yang, X.Y.; Lin, Z.M.; Li, G.H.; Wang, Q.S.; Wang, S.H.; Ding, Y.F. Occurrence of perfect and imperfect grains of six japonica rice cultivars as affected by nitrogen fertilization. Plant Soil. 2011, 349, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancien, M.; Gadal, P.; Hodges, M. Enzyme redundancy and the importance of 2-oxoglutarate in higher plant ammonium assimilation. Plant Physiol. 2000, 123, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshida, H.; Takehisa, K.; Kojima, T.; Ohno, H.; Sasaki, K. Nakagawa, H. Modeling the effects of N application on growth, yield and plant properties associated with the occurrence of chalky grains of rice. Plant Prod. Sci. 2016, 19, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.Y.; Zhou, Q.; Li, E.P.; Yuan, L.M.; Wang, W.L.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L.J.; Wang, Z.Q.; Yang, J.C.; Gu, J.F. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer on structure and physicochemical properties of “super” rice starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 239, 116237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
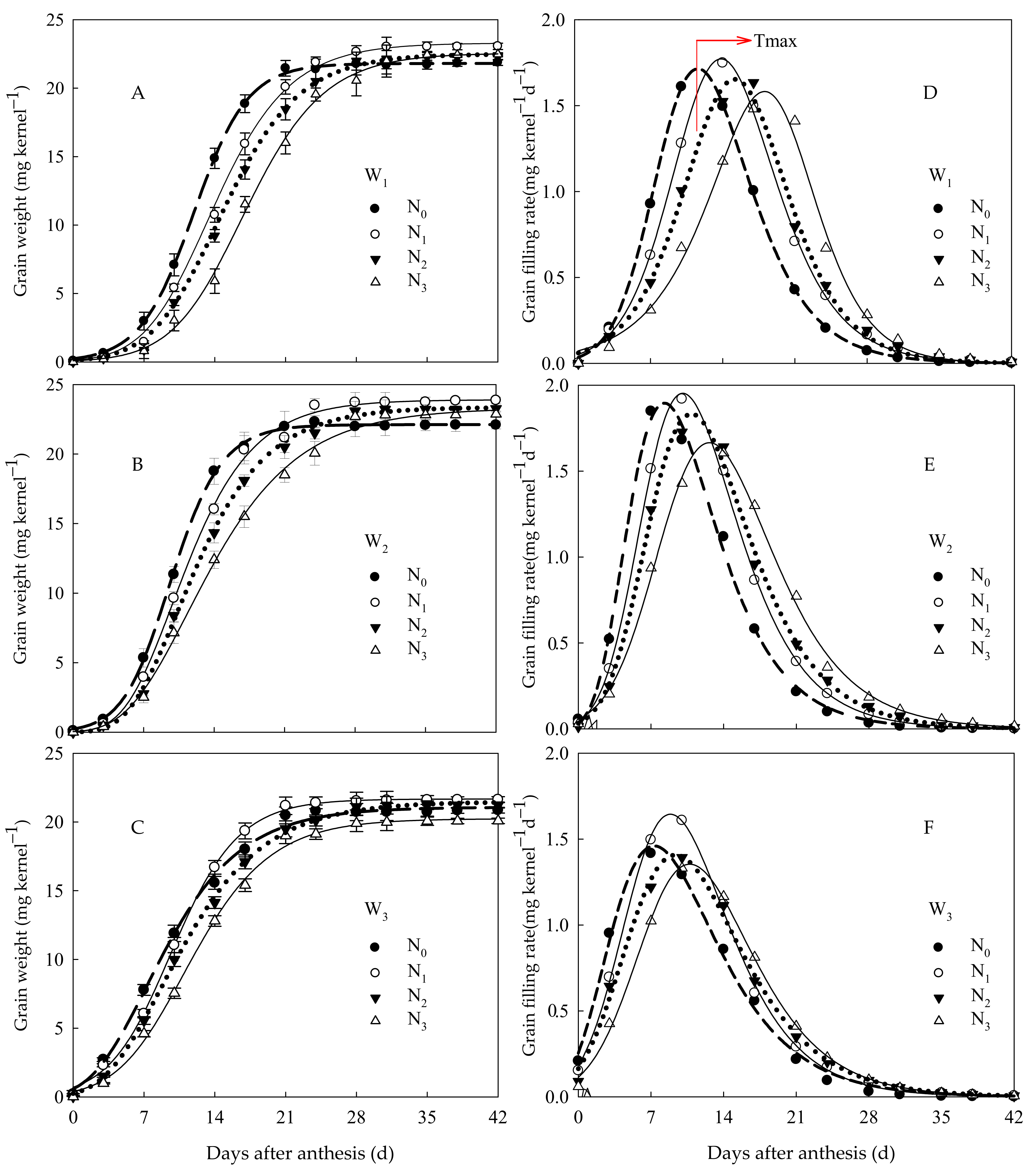

| Irrigation Mode | Grain Position | N Application | Richard Equation Parameters | Grain Filling Parameters | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | k | N | R2 | R0 | Tmax (d) | D (d) | Wmax (mg·kernel−1) | GRmax (mg·kernel−1·d−1) | GRmean (mg·kernel−1·d−1) | |||
| W1 | Superior grain | N0 | 21.16 | 6.77 | 0.257 | 0.343 | 0.9963 | 0.750 | 11.61 | 18.23 | 8.96 | 1.71 | 1.16 |
| N1 | 23.71 | 22.83 | 0.262 | 0.604 | 0.9963 | 0.434 | 13.85 | 19.86 | 10.84 | 1.77 | 1.19 | ||
| N2 | 22.41 | 66.23 | 0.285 | 0.882 | 0.9976 | 0.323 | 15.17 | 20.25 | 10.94 | 1.65 | 1.11 | ||
| N3 | 22.39 | 517.70 | 0.324 | 1.487 | 0.9983 | 0.218 | 18.07 | 21.53 | 12.13 | 1.58 | 1.04 | ||
| Inferior grain | N0 | 15.76 | 28.16 | 0.238 | 0.456 | 0.9971 | 0.523 | 17.30 | 20.61 | 6.91 | 1.13 | 0.76 | |
| N1 | 18.14 | 765.46 | 0.346 | 0.962 | 0.9979 | 0.360 | 19.29 | 17.11 | 9.00 | 1.59 | 1.06 | ||
| N2 | 17.54 | 3612.99 | 0.349 | 1.418 | 0.9989 | 0.246 | 22.50 | 19.61 | 9.41 | 1.36 | 0.89 | ||
| N3 | 17.30 | 4637.02 | 0.332 | 1.407 | 0.9973 | 0.236 | 24.41 | 20.53 | 9.27 | 1.28 | 0.84 | ||
| W2 | Superior grain | N0 | 21.85 | 0.12 | 0.236 | 0.020 | 0.9928 | 11.790 | 7.54 | 17.13 | 8.12 | 1.88 | 1.28 |
| N1 | 24.81 | 1.71 | 0.236 | 0.159 | 0.9972 | 1.479 | 10.07 | 18.34 | 9.61 | 1.95 | 1.35 | ||
| N2 | 24.15 | 1.72 | 0.222 | 0.154 | 0.9969 | 1.445 | 10.90 | 19.42 | 9.53 | 1.83 | 1.24 | ||
| N3 | 24.01 | 4.03 | 0.208 | 0.290 | 0.9976 | 0.718 | 12.63 | 21.99 | 10.31 | 1.66 | 1.10 | ||
| Inferior grain | N0 | 17.25 | 8.14 | 0.223 | 0.224 | 0.9966 | 0.996 | 16.15 | 19.97 | 7.00 | 1.27 | 0.86 | |
| N1 | 21.30 | 26.38 | 0.237 | 0.330 | 0.9993 | 0.718 | 18.49 | 19.67 | 8.98 | 1.60 | 1.08 | ||
| N2 | 18.78 | 107.82 | 0.263 | 0.583 | 0.9987 | 0.450 | 19.89 | 19.68 | 8.54 | 1.42 | 0.95 | ||
| N3 | 18.69 | 331.23 | 0.263 | 0.828 | 0.9986 | 0.318 | 22.76 | 21.49 | 9.02 | 1.30 | 0.87 | ||
| W3 | Superior grain | N0 | 20.29 | 0.11 | 0.196 | 0.025 | 0.9943 | 7.780 | 7.31 | 20.71 | 7.56 | 1.44 | 0.98 |
| N1 | 22.05 | 1.76 | 0.226 | 0.236 | 0.9950 | 0.958 | 8.89 | 19.77 | 8.99 | 1.64 | 1.12 | ||
| N2 | 20.85 | 1.10 | 0.199 | 0.171 | 0.9970 | 1.164 | 9.39 | 21.84 | 8.28 | 1.41 | 0.95 | ||
| N3 | 19.96 | 2.99 | 0.210 | 0.307 | 0.9958 | 0.684 | 10.84 | 21.97 | 8.36 | 1.34 | 0.91 | ||
| Inferior grain | N0 | 14.71 | 6.21 | 0.228 | 0.278 | 0.9966 | 0.820 | 13.62 | 19.98 | 6.09 | 1.09 | 0.74 | |
| N1 | 16.84 | 6.07 | 0.210 | 0.257 | 0.9983 | 0.817 | 15.06 | 21.50 | 6.92 | 1.16 | 0.78 | ||
| N2 | 16.57 | 12.68 | 0.193 | 0.395 | 0.9978 | 0.489 | 17.97 | 24.82 | 7.13 | 0.99 | 0.67 | ||
| N3 | 16.45 | 23.49 | 0.189 | 0.499 | 0.9993 | 0.379 | 20.38 | 26.44 | 7.31 | 0.92 | 0.62 | ||
| Irrigation Mode | Grain Position | N Application | Early-Filling Stage | Middle-Filling Stage | Late-Filling Stage | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Days (d) | MGR (mg·kernel−1·d−1) | RGC % | Days (d) | MGR (mg·kernel−1·d−1) | RGC % | Days (d) | MGR (mg·kernel−1·d−1) | RGC % | |||
| W1 | Superior grain | N0 | 7.32 | 0.365 | 12.64 | 8.58 | 1.490 | 60.37 | 13.60 | 0.404 | 25.99 |
| N1 | 9.30 | 0.415 | 16.28 | 9.11 | 1.547 | 59.44 | 12.98 | 0.425 | 23.28 | ||
| N2 | 10.67 | 0.415 | 19.76 | 9.01 | 1.448 | 58.26 | 11.64 | 0.403 | 20.98 | ||
| N3 | 13.60 | 0.432 | 26.21 | 8.94 | 1.392 | 55.52 | 9.71 | 0.398 | 17.27 | ||
| Inferior grain | N0 | 12.50 | 0.180 | 14.26 | 9.60 | 0.985 | 60.00 | 14.50 | 0.269 | 24.74 | |
| N1 | 15.52 | 0.244 | 20.69 | 7.54 | 1.393 | 57.91 | 9.50 | 0.389 | 20.40 | ||
| N2 | 18.40 | 0.242 | 25.33 | 8.20 | 1.194 | 55.88 | 9.07 | 0.341 | 17.67 | ||
| N3 | 20.11 | 0.219 | 25.45 | 8.60 | 1.124 | 55.89 | 9.54 | 0.321 | 17.66 | ||
| W2 | Superior grain | N0 | 3.42 | 0.486 | 7.62 | 8.24 | 1.617 | 60.96 | 15.39 | 0.432 | 30.42 |
| N1 | 5.70 | 0.421 | 9.77 | 8.75 | 1.690 | 60.87 | 15.15 | 0.454 | 28.36 | ||
| N2 | 6.26 | 0.377 | 9.86 | 9.27 | 1.584 | 60.79 | 16.10 | 0.426 | 28.35 | ||
| N3 | 7.43 | 0.396 | 11.86 | 10.39 | 1.445 | 60.52 | 16.88 | 0.391 | 26.62 | ||
| Inferior grain | N0 | 11.40 | 0.164 | 10.85 | 9.49 | 1.104 | 60.69 | 15.91 | 0.298 | 27.46 | |
| N1 | 13.86 | 0.191 | 12.45 | 9.26 | 1.389 | 60.41 | 14.78 | 0.377 | 26.14 | ||
| N2 | 15.46 | 0.192 | 15.84 | 9.01 | 1.235 | 59.57 | 13.01 | 0.339 | 23.60 | ||
| N3 | 17.95 | 0.200 | 19.12 | 9.62 | 1.142 | 58.50 | 12.65 | 0.317 | 21.39 | ||
| W3 | Superior grain | N0 | 2.34 | 0.670 | 7.71 | 9.95 | 1.243 | 60.96 | 18.54 | 0.332 | 30.34 |
| N1 | 4.18 | 0.580 | 10.02 | 9.38 | 1.426 | 60.81 | 15.64 | 0.385 | 28.17 | ||
| N2 | 4.20 | 0.501 | 10.04 | 10.41 | 1.217 | 60.80 | 17.93 | 0.328 | 28.16 | ||
| N3 | 5.61 | 0.431 | 12.11 | 10.27 | 1.175 | 60.48 | 16.56 | 0.318 | 26.41 | ||
| Inferior grain | N0 | 8.92 | 0.207 | 12.57 | 10.84 | 0.819 | 60.39 | 17.23 | 0.222 | 26.05 | |
| N1 | 9.96 | 0.192 | 11.36 | 10.19 | 1.002 | 60.61 | 16.81 | 0.271 | 27.03 | ||
| N2 | 12.16 | 0.182 | 13.40 | 11.62 | 0.858 | 60.21 | 18.01 | 0.234 | 25.40 | ||
| N3 | 14.25 | 0.172 | 14.86 | 12.26 | 0.803 | 59.84 | 18.20 | 0.220 | 24.30 | ||
| Irrigation Mode | Grain Position | N Application | Daily Average Temperature Difference | Total Temperature Difference | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Early Stage | Middle Stage | Late Stage | Early Stage | Middle Stage | Late Stage | |||
| W1 | Superior grain | N0 | 11.43 a | 14.57 a | 10.49 a | 83.67 c | 125.01 a | 142.66 a |
| N1 | 10.63 b | 13.85 b | 10.25 ab | 98.81 b | 126.17 a | 133.05 a | ||
| N2 | 10.50 b | 13.62 b | 10.01 b | 111.98 a | 122.72 a | 116.52 b | ||
| N3 | 7.41 c | 10.00 c | 7.40 c | 100.78 b | 89.40 b | 71.85 c | ||
| Inferior grain | N0 | 12.25 a | 12.99 a | 10.12 a | 153.13 c | 124.66 a | 146.70 a | |
| N1 | 11.79 a | 12.50 ab | 9.84 ab | 182.98 b | 94.23 b | 93.52 b | ||
| N2 | 10.76 b | 12.44 b | 9.68 b | 197.98 a | 102.05 ab | 87.77 b | ||
| N3 | 7.91 c | 9.81 c | 7.83 c | 159.07 c | 84.33 c | 74.68 c | ||
| W2 | Superior grain | N0 | 11.72 a | 14.19 a | 11.93 a | 40.07 c | 116.93 b | 183.60 a |
| N1 | 11.01 ab | 14.18 a | 11.15 b | 62.73 ab | 124.08 ab | 168.92 b | ||
| N2 | 10.89 b | 14.07 a | 10.90 b | 68.17 a | 130.43 a | 175.49 ab | ||
| N3 | 7.74 c | 9.70 c | 7.45 c | 57.51 b | 100.78 c | 125.76 c | ||
| Inferior grain | N0 | 12.95 a | 13.73 a | 11.04 a | 147.63 c | 130.27 a | 175.62 a | |
| N1 | 12.24 ab | 13.44 a | 11.01 a | 169.65 b | 124.45 a | 162.69 b | ||
| N2 | 11.58 b | 11.27 b | 9.63 b | 179.03 a | 101.59 b | 125.25 c | ||
| N3 | 8.39 c | 10.45 c | 8.17 c | 150.60 c | 100.56 b | 103.37 d | ||
| W3 | Superior grain | N0 | 11.78 a | 13.33 a | 11.18 a | 27.55 b | 132.63 ab | 207.28 a |
| N1 | 10.63 b | 13.16 ab | 11.07 ab | 44.41 a | 123.44 b | 173.13 c | ||
| N2 | 10.31 b | 12.78 b | 10.71 b | 43.28 a | 133.04 a | 192.03 b | ||
| N3 | 8.56 c | 11.14 c | 8.50 c | 43.00 a | 114.41 c | 140.76 d | ||
| Inferior grain | N0 | 13.28 a | 14.08 a | 11.38 a | 118.46 c | 152.59 a | 196.05 a | |
| N1 | 12.48 b | 13.93 a | 11.35 a | 124.30 c | 141.93 b | 190.87 ab | ||
| N2 | 12.01 b | 13.18 b | 10.07 b | 146.04 a | 153.19 a | 181.30 b | ||
| N3 | 9.55 c | 11.83 c | 9.27 c | 136.09 b | 145.04 b | 168.72 c | ||
| Irrigation Mode | Grain Position | N Application | Effective Accumulated Temperature | Daily Average Light Intensity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Early Stage | Middle Stage | Late Stage | Early Stage | Middle Stage | Late Stage | |||
| W1 | Superior grain | N0 | 104.99 d | 144.21 a | 224.31 a | 1212.13 a | 1441.44 a | 1031.46 a |
| N1 | 136.76 c | 146.64 a | 207.69 b | 972.71 b | 1284.93 b | 965.14 b | ||
| N2 | 167.10 b | 150.35 a | 191.31 c | 907.79 c | 1282.56 b | 867.01 c | ||
| N3 | 217.78 a | 146.96 a | 158.88 d | 895.85 c | 909.64 c | 685.90 d | ||
| Inferiorgrain | N0 | 182.34 d | 223.94 a | 195.13 a | 1208.61 a | 1215.85 a | 912.53 a | |
| N1 | 250.13 c | 126.90 c | 159.23 b | 1086.11 b | 1000.47 b | 707.17 b | ||
| N2 | 284.25 b | 124.52 c | 162.13 b | 1043.21 c | 901.97 c | 691.84 b | ||
| N3 | 317.83 a | 142.16 b | 123.27 c | 939.18 d | 544.22 d | 488.49 c | ||
| W2 | Superior grain | N0 | 41.38 c | 125.19 c | 242.04 b | 1029.03 a | 1085.94 c | 1152.70 a |
| N1 | 88.58 b | 142.77 b | 242.49 b | 996.67 b | 1289.00 a | 1159.25 a | ||
| N2 | 88.74 b | 143.66 b | 256.68 a | 759.84 c | 1190.84 b | 874.16 b | ||
| N3 | 103.91 a | 156.40 a | 259.93 a | 650.06 d | 655.17 d | 588.26 c | ||
| Inferiorgrain | N0 | 166.57 d | 123.18 c | 238.15 a | 1138.10 a | 1269.45 a | 891.78 a | |
| N1 | 215.18 c | 147.07 ab | 215.45 b | 1070.42 b | 1190.19 b | 822.70 b | ||
| N2 | 232.24 b | 144.24 b | 191.06 c | 1018.44 c | 981.21 c | 810.69 b | ||
| N3 | 276.24 a | 154.51 a | 165.32 d | 650.03 d | 629.20 d | 551.90 c | ||
| W3 | Superior grain | N0 | 31.17 c | 162.76 a | 314.96 a | 1135.55 a | 1228.73 a | 1185.28 a |
| N1 | 61.58 b | 143.48 b | 263.08 c | 1179.10 a | 1071.52 b | 921.13 b | ||
| N2 | 62.14 b | 161.55 a | 297.72 b | 866.85 b | 576.60 c | 830.90 c | ||
| N3 | 92.79 a | 154.42 a | 247.40 d | 545.06 c | 504.54 d | 347.96 d | ||
| Inferior grain | N0 | 142.77 d | 190.96 a | 249.52 a | 1185.40 a | 1409.65 a | 980.15 a | |
| N1 | 155.66 c | 170.16 b | 255.48 a | 1028.27 b | 1359.72 b | 892.50 b | ||
| N2 | 189.28 b | 196.36 a | 257.74 a | 689.28 c | 955.63 c | 711.18 c | ||
| N3 | 214.05 a | 189.53 a | 220.26 b | 534.54 d | 631.66 d | 496.56 d | ||
| Irrigation Mode | N Application | Superior Grain | Inferior Grain | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 y | 2020 y | 2019 y | 2020 y | ||||||
| Chalky Grain Rate (%) | Chalkiness Degree (%) | Chalky Grain Rate(%) | Chalkiness Degree (%) | Chalky Grain Rate (%) | Chalkiness Degree (%) | Chalky Grain Rate (%) | Chalkiness Degree (%) | ||
| W1 | N0 | 21.51 b | 8.02 b | 20.07 b | 7.70 b | 44.69 a | 16.98 a | 47.88 a | 18.24 a |
| N1 | 18.49 c | 7.46 bc | 19.35 bc | 6.68 c | 33.97 c | 13.70 c | 35.56 bc | 12.27 c | |
| N2 | 17.52 c | 6.95 c | 17.81 c | 5.53 d | 32.19 c | 12.77 d | 32.73 c | 10.15 d | |
| N3 | 24.32 a | 9.14 a | 26.06 a | 9.83 a | 39.52 b | 14.74 b | 36.89 b | 14.14 b | |
| W2 | N0 | 22.11 a | 8.57 a | 21.00 b | 7.05 b | 43.42 a | 16.44 a | 45.57 a | 16.38 a |
| N1 | 16.67 c | 5.91 c | 15.35 c | 5.19 c | 31.51 c | 11.49 c | 29.01 c | 10.08 c | |
| N2 | 18.96 b | 7.63 b | 15.63 c | 5.61 c | 35.84 b | 14.42 b | 29.54 c | 10.61 c | |
| N3 | 22.97 a | 8.90 a | 24.11 a | 8.87 a | 36.11 b | 14.69 b | 34.02 b | 11.56 b | |
| W3 | N0 | 23.22 b | 9.73 ab | 23.25 b | 9.08 a | 46.82 a | 17.17 a | 52.89 a | 18.83 a |
| N1 | 20.84 c | 6.81 c | 18.75 c | 6.10 c | 36.11 c | 11.80 c | 32.48 c | 10.57 d | |
| N2 | 21.93 bc | 8.87 b | 22.10 b | 7.96 b | 37.99 bc | 15.36 b | 38.29 b | 13.79 c | |
| N3 | 27.02 a | 9.91 a | 30.53 a | 10.87 a | 40.24 b | 16.85 a | 40.29 b | 15.73 b | |
| F Value | W | 46.95 ** | 151.43 ** | 88.29 ** | 221.60 ** | 17.55 ** | 17.38 ** | 52.78 ** | 116.85 ** |
| N | 94.61 ** | 428.64 ** | 207.02 ** | 540.10 ** | 92.58 ** | 168.84 ** | 212.60 ** | 406.14 ** | |
| W×N | 3.90 ** | 44.89 ** | 9.64 ** | 49.90 ** | 3.32 * | 18.63 ** | 5.13 ** | 26.77 ** | |
| Index | Superior Grain | Inferior Grain | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chalky grain Rate (%) | Chalkiness Degree (%) | Chalky grain Rate (%) | Chalkiness Degree (%) | ||
| Tmax | 0.058 | 0.049 | −0.506 * | −0.343 | |
| GRmax | −0.745 ** | −0.747 ** | −0.604 * | −0.629 * | |
| Wmax | −0.175 | −0.194 | −0.765 ** | −0.676 * | |
| D | 0.604 * | 0.613 * | 0.151 | 0.269 | |
| GRmean | −0.767 ** | −0.773 ** | −0.586 * | −0.614 * | |
| Early stage | MGR | 0.181 | 0.200 | −0.359 | −0.404 |
| Daily average temperature difference | −0.570 * | −0.507 * | −0.675 * | −0.581 * | |
| Total temperature difference | −0.300 | −0.296 | −0.616 * | −0.530 * | |
| Effective accumulated temperature | 0.031 | 0.009 | −0.537 * | −0.412 | |
| Daily average light intensity | −0.420 | −0.390 | −0.643 * | −0.571 * | |
| Middle stage | MGR | −0.745 ** | −0.750 ** | −0.685 * | −0.676 * |
| Daily average temperature difference | −0.717 ** | −0.671 * | −0.530 * | −0.503 | |
| Total temperature difference | −0.509 * | −0.430 | 0.375 | 0.408 | |
| Effective accumulated temperature | 0.356 | 0.452 | 0.443 | 0.464 | |
| Daily average light intensity | −0.718 ** | −0.644 * | −0.639 * | −0.523 * | |
| Late stage | MGR | −0.718 ** | −0.727 ** | −0.677 * | −0.675 * |
| Daily average temperature difference | −0.599 * | −0.565 * | −0.607 * | −0.574 * | |
| Total temperature difference | −0.228 | −0.167 | 0.436 | 0.342 | |
| Effective accumulated temperature | 0.070 | 0.142 | 0.339 | 0.239 | |
| Daily average light intensity | −0.651 * | −0.550 * | −0.557 * | −0.545 * | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Y.; Wu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Luo, Y.; Guo, C.; Li, B.; Li, F.; Xing, M.; Yang, Z.; Ma, J. Effects of Water and Nitrogen on Grain Filling Characteristics, Canopy Microclimate with Chalkiness of Directly Seeded Rice. Agriculture 2022, 12, 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12010122
Sun Y, Wu Y, Sun Y, Luo Y, Guo C, Li B, Li F, Xing M, Yang Z, Ma J. Effects of Water and Nitrogen on Grain Filling Characteristics, Canopy Microclimate with Chalkiness of Directly Seeded Rice. Agriculture. 2022; 12(1):122. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12010122
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Yongjian, Yunxia Wu, Yuanyuan Sun, Yinghan Luo, Changchun Guo, Bo Li, Feijie Li, Mengwen Xing, Zhiyuan Yang, and Jun Ma. 2022. "Effects of Water and Nitrogen on Grain Filling Characteristics, Canopy Microclimate with Chalkiness of Directly Seeded Rice" Agriculture 12, no. 1: 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12010122
APA StyleSun, Y., Wu, Y., Sun, Y., Luo, Y., Guo, C., Li, B., Li, F., Xing, M., Yang, Z., & Ma, J. (2022). Effects of Water and Nitrogen on Grain Filling Characteristics, Canopy Microclimate with Chalkiness of Directly Seeded Rice. Agriculture, 12(1), 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12010122






