The Toxicity Response of Coccinella septempunctata L. (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) after Exposure to Sublethal Concentrations of Acetamiprid
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insecticide
2.2. Test Species
2.3. Acetamiprid Toxicity Test to C. septempunctata at Different Stages
2.4. Sublethal Effects on Predatory Capacity of C. septempunctata
2.5. Functional Response of C. septempunctata to Acetamiprid
2.6. Effects of Sublethal Acetamiprid Exposure on C. septempunctata Larval Development
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Toxicity of Acetamiprid to C. septempunctata at Different Larval Stages
3.2. Effects of Sublethal Concentrations of Acetamiprid on Predation Capacity of C. septempunctata Larvae
3.3. Influence of Sublethal Exposure to Acetamiprid on the Predatory Functional Response of C. septempunctata
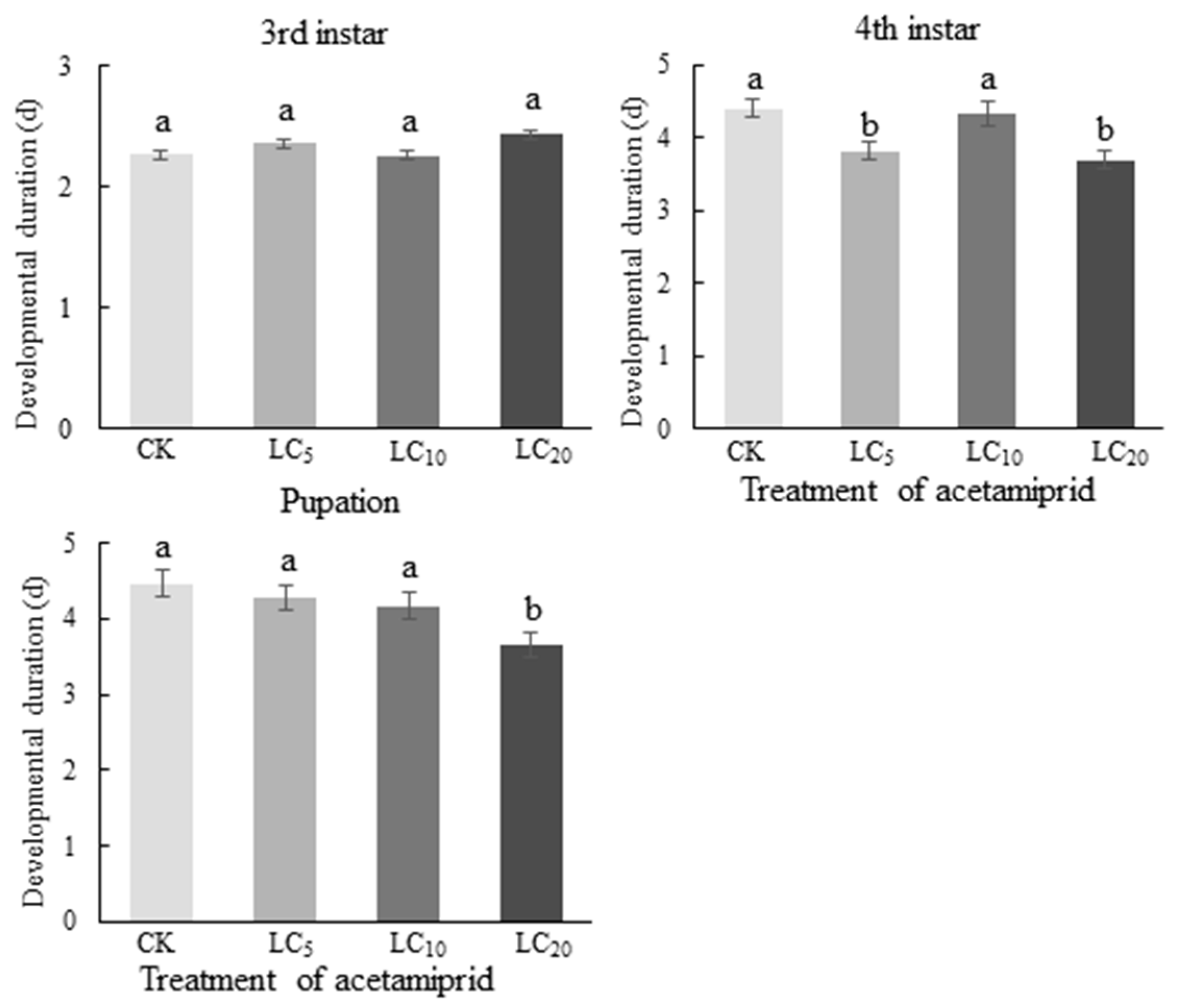
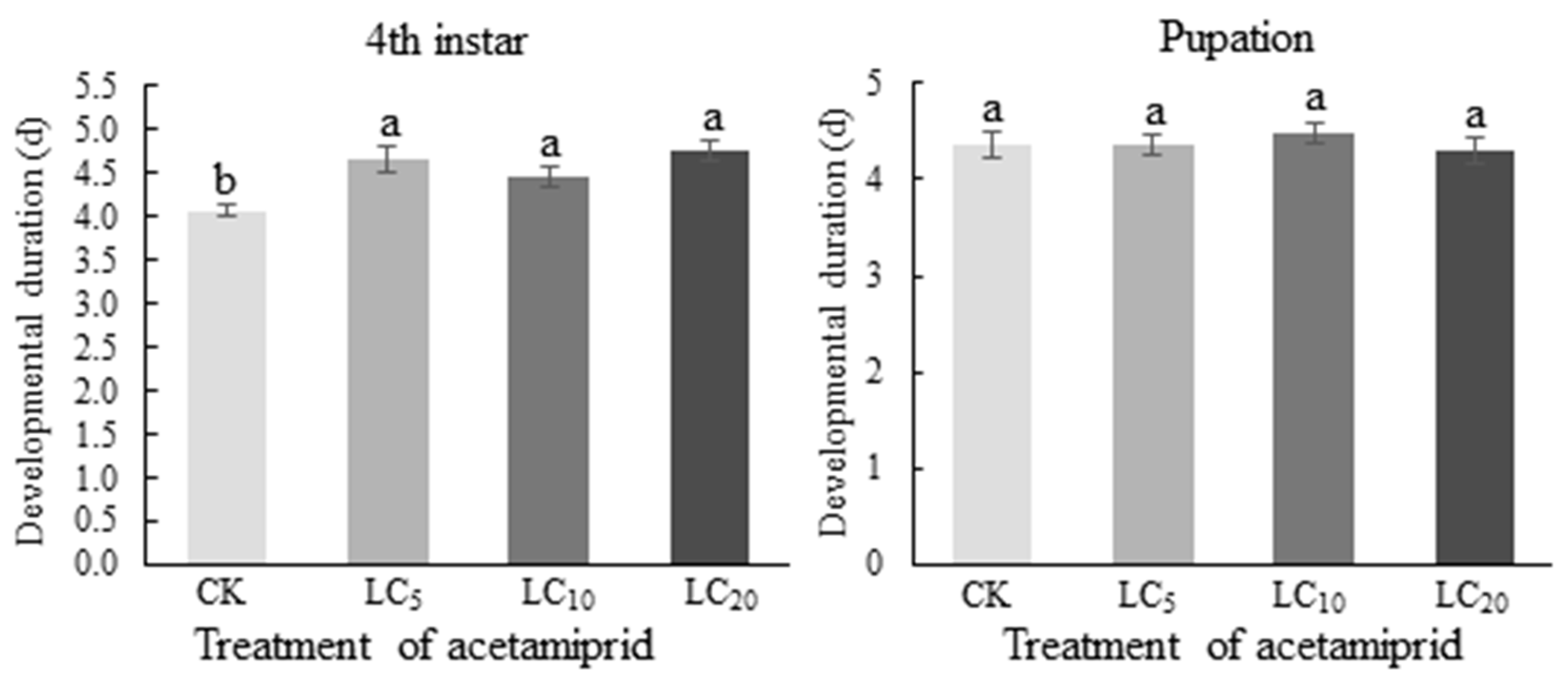
3.4. Effect of Acetamiprid on the Developmental Time of C. septempunctata at Different Larval Stages
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Doddamani, V.; Behere, G.; Firake, D.; Nongkynrih, B. Biology of Coccinella Septempunctata on Mustard Aphid Lipaphis Erysimi. Indian J. Hill Farming 2017, 30, 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Fu, M.; Lin, R.; Zhang, Y.; Yongquan, L.; Jiang, H.; Brock, T. Toxic effects of hexaflumuron on the development of Coccinella septempunctata. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 1418–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahlai, C.A.; Colunga-Garcia, M.; Gage, S.H.; Landis, D.A. The role of exotic ladybeetles in the decline of native ladybeetle populations: Evidence from long-term monitoring. Biol. Invasions 2015, 17, 1005–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhi, J.; Li, F.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Jin, J. Transcriptome sequencing of Coccinella septempunctata adults (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) feeding on artificial diet and Aphis craccivora. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236249. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, Y.H.; Li, F.L. An improved artificial diet for larvae of the seven-spotted ladybird beetle Coccinella septempunctata L. Biol. Control. 2022, 171, 104949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, X.; Yu, C.; Liu, F.; Mu, W. Sublethal and transgenerational effects of thiamethoxam on the demographic fitness and predation performance of the seven-spot ladybeetle Coccinella septempunctata L. (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Chemosphere 2019, 216, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.; Zhang, L.; Han, Y.; Ren, X.; Huang, J.; Chen, H. De novo transcriptome sequencing and analysis of Coccinella septempunctata L. in non-diapause, diapause and diapause-terminated states to identify diapause-associated genes. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, F. Effects of various components of artificial diets on survival, development and reproduction of Coccinella septempunctata L. (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2022, 32, 1122–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Mu, W.; Zhang, Z. Sublethal effects of anthranilic diamide insecticides on the demographic fitness and consumption rates of the Coccinella septempunctata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) fed on Aphis craccivora. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 4178–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casida, J.E. Neonicotinoid Metabolism: Compounds, Substituents, Pathways, Enzymes, Organisms, and Relevance. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 2923–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phogat, A.; Singh, J.; Kumar, V.; Malik, V. Toxicity of the acetamiprid insecticide for mammals: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 1453–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeschke, P.; Nauen, R.; Schindler, M.; Elbert, A. Overview of the status and global strategy for neonicotinoids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 2897–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Ma, S.; Liu, F.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Hou, C.; Wu, Y.; Gao, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y. Acute and chronic toxicity of acetamiprid, carbaryl, cypermethrin and deltamethrin to Apis mellifera larvae reared in vitro. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horgan, A. Acetamiprid: Novel neonicotinoid systemic insecticide. Asp. Appl. Biol. 2007, 83, 47. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Guo, Y.; Wang, L.; He, K.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X.; Gunasekaran, S. Hapten-grafted programmed probe as a corecognition element for a competitive immunosensor to detect acetamiprid residue in agricultural products. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 7815–7821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrissey, C.A.; Mineau, P.; Devries, J.H.; Sanchez-Bayo, F.; Liess, M.; Cavallaro, M.C.; Liber, K. Neonicotinoid contamination of global surface waters and associated risk to aquatic invertebrates: A review. Environ. Int. 2015, 74, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbert, A.; Haas, M.; Springer, B.; Thielert, W.; Nauen, R. Applied aspects of neonicotinoid uses in crop protection. Pest Manag. Sci. 2010, 64, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloyd, R.A.; Bethke, J.A. Impact of neonicotinoid insecticides on natural enemies in greenhouse and interiorscape environments. Pest Manag. Sci. 2011, 67, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirello, P.; Pozzebon, A.; Duso, C. The effect of insecticides on the non-target predatory mite Kampimodromus aberrans: Laboratory studies. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 1139–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gontijo, P.C.; Moscardini, V.F.; Michaud, J.P.; Carvalho, G.A. Non-target effects of chlorantraniliprole and thiamethoxam on Chrysoperla carnea when employed as sunflower seed treatments. J. Pest Sci. 2014, 87, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Lin, R.; Zhang, N.; Yuan, S.; Zhou, X.; Huang, J.; Ren, X.; Wang, S.; Jiang, H.; Yu, C. Toxicity of six insecticides to predatory mite Amblyseius cucumeris (Oudemans) (Acari: Phytoseiidae) in-and off-field. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 161, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Liu, X.; Huang, X.; Yu, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Mu, W. Comparative ecotoxicity of neonicotinoid insecticides to three species of Trichogramma parasitoid wasps (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 183, 109587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, R.Z.R.; Vandervoort, C.; Wise, J.C. Residual toxicity of insecticides to Neoseiulus fallacis (Acari: Phytoseiidae) in apples. J. Econ. Entomol. 2019, 112, 2262–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, S.; Soares, A.O.; Garcia, P. Voracity of Coccinella undecimpunctata: Effects of insecticides when foraging in a prey/plant system. J. Pest Sci. 2011, 84, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.L.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, J.W.; Desneux, N.; He, Y.-X.; Weng, Q.-Y. Lethal and sublethal effects of thiamethoxam on the whitefly predator Serangium japonicum (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) through different exposure routes. Chemosphere 2015, 128, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zheng, Y.; Desneux, N.; Wu, K. Lethal effect of imidacloprid on the coccinellid predator Serangium japonicum and sublethal effects on predator voracity and on functional response to the whitefly Bemisia tabaci. Ecotoxicology 2012, 21, 1291–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Lin, R.; Fu, M.; Zhou, Y.; Zong, F.; Jiang, H.; Lv, N.; Piao, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y. Impact of imidacloprid on life-cycle development of Coccinella septempunctata in laboratory microcosms. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 110, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desneux, N.; Decourtye, A.; Delpuech, J.M. The sublethal effects of pesticides on beneficial arthropods. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2007, 52, 81–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.; Santos, R.; Tomé, H.; Barbosa, W.; Martins, G.; Guedes, R.; Oliveira, E. Imidacloprid-mediated effects on survival and fertility of the Neotropical brown stink bug Euschistus heros. J. Pest Sci. 2016, 89, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holling, C.S. Some characteristics of simple types of predation and parasitism. Can. Entomol. 1959, 91, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Qi, Y.; Desneux, N.; Shi, X.; Biondi, A.; Gao, X. Sublethal and transgenerational effects of short-term and chronic exposures to the neonicotinoid nitenpyram on the cotton aphid Aphis gossypii. J. Pest Sci. 2017, 90, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvan, T.L.; Koch, R.L.; Hutchison, W.D. Toxicity of indoxacarb and spinosad to the multicolored Asian lady beetle, Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae), via three routes of exposure. Pest Manag. Sci. 2006, 62, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kianpour, R.; Fathipour, Y.; Kamali, K.; Omkar. Effects of mixed prey on the development and demographic attributes of a generalist predator, Coccinella septempunctata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2011, 21, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Kranthi, S.; Nitharwal, M.; Jat, S.; Monga, D. Influence of pesticides and application methods on pest and predatory arthropods associated with cotton. Phytoparasitica 2012, 40, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanawi, E.; Budd, R.; Tjeerdema, R.S. Environmental fate and ecotoxicology of fenpropathrin. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2013, 225, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Douglas, M.R.; Tooker, J.F. Meta-analysis reveals that seed-applied neonicotinoids and pyrethroids have similar negative effects on abundance of arthropod natural enemies. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christie, P.T.; Wright, D.J. Activity of abamectin against larval stages of Spodoptera littoralis Boisduval and Heliothis armigera Hübner (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) and possible mechanisms determining differential toxicity. Pestic. Sci. 1990, 29, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, J.-P. Toxicity of two neonicotinoid insecticides via the food chain for larvae of the two spot ladybird Adalia bipunctata. IOBC-WPRS Bull. Pestic. Benef. Org. 2012, 82, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Murdoch, W.W.; Briggs, C.J.; Nisbet, R.M. Consumer-Resource Dynamics; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, J.Y.; Van, D.W.W.; Rabbinge, R. Temperature and Prey Density on Bionomics of Coccinella septempunctata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) Feeding on Aphis gossypii (Homoptera: Aphididae) on Cotton. Environ. Entomol. 1999, 28, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Zhao, J.; Guo, X.; Chen, H.; Qu, M.; Zhai, W.; Desneux, N.; Biondi, A.; Zhang, F.; Wang, S. Sublethal effects of imidacloprid on the predatory seven-spot ladybird beetle Coccinella septempunctata. Ecotoxicology 2016, 25, 1782–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afza, R.; Riaz, M.A.; Afzal, M. Sublethal Effect of Six Insecticides on Predatory Activity and Survival of Coccinella Septempunctata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) Following Contact with Contaminated Prey and Residues. Gesunde Pflanz. 2020, 72, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinou, A.F.; Seraphides, N.; Stavrinides, M.C. Lethal and behavioral effects of pesticides on the insect predator Macrolophus pygmaeus. Chemosphere 2014, 96, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, X.; Ma, D.; Yu, C.; Liu, F.; Mu, W. Influence of lethal and sublethal exposure to clothianidin on the seven-spotted lady beetle, Coccinella septempunctata L. (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 161, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Ma, D.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, C.; Liu, F.; Mu, W. Favorable compatibility of nitenpyram with the aphid predator, Coccinella septempunctata L. (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Environ. Ence Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 27393–27401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courjaret, R.; Lapied, B. Complex intracellular messenger pathways regulate one type of neuronal alpha-bungarotoxin-resistant nicotinic acetylcholine receptors expressed in insect neurosecretory cells (dorsal unpaired median neurons). Mol. Pharmacol. 2001, 60, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.; Galligan, J.J.; Hollingworth, R.M. Agonist actions of neonicotinoids on nicotinic acetylcholine receptors expressed by cockroach neurons. NeuroToxicology 2007, 28, 829–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thany, S.H.; Courjaret, R.; Lapied, B. Effect of calcium on nicotine-induced current expressed by an atypical α-bungarotoxin-insensitive nAChR2. Neurosci. Lett. 2008, 438, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bodereau-Dubois, B.; List, O.; Calas-List, D.; Marques, O.; Communal, P.-Y.; Thany, S.; Lapied, B. Transmembrane Potential Polarization, Calcium Influx, and Receptor Conformational State Modulate the Sensitivity of the Imidacloprid-Insensitive Neuronal Insect Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor to Neonicotinoid Insecticides. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 341, 326–339. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Calas-List, D.; List, O.; Quinchard, S.; Thany, S.H. Calcium pathways such as cAMP modulate clothianidin action through activation of α-bungarotoxin-sensitive and -insensitive nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. NeuroToxicology 2013, 37, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunet, J.-L.; Badiou, A.; Belzunces, L. In vivo metabolic fate of [14C]-acetamiprid in six biological compartments of the honeybee, Apis mellifera L. Pest Manag. Sci. 2005, 61, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Larval Stage | Regression Equation | SE a | χ2 b | df c | P d | R2 e | LC50 f (mg a.i. L−1) g | 95% Confidence Interval (mg a.i. L−1) | LC5 (mg a.i. L−1) | LC10 (mg a.i. L−1) | LC20 (mg a.i. L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | y = 1.861x − 2.229 | 0.450 0.478 | 0.593 | 3 | 0.898 | 0.968 | 15.767 | 12.057–25.662 | 2.061 | 3.230 | 5.567 |
| L2 | y = 2.839x − 2.765 | 0.484 0.492 | 3.275 | 3 | 0.351 | 0.916 | 9.412 | 7.756–11.314 | 2.480 | 3.329 | 4.757 |
| L3 | y = 2.172x − 2.770 | 0.368 0.431 | 2.947 | 4 | 0.567 | 0.932 | 18.850 | 15.175–25.360 | 3.296 | 4.845 | 7.724 |
| L4 | y = 2.420x − 3.395 | 0.415 0.505 | 0.833 | 4 | 0.934 | 0.984 | 25.278 | 20.211–35.765 | 5.285 | 7.468 | 11.350 |
| Instar Larvae | Prey Density (the Number of Aphids Per Tube) | Control | LC5 | LC10 | LC20 | df | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | 5 | 4.30 ± 0.213 a | 4.00 ± 0.333 a | 3.10 ± 0.180 b | 3.10 ± 0.146 b | 3 | 6.288 | <0.05 |
| 10 | 7.10 ± 0.314 a | 6.80 ± 0.389 ab | 5.80 ± 0.389 bc | 5.20 ± 0.573 c | 3 | 4.251 | <0.05 | |
| 15 | 10.30 ± 0.300 a | 10.10 ± 0.277 a | 8.90 ± 0.277 b | 8.00 ± 0.333 c | 3 | 13.119 | <0.05 | |
| 20 | 15.90 ± 0.407 a | 13.10 ± 0.433 b | 12.20 ± 0.490 b | 9.50 ± 0.500 c | 3 | 33.024 | <0.05 | |
| 25 | 18.00 ± 0.558 a | 17.10 ± 0.379 a | 14.30 ± 0.396 b | 12.80 ± 0.442 c | 3 | 28.975 | <0.05 | |
| 2nd | 5 | 4.50 ± 0.167 a | 3.80 ± 0.291 ab | 3.10 ± 0.277 b | 3.30 ± 0.300 b | 3 | 1.510 | 0.228 |
| 10 | 7.70 ± 0.300 a | 7.20 ± 0.249 a | 6.80 ± 0.359 a | 5.30 ± 0.300 b | 3 | 14.666 | <0.05 | |
| 15 | 12.40 ± 0.452 a | 10.90 ± 0.277 b | 9.40 ± 0.476 c | 8.50 ± 0.582 c | 3 | 13.890 | <0.05 | |
| 20 | 16.00 ± 0.298 a | 15.60 ± 0.267 a | 14.20 ± 0.249 b | 12.90 ± 0.379 c | 3 | 21.839 | <0.05 | |
| 25 | 20.20 ± 0.467 a | 18.10 ± 0.433 b | 16.00 ± 0.447 c | 13.90 ± 0.458 d | 3 | 36.049 | <0.05 | |
| 3rd | 30 | 28.20 ± 0.512 a | 27.50 ± 0.671 a | 27.10 ± 0.567 a | 28.00 ± 0.422 a | 3 | 0.815 | 0.494 |
| 50 | 47.20 ± 0.663 a | 45.30 ± 0.989 a | 46.30 ± 1.012 a | 41.30 ± 1.739 b | 3 | 4.954 | <0.05 | |
| 70 | 63.30 ± 1.606 a | 61.00 ± 1.229 a | 60.60 ± 1.470 a | 55.90 ± 1.767 b | 3 | 4.112 | <0.05 | |
| 100 | 94.00 ± 1.382 a | 91.80 ± 1.737 ab | 88.50 ± 1.424 bc | 86.60 ± 1.979 c | 3 | 4.028 | <0.05 | |
| 120 | 110.00 ± 2.113 a | 105.00 ± 2.290 ab | 103.00 ± 2.066 b | 94.90 ± 1.859 c | 3 | 9.057 | <0.05 | |
| 4th | 50 | 46.30 ± 1.121 a | 44.00 ± 1.300 a | 45.10 ± 1.370 a | 46.60 ± 0.859 a | 3 | 0.984 | 0.411 |
| 100 | 91.10 ± 1.278 a | 89.70 ± 1.146 a | 77.60 ± 2.001 b | 66.90 ± 2.627 c | 3 | 37.325 | <0.05 | |
| 150 | 110.10 ± 3.598 a | 107.20 ± 3.359 a | 89.50 ± 3.321 b | 90.30 ± 4.585 b | 3 | 8.436 | <0.05 | |
| 200 | 139.10 ± 5.332 a | 138.40 ± 4.246 a | 129.60 ± 4.206 ab | 121.70 ± 5.428 b | 3 | 2.892 | <0.05 | |
| 250 | 197.10 ± 4.413 a | 173.00 ± 5.787 ab | 150.10 ± 3.093 b | 134.90 ± 7.155 c | 3 | 25.987 | <0.05 |
| Treatment | Equation of Predator Functional Response | R2 a | The Rate of Successful Attack (a’) | Handling Time of Predatory (Th/d) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Instar | Control | Na = 0.747N/(1 + 0.00060N) | 0.981 | 0.747 | 0.0008 |
| LC5 | Na = 0.689N/(1 + 0.00096N) | 0.994 | 0.689 | 0.0014 | |
| LC10 | Na = 0.622N/(1 + 0.00280N) | 0.996 | 0.622 | 0.0045 | |
| LC20 | Na = 0.552N/(1 + 0.00431N) | 0.986 | 0.552 | 0.0078 | |
| 2nd Instar | Control | Na = 0.817N/(1 + 0.00057N) | 0.997 | 0.817 | 0.0007 |
| LC5 | Na = 0.754N/(1 + 0.00083N) | 0.994 | 0.754 | 0.0011 | |
| LC10 | Na = 0.677N/(1 + 0.00122N) | 0.986 | 0.677 | 0.0018 | |
| LC20 | Na = 0.606N/(1 + 0.00188N) | 0.971 | 0.606 | 0.0031 | |
| 3rd Instar | Control | Na = 0.938N/(1 + 0.00019N) | 0.999 | 0.938 | 0.0002 |
| LC5 | Na = 0.916N/(1 + 0.00027N) | 0.997 | 0.916 | 0.0003 | |
| LC10 | Na = 0.932N/(1 + 0.00065N) | 0.998 | 0.932 | 0.0007 | |
| LC20 | Na = 0.886N/(1 + 0.00080N) | 0.988 | 0.886 | 0.0009 | |
| 4th Instar | Control | Na = 0.992N/(1 + 0.00120N) | 0.974 | 0.920 | 0.0013 |
| LC5 | Na = 0.936N/(1 + 0.00159N) | 0.984 | 0.936 | 0.0017 | |
| LC10 | Na = 0.828N/(1 + 0.00149N) | 0.971 | 0.828 | 0.0018 | |
| LC20 | Na = 0.792N/(1 + 0.00182N) | 0.984 | 0.792 | 0.0023 |
| Developmental Time | Prey Density (The Number of Aphids Per Tube) | Treatments | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | LC5 | LC10 | LC20 | ||
| 1st Instar | 5 | 0.745 | 0.743 | 0.741 | 0.738 |
| 10 | 0.736 | 0.686 | 0.682 | 0.679 | |
| 15 | 0.676 | 0.673 | 0.613 | 0.605 | |
| 20 | 0.597 | 0.589 | 0.581 | 0.540 | |
| 25 | 0.529 | 0.518 | 0.508 | 0.498 | |
| 2nd Instar | 5 | 0.815 | 0.813 | 0.810 | 0.808 |
| 10 | 0.805 | 0.751 | 0.747 | 0.744 | |
| 15 | 0.741 | 0.738 | 0.673 | 0.669 | |
| 20 | 0.665 | 0.661 | 0.657 | 0.601 | |
| 25 | 0.595 | 0.589 | 0.584 | 0.579 | |
| 3rd Instar | 30 | 0.934 | 0.931 | 0.928 | 0.924 |
| 50 | 0.922 | 0.908 | 0.903 | 0.898 | |
| 70 | 0.891 | 0.886 | 0.913 | 0.901 | |
| 100 | 0.890 | 0.873 | 0.862 | 0.865 | |
| 120 | 0.852 | 0.839 | 0.820 | 0.808 | |
| 4th Instar | 50 | 0.868 | 0.821 | 0.779 | 0.741 |
| 100 | 0.707 | 0.867 | 0.807 | 0.755 | |
| 150 | 0.710 | 0.669 | 0.771 | 0.721 | |
| 200 | 0.677 | 0.638 | 0.603 | 0.727 | |
| 250 | 0.672 | 0.625 | 0.584 | 0.547 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
You, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Zheng, J.; Zhao, J.; Luo, F.; Chen, Y.; Xie, M.; Liu, X.; Wei, H. The Toxicity Response of Coccinella septempunctata L. (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) after Exposure to Sublethal Concentrations of Acetamiprid. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1642. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12101642
You Y, Zeng Z, Zheng J, Zhao J, Luo F, Chen Y, Xie M, Liu X, Wei H. The Toxicity Response of Coccinella septempunctata L. (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) after Exposure to Sublethal Concentrations of Acetamiprid. Agriculture. 2022; 12(10):1642. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12101642
Chicago/Turabian StyleYou, Yong, Zhaohua Zeng, Jie Zheng, Jianwei Zhao, Fengqiu Luo, Yixin Chen, Miao Xie, Xingang Liu, and Hui Wei. 2022. "The Toxicity Response of Coccinella septempunctata L. (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) after Exposure to Sublethal Concentrations of Acetamiprid" Agriculture 12, no. 10: 1642. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12101642
APA StyleYou, Y., Zeng, Z., Zheng, J., Zhao, J., Luo, F., Chen, Y., Xie, M., Liu, X., & Wei, H. (2022). The Toxicity Response of Coccinella septempunctata L. (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) after Exposure to Sublethal Concentrations of Acetamiprid. Agriculture, 12(10), 1642. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12101642





