Temporal and Spatial Differentiation and Driving Factors of China’s Agricultural Eco-Efficiency Considering Agricultural Carbon Sinks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Super-SBM Model with Unexpected Outputs
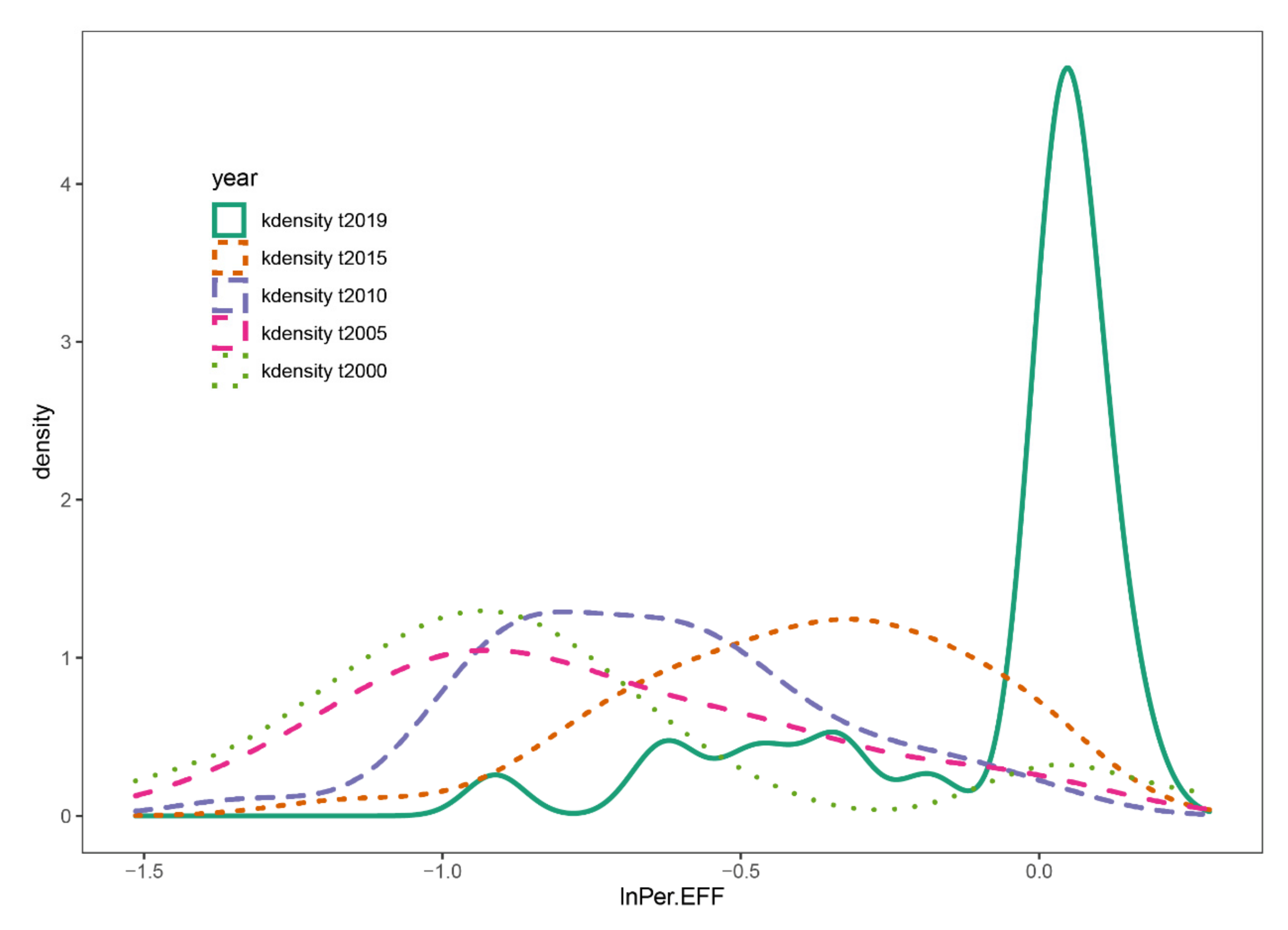
2.2.2. Kernel Density Function
2.2.3. Geodetector
- Factor detection. The factor detector was used to calculate the q value of each factor, which was used to quantitatively analyze the spatial differentiation of AEE and to detect the extent to which a factor explained the spatial differentiation. The formula is:where h = 1, 2, …; m is the stratification or partition of the independent variable X and the dependent variable Y; and are the number of units in layer h and the whole area, respectively; and are the variances of the Y values of layer h and the whole area, respectively; and q is a measurement of the explanatory power, with a range of 0 to 1. The larger the q value, the stronger the explanatory power of the independent variable X to the dependent variable Y, and vice versa.
- Interactive detection was used to identify the interaction between different independent variables, that is, to determine whether the interaction of influencing factors will enhance or weaken the explanatory power of AEE, or whether the influencing factors act independently, the detection calculation formula were from Wang [40].
2.2.4. Indicator Selection
- Explained variable
- 2.
- Explanatory variables
3. Results
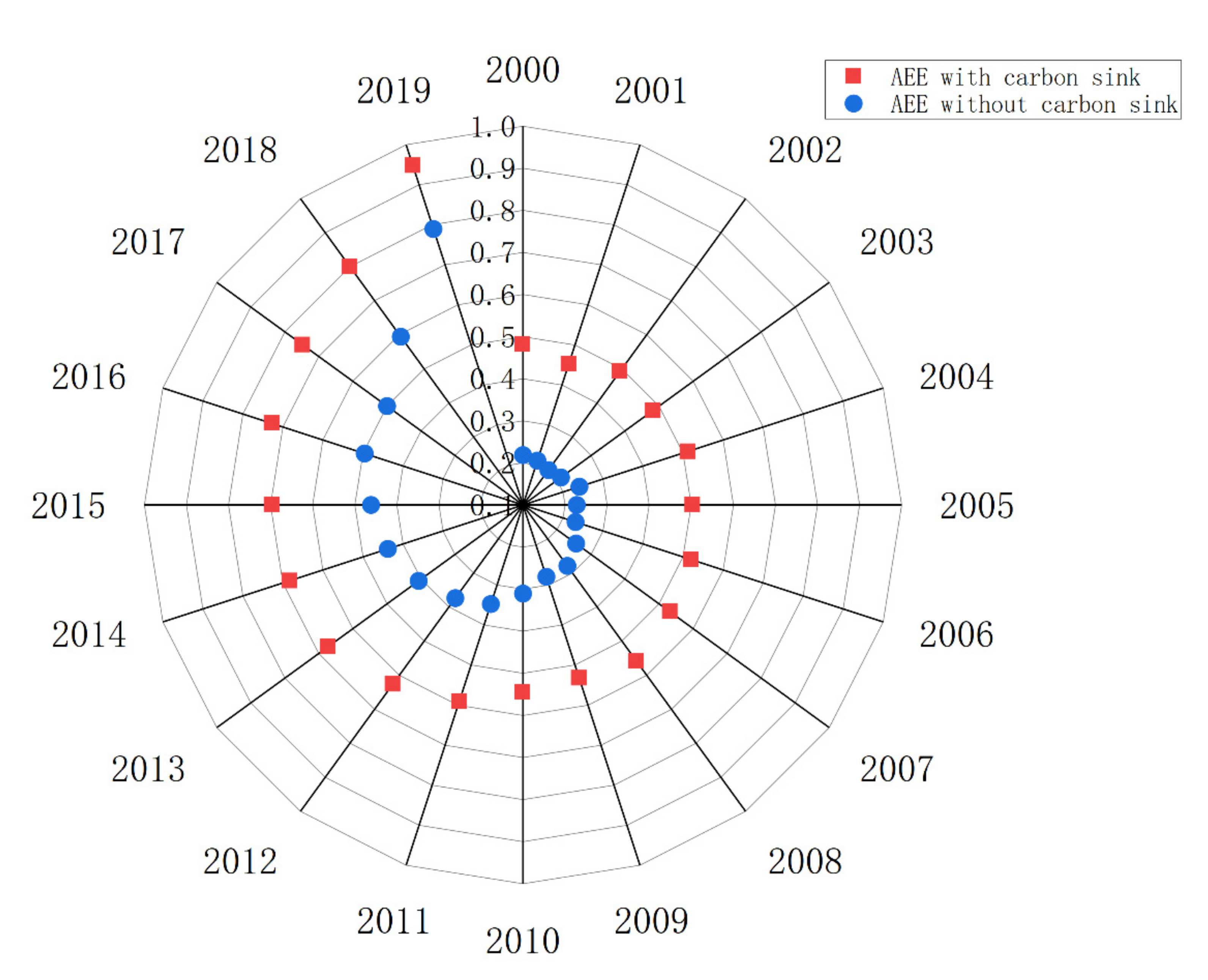
3.1. Measurement Analysis of AEE with and without Carbon Sinks
3.2. Analysis of Time Series Evolution Characteristics of AEE in China
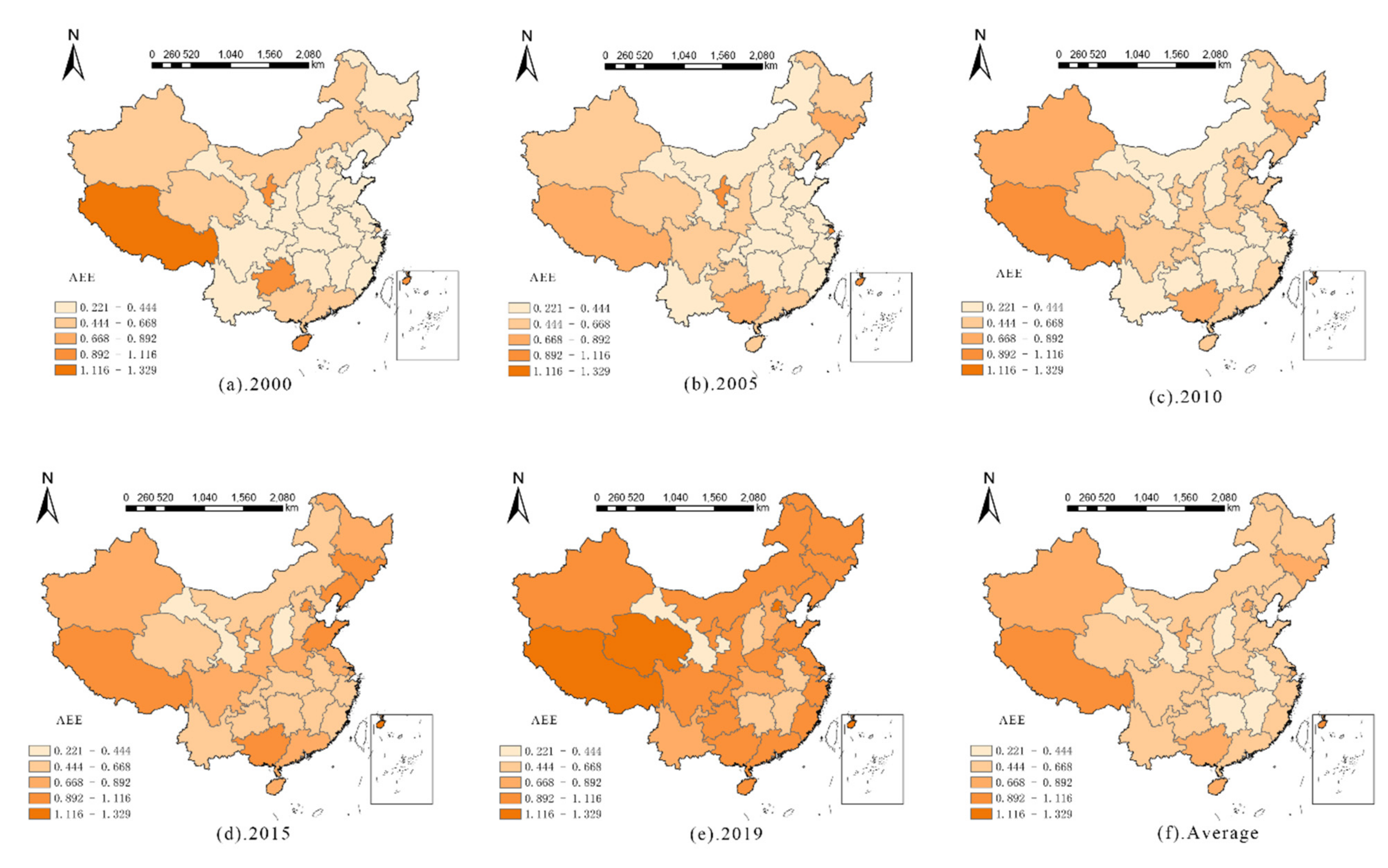
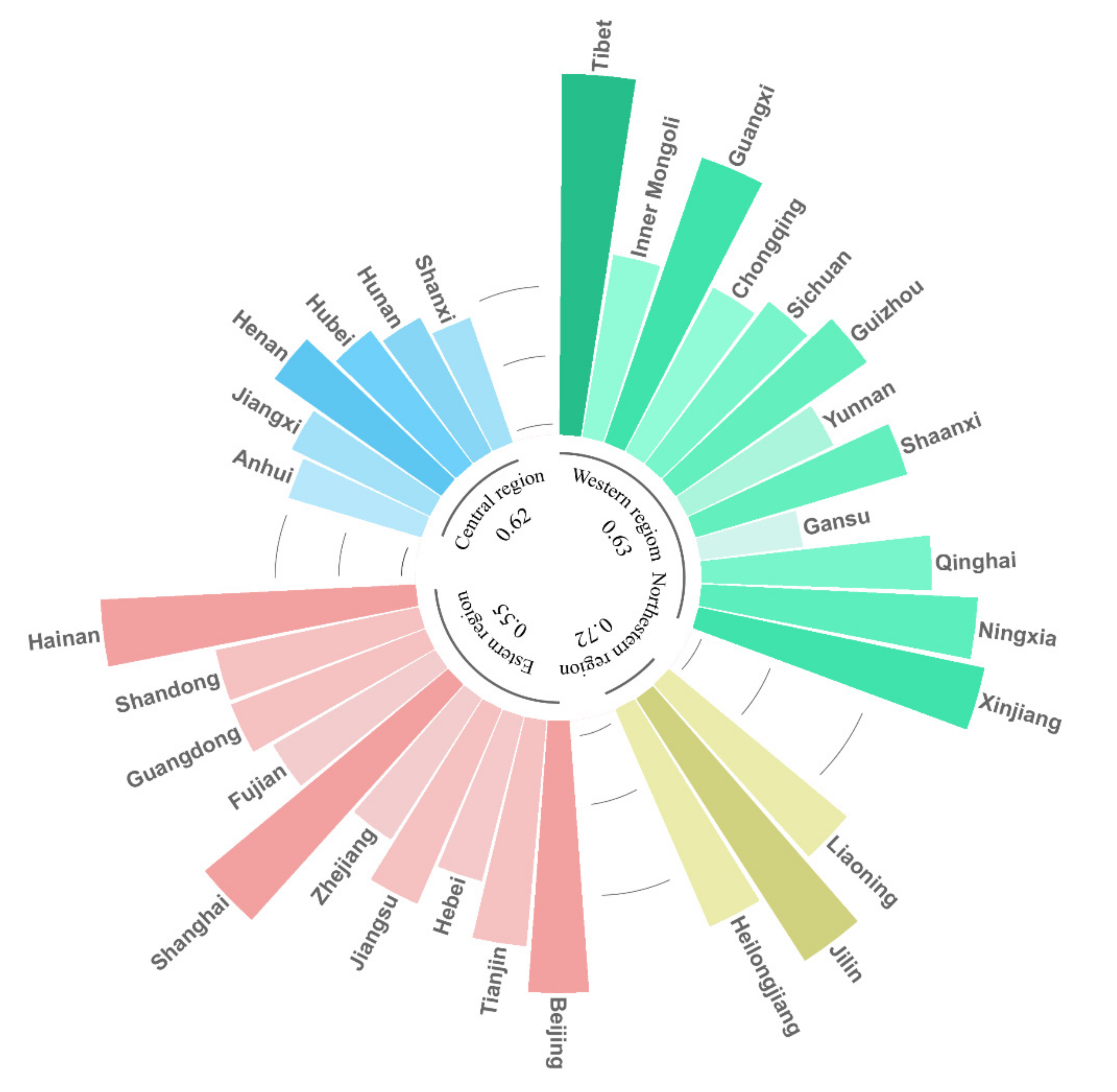
3.3. Spatial Differentiation Characteristics of AEE in China
3.4. Drivers of Spatial Differentiation of AEE in China
3.4.1. Identification of Driving Factors for the Spatial Differentiation of AEE in China
3.4.2. Interaction Identification of the Spatial Differentiation of AEE
4. Discussion
4.1. AEE Considering Carbon Sinks
4.2. Drivers of Spatial Differentiation of AEE
4.3. Measurement Method
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Foley, J.A.; Ramankutty, N.; Brauman, K.A.; Cassidy, E.S.; Gerber, J.S.; Johnston, M.; Mueller, N.D.; O’Connell, C.; Ray, D.K.; West, P.C.; et al. Solutions for a Cultivated Planet. Nature 2011, 478, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matson, P.A.; Parton, W.J.; Power, A.G.; Swift, M.J. Agricultural Intensification and Ecosystem Properties. Science 1997, 277, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cui, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, C.; Ma, W.; Huang, C.; Zhang, W.; Mi, G.; Miao, Y.; Li, X.; et al. Pursuing Sustainable Productivity with Millions of Smallholder Farmers. Nature 2018, 555, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pretty, J.; Benton, T.G.; Bharucha, Z.P.; Dicks, L.V.; Flora, C.B.; Godfray, H.C.J.; Goulson, D.; Hartley, S.; Lampkin, N.; Morris, C.; et al. Global Assessment of Agricultural System Redesign for Sustainable Intensification. Nat. Sustain. 2018, 1, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.; Snapp, S.; Chikowo, R.; Thorne, P.; Bekunda, M.; Glover, J. Measuring Sustainable Intensification in Smallholder Agroecosystems: A Review. Glob. Food Secur. Agric. Policy 2017, 12, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Camarero, M.; Castillo, J.; Picazo-Tadeo, A.J.; Tamarit, C. Eco-Efficiency and Convergence in OECD Countries. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2013, 55, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Desimone, L.D.; Popoff, F. Eco-Efficiency: The Business Link to Sustainable Development; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2000; Volume 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S. Evaluation on Eco-Efficiency from Human Development In The Central China. Econ. Geogr. 2011, 31, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Wang, M.; Ma, X.; Li, P. Study on the Spatial and Temporal Characteristics and Spillover Effects of Eco-Efficiency in China’s Animal Husbandry. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 1–16.
- Wu, X.-Q.; Xu, Y.-C.; Lu, G.-F. The evaluation of agricultural eco-efficiency: A case of rice pot-experiment. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2009, 29, 2481–2488. [Google Scholar]
- Shui, W.; Chen, Y.; SU, Z.; Fan, S. Emergy-based agricultural ecosystem analysis for specialized tea planting: A case study of Anxi County, Fujian Province. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2016, 24, 1703–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, F.; Yang, X.; Guo, A. Study on Ecological Economy Efficiency of Oasis Agriculture in Arid Region Based on LCA and DEA Method: Taking Seed Maize Production in Zhangye City as an Example. Ecol. Econ. 2017, 33, 122–127. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Shi, Y. Spatial Differentiation and Promotion Potential of Agricultural Eco-efficiency in China. J. Guangdong Univ. Financ. Econ. 2020, 35, 51–64. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, W. Cross-provincial Differences in Determinants of Agricultural Eco-efficiency in China: An Analysis Based on Panel Data from 31 Provinces in 1996–2015. Chin. Rural Econ. 2018, 46–62. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, D.; Ying, R. Agricultural eco-efficiency evaluation in China based on SBM model. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2013, 33, 3837–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Wang, B.; Ding, H.; Jia, S. Spatial-temporal evolution and impact effect of agricultural ecological efficiency in the Yellow River Basin. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2022, 61, 54–60+101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Liu, Y. Measurement and Influencing Factors of Agricultural Eco-efficiency in EthnicMinority Areas. J. South-Cent. Univ. Natl. Humanit. Soc. Sci. 2021, 41, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Han, L. Study on the Evaluation and Promotion Path of Agricultural Ecological Efficiency: An Empirical Analysis of 17 Prefecture Level Cities in Shandong Province. Ecol. Econ. 2021, 37, 118–124+131. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, X.; Shang, J. A Study on China’s Agricultural Ecological Efficiency Based on The Third Stage Sbm Model. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2021, 42, 210–217. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.; Yu, S.; Ma, Z.; Zhao, R.; Xin, J. Spatial and Temporal Variance Analysis of Agricultural Eco-efficiency in Jiangsu Province Based on DEA-Malmquist Model. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 38, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Ren, J.; Wang, R. Spatial-temporal distribution of agricultural eco-efficiency in China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2014, 34, 142–148. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Wang, Y.; He, L.; Lu, G. Agricultural Eco-Efficiency Evaluation Based on Ahp and Dea Model—A Case of Wuxi City. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2012, 21, 714–719. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, P.; Zhou, Y. The Spatio-Temporal Evolution and Improvement Path of Agricultural Eco-Efficiency in the Yellow River Basin Study. Ecol. Econ. 2021, 37, 98–105. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Liao, X.; Li, C.; Yang, C.; Yang, S.; Li, Y. Spatio-temporal Characteristics of Agricultural Eco-efficiency and Its Determinants in Hunan Province. Econ. Geogr. 2022, 42, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Qin, G. The Impact of Public Environmental Expenditure on Agricultural Eco-efficiency: Empirical Evidence from the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Econ. Probl. 2022, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M. Research on the Spatiotemporal Pattern and Influencing Factors of Net Carbon Sink in Agricultural Production in China’s Main Grain Producing Areas. Ph.D. Thesis, Harbin University of Commerce, Harbin, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, P.C.C. China’s Hidden Agricultural Revolution, 1980-2010, in Historical and Comparative Perspective. Mod. China 2016, 42, 339–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Qiu, J.; Hong, Q.; Chen, L. Simulation of Spatial and Temporal Distributions of Non-Point Source Pollution Load in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 493, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, W.; Yu, F. Review of methodology and application of agricultural eco-efficiency. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2017, 25, 1371–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frittelli, M.; Madzvamuse, A.; Sgura, I.; Venkataraman, C. Numerical Preservation of Velocity Induced Invariant Regions for Reaction-Diffusion Systems on Evolving Surfaces. J. Sci. Comput. 2018, 77, 971–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frittelli, M.; Madzvamuse, A.; Sgura, I. Bulk-Surface Virtual Element Method for Systems of PDEs in Two-Space Dimensions. Numer. Math. 2021, 147, 305–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacitignola, D.; Frittelli, M.; Cusimano, V.; De Gaetano, A. Pattern Formation on a Growing Oblate Spheroid. An Application to Adult Sea Urchin Development. J. Comput. Dyn. 2021, 9, 185–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zou, L.; Wang, Y. Spatial-Temporal Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Agricultural Eco-Efficiency in China in Recent 40 Years. Land Use Policy 2020, 97, 104794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.; Li, Z.; Deng, X.; Yang, J.; Chen, D.; Li, W. An Analysis of Spatiotemporal Patterns in Chinese Agricultural Productivity between 2004 and 2014. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 105, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K. A Slacks-Based Measure of Efficiency in Data Envelopment Analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2001, 130, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tone, K. A Slacks-Based Measure of Super-Efficiency in Data Envelopment Analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2002, 143, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, R.; Niu, T. A Daily Precipitation Grid Dataset with 0.1° Resolution in Changjiang River Valley and Its Precision. J. Nat. Resour. 2008, 23, 136–149. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblatt, M. Remarks on Some Nonparametric Estimates of a Density Function. Ann. Math. Stat. 1956, 27, 832–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Liu, X. Time-Space Evolution of China’s Agricultural Green Total Factor Productivity. Chin. J. Manag. Sci. 2020, 28, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, C. Geodetector: Principle and prospective. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 116–134. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.-F.; Li, X.-H.; Christakos, G.; Liao, Y.-L.; Zhang, T.; Gu, X.; Zheng, X.-Y. Geographical Detectors-Based Health Risk Assessment and Its Application in the Neural Tube Defects Study of the Heshun Region, China. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-F.; Hu, Y. Environmental Health Risk Detection with GeogDetector. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2012, 33, 114–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.; Hu, H. Calculation of Greenhouse Gases Emission from Agricultural Production in China. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2012, 22, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, S. China’s Agricultural Carbon Emission: Structure, Efficiency and Its Determinants. Issues Agric. Econ. 2014, 35, 18–26+110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Li, J.; Zheng, X. Methane Emission and Mechanisms of Methane Production, Oxidation, Transportation in the Rice Fields. Sci. Atmos. Sin. 1998, 22, 218–230. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, L. Spatial and Temporal Differentiation of China’s Agricultural Carbon Productivity: Mechanism and Demonstration. Ph.D. Thesis, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Z.; Meng, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, N.; Zhou, Z. Modified method of energy carbon footprint and application based on regional land use change. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2012, 28, 190–195. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, J. Regional Differentiation Research on Net Carbon Effect of Agricultural Production in China. J. Nat. Resour. 2013, 28, 1298–1309. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, J.; Tian, Y.; Xue, L. Analysis on China’s Agricultural Carbon Abatement Capacity from the Perspective of Both Equity and Efficiency. J. Nat. Resour. 2015, 30, 1172–1182. [Google Scholar]
- Lü, S.; Zhang, X. Spatial-temporal Characteristics of Agricultural Net Carbon Sink in Shandong Province. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2019, 33, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Yu, C.; Feng, Z.; Zhao, H.; Wu, K.; Ma, X. Spatial Differentiation Characteristics and Driving Factors of Agricultural Eco-Efficiency in Chinese Provinces from the Perspective of Ecosystem Services. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 288, 125466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Mi, L.; Hu, J.; Qian, Z. Spatial Analysis of Agricultural Eco-Efficiency and High-Quality Development in China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 847719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, K.; Chen, C.; Feng, C.; Huang, J. The Spatial Temporal Differences of Agricultural Eco-Efficiency and Its Influential Factors. J. South China Agric. Univ. Soc. Sci. Ed. 2016, 15, 31–41. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y.; Zeng, X. Evaluation and improvement of agricultural eco-efficiency in China. J. Agric. Resour. Environ. 2021, 38, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yao, S.; Hou, M.; Jia, L.; Li, Y.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, X. Spatial-temporal differentiation and its influencing factors of agricultural eco-efficiency in China based on geographic detector. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2021, 32, 4039–4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.; Liu, J. Regional Heterogeneity in China Agricultural Eco-efficiency Evaluation and Spatial Differences: Based on Combined DEA and Sptial Autocorrelation Analysis. Ecol. Econ. 2019, 35, 107–114. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.; Shi, C.; Wang, S.; Zhang, G. Estimation of Eco-Efficiency and Its Influencing Factors in Guangdong Province Based on Super-SBM and Panel Regression Models. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 86, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhou, H. Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity of Agricultural Land Eco-Efficiency: A Case Study of 128 Cities in the Yangtze River Basin. Water 2022, 14, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Feng, X.; Wang, S.; Qiu, H. China’s Poverty Alleviation over the Last 40 Years: Successes and Challenges. Aust. J. Agr. Resour. Econ. 2020, 64, 209–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, Y. Poverty Alleviation in Rural China: Policy Changes, Future Challenges and Policy Implications. China Agric. Econ. Rev. 2018, 10, 241–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, L.L.; Jaeyeon, S. Efficiency Evaluation of Financial Support for Rural Industry Revitalization in Eastern China. Int. J. Adv. Smart Converg. 2022, 11, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Gao, W.; Lv, Y. The Triple Logic and Choice Strategy of Rural Revitalization in the 70 Years since the Founding of the People’s Republic of China, Based on the Perspective of Historical Evolution. Agriculture 2020, 10, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grovermann, C.; Wossen, T.; Muller, A.; Nichterlein, K. Eco-Efficiency and Agricultural Innovation Systems in Developing Countries: Evidence from Macro-Level Analysis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Sarwar, S.; Jin, T. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Improvement Potential of Agricultural Eco-Efficiency in Jiangsu Province. Front. Energy Res. 2021, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Hao, S.; Sun, C. Evaluation of Agricultural Ecological Efficiency and Its Spatial-temporal Differentiation Based on DEA-ESDA. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2018, 38, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Shi, H.; Pan, X.; Liu, F.; Cui, Y.; Xie, H. Integrating Ecological Restoration of Agricultural Non-Point Source Pollution in Poyang Lake Basin in China. Water 2017, 9, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, S.; Hu, Z.; Ma, H.; Xu, D.; He, R. Spatial and Temporal Variations in the Ecological Efficiency and Ecosystem Service Value of Agricultural Land in China. Agriculture 2022, 12, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Jiang, L. Efficiency Performance of Fertilizer Use in Arable Agricultural Production in China. China Agric. Econ. Rev. 2019, 11, 52–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Main Variable | Type | Specific Indicators | Variable Description | Data Sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labor consumption | Labor input | Number of people in the primary industry/104 | stats.gov.cn | |
| Unput indicator | Material consumption | Land input | Crop sown area/103 hm2 | stats.gov.cn |
| Water input | Effective irrigation area/103 hm2 | stats.gov.cn | ||
| Agricultural machinery input | Agricultural mechanization/104 kw | China Rural Statistical Yearbook | ||
| Environmental cost | Fertilizer input | Fertilizer application rate/104 t | stats.gov.cn | |
| Pesticide input | Pesticide usage/104 t | stats.gov.cn | ||
| Agricultural film input | Amount of plastic film used/104 t | stats.gov.cn | ||
| Output indicator | Expected output | Agricultural output value | Agricultural output value/108 ¥ | stats.gov.cn |
| Carbon sink | Agricultural production carbon sink/104 t | by Han et al. [46,47,48,49] | ||
| Undesired output | Carbon emission | Total agricultural carbon emissions/104 t | by Min et al. [42,43,44,45] |
| Type of Representation | Driving Factors | Code | Data Sources | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Driver | Variable Description and Calculation | |||
| Natural Resources | Per capita arable land | Area of arable land/resident population at the end of the year | X1 | resset.com |
| Agricultural disaster rate | Affected area/total sown area | X2 | stats.gov.cn | |
| precipitation | Average annual precipitation | X3 | data.cma.cn | |
| Agricultural Development | Agricultural economic level | Gross Agricultural Output/Number of Permanent Residents | X4 | stats.gov.cn |
| Industrial structure | Gross agricultural output value/gross output value of agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry and fishery | X5 | stats.gov.cn | |
| Degree of agricultural mechanization | Total power of agricultural machinery/total sown area of crops | X6 | stats.gov.cn | |
| Social Environment | Urbanization level | Urban Population/Total Population | X7 | stats.gov.cn |
| Level of industrialization | Industrial value added/Gross regional product | X8 | stats.gov.cn | |
| urban–rural gap | Per capita disposable income of urban residents/per capita disposable income of rural residents | X9 | stats.gov.cn | |
| Years of education per capita in rural areas | (Number of primary school students * 6 + Number of junior high school students * 9 + Number of people above high school * 16) Total number of people | X10 | stats.gov.cn, China Rural Statistical Yearbook | |
| Policy Support | The level of financial support for agriculture | Fiscal expenditure on agriculture, forestry, and water/financial general public budget expenditure | X11 | China Statistical Yearbook, Finance Yearbook Of China |
| Province | Without Carbon Sink | Rank | With Carbon Sink AEE | Rank | Province | Without Carbon Sink | Rank | With Carbon Sink | Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liaoning | 0.3228 | 16 | 0.6414 | 11 | Guangdong | 0.4357 | 6 | 0.5771 | 16 |
| Jilin | 0.2151 | 26 | 0.8682 | 4 | Guangxi | 0.3007 | 17 | 0.8351 | 5 |
| Heilongjiang | 0.2699 | 19 | 0.6574 | 9 | Hainan | 0.6291 | 2 | 0.8770 | 3 |
| Beijing | 0.5705 | 5 | 0.7553 | 8 | Chongqing | 0.2722 | 18 | 0.5149 | 21 |
| Tianjin | 0.4354 | 7 | 0.6285 | 13 | Sichuan | 0.3625 | 12 | 0.5657 | 18 |
| Hebei | 0.2475 | 23 | 0.4697 | 23 | Guizhou | 0.3400 | 13 | 0.6467 | 10 |
| Shanxi | 0.1580 | 30 | 0.3647 | 30 | Yunnan | 0.1971 | 28 | 0.4488 | 26 |
| Inner Mongolia | 0.2214 | 25 | 0.5113 | 22 | Shaanxi | 0.3962 | 11 | 0.6121 | 14 |
| Shanghai | 0.6177 | 3 | 0.8785 | 2 | Gansu | 0.1300 | 31 | 0.2853 | 31 |
| Jiangsu | 0.3962 | 10 | 0.5879 | 15 | Qinghai | 0.5978 | 4 | 0.6393 | 12 |
| Zhejiang | 0.3346 | 15 | 0.4642 | 24 | Ningxia | 0.3365 | 14 | 0.7683 | 7 |
| Anhui | 0.1692 | 29 | 0.3837 | 29 | Xinjiang | 0.2670 | 20 | 0.8120 | 6 |
| Fujian | 0.4333 | 8 | 0.5204 | 20 | Tibet | 0.9245 | 1 | 1.0025 | 1 |
| Jiangxi | 0.2082 | 27 | 0.4240 | 27 | Northeast region | 0.2693 | 4 | 0.7223 | 1 |
| Shandong | 0.4077 | 9 | 0.5751 | 17 | East region | 0.3500 | 3 | 0.5469 | 4 |
| Henan | 0.2633 | 22 | 0.5652 | 19 | Central region | 0.3556 | 2 | 0.6230 | 3 |
| Hubei | 0.2648 | 21 | 0.4638 | 25 | Western region | 0.3824 | 1 | 0.6296 | 2 |
| Hunan | 0.2397 | 24 | 0.4200 | 28 | Average in China | 0.3537 | 0.6053 |
| Factor | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2019 | Total | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| q | Rank | q | Rank | q | Rank | q | Rank | q | Rank | q | Rank | |
| Per capita arable land | 0.24 | 9 | 0.24 | 7 | 0.32 | 4 | 0.15 | 11 | 0.38 | 2 | 0.16 | 11 |
| Agricultural disaster rate | 0.32 | 5 | 0.48 | 1 | 0.39 | 1 | 0.35 | 2 | 0.43 | 1 | 0.22 | 8 |
| Precipitation | 0.35 | 4 | 0.37 | 3 | 0.16 | 10 | 0.31 | 5 | 0.27 | 7 | 0.16 | 10 |
| Agricultural economic level | 0.17 | 10 | 0.19 | 9 | 0.25 | 6 | 0.43 | 1 | 0.23 | 8 | 0.35 | 4 |
| Industrial structure | 0.27 | 7 | 0.18 | 10 | 0.38 | 2 | 0.18 | 10 | 0.34 | 4 | 0.27 | 7 |
| Degree of agricultural mechanization | 0.17 | 11 | 0.25 | 6 | 0.14 | 11 | 0.23 | 9 | 0.30 | 6 | 0.21 | 9 |
| Urbanization level | 0.31 | 6 | 0.28 | 5 | 0.23 | 7 | 0.35 | 3 | 0.33 | 5 | 0.32 | 6 |
| Level of industrialization | 0.75 | 1 | 0.40 | 2 | 0.22 | 8 | 0.28 | 6 | 0.35 | 3 | 0.51 | 1 |
| urban–rural gap | 0.36 | 3 | 0.18 | 11 | 0.19 | 9 | 0.33 | 4 | 0.22 | 9 | 0.40 | 3 |
| Years of education per capita in rural areas | 0.39 | 2 | 0.24 | 8 | 0.33 | 3 | 0.25 | 7 | 0.19 | 11 | 0.34 | 5 |
| The level of financial support for agriculture | 0.26 | 8 | 0.32 | 4 | 0.30 | 5 | 0.25 | 8 | 0.21 | 10 | 0.44 | 2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Zhu, Z.; Dai, Z.; Duan, J.; Wang, D.; Feng, Y. Temporal and Spatial Differentiation and Driving Factors of China’s Agricultural Eco-Efficiency Considering Agricultural Carbon Sinks. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1726. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12101726
Li S, Zhu Z, Dai Z, Duan J, Wang D, Feng Y. Temporal and Spatial Differentiation and Driving Factors of China’s Agricultural Eco-Efficiency Considering Agricultural Carbon Sinks. Agriculture. 2022; 12(10):1726. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12101726
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shilin, Zhiyuan Zhu, Zhenzhong Dai, Jiajia Duan, Danmeng Wang, and Yongzhong Feng. 2022. "Temporal and Spatial Differentiation and Driving Factors of China’s Agricultural Eco-Efficiency Considering Agricultural Carbon Sinks" Agriculture 12, no. 10: 1726. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12101726
APA StyleLi, S., Zhu, Z., Dai, Z., Duan, J., Wang, D., & Feng, Y. (2022). Temporal and Spatial Differentiation and Driving Factors of China’s Agricultural Eco-Efficiency Considering Agricultural Carbon Sinks. Agriculture, 12(10), 1726. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12101726







