N Addition Mitigates Water Stress via Different Photosynthesis and Water Traits for Three Native Plant Species in the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Experimental Design
2.2. Measured Indicators and Measurement Methods
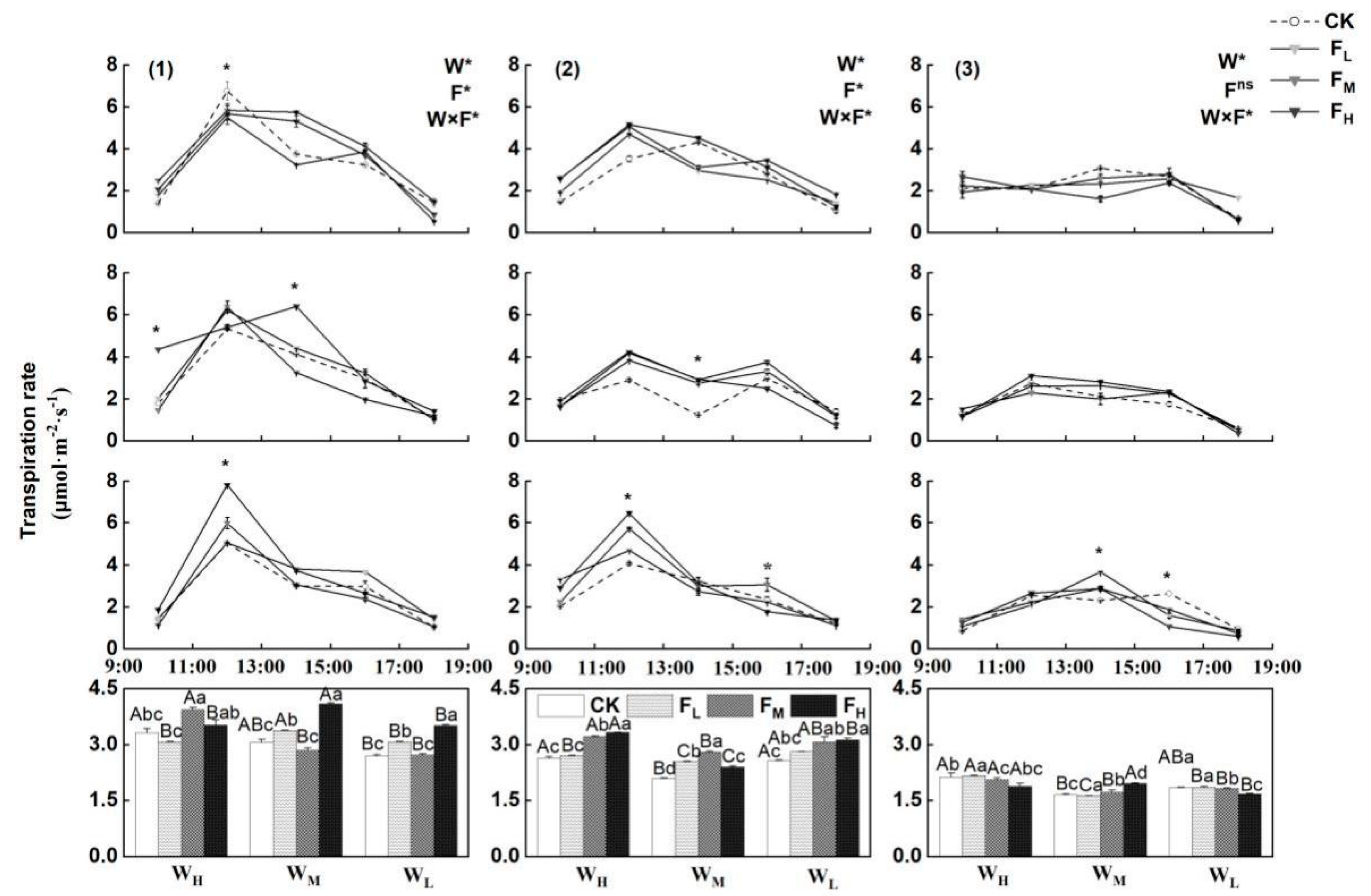
2.2.1. Photosynthetic Characteristics and Water−Use Efficiency (WUE) of Plants
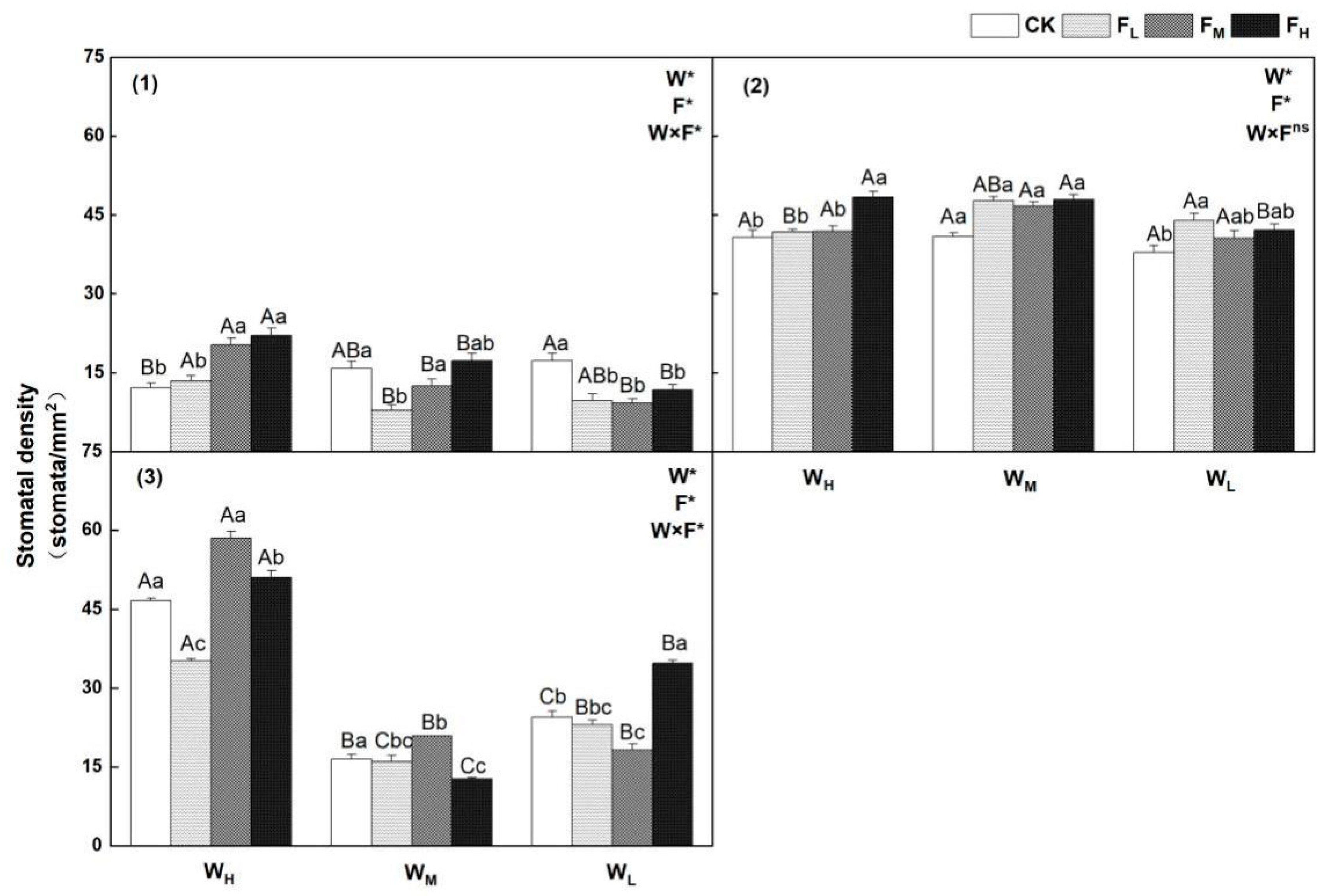
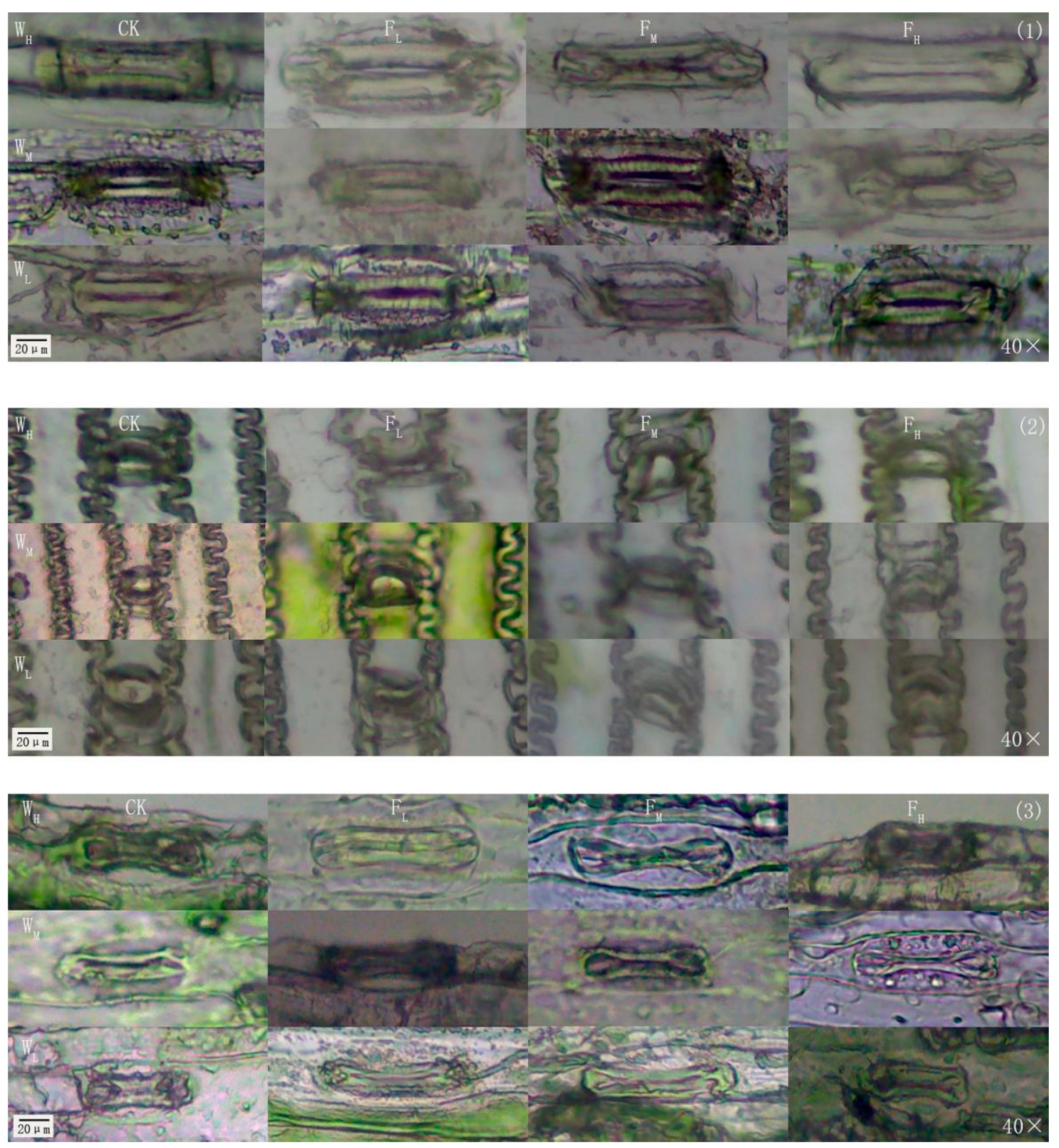
2.2.2. Leaf Blade Stomatal Density and Size Measurements
2.2.3. Plant Traits
2.2.4. Water-Use Efficiency of Plants
2.2.5. Plant Biomass
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
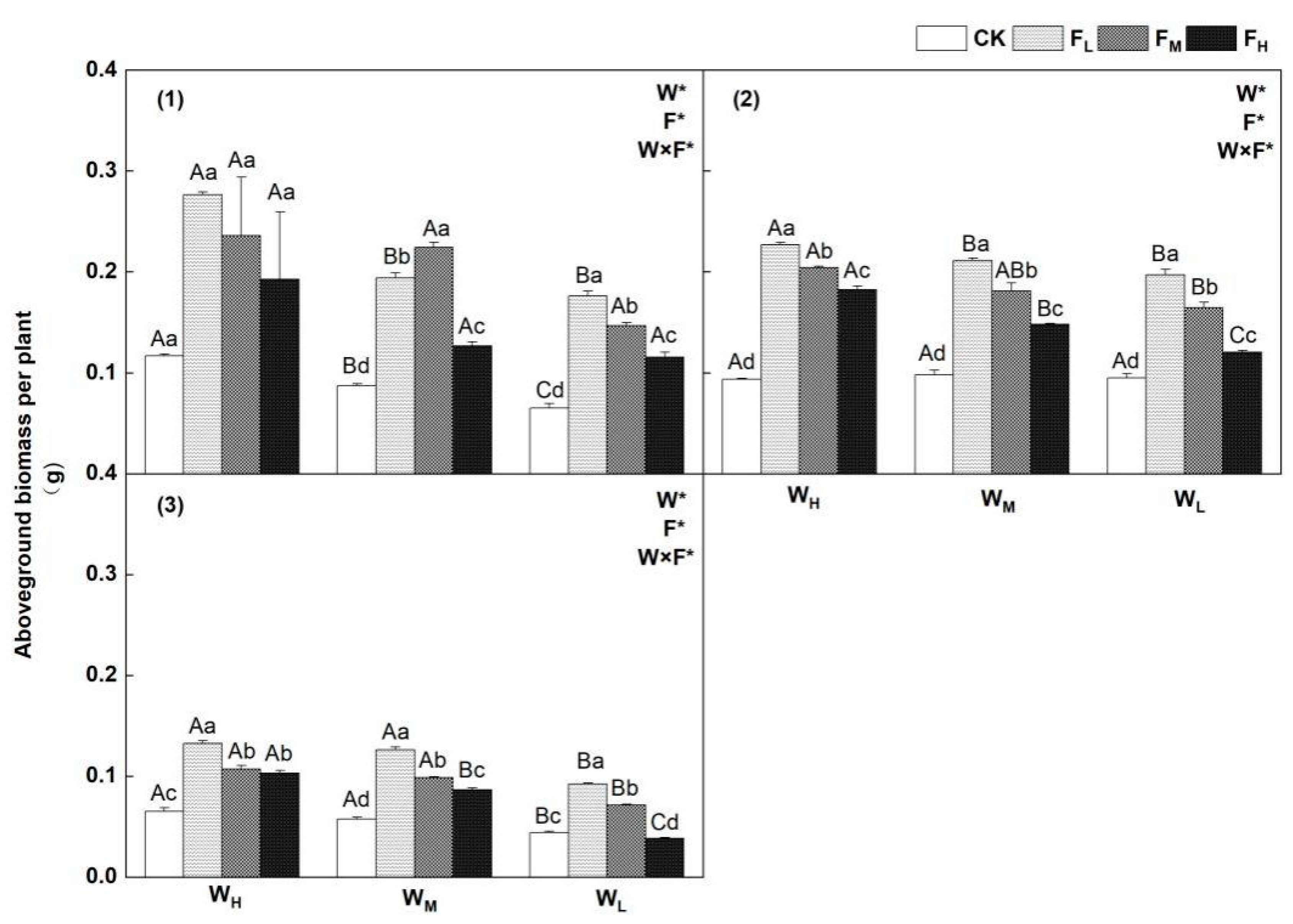
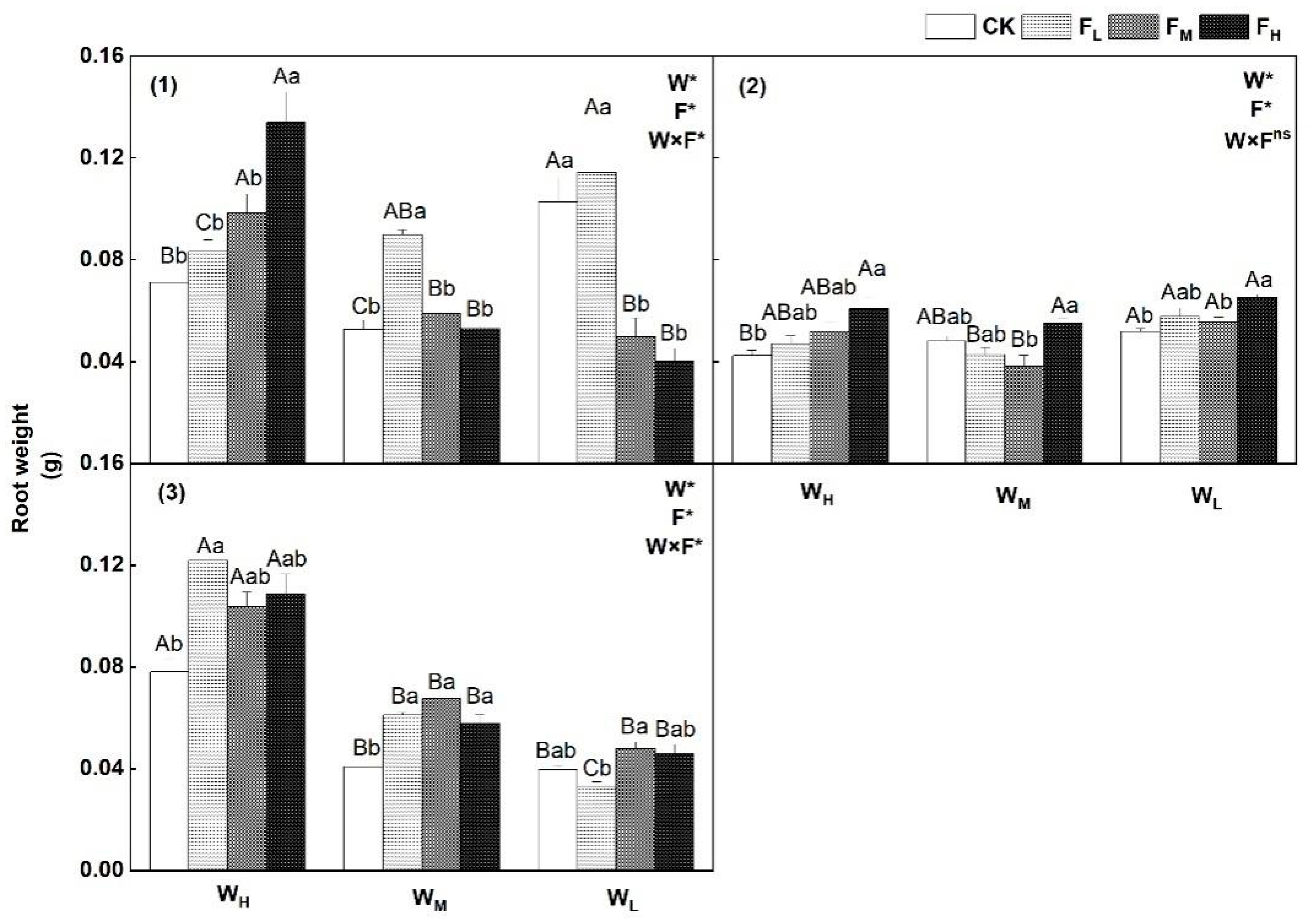
4.1. Effects of Different Water−Fertilizer Treatments on the Biomass
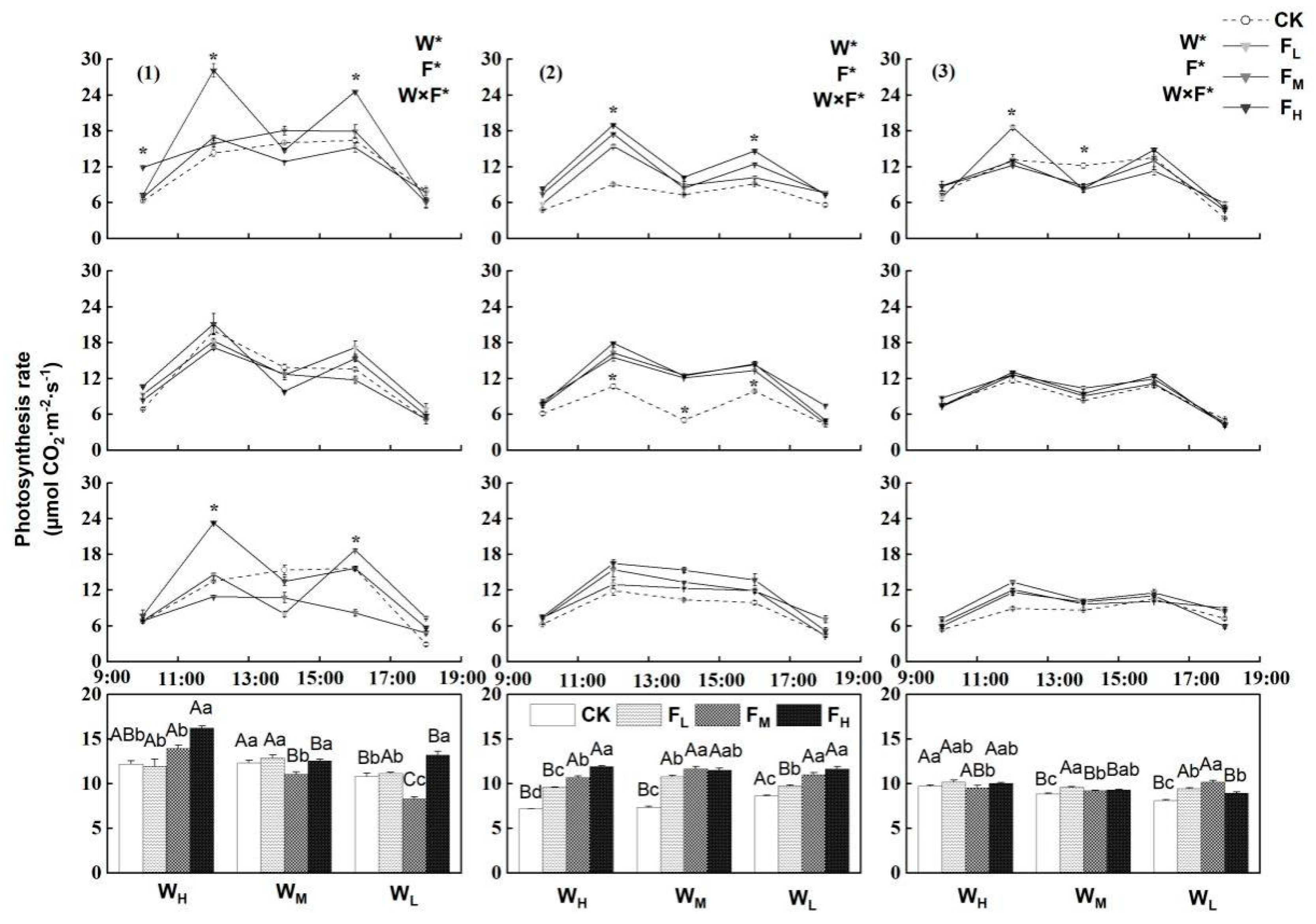
4.2. Effects of Different Water−Fertilizer Treatments on the Pn, Leaf Number and Leaf Thickness
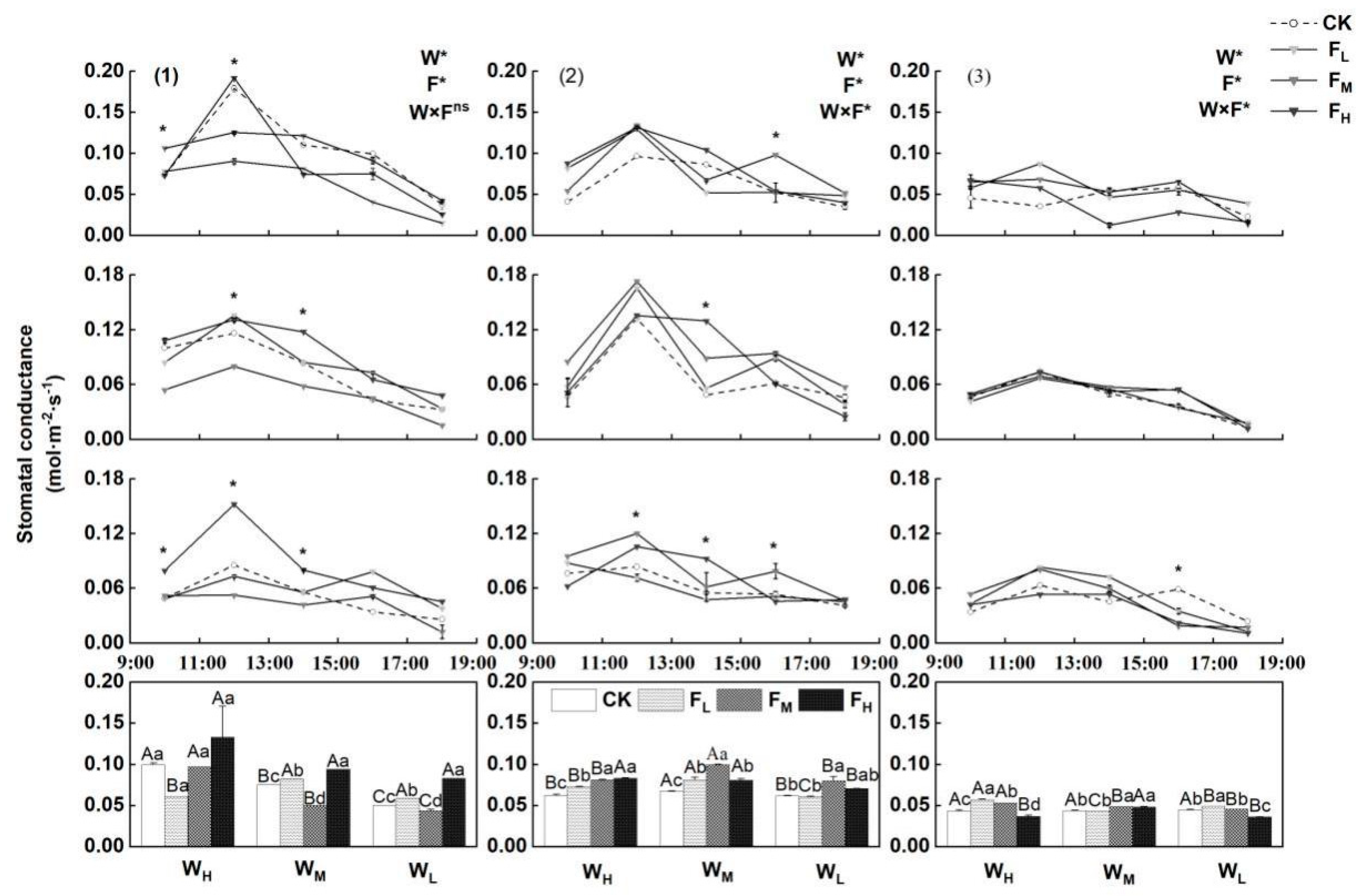
4.3. Effects of Different Water−Fertilizer Treatments on the Gs, Stomatal Frequency, and Stomatal Size
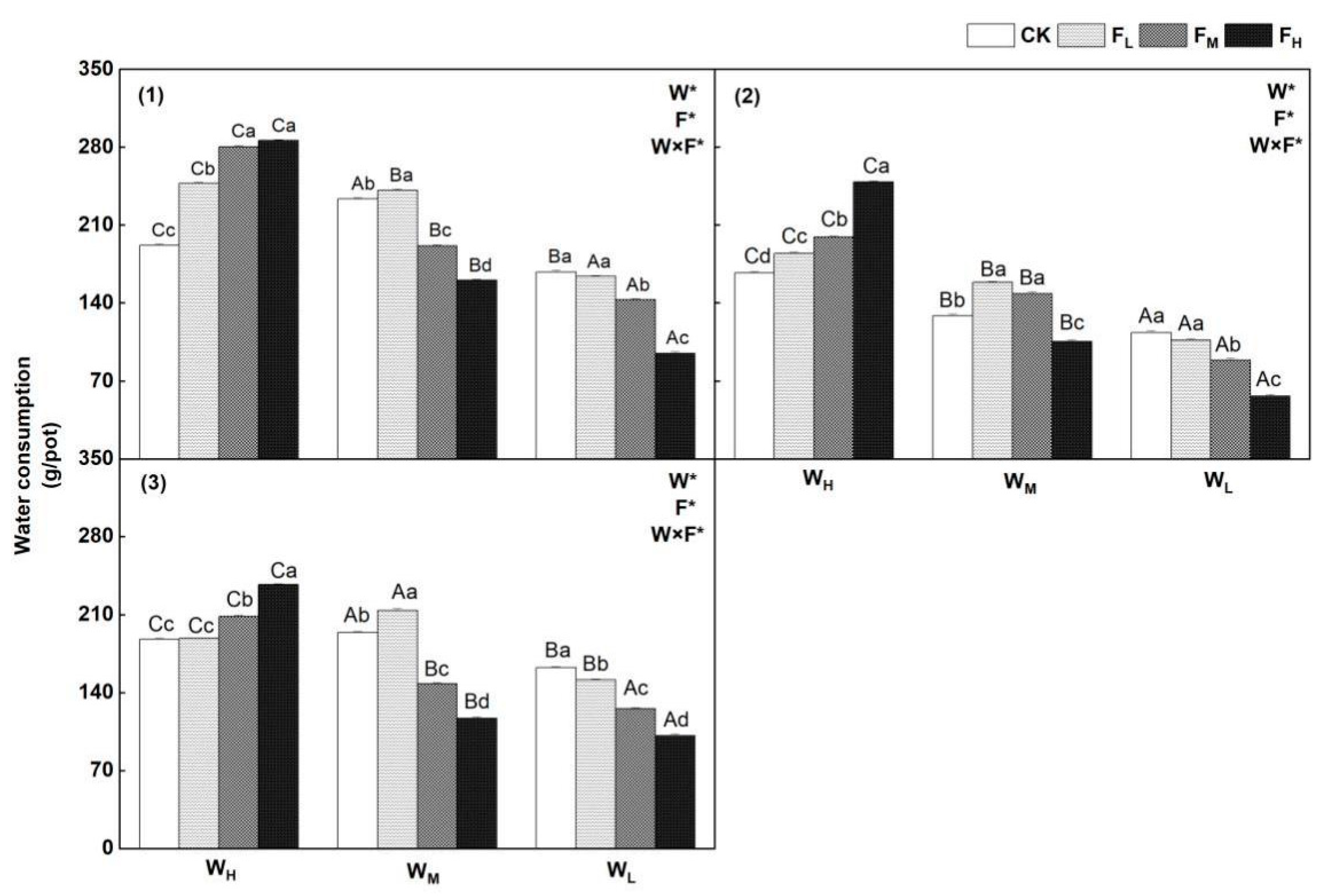
4.4. Effects of Different Water−Fertilizer Treatments on the Tr, Water Consumption and WUE
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, W.; Lu, H.; Yao, T. Drought characteristics and its elevation dependence in the Qinghai–Tibet plateau during the last half-century. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Dong, S.; Li, Y.; Li, X.Y.; Shi, J.J.; Wang, Y.L.; Liu, D.M.; Ma, Y.S. Effect of degradation intensity on grassland ecosystem services in the alpine region of Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Xue, X.; Peng, F.; You, J.; Hao, H. Meta-analysis of the effects of grassland degradation on plant and soil properties in the alpine meadows of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2019, 20, e00774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, N.; Zhu, J.; He, Y.; Zhao, T.; Yu, G. Drought limits alpine meadow productivity in northern Tibet. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2021, 303, 108371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Shang, Z.; Gao, J.; Boone, R.B. Enhancing sustainability of grassland ecosystems through ecological restoration and grazing management in an era of climate change on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 287, 106684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Lü, Y.; Fu, B. Quantifying the impacts of grassland restoration on biodiversity and ecosystem services in China: A meta-analysis. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 95, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.K.; Li, J.P.; Li, X.Y.; Wen, L.; Zhu, L.; Li, Y.Y.; Ma, Y.S.; Shi, J.J.; Dong, Q.M.; Wang, Y.L. Application of design theory for restoring the “black beach” degraded rangeland at the headwater areas of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2010, 5, 3542–3552. [Google Scholar]
- Djebbar, R.; Rzigui, T.; Pétriacq, P.; Caroline, M.; Pierrick, P.; Chantal, F.; Marianne, D.P.; Igor, F.S.; Ghouziel, B.K.; Peter, S.; et al. Respiratory complex I deficiency induces drought tolerance by impacting leaf stomatal and hydraulic conductances. Planta 2012, 235, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, R.; Ansari, W.A.; Jaiswal, D.K.; Singh, A.K.; Prasad, R.; Verma, J.P.; Singh, M. Overexpression of AtDREB1 and BcZAT12 genes confers drought tolerance by reducing oxidative stress in double transgenic tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Plant Cell Rep. 2021, 40, 2173–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, R.; Ansari, W.A.; Jaiswal, D.K.; Singh, A.K.; Verma, J.P.; Singh, M. Co-overexpression of AtDREB1A and BcZAT12 increases drought tolerance and fruit production in double transgenic tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) plants. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2021, 184, 104396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, P.; Wunnava, A.; Verma, P.; Chandra, A.; Sharma, R.K. Strategies to mitigate the adverse effect of drought stress on crop plants—Influences of soil bacteria: A review. Pedosphere 2021, 31, 496–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, E.; Suzaki, E.; Irie, M.; Nagashima, M.; Hirose, T. Architecture and growth of an annual plant Chenopodium album in different light climates. Ecol. Res. 2010, 25, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perakis, S.S.; Sinkhorn, E.R.; Catricala, C.E.; Bullen, T.D.; Fizpatrick, J.A. Forest calcium depletion and biotic retention along a soil nitrogen gradient. Ecol. Appl. 2013, 23, 1947–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, I.S.; Dresbøll, D.B.; Thorup-Kristensen, K. Winter wheat cultivars and nitrogen (N) fertilization—Effects on root growth, N uptake efficiency and N use efficiency. Eur. J. Agron. 2015, 68, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, C. Effects of starter nitrogen fertilizer on soybean root activity, leaf photosynthesis and grain yield. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Zamanian, K.; Schleuss, P.-M.; Mohsen, Z.; Yakov, K. Degradation of Tibetan grasslands: Consequences for carbon and nutrient cycles. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 252, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.F.; Li, S.Q.; Shao, M.A. Effects of spatial coupling of water and fertilizer applications on root growth characteristics and water use of winter wheat. J. Plant Nutr. 2013, 36, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Yuan, Y.; Guo, X.; Du, Y.; Xun, K.; Zhang, F.; Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Lin, L.; Zhou, H.K.; et al. Soil water retention in alpine meadows under different degradation stages on the northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Hydrol. 2020, 590, 125397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.H.; Liu, X.L.; Han, B.; Wei, X.T.; Cai, R.C.; Shao, X. Effects of reseeding with native species on community stability of alpine meadow on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Grassl. J. 2021, 29, 1793–1800. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Y.L.; Li, S.X.; Ma, Y.S. Effects of artificial reseeding on soil fungal community characteristics in degraded alpine meadow. Grassl. J. 2020, 28, 1791–1797. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.S.; Ga, M.J.; Zhang, Y. Research progress on formation mechanism and management methods of degraded alpine meadow steppe in “black soil flat” on Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Grassl. Lawns 2007, 2, 72–77. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.H.; Yang, F.Y.; Sun, L. Effect of reseeding and fertilization on alpine degraded grassland in northern Tibet. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2010, 38, 18155–18156. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Pornaro, C.; DalMaso, M.; Macolino, S. Drought resistance and recovery of kentucky bluegrass (Poa Pratensis, L.) cultivars under different nitrogen fertilisation rates. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Guo, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Qin, L.G.; Shi, Z.J.; Dong, L.L.; Xiong, L.B.; Eun, L.Y.; Deng, W.J.; Wu, H.F.; et al. Differential Metabolomic Responses of Kentucky Bluegrass Cultivars to Low Nitrogen Stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 808772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Ni, R.; Yang, S.; Pu, P.; Qian, M.; Yang, Y. Functional Characterization of the Stipa purpurea P5CS gene under drought stress conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dam, R.F.; Mehdi, B.B.; Burgess, M.S.E.; Madramootooa, C.A.; Mehuys, G.R.; Calluma, I.R. Soil bulk density and crop yield under eleven consecutive years of corn with different tillage and residue practices in a sandy loam soil in central Canada. Soil Tillage Res. 2005, 84, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, L.; Fu, B.; Huang, Z.; Gong, J. The wheat yields and water-use efficiency in the Loess Plateau: Straw mulch and irrigation effects. Agric. Water Manag. 2005, 72, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.J.; Chen, L.H.; Zhang, J.; Hu, X.W.; Xu, R. Effects of drought stress and fertilization on biomass and C, N, P accumulation and allocation of Macrophyte. J. Northwest A F Univ. 2016, 44, 105–112. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Méndez, M.; Karlsson, P.S. Equivalence of three allocation currencies as estimates of reproductive allocation and somatic cost of reproduction in Pinguicula vulgaris. Plant Biol. 2007, 9, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.; Hussain, M.; Wahid, A.; Siddique, K.H.M. Drought stress in plants: An overview. Plant Responses Drought Stress 2012, 1, 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Guretzky, J.; Kering, M.; Mosali, J.; Funderburg, E.; Biermacher, J. Fertilizer rate effects on forage yield stability and nutrient uptake of midland bermudagrass. J. Plant Nutr. 2010, 33, 1819–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.Z.; Lu, Y.J.; Yang, W.Q. Effects of density on nutrient storage, accumulation and distribution of Arro phyllostachys spp. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2005, 25, 1663–1669. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Terzi, R.; Kadioglu, A. Drought stress tolerance and the antioxidant enzyme system. Acta Biol. Crac. Ser. Bot. 2006, 48, 89–96. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yi, X.; Zhang, X.; Fan, D.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, W. Diaheliotropic leaf movement enhances leaf photosynthetic capacity and photosynthetic light and nitrogen use efficiency via optimising nitrogen partitioning among photosynthetic components in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Plant Biol. 2018, 20, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafeez, S.; Jin, T.; Zhou, Y. Factors affecting yield and yield components of main and ratoon rice: A review. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2017, 18, 1228. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, E.L.; Cubas, L.A.; Gray, J.E.; Hepworth, C. The influence of stomatal morphology and distribution on photosynthetic gas exchange. Plant J. 2020, 101, 768–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavente-Valdés, J.R.; Aguilar, C.; Contreras-Esquivel, J.C.; Méndez-Zavala, A.; Montañez, J. Strategies to enhance the production of photosynthetic pigments and lipids in chlorophycae species. Biotechnol. Rep. 2016, 10, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Chai, Q.; Yin, W.; Hu, F.; Qin, A.; Fan, Z.; Yu, A.; Zhao, C.; Fan, H. Yield photosynthesis and leaf anatomy of maize in inter-and mono-cropping systems at varying plant densities. Crop J. 2022, 10, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, M.; Meng, Z.; Liu, K.; Sui, N. Nitrogen increases drought tolerance in maize seedlings. Funct. Plant Biol. 2019, 46, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; He, X.; Li, F.; Deng, H.; Wang, Z.; Huang, C.; Han, Y.; Ba, Y.; Lei, L.; Zhang, C. Effects of water and nitrogen coupling on the photosynthetic characteristics, yield, and quality of Isatis indigotica. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Li, S.; Wang, D.; Huang, Z.; Sarwar, N.; Mubeen, K.; Shakeel, M.; Hussain, M. Effects of water and fertilizer coupling on the physiological characteristics and growth of rabbiteye blueberry. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0254013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suiqi, Z.; Lun, S. Research progress on water use efficiency of plant. Agric. Res. Arid Areas 2002, 20, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.J.; Jia, Z.K.; Li, L.; Ding, R.; Wang, M. Effects of organic fertilizer application rate on leaf photosynthetic characteristics and grain yield of dryland maize. Yingyong Shengtai Xuebao 2012, 23, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Liu, M.; Lu, J.; Yang, H. Effects of shading on the growth and leaf photosynthetic characteristics of three forages in an apple orchard on the Loess Plateau of eastern Gansu China. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, J.R.; Kaldenhoff, R.; Genty, B.; Terashima, I. Resistances along the CO2 diffusion pathway inside leaves. J. Exp. Bot. 2009, 60, 2235–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Gong, W.; Yang, W. Shade inhibits leaf size by controlling cell proliferation and enlargement in soybean. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niinemets, U. Photosynthesis and resource distribution through plant canopies. Plant Cell Environ. 2007, 30, 1052–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casson, S.; Gray, J.E. Influence of environmental factors on stomatal development. New Phytol. 2008, 178, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galmés, J.; Medrano, H.; Flexas, J. Photosynthetic limitations in response to water stress and recovery in Mediterranean plants with different growth forms. N. Phytol. 2007, 175, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamanishi, E.T.; Thomas, B.R.; Campbell, M.M. Drought induces alterations in the stomatal development program in Populus. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 4959–4971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong-hai, L.; Hong-zhi, Z.; Xian-ping, T.; Ya-li, Z.; Wang-feng, Z. Effects of water and nitrogen management modes on the leaf photosynthetic characters and yield formation of cotton with under-mulch drip irrigation. Yingyong Shengtai Xuebao 2013, 24, 407–415. [Google Scholar]
- Doheny-Adams, T.; Hunt, L.; Franks, P.J.; Beerling, D.J.; Gray, J.E. Genetic manipulation of stomatal density influences stomatal size, plant growth and tolerance to restricted water supply across a growth carbon dioxide gradient. Philoso. Trans. Royal Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2012, 367, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.Z.; Cheng, Z.Y. Effects of water stress on leaf water potential, transpiration rate and stomatal conductance of Alfalfa. Grassl. J. 2011, 19, 215–221. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Kang, S.; Zhang, J. Interactive effects of elevated CO2, nitrogen and drought on leaf area, stomatal conductance, and evapotranspiration of wheat. Agric. Water Manag. 2004, 67, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhou, G. Responses of leaf stomatal density to water status and its relationship with photosynthesis in a grass. J. Exp. Bot. 2008, 59, 3317–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.L.; Wang, J.X.; Duan, Z.Q.; Wen, J.; Wang, H.; Wen, J. Study on stomatal density and diurnal variation of wheat. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2006, 2, 237–242. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qi, X.; Torii, K.U. Hormonal and environmental signals guiding stomatal development. BMC Biol. 2018, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggard, A.O.; Will, R.E.; Wilson, D.S.; Wilson, D.R.; Meek, C.R.; Vogel, M.G. Fertilization reduced stomatal conductance but not photosynthesis of Pinus taeda which compensated for lower water availability in regards to growth. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 381, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Luo, Z.Z.; Niu, Y.N. Effects of water and nitrogen levels on photosynthetic characteristics and water use of spring wheat. Crop Res. 2020, 34, 308–314. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, B.; Gao, Y.H.; Li, P.H.; Yan, B.; Cui, Z.J.; Niu, J.Y. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer and density on water, nitrogen utilization and yield of flax. Agric. Res. Arid Reg. 2020, 38, 163–171. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Stutzel, H. Leaf expansion, stomatal conductance, and transpiration of vegetable amaranth (Amaranthus sp.) in response to soil drying. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2002, 127, 878–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.M.; Qi, H.; Luo, X.L. Research progress on the interaction between stomatal gas water loss and liquid water supply in SPAC system. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2008, 19, 2067–2073. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hetherington, A.M.; Woodward, F.I. The role of stomata in sensing and driving environmental change. Nature 2003, 424, 901–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Y.N.; Liu, K.; Deng, Z.W.; Su, J.L.; Rong, J.D.; Chen, L.G. Photosynthetic Characteristics of Phyllostachys edulis under Different Water and Fertilizer Coupling Treatment. J. Trop. Crops 2020, 41, 2253–2258. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jaleel, C.A.; Gopi, R.; Sankar, B.; Gomathayagam, M.; Panneerselvam, R. Differential responses in water use efficiency in two varieties of Catharanthus roseus under drought stress. Comptes Rendus. Biol. 2008, 331, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.H.; Xiao, H.L.; Zhao, L.J. Water consumption and water utilization of spring wheat under different water and fertilizer conditions. Agric. Res. Arid Reg. 2006, 24, 56–59. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, N.; Sun, X.; Hou, S.; Chen, G.; Zhang, H.; Han, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z. N Addition Mitigates Water Stress via Different Photosynthesis and Water Traits for Three Native Plant Species in the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12111873
Zhao N, Sun X, Hou S, Chen G, Zhang H, Han Y, Zhou J, Wang X, Zhang Z. N Addition Mitigates Water Stress via Different Photosynthesis and Water Traits for Three Native Plant Species in the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Agriculture. 2022; 12(11):1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12111873
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Ningning, Xingrong Sun, Shuai Hou, Guohao Chen, He Zhang, Yuxin Han, Jie Zhou, Xiangtao Wang, and Zhixin Zhang. 2022. "N Addition Mitigates Water Stress via Different Photosynthesis and Water Traits for Three Native Plant Species in the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau" Agriculture 12, no. 11: 1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12111873
APA StyleZhao, N., Sun, X., Hou, S., Chen, G., Zhang, H., Han, Y., Zhou, J., Wang, X., & Zhang, Z. (2022). N Addition Mitigates Water Stress via Different Photosynthesis and Water Traits for Three Native Plant Species in the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Agriculture, 12(11), 1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12111873




