Effect of Mechanized Ridge Tillage with Rice-Rape Rotation on Paddy Soil Structure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
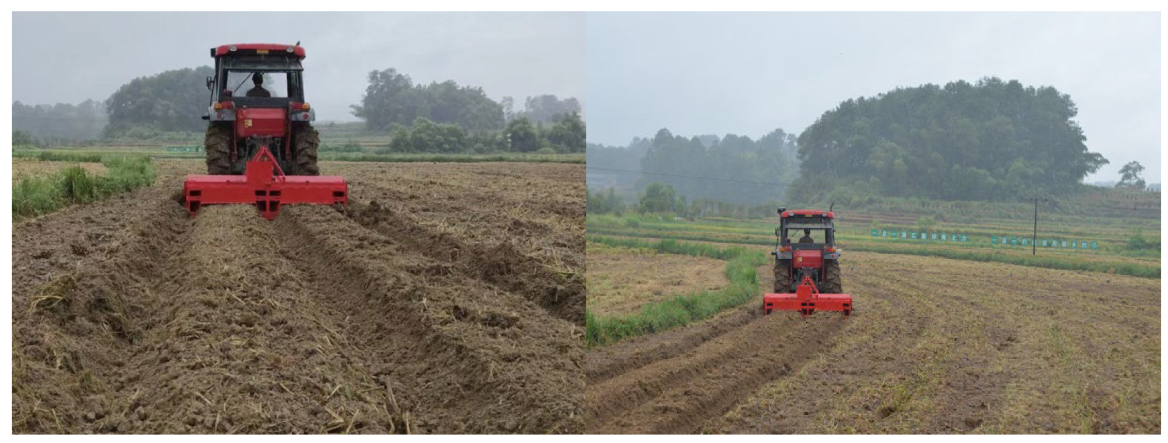
2.1. Experimental Site Description
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Measurements
2.3.1. Soil Porosity
2.3.2. Soil Aggregate
2.3.3. Aggregate Degree of Soil Particles
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
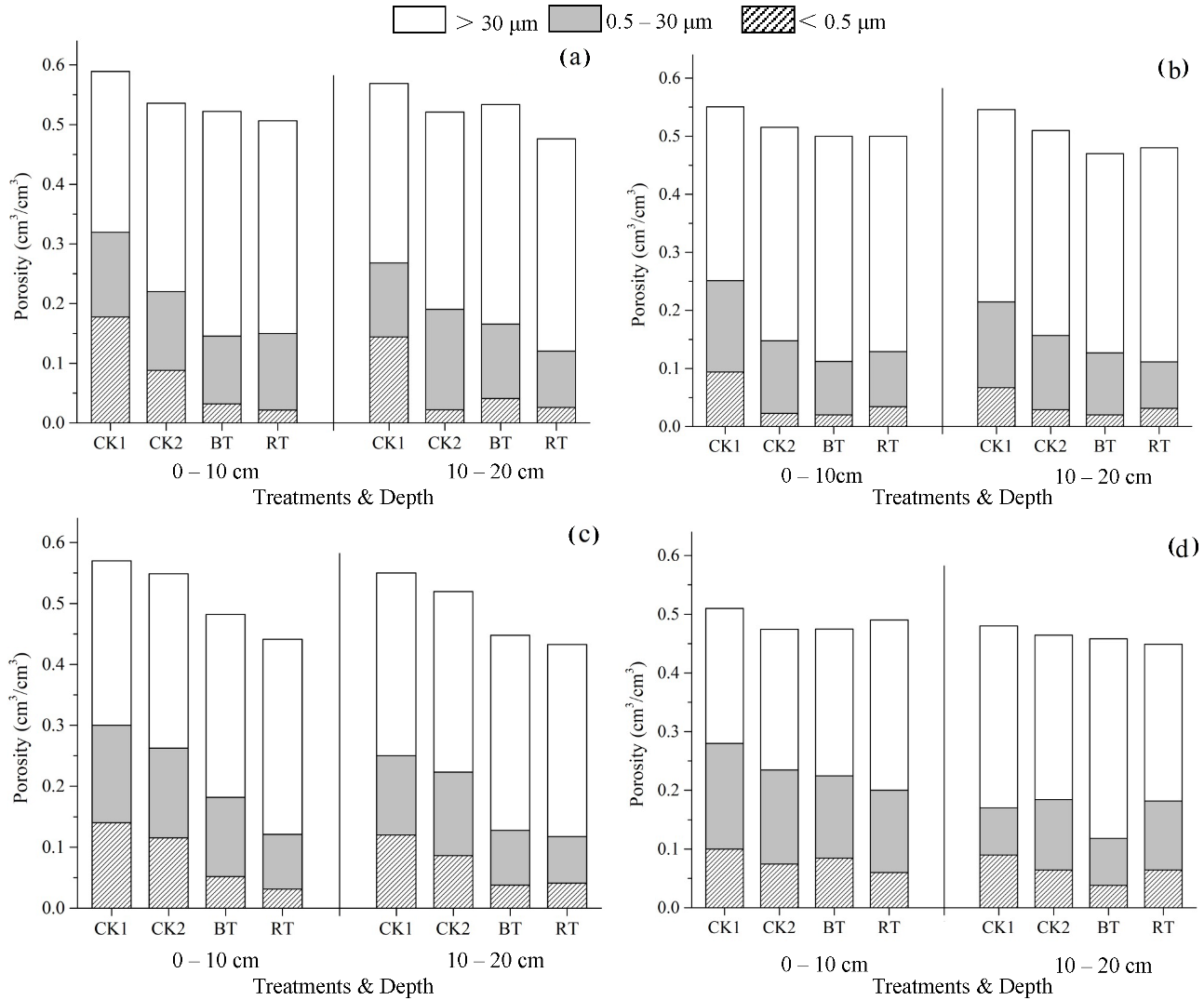
3.1. Soil Porosity
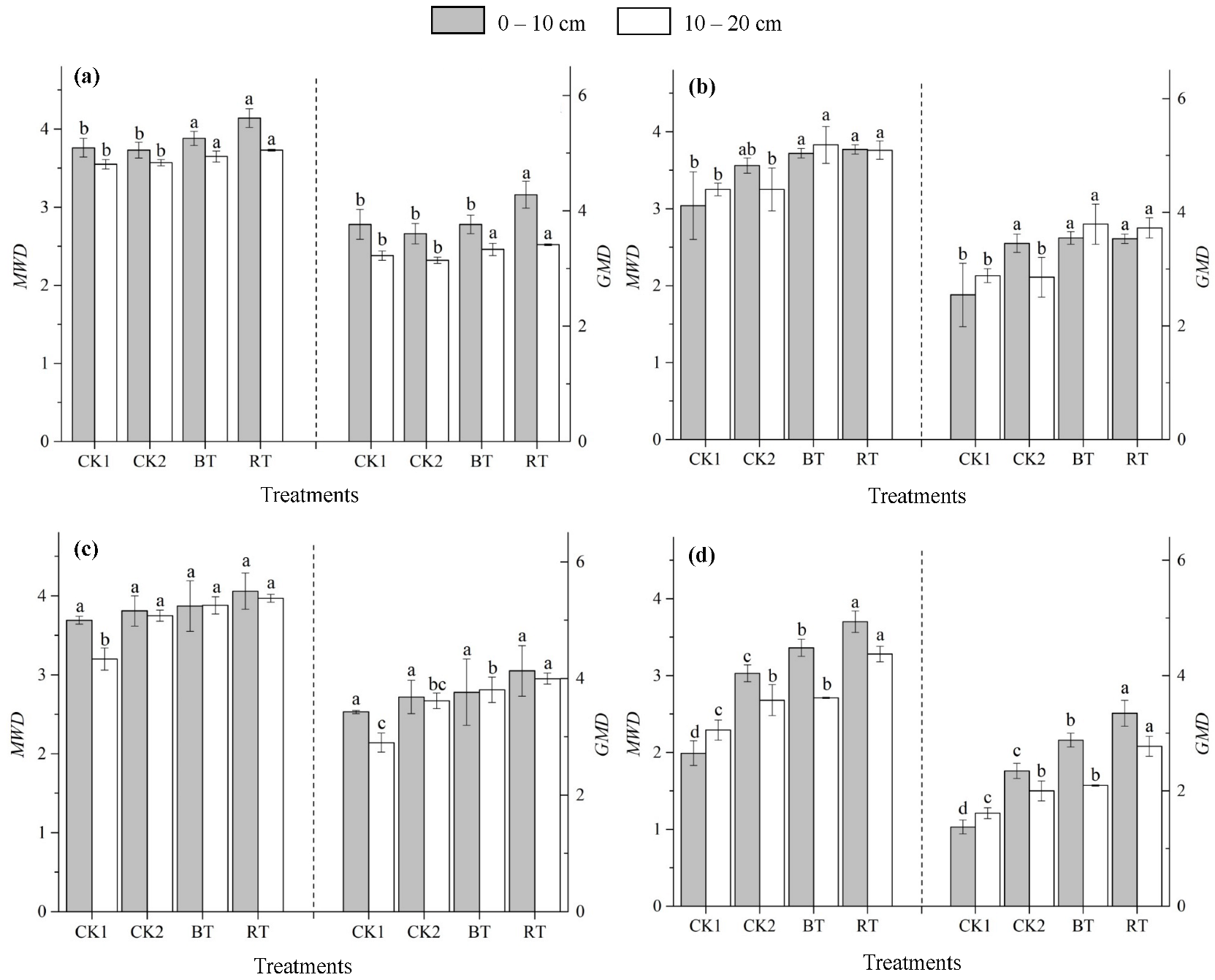
3.2. Aggregate Stability
3.3. Aggregation of Soil Particles
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Mechanized Ridge Tillage of Rice-Rape on Soil Porosity
4.2. Effect of Mechanized Ridge Tillage of Rice-Rape on Soil Aggregates
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Woodhead, T.; Zhang, J.B. Problemsand Countermeasures of soil physical management in rice farming system. Adv. Pedol. 1992, 20, 19–21. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, C. Study on the Mechanism of Improving Soil Nitrogen Fertility by Combination Ridge with No-Tillage in Paddy Field; Southwest University: Chongqing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Li, F.Q.; Liao, P.Z.; Khan, A.; Hussain, I.; Iqbal, A.; Ali, I.; Wei, B.H.; Jiang, L.G. Smash ridge tillage strongly influence soil functionality, Physiology and Rice Yield. Saudi. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 1297–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.J.; Fu, Z.Q.; Li, C.; He, B.L.; Yan, L.L.; Xu, Y.; Long, P. Research progress on the application of ridge rice field in ecological cultivation. Chin. J. Ecol. 2020, 39, 2416–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.T.; Wei, C.F.; Huang, Z.X.; Lang, J.W. Study on natural no tillage technology in paddy field. Tillage Cultiv. 1986, 6, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.F.; Cao, C.G.; Wang, J.P.; Zhan, M.; Yuan, W.L.; Ahmad, S. Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Wetland Rice-Duck Cultivation Systems in Southern China. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2008, 56, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.W.; Huang, W.; Li, Y.C.; Wang, N.; Zhang, X.S. Effects of ecological comprehensive planting and breeding patterns on soil physical and chemical properties and humus in paddy fields. J. Biol. 2020, 37, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.T.; Chen, Z.L. Theory and Technology of Paddy Field under Soil Virginization; Chongqing Publishing House: Chongqing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, X.; Horn, R.; Hallett, P. Soil structure and its functions in ecosystems: Phase matter &scale matter. Soil Till. Res. 2015, 146, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weil, R.R.; Brady, N.C. The Nature and Properties of Soils, 15th ed.; Pearson: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rabot, E.; Wiesmeier, M.; Schlueter, S.; Vogel, H.J. Soil structure as an indicator of soil functions: A review. Geoderma 2018, 314, 122–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.C.; Wang, Y.; Wei, L.; Wang, J.Z.; Nie, S.W.; Liu, S.W. Research Progress on Crop Raised-bed Planting in China. J. Henan Agric. Univ. 2005, 39, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.W.; Han, Z.; Zhong, S.Q.; Gao, P.F.; Wei, C.F. Pore size distribution and pore functional characteristics of soils as affected by rock fragments in the hilly regions of the Sichuan Basin, China. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2020, 101, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.A.; Wang, Q.J.; Huang, M.B. Soil Physics; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, D.H.; Huang, J.L.; Wang, M.S.; Deng, H.W. Effect of deep vertically rotary tillage on particle size distribution and stability of latosolic red soil aggregates. Chin. J. Ecol. 2021, 40, 3922–3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.W.; Zhou, W.T.; Wang, B.R.; Zhong, Y.Y.; Xiong, R.; Long, P.; Xu, Y.; Fu, Z.Q. Effects of ridge-bed cultivation on rice root characteristics and soil physical properties. Chin. J. Ecol. 2021, 40, 3961–3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.Q.; Xu, J.L.; Zhu, Z.L.; An, S. Application of ultrasonic energy for assessing aggregate stability. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 23, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Z.L.; Zhong, S.Q.; Liu, B.; Wei, C.F. Particle Characteristics of purple shale soil and their mechanism of shear strength. Soils 2019, 51, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.J.; Xu, W.N.; Xia, L.; Chen, J.G.; Cheng, H.; Yu, F.; Xia, D.; Liu, D.X.; Yu, S.P. Effects of Land Use Patterns on Soil Aggregate Stability in Small Watershed of Yangtze River, Located in Western Hubei. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2020, 30, 925–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, N. Difference of Physical Properties of Soil Profiles under Different Vegetations in Karst Mountainous Area; Guizhou University: Guiyang, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Dane, J.H.; Topp, C.G. Methods of Soil Analysis Part 4: Physical Methods; Soil Science Society of America Book Series No.5 Soil; Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, S.Q.; Liu, B.; Wei, C.F.; Hu, F.N. The Rock Fragments (<2 mm) and Their Action Mechanism on the Shear Strength of Purple Mudstone-Developed Soils. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2015, 48, 4846–4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z. Rill Erosion Process and Mechanics Mechanism of Partially Saturated Soil; Southwest University: Chongqing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.L.; Gong, Z.T. Soil Investigation Laboratory Analysis Method; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, C.F. The influence of capillary infiltration on soil aggregate. J. Southwest Agric. Univ. 1987, S2, 136–140. [Google Scholar]
- Kay, B.D.; Vandenbygaart, A.J. Conservation tillage and depth stratification of porosity and soil organic matter. Soil Till. Res. 2002, 66, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaffar, M.; Lu, S.G. Pore Size Distribution of Clayey Soils and Its Correlation with Soil Organic Matter. Pedosphere 2015, 25, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.W.; Zhang, X.P.; Liang, Z.A.; Jia, S.X.; Shi, X.H.; Fan, R.Q.; Wei, S.C. Tillage effects on soil pore size distribution and soil moisture in Northeast China. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2012, 26, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.F.; Henry, L.; Li, S.C. Quantification of 3-D soil macropore networks in different soil types and land uses using computed tomography. J. Hydrol. 2010, 393, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomasson, A.J. Towards an objective classification of soil structure. J. Soil. Sci. 1978, 29, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.J.; Liu, F.; Jiao, F.; Chang, B.C.; Jiang, H.; Gong, X.J. Effects of strip-collected chopping and mechanical deep-buried return of straw on physical properties of soil. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2019, 35, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhoff, S.; Ghiberto, P.J.; Grioni, A.; Gay, J.P. Porosity characterization of Argiudolls under different management systems in the Argentine Flat Pampa. Geoderma 2010, 158, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, W.M.; Shipitalo, M.J.; Traina, S.J.; Edwards, C.A.; Owens, L.B. Role of lumbricus terrestris (L.) burrows on quality of infiltrating water. Soil Boil. Biochem. 2006, 24, 1555–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.N.; Evans, A.; Zhang, L.Y.; Tian, K.; Yang, D.T.; Li, J.H. Effects of Tillage Methods on the physical characteristics of red soil of upland. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 25, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.X.; Han, X.Z.; Yan, J.; Chen, X.; Lu, X.C.; Qiu, C.; Hao, X.X. Effects of incorporation depth of tillage and straw returning on soil physical properties of black soil in Northeast China. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 36, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Lv, Y.Z.; Yang, Z.C.; Li, B.G. Effects of Conservation Tillage on Soil Aggregates in Huabei Plain, China. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2007, 40, 1973–1979. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, R.; Yang, S.; Qin, X.; Zheng, Z.C.; Li, T.X. Effects of Different Tillage Measures and Maize Growing Seasons on Soil Aggregates’ Stability in Sloping Yellow Soil Cropland. J. Yangtze River Sci. Res. Inst. 2020, 37, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.Y. Variation Characteristics of Soil Aggregates and Aggregate Carbon in Orchards Covered with Living Mulching; Northwest A&F University: Xianyang, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, E.F.; Guan, L.Z.; Wang, J.K.; Yan, L.; Wang, T.Y.; Zhang, J.H.; Zhou, J.K.; Li, R.H. Composition proportion and fertility evaluation of soil characteristic micro aggregates. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2001, 38, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.L.; Wang, L.L.; Zhao, J.N.; Li, G.; Xiu, W.M.; Yang, Q.C.; Zhang, G.L. Effects of tillage managements on soil microbial community structure in soil aggregates of fluvo-aquic soil. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2021, 32, 2713–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.L.; Liu, Y.H.; Song, X.L.; Wei, S.B.; Li, J.P.; Nie, J.J.; Qin, D.L.; Sun, X.Z. Effects of cotton straw returning on soil organic carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium contents in soil aggregates. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2016, 27, 3944–3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

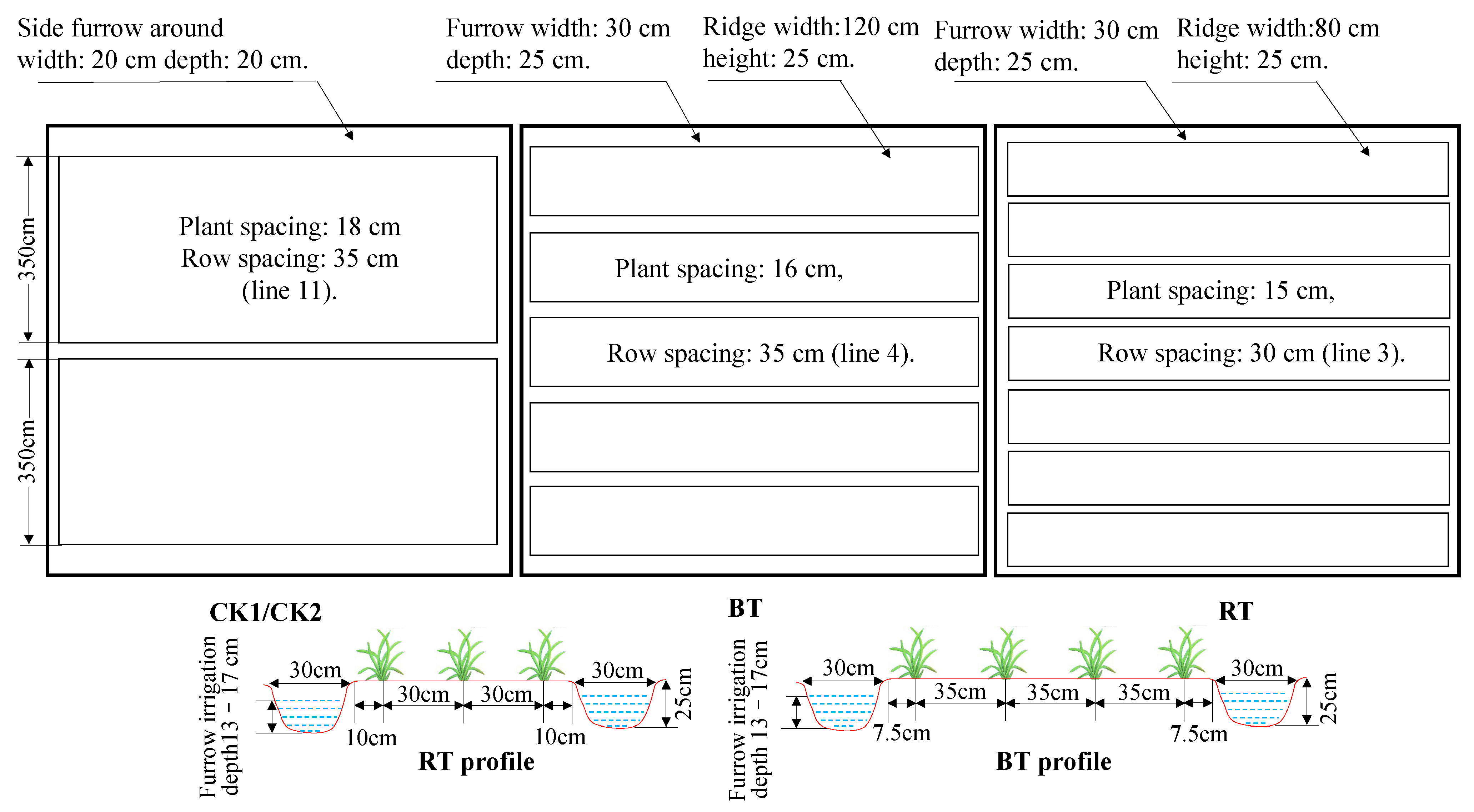

| Crops | Variety Name | Sowing Method | Harvesting Method | Sowing/Harvest Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rice | Chuanhuayou 320 | Direct seeding | Wold (Ryzen Classic edition) harvester | 4 May/1 September |
| Rape | Dezayou No. 5. | 15 September/28 April | ||
| Name | Model | Ridge height | Ridge spacing | Ridge top width |
| Rotary tillage and ridging machine | YGZ-01 | 28 cm | 120 cm | 80 cm |
| Crops | Nitrogenous fertilizer(N) | Phosphate(P2O5) | Potash(K2O) | Borax (Na2B4O7·10H2O) |
| Rice | 120 kg/ha | 90 kg/ha | 75 kg/ha | - |
| Rape | 180 kg/ha | 105 kg/ha | 90 kg/ha | 15 kg/ha |
| Growth Period | Layer (cm) | Degree of Aggregation (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK1 | CK2 | BT | RT | ||
| Flowering stage of rape | 0–10 | 37.33 ± 0.95 Cb | 48.97 ± 6.70 Ba | 57.34 ± 2.87 Aa | 62.12 ± 1.97 Aa |
| 10–20 | 48.32 ± 1.61 Aa | 50.79 ± 11.28 Aa | 54.76 ± 7.66 Aa | 65.15 ± 4.28 Aa | |
| Maturity stage of rape | 0–10 | 33.92 ± 2.36 Ab | 36.09 ± 8.73 Aa | 40.67 ± 1.91 Ab | 44.81 ± 5.90 Ab |
| 10–20 | 46.34 ± 6.13 Ba | 45.72 ± 2.48 Ba | 50.19 ± 3.40 Aba | 58.19 ± 5.84 Aa | |
| Heading stage of rice | 0–10 | 29.50 ± 1.09 Bb | 47.61 ± 2.11 Aa | 50.57 ± 9.74 Aa | 57.28 ± 10.06 Aa |
| 10–20 | 52.25 ± 5.74 Aa | 56.91 ± 9.01 Aa | 55.17 ± 10.78 Aa | 69.20 ± 3.99 Aa | |
| Maturity stage of rice | 0–10 | 28.06 ± 8.81 Ca | 40.41 ± 9.68 Ba | 42.27 ± 3.85 Ba | 57.81 ± 2.26 Aa |
| 10–20 | 29.48 ± 1.09 Ca | 43.80 ± 3.90 Bca | 45.47 ± 1.40 Ba | 59.07 ± 5.40 Aa | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, L.; Li, J.; Wei, C.; Yang, C.; Zhong, S. Effect of Mechanized Ridge Tillage with Rice-Rape Rotation on Paddy Soil Structure. Agriculture 2022, 12, 2147. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12122147
Li L, Li J, Wei C, Yang C, Zhong S. Effect of Mechanized Ridge Tillage with Rice-Rape Rotation on Paddy Soil Structure. Agriculture. 2022; 12(12):2147. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12122147
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Lanting, Jiangwen Li, Chaofu Wei, Chaoxian Yang, and Shouqin Zhong. 2022. "Effect of Mechanized Ridge Tillage with Rice-Rape Rotation on Paddy Soil Structure" Agriculture 12, no. 12: 2147. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12122147
APA StyleLi, L., Li, J., Wei, C., Yang, C., & Zhong, S. (2022). Effect of Mechanized Ridge Tillage with Rice-Rape Rotation on Paddy Soil Structure. Agriculture, 12(12), 2147. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12122147




