Abstract
To establish the uncertain influence that the joint distribution of precipitation and reference evapotranspiration has on net irrigation water requirement, a Copula function–Monte Carlo method (CFMC) was proposed to calculate the probability of irrigation water requirement. Taking the Jingdian Irrigation District in Northwest China as an example, the distribution laws of precipitation and reference evapotranspiration were studied. Furthermore, five typical years under different crop planting structure conditions were selected, and the variation characteristics of net irrigation water requirement in each typical year under the conditions of climate uncertainty were analyzed. The results revealed the optimal distribution functions of precipitation and reference evapotranspiration to be gamma distribution and lognormal distribution. The probability density map of the joint distribution of precipitation and reference evapotranspiration has a “saddle” shape; that is, irrigation water requirement and reference evapotranspiration are usually inversely related. As the probability of the irrigation water requirement increases, the net irrigation water requirement in the irrigation area also increases. The CFMC method can determine the design value of the net irrigation water requirement under a specific probability for typical years under different crop planting structure conditions, which can provide a reference for agricultural water resource allocation in irrigation areas.
1. Introduction
The irrigated area in Asia has increased steadily during the last 50 years [1,2]. The use of agricultural water has increased significantly as the irrigated area has increased, leading to increasing water scarcity in a number of regions [3,4,5]. Some developing countries use over 90 percent of their water for irrigation [6]. As a large agricultural country, the average water consumption per unit area in China is only 50% of the global average level [7], and the issue of irrigation water shortage has become increasingly obvious [8,9]. Due to the greater demand for irrigation, the contradiction between the supply and demand of agricultural water resources has intensified [10,11,12,13]. Crop water demand and net irrigation water requirement are important bases for the management planning and design of irrigation water. Therefore, the rational design of net irrigation water requirement can serve to improve irrigation water use efficiency [14,15,16].
Many studies have been conducted on calculating the net irrigation water requirement. Liu et al. used the crop coefficient method and empirical formula for the calculation of crop water demand, effective precipitation, and net irrigation water requirement of major crops in China before analyzing their spatial distribution characteristics [17]. Nkomozepi et al. used a sensitivity analysis method for studying the impact that climate change has on the net irrigation water requirement in the natural agro-ecological areas of Zimbabwe [18]. Wang et al. used meteorological data and crop data for calculating the water requirement of maize in the Chengde area, analyzing the influence meteorological factors have on the water demand of spring maize [19]. Liu et al. calculated the net irrigation water requirement for cotton in Hebei Province, China to be an average of 190.6 mm by using the water balance method, and the irrigation demand index was found to be 0.29 [20]. Wang et al. conducted research on the net irrigation water requirement of rice, finding precipitation to be the primary factor that affects the net irrigation water requirement, followed by crop water demand [21]. Liu et al. used the path analysis method to determine the causes of water requirements of staple crops in Henan Province, China [22]. Xie et al. decomposed the driving factors of the net irrigation water requirement in Wuwei City using the LMDI method, also calculating the effect values of the influencing factors of net irrigation water requirement [23]. Feng et al. used the water balance method for the calculation of the net irrigation water requirement in the Sanyizhai Yellow River Diversion Irrigation District, analyzing its temporal and spatial variation [24]. In addition, several studies have attempted the use of crop models including CROPWAT for the estimation of the irrigation needs of a variety of crops in different agro-ecological units [25,26]. The CROPWAT model estimates crop water demands during different stages and uses input climate, soil, and crop data for the generation of irrigation schedules [27].
The majority of the aforementioned studies use the crop coefficient method and Penman–Monteith formula for the calculation of crop water demand and the empirical formula for the estimation of effective precipitation. The net irrigation water requirement is generally calculated by a water balance equation [28,29]. Precipitation and reference evapotranspiration are two of the key factors in the design and implementation of irrigation schedules, and the relationship between them has important implications for the study of the uncertainty of net irrigation water requirements [30]. The Penman–Monteith formula [31] only requires simple meteorological data for the calculation of reference evapotranspiration. This formula has the advantage of high calculation accuracy and is therefore widely used [32,33,34,35]. As they are both affected by meteorological factors, crop water demand and precipitation are uncertain. The frequency distribution curve is a simple one-way frequency analysis method [36] that is widely used in hydrological research [37,38,39,40]. Due to the correlation between meteorological factors, the design of irrigation schedules must be based on the joint probability distribution of precipitation and crop water demand [41]. Zhang et al. demonstrated that a copula function can be used for the accurate description of the joint probability distribution characteristics of precipitation and reference evapotranspiration and for determining the joint return period of both [30]. However, when the joint return period is determined by a copula function, it is difficult to apply it directly to the design of the net irrigation water requirement due to the infinite possible combinations of precipitation and reference evapotranspiration during a given return period. Therefore, for the utilization efficiency of agricultural water resources to be improved, a calculation method for net irrigation water requirement where uncertainty is considered is urgently required.
In this study, a copula function and Monte Carlo simulation were combined to construct a net irrigation water requirement calculation method considering the joint probability distribution of precipitation and reference evapotranspiration, which can be used to determine the net irrigation water requirement with different probabilities of irrigation. Taking the Jingdian Irrigation District in Gansu Province, China as an example, five typical years under different crop planting structure conditions were selected, and the variation characteristics of net irrigation water requirement in each typical year from 2000 to 2020 were analyzed. This study will provide a reference for the calculation of water demand in irrigation areas under the condition of climate uncertainty, which is of great significance to the efficient use of water resources in irrigation areas.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Calculation of Net Irrigation Water Requirement
The water balance method is widely used for the calculation of the net irrigation water requirement. When groundwater depth is more than 5 m, the impact groundwater recharge has can generally be ignored [34], and the calculation formula that is used for the net irrigation water requirement during the growing period is expressed as [17,42]:
where IRw is the net irrigation water requirement of the whole growing period, mm; EPw is the effective precipitation of the whole growing period, mm; and ETcw is the crop water demand of the whole growing period, mm.
IRw = ETcw − EPw
In Equation (1), effective precipitation refers to the part of precipitation that actually enters the root layer and can be used by crops, excluding surface runoff and deep percolation. When Equation (1) is used for the calculation of the net irrigation water requirement, only effective precipitation during the growth period and crop water demand need to be calculated.
In arid regions with less snowfall, when Equation (1) is used for the calculation of net irrigation water requirement during the entire growth period, the influence of soil moisture changes can generally be ignored. However, when the net irrigation water requirement is calculated for short periods (including daily or monthly scales), changes in soil moisture must be considered, and monthly net irrigation water requirement is then expressed as [34,43]:
where IRi is the net irrigation water requirement in month i, mm; ETci is the crop water demand in month i, mm; EPi is the effective precipitation in month i, mm; and Si is the soil water storage at the end of month i, mm.
IRi = ETci − EPi + Si − Si−1,
Monthly effective precipitation is calculated using the empirical formula [44,45]:
where APi represents cumulated precipitation in month i, mm, which is converted from the daily precipitation data of the weather station.
Monthly crop water demand is calculated based on the daily crop water demand, and the daily crop water demand is calculated using the crop coefficient method:
where ni is the number of days in the month i; Kcj is the crop coefficient on day j; and EToj is the reference evapotranspiration on day j, mm, which can be calculated using the Penman–Monteith formula that is recommended by FAO [31]:
where Rn is the net radiation on the crop surface, MJ/(m2∙d); G is the soil heat flux, MJ/(m2∙d); T is the average temperature at a height of 2 m, °C; u2 is the wind speed at a height of 2 m, m/d; es is the saturated water pressure, kPa; ea is the actual vapor pressure, kPa; ∆ is the slope of the saturated water pressure and temperature curve, kPa/℃; and λ is the psychrometric constant, kPa/°C.
The crop coefficient refers to the ratio of the crop water demand to the reference evapotranspiration in a certain period of time. Different crops have different crop coefficients in each growth period. In this study, the daily crop coefficient of the study area is calculated according to the planting area of each crop:
where nk is the number of crop types in the study area; Kck is the crop coefficient of the k-th crop; Ak is the planting area of the k-th crop, km2; and A is the total planting area, km2.
The monthly effective precipitation and monthly reference evapotranspiration can be calculated using Equations (3) and (4); however, according to Equation (2), it is necessary to calculate the changes of soil water storage in each month to obtain the monthly net irrigation water demand. According to the principle of water balance, the monthly soil water storage can be calculated by the following equation:
According to the above equations, as long as the initial soil water storage is determined, the soil water storage in any month can be calculated. In this study, the monthly effective precipitation one month before the crop growth period is used as the initial soil water storage.
2.2. Joint Probability Distribution Based on a Copula Function
Effective precipitation and reference evapotranspiration are both key variables that affect net irrigation water requirement. The two variables are affected by meteorological conditions and have a certain correlation. A copula function is an effective tool for the construction of multivariate joint distribution and can completely retain the correlation information between variables. It also possesses strong flexibility and excellent applicability [46]. Therefore, a copula function is used in this study for establishing the joint probability distribution model of the monthly effective precipitation and reference evapotranspiration. The use of a copula function for establishing the joint probability distribution is divided into two stages. The first is the determination of the optimal distribution of monthly effective precipitation and reference evapotranspiration, and the second is the determination of copula function parameters.
Gamma distribution, lognormal distribution, and generalized extreme value (GEV) distribution are the marginal distribution types that are most commonly used for hydrological analysis [47]. The probability density functions of the three distributions are expressed as:
(1) Gamma distribution:
where α and β are shape and scale parameters.
(2) Lognormal distribution:
where μ and σ are the mean and standard deviation of the logarithm of the variable.
(3) GEV distribution:
where k, σ, and μ are shape, scale, and position parameters.
The K–S test method (Kolmogorov–Smirnov) is used for testing the hypothesis of marginal distribution, and the Akaike information criterion (AIC) is used for selecting the optimal marginal distribution. The model with the smallest AIC value should be selected from the alternative functions as the optimal model. The expression of the AIC value is [47]:
where N is the total number of independent parameters, and L is the maximum likelihood value.
AIC = 2N − 2lnL,
Assuming that X and Y represent effective precipitation and reference evapotranspiration, the corresponding design values are x and y, and their marginal distributions are FX(x) and FY(y). According to Sklar’s theorem, the joint distribution function of X and Y is expressed using a two-dimensional copula function [48]:
F(x,y) = Cθ [FX(x),FY(y)],
Copula functions are divided into elliptic, quadratic, and Archimedean types, and Archimedean copula functions are those that are most widely used in the field of hydrology. These include the Gumbel copula, Clayton copula, and Frank copula functions. The first two are generally used for positive correlation variables, whereas the Frank copula is suitable for negative correlation variables. A negative correlation generally exists between precipitation and reference evapotranspiration. Therefore, the Frank copula function was chosen for the construction of the joint distribution function, which is expressed in the following way [49]:
where u and v represent the cumulative probability of marginal distribution for two variables; and θ is a shape parameter.
2.3. Calculation of Probability of Irrigation Water Requirement
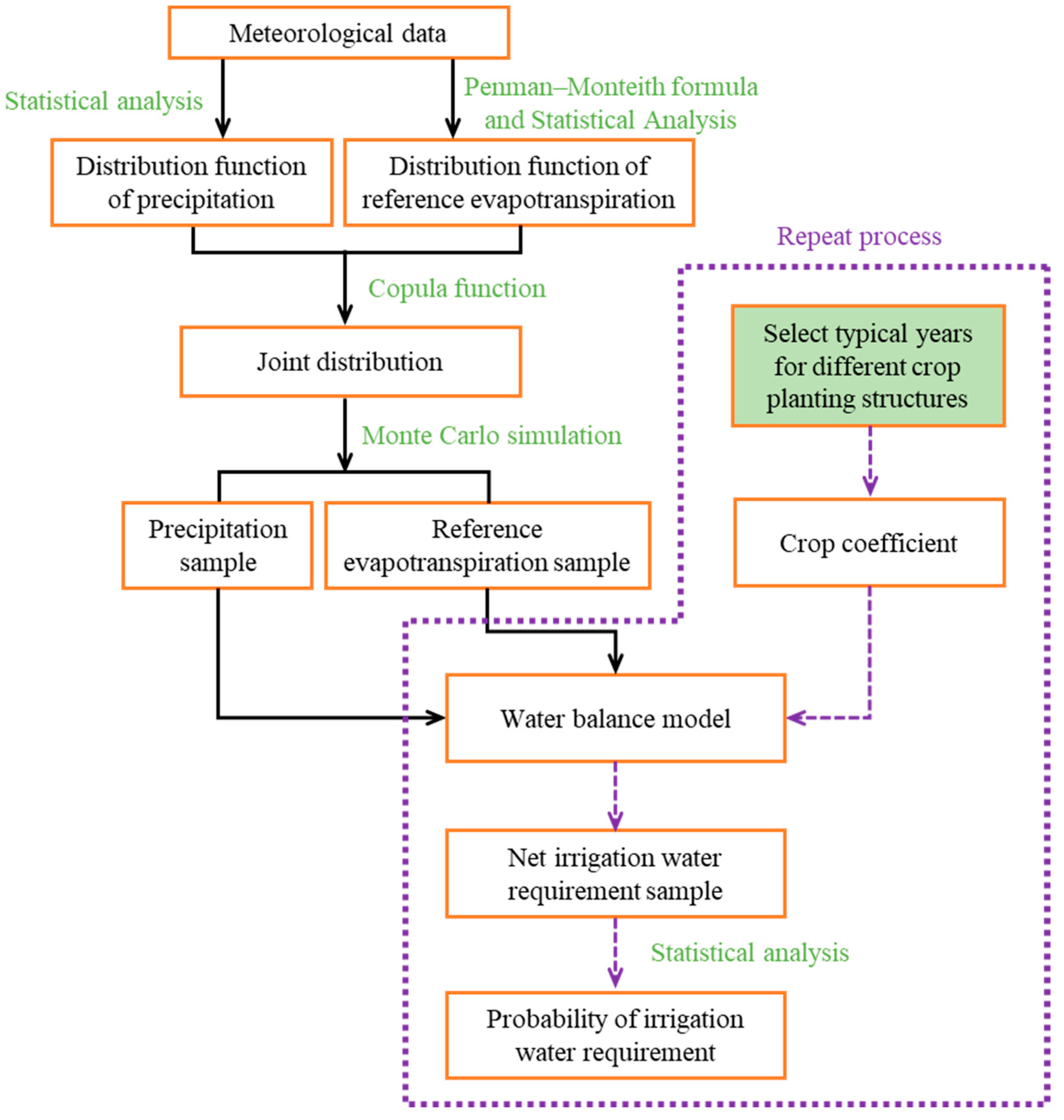
The probability of irrigation water requirement refers to the probability that the water consumption of the irrigation area can be fully satisfied. Usually, it is expressed as the percentage of the number of years in which the design irrigation water consumption is fully satisfied to the total number of years [43]. The probability of irrigation water requirement is usually determined by the typical year method. The selection of the typical year usually only considers the amount of precipitation and does not consider the uneven distribution of precipitation in time. The problem of the uneven distribution of precipitation can only be solved when there are enough precipitation samples. The Monte Carlo method is based on the theory of probability and statistics and is used for the analysis of a variety of uncertain problems. Monte Carlo methods are often used to solve uncertain problems. The method is to generate possible situations through a large number of simulations so as to obtain different results and probability distributions under a certain probability. Then, by performing statistical analysis on a large number of sample values, a result that meets a certain accuracy can be obtained. Therefore, Monte Carlo simulation is a powerful tool for uncertain and risky problems. When using the Monte Carlo method, it is necessary to input a given distribution function and parameters and then use a computer to generate a series of random numbers that satisfy the distribution function. The more random samples there are, the more likely it is to cover all situations. The given distribution function can be a univariate distribution function or a multivariate distribution function. The Monte Carlo method is used in this paper for evaluating the impact that sample uncertainty has on the net irrigation water requirement. Combining the Monte Carlo method and a copula function, the Copula function–Monte Carlo method (CFMC) was established as shown in Figure 1.
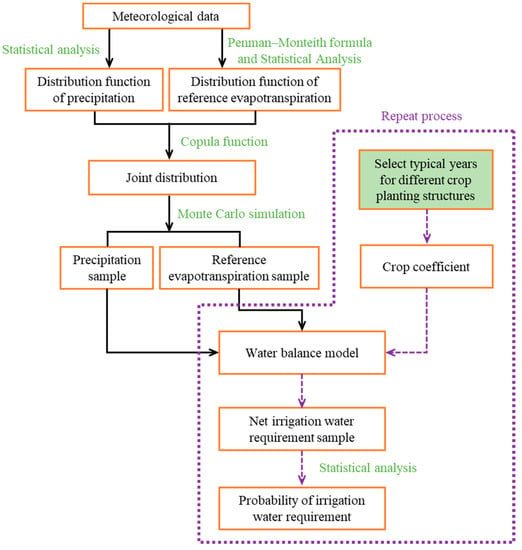
Figure 1.
Process diagram of Copula function–Monte Carlo method. (Purple line and arrows are processes that need to be repeated, black arrows do not need to be repeated).
From Figure 1, the following steps are taken for determining the probability of the irrigation water requirement:
Step 1: Calculate the reference evapotranspiration according to the meteorological data and the Penman–Monteith formula.
Step 2: Determine the optimal marginal distribution model and parameters of monthly precipitation and reference evapotranspiration based on the Akaike information criterion.
Step 3: Determine the joint distribution parameters of precipitation and reference evapotranspiration based on the Frank copula function, use the joint distribution model to represent the population, randomly generate 1000 sets of cumulative probability samples of the joint distribution function, and then use the marginal distribution model of precipitation and reference evapotranspiration. Calculate the corresponding precipitation and reference evapotranspiration.
Step 4: Select a typical year under a specific crop planting structure and use Equation (6) to calculate the crop coefficient. Take 1000 groups of randomly simulated precipitation and reference evapotranspiration data as input items, and calculate the net irrigation water demand corresponding to 1000 groups of samples.
Step 5: Calculate the probability of irrigation water requirement according to the 1000 groups of net irrigation water requirements so that the net irrigation water requirements corresponding to different probabilities of irrigation water requirements can be determined. The formula for calculating the probability of irrigation water requirement is:
where P(Q) is the probability of the irrigation water requirement corresponding to the net irrigation water requirement of Q, %; n is the total number of years, where n = 1000; and m is the number of years when the net irrigation water requirement is greater than Q.
Step 6: Select different typical years and repeat steps 4 to 5 to obtain the relationship between the net irrigation water requirement and the probability of the irrigation water requirement under different crop planting structures.
2.4. Study Area
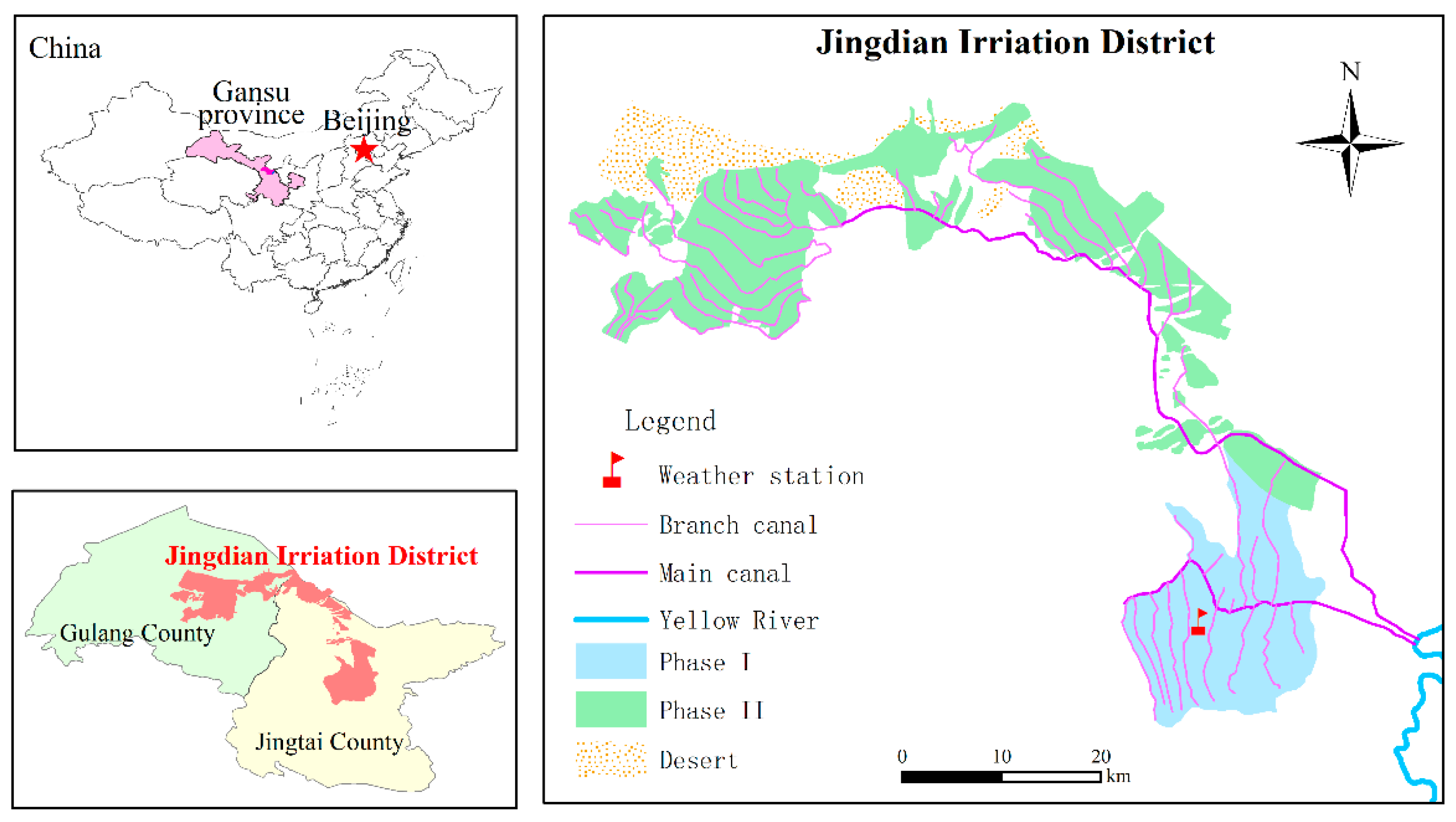
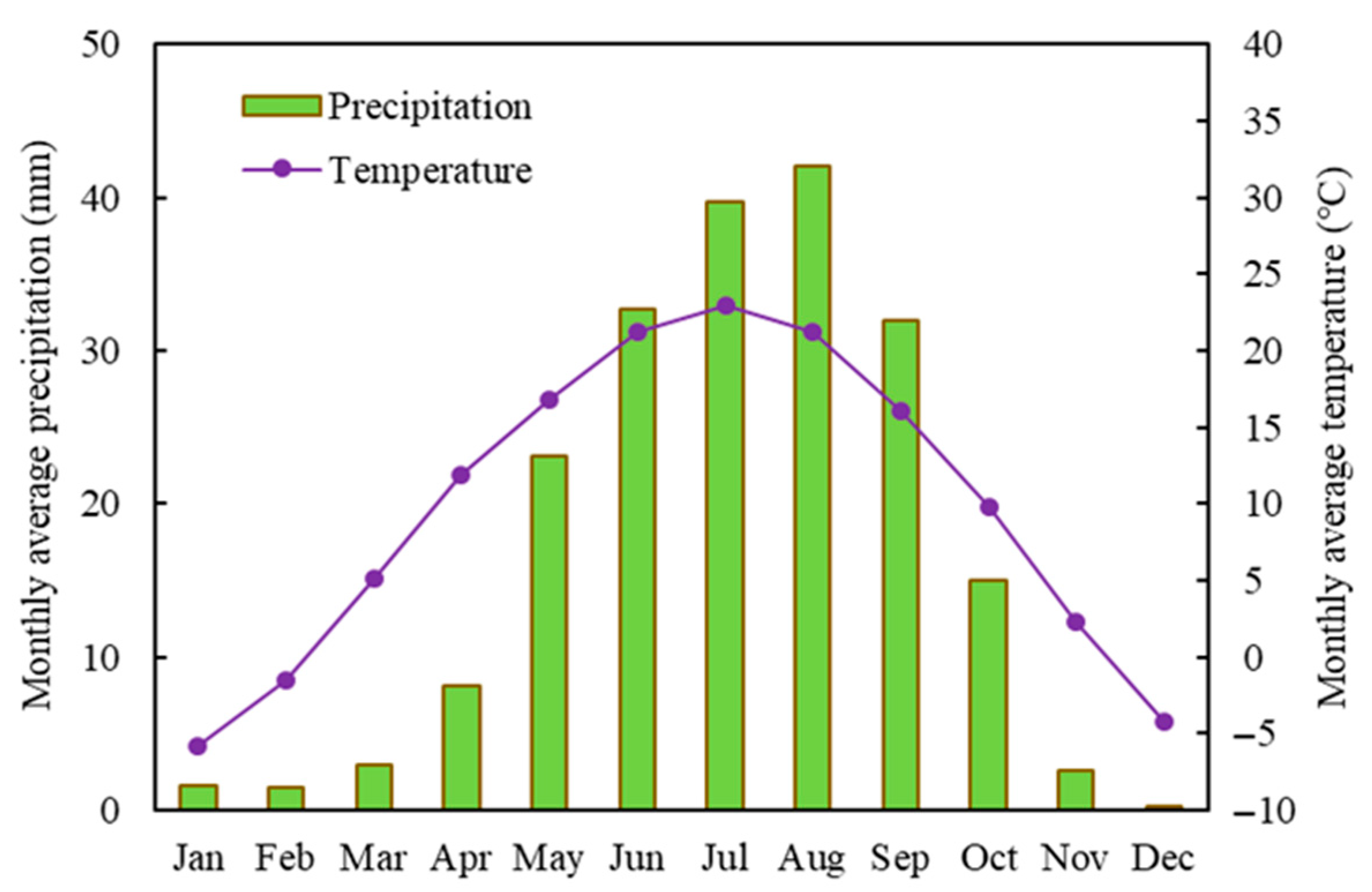
The Jingdian Irrigation District is situated in the middle of Gansu Province, China (Figure 2). Its north side is bordered by the Tengger Desert, its east side is in close proximity to the Yellow River, and at its south side are the Changling mountains. According to raw National Meteorological data for Jingtai County, the annual average precipitation in the irrigation area is 186 mm, the annual variation range is 103.5–298.4 mm, and the annual water surface evaporation intensity is 2123 mm (E601 evaporating dish). The annual average temperature is 8.8 °C. Figure 3 shows the monthly average precipitation and temperature. The maximum and minimum temperatures in the Jingdian Irrigation District occur in July and January, respectively, and the maximum and minimum precipitation occur in August and December. The total area of the Jingdian Irrigation District is 1496 km2, and the irrigation area is 607.7 km2, which includes 201.1 km2 in phase I and 406.6 km2 in phase II. The main crop types that are found in the irrigation area include spring wheat, barley, corn, soybean, flax, potato, melon, medlar, and forest fruit. From the test results of soil samples, it was found that the soil texture of the root layer in the irrigation area is mainly sandy loam.
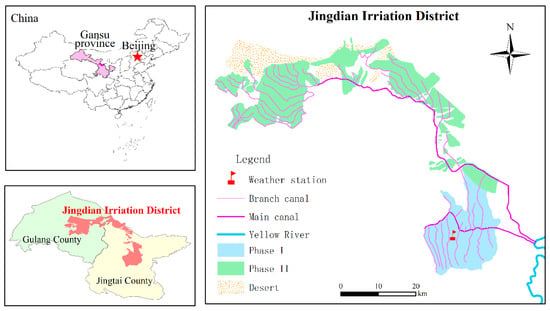
Figure 2.
Location map of the study area.
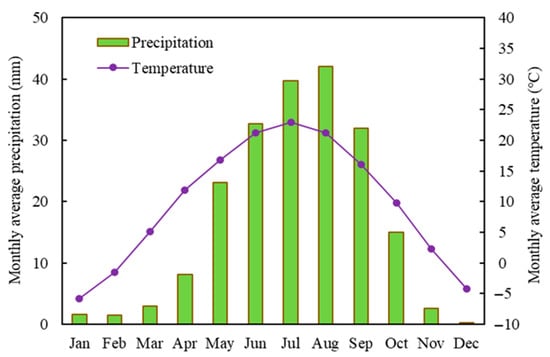
Figure 3.
Monthly means of temperature and precipitation.
2.5. Data Source
Meteorological data for the Jingdian Irrigation District from 1960 to 2020, which includes rainfall (mm), average temperature (°C), sunshine hours (h), relative humidity (%), and wind speed (m/s), were obtained from the Jingtai County National Meteorological Station and China Meteorological Administration. The data for the crop planting area and planting structure in the irrigation area between 2000 and 2020 were obtained from the Jingtaichuan Electric Power Lifting Irrigation Water Resources Utilization Center, and the crop coefficient (Table 1) was obtained from [34].

Table 1.
Crop coefficient for Jingdian Irrigation District.
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Effects of Crop Planting Structure on Net Irrigation Water Requirement
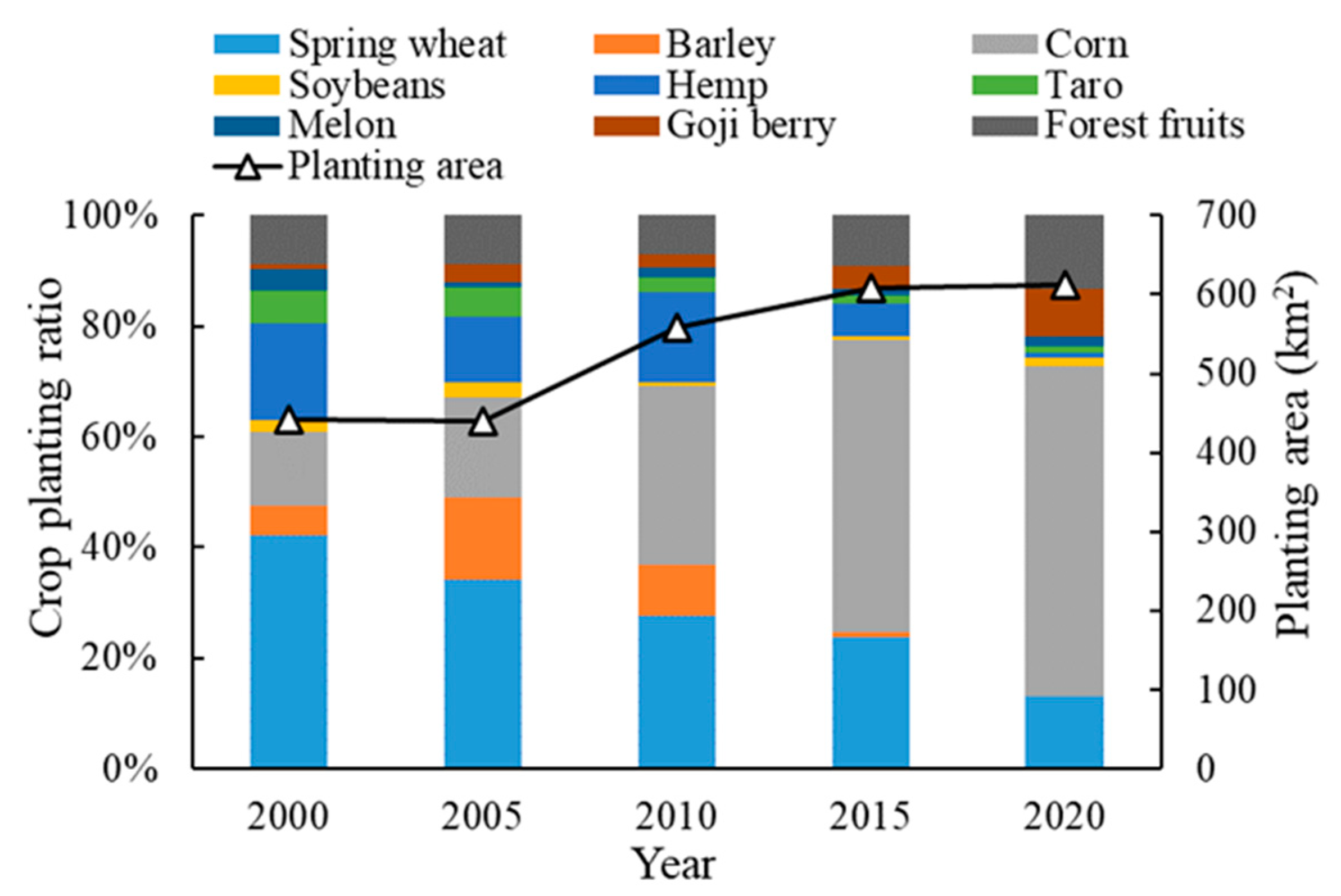
Figure 4 displays changes in the crop planting area and planting proportion in the Jingdian Irrigation District between 2000 and 2020. As agriculture developed in the irrigation area, the crop planting area has increased, from 441 km2 in 2000 to 612 km2 in 2020. The crops that have the largest planting proportion in the irrigation area are spring wheat and corn, with a multi-year average planting proportion of 60.1%. Between 2000 and 2020, the planting proportion of spring wheat decreased from 42.2 to 13.0%, and that of corn increased from 13.3 to 59.6%. The crop planting structure has changed significantly over time; therefore, we selected five years (2000, 2005, 2010, 2015, and 2020) with different planting structures as “typical years” to study the impact of climate uncertainty on the net irrigation water demand under these conditions.
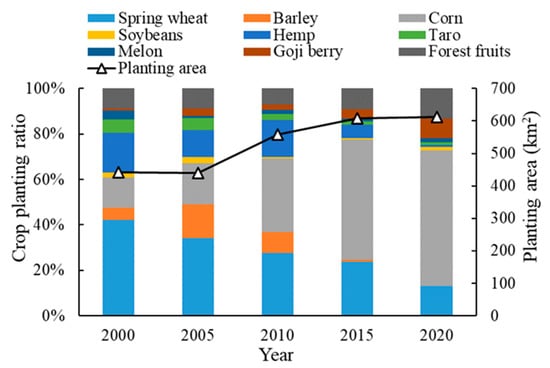
Figure 4.
Crop planting area and proportion for typical years.
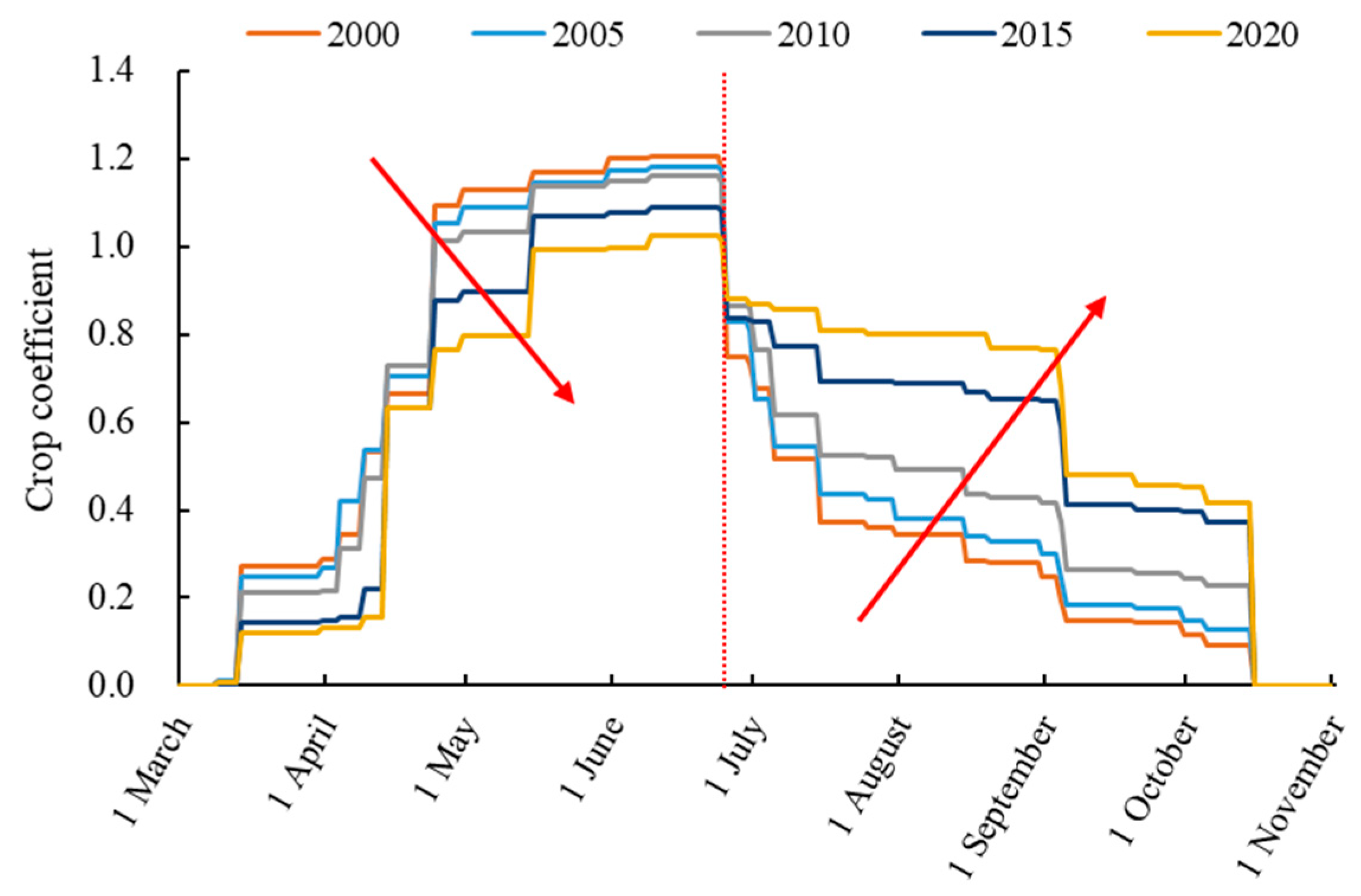
The daily crop coefficient calculated based on the crop planting area in the Jingdian Irrigation District is shown in Figure 5. The crop growth period in the entire irrigation area is March to October. The crop coefficient for each typical year increases gradually between March and June and decreases gradually between July and October. From 2000 to 2020, the crop coefficient for the months between March and June demonstrated a year-to-year decrease, and the crop coefficient for each month between July and October demonstrated a year-to-year increase. This is mainly due to the growth period of spring wheat being March to June. As the planting proportion of spring wheat decreases, the crop coefficient between March and June decreases each year. The growth period for maize is from July to October. As the maize planting proportion increases, the crop coefficient between July and October also increases each typical year.
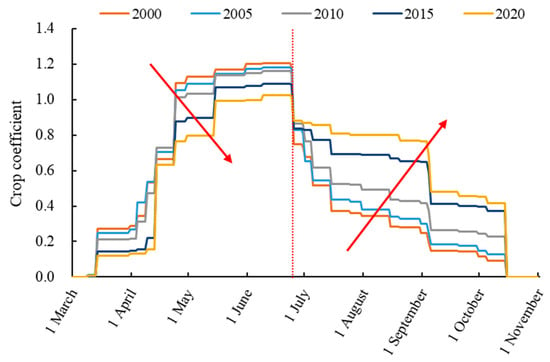
Figure 5.
Daily crop coefficient based on the crop planting area. (Arrows indicate the changing trend of crop coefficients from 2000 to 2020).
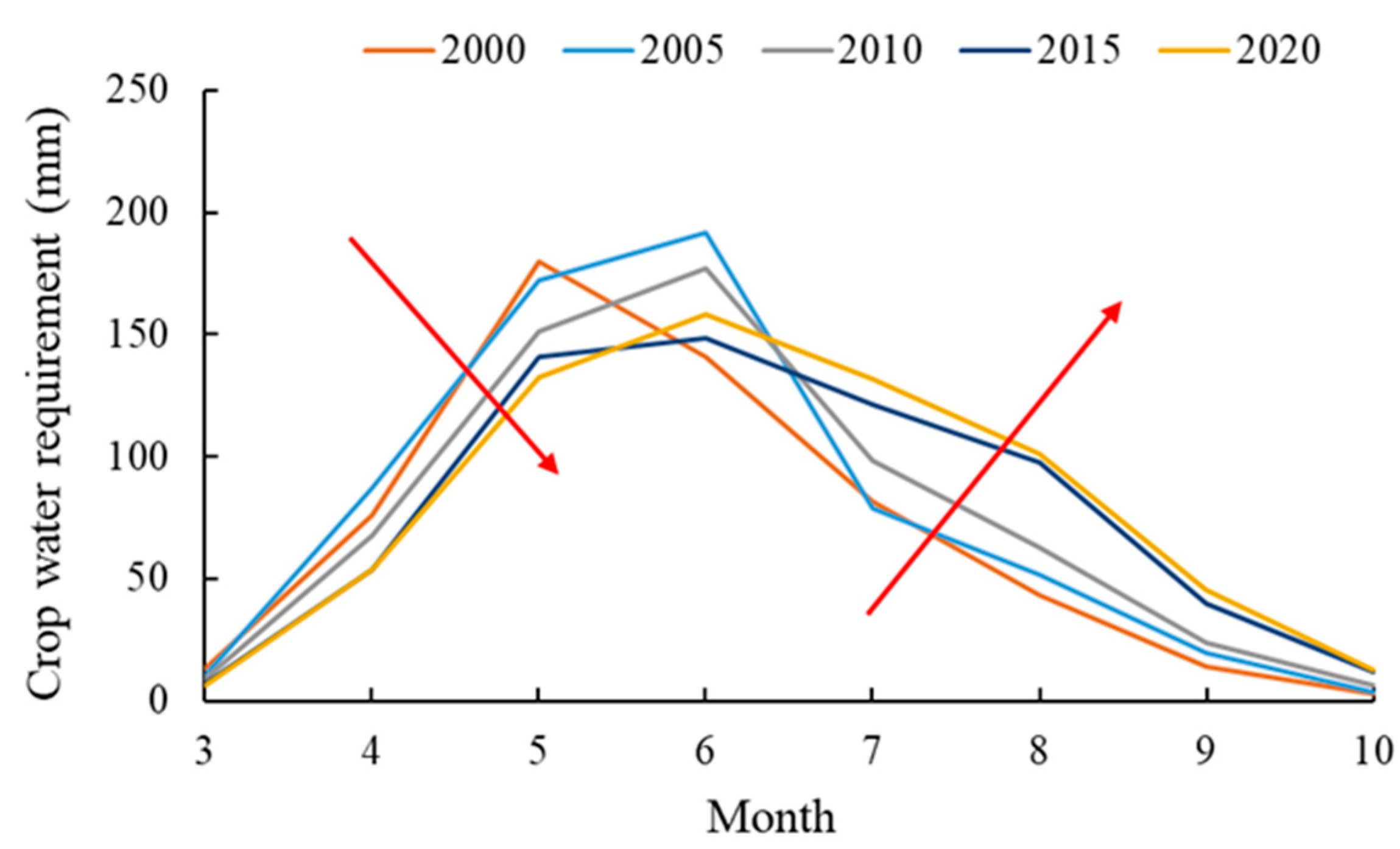
Figure 6 displays the calculation results for crop water demand. The crop water demand of each typical year demonstrates a single peak change, and the peak value concentration is from May to June. This is due to the development period for most crops in the irrigation area being concentrated between May and June and the crop coefficient during the development period being relatively large, meaning that the reference evapotranspiration is also large. In addition, as a result of the influence of climate factors, the peak value of reference evapotranspiration is also in June, meaning that the peak value of crop water demand each year is mainly concentrated in the same month. From 2000 to 2020, the crop water demand between March and June mainly demonstrated an increasing trend each year, whereas the crop water demand between July and October demonstrated a yearly decreasing trend. This is due to the change of the planting proportions of spring wheat and corn, resulting in the crop coefficient and crop water demand changing accordingly.
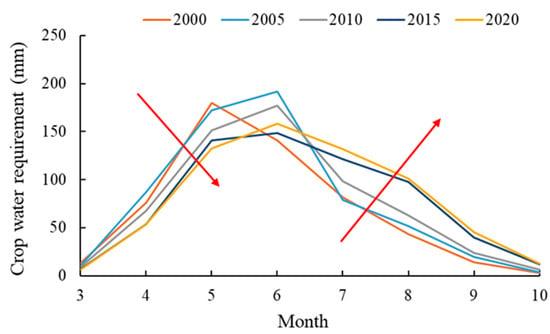
Figure 6.
Monthly crop water demand for typical years. (Arrows indicate the changing trend of crop water demand from 2000 to 2020).
3.2. Joint Distribution of Precipitation and Reference Evapotranspiration
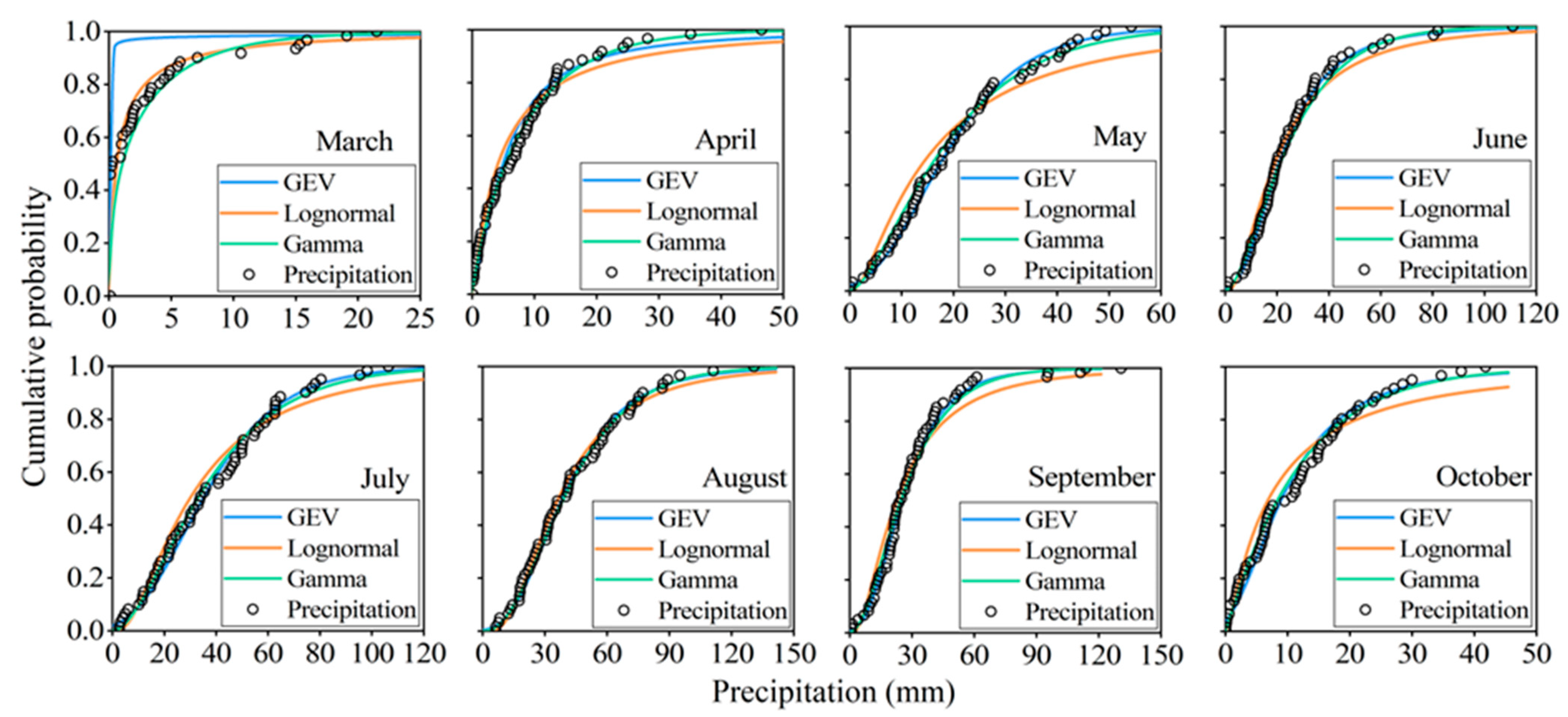
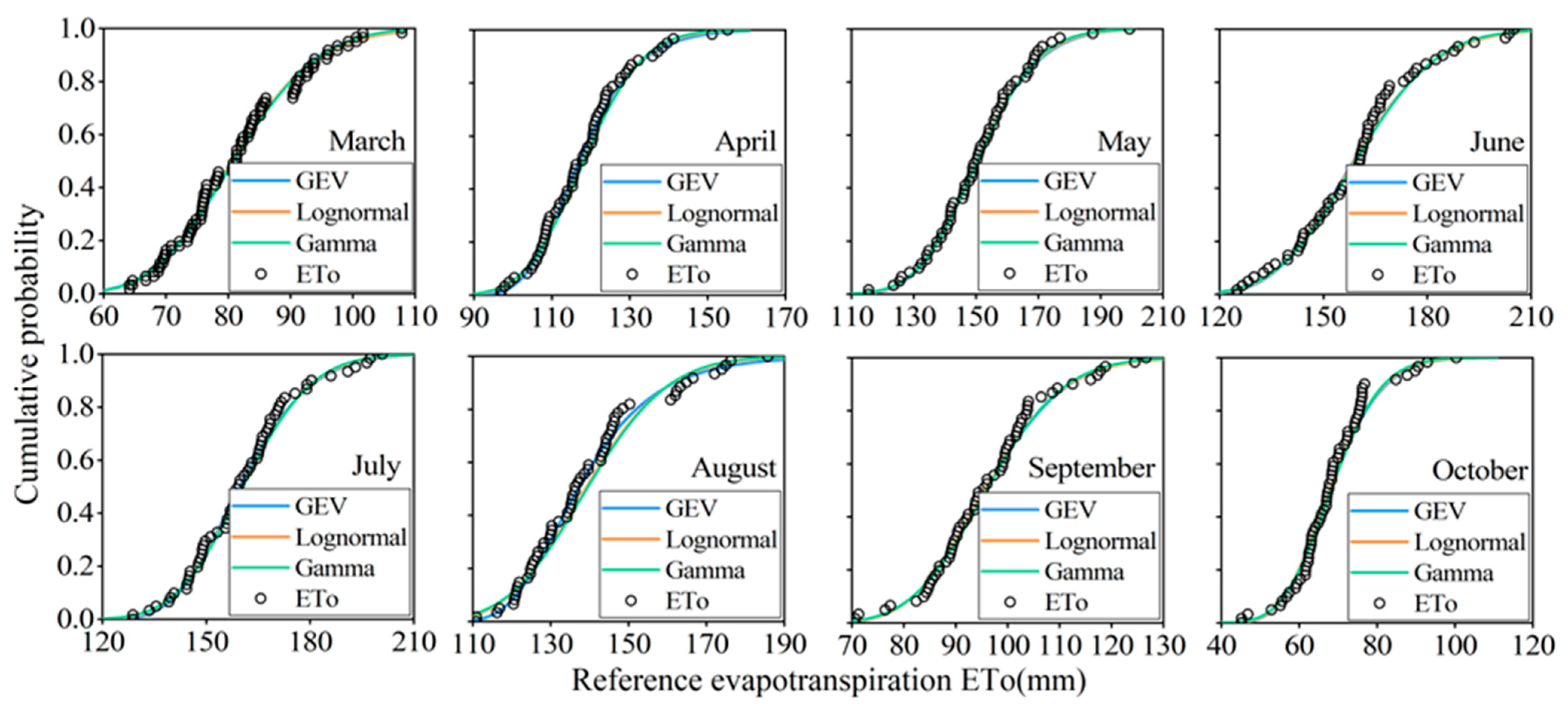
From data relating to the monthly precipitation and reference evapotranspiration of Jingdian Irrigation District between 1960 and 2020, the marginal distribution parameters of precipitation and reference evapotranspiration can be fitted. Table 2 shows that the monthly precipitation for every month, with the exception of March, passed the K–S test at the significance level of 0.05, which indicates that the fitting effects of the three distribution functions are good (Figure 7). The AIC value is used for judging the optimal precipitation distribution function. The AIC of gamma distribution or most months is the minimum, so gamma distribution is the optimal distribution function of monthly precipitation. Table 3 shows that the reference evapotranspiration for every month passed the K–S test at the significance level of 0.05, which indicates that the fitting effects of the three distribution functions are good (Figure 8). The AIC of lognormal distribution for most months is the minimum, meaning that the optimal distribution function of monthly reference evapotranspiration is lognormal distribution.

Table 2.
Parameters of marginal distribution for monthly precipitation.
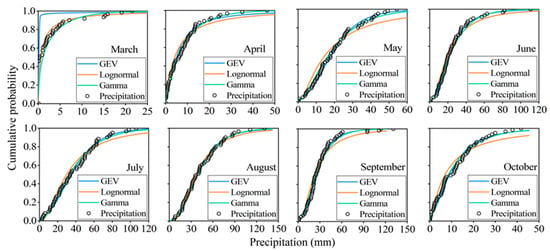
Figure 7.
Fitting diagram of marginal distribution for monthly precipitation. (The points represent monthly precipitation monitored by the weather station from 1960 to 2020. The curves represent the fitting results of three marginal distribution functions).

Table 3.
Parameters of marginal distribution for monthly reference evapotranspiration.
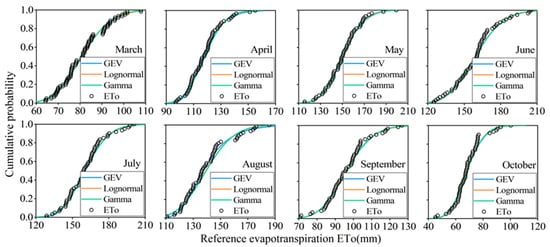
Figure 8.
Fitting diagram of marginal distribution for monthly reference evapotranspiration. (The points represent monthly reference evapotranspiration calculated by weather data from 1960 to 2020. The curves represent the fitting results of three marginal distribution functions).
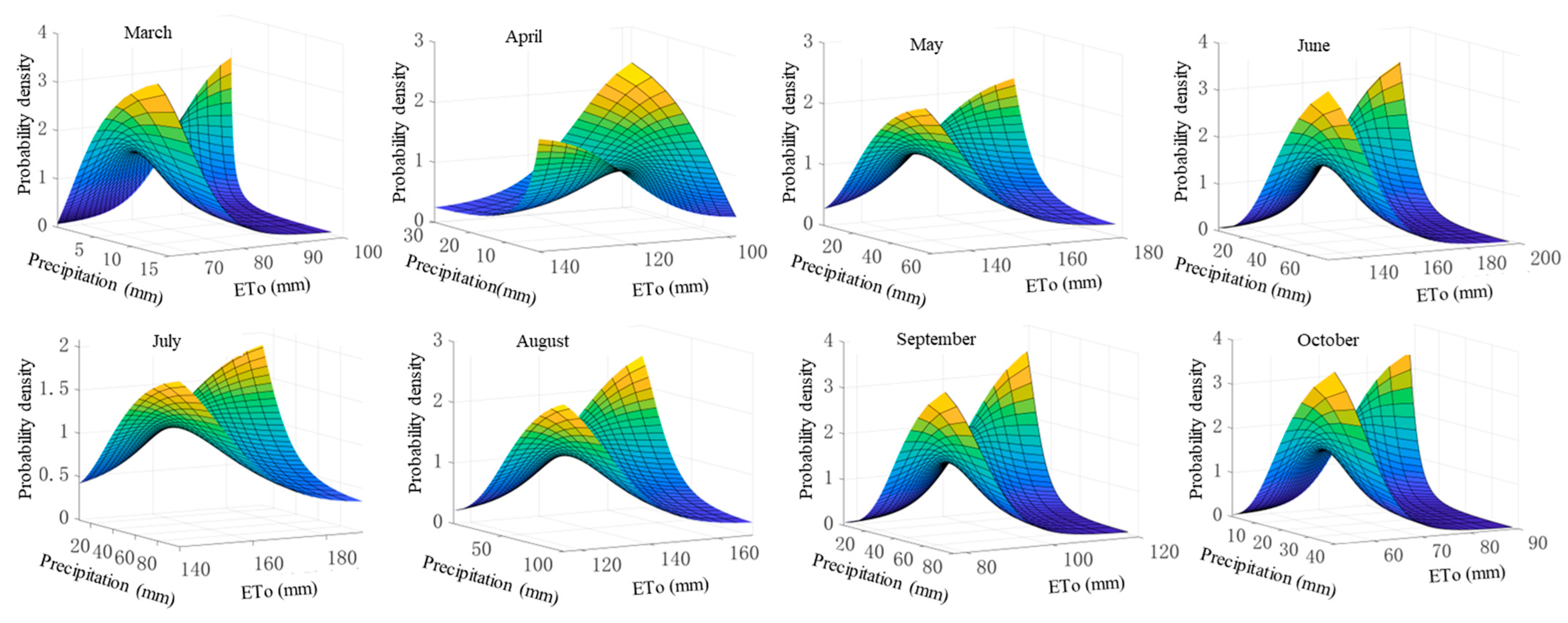
For the further analysis of the influence that the coupling effect of precipitation and reference evapotranspiration has on the net irrigation water requirement, a joint distribution model of two related variables must be established. Table 4 displays the parameter fitting results or the joint distribution function of monthly precipitation and reference evapotranspiration based on the Frank copula function. From Figure 9, the probability density map demonstrates a “saddle” shape. When one of precipitation and reference evapotranspiration is large and the other is small, the occurrence probability is high. When both are simultaneously large or small, the occurrence probability is low. It can be seen from Table 4 and Figure 9 that the larger the θ is, the smoother the joint distribution probability density graph is, and the smaller the θ is, the steeper the graph is. This shows that with the decrease of θ, the opposite trend of precipitation and reference evapotranspiration is more obvious.

Table 4.
Parameters of marginal distribution for monthly reference evapotranspiration.
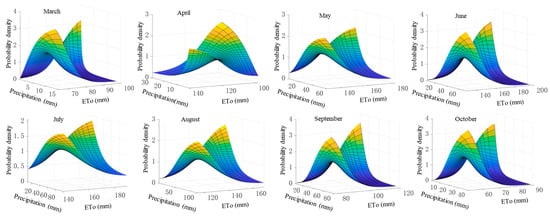
Figure 9.
Probability density diagram of joint distribution of precipitation and reference.
3.3. Uncertainty Analysis of Net Irrigation Water Requirement
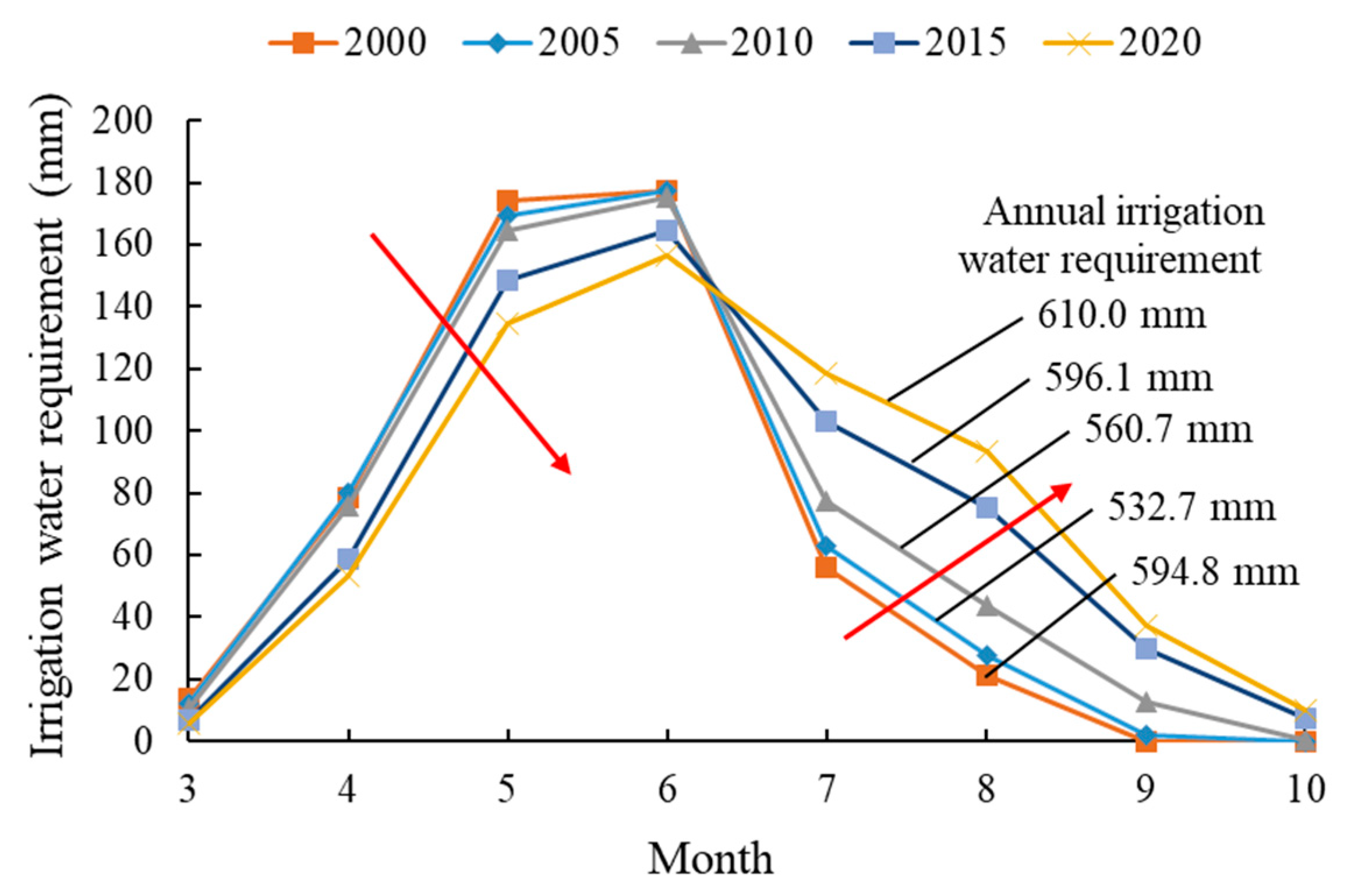
The net irrigation water requirement under different probabilities for each typical year was calculated using the CFMC method as shown in Table 5. Table 5 displays the monthly net irrigation water requirement under different probabilities in each typical year. As the probability of irrigation increases, net irrigation water requirement also increases. From Figure 10, the monthly net irrigation water requirement for each typical year when the probability of irrigation is 75% can be seen. The monthly net irrigation water requirement demonstrates a single peak distribution, and the maximum value that is affected by crop water demand is between May and June. For each typical year, the net irrigation water requirement from March to June demonstrated an increasing trend, whereas the net irrigation water requirement from July to October demonstrated a decreasing trend. From 2000 to 2020, year-to-year, the net irrigation water requirement from March to June decreased, with the contrary from July to October. The changing trend of net irrigation water requirement is consistent with that of crop water demand, which indicates that crop water demand significantly affects the net irrigation water requirement.

Table 5.
Monthly net irrigation water requirement under different probabilities for typical years.
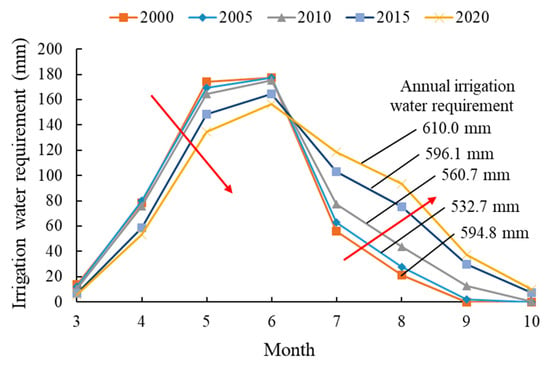
Figure 10.
Monthly net irrigation water requirement with a probability of irrigation of 75% for typical years. (Arrows indicate the changing trend of net irrigation water requirement from 2000 to 2020).
3.4. Advantages of the CFMC Model
Although previous research on the joint distribution of precipitation and reference evapotranspiration has been conducted [30,41], these studies failed to quantify the impact that joint distribution has on net irrigation water requirement. The main reason is that although a copula function can establish the coupling relationship between precipitation and reference evapotranspiration, the number of samples limits the statistical analysis of the net irrigation water requirement. However, determining the probability of irrigation water requirement is very important in the design of irrigation. If the probability of irrigation water requirement is determined by hydrological years, the problem of the uneven time distribution of the irrigation water requirement exists. With the aim of overcoming some of the shortcomings of previous research, and by using a Monte Carlo simulation, this paper addressed the problems of insufficient samples and uneven time distribution of the net irrigation water requirements. The CFMC method considers the influence of the joint distribution of precipitation and reference evapotranspiration on net irrigation water requirement but can also calculate the probability of the irrigation water requirement for a typical year of planting structures. The example of the Jingdian Irrigation District demonstrates the application value of the CFMC method, showing that it can provide a reference for the allocation of agricultural water resources and is certainly significant for the efficient utilization of water resources in the irrigation area.
4. Conclusions
Using a combination of a copula function and the Monte Carlo method, a CFMC method for calculating the probability of the net irrigation water requirement under a typical year of planting structures was proposed in this paper. The research results of the Jingdian Irrigation District demonstrated that:
(1) The optimal distribution functions of precipitation and reference evapotranspiration in the irrigation area are gamma and lognormal distributions.
(2) The probability density diagram of the joint distribution function of precipitation and reference evapotranspiration demonstrates a “saddle” shape. When either precipitation or reference evapotranspiration is larger and the other is smaller, the occurrence probability is high, but when both are simultaneously large or small, the occurrence probability is low.
(3) The maximum monthly net irrigation water requirement is between May and June. From 2000 to 2020, the net irrigation water requirement between March and June demonstrated an increasing trend year-to-year, whereas the net irrigation water requirement between July and October demonstrated a decreasing yearly trend. As the probability of irrigation water requirement increases, the net irrigation water requirement in the irrigation area also increases.
(4) Climate uncertainty has a significant impact on the regional irrigation water requirement, and this study provides a quantitative analysis of agricultural water requirements under different probabilities. For the water resources management department of a basin, the results of this study can provide a reference for the assessment of the water shortage risk and economic benefits in the basin.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agriculture12060801/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.F.; methodology, F.J.; data curation, F.J., K.H., L.L. and Y.P.; writing—original draft preparation, F.J.; writing—review and editing, L.F. and S.L.; supervision, L.F.; funding acquisition, L.F., S.L. and F.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 52079105, 51779205, and 51909209), the Shaanxi Provincial Water Conservancy Science and Technology Project (grant number 2020SLKJ-11), and the Doctoral Dissertations Innovation Fund of Xi’an University of Technology (grant number 310-252072019).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data relevant to this paper can be found in the Supplementary Materials.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interest.
References
- Asian Development Bank. Asian Water Development Outlook 2016: Description of Methodology and Data; Asian Development Bank: Mandaluyong, Philippines, 2017. Available online: http://www.adb.org/publications/awdo-2016-description-methodology-data (accessed on 22 January 2022).
- Wang, W.; Zhao, J.; Duan, L. Simulation of irrigation-induced groundwater recharge in an arid area of China. Hydrogeol. J. 2021, 29, 525–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, J.; Deryng, D.; Müller, C.; Frieler, K.; Konzmann, M.; Gerten, D.; Glotter, M.; Flörke, M.; Wada, Y.; Best, N.; et al. Constraints and potentials of future irrigation water availability on agricultural production under climate change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 3239–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wada, Y.; Van Beek, L.P.H.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Modelling global water stress of the recent past: On the relative importance of trends in water demand and climate variability. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 8, 7399–7460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, T.; Li, P.; Li, Z.; Hou, J.; Xiao, L.; Ren, Z.; Xu, G.; Yu, K.; Su, Y. The effects of freeze–thaw process on soil water migration in dam and slope farmland on the Loess Plateau, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 666, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siebert, S.; Döll, P.; Hoogeveen, J.; Faures, J.M.; Frenken, K.; Feick, S. Development and validation of the global map of irrigation areas. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2005, 9, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Wang, S.; Li, T.; Li, M.; Liu, D.; Cui, S. Temporal-spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors of regional agricultural water requirement indicators. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2019, 145, 04019019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Ding, W.; Fu, G. Water-energy-food nexus: Concepts, questions and methodologies. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 195, 625–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Li, L.; Li, M.; Li, T.; Liu, D.; Hou, R.; Zhou, Z. An interval parameter conditional value-at-risk two-stage stochastic programming model for sustainable regional water allocation under different representative concentration pathways scenarios. J. Hydrol. 2018, 564, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, V.K.; Haden, V.R.; Joyce, B.A.; Purkey, D.R.; Jackson, L.E. Irrigation demand and supply, given projections of climate and land-use change, in Yolo County, California. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 117, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, X.G.; Liu, S.X.; Lin, Z.H.; Guo, R.P. Regional crop yield, water consumption and water use efficiency and their responses to climate change in the North China Plain. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2009, 134, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojekunle, Z.O.; Lin, Z.; Xin, T.; Harrer, G.; Martins, A.O.; Bangura, H. Global climate change: The empirical study of sensitivity model in china’s sustainable development. Energy Source 2009, 31, 1777–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadi, S.; Todorovic, M.; Tanasijevic, L.; Pereira, L.S.; Pizzigalli, C.; Lionello, P. Climate change and Mediterranean agriculture: Impacts on winter wheat and tomato crop evapotranspiration, irrigation requirements and yield. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 147, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Kang, S.; Zhang, L. Temporal and spatial variations of evapotranspiration for spring wheat in the Shiyang river basin in northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 87, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Gong, L.; Jiang, T.; Chen, D.; Singh, V.P. Analysis of spatial distribution and temporal trend of reference evapotranspiration and pan evaporation in Changjiang (Yangtze River) catchment. J. Hydrol. 2006, 327, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McVicar, T.R.; Niel, T.G.V.; Li, L.; Hutchinson, M.F.; Mu, X.; Liu, Z. Spatially distributing monthly reference evapotranspiration and pan evaporation considering topographic influences. J. Hydrol. 2007, 338, 196–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Ni, G.; Cong, Z. Spatial distribution characteristics of irrigation water requirement for main crops in China. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2009, 25, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkomozepi, T.; Chung, S.O. Assessing the trends and uncertainty of maize net irrigation water requirement estimated from climate change projections for Zimbabwe. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 111, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tan, G.; Sun, Q.; Zhou, H. Variation of spring corn water requirement and its relationship with the meteorological factors in Chengde, Hebei province. J. Meteorol. Environ. 2012, 28, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, H.; Li, C.; Huang, H.; Pan, Z.; Chai, C. Analysis of irrigation water requirement and irrigation requirement index for cotton of Hebei province. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2013, 29, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Sun, F.; Peng, S.; Xu, J.; Luo, Y.; Jiao, X. Simulation of response of water requirement for rice irrigation to climate change. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2013, 29, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Fu, N.; Li, C.; Wang, L.; Yang, Q. Trends and causes analysis of water requirement for main grain crops in Henan Province. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2015, 46, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Su, X. Decomposition of influencing factors on irrigation water requirement based on LMDI method. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2017, 33, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, F.; Jiang, N.; Feng, Y.; Wang, M.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, Z. Water requirement calculation and trend analysis of main crops in Yellow River irrigation area. Yellow River 2021, 43, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surendran, U.; Sushanth, C.M.; George, M.; Joseph, E.J. Modelling the crop water demand using FAO-CROPWAT and assessment of water resource management: A case study of Palakkad district of humid tropical Kerala, India. Aquat. Procedia 2015, 4, 1211–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surendran, U.; Sushanth, C.M.; George, M.; Joseph, E.J. FAO-CROPWAT model based estimation of crop water need and appraisal of water resource management: Pilot study for Kollam district- humid tropical region of Kerala. Curr. Sci. 2017, 112, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S.F.; Ho, H.H.; Liu, C.W. Estimation irrigation water requirements with derived crop coefficients of upland and paddy crops in Chian Nan Irrigation Association Taiwan. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 82, 433–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Qi, X.; Fan, X.; Qiao, D.; Liang, Z. Impact of rainfall and evapotranspiration on estimation of irrigation requirement of summer maize. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2015, 31, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.; Huang, Z.; Qi, X.; Han, Y.; Liang, Z. Analysis on spatio-temporal variability and influencing factors of net irrigation requirement in People’s Victory Canal Irrigation Area. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2017, 33, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Ding, Z. Research on the joint probability distribution of rainfall and reference crop evapotranspiration. Paddy Water Environ. 2017, 15, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop evapotranspiration-guidelines for computing crop water requirements-FAO irrigation and drainage paper 56. J. Hydrol. 1998, 285, 19–40. Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/X0490E/X0490E00.htm (accessed on 22 January 2022).
- Zhou, J.L.; Dong, X.G. An experimental study on potential evapotranspiration in arid area in Xinjiang Province. J. Irrig. Drain. 2002, 21, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolk, J.A.; Howell, T.A.; Evett, S.R. Evapotranspiration and yield of corn grow on three high plains soils. Agron. J. 1998, 90, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Fei, L.; Li, S.; Xue, C.; Shi, Z.; Hinkelmann, R. Development of “water suitable” agriculture based on a statistical analysis of factors affecting irrigation water demand. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 744, 140986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jie, F.; Fei, L.; Li, S.; Hao, K.; Liu, L.; Zhu, H. Prediction model for irrigation return flow considering lag effect for arid areas. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 256, 107119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.P.; Zhang, L. IDF curves using the Frank Archimedean copula. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2007, 12, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, E.J.; Reed, D.W.; Faulkner, D.S.; Reynard, N.S. The FORGEX method of rainfall growth estimation I: Review of requirement. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 1999, 3, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goel, N.K.; Kurothe, R.S.; Mather, B.S.; Vogel, R.M. A derived flood frequency distribution for correlated rainfall intensity and duration. J. Hydrol. 2000, 228, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, H.; Mikkelsen, R.S.; Rosbjerg, D.; Harremoes, P. Regional estimation of rainfall intensity-duration-frequency curve using generalized least square regression of partial duration series. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabri, A.B.; Darud, Z.M.; Ariff, N.M. Regional analysis of annual maximum rainfall using TL-moments method. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2011, 140, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, S.; Duan, A. Least squares support vector machines model for predicting reference evapotranspiration based on weather forecasts. Adv. Water Sci. 2010, 21, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Kang, S.; Su, X.; Tong, L. Simulation and uncertainty analysis of net irrigation requirement in agricultural area. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2012, 28, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z. Irrigation and Drainage Engineering; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2010; Available online: http://hn.sslibrary.com/showbook.do?dxNumber=10253024&d=38712C21D2FB0683E2A156055DD36BD2&fFenleiID=0S2070 (accessed on 22 January 2022).
- Patwardhan, A.S.; Nieber, J.L.; Johns, E.L. Effective rainfall estimation methods. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 1990, 116, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Düll, P.; Siebert, S. Global modeling of irrigation water requirements. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweizer, B. Introduction to copulas. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2007, 12, 346. Available online: http://ascelibrary.org/doi/abs/10.1061/%28ASCE%291084-0699%282007%2912%3A4%28346%29 (accessed on 22 January 2022). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, C.; Huang, Q.; Guo, A. Characteristic analysis and uncertainty assessment of joint distribution of flow and sand in Jinghe River basin. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2019, 50, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Yu, K.; Gottschalk, L. Estimation of the distribution of annual runoff from climatic variables using copulas. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 7134–7152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Guo, S.; Xiong, L.; Xu, C.Y. Hydrological uncertainty processor based on a copula function. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2017, 63, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).