Abstract
Succinea snails are considered to be invasive and pestiferous gastropods to those in the floricultural industry. Their small size makes them difficult to locate within large plant shipments, and their presence on decorative plants can constitute for an entire shipment to be rejected for sale and distribution. Research performed on Succinea snails is limited, especially in terms of effective mitigation strategies. The nematode Phasmarhabditis hermaphrodita is a biological control agent used on pestiferous gastropods throughout some European nations. Here, three strains of Phasmarhabditis from the United States (P. hermaphrodita, P. californica, and P. papillosa) were assessed as biological control agents against Succinea snails in controlled laboratory conditions, along with the molluscicide Sluggo Plus® as a control. All species of Phasmarhabditis applied at 30 IJs/cm2 caused significant mortality compared to the non-treated control and treatment with Sluggo Plus®. P. californica caused 100% mortality 6 days after exposure, while P. hermaphrodita and P. papillosa caused the same mortality rate 7 days after exposure. The molluscicide was unable to cause significant mortality compared to the non-treated control. Additional research with US Phasmarhabditis strains, including their non-target effects and distribution may lead to their being a viable option for biological control against Succinea snails.
1. Introduction
Snails and slugs belong to the class Gastropoda (Phylum: Mollusca) and are the only gastropods who have successfully invaded and occupied a terrestrial landscape [1]. They serve vital roles in multiple ecosystems where they act as detritovores decomposing plant and animal litter which falls to the ground, while also playing a herbivorous role with live plant matter [2,3]. While gastropods can play important roles throughout these ecosystems, they are considered serious pests in most agricultural settings. Snail and slug pests can cause damage to plants both above and below ground. Damage can be severe, causing death, thinning, or wilting to the plant, and can also cause less fruit production [4,5,6]. In a horticultural setting, in addition to damage inflicted to plants from gastropod pests, the presence of slime, feces, or whole slugs significantly reduces the value to retailers. In some cases, entire shipments can be rejected with the loss of payment to the grower due to finding evidence of slug or snail contamination [4]. The economic damage caused by terrestrial gastropods is difficult to assess due to a lack of reporting and the confusion of symptoms of gastropod attack with other pests and vice versa. Additionally, economic damage caused by gastropods happens to be greater when sale prices are high and a crop is more valuable, which leads to a misleading economic assessment [4,7].
Slugs and snails can also spread a variety of diseases to a diverse set of hosts, negatively affecting their sale and health. They can affect livestock by vectoring sheep and pig lungworms in an agricultural setting where they act as intermediate hosts to the parasites [8]. They can also spread disease to humans, acting as an intermediate host and vector source of Angiostrongylus cantonensis (Chen, 1935) (Strongylida: Metastrongylidae), the causative agent for rat lung worm disease [9]. Additionally, they are known to vector plant pathogens such as Alternaria brassicicola, the causative agent for black leaf spot, and other plant pathogenic fungi [10,11,12]. Furthermore, they have been suspected to have contributed to multiple salad crop recalls due to the identification of Campylobacter spp. and Escherichia coli in gastropod feces [13,14]. Business can also be affected simply by the presence of slugs or snails. Some invasive species, such as Theba pisana (Müller, 1774) (Stylommatophora: Helicidae) can grow to such large populations that they ruin the aesthetics and use of an area by being present or aestevating in windows, tree trunks, sidewalks, and various other public spaces [15,16].
One particular snail of interest is the Succinea spp., also known as the amber snail. Although visible damage on produce by Succinea snails has not been reported, it is nevertheless a nuisance pest, and considered one of the major gastropod pests as they are often the most common snails found by US inspectors of plant shipments; likely due to their small size where they may be overlooked [17,18]. The common amber snail Succinea putris (Linnaeus, 1758) (Stylommatophora: Succineidae) ranges from 6 to 8 mm in length, however there are multiple species of Succinea snails and it is extremely difficult to morphologically identify them without genetic sequencing (http://www.molluscs.at/gastropoda/terrestrial.html?/gastropoda/terrestrial/succineidae.html, accessed on 13 March 2022). To date, there are three species on record in California, the latter of which was introduced [19]: S. california (Groose and Fisher 1878) (Stylommatophora: Succineidae); S. rusticana (Gould 1846) (Stylommatophora: Succineidae); and S. luteola) Gould 1848) (Stylommatophora: Succineidae). Due to the difficulty of identification, the exact range of habitat for these snails needs further study. Previous records of these species were limited mostly to Northern California: S. rusticana was found in Sonoma, San Francisco, San Benito, Kern, and San Luis Obispo, while S. california was found in Monterey and San Diego. During a series of gastropod surveys in California nurseries and garden centers, Succinea sp. was recorded as one of 18 recovered species [20]. It was found in 5 out of 28 counties surveyed (Humboldt, San Diego, Tulare, San Bernardino, and Stanislaus). The highest recovery was from Central California, with 8.4% of the total collected in the area. Currently, there are 16 counties where this snail has been detected (Table 1), and with more surveys and increased horticultural trade, it is likely that this snail will increasingly become a threat to the industry.

Table 1.
The species of Succinea found in California and the counties they were collected from.
Several reports affirm that this snail causes damage to plants and the horticultural trade industry on a regular basis [21,22]. Managing Succinea spp. is therefore a necessity to prevent further losses to the industry.
A common method for mitigating gastropod pests includes the use of chemical molluscicides. They have been used with varying levels of success against Succinea snails [22]. While chemical control methods can be effective, methods such as methiocarb and metaldehyde baits are non-targeted and can harm beneficial/native molluscs, fishes, earthworms, and more [23,24]. A common molluscicide marketed as a safer alternative is Sluggo Plus®, a newer formulation of iron phosphate and Spinosad (an insecticide) developed to kill gastropods as well as some insects, e.g. earwigs, cutworms, sowbugs, and pillbugs [25,26]. This new formulation has not had a large amount of non-target testing and therefore non-target effects are not known. However, iron phosphate has been found to decrease the survival and growth of earthworms Lumbricus terrestris (Linnaeus, 1758) (Opisthopora: Lumbricidae) and Eisenia fetida (Savigny, 1826) (Opisthopora: Lumbricidae) [27,28]. Therefore, Sluggo Plus® is not completely safe to the ecosystem as it can have deleterious effects on non-target earthworms.
Biological control may offer a more targeted approach to gastropod pest control which lacks many of the issues that arise with the use of chemical molluscicides. One biological control strategy is the use of the nematode Phasmarhabditis hermaphrodita (Schneider, 1859) (Rhabditida: Rhabditidae). Phasmarhabditis hermaphrodita and other members of its genus may not be as target specific as parasitoids which can target insects belonging to a specific species or genus. However, the nematode does solely target terrestrial organisms within the class Gastropoda. This quality makes it more target specific than commercially available molluscicides. Phasmarhabditis hermaphrodita was discovered in Europe where it has been commercialized under the brand name Nemaslug®. Although P. hermaphrodita, along with P. californica (Tandingan De Ley et al., 2016) (Rhabditida: Rhabditidae) and P. papillosa (Schneider, 1866) (Rhabditida: Rhabditidae) has been recovered in California [29,30,31] as well as Oregon (McDonnell et al., 2018b), the nematode is not yet available commercially and registered for use in the United States. P. hermaphrodita, as well as the other 2 species have been found to cause significant mortality on a number of gastropod pests in laboratory and field experimental settings [15,32,33,34,35,36]. P. hermaphrodita is also safe to most non-targets tested with no reported detrimental impacts to the local ecosystem [37,38,39,40]. However, it should be noted that some endemic species are susceptible to Phasmarhabditis infections, and further non-target testing is needed before commercial application occurs in places that the nematode has been discovered [41,42].
Data from recent surveys revealed that Phasmarhabditis species are distributed and established throughout the entire state of California with P. californica being the most widely distributed [20]. Preliminary studies also demonstrated the nematode’s biological control potential, which was either comparable to or better than the molluscicide Sluggo Plus® against the giant African land snail (Lissachatina fulica) (Férussac, 1821) (Stylommatophora: Achatinidae) (Mc Donnell et al., 2018a), Deroceras reticulatum (Müller, 1774) (Stylommatophora: Agriolimacidae) [43] and Theba pisana in the laboratory [15,16]; and D. reticulatum in the lath house [34]. In the latter assays, Phasmarhabditis spp. helped to protect ornamental Canna from further plant damage [34]. In this experiment, we assessed the mortality of Succinea spp. after exposure to the three US strains of P. californica, P. hermaphrodita, and P. papillosa. This is the first report of the potential of Phasmarhabditis spp. in mitigating Succinea snails in a laboratory setting.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Arena Design
The arenas consisted of 350 mL, 104 cm2 deli containers (11.5 cm diameter, 3.5 cm height). Previous testing showed that copper was effective at thwarting snails, so the inside walls of the arenas were covered with 3 cm wide copper tape and each were fitted with a perforated lid to allow for air flow [15]. Arenas were filled with 40–45 g of soil composed of 25% UC Mix #3 and 75% Sungro Sunshine no. 4 Mix [44]. Soil moisture was then adjusted by adding about 45 mL of DI H2O and mixing. Arenas were kept in lab at room temperature which ranged between 22 °C and 23 °C.
2.2. Preparation of Nematode Inocula
Phasmarhabditis infective juveniles (IJs) were collected from modified white traps [45] with freshly killed Ambigolimax valentianus (Férrusac 1822) (Stylommatophora: Limacidae) previously inoculated with mixed stages of nematodes from agar plate cultures [15]. All mass-produced nematodes from the latter were grown on Nematode Growth Medium (NGM; 1 L: 3 g NaCl, 20 g Agar, 2.5 g Peptone, 975 mL deionized H2O, 10 mL Uracil (2 g/L) were added to a liter of deionized water, autoclaved, and let cool, to which 25 mL filtered 1 M KPO4, 1 mL filtered 1 M MgSO4, 1 mL 1 M CaCl2, and 1 mL Cholesterol (5 mg/mL) were added. Collected IJs were stored in tissue culture flasks with water and kept in the incubator at 17 °C until ready for use. The number of nematodes in each tissue culture flask was quantified by counting the number of IJs in 10μL droplets five times and taking an average of the counts. Before applying nematodes to the arena, the desired number of nematodes per treatment was pipetted into 10 mL falcon tubes, and the total volume was adjusted by adding deionized (DI) H2O to standardize the volume and density of the inoculum.
All trials and replicates of lethality assays used a standardized concentration of nematodes based on the recommended dose for the biological control product Nemaslug® (BASF Agricultural Solutions, Stockport, United Kingdom). Therefore, all tested Phasmarhabditis species were applied at a rate of 30 IJs/cm2. For chemical control, the molluscicide Sluggo Plus® (Monterey Lawn and Garden, Fresno, CA, USA) (0.97% iron phosphate and 0.07% Spinosad a mixture of spinosyn A and spinosyn D) was used at the higher recommended dose of 4.88 kg/m2. Non-treated control treatments consisted of arenas with snails only without any nematodes.
2.3. Experimental Setup
Succinea snails provided by Monrovia Nursery were collected from their nurseries in Visalia, CA, USA and shipped to UC Riverside under CDFA permit 3449. Upon delivery, the snails were organized into 3 different groups based on size and weight. One group composed of small snails, one of medium snails, and the last of larger snails. The mean weights of Succinea snail used was 0.451 g while the average length was 0.78 cm (SD = 0.247). Mean weights were determined by weighing all snails together and dividing the total weight by ten. All snails were observed to be quite similar in size and weight.
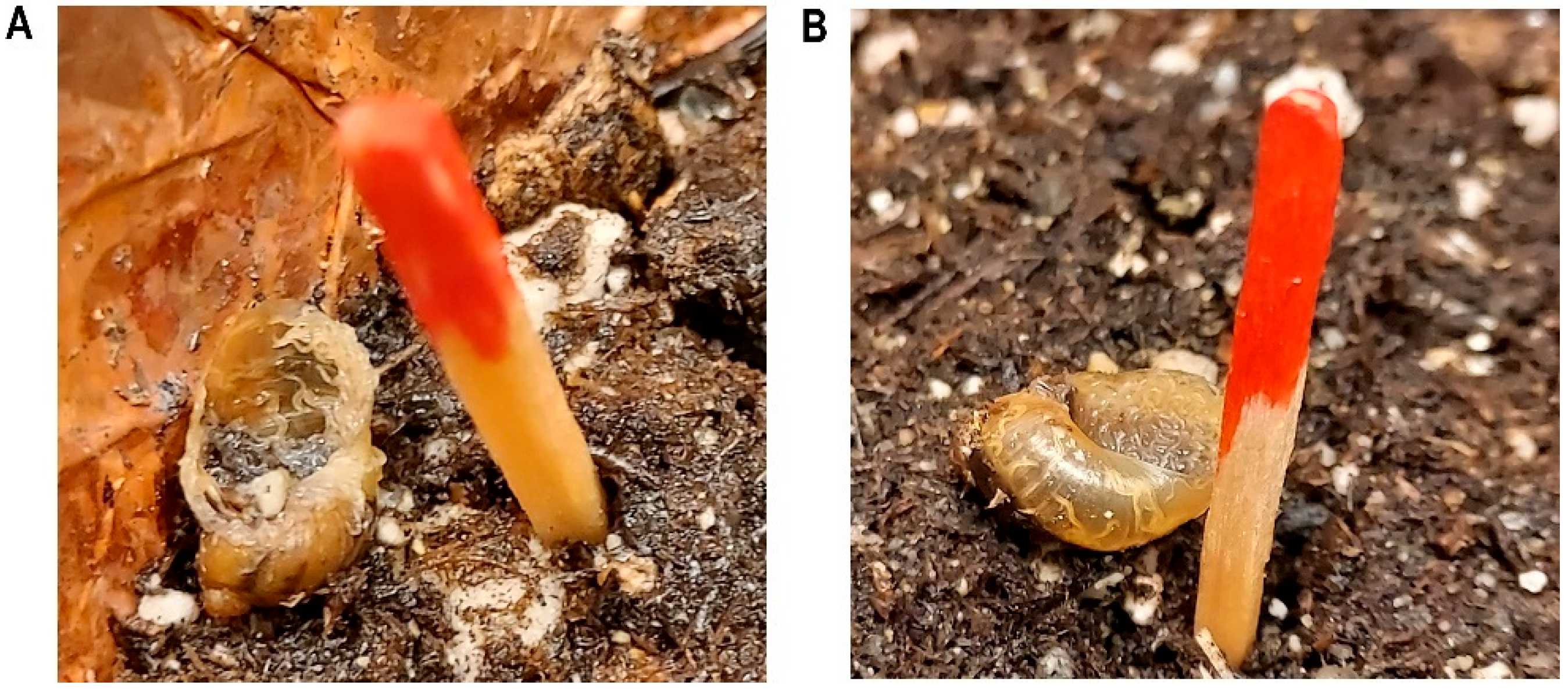
Ten pre-weighed and measured snails from each organized group were introduced onto the soil of the arena. Immediately after placing the snails in the arena, the nematode inoculum was slowly applied to the arena using an auto pipettor. The number of dead snails was recorded daily for one week. A toothpick method was utilized to check whether the snails were successfully killed [15]. In summary, if a snail was suspected to be dead, a toothpick was placed next to it. If the snail did not move from the toothpick after 24 h, then it was considered dead. All killed snails also exhibited similar symptomology in which mixed stages of nematodes were present on the foot of the snail or inside of the shell (Figure 1A,B). Also, snails which were dead did not respond to any stimuli when touched or prodded with a toothpick, and exhibited zero tissue movement. They also had a retracted or dissolved muscular foot (Figure 1A,B). The experiments were repeated three times and each trial had a total of three replicates. Each replicate was organized by snail size utilizing the small, medium, and large snail groups to account for size bias.

Figure 1.
Dead Succinea snails with mixed stages of Phasmarhabditis nematodes present four days after being exposed to the recommended dose of Phasmarhabditis (30 IJs/cm2) (A,B).
2.4. Statistical Analysis
All statistical analyses were performed with GraphPad Prism 9 (San Diego, CA, USA), utilizing Mantel-Cox log-rank analyses to compare each treatment to each other.
3. Results
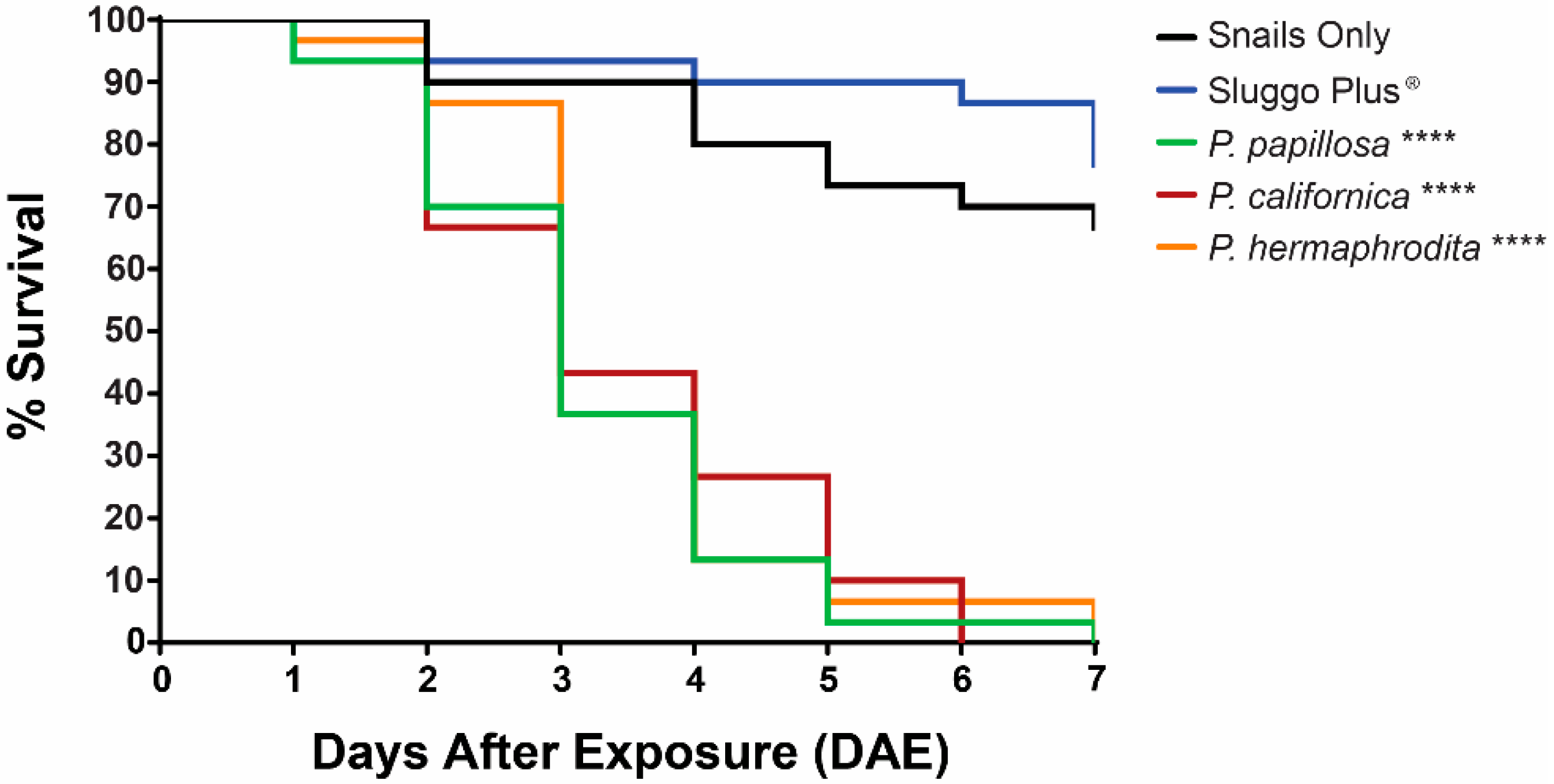
Succinea snails began to die one day after exposure (DAE) to P. papillosa at the recommended rate of 30 IJs/cm2. All other Phasmarhabditis treatments caused mortality two DAE at the recommended rate of 30 IJs/cm2. Phasmarhabditis treatments caused significantly higher mortality than the snail only control (p < 0.0001 for all Phasmarhabditis treatments) and the Sluggo Plus® control (p < 0.0001 for all Phasmarhabditis treatments). All Phasmarhabditis treatments caused 100% mortality within seven DAE; however P. californica was able to cause 100% mortality within the shortest amount of time, causing 100% mortality six DAE (Figure 2). All dead snails treated with Phasmarhabditis were observed to have mixed stages of nematodes present within their shell (Figure 1). Based on low mortality differences, Sluggo Plus® and untreated control mortality rates did not significantly differ from each other (p = 0.340).
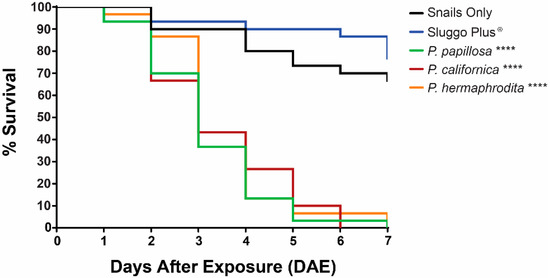
Figure 2.
Kaplan-Meyer Graph indicating the percent survival of Succinea snails treated with the recommended dose (30 IJs/cm2) of Phasmarhabditis papillosa (green), Phasmarhabditis californica (Red), Phasmarhabditis hermaphrodita (Orange), the molluscicide Sluggo Plus® (Blue), or the control treatment with Succinea snails only (Black), over the course of 7 days. **** indicates a p value of less than 0.0001 when compared to the control treatment.
4. Discussion
This is the first report on the mortality and susceptibility of Succinea spp. exposed to the three United States strains of Phasmarhabditis spp. This demonstrates for the first time that the local strains of Phasmarhabditis can be used effectively to mitigate the presence of Succinea. However, more research on their ecological impact and non-target effects needs to be assessed. Due to the similarities of virulence, behavior, and genetics in European strains and United States strains, it is likely that the US strains will have similar non-target effects to the well tested and commercialized European P. hermaphrodita strain [37,38,39,40]. This is especially true for the US strain of P. hermaphrodita.
Based on our results, the local strains caused 100% mortality to Succinea snails within one week (Figure 2). Persistence of the nematodes should be further assessed to explore how frequently treatments are necessary. The commercialized strain of P. hermaphrodita (Nemaslug®) states that the strain protects crops from pestiferous gastropods for six weeks, indicating that the nematodes persist for the same amount of time (https://www.nematodesdirect.co.uk/ (accessed on 18 March 2022)). It was previously found that soil recovery of Phasmarhabditis was relatively low three weeks after application in a lath house setting [34]. However, that particular aspect of the study was performed in one assay and further experimentation is needed for that to be conclusive.
The mortality of the Succinea snails during the pathogenicity assay was comparable to the mortality results of juvenile T. pisana being exposed to the same three strains of Phasmarhabditis [15]. In both experiments, we observed near 100% mortality about one week after exposure to Phasmarhabditis treatment. The T. pisana mortality assay observed 100% mortality across all Phasmarhabditis treatments six DAE, while it took seven DAE to achieve similar results with Succinea. Due to the small stature of each of these gastropods, it is possible that the three US strains of Phasmarhabditis typically kill smaller gastropods within a week. However, larger gastropods likely endure a longer infection period until death, as seen with larger adult T. pisana, and the grey field slug, D. reticulatum [16,34]. Due to some gastropods requiring time for mortality to occur upon exposure to treatment, it is possible that the Sluggo Plus® treatment could have caused mortality after prolonged exposure. Succinea snails were exposed to the molluscicide treatment for the same length of time as those exposed to Phasmarhabditis treatment. Future experimentation with the molluscicide may benefit from observing the mortality of the snails for a longer period of time.
Results showed that a larger number of Succinea snails in the control group died than those exposed to the iron phosphate molluscicide Sluggo Plus® (Figure 2). However, only a total of three additional snails died in the control group compared to the Sluggo Plus® treated snails throughout the entire experiment. There were no statistical differences between the two treatments. Ultimately, Sluggo Plus® was shown to be ineffective at killing Succinea snails. It is possible that control mortality was observed due to the small size of the snails. Some species of snails show a strong correlation between size and susceptibility to Phasmarhabditis treatments, where smaller gastropods are killed more easily [15,16,46,47]. Susceptibility to Phasmarhabditis also seems to be species dependent as well [33,36,40].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.S. and I.T.D.L.; methodology, J.S. and I.T.D.L.; software, J.S.; validation, J.S., I.T.D.L. and A.R.D.; formal analysis, J.S.; investigation, J.S. and I.T.D.L.; resources, I.T.D.L. and A.R.D.; data curation, J.S.; writing—original draft preparation, J.S.; writing—review and editing, I.T.D.L. and A.R.D.; visualization, J.S.; supervision, I.T.D.L. and A.R.D.; project administration, I.T.D.L. and A.R.D.; funding acquisition, I.T.D.L. and A.R.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Please add: This research was funded by the United States Department of Agriculture Specialty Crop Multi-state Program (USDA-SCMP) in partnership with the California Department of Food and Agriculture (CDFA) (2018–2022), grant number 12509488 and also the CANERS Foundation through California Association of Nurseries and Garden Centers (GANGC) and the Plant California Alliance (2019–2022).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All raw datasets can be found on Mendeley Data at Jacob, Jacob; Tandingan De Ley, Irma (2022), “Succinea Pathogenicity Assay”, Mendeley Data, V1, doi: 10.17632/xpbj4m4kbb.1.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank John Keller, Vice President of Planning and Research, Monrovia, for providing snail and slug specimens and valuable information on the importance of Succinea spp. in California’s horticultural industry.
Conflicts of Interest
Irma Tandingan De Ley declares that she is a co-inventor on a patent entitled Mollusk-killing Biopesticide (WO2017059342A1).
References
- Sallam, A.; El-Wakeil, N. Biological and Ecological Studies on Land Snails and Their Control. In Pest Management and Pest Control-Current and Future Tactics; InTech Publishing: Shanghai, China, 2012; pp. 413–444. [Google Scholar]
- Jennings, T.J.; Barkham, J.P. Litter Decomposition by Slugs in Mixed Deciduous Woodland. Ecography 1979, 2, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prather, C.M.; Pelini, S.L.; Laws, A.; Rivest, E.; Woltz, M.; Bloch, C.P.; Del Toro, I.; Ho, C.K.; Kominoski, J.; Newbold, T.A.S.; et al. Invertebrates, Ecosystem Services and Climate Change. Biol. Rev. 2013, 88, 327–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howlett, S.A. Terrestrial Slug Problems: Classical Biological Control and Beyond. CAB Rev. 2012, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Port, C.M. The Biology and Behavior of Slugs in Relation to Crop Damage and Control. Agric. Zool. Rev. 1986, 1, 255–299. [Google Scholar]
- Barker, G.M. Molluscs as Crop Pests; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, A.; Crook, M. The Use of Molluscicides in UK Agriculture and Their Effects on Non-Target Organisms. Malacol. Soc. Lond. Mini-Rev. 2003. Available online: https://malacsoc.org.uk/malacological_bulletin/Mini-Reviews/2Molluscicides/molluscicide.htm (accessed on 13 March 2022).
- Rose, J.H. Lungworms of the Domestic Pig and Sheep. Adv. Parasitol. 1973, 11, 559–599. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.R.; Hayes, K.A.; Yeung, N.W.; Cowie, R.H. Diverse Gastropod Hosts of Angiostrongylus cantonensis, the Rat Lungworm, Globally and with a Focus on the Hawaiian Islands. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, S.; Vago, C. Transmission of Alternaria brassicicola by Slugs. Plant Dis. Report. 1966, 50, 764–767. [Google Scholar]
- Turchetti, T.; Chelazzi, G. Possible Role of Slugs as Vectors of the Chestnut Blight Fungus. Eur. J. For. Pathol. 1984, 14, 125–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wester, R.E.; Goth, R.W.; Webb, R.E. Transmission of Downy Mildew of Lima Beans by Slugs. Phytopathology 1964, 54, 749. [Google Scholar]
- Raloff, J. Lettuce Liability: Programs to Keep Salad Germ-Free, Raise Wildlife, and Conservation Concerns. Sci. News 2007, 172, 362–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sproston, E.L.; Macrae, M.; Ogden, I.D.; Wilson, M.J.; Strachan, N.J.C. Slugs: Potential Novel Vectors of Escherichia coli O157. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tandingan De Ley, I.; Schurkman, J.; Wilen, C.; Dillman, A.R. Mortality of the Invasive White Garden Snail Theba pisana Exposed to Three US Isolates of Phasmarhabditis Spp. (P. hermaphrodita, P. californica, and P. papillosa). PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schurkman, J.; Tandingan De Ley, I.; Dillman, A.R. Size and Dose Dependence of Phasmarhabditis Isolates (P. hermaphrodita, P. californica, P. papillosa) on the Mortality of Adult Invasive White Garden Snails (Theba pisana). PLoS ONE, 2022; in review. [Google Scholar]
- Hayes, K.; Tran, C.; Cowie, R. New Records of Alien Mollusca in the Hawaiian Islands: Non-Marine Snails and Slugs (Gastropoda) Associated with the Horticultural Trade; Bishop Museum Occasional Papers; Department of Biology Faculty Publications: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2007; p. 54. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, D.G. Alien Invasions: The Effects of the Global Economy on Non Marine Gastropod Introductions into the United States. Malacologia 1999, 42, 413–438. [Google Scholar]
- Roth, B.; Sadeghian, P.S. Checklist of the Land Snails and Slugs of California; Santa Barbara Museum of Natural History: Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 2003; Volume 3, ISBN 0936494344. [Google Scholar]
- Schurkman, J.; Tandingan De Ley, I.; Anesko, K.; Paine, T.; Mc Donnell, R.; Dillman, A.R. Distribution of Phasmarhabditis (Nematoda: Rhabditidae) and Their Gastropod Hosts in California Plant Nurseries and Garden Centers. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-Zaid, A.; El-Hawary, I.S.; Mahrous, M.E.; El-Sheikh, M.F. Field Observation on Biology and Ecology of Terrestrial Snails Infesting Field and Vegetable Crops at Gharbia Governorate. Egypt. Acad. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 13, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosetta, R.; Coupland, J.; Wells, D.; Mack, C. Investigation of Amber Snail Management Treatments in Nursery Production Facilities; Oregon State University: Corvallis, OR, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Gurr, G.M.; Wratten, S.D.; Barbosa, P. Success in Conservation Biological Control of Arthropods. In Biological Control: Measures of Success; Springer: Singapore, 2000; pp. 105–132. [Google Scholar]
- South, A. Terrestrial Slugs: Biology, Ecology and Control; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Salgado, V.L. Studies on the Mode of Action of Spinosad: Insect Symptoms and Physiological Correlates. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 1998, 60, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triebskorn, R.A.; Henderson, I.F.; Martin, A.P. Detection of Iron in Tissues from Slugs (Deroceras reticulatum Müller) after Ingestion of Iron Chelates, by Means of Energy-Filtering Transmission Electron Microscopy (EFTEM). Pestic. Sci. 1999, 55, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, C.A.; Arancon, N.Q.; Vasko-Bennett, M.; Little, B.; Askar, A. The Relative Toxicity of Metaldehyde and Iron Phosphate Based Molluscicides to Earthworms. Crop Prot. 2009, 28, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langan, A.M.; Shaw, E.M. Responses of Earthworm Lumbricus terrestris (L.) to Iron Phosphate and Metaldehyde Slug Pellet Formulations. Appl. Soil Ecol. 1993, 34, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandingan De Ley, I.; McDonnell, R.; Lopez, S.; Paine, T.D.; De Ley, P. Phasmarhabditis hermaphrodita (Nematoda: Rhabditidae), a Potential Biocontrol Agent Isolated for the First Time in North America. Nematology 2014, 16, 1129–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandingan De Ley, I.; McDonnell, R.J.; Aronson, E.; Wilen, C. Discovery of Multiple Phasmarhabditis spp. in North America and Description of Phasmarhabditis californica n. sp. and First Report of P. papillosa (Nematoda: Rhabditidae) from Invasive Slugs in the USA. Nematology 2016, 18, 175–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mc Donnell, R.J.; Lutz, M.S.; Howe, D.K.; Denver, D.R. First Report of the Gastropod-Killing Nematode, Phasmarhabditis hermaphrodita, in Oregon, USA. J. Nematol. 2018, 50, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coupland, J.B. Susceptibility of Helicid Snails to Isolates of the Nematode Phasmarhabditis hermaphrodita from Southern France. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 1995, 66, 207–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rae, R.; Verdun, C.; Grewal, P.S.; Robertson, J.F.; Wilson, M.J. Biological Control of Terrestrial Molluscs Using Phasmarhabditis hermaphrodita Progress and Prospects. Pest Manag. Sci. 2007, 63, 1153–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schurkman, J.; Dodge, C.; McDonnell, R.; Tandingan De Ley, I.T.; Dillman, A.R. Lethality of Phasmarhabditis spp. (P. hermaphrodita, P. californica, and P. papillosa) Nematodes to the Grey Field Slug Deroceras reticulatum on Canna Lilies in a Lath House. Agronomy 2022, 12, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.J.; Glen, S.K.; George, S.K.; Pearce, J.D.; Wiltshire, C.W. Biological Control of Slugs in Winter Wheat Using the Rhabditid Nematode Phasmarhabditis hermaphrodita. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1994, 125, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.J.; Rae, R. Phasmarhabditis hermaphrodita as a Control Agent for Slugs. In Nematode Pathogenesis of Insects and Other Pests. Sustainability in Plant and Crop Protection; Campos-Herrera, R., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Grewal, S.K.; Grewal, P.S. Survival of Earthworms Exposed to the Slug-Parasitic Nematode Phasmarhabditis hermaphrodita. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2003, 82, 72–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeNardo, E.A.B.; Sindermann, A.B.; Grewal, S.K.; Grewal, P.S. Non-Susceptibility of Earthworm Eisenia fetida to the Rhabditid Nematode Phasmarhabditis hermaphrodita, a Biocontrol Agent of Slugs. Biol. Sci. Technol. 2004, 14, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rae, R.G.; Robertson, J.; Wilson, M.J.; Rae, R.G.; Robertson, J. Susceptibility of Indigenous UK Earthworms and an Invasive Pest Flatworm to the Slug Parasitic Nematode Phasmarhabditis hermaphrodita. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2007, 15, 623–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.J.; Hughes, L.A.; Hamacher, G.M.; Glen, D.M. Effects of Phasmarhabditis hermaphrodita on Non-Target Molluscs. Pest Manag. Sci. 2000, 56, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, C.C.; Cowie, R.H.; Yeung, N.W.; Hayes, K.A. Biological control of pest non-marine molluscs: A pacific perspective on risks to non-target organisms. Insects 2021, 12, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mc Donnell, R.; Tandingan De Ley, I.; Paine, T.D. Susceptibility of Neonate Lissachatina fulica (Achatinidae: Mollusca) to a US Strain of the Nematode Phasmarhabditis hermaphrodita (Rhabditidae: Nematoda). Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2018, 28, 1091–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mc Donnell, R.J.; Colton, A.J.; Howe, D.K.; Denver, D.R. Lethality of Four Species of Phasmarhabditis (Nematoda: Rhabditidae) to the Invasive Slug, Deroceras reticulatum (Gastropoda: Agriolimacidae) in Laboratory Infectivity Trials. Biol. Control. 2020, 150, 104349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matkin, O.A.; Chandler, P.A. The U.C.-Type Soil Mixes. In The UC System for Producing Healthy Container-Grown Plants through the Use of Clean Soil, Clean Stock, and Sanitation. Manual 23; Baker, K., Ed.; California Agricultural Experiment Station [and California Agricultural] Extension Service: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1957; pp. 68–85. [Google Scholar]
- Kaya, H.K.; Stock, S.P. Techniques in Insect Nematology. In Manual of Techniques in Insect Pathology; Lacey, L.A., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1997; pp. 281–324. [Google Scholar]
- Grannell, A.; Cutler, J.; Rae, R. Size-Susceptibility of Cornu aspersum Exposed to the Malacopathogenic Nematodes Phasmarhabditis hermaphrodita and P. californica. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2021, 31, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speiser, B.; Zaller, J.G.; Neudecker, A. Size-Specific Susceptibility of the Pest Slugs Deroceras reticulatum and Arion lusitanicus to the Nematode Biocontrol Agent Phasmarhabditis hermaphrodita. BioControl 2001, 46, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).