Coordinate Inheritance of Seed Isoflavone and Protein in Soybean
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
2.2. Isoflavone Extraction and Quantification
2.3. Protein and Oil Determination
2.4. Genotyping by Sequencing and SNP Calling
2.5. Map Construction and QTL Detection
2.6. QTL Integration
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of Isoflavone, Protein and Oil Contents among Parents
3.2. Genetic and Phenotypic Variation within the RIL Population
3.3. Correlation Analysis of Isoflavone, Protein and Oil Contents in Soybean Seeds
3.4. Map Construction and Verification
3.5. Identification of QTLs for Soybean Seed Isoflavone, Protein and Oil Content
3.6. Colocalization of Isoflavone, Protein and Oil Seed Content Loci in Soybean
3.7. Effect of Combination of Isoflavone Loci on Isoflavone and Protein/Oil Content
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Soybean Association. 2021 SoyStats. 2021. Available online: https://soygrowers.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/2021-Soy-Stats-WEB.pdf. (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Li, X.H.; Shao, Z.Q.; Tian, R.; Zhang, H.; Du, H.; Kong, Y.B.; Li, W.L.; Zhang, C.Y. Mining QTLs and candidate genes for seed protein and oil contents across multiple environments and backgrounds in soybean. Mol. Breed. 2019, 39, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, S.; Graham, M.Y.; Yu, O.; Graham, T.L. RNA interference of soybean isoflavone synthase genes leads to silencing in tissues distal to the transformation site and to enhanced susceptibility to Phytophthora sojae. Plant. Physiol. 2005, 137, 1345–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, D.P.; Li, D.M.; Zhao, X.; Zhan, Y.H.; Teng, W.L.; Qiu, L.J.; Zheng, H.K.; Li, W.B.; Han, Y.P. Identification of a candidate gene associated with isoflavone content in soybean seeds using genome-wide association and linkage mapping. Plant J. 2020, 104, 950–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, A.; Tenuta, A.; Rajcan, I.; Welacky, T.; Woodrow, L.; Eskandari, M. Identification of quantitative trait loci for seed isoflavone concentration in soybean (Glycine max) against soybean cyst nematode stress. Plant. Breed. 2018, 137, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, S.M.; Antonelli, A.; Guidi, P.; Bernardeschi, M.; Scarcelli, V.; Fallahi, P.; Frenzilli, G. Genotoxicity evaluation of the soybean isoflavone genistein in human papillary thyroid cancer cells. Study of its potential use in thyroid cancer therapy. Nutr. Cancer 2019, 71, 1335–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleason, C.E.; Fischer, B.L.; Dowling, N.M.; Setchell, K.D.; Atwood, C.S.; Carlsson, C.M.; Asthana, S. Cognitive effects of soy isoflavones in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2015, 47, 1009–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoshikata, R.; Myint, K.Z.; Ohta, H. Relationship between equol producer status and metabolic parameters in 743 Japanese women: Equol producer status is associated with antiatherosclerotic conditions in women around menopause and early postmenopause. Menopause 2017, 24, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, N.; Garrido, A.; Acevedo, I.; Valladares, L. In vitro effect of soy isoflavone and equol on soluble CD40L release stimulated by ristocetin in platelets from postmenopause women. J. Biomed. Sci. Eng. 2015, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azam, M.; Zhang, S.R.; Abdelghany, A.M.; Shaibu, A.S.; Feng, Y.; Li, Y.F.; Tian, Y.; Hong, H.L.; Li, B.; Sun, J.M. Seed isoflavone profiling of 1168 soybean accessions from major growing ecoregions in China. Food Res. Int. 2020, 130, 108957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Gonzalez, J.J.; Wu, X.L.; Zhang, J.; Lee, J.D.; Ellersieck, M.; Shannon, J.G.; Yu, O.; Nguyen, H.T.; Sleper, D.A. Genetic control of soybean seed isoflavone content: Importance of statistical model and epistasis in complex traits. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2009, 119, 1069–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pei, R.L.; Zhang, J.Y.; Tian, L.; Zhang, S.R.; Han, F.X.; Yan, S.R.; Wang, L.Z.; Li, B.; Sun, J.M. Identification of novel QTL associated with soybean isoflavone content. Crop. J. 2018, 6, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knizia, D.; Yuan, J.; Bellaloui, N.; Vuong, T.; Usovsky, M.; Song, Q.; Betts, F.; Register, T.; Williams, E.; Lakhssassi, N. The soybean high density ‘forrest’ by ‘williams 82’ snp-based genetic linkage map identifies QTL and candidate genes for seed isoflavone content. Plants 2021, 10, 2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.P.; Teng, W.L.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wu, L.; Li, D.M.; Li, W.B. Unconditional and conditional QTL underlying the genetic interrelationships between soybean seed isoflavone, and protein or oil contents. Plant. Breed. 2015, 134, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primomo, V.S.; Poysa, V.; Ablett, G.R.; Jackson, C.J.; Gijzen, M.; Rajcan, I. Mapping QTL for individual and total isoflavone content in soybean seeds. Crop. Sci. 2005, 45, 2454–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.Z.; Yu, Y.L.; Wang, S.F.; Lian, Y.; Wang, T.F.; Wei, Y.L.; Gong, P.T.; Liu, X.Y.; Fang, X.J.; Zhang, M.C. QTL mapping of isoflavone, oil and protein contents in soybean (Glycine max L. Merr.). Agric. Sci. China 2010, 9, 1108–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.I.P.; Piovesan, N.D.; Jose, I.C.; Barros, E.G.; Moreira, M.A.; Oliveira, L.O. Protein, oil, and isoflavone contents in lipoxygenase- and kunitz trypsin inhibitor-deficient soybean seeds. Chromatographia 2007, 66, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.Y.; Wan, J.M.; Jiang, L.; Wang, J.K.; Zhai, H.Q.; Weng, J.F.; Wang, H.L.; Lei, C.L.; Wang, J.L.; Zhang, X. QTL analysis for rice grain length and fine mapping of an identified QTL with stable and major effects. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2006, 112, 1258–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.D.; Park, J.R.; Jang, Y.H.; Kim, E.G.; Du, X.X.; Farooq, M.; Yun, B.J.; Kim, K.M. Identification of one major QTL and a novel gene OsIAA17q5 associated with tiller number in rice using QTl analysis. Plants 2022, 11, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanichamy, D.; Smith, M. QTL mapping and colocalization analysis reveal novel candidate genes for multiple disease resistance in maize. Crop. Sci. 2022, 62, 624–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, S.; Zhu, P.; Pan, T.; Xu, Y.; Wang, J.; Hao, D.; Fang, H.; Xu, C. QTL-by-environment interaction in the response of maize root and shoot traits to different water regimes. Front. Plant. Sci. 2018, 9, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alahmad, S.; El Hassouni, K.; Bassi, F.M.; Dinglasan, E.; Youssef, C.; Quarry, G.; Aksoy, A.; Mazzucotelli, E.; Juhasz, A.; Able, J.A.; et al. A major root architecture QTL responding to water limitation in durum wheat. Front. Plant. Sci. 2019, 10, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, J.M.; Wang, X.Q.; Zhang, G.X.; Jiang, P.; Chen, W.Y.; Hao, Y.C.; Ma, X.; Xu, S.S.; Jia, J.Z.; Kong, L.R. QTL mapping for yield-related traits in wheat based on four RIL populations. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2020, 133, 917–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dachapak, S.; Tomooka, N.; Somta, P.; Naito, K.; Kaga, A.; Srinives, P. QTL analysis of domestication syndrome in zombi pea (vigna vexillata), an underutilized legume crop. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jha, U.C.; Kole, P.C.; Singh, N.P. QTL mapping for heat stress tolerance in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Legume Res. 2021, 44, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murphy, S.E.; Lee, E.A.; Woodrow, L.; Seguin, P.; Ablett, G.R. Genotype × environment interaction and stability for isoflavone content in soybean. Crop. Sci. 2009, 49, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soybase. Available online: https://www.soybase.org/ (accessed on 20 June 2022).
- Diers, B.W.; Keim, P.; Fehr, W.; Shoemaker, R. RFLP analysis of soybean seed protein and oil content. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1992, 83, 608–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fliege, C.E.; Ward, R.A.; Vogel, P.; Nguyen, H.; Quach, T.; Guo, M.; Viana, J.P.G.; Santos, L.B.; Specht, J.E.; Clemente, T.E.; et al. Fine mapping and cloning of the major seed protein quantitative trait loci on soybean chromosome 20. Plant J. 2022, 110, 114–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goettel, W.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Qiao, Z.; Jiang, H.; Hou, D.; Song, Q.; Pantalone, V.R.; Song, B.-H.; Yu, D.; et al. POWR1 is a domestication gene pleiotropically regulating seed quality and yield in soybean. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njiti, V.N.; Meksem, K.; Yuan, J.; Lightfoot, D.A.; Banz, W.J.; Winters, T.A. DNA markers associated with loci underlying seed phytoestrogen content in soybeans. J. Med. Food 1999, 2, 185–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.D.; Cheng, Y.B.; Ma, Z.W.; Liu, X.G.; Ma, Q.B.; Xia, Q.J.; Zhang, G.Y.; Mu, Y.H.; Nian, H. Fine-mapping of QTLs for individual and total isoflavone content in soybean (Glycine max L.) using a high-density genetic map. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2017, 131, 555–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Kamala, S.; Tian, R.; Du, H.; Li, W.L.; Kong, Y.B.; Zhang, C.Y. Identification and validation of quantitative trait loci controlling seed isoflavone content across multiple environments and backgrounds in soybean. Mol. Breed. 2018, 38, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Gonzalez, J.J.; Vuong, T.D.; Zhong, R.; Yu, O.; Lee, J.D.; Shannon, G.; Ellersieck, M.; Nguyen, H.T.; Sleper, D.A. Major locus and other novel additive and epistatic loci involved in modulation of isoflavone concentration in soybean seeds. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2011, 123, 1375–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smallwood, C.J. Detection of Quantitative Trait Loci for Marker-Assisted Selection of Soybean Isoflavone Genistein; The University of Tennessee: Knoxville, TN, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa, T.; Okumoto, Y.; Ogata, D.; Sayama, T.; Teraishi, M.; Terai, M.; Toda, T.; Yamada, K.; Yagasaki, K.; Yamada, N.; et al. Transgressive segregation of isoflavone contents under the control of four QTLs in a cross between distantly related soybean varieties. Breed. Sci. 2010, 60, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.M.; Sun, B.L.; Han, F.X.; Yan, S.R.; Yang, H.; Akio, K. Rapid HPLC method for determination of 12 isoflavone components in soybean seeds. Agric. Sci. China 2011, 10, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiny_HPLC v1.0. Available online: https://github.com/zhaoqingsonga/shiny_HPLC (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Yan, L.; Jiang, C.; Yu, X.; Yang, C.; Zhang, M. Development and reliability of near infrared spectroscopy(NIS) models of protein and oil content in soybean. Soybean Sci. 2008, 27, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.Z.; Pei, C.J.; Jing, H.X.; Zhang, M.C.; Wang, T.; Di, R.; Liu, B.Q.; Yan, L. QTL analysis of soybean quality and yield related characters. Acta Agric. Boreali-Sin. 2011, 26, 127–130. [Google Scholar]
- Chodak, M.; Niklińska, M.; Beese, F. The Use of near Infrared Spectroscopy to Quantify Lignite-Derived Carbon in Humus-Lignite Mixtures. J. Near Infrared Spectrosc. 2017, 15, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, G.C.; Flores-Vergara, M.A.; Krasynanski, S.; Kumar, S.; Thompson, W.F. A modified protocol for rapid DNA isolation from plant tissues using cetyltrimethylammonium bromide. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2320–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Richard, D. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows–Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. The sequence alignment/map format and samtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meng, L.; Li, H.H.; Zhang, L.Y.; Wang, J.K. QTL IciMapping: Integrated software for genetic linkage map construction and quantitative trait locus mapping in biparental populations. Crop. J. 2015, 3, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.H.; Bhat, P.R.; Close, T.J.; Lonardi, S. Efficient and accurate construction of genetic linkage maps from the minimum spanning tree of a graph. PLoS Genet. 2008, 4, e1000212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MapQTL6.0. Available online: https://www.kyazma.nl/index.php/MapQTL/ (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- QTL Cartographer V2.5_011. Available online: https://brcwebportal.cos.ncsu.edu/qtlcart/WQTLCart.htm (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Voorrips, R. MapChart: Software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J. Hered. 2002, 93, 77–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ihaka, R.; Gentleman, R. R: A language for data analysis and graphics. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 1996, 5, 299–314. [Google Scholar]
- Revelle, W.; Revelle, M.W. psych: Procedures for personality and psychological research. Compr. R Arch. Netw. 2015, 337, 338. [Google Scholar]
- R Package lme4. Available online: https://github.com/lme4 (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Peterson, B.G.; Carl, P.; Boudt, K.; Bennett, R.; Ulrich, J.; Zivot, E.; Cornilly, D.; Hung, E.; Lestel, M.; Balkissoon, K. Package ‘performanceanalytics’. R. Team Coop. 2018, 3, 13–14. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.K.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Gou, Z.H.; Lyu, J.; Li, W.I.; Yu, Y.J.; Shu, L.P.; Zhao, Y.J.; Ma, Y.M.; et al. Resequencing 302 wild and cultivated accessions identifies genes related to domestication and improvement in soybean. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Han, Y.P.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.G.; Teng, W.L.; Li, D.M.; Zhan, Y.; Li, W.B. Mapping isoflavone QTL with main, epistatic and QTL X environment effects in recombinant inbred lines of soybean. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.K.; Wang, Y.J.; Luo, G.Z.; Zhang, J.S.; He, C.Y.; Wu, X.L.; Gai, J.Y.; Chen, S.Y. QTL mapping of ten agronomic traits on the soybean (Glycine max L. Merr.) genetic map and their association with EST markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2004, 108, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomeque, L.; Liu, L.J.; Li, W.; Hedges, B.; Cober, E.R.; Rajcan, I. QTL in mega-environments: II. Agronomic trait QTL co-localized with seed yield QTL detected in a population derived from a cross of high-yielding adapted × high-yielding exotic soybean lines. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2009, 119, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinprecht, Y.; Poysa, V.W.; Yu, K.F.; Rajcan, I.; Ablett, G.R.; Pauls, K.P. Seed and agronomic QTL in low linolenic acid, lipoxygenase-free soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merrill) germplasm. Genome 2006, 49, 1510–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.E.; Orf, J.H.; Liu, L.J.; Dong, Z.; Rajcan, I. Genetic basis of soybean adaptation to North American vs. Asian mega-environments in two independent populations from Canadian × Chinese crosses. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2013, 126, 1809–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.M.; Han, X.; Sun, Y.N.; Wu, Q.; Shan, D.P.; Du, X.Y.; Liu, C.Y.; Jiang, H.W.; Hu, G.H.; Chen, Q.S. An integrated quantitative trait locus map of oil content in soybean, Glycine max (L.) Merr., generated using a meta-analysis method for mining genes. Agric. Sci. China 2011, 10, 1681–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.M.; Wu, Q.; Han, X.; Sun, Y.N.; Du, X.Y.; Liu, C.Y.; Jiang, H.W.; Hu, G.H.; Chen, Q.S. Soybean oil content QTL mapping and integrating with meta-analysis method for mining genes. Euphytica 2011, 179, 499–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyten, D.L.; Pantalone, V.R.; Sams, C.E.; Saxton, A.M.; Landau-Ellis, D.; Stefaniak, T.R.; Schmidt, M.E. Seed quality QTL in a prominent soybean population. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2004, 109, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teuku, T.; Satoshi, W.; Naoki, Y.; Kyuya, H. Analysis of quantitative trait loci for protein and lipid contents in soybean seeds using recombinant inbred lines. Breed. Sci. (Jpn.) 2003, 53, 133–140. [Google Scholar]
- Pathan, S.M.; Vuong, T.; Clark, K.; Lee, J.D.; Shannon, J.G.; Roberts, C.A.; Ellersieck, M.R.; Burton, J.W.; Cregan, P.B.; Hyten, D.L.; et al. Genetic mapping and confirmation of quantitative trait loci for seed protein and oil contents and seed weight in soybean. Crop. Sci. 2013, 53, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, W.; Wen, Z.; Li, H.; Yuan, D.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Huang, Z.; Cui, S.; Du, W. Identification of the quantitative trait loci (QTL) underlying water soluble protein content in soybean. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2013, 126, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, T.T.; Jiang, Z.F.; Han, Y.P.; Teng, W.L.; Zhao, X.; Li, W.B. Identification of quantitative trait loci underlying seed protein and oil contents of soybean across multi-genetic backgrounds and environments. Plant. Breed. 2013, 132, 630–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.M.; Hou, M.; Han, X.; Liu, C.Y.; Jiang, H.W.; Xin, D.W.; Hu, G.H.; Chen, Q.S.; Singh, R. Identification of quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for seed protein concentration in soybean and analysis for additive effects and epistatic effects of QTLs under multiple environments. Plant. Breed. 2014, 133, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, T.H.; Van, K.; Kim, M.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Walker, D.R. Association analysis using SSR markers to find QTL for seed protein content in soybean. Euphytica 2007, 162, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, J.Y.; Wang, Y.J.; Wu, X.L.; Chen, S.Y. A comparative study on segregation analysis and QTL mapping of quantitative traits in plants-with a case in soybean. Front. Agric. China 2007, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Z.; Jiang, G.L.; Green, M.; Scott, R.A.; Hyten, D.L.; Cregan, P.B. Quantitative trait locus analysis of saturated fatty acids in a population of recombinant inbred lines of soybean. Mol. Breed. 2012, 30, 1163–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shibata, M.; Takayama, K.; Ujiie, A.; Yamada, T.; Abe, J.; Kitamura, K. Genetic relationship between lipid content and linolenic acid concentration in soybean seeds. Breed. Sci. 2008, 58, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fasoula, V.A.; Harris, D.K.; Roger, B.H. Validation and designation of quantitative trait loci for seed protein, seed oil, and seed weight from two soybean populations. Crop. Sci. 2004, 44, 1218–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Bailey, M.A.; Mian, M.A.R.; Carter, T.E.; Shipe, E.R.; Ashley, D.A.; Parrott, W.A.; Hussey, R.S.; Boerma, H.R. RFLP loci associated with soybean seed protein and oil content across populations and locations. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1996, 93, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrington, C.V.; Abdel-Haleem, H.; Hyten, D.L.; Cregan, P.B.; Orf, J.H.; Killam, A.S.; Bajjalieh, N.; Li, Z.; Boerma, H.R. QTL for seed protein and amino acids in the Benning × Danbaekkong soybean population. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2015, 128, 839–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brummer, E.C.; Graef, G.L.; Orf, J.; Wilcox, J.R.; Shoemaker, R.C. Mapping QTL for seed protein and oil content in eight soybean populations. Crop. Sci. 1997, 37, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebolt, A.M.; Shoemaker, R.C.; Diers, B.W. Analysis of a Quantitative Trait Locus Allele from Wild Soybean That Increases Seed Protein Concentration in Soybean. Crop. Sci. 2000, 40, 1438–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandurangan, S.; Pajak, A.; Molnar, S.J.; Cober, E.R.; Dhaubhadel, S.; Hernández-Sebastià, C.; Kaiser, W.M.; Nelson, R.L.; Huber, S.C.; Marsolais, F. Relationship between asparagine metabolism and protein concentration in soybean seed. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 3173–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, D.M.; Glover, K.D.; Carlson, S.R.; Specht, J.E.; Diers, B.W. Fine mapping of a seed protein QTL on soybean linkage group I and its correlated effects on agronomic traits. Crop. Sci. 2006, 46, 834–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Z.; Jiang, G.L.; Green, M.; Scott, R.A.; Song, Q.; Hyten, D.L.; Cregan, P.B. Identification and validation of quantitative trait loci for seed yield, oil and protein contents in two recombinant inbred line populations of soybean. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2014, 289, 935–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Specht, J.E.; Chase, K.; Macrander, M.; Graef, G.L.; Chung, J.; Markwell, J.P.; Germann, M.; Orf, J.H.; Lark, K.G. Soybean response to water: A QTL analysis of drought tolerance. Crop. Sci. 2001, 41, 493–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.; Babka, H.L.; Graef, G.L.; Staswick, P.E.; Lee, D.J.; Cregan, P.B.; Shoemaker, R.C.; Specht, J.E. The seed protein, oil, and yield QTL on soybean linkage group I. Crop. Sci. 2003, 43, 1053–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orf, J.H.; Chase, K.; Jarvik, T.; Mansur, L.M.; Lark, K.G. Genetics of soybean agronomic traits: I. Comparison of three related recombinant inbred populations. Crop. Sci. 1999, 39, 1642–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mansur, L.M.; Orf, J.H.; Chase, K.; Jarvik, T.; Cregan, P.B.; Lark, K.G. Genetic mapping of agronomic traits using recombinant inbred lines of soybean. Crop. Sci. 1996, 36, 1327–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Moon, J.K.; Jeong, N.; Chun, H.K.; Kang, S.T.; Back, K.; Jeong, S.C. Novel major quantitative trait loci regulating the content of isoflavone in soybean seeds. Genes Genom. 2011, 33, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.J.; Li, J.W.; Liu, Y.J.; Jiang, W.Z.; Du, X.L.; Li, L.; Li, X.W.; Su, L.T.; Wang, Q.Y.; Wang, Y. Quantitative trait loci analysis of individual and total isoflavone contents in soybean seeds. J. Genet. 2014, 93, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, G.L.; Li, D.M.; Han, Y.P.; Teng, W.L.; Wang, J.; Qiu, L.Q.; Li, W.B. Identification of QTL underlying isoflavone contents in soybean seeds among multiple environments. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2009, 118, 1455–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, O.; McGonigle, B. Metabolic engineering of isoflavone biosynthesis. Adv. Agron. 2005, 86, 147–190. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, L.; Yang, S.N.; Zhang, K.; He, J.B.; Wu, C.H.; Ren, Y.H.; Gai, J.Y.; Li, Y. Natural variation and selection in GmSWEET39 affect soybean seed oil content. New Phytol. 2020, 225, 1651–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aastveit, A.H.; Aastveit, K. Effects of genotype-environment interactions on genetic correlations. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1993, 86, 1007–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Yu, O. Metabolic engineering of isoflavone biosynthesis in seeds. Modif. Seed Compos. Promot. Health Nutr. 2009, 51, 151–176. [Google Scholar]
- Yellayi, S.; Naaz, A.; Szewczykowski, M.A.; Sato, T.; Woods, J.A.; Chang, J.; Segre, M.; Allred, C.D.; Helferich, W.G.; Cooke, P.S. The phytoestrogen genistein induces thymic and immune changes: A human health concern? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 7616–7621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
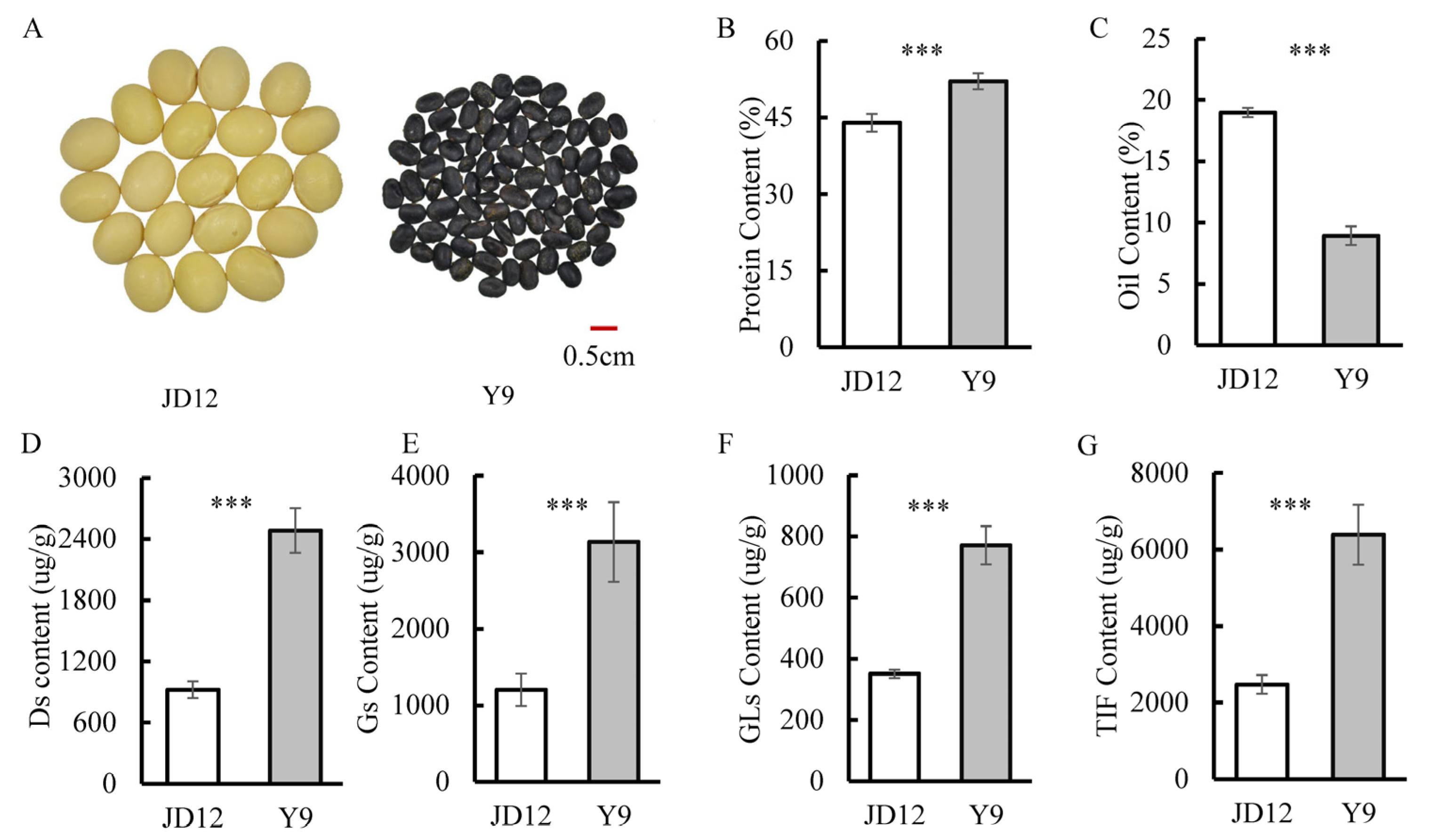
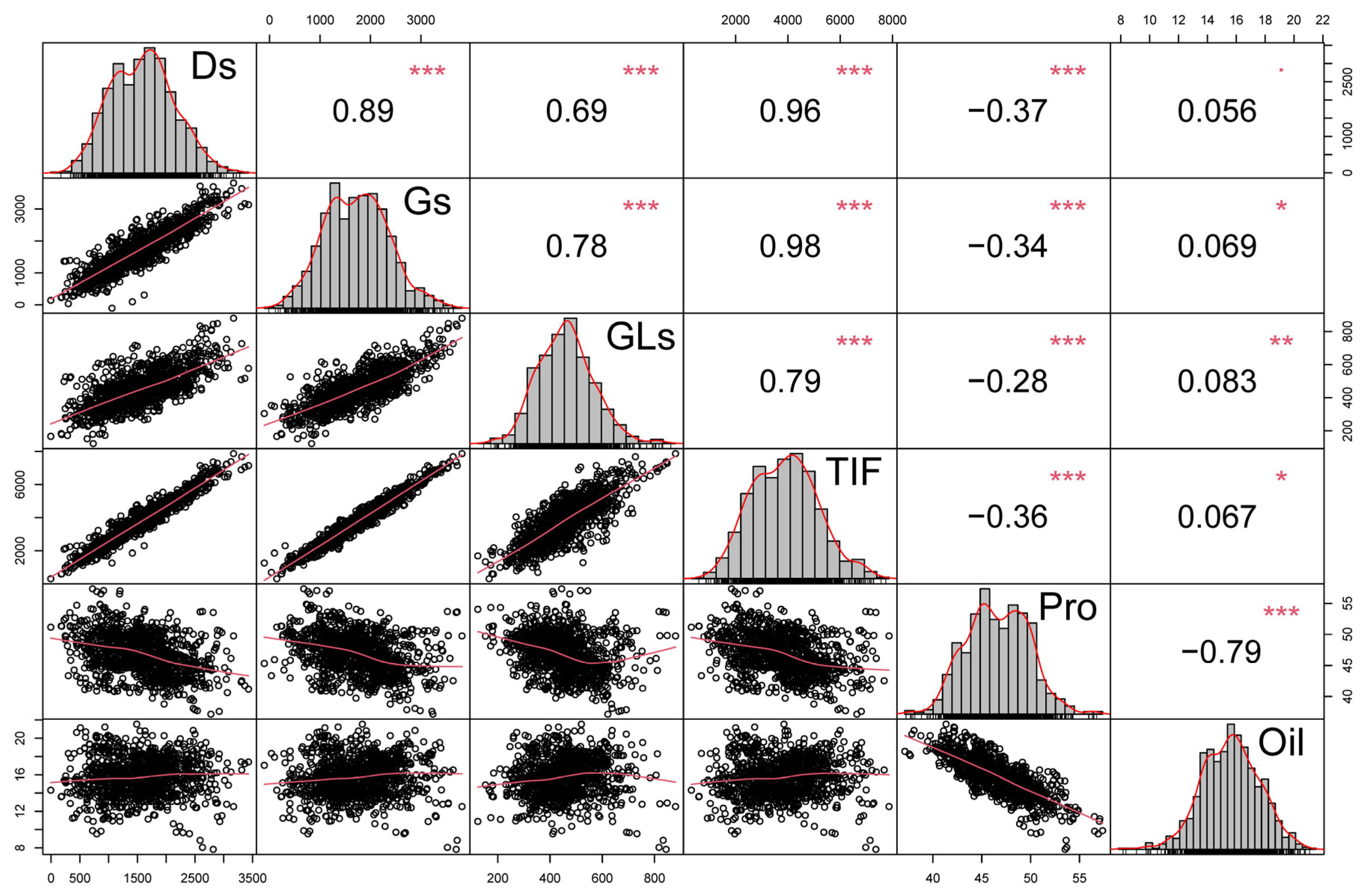

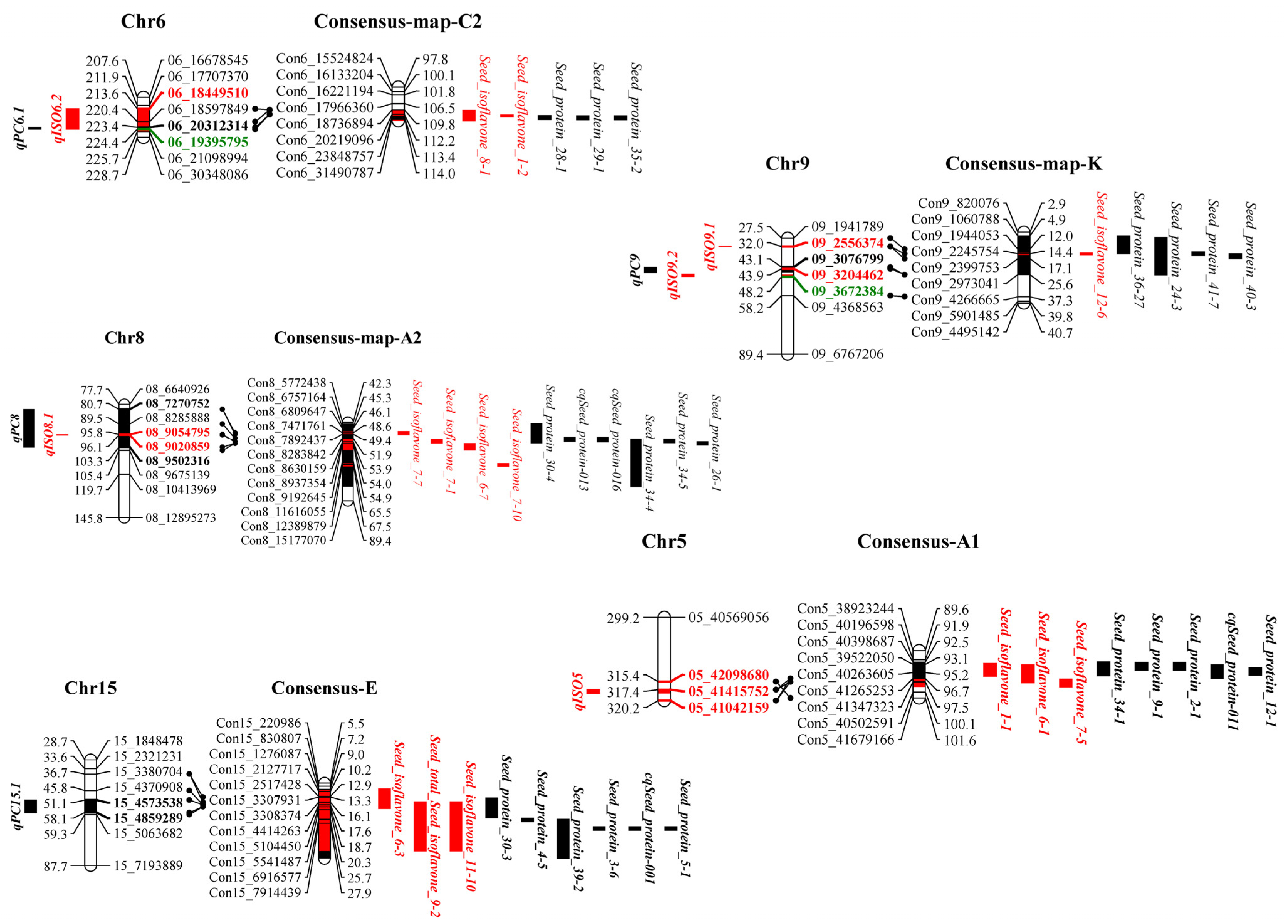

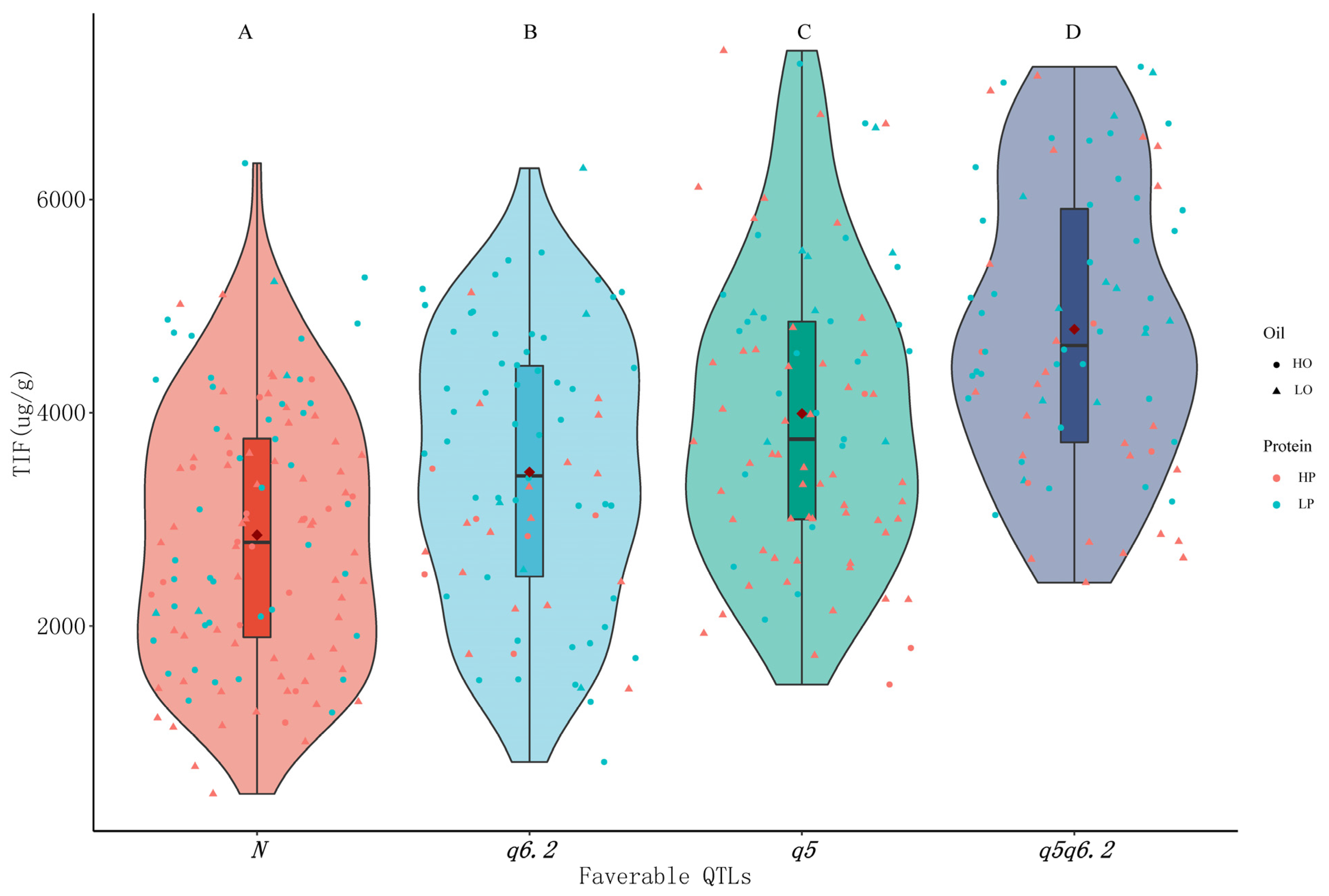
| Traits | Year | Parents | RILs | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JD12 | Y9 | Min | Max | Mean | SD | CV% | Skew | Kurt | h2b | ||
| D | 2020 | 157.71 | 392.23 | 10.95 | 635.36 | 273.69 | 119.81 | 43.78 | 0.24 | −0.52 | 0.75 |
| 2021 | 106.95 | 417.70 | 7.85 | 514.92 | 229.13 | 105.01 | 45.83 | 0.30 | −0.28 | ||
| MD | 2020 | 718.08 | 1783.34 | 72.74 | 2590.86 | 1164.66 | 493.15 | 42.34 | 0.19 | −0.62 | 0.72 |
| 2021 | 699.90 | 2095.33 | 95.55 | 2385.68 | 1254.32 | 414.19 | 33.02 | 0.21 | −0.08 | ||
| AD | 2020 | 45.24 | 114.64 | 3.01 | 174.77 | 83.66 | 34.18 | 40.86 | 0.09 | −0.66 | 0.83 |
| 2021 | 117.48 | 166.65 | 1.27 | 238.03 | 128.94 | 42.37 | 32.86 | −0.47 | 0.21 | ||
| Ds | 2020 | 921.03 | 2290.21 | 118.59 | 3367.06 | 1522.02 | 638.15 | 41.93 | 0.20 | −0.63 | 0.75 |
| 2021 | 924.33 | 2679.69 | 268.91 | 3080.17 | 1612.38 | 533.34 | 33.08 | 0.25 | −0.20 | ||
| G | 2020 | 109.83 | 448.79 | 14.18 | 580.52 | 257.63 | 112.81 | 43.79 | 0.19 | −0.44 | 0.85 |
| 2021 | 264.09 | 685.19 | 12.05 | 685.19 | 347.84 | 129.23 | 37.15 | −0.01 | −0.21 | ||
| MG | 2020 | 900.45 | 2171.38 | 189.81 | 2839.65 | 1406.51 | 545.48 | 38.78 | 0.10 | −0.58 | 0.81 |
| 2021 | 1125.64 | 2963.02 | 59.46 | 2976.68 | 1506.45 | 544.94 | 36.17 | 0.27 | 0.03 | ||
| Gs | 2020 | 1010.28 | 2620.16 | 203.99 | 3420.17 | 1664.14 | 655.79 | 39.41 | 0.12 | −0.56 | 0.82 |
| 2021 | 1389.73 | 3648.21 | 99.98 | 3648.21 | 1854.29 | 664.46 | 35.83 | 0.21 | −0.03 | ||
| GL | 2020 | 50.53 | 109.08 | 4.71 | 127.87 | 64.23 | 19.72 | 30.71 | −0.09 | 0.84 | 0.85 |
| 2021 | 62.44 | 136.68 | 11.04 | 136.81 | 84.05 | 24.89 | 29.61 | −0.23 | −0.36 | ||
| MGL | 2020 | 299.58 | 590.92 | 147.61 | 594.40 | 348.87 | 86.56 | 24.81 | 0.30 | −0.09 | 0.80 |
| 2021 | 229.44 | 672.04 | 175.66 | 696.02 | 349.30 | 86.97 | 24.90 | 0.85 | 1.53 | ||
| AGL | 2020 | 6.71 | 9.74 | 0.99 | 47.99 | 18.89 | 12.06 | 63.86 | 0.59 | −0.96 | 0.77 |
| 2021 | 53.09 | 22.82 | 0.97 | 86.80 | 46.00 | 19.08 | 41.49 | −0.23 | −0.79 | ||
| GLs | 2020 | 356.82 | 709.73 | 169.19 | 713.56 | 431.99 | 106.32 | 24.61 | 0.14 | −0.12 | 0.84 |
| 2021 | 344.97 | 831.54 | 255.58 | 849.78 | 479.34 | 108.07 | 22.54 | 0.53 | 0.58 | ||
| TIF | 2020 | 2288.13 | 5620.11 | 498.75 | 7028.18 | 3618.14 | 1357.62 | 37.52 | 0.15 | −0.60 | 0.81 |
| 2021 | 2659.03 | 7159.43 | 1383.42 | 7397.73 | 3946.01 | 1237.25 | 31.35 | 0.37 | −0.08 | ||
| PC | 2020 | 42.26 | 50.55 | 37.47 | 54.53 | 46.45 | 3.35 | 7.22 | −0.07 | −0.45 | 0.86 |
| 2021 | 45.65 | 53.62 | 41.30 | 56.95 | 47.23 | 3.11 | 6.58 | 0.30 | −0.26 | ||
| OC | 2020 | 18.81 | 9.64 | 9.64 | 21.04 | 15.46 | 2.12 | 13.74 | 0.11 | −0.25 | 0.87 |
| 2021 | 19.16 | 8.24 | 8.24 | 21.02 | 16.01 | 2.00 | 12.51 | −0.38 | 0.78 | ||
| Integrated QTL | Separated QTL | Chr | Position (cM) | Locus/Interval | LOD | ADD | PVE (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qISO1 | qGL1(21), qD1(20), qDs1(20), qMD1(20), qGL1(20) | 1 | 231.938–275.569 | 01_51600690–01_54799844 | 2.52–3.96 | −80.46 | 6.1–9.5 | Novel (two year) |
| qISO2.1 | qTIF2.1(21), qGs2.1(21), qMD2.1(21), qMG2.1(21), qDs2.1(21), qGLs2.1(21), qMGL2.1(21) | 2 | 15.149–32.887 | 02_2149517–02_3621233 | 2.67–3.06 | −136.35 | 6.5–7.4 | Seed_isoflavone_6-2 [11] |
| qISO2.2 | qMGL2.2(20) | 2 | 249.842 | 02_48470807–02_48176139 | 2.73 | −31.92 | 6.6–6.6 | Novel |
| qISO3 | qAD3(20), qTIF3(20), qG3(20) | 3 | 1.786–14.983 | 03_314515–03_601813 | 2.53–2.81 | −166.70 | 6.2–6.8 | Novel |
| qISO5 | qDs5(20), qGL5(21), qMD5(20), qAD5(20), qG5(20), qG5(21), qTIF5(20), qGs5(20), qGLs5(20), qMG5(20), qMG5(21), qMGL5(20), qGs5(21), qD5(20), qD5(21), qDs5(21), qGL5(20), qTIF5(21), qMD5(21), qMGL5(21), qGLs5(21) | 5 | 317.424–318.438 | 05_41415752–05_42098680 | 3.1–11.11 | −188.13 | 7.5–24.4 | Seed_isoflavone_1-1 [15], Seed_isoflavone_6-1 [11], Seed_isoflavone_7-5 [36] |
| qISO6.1 | qMD6.1(20), qAD6.1(21), qGs6.1(20), qMG6.1(20), qD6.1(20), qTIF6.1(20), qG6.1(20), qDs6.1(20) | 6 | 179.84–191.072 | 06_14871510–06_15642762 | 2.53–5.34 | −214.21 | 6.2–12.6 | Novel (two year) |
| qISO6.2 | qG6.2(21), qGLs6.2(21), qGLs6.2(20), qGs6.2(21), qMG6.2(21), qMGL6.2(21), qTIF6.2(21), qMGL6.2(20), qD6.2(20), qTIF6.2(20), qMD6.2(20), qDs6.2(20) | 6 | 213.609–225.650 | 06_18449510–06_21098994 | 2.94–11.34 | −160.98 | 7.1–24.8 | Seed_isoflavone_8-1 [35], Seed_isoflavone_1-2 [15] |
| qISO6.3 | qG6.3(21), qGL6.3(21), qGLs6.3(21), qTIF6.3(20), qGs6.3(20), qMG6.3(20), qMGL6.3(21), qGs6.3(21), qD6.3(20), qGLs6.3(20), qGL6.3(20), qDs6.3(20), qMD6.3(20), qMGL6.3(20) | 6 | 241.934–242.934 | 06_35913434–36835583 | 2.53–8.26 | −124.50 | 6.2–18.8 | Novel (two year) |
| qISO6.4 | qGs6.4(20), qMG6.4(20), qD6.4(20), qD6.4(21), qGLs6.4(20), qG6.4(21), qGLs6.4(21), qDs6.4(20), qTIF6.4(20), qMD6.4(20), qMG6.4(21), qMGL6.4(20), qMGL6.4(21), qGs6.4(21), qTIF6.4(21), qGL6.4(21) | 6 | 271.344–273.163 | 06_42113786–06_43887351 | 2.55–8.87 | −153.17 | 6.2–20 | Novel (two year) |
| qISO8.1 | qAD8.1(21), qD8.1(20), qDs8.1(20), qGL8.1(21), qGLs8.1(20), qMD8.1(20), qMGL8.1(20), qTIF8.1(20), qD8.1(21), qG8.1(21), qGs8.1(21), qTIF8.1(21) | 8 | 95.815–96.096 | 08_9020859–08_9054795 | 2.52–4.59 | 128.77 | 6.1–10.9 | Seed_isoflavone_7-1 [36], Seed_isoflavone_6-7 [11] |
| qISO8.2 | qD8.2(20), qDs8.2(20), qG8.2(20), qTIF8.2(20), qMD8.2(20), qMG8.2(20), qGs8.2(20) | 8 | 178.241 | 08_15716820 | 3.11–4.26 | 220.78 | 7.5–10.2 | Seed_isoflavone_3-3 [34] |
| qISO9.1 | qG9.1(20), qGL9.1(20), qGLs9.1(20), qMGL9.1(20) | 9 | 31.954 | 09_2556374 | 2.66–4.63 | 35.35 | 6.5–11 | Seed_isoflavone_12-6 [32] |
| qISO9.2 | qTIF9.2(20), qD9.2(20), qDs9.2(20), qMD9.2(20) | 9 | 46.908–48.224 | 09_3204462–09_3672384 | 2.83–3.09 | 225.28 | 6.9–7.5 | Seed_isoflavone_12-6 [32] |
| qISO10.1 | qD10.1(20), qMD10.1(20), qDs10.1(20) | 10 | 2.436–3.436 | 10_570120–10_1109902 | 2.83–3.04 | −144.96 | 6.9–7.4 | Novel |
| qISO10.2 | qAD10.2(20), qG10.2(20), qTIF10.2(20), qMG10.2(20), qGs10.2(20) | 10 | 20.954 | 10_1237908 | 2.77–3.21 | −195.80 | 6.7–7.8 | Novel |
| qISO10.3 | qG10.3(21), qAD10.3(20), qG10.3(20), qGs10.3(20), qMG10.3(20), qTIF10.3(20) | 10 | 259.847–305.896 | 10_43610530–10_48649271 | 2.54–2.93 | −159.48 | 6.2–7.1 | Seed_isoflavone_12-8 [32], Seed_isoflavone_12-9 [32] |
| qISO11 | qG11(21), qGL11(21), qGLs11(21), qGs11(21), qMGL11(21), qMD11(20), qDs11(20), qGLs11(20), qMGL11(20) | 11 | 178.874–182.918 | 11_25422320–11_26086398 | 2.57–3.54 | −77.86 | 6.2–8.5 | Seed_isoflavone_12-10 [32], Seed_isoflavone_11-16 [14] |
| qISO12 | qAD12(21), qGL12(21), qG12(20), qGs12(20), qMG12(20), qG12(21), qGs12(21), qMG12(21), qTIF12(21) | 12 | 74.532–93.476 | 12_5008803–12_5797776 | 2.56–4.29 | −127.06 | 6.2–10.2 | Seed_isoflavone_6-4 [11] |
| qISO14 | qAD14(20), qGLs14(20), qD14(20), qG14(20), qTIF14(20), qDs14(20), qGs14(20), qMD14(20), qMG14(20), qGL14(21) | 14 | 200.845–216.814 | 14_45868867–14_46953015 | 2.55–3.83 | −149.60 | 6.2–9.2 | Seed_isoflavone_11-17 [14] |
| qISO15 | qAD15(20), qGs15(20), qMG15(20), qG15(20) | 15 | 11.737–12.737 | 15_635901–15_1251734 | 3.26–3.58 | −129.16 | 7.9–8.6 | Seed_isoflavone_7-8 [36] |
| qISO17 | qGL17(20), qGLs17(21), qGLs17(20), qMGL17(21) | 17 | 86.186–86.186 | 17_6343179 | 3.02–4.28 | −26.22 | 7.3–10.2 | Seed_isoflavone_9-8 [55] |
| qISO19.1 | qGLs19.1(21), qMGL19.1(21) | 19 | 49.333–49.333 | 19_4172732 | 2.62–3.19 | −25.80 | 6.4–7.7 | Novel |
| qISO19.2 | qGLs19.2(21), qMGL19.2(21), qD19.2(20) | 19 | 144.521–171.62 | 19_36928466–19_39216482 | 2.89–3.22 | −4.51 | 7–7.8 | Seed_isoflavone_7-3 [36], Seed_isoflavone_11-3 [14] |
| qISO19.3 | qTIF19.3(21), qMG19.3(21), qGs19.3(21), qAGL19.3(20), qAGL19.3(21) | 19 | 229.515–279.382 | 19_42466443–19_46653707 | 2.54–2.85 | −124.14 | 6.2–6.9 | Seed_isoflavone_6-5 [11] |
| qISO20 | qGLs20(20), qMGL20(20) | 20 | 59.055 | 20_2260193 | 2.53–2.81 | 34.31 | 6.2–6.8 | Novel |
| Integrated QTL | Year | Separated QTL | Position | Chr | Locus/Interval | LOD | ADD | PVE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qISO5 | 2020 | qD5 | 318.438 | 5 | 05_41042159–05_41415752 | 10.37 | −75.1096 | 23 |
| 2021 | qD5 | 318.438 | 5 | 05_41042159–05_41415752 | 8.63 | −48.3228 | 19.5 | |
| 2020 | qDs5 | 317.424 | 5 | 05_41415752–05_42098680 | 11.11 | −388.854 | 24.4 | |
| 2021 | qDs5 | 318.438 | 5 | 05_41042159–05_41415752 | 8.89 | −248.71 | 20.1 | |
| 2020 | qG5 | 317.438 | 5 | 05_41415752 | 6.26 | −63.5598 | 14.6 | |
| 2021 | qG5 | 317.438 | 5 | 05_41415752 | 3.2 | −36.3361 | 7.7 | |
| 2021 | qGL5 | 317.424 | 5 | 05_41415752–05_42098680 | 3.1 | −6.89811 | 7.5 | |
| 2020 | qGL5 | 318.438 | 5 | 05_41042159–05_41415752 | 6.3 | −12.044 | 14.7 | |
| 2020 | qGLs5 | 317.438 | 5 | 05_41415752 | 6.73 | −59.6474 | 15.6 | |
| 2021 | qGLs5 | 318.438 | 5 | 05_41042159–05_41415752 | 3.88 | −34.3259 | 9.3 | |
| 2020 | qGs5 | 317.438 | 5 | 05_41415752 | 7.12 | −357.82 | 16.4 | |
| 2021 | qGs5 | 317.438 | 5 | 05_41415752 | 4.84 | −227.513 | 11.5 | |
| 2020 | qMD5 | 317.424 | 5 | 05_41415752–05_42098680 | 11.04 | −297.505 | 24.2 | |
| 2021 | qMD5 | 318.438 | 5 | 05_41042159–05_41415752 | 8.93 | −193.463 | 20.1 | |
| 2020 | qMG5 | 317.438 | 5 | 05_41415752 | 7.2 | −294.26 | 16.6 | |
| 2021 | qMG5 | 317.438 | 5 | 05_41415752 | 5.1 | −191.177 | 12 | |
| 2020 | qMGL5 | 317.438 | 5 | 05_41415752 | 6.4 | −46.406 | 14.9 | |
| 2021 | qMGL5 | 318.438 | 5 | 05_41042159–05_41415752 | 3.88 | −27.6317 | 9.3 | |
| 2020 | qTIF5 | 317.438 | 5 | 05_41415752 | 9.94 | −806.12 | 22.1 | |
| 2021 | qTIF5 | 318.438 | 5 | 05_41042159–05_41415752 | 6.96 | −516.56 | 16.1 | |
| qISO6.2 | 2020 | qGLs6.2 | 213.609 | 6 | 06_18449510 | 10.15 | −72.0882 | 22.5 |
| 2021 | qGLs6.2 | 213.609 | 6 | 06_18449510 | 10.23 | −52.4258 | 22.7 | |
| 2020 | qMGL6.2 | 225.408 | 6 | 06_19395795–06_21098994 | 11.34 | −60.4788 | 24.8 | |
| 2021 | qMGL6.2 | 213.609 | 6 | 06_18449510 | 10.65 | −42.9397 | 23.5 | |
| 2020 | qTIF6.2 | 225.65 | 6 | 06_21098994 | 3.76 | −515.976 | 9 | |
| 2021 | qTIF6.2 | 213.609 | 6 | 06_18449510 | 2.94 | −336.537 | 7.1 |
| Integrated QTL | Separated QTL | Chr | Position | Locus/Interval | LOD | ADD | PVE (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qQ2 | qOC2(21) | 2 | 31.253 | 02_3264911 | 2.84 | 0.53 | 6.9 | Seed oil 26-1 [56] |
| qQ6.1 | qOC6.1(20), qOC6.1(21) | 6 | 211.941–220.397 | 06_17707370–06_18597849 | 3.02–3.56 | −0.59 | 7.3–8.6 | Seed oil 33-2 [57], Seed oil 27-1 [58] |
| qPC6.1(20), qPC6.1(21) | 6 | 224.401–224.408 | 06_19395795–06_20312314 | 3.16–4.65 | 1.00 | 7.6–11.1 | Seed protein 28-1 [16], Seed protein 29-1 [57], Seed protein 35-2 [59] | |
| qQ6.2 | qOC6.2(20) | 6 | 268.273 | 06_39743079 | 3.01 | −0.58 | 7.3 | mqSeed_Oil-009 [60], Seed oil 24-19 [61] |
| qPC6.2(20) | 6 | 271.344 | 06_42113786 | 3.45 | 0.97 | 8.4 | Seed protein 24-1 [62] | |
| qQ8 | qOC8(21), qOC8(20) | 8 | 80.663–103.272 | 08_7270752–08_9502316 | 2.78–5.3 | 0.64 | 6.8–12.5 | Seed oil 30-2 [16], Seed oil 30-3 [16], Seed oil 34-1 [63] |
| qPC8(21), qPC8(20) | 8 | 80.663–103.272 | 08_7270752–08_9502316 | 6.85–8.61 | −1.387 | 15.9–19.5 | cqSeed_protein-013 [64], cqSeed_protein-016 [64], Seed protein 26-1 [58], Seed protein 30-4 [63], Seed protein 34-4 [65], Seed protein 34-5 [65] | |
| qQ9 | qOC9(21) | 9 | 43.066 | 09_3076799 | 2.64 | 0.51 | 6.4 | Seed oil 42-26 [14], Seed oil 43-22 [66] |
| qQ11.1 | qOC11(21) | 11 | 155.446 | 11_12818547 | 3.45 | 0.59 | 8.3 | Seed protein 24_3 [62], Seed protein 36-27 [66], Seed protein 40-3 [67], Seed protein 41-7 [68] |
| qPC11.1(21) | 11 | 155.446 | 11_12818547 | 2.72 | −0.82 | 6.6 | Novel | |
| qQ11.2 | qPC11.2(21) | 11 | 210.208 | 11_20292294–11_29740152 | 2.8 | −0.84 | 6.8 | Seed protein 25-2 [69] |
| qPC11.3(21) | 11 | 231.455 | 11_30752151 | 3.68 | −0.93 | 8.8 | Seed protein 26-6 [58] | |
| qQ13.1 | qOC13(20), qOC13(21) | 13 | 80.692–102.982 | 13_17332728–13_19878509 | 3.24–4.03 | 0.61 | 7.9–9.6 | Seed oil 36-4 [70] |
| qPC13.1(20) | 13 | 95.039 | 13_18585206–13_18654598 | 3.13 | −0.95 | 7.6 | Novel | |
| qQ13.2 | qPC13.2(21) | 13 | 175.227 | 13_23043289 | 3.81 | −0.96 | 9.1 | Seed protein 36 [66] |
| qQ15.1 | qOC15.1(20), qOC15.1(21) | 15 | 36.551–45.848 | 15_2321231–15_4370908 | 4.53–5.45 | 0.72 | 10.8–12.8 | Seed oil 2-3 [28], Seed oil 32-1 [71] |
| qPC15(20), qPC15(21) | 15 | 51.149–58.117 | 15_4573538–15_4859289 | 4.8–5.8 | −1.16 | 11.4–13.6 | Seed protein 30-3 [63] | |
| qQ15.2 | qOC15.2(20) | 15 | 98.598 | 15_7891207 | 4.22 | 0.68 | 10.1 | cqSeed_protein-001 [72], cqSeed_protein-008 [64], Seed protein 3-6 [64], Seed protein 4-5 [73], Seed protein 5-1 [73], Seed protein 30-3 [63], Seed protein 39-2 [74] |
| qPC9(20), qPC9(21) | 20 | 43.066–45.908 | 09_3076799–09_3672384 | 3.14–3.96 | −0.98 | 7.6–9.5 | Seed protein 1-3 [28], Seed protein 3-12 [75], Seed protein 11-1 [76] | |
| qQ20.1 | qPC20.1(20), qPC20.1(21) | 20 | 69.367–70.367 | 20_2916159–20_3536505 | 7.05–7.73 | −1.35 | 16.3–17.8 | Seed protein 1-4 [28], Seed protein 11-1 [76], Seed protein 3-12 [75], Seed protein 1-3 [28] |
| qOC20.1(20), qOC20.1(21) | 20 | 82.612–84.337 | 20_5834525–20_6101553 | 9.96–10.30 | 0.98 | 22.3–22.8 | Seed oil 13-4 [62], mqSeed_Oil-020 [60], Seed oil 24-30 [61] | |
| qQ20.2 | qPC20.2(20), qPC20.2(21) | 20 | 92.651 | 20_22632082 | 8.77–9.41 | −1.48 | 19.9–21.1 | Seed protein 31-1 [77], cqSeed_protein-003 [78], Seed protein 10-1 [76], Seed protein 37-8 [79] |
| qOC20.2(21) | 20 | 110.448 | 20_15355398–20_19182017 | 8.92 | 0.91 | 20.1 | cqSeed_oil-004 [78] | |
| qQ20.3 | qOC20.3(21), qOC20.3(20) | 20 | 126.455–131.287 | 20_25307871–20_25691060 | 8.86–9.78 | 0.95 | 20.1–21.8 | Seed oil 13-4 [80], Seed oil 24-30 [61], mqSeed_Oil-020 [60], Seed oil 15-1 [81] |
| qOC20.4(20), qOC20.4(21) | 20 | 144.078 | 20_32381606 | 9.74–10.10 | 0.98 | 21.7–22.5 | Seed oil 2-1 [28] | |
| qPC20.3(20), qPC20.3(21) | 20 | 144.078–149.964 | 20_32381606–20_33290104 | 7.53–8.19 | −1.39 | 17.4–18.6 | Seed protein 1-1 [28], Seed protein 1-2 [28], Seed protein 39-4 [74], Seed protein 26-5 [58] | |
| qQ20.4 | qOC20.5(20), qOC20.5(21) | 20 | 203.517 | 20_37787855 | 2.51–4.54 | 0.60 | 6.1–10.8 | Seed oil 27-8 [58], Seed oil 42-39 [14], Seed oil 43-18 [66] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Q.; Qin, J.; Li, X.; Liu, B.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Q.; Liu, S.; Zhao, X.; Ma, N.; Yan, L.; et al. Coordinate Inheritance of Seed Isoflavone and Protein in Soybean. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1178. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12081178
Zhao Q, Qin J, Li X, Liu B, Liu Y, Yang Q, Liu S, Zhao X, Ma N, Yan L, et al. Coordinate Inheritance of Seed Isoflavone and Protein in Soybean. Agriculture. 2022; 12(8):1178. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12081178
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Qingsong, Jun Qin, Xinxin Li, Bingqiang Liu, Yang Liu, Qing Yang, Song Liu, Xin Zhao, Niannian Ma, Long Yan, and et al. 2022. "Coordinate Inheritance of Seed Isoflavone and Protein in Soybean" Agriculture 12, no. 8: 1178. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12081178
APA StyleZhao, Q., Qin, J., Li, X., Liu, B., Liu, Y., Yang, Q., Liu, S., Zhao, X., Ma, N., Yan, L., Zhang, M., Yang, C., & Liao, H. (2022). Coordinate Inheritance of Seed Isoflavone and Protein in Soybean. Agriculture, 12(8), 1178. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12081178









