Subcellular Responses and Avoidance Behavior in Earthworm Eisenia andrei Exposed to Pesticides in the Artificial Soil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Test Organism
2.3. Determination of Acute Toxicity
2.4. Assessment of Biomarker Responses
2.5. Assessment of Avoidance Behavior
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Acute Toxicity of Investigated Pesticides
3.2. Avoidance Behavior
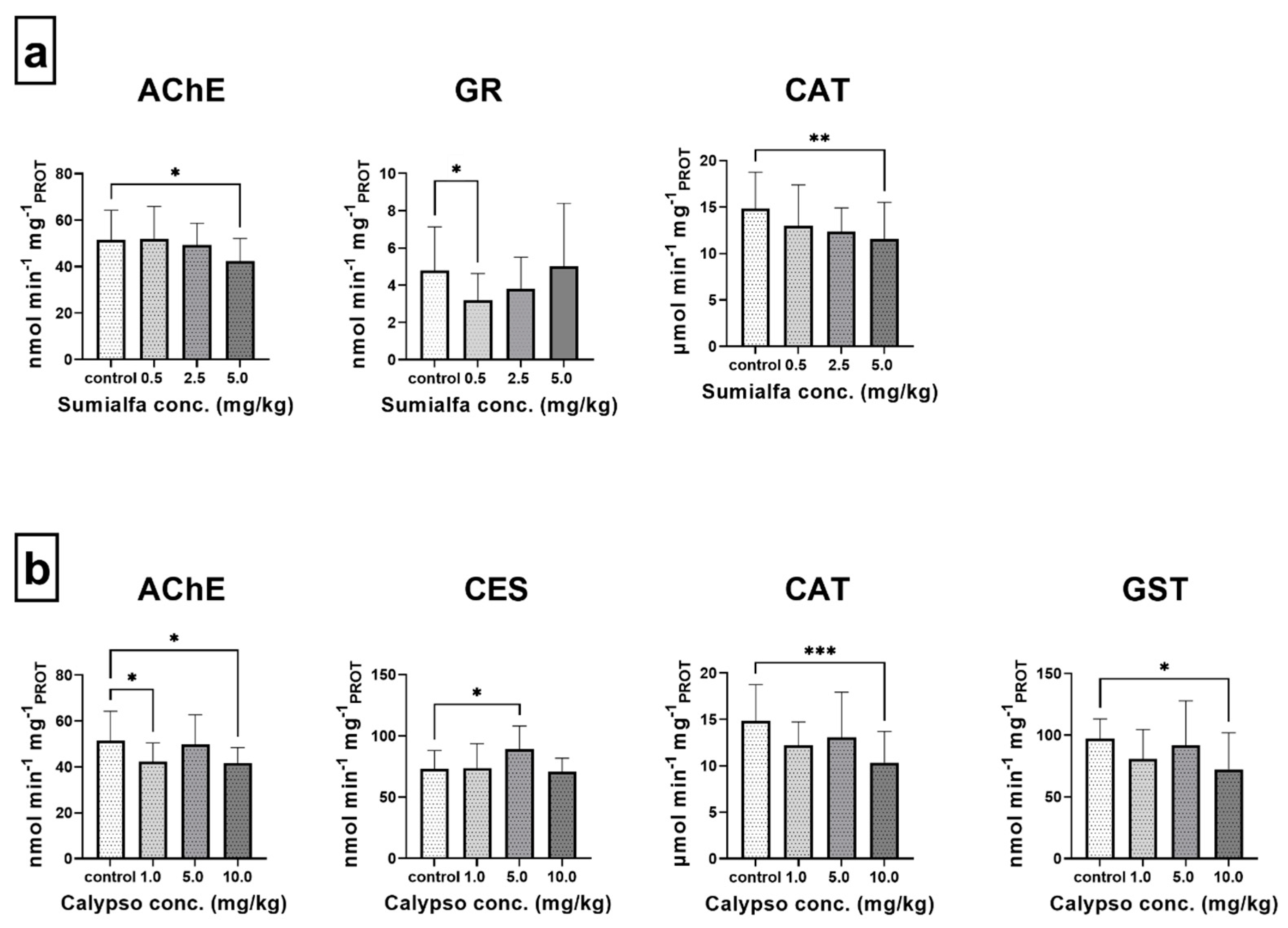
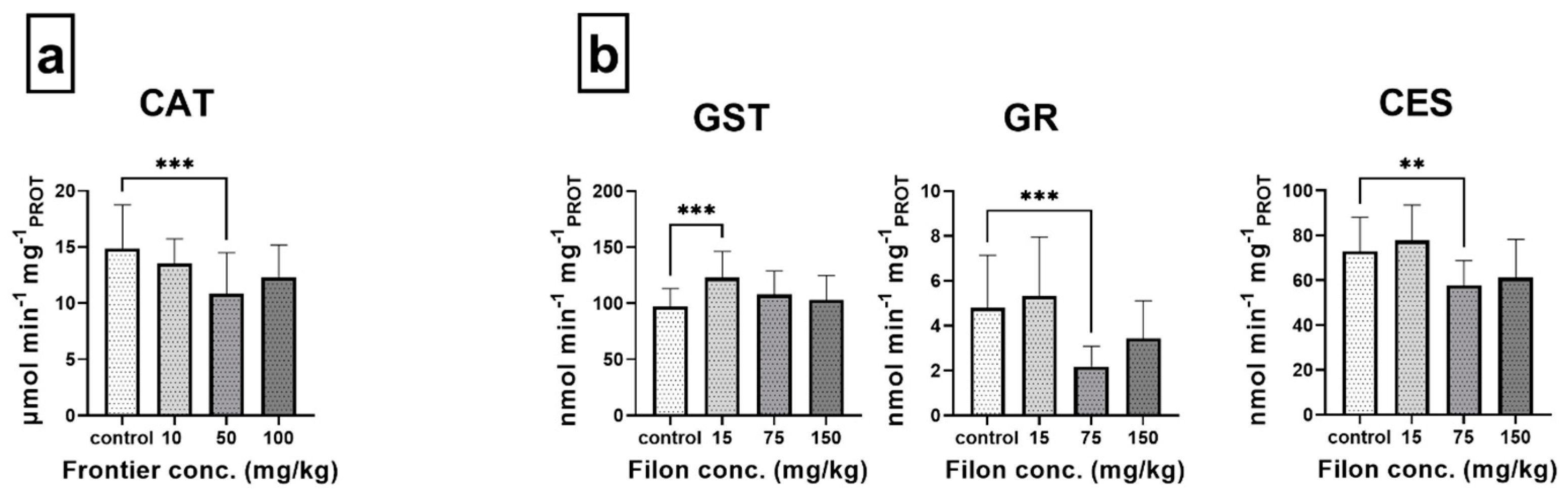
3.3. Biomarker Responses
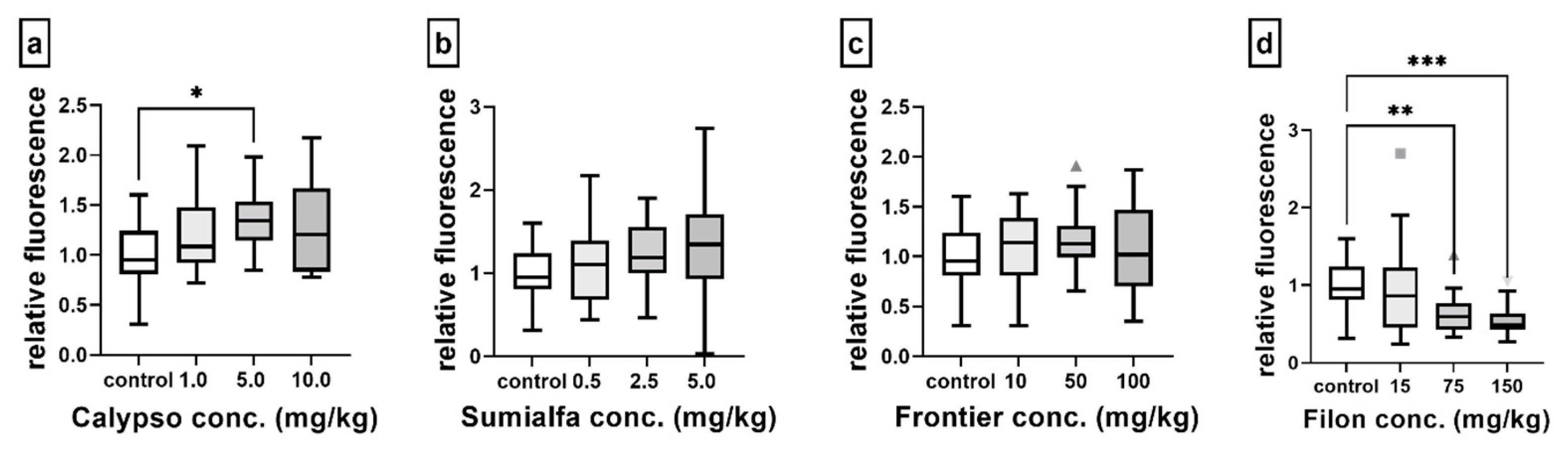
3.4. Fluorescence-Based ROS and GSH Determination
3.5. MXR Activity
4. Discussion
4.1. Acute Toxicity
4.2. Avoidance Behavior
4.3. Enzymatic Biomarker Responses
4.4. Non-Enzymatic Oxidative Stress-Related Responses
4.5. MXR Activity
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oerke, E.C. Crop losses to pests. J. Agric. Sci. 2006, 144, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Kumar, V.; Shahzad, B.; Tanveer, M.; Sidhu, G.P.S.; Handa, N.; Kohli, S.K.; Yadav, P.; Bali, A.S.; Parihar, R.D.; et al. Worldwide pesticide usage and its impacts on ecosystem. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.H.M.; Lenzen, M.; McBratney, A.; Maggi, F. Risk of pesticide pollution at the global scale. Nat. Geosci. 2021, 14, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Miao, R.; Khanna, M. Neonicotinoids and decline in bird biodiversity in the United States. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 1027–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockström, J.; Steffen, W.; Noone, K.; Persson, Å.; Chapin, F.S.; Lambin, E.F.; Lenton, T.M.; Scheffer, M.; Folke, C.; Schellnhuber, H.J.; Nykvist, B.; et al. A safe operating space for humanity. Nature 2009, 461, 472–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persson, L.; Carney Almroth, B.M.; Collins, C.D.; Cornell, S.; de Wit, C.A.; Diamond, M.L.; Fantke, P.; Hassellöv, M.; MacLeod, M.; Ryberg, M.W.; et al. Outside the Safe Operating Space of the Planetary Boundary for Novel Entities. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 1510–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopittke, P.M.; Menzies, N.W.; Dalal, R.C.; McKenna, B.A.; Husted, S.; Wang, P.; Lombi, E. The role of soil in defining planetary boundaries and the safe operating space for humanity. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominati, E.; Mackay, A.; Green, S.; Patterson, M. A soil change-based methodology for the quantification and valuation of ecosystem services from agro-ecosystems: A case study of pastoral agriculture in New Zealand. Ecol. Econ. 2014, 100, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopittke, P.M.; Menzies, N.W.; Wang, P.; McKenna, B.A.; Lombi, E. Soil and the intensification of agriculture for global food security. Environ. Int. 2019, 132, 105078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, A.P.; Eugenio, N.R. Status of Local Soil Contamination in Europe; Publications Office of the EU: Brussels, Belgium, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Montanarella, L.; Panagos, P. The Relevance of Sustainable Soil Management within the European Green Deal. Land Use Policy 2021, 100, 104950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ockleford, C.; Adriaanse, P.; Berny, P.; Brock, T.; Duquesne, S.; Grilli, S.; Hernandez-Jerez, A.F.; Bennekou, S.H.; Klein, M.; Kuhl, T.; et al. Scientific Opinion addressing the state of the science on risk assessment of plant protection products for in-soil organisms. EFSA J. 2017, 15, e04690. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pérès, G.; Vandenbulcke, F.; Guernion, M.; Hedde, M.; Beguiristain, T.; Douay, F.; Houot, S.; Piron, D.; Richard, A.; Bispo, A.; et al. Earthworm indicators as tools for soil monitoring, characterization and risk assessment. An example from the national Bioindicator programme (France). Pedobiologia 2011, 54, S77–S87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelosi, C.; Barot, S.; Capowiez, Y.; Hedde, M.; Vandenbulcke, F. Pesticides and earthworms. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2014, 34, 199–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, C.; Pereira, R.; Gonçalves, F. Using earthworm avoidance behaviour to assess the toxicity of formulated herbicides and their active ingredients on natural soils. J. Soils Sediments 2009, 9, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuerst, E.P. Understanding the Mode of Action of the Chloroacetamide and Thiocarbamate Herbicides. Weed Technol. 1987, 1, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattelle, D.B.; Yamamoto, D. Molecular Targets of Pyrethroid Insecticides. In Advances in Insect Physiology; Evans, P.D., Wigglesworth, V.B., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1985; Volume 20, pp. 147–213. [Google Scholar]
- Soderlund, D.M.; Bloomquist, R. Neurotoxic actions of pyrethroid insecticides. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1989, 34, 77–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Jiang, H. Inhibition and recovery of biomarkers of earthworm Eisenia fetida after exposure to thiacloprid. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 9475–9482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima Silva, C.; De Brennan, N.; Brouwer, J.M.; Commandeur, D.; Verweij, R.A.; van Gestel, C.A.M. Comparative toxicity of imidacloprid and thiacloprid to different species of soil invertebrates. Ecotoxicology 2017, 26, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renaud, M.; Akeju, T.; Natal-da-luz, T.; Leston, S.; Ramos, F.; Sousa, J.P.; Azevedo-Pereira, H.M. Effects of the neonicotinoids acetamiprid and thiacloprid in their commercial formulations on soil fauna. Chemosphere 2018, 194, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, R.; Bordalo, M.D.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Pestana, J.L.T. Effects of the pyrethroid esfenvalerate on the oligochaete, Lumbriculus variegatus. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2016, 96, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Xiong, K.; Liu, J. Comparative toxicity and bioaccumulation of fenvalerate and esfenvalerate to earthworm Eisenia fetida. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 310, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lackmann, C.; Velki, M.; Bjedov, D.; Ečimović, S.; Seiler, T.-B.; Hollert, H. Commercial preparations of pesticides exert higher toxicity and cause changes at subcellular level in earthworm Eisenia andrei. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2021, 33, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Løkke, H.; van Gestel, C.A.M. Handbook of Soil Invertebrate Toxicity Tests; John Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. OECD Guideline 207: Earthworm, Acute Toxicity Tests; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Habig, W.H.; Jakoby, W.B. Assays for differentiation of glutathione S-transferases. Methods Enzymol. 1981, 77, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.D.; Andres, V., Jr.; Featherstone, R.M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosokawa, M.; Satoh, T. Measurement of carboxylesterase (CES). Curr. Protoc. Toxicol. 2001, 10, 4.7.1–4.7.14. [Google Scholar]
- Claiborne, A.I. Catalase activity. In Handbook of Methods in Oxygen Radical Research; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1985; pp. 283–284. [Google Scholar]
- Hackenberger, B.K.; Velki, M.; Stepic, S.; Hackenberger, D.K. First evidence for the presence of efflux pump in the earthworm Eisenia andrei. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 75, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lackmann, C.; Velki, M.; Seiler, T.-B.; Hollert, H. Herbicides diuron and fluazifop-p-butyl affect avoidance response and multixenobiotic resistance activity in earthworm Eisenia andrei. Chemosphere 2018, 210, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, F.P. Pesticides, environment, and food safety. Food Energy Secur. 2017, 6, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, R.M.; Seibert, D.; Quesada, H.B.; de Jesus Bassetti, F.; Fagundes-Klen, M.R.; Bergamasco, R. Occurrence, impacts and general aspects of pesticides in surface water: A review. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 135, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignet, C.; Cappello, T.; Fu, Q.; Lajoie, K.; de Marco, G.; Clérandeau, C.; Mottaz, H.; Maisano, M.; Hollender, J.; Schirmer, K.; et al. Imidacloprid induces adverse effects on fish early life stages that are more severe in Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes) than in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Chemosphere 2019, 225, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, C.; Surgan, M. Unidentified inert ingredients in pesticides: Implications for human and environmental health. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 1803–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Pang, S.; Mu, X.; Qi, S.; Li, D.; Cui, F.; Wang, C. Biological response of earthworm, Eisenia fetida, to five neonicotinoid insecticides. Chemosphere 2015, 132, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, B.L.; Dorough, H.W. Relative toxicities of chemicals to the earthworm Eisenia Foetida. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1984, 3, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Conclusion on the peer review of the pesticide risk assessment of the active substance esfenvalerate. EFSA J. 2014, 12, 3873. [Google Scholar]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA); Abdourahime, H.; Anastassiadou, M.; Arena, M.; Auteri, D.; Barmaz, S.; Brancato, A.; Brocca, D.; Bura, L.; Carrasco Cabrera, L.; Chiusolo, A.; et al. Peer review of the pesticide risk assessment of the active substance thiacloprid. EFSA J. 2019, 17, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Conclusion regarding the peer review of the pesticide risk assessment of the active substance prosulfocarb. EFSA J. 2007, 5, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA); Arena, M.; Auteri, D.; Barmaz, S.; Bellisai, G.; Brancato, A.; Brocca, D.; Bura, L.; Byers, H.; Chiusolo, A.; et al. Peer review of the pesticide risk assessment of the active substance dimethenamid-P. EFSA J. 2018, 16, 5211. [Google Scholar]
- Damalas, C.A.; Eleftherohorinos, I.G. Pesticide Exposure, Safety Issues, and Risk Assessment Indicators. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2011, 8, 1402–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, K.; Duca, R.C.; Lovas, S.; Creta, M.; Scheepers, P.T.J.; Godderis, L.; Ádám, B. Systematic review of comparative studies assessing the toxicity of pesticide active ingredients and their product formulations. Environ. Res. 2020, 181, 108926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hund-Rinke, K.; Achazi, R.; Römbke, J.; Warnecke, D. Avoidance test with Eisenia fetida as indicator for the habitat function of soils: Results of a laboratory comparison test. J. Soils Sediments 2003, 3, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, B.B.M.; Candolin, U. Behavioral responses to changing environments. Behav. Ecol. 2015, 26, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, A.T.; Ågerstrand, M.; Brooks, B.W.; Allen, J.; Bertram, M.G.; Brodin, T.; Dang, Z.; Duquesne, S.; Sahm, R.; Hoffmann, F.; et al. The Role of Behavioral Ecotoxicology in Environmental Protection. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 5620–5628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sousa, A.P.A.; de Andréa, M.M. Earthworm (Eisenia andrei) avoidance of soils treated with cypermethrin. Sensors 2011, 11, 11056–11063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeardley, R.B.; Lazorchak, J.M.; Gast, L.C. The potential of an earthworm avoidance test for evaluation of hazardous waste sites. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1996, 15, 1532–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.L.; Antunes, S.C.; Ferreira, A.C.; Gonçalves, F.; Pereira, R. Avoidance behavior of earthworms under exposure to pesticides: Is it always chemosensorial? J. Environ. Sci. Health-Part B Pestic. Food Contam. Agric. Wastes 2010, 45, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrino, V.; De Marco, G.; Minutoli, R.; Lo Paro, G.; Giannetto, A.; Cappello, T.; De Plano, L.M.; Cecchini, S.; Fazio, F. Effects of pesticides on Chelon labrosus (Risso, 1827) evaluated by enzymatic activities along the north eastern Sicilian coastlines (Italy). Eur. Zool. J. 2021, 88, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missawi, O.; Bousserrhine, N.; Zitouni, N.; Maisano, M.; Boughattas, I.; De Marco, G.; Cappello, T.; Belbekhouche, S.; Guerrouache, M.; Alphonse, V.; et al. Uptake, accumulation and associated cellular alterations of environmental samples of microplastics in the seaworm Hediste diversicolor. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 406, 124287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, R.; Silvestro, S.; Coppola, F.; Meucci, V.; Battaglia, F.; Intorre, L.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Pretti, C.; Faggio, C. Biochemical and Physiological Responses Induced in Mytilus galloprovincialis After a Chronic Exposure to Salicylic Acid. Aquat. Toxicol. 2019, 214, 105258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.M.M.; Rocha, C.P.; Marques, J.C.; Gonçalves, F.J.M. Enzymes as useful biomarkers to assess the response of freshwater communities to pesticide exposure—A review. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 122, 107303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, G.V.; Rao, K.S.J. Modulation in Acetylcholinesterase of Rat Brain by Pyrethroids In Vivo and an In Vitro Kinetic Study. J. Neurochem. 1995, 65, 2259–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikinmaa, M. An Introduction to Aquatic Toxicology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Colle, D.; Farina, M.; Ceccatelli, S.; Raciti, M. Paraquat and Maneb Exposure Alters Rat Neural Stem Cell Proliferation by Inducing Oxidative Stress: New Insights on Pesticide-Induced Neurodevelopmental Toxicity. Neurotox. Res. 2018, 34, 820–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukaszewicz-Hussain, A. Role of oxidative stress in organophosphate insecticide toxicity—Short review. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2010, 98, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velki, M.; Hackenberger, B.K. Biomarker responses in earthworm Eisenia andrei exposed to pirimiphos-methyl and deltamethrin using different toxicity tests. Chemosphere 2013, 90, 1216–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, G.; Zhu, L.; Wang, J. DNA damage and oxidative stress induced by imidacloprid exposure in the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Active Ingredient | Mortality 1 in % | Commercial Preparation | Concentration in mg/kg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| thiacloprid | 53% at 850 mg/kg | Calypso | LC10 | 29.720 |
| LC50 | 102.035 | |||
| LC90 | 350.312 | |||
| esfenvalerate | 80% at 300 mg/kg | Sumialfa | LC10 | 5.723 |
| LC50 | 10.149 | |||
| LC90 | 17.800 | |||
| dimethenamid-p | 80% at 1000 mg/kg | Frontier | LC10 | 108.468 |
| LC50 | 249.804 | |||
| LC90 | 575.302 | |||
| prosulfocarb | 0% at 1200 mg/kg | Filon | LC10 | 312.452 |
| LC50 | 558.376 | |||
| LC90 | 982.145 |
| Pesticide | Concentration (mg/kg) | Distribution (%) | Net Response (%) | Toxicity Evaluation 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Treated | ||||
| Calypso | 1 | 60 | 40 | 20 | NRHF |
| 5 | 50 | 50 | 0 | NRHF | |
| 10 | 68 | 32 | 36 | NRHF | |
| Sumialfa | 0.5 | 48 | 52 | −4 | NRHF |
| 2.5 * | 70 | 30 | 40 | NRHF | |
| 5 *** | 76 | 24 | 52 | NRHF | |
| Frontier | 10 | 48 | 52 | −4 | NRHF |
| 50 * | 70 | 30 | 40 | NRHF | |
| 100 *** | 100 | 0 | 100 | RHF | |
| Filon | 15 | 70 | 30 | 40 | NRHF |
| 75 ** | 87 | 13 | 73.33 | RHF | |
| 150 *** | 94 | 6 | 87.5 | RHF | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lackmann, C.; Šimić, A.; Ečimović, S.; Mikuška, A.; Seiler, T.-B.; Hollert, H.; Velki, M. Subcellular Responses and Avoidance Behavior in Earthworm Eisenia andrei Exposed to Pesticides in the Artificial Soil. Agriculture 2023, 13, 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13020271
Lackmann C, Šimić A, Ečimović S, Mikuška A, Seiler T-B, Hollert H, Velki M. Subcellular Responses and Avoidance Behavior in Earthworm Eisenia andrei Exposed to Pesticides in the Artificial Soil. Agriculture. 2023; 13(2):271. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13020271
Chicago/Turabian StyleLackmann, Carina, Antonio Šimić, Sandra Ečimović, Alma Mikuška, Thomas-Benjamin Seiler, Henner Hollert, and Mirna Velki. 2023. "Subcellular Responses and Avoidance Behavior in Earthworm Eisenia andrei Exposed to Pesticides in the Artificial Soil" Agriculture 13, no. 2: 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13020271
APA StyleLackmann, C., Šimić, A., Ečimović, S., Mikuška, A., Seiler, T.-B., Hollert, H., & Velki, M. (2023). Subcellular Responses and Avoidance Behavior in Earthworm Eisenia andrei Exposed to Pesticides in the Artificial Soil. Agriculture, 13(2), 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13020271








