Optimization and Experiment of Hot Air Drying Process of Cyperus esculentus Seeds
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
2.2. Instruments and Equipment
2.3. Experimental Method
2.3.1. Drying Characteristics Experiment Results and Analysis
2.3.2. Single-Factor Experiment
2.3.3. Multi-Factor Experiment
2.4. Detection Method and Evaluation Index
2.4.1. Moisture Detection Method
2.4.2. Single-Factor Experiment Evaluation Index
2.4.3. Multi-Factor Experiment Evaluation Index
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Drying Characteristics Experiment
3.2. Single-Factor Experiment
- (1)
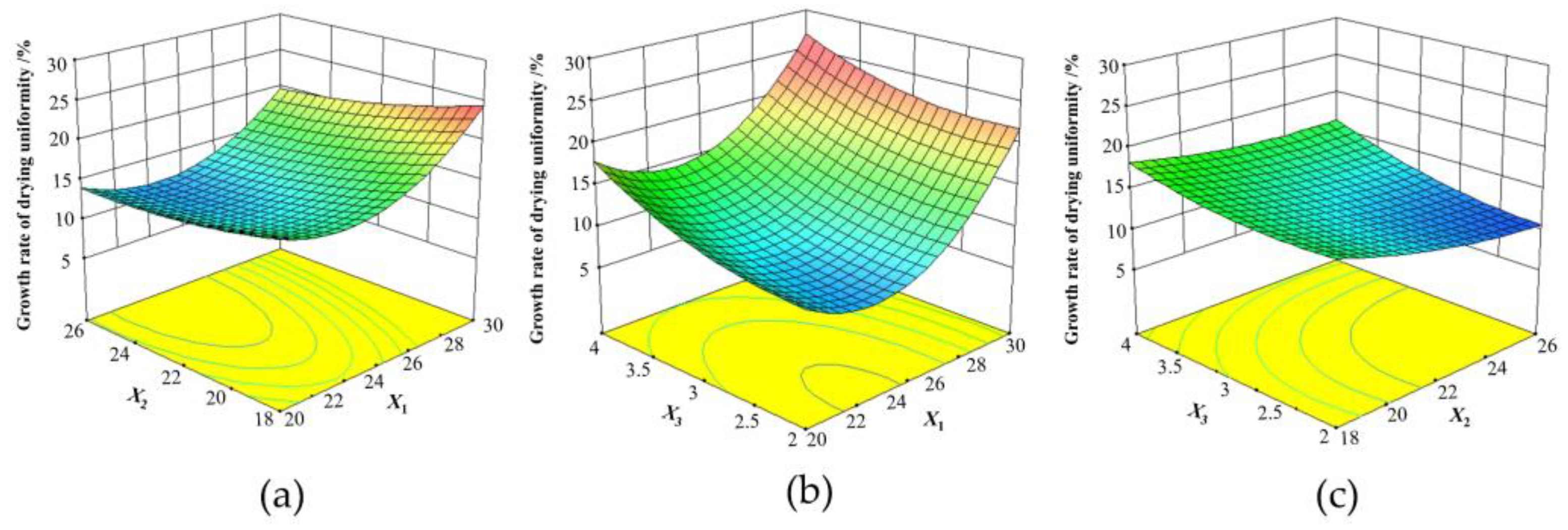
- The effect of experimental factors on the drying uniformity
- (2)
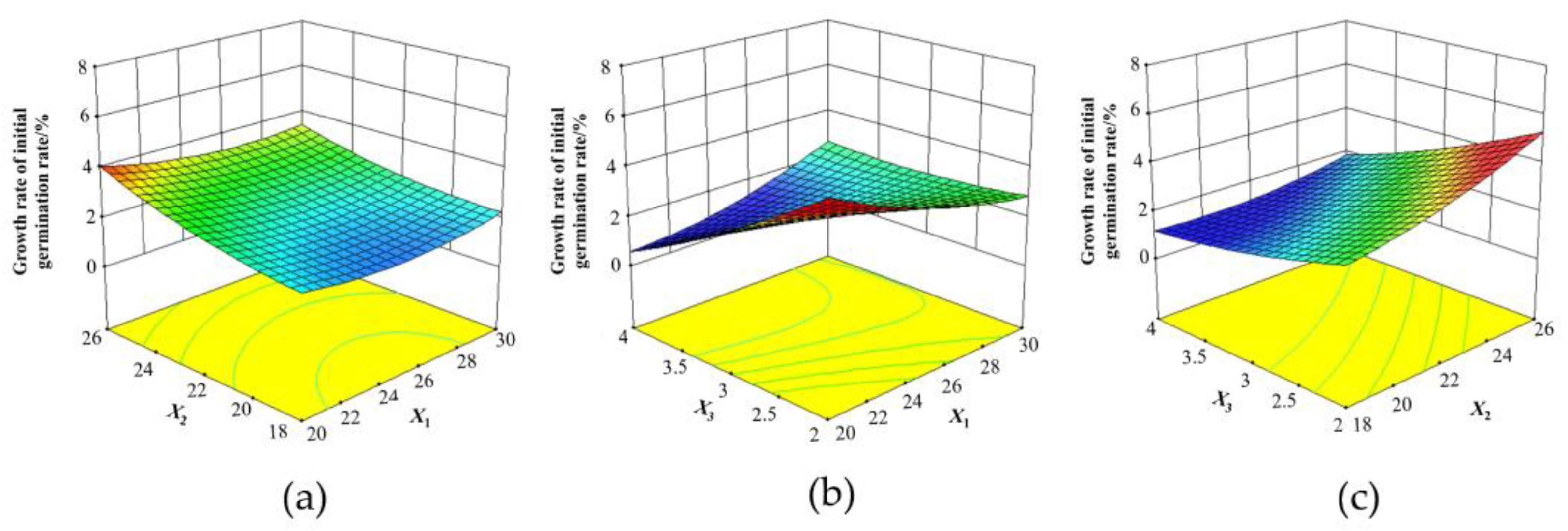
- Effect of test factors on initial germination rate
- (3)
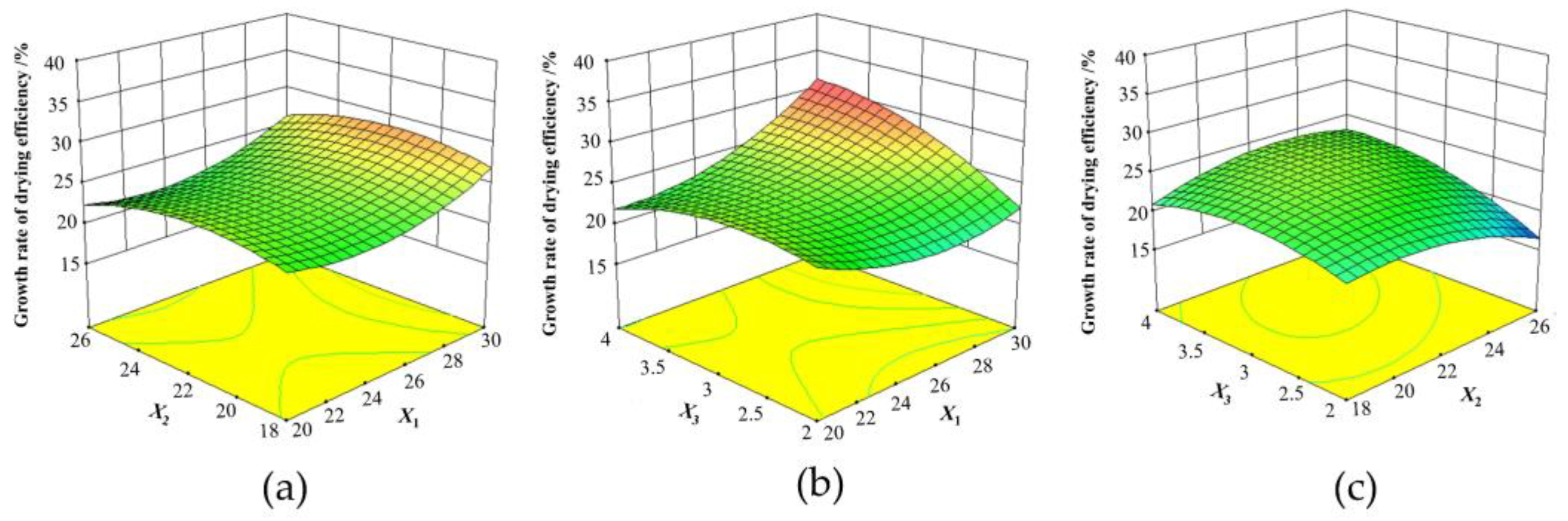
- Effect of test factors on the drying time
3.3. Multi-Factor Experiment
- (1)
- Effect of experimental factors on the growth rate of drying uniformity
- (2)
- Effect of test factors on the growth rate of initial germination rate
- (3)
- Effect of test factors on the growth rate of drying efficiency
3.4. Model Validation of Tempering Process Parameters
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z.; Li, S.; Liang, X.; Xu, L.; Zou, Y. Development status and prospect of Cyperus esculentus industry in China. Sci. Technol. Ind. 2022, 22, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Lu, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhou, Z.; He, H. Effects of moisture content on physical and mechanical properties of Cyperus esculentus. J. Chin. Agric. Mech. 2022, 43, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, M.; Zhang, J.; Han, X.; Yao, D.; Ye, Y.; Qian, H.; Li, X. Sprouting characteristics of yellow nutsedge tubers stored in winter. J. Jilin Agric. Univ. 2023, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, S.; Ouyang, W.; Ren, Z.; Xiang, H.; Ma, Z. The In Vitro and In Vivo antioxidant properties of Cyperus esculentus oil from Xinjiang, China. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 1505–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Guo, P.; Yang, F.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhu, W. Drying characteristics and quality of wet peeling Cyperus esculentus under different drying processes. Chin. J. Oil Crop Sci. 2022, 44, 1117–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, A.; Sadeghi, M.; Mireei, S. Multi-stage intermittent drying of rough rice in terms of tempering and stress cracking indices and moisture gradients interpretation. Dry. Technol. Int. J. 2017, 36, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, W.; Xie, J.; Zheng, B.; Miao, S.; Lo, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhuang, W.; Tian, Y. Microwave vacuum drying of lotus seeds: Effect of a single-stage tempering treatment on drying characteristics, moisture distribution, and product quality. Dry. Technol. 2017, 35, 1561–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Tao, Y.; Li, W.; Sherif, S.; Tang, X. Heat transfer characteristics and kinetics of Camellia oleifera seeds during hot-air drying. J. Therm. Sci. Eng. Appl. 2019, 12, 031017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Yu, S.; Wang, D. Effect of drying temperatures on the peanut quality during hot air drying. J. Oleo Sci. 2020, 69, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Khalifa, I.; Hu, L.; Zhu, W.; Li, C. Influence of three different drying techniques on persimmon chips’ characteristics: A comparison study among hot-air, combined hot-air-microwave, and vacuum-freeze drying techniques. Food Bioprod. Process. 2019, 118, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Yang, F.; Liu, Y. Characteristics and mathematical model of Cyperus esculentus drying by hot air. J. Chin. Cereals Oils Assoc. 2021, 36, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, S.; Dong, X.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Z. Numerical simulation and optimization of isothermal drying-tempering paddy. Food Sci. 2019, 40, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Yu, Y.; Qin, J.; Lin, J. Optimization of shiitake mushroom vacuum tempering drying process based on imaginary calculation of its shrinking rate. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2010, 26, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Siebenmorgen, T.; Mauromoustakos, A. Effect of tempering approach following cross-flow drying on rice milling yields. Dry. Technol. 2019, 37, 2137–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Yin, J.; Xie, H.; Zhang, Z. Reconstruction of rice drying model and analysis of tempering characteristics based on drying accumulated temperature. Appl. Sci. 2022, 11, 11113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Gao, R.; Zhuang, W.; Xiao, J.; Zheng, B.; Tian, Y. Combined single-stage tempering and microwave vacuum drying of the edible mushroom Agrocybe chaxingu: Effects on drying characteristics and physical-chemical qualities. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 128, 109372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golmohammadi, M.; Rajabi-Hamane, M.; Hashemi, S. Optimization of drying-tempering periods in a paddy rice dryer. Dry. Technol. 2012, 30, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Liu, B.; Wang, D.; Kang, N.; Zhao, L. Drying-tempering characteristics and fissuring law of paddy rice kernel. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2018, 49, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golmohammadi, M.; Assar, M.; Mehdi, R.; Hashemi, S. Energy efficiency investigation of intermittent paddy rice dryer: Modeling and experimental study. Food Bioprod. Process. 2015, 94, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, P.; Yang, D.; Liu, X.; Zhou, J. Analysis of drying-temping kinetics for corn kernel. J. Chin. Cereals Oils Assoc. 2017, 32, 1–5+18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Liu, W.; Ren, G. Hot air drying combined vacuum ventilation tempering improving quality of dried okra products. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2016, 32, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, J.; Qiu, S.; Zhan, Y.; Tao, D.; Zhang, B. Optimization and experimental study of tempering process parameters during hot air drying of paddy rice. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2021, 37, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, J.; Yu, W.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, B.; Xu, B.; Gao, H. Tempering drying characteristics of paddy rice and construction of kinetic model. J. Shenyang Agric. Univ. 2021, 52, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Wang, D.; Wang, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhan, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, L. Effect on drying characteristics and additional crack percentage of paddy rice under the tempering drying process conditions in deep bed. J. Shenyang Agric. Univ. 2021, 52, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Wang, J.; Wu, H.; Ling, F. Quality characteristics analysis and process optimization of hot air drying of Lentinus edodes. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2022, 48, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wankhade, P.; Sapkal, R.; Sapkal, V. Drying characteristics of okra slices on drying in hot air dryer. Procedia Eng. 2013, 51, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhu, E.; Zhu, Z. Water desorption isotherm and drying characteristics of green soybean. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2015, 60, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golmohammadi, M.; Foroughi-dahr, M.; Rajabi-Hamaneh, M.; Shojamoradi, A.; Hashemi, S. Study on drying kinetics of paddy rice: Intermittent drying. Iran. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. 2016, 35, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Lu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Koide, S.; Cao, W. Effect of drying and tempering on rice fissuring analysed by integrating intra-kernel moisture distribution. J. Food Eng. 2010, 97, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquerreta, J.; Iguaz, A.; Arroqui, C.; Virseda, P. Effect of high temperature intermittent drying and tempering on rough rice quality. J. Food Eng. 2007, 80, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrozo, M.; Mujumdar, A.; Freire, J. Air-drying of seeds: A review. Dry. Technol. 2014, 32, 1127–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onwude, D.; Hashim, N.; Chen, G. Recent advances of novel thermal combined hot air drying of agricultural crops. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 57, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yemmireddy, V.; Chinnan, M.; Kerr, W.; Hung, Y. Effect of drying method on drying time and physico-chemical properties of dried rabbiteye blueberries. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 50, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, D.; Lv, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, L. Drying characteristics and water dynamics during microwave hot-air flow rolling drying of Pleurotus eryngii. Dry. Technol. 2020, 38, 1493–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Box, G.; Wilson, K. On the experimental attainment of optimum conditions. J. R. Stat. Soc. 1951, 13, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthukumar, V.; Rajesh, N.; Venkatasamy, R.; Sureshbabu, A.; Senthilkumar, N. Mathematical modeling for radial overcut on electrical discharge machining of incoloy 800 by response surface methodology. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2014, 6, 1674–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Fang, M.; Liu, Y. Optimization of a phase adjuster in a thermo-acoustic stirling engine using response surface methodology. Energy Procedia 2014, 61, 1772–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orikasa, T.; Koide, S.; Okamoto, S.; Imaizumi, T.; Muramatsu, Y.; Takeda, J.; Shiina, T.; Tagawa, A. Impacts of hot air and vacuum drying on the quality attributes of kiwifruit slices. J. Food Eng. 2014, 125, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Lia, D.; Liu, C.; Xiao, Y.; Lagnika, C.; Zhang, M. Effects of different combined drying methods on drying uniformity and quality of dried taro slices. Dry. Technol. 2019, 37, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


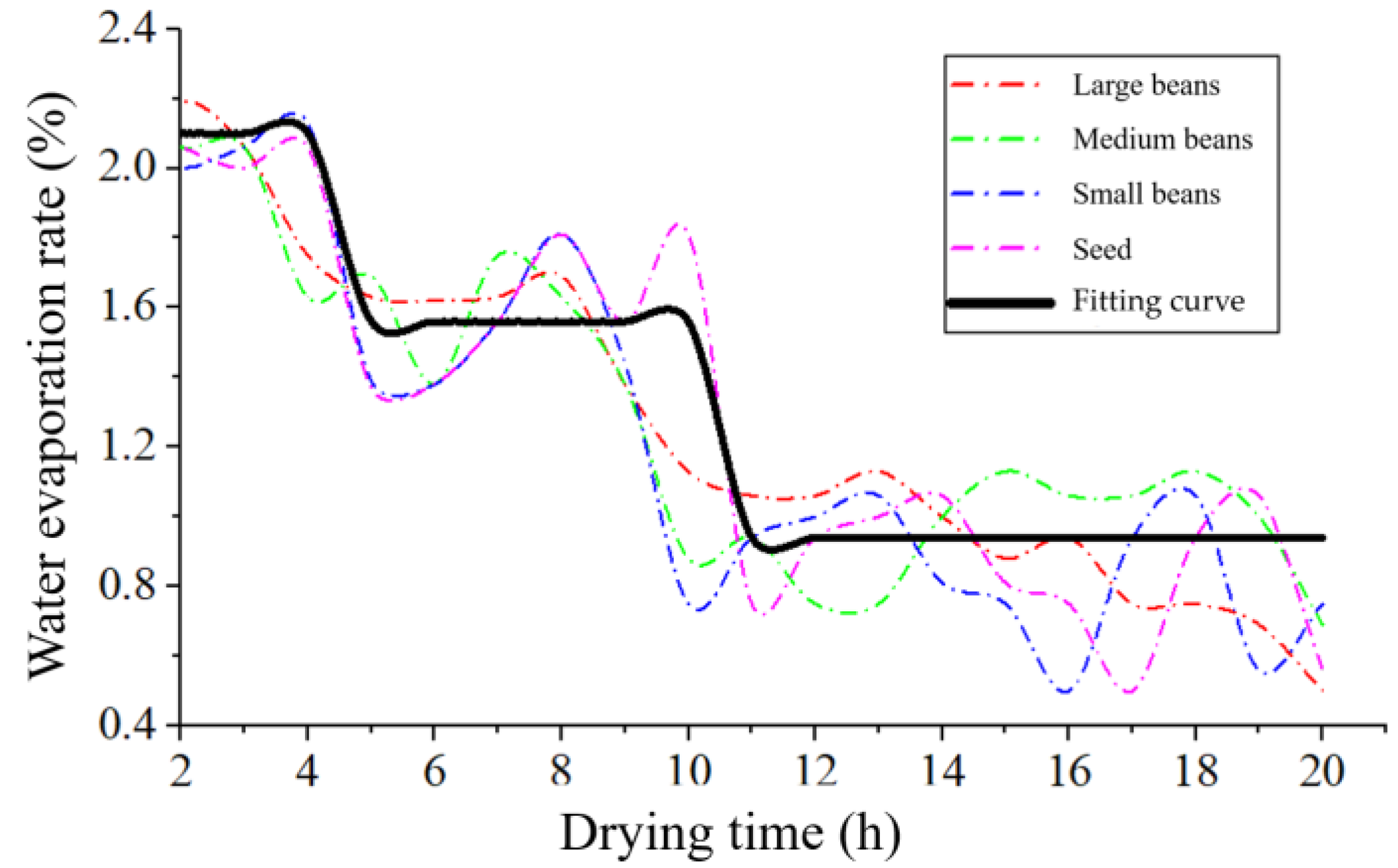
| Sample Type | Quality Range (g) | Actual Proportion (%) | Proportion of Beans as Seeds (%) | Proportion of Beans as Commodities (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Large beans | >1.3 | 20 | 40 | 20 |
| Medium beans | 0.8~1.3 | 45 | 60 | 50 |
| Small beans | 0.5~0.8 | 30 | 0 | 30 |
| Broken beans | <0.5 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| Levels | Drying Method | Tempering Temperature (°C) | Moisture Content of Cyperus esculentus at the Beginning of Tempering (%) | Tempering Duration (h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Vacuum drying | 20 | 30 | 1 |
| 2 | Hot air drying | 25 | 28 | 2 |
| 3 | Single-stage tempering treatment during hot air drying | 30 | 26 | 2.5 |
| 4 | 35 | 24 | 3 | |
| 5 | 22 | 3.5 | ||
| 6 | 20 | 4 | ||
| 7 | 18 | 4.5 | ||
| 8 | 16 | 5 |
| Factors | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Tempering Temperature X1 (°C) | Moisture Content of Cyperus esculentus at the Beginning of Tempering X2 (%) | Tempering Duration X3 (h) | |
| 34 | 29 | 4.5 | |
| 1 | 30 | 26 | 4 |
| 0 | 25 | 22 | 3 |
| −1 | 20 | 18 | 2 |
| 16 | 15 | 1.5 | |
| No. | Factors | Evaluation Indexes | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 (°C) | X2 (%) | X3 (h) | Y1 (%) | Y2 (%) | Y3 (%) | |
| 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | 17.97 | 4.00 | 26.46 |
| 2 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 27.31 | 3.00 | 21.67 |
| 3 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 14.26 | 7.50 | 21.67 |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 20.23 | 4.50 | 17.42 |
| 5 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 20.57 | 0.01 | 21.54 |
| 6 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 26.77 | 2.50 | 28.38 |
| 7 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 18.69 | 0.50 | 23.17 |
| 8 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 24.48 | 3.50 | 30.58 |
| 9 | −1.682 | 0 | 0 | 19.31 | 4.50 | 24.54 |
| 10 | 1.682 | 0 | 0 | 29.98 | 2.50 | 35.92 |
| 11 | 0 | −1.682 | 0 | 17.00 | 2.00 | 17.88 |
| 12 | 0 | 1.682 | 0 | 11.06 | 4.50 | 16.67 |
| 13 | 0 | 0 | −1.682 | 9.71 | 4.50 | 15.25 |
| 14 | 0 | 0 | 1.682 | 19.99 | 1.50 | 19.33 |
| 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 14.33 | 2.00 | 22.58 |
| 16 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 14.31 | 2.50 | 23.00 |
| 17 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 14.71 | 1.50 | 29.75 |
| 18 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 13.69 | 3.00 | 25.79 |
| 19 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 11.02 | 2.00 | 25.08 |
| 20 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 12.14 | 2.50 | 20.92 |
| Evaluation Indexes | Source of Variation | Sum of Squares | Degree of Freedom | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Growth rate of drying uniformity | Model | 584.02 | 9 | 64.89 | 12.03 | 0.0003 ** |
| Residual | 53.92 | 10 | 5.39 | |||
| Lack of fit | 43.19 | 5 | 8.64 | 4.02 | 0.0764 | |
| Error | 10.74 | 5 | 2.15 | |||
| Growth rate of initial germination rate | Model | 48.40 | 9 | 5.38 | 9.37 | 0.0008 ** |
| Residual | 5.74 | 10 | 0.5738 | |||
| Lack of fit | 4.36 | 5 | 0.8725 | 3.17 | 0.1154 | |
| Error | 1.38 | 5 | 0.2750 | |||
| Growth rate of drying efficiency | Model | 408.99 | 9 | 45.44 | 4.80 | 0.0111 * |
| Residual | 94.69 | 10 | 9.47 | |||
| Lack of fit | 46.36 | 5 | 9.27 | 0.9591 | 0.5177 | |
| Error | 48.33 | 5 | 9.67 |
| Test Number | Growth Rate of Drying Uniformity (%) | Growth Rate of Initial Germination Rate (%) | Growth Rate of Drying Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20.570 | 4.211 | 22.754 |
| 2 | 22.310 | 4.117 | 22.313 |
| 3 | 21.477 | 4.341 | 23.677 |
| Average | 21.452 | 4.223 | 22.915 |
| Error | 1.564 | 0.428 | 0.362 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, X.; Jin, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wang, G.; Huang, D. Optimization and Experiment of Hot Air Drying Process of Cyperus esculentus Seeds. Agriculture 2023, 13, 617. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13030617
Xia X, Jin Y, Zhao H, Wang G, Huang D. Optimization and Experiment of Hot Air Drying Process of Cyperus esculentus Seeds. Agriculture. 2023; 13(3):617. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13030617
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Xiaomeng, Yvhan Jin, Huiyan Zhao, Gang Wang, and Dongyan Huang. 2023. "Optimization and Experiment of Hot Air Drying Process of Cyperus esculentus Seeds" Agriculture 13, no. 3: 617. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13030617
APA StyleXia, X., Jin, Y., Zhao, H., Wang, G., & Huang, D. (2023). Optimization and Experiment of Hot Air Drying Process of Cyperus esculentus Seeds. Agriculture, 13(3), 617. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13030617







