Effect of SOD-Rich Melon Supplement on Performance, Serum Biochemical, Antioxidant and Meat Quality Characteristics of Tuj Lambs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Animals and Diet
2.2. Performance Traits
2.3. Serum Biochemical Profile
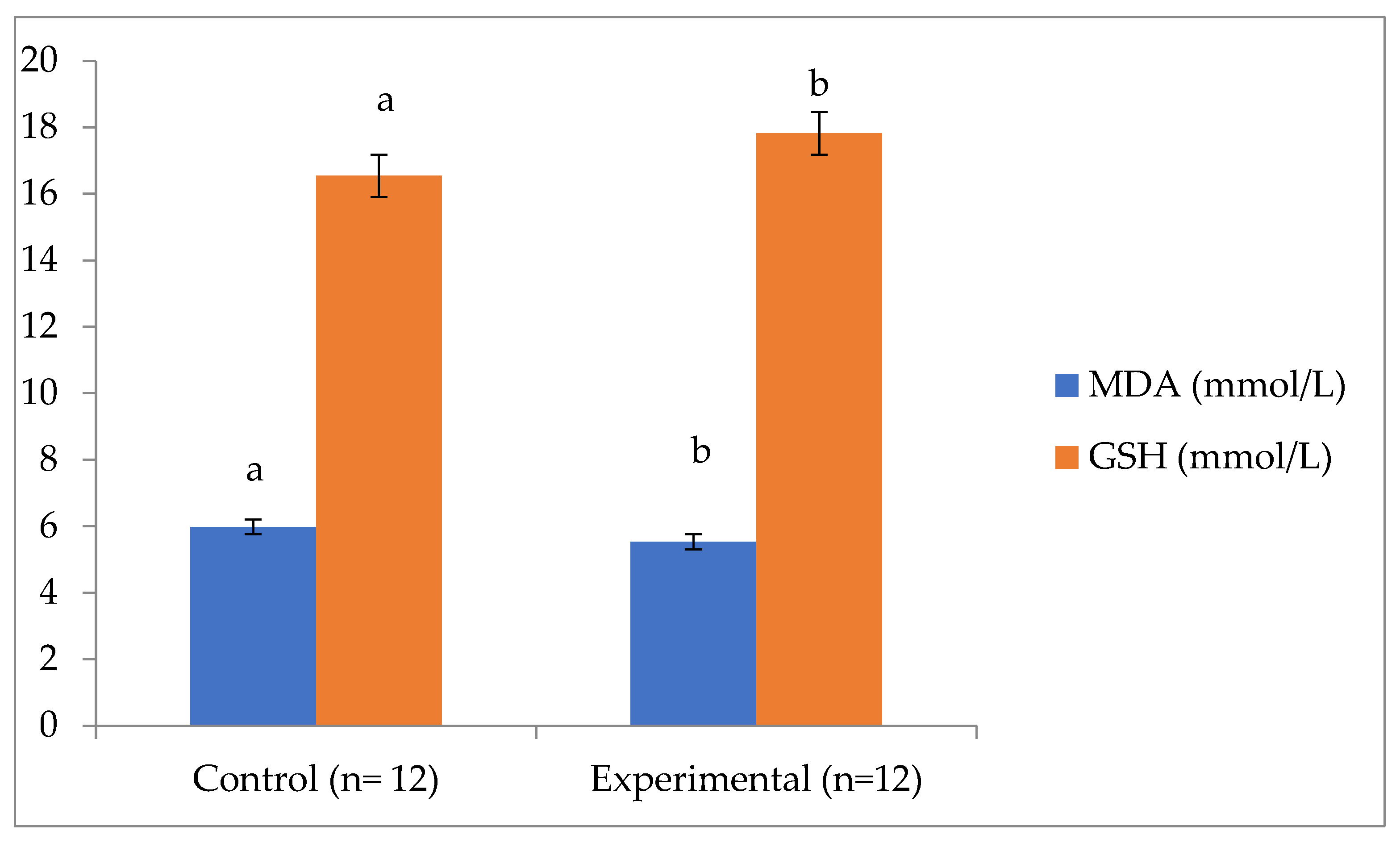
2.4. Antioxidant Profile
2.5. Meat Quality Characteristics
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thornton, P.K. Livestock production: Recent trends, future prospects. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. Biol. Sci. 2010, 365, 2853–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakshi, M.; Wadhwa, M.; Makkar, H.P. Waste to worth: Vegetable wastes as animal feed. CABI Rev. 2016, 2016, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, M.; Ibrahimi Khorram Abadi, E.; Mokhtarpour, A. Evaluation of the nutritional value of Iranian melon (Cucumis melo cv. Khatooni) wastes before and after ensiling in sheep feeding. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2019, 7, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Salem, H.B.; Nefzaoui, A. Feed blocks as alternative supplements for sheep and goats. Small Rumin. Res. 2003, 49, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebowale, E.; Taiwo, A. Utilization of crop residues and agro-industrial by-products as complete diets for West African dwarf sheep and goats. Niger. J. Anim. Prod. 1996, 23, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbar, M.; Anjum, M.; Rehman, S.; Shahzad, W. Comparative efficiency of sunflower meal and cottonseed cakes in the feed of crossbred calves for meat production. Pak. Vet. J. 2006, 26, 126–128. [Google Scholar]
- Ngwa, A.; Nsahlai, I.; Bonsi, M. Feed intake and dietary preferences of sheep and goats offered hay and legume-tree pods in South Africa. Agrofor. Syst. 2003, 57, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanum, S.; Yaqoob, T.; Sadaf, S.; Hussain, M.; Jabbar, M.; Hussain, H.; Kausar, R.; Rehman, S. Nutritional evaluation of various feedstuffs for livestock production using in vitro gas method. Pak. Vet. J. 2007, 27, 129. [Google Scholar]
- Jabbar, M.; Anjum, M. Effect of diets with different forage to concentrate ratio for fattening of Lohi lambs. Pak. Vet. J. 2008, 28, 150–152. [Google Scholar]
- Salem, H.B. Nutritional management to improve sheep and goat performances in semiarid regions. Rev. Bras. Zootec. 2010, 39, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blache, D.; Maloney, S.K.; Revell, D.K. Use and limitations of alternative feed resources to sustain and improve reproductive performance in sheep and goats. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2008, 147, 140–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasta, V.; Nudda, A.; Cannas, A.; Lanza, M.; Priolo, A. Alternative feed resources and their effects on the quality of meat and milk from small ruminants. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2008, 147, 223–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostagno, M.H. Can stress in farm animals increase food safety risk? Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2009, 6, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Manuja, A.; Aich, P. Stress and its impact on farm animals. Front. Biosci. 2012, 4, 1759–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, D.; Damon, M.; Gobert, M. Oxidative stress in farm animals: General aspects. Cah. Nutr. Diet 2013, 48, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lykkesfeldt, J.; Svendsen, O. Oxidants and antioxidants in disease: Oxidative stress in farm animals. Vet. J. 2007, 173, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arangoa, M.A.; Campanero, M.A.; Renedo, M.J.; Ponchel, G.; Irache, J.M. Gliadin nanoparticles as carriers for the oral administration of lipophilic drugs. Relationships between bioadhesion and pharmacokinetics. Pharm. Res. 2001, 18, 1521–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vouldoukis, I.; Conti, M.; Krauss, P.; Kamaté, C.; Blazquez, S.; Tefit, M.; Mazier, D.; Calenda, A.; Dugas, B. Supplementation with gliadin-combined plant superoxide dismutase extract promotes antioxidant defences and protects against oxidative stress. Phytother. Res. 2004, 18, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carillon, J.; Rugale, C.; Rouanet, J.-M.; Cristol, J.-P.; Lacan, D.; Jover, B. Endogenous antioxidant defense induction by melon superoxide dismutase reduces cardiac hypertrophy in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 65, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decorde, K.; Agne, A.; Lacan, D.; Ramos, J.; Fouret, G.; Ventura, E.; Feillet-Coudray, C.; Cristol, J.-P.; Rouanet, J.-M. Preventive effect of a melon extract rich in superoxide scavenging activity on abdominal and liver fat and adipokine imbalance in high-fat-fed hamsters. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 6461–6467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Décordé, K.; Ventura, E.; Lacan, D.; Ramos, J.; Cristol, J.-P.; Rouanet, J.-M. An SOD rich melon extract Extramel® prevents aortic lipids and liver steatosis in diet-induced model of atherosclerosis. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2010, 20, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carillon, J.; Romain, C.; Bardy, G.; Fouret, G.; Feillet-Coudray, C.; Gaillet, S.; Lacan, D.; Cristol, J.-P.; Rouanet, J.-M. Cafeteria diet induces obesity and insulin resistance associated with oxidative stress but not with inflammation: Improvement by dietary supplementation with a melon superoxide dismutase. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 65, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanwo, K.; Iposu, S.; Oso, A.; Fanimo, A.; Abiola, S. Growth Performance, nutrient intake and digestibility of goats fed melon husk and palm oil slurry at 30% inclusion level. Niger. J. Anim. Prod. 2011, 38, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanwo, K.; Iposu, S.; Okwelum, N.; Aderinboye, R.; Oso, A.; Fanimo, A.; Abiola, S. Growth performance, nutrient intake, digestibility and carcass characteristics of goats fed melon Husk (Colocynthis citrillus) and palm oil slurry (Elaeis guineensis) at 50% inclusion level. Niger. J. Anim. Prod. 2014, 41, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhong, X.; Shi, W.-y.; Guo, B. Study of malondialdehyde (MDA) content, superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) activities in chickens infected with avian infectious bronchitis virus. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 9213–9217. [Google Scholar]
- Carillon, J.; Barbé, F.; Barial, S.; Saby, M.; Sacy, A.; Rouanet, J.-M. Diet supplementation with a specific melon concentrate improves oviduct antioxidant defenses and egg characteristics in laying hens. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 1898–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Alagbe, J.; Sharma, S.; Oluwafemi, R.; Agubosi, O. Effect of dietary supplementation of melon (Citrallus lanatus) seed oil on the growth performance and antioxidant status of growing rabbits. Indones. J. Innov. Appl. Sci. 2021, 1, 134–143. [Google Scholar]
- Lallès, J.-P.; Lacan, D.; David, J.-C. A melon pulp concentrate rich in superoxide dismutase reduces stress proteins along the gastrointestinal tract of pigs. Nutrition 2011, 27, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ölmez, M.; Kanber, K.; Karadağoğlu, Ö.; Metin, Ö.; Şahİn, T.; Şerbetçİ, İ. Chia tohumu ve probiyotik/enzim İlavesinin ayrı ve kombine olarak tuj koyunları rasyonlarında kullanımının performans, rumen ve bazı kan parametreleri üzerine etkisi. OKÜ Fen Bil. Enst. 2022, 5, 1201–1215. [Google Scholar]
- Saatci, M.; Yildiz, S.; Kaya, I. New rearing systems for Tuj (Tushin) lambs. Small Rum. Res. 2003, 50, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarı, M.; Aksoy, A.R.; Tilki, M.; Kaya, İ.; Işık, S. Effect of different fattening methods on slaughter and carcass characteristics of Tuj male lambs. Arch. Anim. Breed. 2012, 55, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onk, K.; Sari, M.; Gurcan, I.S. Estimation of live weights at the beginning and the end of grazing season in Tuj lambs via scores of factor analysis. Ankara Üniv. Vet. Fak. Derg 2018, 65, 261–266. [Google Scholar]
- NARC. Nutrient Requirements of Small Ruminants: Sheep, Goats, Cervids, and New World Camelids; China Legal Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis, 21st ed.; AOAC International: Rockville, MD, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, D.; Selaive-Villarroel, A.; Pereira, E.; Osório, J.; Teixeira, A. Growth performance, feed efficiency and carcass characteristics of lambs produced from Dorper sheep crossed with Santa Inês or Brazilian Somali sheep. Small Rum. Res. 2013, 114, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, A.; Santra, A.; Karim, S. Carcass yield, composition and meat quality attributes of sheep and goat under semiarid conditions. Meat Sci. 2004, 66, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarali, E.; Yilmaz, O.; Cemal, I.; Karaca, O.; TAŞKIN, T. Meat quality characteristics in Kıvırcık lambs. Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2014, 38, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaolu, V.; Binuomote, R.; Akinlade, J.; Aderinola, O.; Oyelami, O. Intake and growth performance of West African Dwarf goats fed Moringa oleifera, Gliricidia sepium and Leucaena leucocephala dried leaves as supplements to cassava peels. J. Biol. Agric. Healthc. 2012, 2, 76–88. [Google Scholar]
- Raza, I. Effect of Dietary Herbal Extract and Probiotic Supplementation Alone or in Combination on Growth Performance, Meat Quality, and Stress Indicators of Broilers Subjected to High Stocking Density. Ph.D. Thesis, Aydin Adnan Menderes University, Aydin, Turkey, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bezerra, H.V.A.; Buarque, V.L.M.; Silva, L.S.B.; Leme, P.R.P.; Vidal, A.M.C.; Vaz, A.C.N.; Gallo, S.B.; Silva, S.L.; Leme, P.R. Effect of Castor and Cashew Nut Shell Oils, Selenium and Vitamin E as Antioxidants on the Health and Meat Stability of Lambs Fed a High-Concentrate Diet. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoruwa, M. Effects of locust bean pulp with melon husk supplementation on nitrogen utilization and blood chemistry of West African dwarf goats. Niger. J. Animal Sci. 2017, 19, 199–208. [Google Scholar]
- Comba, A.; Mert, H.; Comba, B. Leptin Levels and Lipids Profile Determination in Different Sheep Breeds. Pak. Vet. J. 2016, 36, 169–173. [Google Scholar]
- Soares, G.; Souto, R.; Cajueiro, J.; Afonso, J.; Rego, R.; Macêdo, A.; Soares, P.; Mendonça, C. Adaptive changes in blood biochemical profile of dairy goats during the period of transition. Rev. Méd. Vét. 2018, 169, 65–75. [Google Scholar]
- Anwar, M.; Ramadan, T.; Taha, T. Serum metabolites, milk yield, and physiological responses during the first week after kidding in Anglo-Nubian, Angora, Baladi, and Damascus goats under subtropical conditions. J. Anim. Sci. 2012, 90, 4795–4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappai, M.G.; Liesegang, A.; Dimauro, C.; Mossa, F.; Pinna, W. Circulating electrolytes in the bloodstream of transition Sarda goats make the difference in body fluid distribution between single vs. twin gestation. Res. Vet. Sci. 2019, 123, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlumbohm, C.; Sporleder, H.; Gurtler, H.; Harmeyer, J. The influence of insulin on metabolism of glucose, free fatty acids and glycerol in normo-and hypocalcemic ewes during different reproductive states. DTW. Dtsch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 1997, 104, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Swarbrick, M.; Zhou, H.; Seibel, M. Mechanisms in endocrinology: Local and systemic effects of glucocorticoids on metabolism: New lessons from animal models. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2021, 185, R113–R129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reece, W.O.; Erickson, H.H.; Goff, J.P.; Uemura, E.E. Dukes’ Physiology of Domestic Animals; John Wiley & Sons: Indianapolis, IN, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Okunlola, D.; Olorunnisomo, O.; Binuomote, R.; Amuda, A.; Agboola, A.; Omole, O. Heamatology and serum quality of red Sokoto goats fed baobab (Adansonia digitata L.) fruit meal supplement. J. Nat. Sci. Res. 2015, 5, 54–56. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, N.; Garg, A.K.; Mudgal, V.; Dass, R.S.; Chaturvedi, V.K.; Varshney, V.P. Effect of different levels of selenium supplementation on growth rate, nutrient utilization, blood metabolic profile, and immune response in lambs. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2008, 126, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudgal, V.; Garg, A.K.; Dass, R.S.; Varshney, V.P. Effect of selenium and copper supplementation on blood metabolic profile in male buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) calves. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2008, 121, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Wang, Z.; Ma, Y.; Qu, Y.; Lu, X.; Luo, H. Effects of dietary lycopene supplementation on plasma lipid profile, lipid peroxidation and antioxidant defense system in feedlot Bamei lamb. Asian-australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 28, 958. [Google Scholar]
- El-Kady, R.; Abo Seder, S. Effect of natural plant supplements to diet of local goats on their growth performance. J. Animal Poult. prod. 2002, 27, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarenco, P.; Goldstein, L.B.; Szarek, M.; Sillesen, H.; Rudolph, A.E.; Callahan III, A.; Hennerici, M.; Simunovic, L.; Zivin, J.A.; Welch, K.M.A. Effects of intense low-density lipoprotein cholesterol reduction in patients with stroke or transient ischemic attack: The Stroke Prevention by Aggressive Reduction in Cholesterol Levels (SPARCL) trial. Stroke 2007, 38, 3198–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, N.; Sahin, K.; Onderci, M.; Karatepe, M.; Smith, M.; Kucuk, O. Effects of dietary lycopene and vitamin E on egg production, antioxidant status and cholesterol levels in Japanese quail. Asian-australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2006, 19, 224–230. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, M.; Kumar, S.; Dangi, S.; Jangir, B.L. Physiological, biochemical and molecular responses to thermal stress in goats. Int. J. Livest. Res. 2013, 3, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsikas, D. Assessment of lipid peroxidation by measuring malondialdehyde (MDA) and relatives in biological samples: Analytical and biological challenges. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 524, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juniper, D.T.; Phipps, R.H.; Ramos-Morales, E.; Bertin, G. Effects of dietary supplementation with selenium enriched yeast or sodium selenite on selenium tissue distribution and meat quality in lambs. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2009, 149, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, X.Y.; Du, J.; Li, Y.F.; Chen, Y.J.; Cao, Y. RNA-seq-based quanitative transcriptome analysis of meat color and taste from chickens administered by eucalyptus leaf polyphenols extract. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 1319–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Önenç, S.S.; Özdoğan, M. Relationship between meat quality and animal nutrition. Hayvansal Üretim 2022, 63, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, A.; Goh, Y.; Samsudin, A.; Alimon, A.; Sazili, A. Growth performance, carcass characteristics and meat yield of Boer goats fed diets containing leaves or whole parts of Andrographis paniculata. Asian-australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 27, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priolo, A.; Micol, D.; Agabriel, J.; Prache, S.; Dransfield, E. Effect of grass or concentrate feeding systems on lamb carcass and meat quality. Meat Sci. 2002, 62, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheridan, R.; Ferreira, A.; Hoffman, L. Production efficiency of South African Mutton Merino lambs and Boer goat kids receiving either a low or a high energy feedlot diet. Small Rum. Res. 2003, 50, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasevic, I.; Djekic, I.; Font-i-Furnols, M.; Terjung, N.; Lorenzo, J.M. Recent advances in meat color research. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 41, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.D.; Jeong, J.Y.; Hur, S.J.; Yang, H.S.; Jeon, J.T.; Joo, S.T. The relationship between meat color (CIE L* and a*), myoglobin content, and their influence on muscle fiber characteristics and pork quality. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2010, 30, 626–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khliji, S.; Van de Ven, R.; Lamb, T.; Lanza, M.; Hopkins, D. Relationship between consumer ranking of lamb colour and objective measures of colour. Meat Sci. 2010, 85, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adzitey, F.; Huda, N. Effects of post-slaughter carcass handling on meat quality. Pak. Vet. J. 2012, 32, 161–164. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Zhao, G.; Jiang, R.; Zheng, M.; Chen, J.; Liu, R.; Wen, J. Effects of diet-induced differences in growth rate on metabolic, histological, and meat-quality properties of 2 muscles in male chickens of 2 distinct broiler breeds. Poult. Sci. 2012, 91, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duclos, M.J.; Berri, C.; Le Bihan-Duval, E. Muscle growth and meat quality. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2007, 16, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wismer–Perdersen, J. Chemistry of animal tissues: Water. In The Science of Meat and Meat Products; Food and Nutrition Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1986; pp. 141–154. [Google Scholar]
- Mir, N.A.; Rafiq, A.; Kumar, F.; Singh, V.; Shukla, V. Determinants of broiler chicken meat quality and factors affecting them: A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 2997–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksoy, Y.; Çiçek, Ü.; Şen, U.; Şirin, E.; Uğurlu, M.; Önenç, A.; Kuran, M.; Ulutaş, Z. Meat production characteristics of Turkish native breeds: II. meat quality, fatty acid, and cholesterol profile of lambs. Arch. Anim. Breed. 2019, 62, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esenbuga, N.; Macit, M.; Karaoglu, M.; Aksakal, V.; Aksu, M.I.; Yoruk, M.A.; Gul, M. Effect of breed on fattening performance, slaughter and meat quality characteristics of Awassi and Morkaraman lambs. Livest. Sci. 2009, 123, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakan, A.; Ünal, N. Meat production traits of a new sheep breed called Bafra in Turkey 2. Meat quality characteristics of lambs. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2010, 42, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Ingredients | % |
|---|---|
| Barley | 41.00 |
| Corn | 18.00 |
| Wheat bran | 10.20 |
| Cotton seed meal, 38% CP | 23.70 |
| Sunflower oil | 3.40 |
| Dicalcium phosphate (DCP) | 0.15 |
| Marble dust | 2.50 |
| Salt | 0.80 |
| Vit-min mix a | 0.25 |
| Chemical analyses | (%) |
| Dry matter | 90 |
| Metabolized Energy (kcal/kg) | 2700 |
| Crude protein | 17.00 |
| Crude fiber | 6.65 |
| Ether extract | 6.30 |
| Ash | 6.82 |
| Ca | 1.09 |
| P | 0.55 |
| Traits | Control (n = 12) | Experimental (n = 12) | p * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Body Weight (kg) | 24.48 ± 3.18 | 24.89 ± 2.99 | 0.767 |
| Final Body Weight (kg) | 35.71 ± 3.30 | 38.20 ± 3.15 | 0.101 |
| Average Body Weight Gain (kg/day) | 0.20 ± 0.06 | 0.24 ± 0.04 | 0.131 |
| Average Daily Feed Intake (kg/day) | 1.30 ± 0.38 | 1.40 ± 0.25 | 0.483 |
| Feed Efficiency Ratio (kg/kg) | 6.59 ± 0.86 | 5.88 ± 0.40 | 0.029 |
| Carcass Yield (%) | 60.11 ± 1.07 | 61.76 ± 0.80 | 0.001 |
| Serum Profile | Control (n = 12) | Experimental (n = 12) | p * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 48.94 ± 5.26 | 53.97 ± 6.47 | 0.010 |
| Total proteins (g/dL) | 7.71 ± 1.35 | 10.35 ± 7.22 | 0.116 |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 145.92 ± 21.55 | 132.35 ± 12.51 | 0.021 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 18.60 ± 2.05 | 16.45 ± 1.64 | 0.001 |
| High density lipoproteins (mg/dL) | 47.53 ± 15.94 | 59.79 ± 20.96 | 0.044 |
| Low density proteins (mg/dL) | 94.66 ± 22.82 | 69.26 ± 20.77 | 0.001 |
| Calcium (mg/dL) | 10.70 ± 2.97 | 11.71 ± 2.35 | 0.241 |
| Phosphorus (mg/dL) | 8.13 ± 1.58 | 8.74 ± 1.10 | 0.164 |
| Traits | Control (n = 12) | Experimental (n = 12) | p * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cooking Loss (%) | 28.6 ± 1.3 | 26.9 ± 1.5 | 0.016 |
| Lightness (L *) | 41.5 ± 2.3 | 43.6 ± 2.2 | 0.059 |
| Redness (a *) | 14.6 ± 0.7 | 15.2 ± 0.5 | 0.086 |
| Yellowness (b *) | 7.2 ± 1.1 | 7.6 ± 1.8 | 0.532 |
| pH | 5.9 ± 0.4 | 5.9 ± 0.6 | 0.911 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ölmez, M.; Riaz, R.; Karadağoğlu, Ö.; Şahin, T.; Şerbetçi, İ.; Yılmaz, B.; Uysal, S.; Yörük, M.A. Effect of SOD-Rich Melon Supplement on Performance, Serum Biochemical, Antioxidant and Meat Quality Characteristics of Tuj Lambs. Agriculture 2023, 13, 625. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13030625
Ölmez M, Riaz R, Karadağoğlu Ö, Şahin T, Şerbetçi İ, Yılmaz B, Uysal S, Yörük MA. Effect of SOD-Rich Melon Supplement on Performance, Serum Biochemical, Antioxidant and Meat Quality Characteristics of Tuj Lambs. Agriculture. 2023; 13(3):625. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13030625
Chicago/Turabian StyleÖlmez, Mükremin, Roshan Riaz, Özlem Karadağoğlu, Tarkan Şahin, İdil Şerbetçi, Benian Yılmaz, Soner Uysal, and Mehmet Akif Yörük. 2023. "Effect of SOD-Rich Melon Supplement on Performance, Serum Biochemical, Antioxidant and Meat Quality Characteristics of Tuj Lambs" Agriculture 13, no. 3: 625. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13030625
APA StyleÖlmez, M., Riaz, R., Karadağoğlu, Ö., Şahin, T., Şerbetçi, İ., Yılmaz, B., Uysal, S., & Yörük, M. A. (2023). Effect of SOD-Rich Melon Supplement on Performance, Serum Biochemical, Antioxidant and Meat Quality Characteristics of Tuj Lambs. Agriculture, 13(3), 625. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13030625







