Experimental Research for Digging and Inverting of Upright Peanuts by Digger-Inverter
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
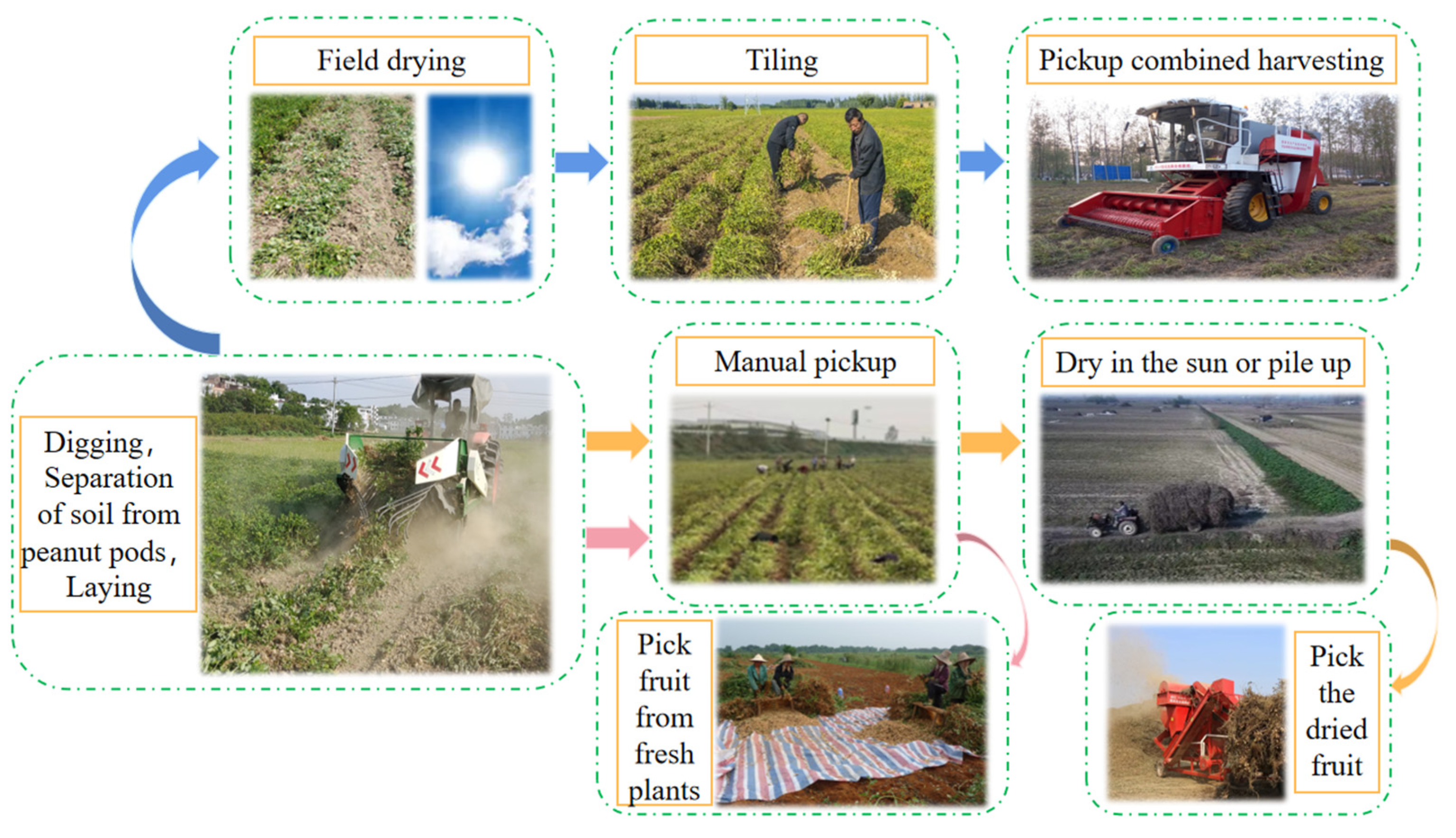
2.1. Agronomic Process Based on Peanut Two-Stage Harvesting Operation Mode
2.2. Design of Overall Structure and Principle
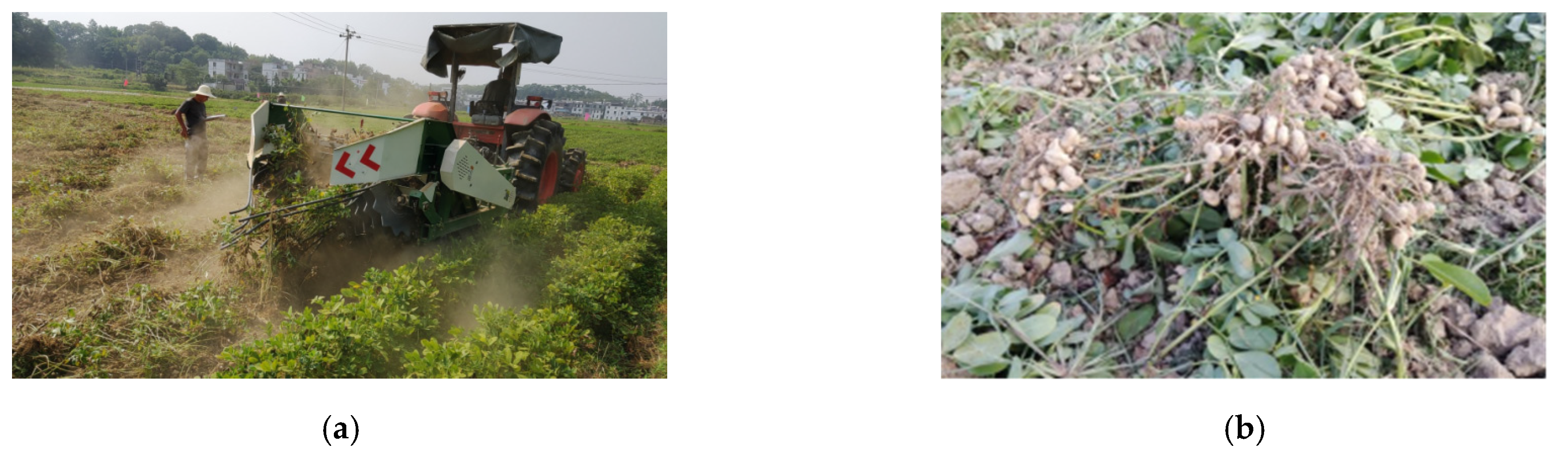
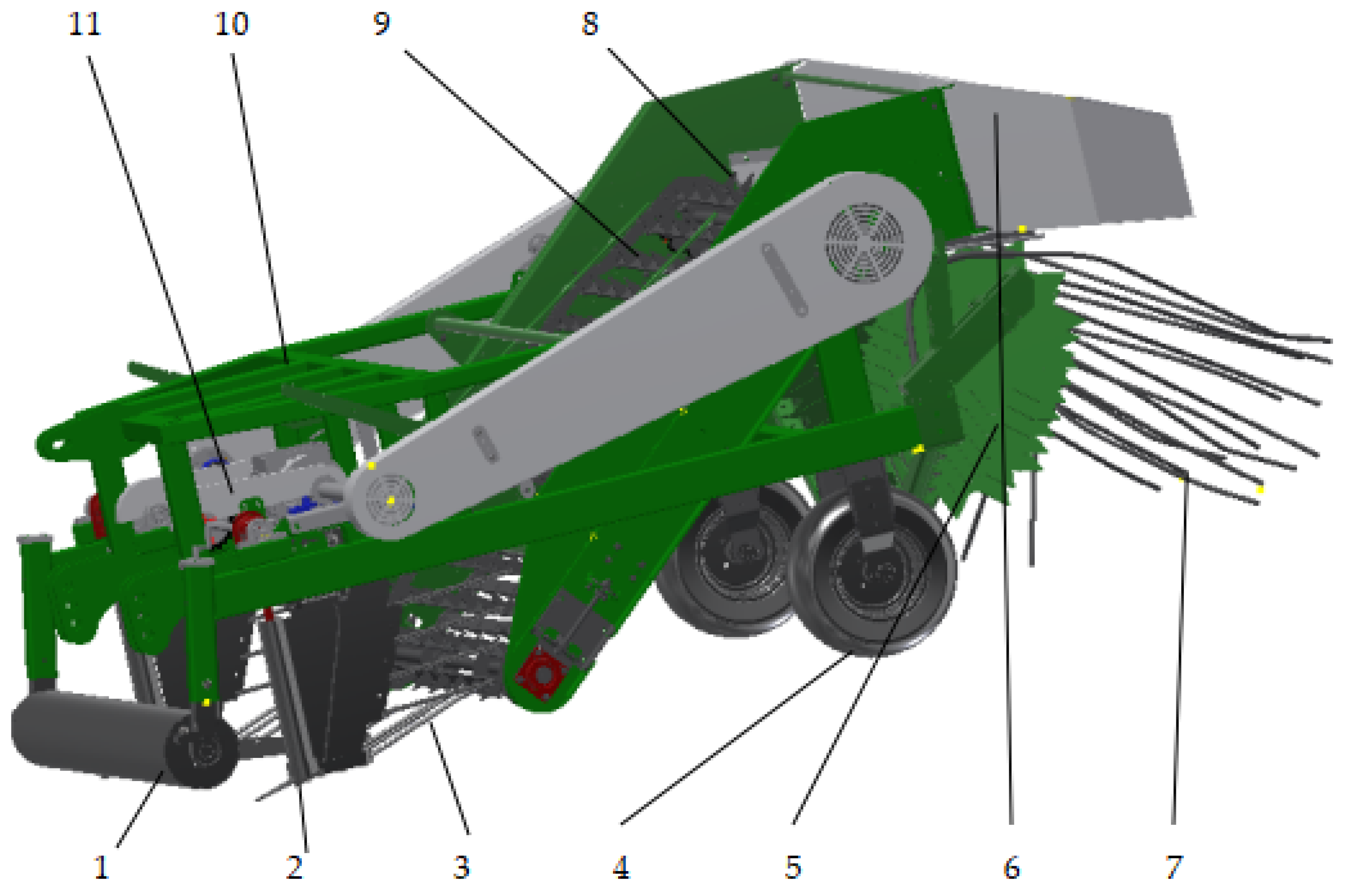
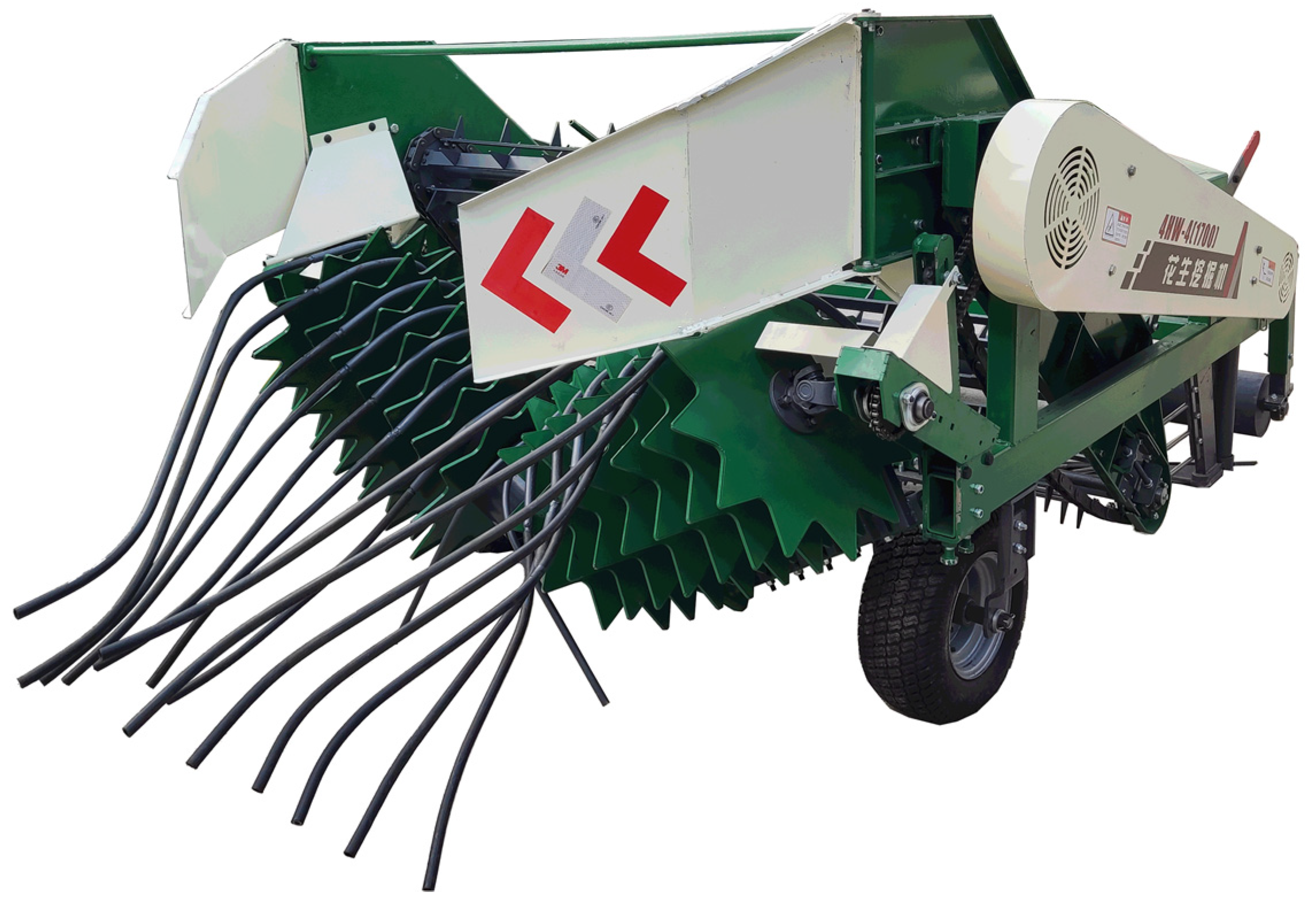
2.2.1. Overall Structure
2.2.2. Working Principle
2.3. Experimental Instruments and Conditions
2.3.1. Experimental Instruments
2.3.2. Experimental Conditions
2.4. Experimental Factors, Indicators, and Methods
2.4.1. Experimental Factors
2.4.2. Experimental Indexes
- V—The traveling speed of the tractor, expressed in meters per second (m/s);
- L—The length of the entire test area, expressed in meters (m);
- T—Time to pass through the test area, expressed in seconds (s).
- Pm—The rate of buried pods, the weight of the pod buried in the soil layer in the plot divided by the total weight of the pod in the whole plot (%);
- Mm—The pod mass (excluding naturally fallen pods) buried in the soil layer in the plot, expressed in grams (g);
- Mx—The total pod weight of crops in the plot, expressed in grams (g);
- Ps—The rate of fallen pods, the mass of pods dropped in the cell divided by the total mass of pods in the whole cell (%);
- Ms—Mass of pods dropped in the plot, expressed in grams (g);
- Pf—The rate of vines inverting; the number of peanut vines with no pod in the community divided by the total number of peanut vines in the community (%);
- l—The number of peanut vines without pods on the ground after peanut harvest in the community; unit is the number of vines;
- L—Total number of peanut vines in the community; unit is the number of vines.
2.4.3. Experimental Methods
3. Results
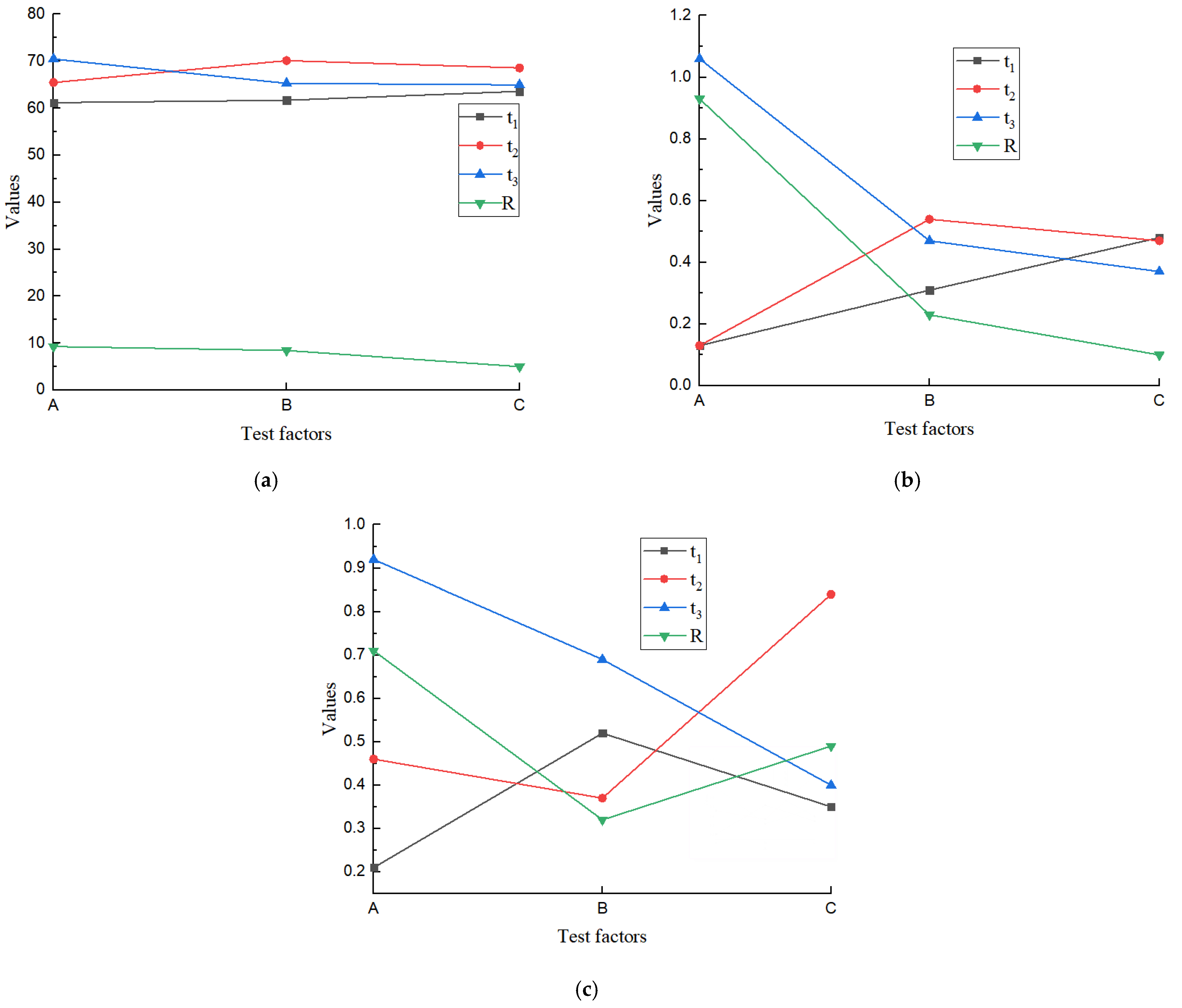
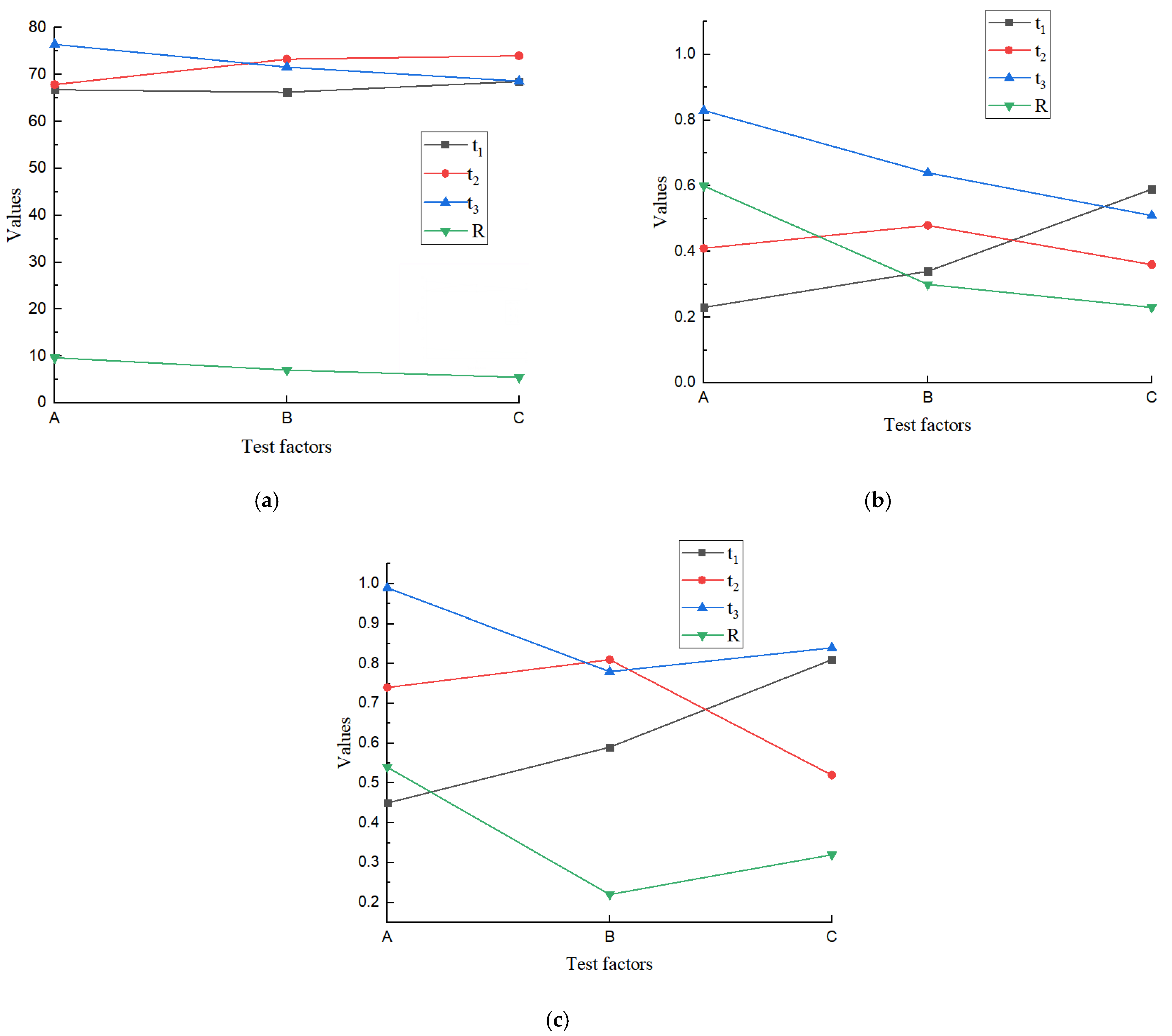
3.1. Results of Unpressed Vines Experiment
3.2. Results of Pressed Vines Experiment
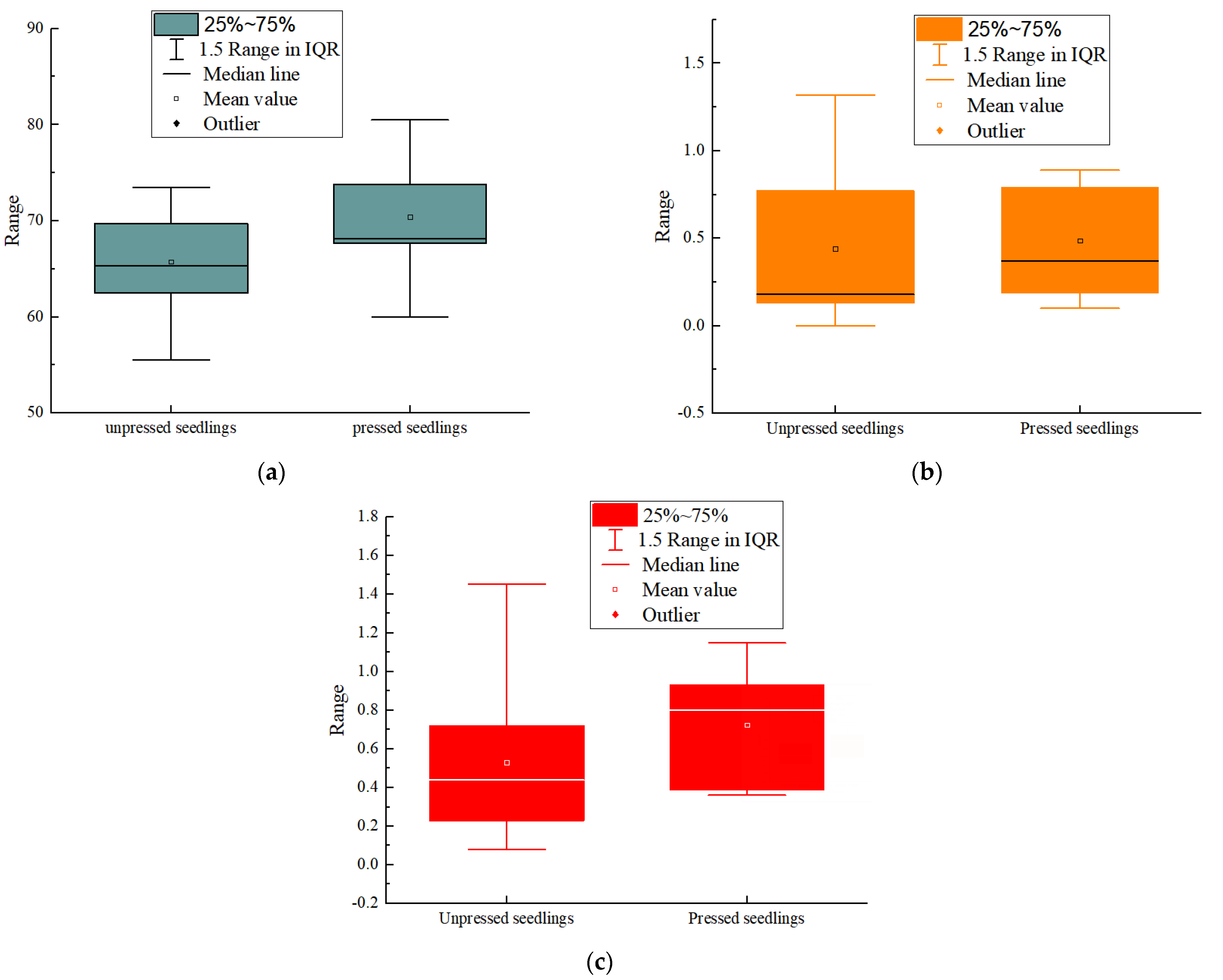
3.3. Results of Pairing Analysis between Unpressed Vines and Pressed Vines
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Y.C. Falling peanut in Ming Dynasty, shaped like taro but not peanut in early Qing Dynasty, the first real peanut in Chongming. Local Chron. Jiangsu 2018, 174, 85–88. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.L.; Geng, Y.; Guo, F.; Li, X.G.; Wan, S.B. Research progress on the mechanism of improving peanut yield by single-seed precision sowing. J. Integr. Agric. 2020, 19, 1919–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Wang, B.; Hu, Z.; Yang, H. Mechanism and Experiment of Full-Feeding Tangential-Flow Picking for Peanut Harvesting. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.K.; Wu, H.C.; Zhang, Y.H.; Peng, B.L.; Gu, F.W.; Hu, Z.C. Development of automatic depth control device for semi-feeding four-row peanut combine harvester. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 10–18. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.S.; Ran, W.J.; Hao, J.J.; Bai, W.J.; Yang, X.L. Design and experiment of the double-seed hole vines precision seed metering device for peanuts. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2022, 15, 107–114. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.K.; Lin, Y.W.; Li, X.Y.; Yang, H.; Han, J.H.; Shang, C.J.; Li, A.Q.; Xiao, H.W.; Lu, F.Y. Peanut drying: Effects of various drying methods on drying kinetic models, physicochemical properties, germination characteristics and microstructure. Inf. Process. Agric. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Hu, Z.C.; Peng, B.L.; Zhang, Y.H.; Gu, F.W.; Shi, L.L.; Gao, X.M. Structure operation parameter optimization for elastic steel pole oscillating screen of semi-feeding four rows peanut combine harvester. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2017, 33, 20–28. [Google Scholar]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations Database. 2022. Available online: http://faostat3.fao.org/download/Q/QC/E (accessed on 25 December 2022).
- Hu, Z.C. Study on Key Technologies of Half-Feed Peanut Combine Harvester; Nanjing Agricultural University: Nanjing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.Y.; Gao, L.X.; Chen, C.; Butts, C.L. Analysis on technology status and development of peanut harvest mechanization of China and the United States. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2017, 48, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.S. Exploring the main points of mechanization technology of peanut production. Shihezi Sci. Technol. 2022, 261, 6–7. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.D.; Zhai, X.T.; Zhang, H.; Yang, R.B.; Wang, D.W.; Shang, S.Q. Study on control strategy of the vine clamping conveying system in the peanut combine harvester. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 178, 105744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Comprehensive Mechanization Rate of Peanuts in China has Reached 52.14%. 2017. Available online: http//www.nongjitong.com/news/2017/42210.html (accessed on 25 December 2022).
- Wang, B.; Gu, F.; Cao, M.; Xie, H.; Wu, F.; Peng, B.; Hu, Z. Analysis and Evaluation of the Influence of Different Drum Forms of Peanut Harvester on Pod-Pickup Quality. Agriculture 2022, 12, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.S. Design and experiment of peanut digging and placing machine based on two-stage harvest. J. Agric. Mech. Res. 2022, 44, 133–139. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, T.; Shen, Y.Z.; Gao, L.X.; Zhang, X.D.; Lv, C.Y.; Liu, Z.X. Spring-finger peanut pickup mechanism based on two-stage harvest. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2016, 47, 90–97. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.X.; Chen, Z.Y.; Charles, C.; Butts, C.L. Development course of peanut harvest mechanization technology of the United States and enlightenment to China. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2017, 33, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- AMADAS INDUSTRIES. Peanut Diggers. 2015. Available online: http://www.amadas.com/agriculture/peanuts/peanut-diggers (accessed on 25 December 2022).
- Kelly Manufacturing Co. Vine Conditioner and Vine Lifter. 2015. Available online: http://www.Kelleymfg.com/products/peanut/vine_conditioner_lifter.aspx (accessed on 25 December 2022).
- COLOMBO. Colombo Dump Cart 61.52.12. 2015. Available online: http://colombona.com/colombo-dump-cart-cta-61.52.12 (accessed on 25 December 2022).
- Mike, B. Peanut Digger and Combine Efficiency. Cooperative Extension of Colleges of Agricultural and Environmental Science; The University of Georgia: Athens, GA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- NC State University, BAE. Peanut Harvesting Equipment: Diggers and Combines. 2017. Available online: http://www.bae.ncsu.edu/topic/agmachine/farmequip/harvest/peanut_harvest_guide.htm (accessed on 25 December 2022).
- Wang, L.; Wei, J.J.; Li, Y. Development of peanut’s whole course mechanization in our country and the application in Xinjiang. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2014, 30, 161–168. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.B. Development of 4HS-80 Peanut Harvester; Henan Province, Zhengzhou Xechuang Mechanical and Electrical Equipment Co., Ltd.: Zhengzhou, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.M. Research on 4H-1 peanut harvester. Mech. Rural. Pastor. Areas 2008, 1, 14–15. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.C.; Peng, B.L.; Xie, H.X.; Tian, L.J.; Wang, H.O.; Wu, F. Design and Experiment of Peanut Hoist Chain Harvester. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2008, 11, 220–222. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.C.; Tang, Z.H.; Yang, H.J.; Meng, X.J.; Qin, T.R.; Zhang, D.C. Design and experiment of 4HQ-150 peanut plucking harvester. J. Gansu Agric. Univ. 2018, 53, 180–186. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Wang, H.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.L. A Kind of Tilting Peanut Excavator. CN213755725U, 23 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.J. A Kind of Peanut Excavator and Its Flipping Device. CN213427033U, 15 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Guo, W.H. A Small Peanut Digging and Recycling Machine. CN209151579U, 26 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.X.; Wang, D.W.; Dong, H.S. Design and Test of Turnover Laying Device of Peanut Harvester. J. Shenyang Agric. Univ. 2016, 47, 57–63. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.Y.; Hu, Z.C.; Chen, Y.Q.; Wu, H.C.; Wang, Y.W.; Wu, F.; Gu, F.W. Integration of agricultural machinery and agronomy for mechanised peanut production using the vine for animal feed. Biosyst. Eng. 2022, 219, 113–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.K.; W, N.; Hu, Z.C.; Wang, H.O.; Chen, Y.Q. Experience and thought of development of peanut harvesting mechanization at home and abroad. J. Chin. Agric. Mech. 2011, 4, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, S.S.; Zhao, J.X.; Chen, Y. Experimental Design; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- DB34/T534-2022; Technical Specification for Mechanization of Peanut Harvesting. Local Standard of Anhui Province: Hefei, China, 2022.
- DG/T077-2019; Peanut Harvest. Agricultural Machinery Extension Appraisal Outline: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Xu, X.H.; He, M.Z. Experimental Design and Application of Design Expert and SPSS; Scientific Press: Beijing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.Y.; Hu, Z.C.; Yao, L.J.; Peng, B.L.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.W. Simulation and parameter optimisation of pickup device for full-feed peanut combine harvester. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 192, 106602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Cao, M.; Wang, B.; Hu, Z.; Xu, H.; Wang, S.; Yu, Z. Design and Test of a Tangential-Axial Flow Picking Device for Peanut Combine Harvesting. Agriculture 2022, 12, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.X.; Shang, S.Q.; Wang, D.W.; Shen, S.L. Development and experiment of 4HT-2 peanut strip laying harvester. Agric. Mech. Res. 2018, 40, 87–91. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.J.; Yang, R.B.; Shang, S.Q.; Shi, C.; Yang, H.G. Shovel sieve modular design and test of peanut segment harvester. J. Agric. Mech. Res. 2016, 38, 163–166, 171. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.J.; Wang, D.W.; Wang, Y.Y.; Luan, G.D.; Sun, Q.W. Orderly laid the development of peanut harvester. J. Agric. Mech. Res. 2013, 35, 73–75, 79. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.H.; Guo, H.; Yu, X.D.; Wang, M.C.; Xing, S.K.; Peng, B. Based on a two-part process of peanut harvest machine is designed with the test. J. Chin. Agric. Mech. 2020, 9, 34–39. [Google Scholar]


| Parameters | Design Value |
|---|---|
| Type | Suspension-type |
| Machine dimensions: size (Length × width × height)/(mm × mm × mm) | 3500 × 2100 × 1550 |
| Total weight/kg | 1500 |
| Most suitable row spacing/mm | 800 |
| Numbers of ridge | Double ridge |
| Working width/mm | 1800 |
| Digging depth/mm | ≤250 |
| Travelling speed/(m/s) | 0.7~1.3 |
| Efficiency/(ha/h) | 0.45~0.84 |
| Factors | Levels | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| Traveling speed of the tractor A/(m/s) | 0.7~0.9 | 0.9~1.1 | 1.1~1.3 |
| Line speed of the conveyor chain B/(m/s) | 0.84 | 1.02 | 1.13 |
| Line speed of the inverting roller C/(m/s) | 1.57 | 1.88 | 2.12 |
| Test Number | Travelling Speed of the Tractor A/(m/s) | Line Speed of the Conveyor Chain B/(m/s) | Line Speed of the Inverting Roller C/(m/s) | Rate of Vines Inverting Pf/(%) | Rate of Buried Pods Pm/(%) | Rate of Fallen Pods Ps/(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 (0.89) | 1 (0.84) | 1 (1.57) | 55.56 | 0 | 0.08 |
| 2 | 1 (0.86) | 2 (1.02) | 2 (1.88) | 68.06 | 0.18 | 0.35 |
| 3 | 1 (0.84) | 3 (1.13) | 3 (2.12) | 60 | 0.21 | 0.19 |
| 4 | 2 (1.04) | 1 (0.84) | 2 (1.88) | 64.29 | 0.15 | 0.72 |
| 5 | 2 (1.01) | 2 (1.02) | 3 (2.12) | 69.7 | 0.13 | 0.23 |
| 6 | 2 (1.05) | 3 (1.13) | 1 (1.57) | 62.5 | 0.12 | 0.44 |
| 7 | 3 (1.25) | 1 (0.84) | 3 (2.12) | 65.31 | 0.77 | 0.77 |
| 8 | 3 (1.29) | 2 (1.02) | 1 (1.57) | 72.73 | 1.32 | 0.54 |
| 9 | 3 (1.13) | 3 (1.13) | 2 (1.88) | 73.44 | 1.08 | 1.45 |
| Indexes | Variance Source | Sum of Squares | Free Degree | F-Value | p-Value | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pf | A | 129.613 | 2 | 95.98 | 0.01 | ** |
| B | 107.724 | 2 | 79.771 | 0.012 | ** | |
| C | 39.891 | 2 | 29.539 | 0.033 | ** | |
| Error | 1.35 | 2 | ||||
| T | 278.579 | 8 | ||||
| Pm | A | 1.711 | 2 | 25.141 | 0.038 | * |
| B | 0.088 | 2 | 1.294 | 0.436 | ||
| C | 0.022 | 2 | 0.326 | 0.754 | ||
| Error | 0.068 | 2 | ||||
| T | 1.89 | 8 | ||||
| Ps | A | 0.783 | 2 | 47.567 | 0.021 | ** |
| B | 0.154 | 2 | 9.34 | 0.097 | * | |
| C | 0.435 | 2 | 26.433 | 0.036 | ** | |
| Error | 0.016 | 2 | ||||
| T | 1.389 | 8 |
| Index | Factor Importance Order | The Best Level and the Next Best Level | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | ||
| Pf | A, B, C | A3 or A2 | B2 | C2 or C3 |
| Pm | A | A1 and A2 | ||
| Ps | A, C, B | A1 or A2 | B2 | C1 or C3 |
| Test Number | Travelling Speed of the Tractor A/(m/s) | Line Speed of the Conveyor Chain B/(m/s) | Line Speed of the Inverting Roller C/(m/s) | Rate of Vines Inverting Pf/(%) | Rate of Buried Pods Pm/(%) | Rate of Fallen Pods Ps/(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 (0.74) | 1 (0.84) | 1 (1.57) | 60 | 0.13 | 0.36 |
| 2 | 1 (0.71) | 2 (1.02) | 2 (1.88) | 73.77 | 0.19 | 0.38 |
| 3 | 1 (0.82) | 3 (1.13) | 3 (2.12) | 66.67 | 0.37 | 0.6 |
| 4 | 2 (0.96) | 1 (0.84) | 2 (1.88) | 67.8 | 0.1 | 0.39 |
| 5 | 2 (1.01) | 2 (1.02) | 3 (2.12) | 68.18 | 0.36 | 0.89 |
| 6 | 2 (1.09) | 3 (1.13) | 1 (1.57) | 67.69 | 0.76 | 0.93 |
| 7 | 3 (1.26) | 1 (0.84) | 3 (2.12) | 70.97 | 0.79 | 1.02 |
| 8 | 3 (1.29) | 2 (1.02) | 1 (1.57) | 77.92 | 0.89 | 1.15 |
| 9 | 3 (1.15) | 3 (1.13) | 2 (1.88) | 80.49 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| Indexes | Variance Source | Sum of Squares | Free Degree | F-Value | p-Value | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pm | A | 167.662 | 2 | 53.935 | 0.018 | ** |
| B | 80.997 | 2 | 26.056 | 0.037 | ** | |
| C | 59.376 | 2 | 19.1 | 0.05 | ** | |
| Error | 3.109 | 2 | ||||
| T | 311.144 | 8 | ||||
| Ps | A | 0.564 | 2 | 14.419 | 0.065 | * |
| B | 0.138 | 2 | 3.538 | 0.22 | ||
| C | 0.081 | 2 | 2.071 | 0.326 | ||
| Error | 0.039 | 2 | ||||
| T | 0.822 | 8 | ||||
| Pf | A | 0.443 | 2 | 32.556 | 0.03 | ** |
| B | 0.083 | 2 | 6.07 | 0.141 | ||
| C | 0.183 | 2 | 13.421 | 0.069 | * | |
| Error | 0.014 | 2 | ||||
| T | 0.723 | 8 |
| Index | Factor Importance Order | The Best Level and the Next Best Level | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | ||
| Pf | A, B, C | A3 or A2 | B2 | C2 |
| Pm | A | A1 or A2 | ||
| Ps | A, C | A1 or A2 | C2 | |
| Sample Group | Correlation | p-Value | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traveling speed of tractor A | 0.913 | 0.001 | *** |
| Line speed of the conveyor chain B | 0.787 | 0.012 | ** |
| Line speed of the inverting roller C | 0.281 | 0.464 |
| Sample Group | T | df | p-Value | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traveling speed of tractor A | −5.479 | 8 | 0.001 | *** |
| Line speed of the conveyor chain B | −0.468 | 8 | 0.652 | |
| Line speed of the inverting roller C | −1.326 | 8 | 0.222 |
| Type of Peanut Harvesting Structure | Sources | Performance Indexes | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rate of Vines Inverting/(%) | Rate of Fallen Pods/(%) | ||
| The peanut digger-inverter | This study (unpressed vines) | 71.07 | 0.22 |
| This study (pressed vines) | 74.29 | 0.33 | |
| Turnover Laying Device | Ref. [32] | 72 | 2.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, H.; Yang, H.; Gao, Q.; Gu, F.; Hu, Z.; Wu, F.; Chen, Y.; Cao, M. Experimental Research for Digging and Inverting of Upright Peanuts by Digger-Inverter. Agriculture 2023, 13, 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13040847
Shen H, Yang H, Gao Q, Gu F, Hu Z, Wu F, Chen Y, Cao M. Experimental Research for Digging and Inverting of Upright Peanuts by Digger-Inverter. Agriculture. 2023; 13(4):847. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13040847
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Haiyang, Hongguang Yang, Qimin Gao, Fengwei Gu, Zhichao Hu, Feng Wu, Youqing Chen, and Mingzhu Cao. 2023. "Experimental Research for Digging and Inverting of Upright Peanuts by Digger-Inverter" Agriculture 13, no. 4: 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13040847
APA StyleShen, H., Yang, H., Gao, Q., Gu, F., Hu, Z., Wu, F., Chen, Y., & Cao, M. (2023). Experimental Research for Digging and Inverting of Upright Peanuts by Digger-Inverter. Agriculture, 13(4), 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13040847









