Abstract
Microbial water quality is a major concern in the world, since the ingestion of water contaminated with microorganisms poses risks to human and animal health. The aim of this study was to evaluate the microbiological quality of drinking water on dairy cattle farms. The study was carried out to determine the occurrence of coliforms and enterococcus species in drinking water samples obtained from selected dairy cattle farms located in four different areas of Portugal (north, central, south and islands). A questionnaire was used to collect relevant information regarding farmer demographics, characteristics of the cattle farms, as well as number of animals per herd, number of adult cows, production type, water source, use of disinfectants and pasture area. In this study, a convenience sample of 32 dairy cattle farms was subjected to screening for water quality. The numbers of animals in the study were 8086 cattle, with a mean herd size of 253, of which 51.7% were cows. Coliform and enterococcus bacterial species were identified by performing the membrane filtration method. The occurrence of poor water quality was recorded in 19 (59.4%) cattle farms. Isolated bacteria included Escherichia coli (20.0%), Enterococcus faecalis (25.0%), total coliforms (65.6%) and fecal coliforms (43.8%). Farms that did not routinely perform disinfection had the worst water quality (70.8%) when compared with farms that performed disinfection (25.0%) (p = 0.022). This research revealed the importance of screening the quality of drinking water on cattle farms, which could contribute to improved animal, human and environmental health in a One Heath approach.
1. Introduction
Usually, coliform bacteria are shed in the feces of healthy livestock, including dairy cattle. The poor hygienic condition of animals, contaminated water, unsanitary milking practices and management conditions may increase coliform counts. Microbial water quality is a major issue in animal, human and environment health [1]. Water must be free of pathogenic, dangerous agents and adequate to provide the nutritional requirements in animal production [2]. The consumption of water contaminated with excreta containing pathogenic microorganisms carries a risk to both humans and animals because it can increase the incidence of zoonotic diseases [3]. Escherichia coli (E. coli) is used as the principal indicator for drinking water pollution monitoring, and it is considered a superior indicator. This bacterium is found in all mammal feces and was chosen as a biological indicator based on its capacity for survival in drinking water for 4 to 12 weeks [4]. E. coli is a member of fecal coliforms in drinking water contaminated by human and animal fecal waste. It has been the primary indicator of fecal contamination in water quality monitoring for many decades. During rainfalls, these coliforms may be washed into creeks, rivers, streams, lakes or ground water. Untreated drinking water coming from these sources contains coliforms including E. coli [5]. Due to their ubiquity in human feces and persistence in the environment, Enterococcus species have been adopted as indicators of fecal pollution in water [6], given that most zoonotic outbreaks are caused by water contaminated with feces from infected animals or humans [7]. Livestock animals’ drinking water comes from different sources: town water, water wells, rivers, etc. Depending on the hygienic status of those sources, public health problems may occur [8]. Consequently, the consumption of water from a contaminated water supply by production animals can introduce a high number of microorganisms into this animal group but also can create a “multiplier” effect through the food chain. To preserve animal health and productivity, it is important to identify and correct water problems and mandatory that dairy farmers adopt good farming practices, such as the use of clean and pure water [9,10]. Potable water should also be used to wash hands, udders and utensils before milking, guaranteeing the milk′s safety [11]. The parameters in water typically subjected to assessment are physical properties, chemical constituents and the presence of microbiological agents [12]. Animal production farms represent a source of a large number of microorganisms that can have pathogenic potential, such as Escherichia coli, Enterococcus spp. or Salmonella sp. [13]. E. coli is predominant in animal wastes and serves as an indicator of fecal contamination [14], with epidemiological data indicating that the serotype E. coli O157:H7 may exist in up to 8.3% of dairy and beef cattle and that exist asymptomatically in their feces [15]. Based on their abundance in the feces of mammals and their long survival in the environment, Enterococci are commonly used as fecal indicators in water management and in studies that focus on these microorganisms as indicators of sources of fecal pollution [16]. Enterococcus spp. are facultative anaerobic organisms that can survive in high salt concentrations and survive in pH extremes (as low as 4.8 and as high as 9.6). For many years, Enterococcus species were believed to be harmless to humans and unimportant medically. Although these bacteria do not produce toxins, they have virulence factors in the form of aggregation substances, so they can cause disease based on the way they adhere to the host tissues. Based on their production of virulence factors and high antibiotic resistance, Enterococcus species are now considered emerging pathogens. The medical importance of enterococci in nosocomial, iatrogenic and bacteremia infections has grown; they are a cause of urinary tract infections, endocarditis, meningitis, wound infections, and abdominal and pelvic infections [17,18].
Water is a major source of exposure of cattle to enteric bacteria, including a number of foodborne pathogens. Adequate, safe, and accessible water constitutes an essential resource for life. In order to ensure uncontaminated water for the water supply, industry and agriculture, water quality is defined by microbiological, biological, chemical and physical indicators [19]. Drinking water for cattle that is highly contaminated with enteric bacteria could be a common source of exposure to potential pathogens for livestock that could result in infection. The extent and frequency of waterborne transmission of these pathogens from water to livestock is not fully understood [20].
This study aims to assess and describe water quality in Portuguese dairy farms and study some aspects related to occurrence of microbiological contamination of water.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
A convenience sample of 32 dairy cattle farms were included in the study. The number of animals in the study totaled 8086, with a mean herd size of 253 animals per farm. Inclusion criteria were geographic location in Portugal, milk production on the farm, and dairy breed.
The study was conducted between March and August of 2018 in four different areas of Portugal (north, central, south and islands). Each farm was visited once by 1 of 2 trained assessors. A structured questionnaire was developed to assess the water quality in the cattle farms. This questionnaire was developed after a review of the literature, and it was previously pre-tested. The questionnaire was designed with multiple-choice questions to survey factors associated with water quality. During the visit, the questionnaire was completed by the farmer and mediated by the assessor, and all information was collected through face-to-face interviews. The questionnaire comprised 26 questions (21 multiple-choice questions and 5 open questions). It was divided into two sections. One section consisted of 5 questions that covered the demographics of the farmers being surveyed, such as gender, age, place of residence, and educational level, and the another section consisted of 21 questions about the characteristics of the cattle farm, as well as number of animals per herd, number of adult cows, production type, water source, use of disinfectants and pasture area. On average, the farmers spent around 15–20 min to complete the survey. In this study, a farm was considered to have poor water quality if coliform and/or E. coli and/or Enterococcus colony forming units (CFU) were higher than zero.
2.2. Microbiological Analysis
In total, 32 water samples (one per farm) were collected under aseptic conditions. Samples were collected from holes, wells, mines and tap water. All water sampling and preservation procedures were performed according to Standard Methods for the examination of water and wastewater (APHA, 1995; APHA, 1998). Sampling for bacteriological analysis was performed aseptically with care in 500 mL sterile bottles, ensuring no external contamination of samples. All samples were transported to the Laboratory of Medical Microbiology, UTAD, Portugal within 24 h.
The membrane filter test was conducted according to Standard Methods to detect coliforms and enterococci. An appropriate volume of sample (100 mL) was filtered through a 0.45 µm pore size nitrocellulose filter of 47 mm in diameter (Millipore Corporation, Bedford, MA, USA) to retain the bacteria present in the sample. One filter was then placed on a HiCrome™ Coliform Agar (Sigma-Aldrich St. Louis, Missouri, EUA) plate and incubated at 37 ± 0.5 °C for 24 ± 2 h, and the salmon to red colonies were counted as total coliforms. Another filter was plated in the same culture medium and incubated at 44 ± 0.5 °C for 24 ± 2 h, and dark blue to violet colored coliform colonies were counted as E. coli. To confirm E. coli identification, a drop of Kovac′s reagent was added on the dark blue to violet colonies; the formation of a cherry-red color indicated a positive reaction. Positive coliform colonies were subcultured on MacConkey agar for confirmation of E. coli and other enteric coliforms. The filters were placed on plates in triplicate.
All of the strains isolated were identified by the IMVIC method (indole, methyl red, Voges–Proskauer, citrate) and the triple sugar iron test. Bacteria not identifiable by these methods were examined using the API 20E® System (BioMerieux®, Marcyl’Etoile, France).
Kanamycin Aesculin Azide agar® (KEA) (Sigma-Aldrich St. Louis, Missouri, EUA) medium was used for the recovery of fecal streptococci/enterococci. A 100 mL sample was filtered through a 0.45 µm pore size nitrocellulose filter of 47 mm in diameter. The filter was then placed on a KEA agar plate and incubated at 36 ± 1 °C for 24–48 h. The filters were placed on plates in triplicate. Typical colony appearance was translucent to whitish, with colonies surrounded by dark brown to black halos. Strains were further confirmed by using the API 20 NE® System.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
Data from the farm visit questionnaires were coded, and a database established in Excel® for Windows. Statistical analyses were carried out employing a Pearson Chi square test and Fisher exact test to compare values relative to categorical variables. Analyses were performed with SPSS® 22.0 software for Windows (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA), considering 0.05 as the level of significance (p). Several continuous variables were transformed into categories, as number of animals in the herd.
3. Results
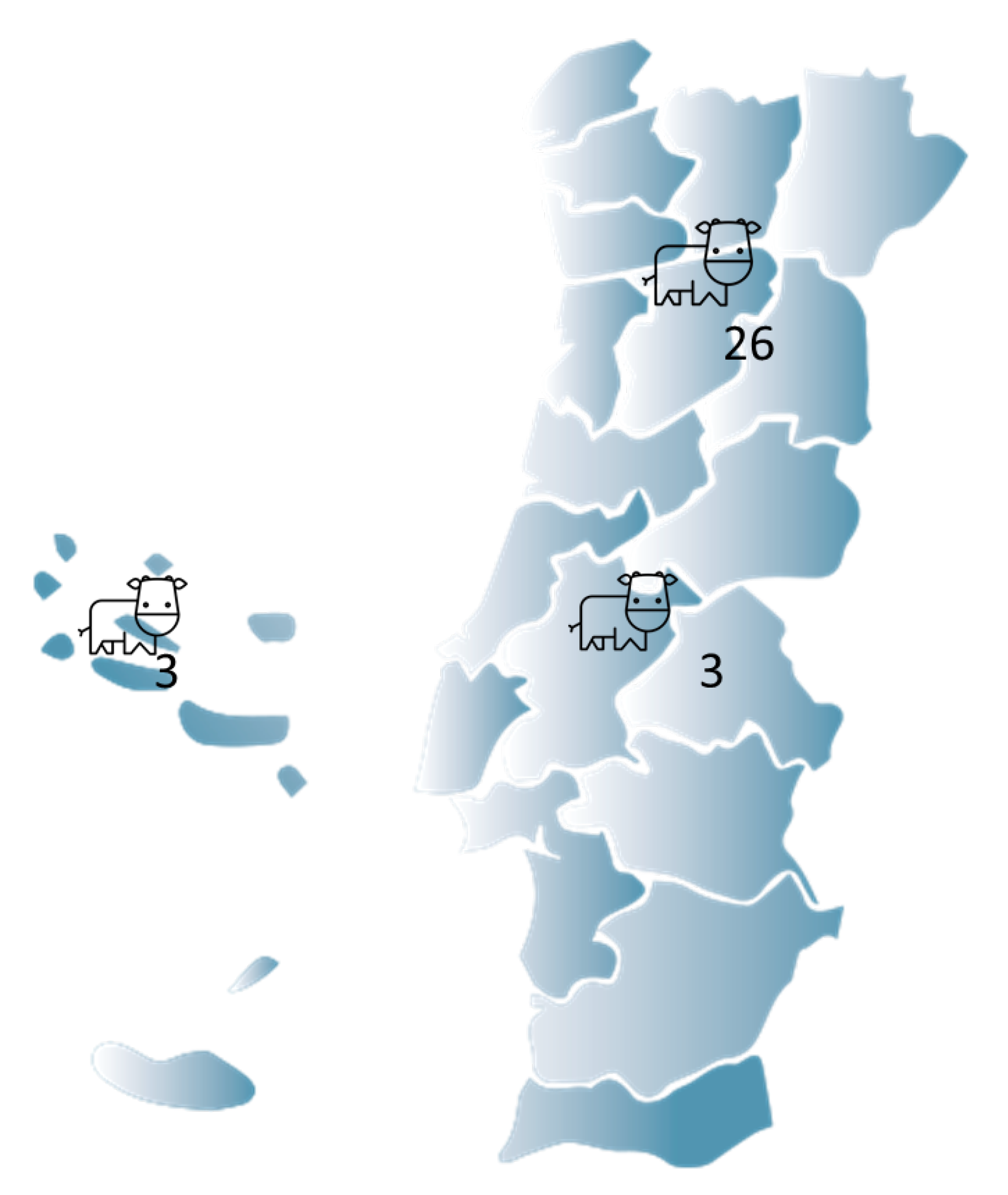
In this study, a total of 32 cattle farms and 8086 cattle, of which 51.7% were cows, were subject to screening for water quality. Figure 1 summarizes the farms′ locations, with the north being the most represented region.
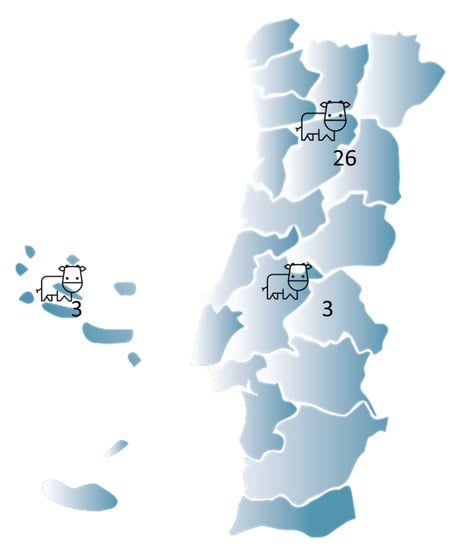
Figure 1.
A graphical illustration of the cattle farm distribution in Portugal.
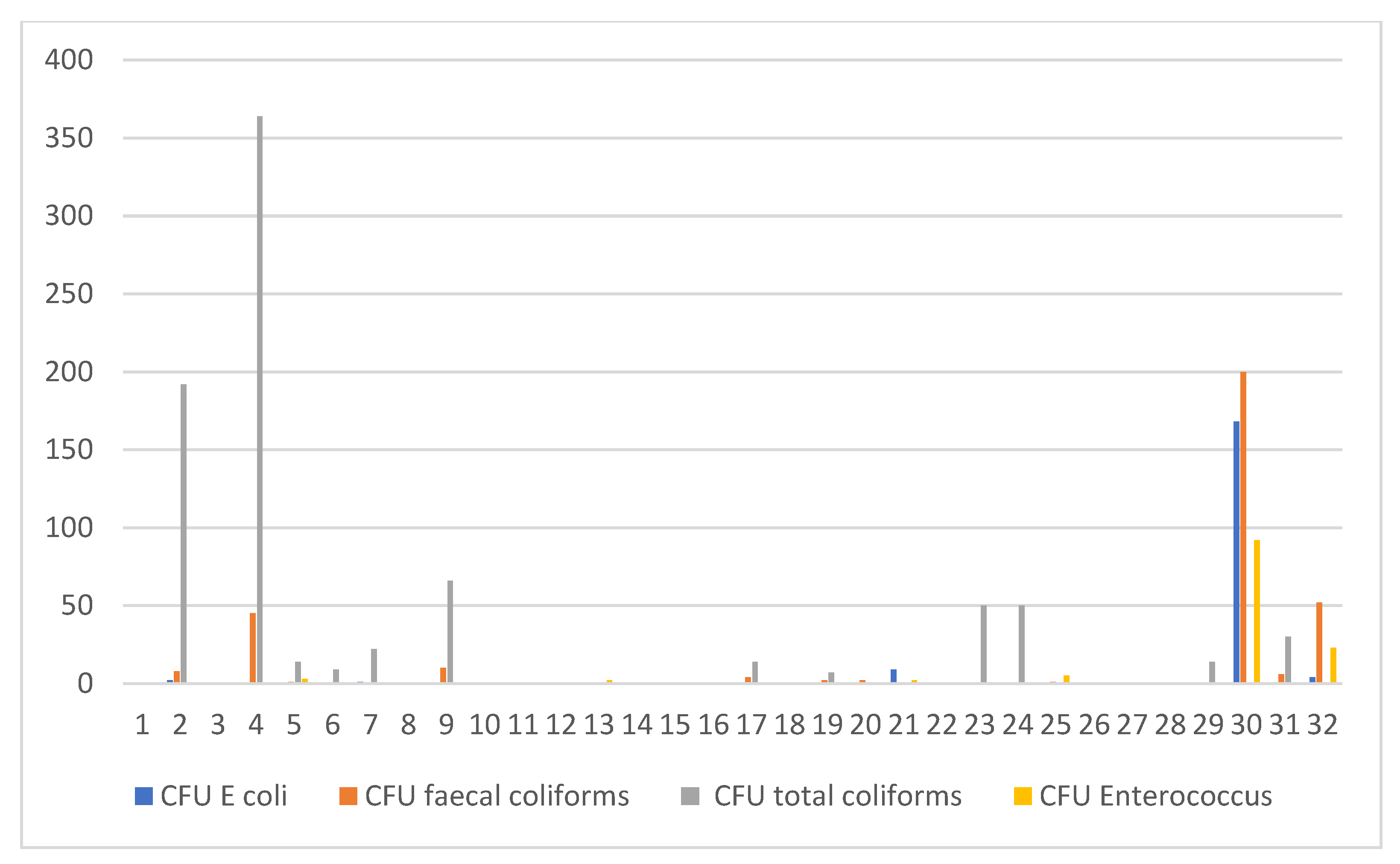
The mean herd size for all farms visited was 253, ranging from 51 to 127,951. All cattle included in the study were of the Holstein Friesian breed. The occurrence of poor water quality was detected in 19 out of 32 (59.4%) studied farms. Bacteria isolated included E. coli (20.0%), Enterococcus faecalis (25.0%), total coliforms (65.6%) and fecal coliforms (43.8%) (Figure 2). No Salmonella sp. were recorded.
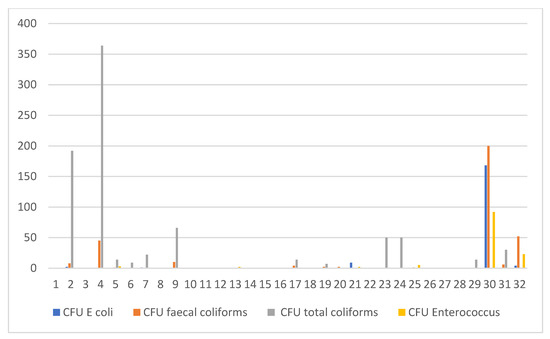
Figure 2.
A graphical illustration, in cfu/mL, of E.coli, Enterococcus, total coliforms and fecal coliforms per farm.
Table 1 summarizes the proportion of farms with poor water quality, according to characteristics of the herd. Poor water quality was mostly found in the north of Portugal (60.0%) (p = 0.892). The quality of water collected during the spring (50.0%) or summer (66.7%) was not significantly different (p = 0.341).

Table 1.
Proportion of cattle farms in Portugal with poor water quality according to characteristics of the herds.
Regarding the constitution, poor water quality on cattle farms with 204 or more animals (68.8%) was worse than that on farms with fewer animals (50.0%), though the differences were not statistically significant (p = 0.279). The number of females in the farm was not significant (p = 0.719), with poor water quality identified for 62.5% of the farms with 199 or more females and 56.3% of farms with less than 199 females. The number of males and the number of heifers were also not significant (p = 0.926 and p = 0.821, respectively).
The occurrence of poor water quality was higher on farms of the milk production type (61.5%) than on farms of the mixed production type (50.0%), though without statistical significance (p = 0.604).
The occurrence among farms with intensive husbandry was higher (59.3%) but not statistically significant (p = 0.933). The farms with their own pasture area showed a similar frequency of poor water quality (60.0%) compared with farms that shared pastures with other owners (59.3%). Differences were not statistically significant (p = 0.975).
Poor water quality was most frequent on farms where the water came from a hole (62.5%) or well (58.3%) compared with other water sources, but the differences were not statistically significant (p = 0.560).
Farms that did not use routine disinfectants showed the worst water quality (70.8%) when compared with those that used disinfectants (25.0%). Differences were statistically significant (p = 0.022).
Table 2 presents the proportion of farms in Portugal with poor water quality according to the characteristics of their farmers. The two farms where women were responsible for the husbandry were both positive. The occurrence of poor water quality was higher on farms where the farmer was aged 50 years or less (63.6%) and if the farmer had a higher level of education (73.7%), but none of these differences were statistically significant.

Table 2.
Proportion of cattle farms in Portugal with poor water quality according to characteristics of the farmer.
About 94.7% of farmers had training in husbandry (94.7%). The occurrence of poor water quality on farms managed by farmers with training was 58.1% (p = 0.302).
Farms with farmers with exclusive dedication to the herd showed a lower occurrence of poor water quality (57.7%), but the differences were not statistically significant (p = 0.684).
4. Discussion
Knowledge is one of the cornerstones of surveillance and monitoring programs, since it determines whether to apply control measures or not, provides delivering data for evaluation of the effectiveness of these measures, and is the basis for modification [21].
This is the first epidemiological study that describes the quality of water in dairy farms in Portugal. The aim of this study was to characterize the water quality by herd size, species, constitution of the herd and type of production, using only animals and herds with this information properly registered. Bacteria can contaminate groundwater by several routes, and slurry and manure can be potential sources [22]. Comparing our data with those of other studies [23,24], we observed contamination by E. coli and other pathogenic microorganisms in the drinking water for dairy cattle. These findings were also in accordance with other studies [22,25] that identified coliform bacterial species as E. coli in drinking water. E. coli is the bacterium usually established to be the main contaminant in dairy farms [26,27].
E. coli is a Gram-negative facultative anaerobic bacterium that is found in the gastrointestinal tract and exhibits long-term survival in environmental habitats. Because of the virulence factors and phenotypic characteristics of this bacterium, there are strains that differentiate into diarrheic, non-pathogenic, and extraintestinal pathogenic E. coli, among which the diarrheic strains are a major cause of bacterial diarrhea [27].
Poor water quality is assumed to contribute to the contamination of milk and to poor milk quality. Additionally, the presence of E. coli in the various water sources may spell health hazards such as diarrheal diseases and problems of antibiotic resistance, since E. coli is known to be resistant to a wide range of antibiotics [28,29,30].
The presence of fecal enterococci correlates with the incidence of gastrointestinal diseases in bathers; therefore, it has been suggested to be a superior bacterial indicator of fecal contamination in water [31].
Enterococcus and coliforms were also isolated from drinking water on cattle farms. Coliforms, including total and fecal coliforms, are the primary indicators for assessment of contamination by Enterococcus spp. in the European Union and are indicators of fecal water contamination of human or animal origin [32]. Contamination by gastrointestinal pathogenic bacteria is a serious public health concern [33].
Water is a major route for the transmission of infectious diseases, and fecal contamination of water sources occurs mainly in developing and underdeveloped countries [34]. Given that most zoonotic outbreaks are caused by water contamination with feces from infected animals or humans [35], environmental contamination is one of the most serious difficulties facing ecosystems and biodiversity [36].
The bacterial loads/populations in the studied water samples of different dairy farms in Portugal were higher than the standard bacterial concentration level set by the World Health Organization (WHO). Water quality has an important role for farmers in terms of animal performance, nutrition and health. Nevertheless, the bacteriological quality does not always reach accepted values. Furthermore, water quality is not frequently measured in some dairy farms [37]. Despite the fact that the quality of water samples taken directly from the source is frequently measured, the quality of water at the endpoints of the distribution system, where cattle actually drink the water, is measured less regularly. For that reason, there may be large differences in quality between sources and endpoints [38].
Animals that drink water contaminated with enteric bacteria could serve as a common source of exposure of cattle to potential pathogens. That could result in an infection of a large number of animals within a brief period of time. To date, the period of time in which water troughs serve as reservoirs for enteric microorganisms, as well as the frequency with which waterborne transmission of these pathogens from water to cattle occurs, are not fully known [27]. Poor water quality is often defined in terms such as “unsatisfactory” or “unsafe”, but not enough is yet understood about the effects of coliform bacteria in water on animal health or on the rumen microflora. Contamination of livestock drinking water with microorganisms can ultimately pose a risk to public health, considering contaminated milk or the contaminated drinking water source itself [38]. Considering that high-producing cows drink about 120 L of water per day, according to the dry matter intake of the feed, milk production rate, ambient temperature and sodium consumption, water is considered the most important “nutrient” for cattle [26]. Cows are especially vulnerable to different disorders when they ingest contaminated water, as they are often in a negative energy balance, can either develop ketosis or ruminal acidosis, and, when subjected to several stressors (e.g., social stress, housing relocation stress, hormonal stress), can develop other health (mastitis) and reproductive disorders [34]. Related to all these data, water quality on dairy farms could affect the health and productivity of the herd, and even public health and food safety [36]. Even though the main strategies related to improving the quality of drinking water, sanitation and hygiene have resulted in significant improvements worldwide, there are social, economic, institutional and geographic barriers that obstruct the improvement of these indicators [27]. The protection of the microbial status of drinking water continues to be a global challenge. The presence of coliforms in drinking water is a reason for assuming that there is a potential health risk due to the possible presence of pathogens. Fostering public education on the significance of protecting water resources, as well as monitoring its quality and its effects on human and animal health, is strongly recommended [38].
Previous studies have highlighted the role of disinfectants in water quality [8,39]. The only factor associated with poor water quality was the absence of effective periodic disinfection. Microbial pathogens can grow in biofilms on conduit walls in case of water stagnation and warmer situations [38,40]. The use of correct disinfectants is required for inactivation of pathogenic microorganisms during water treatment [41].
It was not possible to ascertain the origin of fecal contamination of water, but it was possibly due to contamination of groundwater by manure and slurry, which strengthens the need for studies to reduce microorganisms in manure and slurry.
The pathogens can be directly transmitted to humans through contact with animal wastes or indirectly through contaminated products, and water can also be contaminated [42]. On dairy farms, high quality drinking water is crucial for animal health, welfare and development. Moreover, microbiological and fecal contamination of drinking water is linked to its rejection by livestock, even at relatively low levels of contamination [43].
Conventional drinking water treatments involving filtration, flocculation, and disinfection are used for tap water [44]. This may explain the existence of greater contamination in the remaining sources, which are not subject to the same treatments. Water is one of the most important natural resources and is, therefore, an essential element for life. Research information on water quality conditions is highly important [38].
The limitations and potential sources of bias must be considered when weighing the results. This survey did not adequately capture the farms of Portugal since it was a convenience sample. The studied farms were selected on a voluntary basis. Due to the sample size and purposive sampling strategy used, the results cannot be generalized to describe the farms of all Portuguese farmers. Other farmers not sampled in the present study may have different practices. Another limitation is that the study was not replicated for at least two consecutive years to find out if there were differences due to economic constraints. Despite these limitations, our study indicates that a high percentage of cows drink water of poor quality. Many common and general biology research techniques rely on microorganisms. Machine learning (ML) has been gradually integrated into multiple fields of study, because traditional methods using microscopes and biological cultures are labor- intensive. Therefore, ML has been gradually applied to microbial studies. Literature reviews have shown that ML can be used in many aspects of microbiology research, especially classification problems, and for exploring the interaction between microorganisms and the surrounding environment, including prediction of microbial species [45,46]. More advanced measuring techniques for parameters were not applied in our study due to factors such as the cost of monitoring.
Because of the existence of different water quality models and the potential promise they have exhibited, it is timely to evaluate the state-of-the-art in this area, to address potential challenges, and to provide insights for future research directions [31].
5. Conclusions
This study assessed the water quality on 32 Portuguese farms. Based on the research findings, 59.4% of the studied farms had poor water quality. E. coli was recovered from 20.0% of the water samples. This information could be used as a starting point to design control measures associated with the use of disinfectants that are needed in order to help decrease poor water quality on farms and to improve animal and environment health and productivity.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.C.C. and H.T.; methodology, A.C.C. and A.S.S.; software, A.C.C. and A.S.S.; validation, A.C.C., C.M. and H.T.; formal analysis, A.S.S. and A.C.C.; investigation, A.S.S.; resources, A.S.S. and A.C.C.; data curation, A.S.S.; writing—original draft preparation, A.S.S.; writing—review and editing, A.S.S., A.C.C., C.M. and H.T.; visualization, H.T. and C.M.; supervision, A.C.C. and H.T.; project administration, A.C.C. and H.T.; funding acquisition, A.C.C. and A.S.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the project UIDB/CVT/00772/2020 and LA/P/0059/2020 funded by the Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology (FCT).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank to Fátima Fraga, Sonia Dias and Áurea Queirós for technical assistance, and to Stephanie Lourenço for providing language help.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Pachepsky, Y.A.; Allende, A.; Boithias, L.; Cho, K.; Jamieson, R.; Hofstra, N.; Molina, M. Microbial Water Quality: Monitoring and Modeling. J. Environ. Qual. 2018, 47, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazemi, K.; Salari, S.; Eskandani, M.A. Assessment of the Escherichia Coli Pollution in Drinking Water and Water Sources in Sistan, Iran. J. Water Reuse Desalination 2018, 8, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.N. Field Study on Evaluation of the Efficacy and Usability of Two Disinfectants for Drinking Water Treatment at Small Cattle Breeders and Dairy Cattle Farms. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edberg, S.; Rice, E.; Karlin, R.; Allen, M. Escherichia Coli: The Best Biological Drinking Water Indicator for Public Health Protection. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 88, 1068–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odonkor, S.T.; Addo, K.K. Prevalence of Multidrug-Resistant Escherichia Coli Isolated from Drinking Water Sources. Int. J. Microbiol. 2018, 2018, 7204013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilmore, M.S.; Clewell, D.B.; Ike, Y.; Shankar, N. Enterococci: From Commensals to Leading Causes of Drug. Mass. Eye Ear Infirm. 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lobna, M.A.S.; Metawea, Y.F. Detection of Some Water Borne Zoonotic Pathogens in Untreated Ground Water and Its Impact on Human and Animal Health in Kalyoubia Province (Rural Areas). Glob. Vet. 2013, 10, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.N. A Potential Approach for Monitoring and Evaluation of Drinking Water Sources and Quality for Livestock Animals at Beni-Suef Province. Glob. Vet. 2014, 13, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lardner, H.A.; Kirychuk, B.D.; Braul, L.; Willms, W.D.; Yarotski, J.; Lardner, H.A.; Kirychuk, B.D.; Braul, L.; Willms, W.D.; Yarotski, J. The Effect of Water Quality on Cattle Performance on Pasture. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 2005, 56, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemma, D.H.; Mengistu, A.; Kuma, T.; Kuma, B. Improving Milk Safety at Farm-Level in an Intensive Dairy Production System: Relevance to Smallholder Dairy Producers. Food Qual. Saf. 2018, 2, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanitha, H.D.; Sethulekshmi, C.; Latha, C. An Epidemiological Investigation on Occurrence of Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia Coli in Raw Milk. Vet. World 2018, 11, 1164–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beede, D.K. What Will Our Ruminants Drink? Anim. Front. 2012, 2, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, S.; Waters, N.R.; Brennan, F.; Auer, A.; Fenton, O.; Richards, K.; Bolton, D.J.; Pritchard, L.; O’Flaherty, V.; Abram, F. Toward Assessing Farm-Based Anaerobic Digestate Public Health Risks: Comparative Investigation with Slurry, Effect of Pasteurization Treatments, and Use of Miniature Bioreactors as Proxies for Pathogen Spiking Trials. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2018, 2, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, M.D.; Pachepsky, Y.A.; Hill, R.L.; Martinez, G. Escherichia coli Export from Manured Fields Depends on the Time between the Start of Rainfall and Runoff Initiation. Wiley Online Libr. 2018, 47, 1293–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, E.B.; Yaron, S.; Matthews, K.R. Transmission of Escherichia Coli O157:H7 from Contaminated Manure and Irrigation Water to Lettuce Plant Tissue and Its Subsequent Internalization. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manero, A.; Vilanova, X.; Cerdà-Cuéllar, M.; Blanch, A.R. Characterization of Sewage Waters by Biochemical Fingerprinting of Enterococci. Water Res. 2002, 36, 2831–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hricová, K.; Štosová, T.; Kučová, P.; Fišerová, K.; Bardoň, J.; Kolář, M. Analysis of Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci in Hemato-Oncological Patients. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.O.; Baptiste, K.E. Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci: A Review of Antimicrobial Resistance Mechanisms and Perspectives of Human and Animal Health. Microb. Drug Resist. 2018, 24, 590–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siročić, A.P.; Ojdanić, K.; Dogančić, D.; Plantak, L. Water Quality for Human Consumption from the Public Water Supply System †. Environ. Sci. 2023, 25, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeJeune, J.T.; Besser, T.E.; Merrill, N.L.; Rice, D.H.; Hancock, D.D. Livestock Drinking Water Microbiology and the Factors Influencing the Quality of Drinking Water Offered to Cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2001, 84, 1856–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousing, J.; Jensen, P.T.; Halgaard, C.; Bager, F.; Feld, N.; Nielsen, B.; Nielsen, J.P.; Bech-Nielsen, S. Nation-Wide Salmonella Enterica Surveillance and Control in Danish Slaughter Swine Herds. Prev. Vet. Med. 1997, 29, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Doyle, M.P.; Shere, J.; Garber, L. Prevalence of Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia Coli O157:H7 in a Survey of Dairy Herds. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 1290–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, D.D.; Besser, T.E.; Kinsel, M.L.; Tarr, P.I. Prevalence Escherichia. Vet. Microbiol. 1994, 199–207. [Google Scholar]
- Din, M.; Aleem, A.; Pirkani, G.S.; Mohammad, A. Pathogens From Drinking Water; Isolation and Antibiogram of Pathogenic Organisms from Drinking Water in Quetta City. Prof. Med. J. 2014, 21, 760–765. [Google Scholar]
- Fairbrother, J.M.; Nadeau, É. Escherichia Coli: On-Farm Contamination of Animals. OIE Rev. Sci. Tech. 2006, 25, 555–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeJeune, J.T.; Wetzel, A.N. Preharvest Control of Escherichia coli O157 in Cattle. J. Anim. Sci. 2007, 85, E73–E80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Vásquez, A.; Visconti-Lopez, F.J.; Vargas-Fernández, R. Escherichia Coli Contamination of Water for Human Consumption and Its Associated Factors in Peru: A Cross-Sectional Study. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2023, 108, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adesiyun, A.A.; Webb, L.A.; Romain, H.; Kaminjolo, J.S. Prevalence and Characteristics of Strains of Escherichia Coli Isolated from Milk and Feces of Cows on Dairy Farms in Trinidad. J. Food Prot. 1997, 60, 1174–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.; Igrejas, G.; Radhouani, H.; Estepa, V.; Alcaide, E.; Zorrilla, I.; Serra, R.; Torres, C.; Poeta, P. Detection of Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia Coli Isolates in Faecal Samples of Iberian Lynx. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 54, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, D.; Poeta, P.; Sáenz, Y.; Vinué, L.; Coelho, A.C.; Matos, M.; Rojo-Bezares, B.; Rodrigues, J.; Torres, C. Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance in Escherichia Coli Isolates Recovered from Wild Animals. Microbial. Drug Resist. 2008, 14, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Zheng, F.; Maier, H.R.; Ostfeld, A.; Creaco, E.; Savic, D.; Langeveld, J.; Kapelan, Z. Water Quality Modeling in Sewer Networks: Review and Future Research Directions. Water Res. 2021, 202, 117419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Council of the European Union Council. The Council of the European Union Council Directive 98/83/EC of 3 November 1998 on the Quality of Water Intended for Human Consumption (OJ L 330 05.12.1998 p. 32). Doc. Eur. Community Environ. Law 1998, 865–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, A.S.; Miranda, C.; Teixeira, C.A.; Coutinho, J.; Trindade, H.; Coelho, A.C. Impact of Different Treatments on Escherichia Coli during Storage of Cattle Slurry. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 236, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hout, J.J. Lead in Drinking Water. J. Environ. Health 2012, 75, 56. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Davies-Colley, R.J.; Nagels, J.W.; Smith, R.A.; Young, R.G.; Phillips, C.J. Water Quality Impact of a Dairy Cow Herd Crossing a Stream. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2004, 38, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eenige Van, M.; Kononoff, P.J.; Snow, D.D.; Christensen, D.A. Drinking Water for Dairy Cattle. Large Dairy Herd Manag. 2013, 611–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://biblio.ugent.be/publication/01GVJKHN3DVVY9P68JARE18B5S (accessed on 13 April 2023).
- Ashbolt, N.J. Microbial Contamination of Drinking Water and Human Health from Community Water Systems. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2015, 2, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi-Fedele, G.; de Figueiredo, J.A.P.; Steier, L.; Canullo, L.; Steier, G.; Roberts, A.P. Evaluation of the Antimicrobial Effect of Super-Oxidized Water (Sterilo®) and Sodium Hypochlorite against Enterococcus Faecalis in a Bovine Root Canal Model. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2010, 18, 498–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingender, J.; Flemming, H.C. Biofilms in Drinking Water and Their Role as Reservoir for Pathogens. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2011, 214, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Deng, Y.; Bond, T.; Fang, C.; Cao, Z.; Chu, W. Disinfection Byproduct Formation during Drinking Water Treatment and Distribution: A Review of Unintended Effects of Engineering Agents and Materials. Water Res. 2019, 160, 313–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Jiang, X. Microbiological Safety of Chicken Litter or Chicken Litter-Based Organic Fertilizers: A Review. Agriculture 2014, 4, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhardt, F.K.; Hayer, J.J.; Heinemann, C.; Steinhoff-Wagner, J. Drinking Behavior of Dairy Cows under Commercial Farm Conditions Differs Depending on Water Trough Design and Cleanliness. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2022, 256, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czyzewska, W.; Piontek, M.; Łuszczyńska, K. The Occurrence of Potential Harmful Cyanobacteria and Cyanotoxins in the Obrzyca River (Poland), a Source of Drinking Water. Toxins 2020, 12, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, K.; Guo, F.; Liu, X.; Lin, Y.; Zou, Q. Application of Machine Learning in Microbiology. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Luo, J.; Huang, D.; Liu, Y.; Li, D.D. Machine Learning Advances in Microbiology: A Review of Methods and Applications. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).