Identification of Characteristic Parameters in Seed Yielding of Selected Varieties of Industrial Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Using Artificial Intelligence Methods
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Material
2.2. Collected Data and Methods
- plantation size (ha);
- weight of seeds sown on the plantation (kg);
- soil class—according to the soil quality classification adopted in Poland [33];
- forecrop—a plant grown on the same field in the growing season preceding the hemp cultivation season;
- category—category of seed material sown on a given plantation, according to the Seed Law [34];
- form of harvesting—one- or two-stage harvesting;
- seed moisture (%)—on the basis of data from the ISTA Certificate;
- crop quality—germination in % given on the ISTA Certificate;
- weather conditions—average monthly temperature and monthly rainfall from April to November, based on data provided by the Institute of Meteorology and Water Management—National Research Institute (IM&WM-NRI) on its website [35].
- “Germination and yield 1”, with two output variables: yield per hectare and seed germination (%);
- “Germination 1”, with one output variable: seed germination (%);
- “Yield 1”, with one output variable: yield per hectare.
- Training subset (U) used to teach the network;
- Validation subset (W), allowing the control of the effects of the learning algorithm during the learning process;
- Test subset (T)—which allows the assessment of the quality of the generated neural network.
- “Germination and yield 2”;
- “Germination 2”;
- “Yield 2”.
- SS—SubSample;
- EX—by user (Explicit)—determination of radial deviation;
- PI—Pseudoinversion.
3. Results
3.1. Qualitative Characteristics and Sensitivity Assessment of the Generated Neural Network Models Created Using the Automatic Designer Function
3.2. Qualitative Characteristics and Sensitivity Assessment of the Generated Neural Network Models Created Using the User Network Designer Function
3.3. Sensitivity Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kujawa, S.; Niedbała, G. Artificial Neural Networks in Agriculture. Agriculture 2021, 11, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybylak, A.; Bonieki, P.; Zaborowicz, M.; Mo, Z.; Przybył, K. Przykłady wykorzystania modelowanie neuronowego w praktyce rolniczej. Tech. Rol. Ogrod. Leśna 2013, 1, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Boniecki, P. Elementy Modelowania Neuronowego w Rolnictwie; Wydawnictwo Uniwersytetu Przyrodniczego: Poznań, Poland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Niedbała, G.; Lenartowicz, T.; Kozłowski, R.J.; Zaborowicz, M. Neural modelling as a prediction method of starch content in potatoes for post-registration and specific agricultural experimentation. Nauk. Przyr. Technol. 2015, 9, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francik, S.; Łapczyńska-Kordon, B.; Francik, R.; Wójcik, A. Modeling and Simulation of Biomass Drying Using Artificial Neural Networks. In Renewable Energy Sources: Engineering, Technology, Innovation; Springer Proceedings in Energy; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neugebauer, M.; Nalepa, K.; Sołowiej, P. Sieci neuronowe jako narzędzie umożliwiające prognozowanie zapotrzebowania na wodę w uprawach rolnych. Inżynieria Rol. 2007, 2, 205–210. [Google Scholar]
- Frankowski, J.; Zaborowicz, M.; Dach, J.; Czekała, W.; Przybył, J. Biological Waste Management in the Case of a Pandemic Emergency and Other Natural Disasters. Determination of Bioenergy Production from Floricultural Waste and Modeling of Methane Production Using Deep Neural Modeling Methods. Energies 2020, 13, 3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szwedziak, K.; Polańczyk, E.; Grzywacz, Ż.; Niedbała, G.; Wojtkiewicz, W. Neural Modeling of the Distribution of Protein, Water and Gluten in Wheat Grains during Storage. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szwedziak, K.; Tukiendorf, M. Use of geostatic function to describe wheat grain mass quality. J. Res. Appl. Agric. Eng. 2014, 59, 126–130. [Google Scholar]
- Zaborowicz, M.; Boniecki, P.; Koszela, K.; Przybylak, A.; Przybył, J. Application of neural image analysis in evaluating the quality of greenhouse tomatoes. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 218, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraniecki, P.; Latterini, F.; Stefanoni, W.; Frankowski, J.; Wielgusz, K.; Pari, L. Assessment of the Working Performance of an Innovative Prototype to Harvest Hemp Seed in Two Different Conditions of Terrain Slope. Agronomy 2022, 12, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Industrial Hemp Association. Available online: www.eiha.org (accessed on 9 March 2023).
- Hesami, M.; Pepe, M.; Monthony, A.S.; Baiton, A.; Jones, A.M.P. Modeling and optimizing in vitro seed germination of industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L.). Ind. Crop. Prod. 2021, 170, 113753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, B.; Priya, J.; Welekar, S.; Gao, Z. Hemp Disease Detection and Classification Using Machine Learning and Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Intl Conf on Parallel & Distributed Processing with Applications, Big Data & Cloud Computing, Sustainable Computing & Communications, Social Computing & Networking, Exeter, UK, 17–19 December 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Yu, T.; Zheng, S.; Niu, C.; Gao, J.; Tang, J. Hemp Disease Detection and Classification Using Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conferences on Internet of Things (iThings) and IEEE Green Computing and Communications (GreenCom) and IEEE Cyber, Physical and Social Computing (CPSCom) and IEEE Smart Data (SmartData) and IEEE Congress on Cybermatics (Cybermatics), Rhodes, Greece, 2–6 November 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.R.; Chen, B.; Dai, J.-G.; Kazmi, S.M.S.; Munir, M.J. Evolutionary artificial intelligence approach for performance prediction of bio-composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 290, 123254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaratunga, V.; Wickramasinghe, L.; Perera, A.; Jayasinghe, J.; Rathnayake, U. Artificial Neural Network to Estimate the Paddy Yield Prediction Using Climatic Data. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 8627824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barwicki, J.; Hryniewicz, M.; Grzybek, A. Yield forecasting using artificial intelligence. Pol. Tech. Rev. 2020, 1, 19–22. [Google Scholar]
- Emamgholizadeh, S.; Parsaeian, M.; Baradaran, M. Seed yield prediction of sesame using artificial neural network. Eur. J. Agron. 2015, 68, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankowski, J.; Zaborowicz, M.; Sieracka, D.; Łochyńska, M.; Czeszak, W. Prediction of the Hemp Yield Using Artificial Intelligence Methods. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 13725–13735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandepitte, K.; Vasile, S.; Vermeire, S.; Vanderhoeven, M.; Van der Borght, W.; Latré, J.; De Raeve, A.; Troch, V. Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) for high-value textile applications: The effective long fiber yield and quality of different hemp varieties, processed using industrial flax equipment. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2020, 158, 112969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mańkowski, J. The Effect of Some Agronomic Factors on the Amount and Quality of Homomorphic Fibre. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2003, 11, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Research Centre for Cultivar Testing. Available online: www.coboru.gov.pl/index_en/ (accessed on 9 March 2023).
- Grabowska, L.; Jaranowska, B.; Baraniecki, P.; Tymków, J. The Results of Hemp Breeding in Poland. Natural Fibres 1998, 2, 103–109. [Google Scholar]
- Tsaliki, E.; Kalivas, A.; Jankauskiene, Z.; Irakli, M.; Cook, C.; Grigoriadis, I.; Panoras, I.; Vasilakoglou, I.; Dhima, K. Fibre and Seed Productivity of Industrial Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Varieties under Mediterranean Conditions. Agronomy 2021, 11, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New Frontier Data. Poland Embraces European Potential for Industrial Hemp. Available online: https://newfrontierdata.com/cannabis-insights/polands-rise-to-a-new-european-hemp-powerhouse/ (accessed on 9 March 2023).
- Polish Hemp Program. Available online: www.polishhempprogram.com/polish-hemp-program---on-media.html (accessed on 9 March 2023).
- Burczyk, H.; Oleszak, G. Konopie oleiste (Cannabis sativa L. var. olrifera) uprawiane na nasiona do produkcji oleju i biogazu. Probl. Inżynierii Rol. 2016, 94, 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- Burczyk, H.; Frankowski, J. Henola—Pierwsza polska odmiana konopi oleistych. Zag. Doradz. Rol. 2018, 93, 89–101. [Google Scholar]
- Wójtowicz, A.; Strażyński, P.; Mrówczyński, M. (Eds.) Metodyka Integrowanej Ochrony Konopi dla Doradców; Instytut Ochrony Roślin—Państwowy Instytut Badawczy: Poznań, Poland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Grzebisz, W. (Ed.) Rolnictwo cz. VI. Produkcja roślinna. In Technologie Produkcji Roślinnej; Hortpress: Warszawa, Poland, 2015; pp. 280–288. [Google Scholar]
- Cierpucha, W. (Ed.) Technologia Uprawy i Przetwórstwa Konopi Włóknistych; Instytut Włókien Naturalnych i Roślin Zielarskich: Poznań, Poland, 2013; pp. 22–31. [Google Scholar]
- Regulation of the Council of Ministers on Soil Classification/Rozporządzenie Rady Ministrów z Dnia 12 Września 2012 r. w Sprawie Gleboznawczej Klasyfikacji Gruntów z Dnia 12 Września 2012 r. (Dz. U. 2012, poz. 1246). Available online: https://isap.sejm.gov.pl/isap.nsf/DocDetails.xsp?id=wdu20120001246 (accessed on 9 March 2023).
- Seed Law/Ustawa o Nasiennictwie, z dn. 9 Listopada 2012 (Dz. U. 2012 poz. 1512). Available online: https://isap.sejm.gov.pl/isap.nsf/DocDetails.xsp?id=WDU20120001512 (accessed on 9 March 2023).
- Institute of Meteorology and Water Management—National Research Institute. Available online: www.imgw.pl (accessed on 9 March 2023).
- Tadeusiewicz, R. Sieci Neuronowe. In Akademicka Oficyna Wydawnicza; RM: Warszawa, Poland, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Medar, R.A.; Rajpurohit, V.S.; Ambekar, A.M. Sugarcane Crop Yield Forecasting Model Using Supervised Machine Learning. Int. J. Intell. Syst. Appl. 2019, 11, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedbała, G.; Kozłowski, J.R. Application of Artificial Neural Networks for Multi-Criteria Yield Prediction of Winter Wheat. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2019, 21, 51–61. [Google Scholar]
- Gandhi, N.; Petkar, O.; Armstrong, L.J. Rice crop yield prediction using artificial neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Technological Innovations in ICT for Agriculture and Rural Development (TIAR), Chennai, India, 15–16 July 2016; pp. 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumar, V.; Ampatzidis, Y.; Costa, L. Tree-level citrus yield prediction utilizing ground and aerial machine vision and machine learning. Smart Agric. Technol. 2023, 3, 100077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

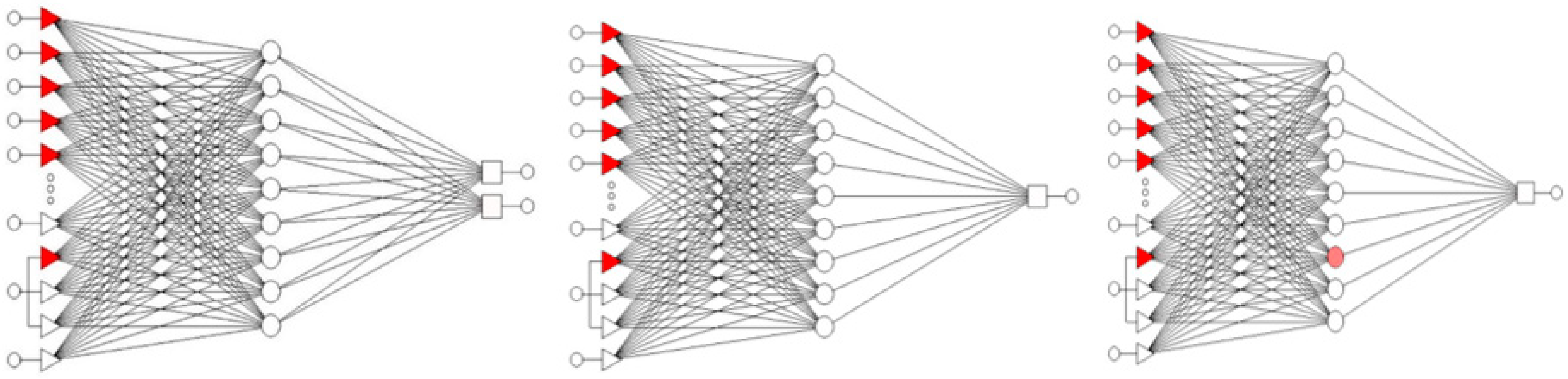
| Model | Network | Learning Quality | Validation Quality | Testing Quality | Learning Error | Validation Error | Testing Error | Learning Algorithm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Germination and yield 1 | RBF 15:41-3-2:2 | 0.9626 | 0.9756 | 0.9837 | 0.1359 | 0.1874 | 0.1619 | KM, KN, PI |
| Germination 1 | RBF 15:41-6-1:1 | 0.9685 | 0.9624 | 0.9252 | 0.1755 | 0.1617 | 0.1742 | KM, KN, PI |
| Yield 1 | RBF 17:49-13-1:1 | 0.7659 | 1.2494 | 0.9799 | 0.0019 | 0.0035 | 0.0029 | KM, KN, PI |
| Model | Network | Learning Quality | Validation Quality | Testing Quality | Learning Error | Validation Error | Testing Error | Learning Algorithm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Germination and yield 2 | RBF 22:49-9-2:2 | 0.9847 | 0.9934 | 0.9992 | 0.1135 | 0.1096 | 0.1195 | SS, EX, PI |
| Germination 2 | RBF 22:51-9-1:1 | 0.9841 | 0.9997 | 0.9999 | 0.1867 | 0.2147 | 0.2001 | SS, EX, PI |
| Yield 2 | RBF 22:45-9-1:1 | 0.9898 | 0.9905 | 0.9790 | 0.0023 | 0.0025 | 0.0020 | SS, EX, PI |
| Network | RBF 22:49-9-2:2 | RBF 22:45-9-1:1 | RBF 22:51-9-1:1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Quotient | Rank | Quotient | Rank | Quotient | Rank |
| total precipitation _4 | 1.0622 | 8 | 1.0120 | 6 | 1.0066 | 10 |
| total precipitation _5 | 1.0640 | 7 | 1.0120 | 1 | 1.0074 | 2 |
| total precipitation _6 | 1.0657 | 2 | 1.0120 | 3 | 1.0074 | 6 |
| total precipitation _7 | 1.0657 | 3 | 1.0120 | 4 | 1.0074 | 1 |
| total precipitation _8 | 1.0655 | 6 | 1.0112 | 8 | 1.0074 | 5 |
| total precipitation _9 | 1.0657 | 1 | 1.0079 | 9 | 1.0074 | 3 |
| total precipitation _10 | 1.0657 | 4 | 1.0120 | 2 | 1.0074 | 4 |
| total precipitation _11 | 1.0657 | 5 | 1.0120 | 5 | 1.0074 | 7 |
| average monthly temperature _4 | 1.0221 | 11 | 0.9982 | 18 | 1.0028 | 13 |
| average monthly temperature _5 | 1.0266 | 10 | 1.0051 | 11 | 1.0039 | 11 |
| average monthly temperature _6 | 1.0311 | 9 | 1.0079 | 10 | 1.0074 | 8 |
| average monthly temperature _7 | 1.0207 | 12 | 1.0020 | 12 | 1.0023 | 15 |
| average monthly temperature _8 | 1.0143 | 15 | 0.9992 | 14 | 1.0016 | 16 |
| average monthly temperature _9 | 1.0027 | 20 | 0.9979 | 20 | 1.0005 | 21 |
| average monthly temperature _10 | 1.0057 | 19 | 0.9989 | 15 | 1.0003 | 22 |
| average monthly temperature _11 | 1.0176 | 14 | 0.9981 | 19 | 1.0014 | 18 |
| quantity of seeds sown per hectare [kg] | 1.0016 | 21 | 1.0113 | 7 | 1.0071 | 9 |
| variety | 1.0007 | 22 | 0.9973 | 21 | 1.0006 | 20 |
| soil class | 1.0121 | 16 | 0.9967 | 22 | 1.0035 | 12 |
| forecrop | 1.0203 | 13 | 1.0003 | 13 | 1.0027 | 14 |
| seeds category | 1.0078 | 17 | 0.9985 | 16 | 1.0015 | 17 |
| harvesting form | 1.0062 | 18 | 0.9984 | 17 | 1.0008 | 19 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sieracka, D.; Zaborowicz, M.; Frankowski, J. Identification of Characteristic Parameters in Seed Yielding of Selected Varieties of Industrial Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Using Artificial Intelligence Methods. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1097. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13051097
Sieracka D, Zaborowicz M, Frankowski J. Identification of Characteristic Parameters in Seed Yielding of Selected Varieties of Industrial Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Using Artificial Intelligence Methods. Agriculture. 2023; 13(5):1097. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13051097
Chicago/Turabian StyleSieracka, Dominika, Maciej Zaborowicz, and Jakub Frankowski. 2023. "Identification of Characteristic Parameters in Seed Yielding of Selected Varieties of Industrial Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Using Artificial Intelligence Methods" Agriculture 13, no. 5: 1097. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13051097
APA StyleSieracka, D., Zaborowicz, M., & Frankowski, J. (2023). Identification of Characteristic Parameters in Seed Yielding of Selected Varieties of Industrial Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Using Artificial Intelligence Methods. Agriculture, 13(5), 1097. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13051097







