N-Nitrosamine Impurities in Ethalfluralin: Determination of an Overlooked Deleterious Source in Pesticides
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
Quality Assurance/Quality Control—Method Validation (Table 1)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). Agents Classified by the IARC Monographs, Volumes 1–132. Available online: https://monographs.iarc.who.int/agents-classified-by-the-iarc (accessed on 5 April 2023).
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Nitrosamine Impurities in Human Medicinal Products: CHMP Assessment Report for the Article 5(3) of Regulation EC (No) 726/2004 procedure; EMA: 25 June 2020. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/referral/nitrosamines-emea-h-a53-1490-assessment-report_en.pdf (accessed on 5 April 2023).
- Akkaraju, H.; Tatia, R.; Mane, S.S.; Khade, A.B.; Dengale, S.J. A comprehensive review of sources of nitrosamine contamination of pharmaceutical substances and products. Regul. Toxicol. Pharm. 2023, 139, 105355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brambilla, G.; Martelli, A. Genotoxic and carcinogenic risk to humans of drug–nitrite interaction products. Mutat. Res./Rev. Mutat. Res. 2007, 635, 17–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, R.D.; Morrison, J.; Rounbehler, D.P.; Fan, S.; Fine, D.H. Normal-Nitroso Compound Impurities in Herbicide Formulations. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 1977, 25, 1416–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fishbein, L. Overview of Potential Mutagenic Problems Posed by Some Pesticides and Their Trace Impurities. Environ. Health Perspect. 1978, 27, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, P.C. Nitrosamines and Pesticides: A Special Report on the Occurrence of Nitrosamines as Terminal Residues Resulting from Agricultural Use of Certain Pesticides. Pure Appl. Chem. 1980, 52, 499–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reportlinker.com, Ethalfluralin: Global Product Intelligence (2020–2025). Available online: https://www.reportlinker.com/p04098753/Ethalfluralin-Global-Product-Intelligence.html (accessed on 5 April 2023).
- Reportlinker, Trifluralin: Global Product Intelligence (2020–2025). Available online: https://www.reportlinker.com/p03971327/Trifluralin-Global-Product-Intelligence.html (accessed on 5 April 2023).
- Reportlinker, Pendimethalin: Global Product Intelligence (2020–2025). Available online: https://www.reportlinker.com/p03971303/Pendimethalin-Global-Product-Intelligence.html (accessed on 5 April 2023).
- Reportlinker, Benfluralin: Global Product Intelligence (2020–2025). Available online: https://www.reportlinker.com/p05245011/Benfluralin-Global-Product-Intelligence.html (accessed on 5 April 2023).
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Control of Nitrosamine Impurities in Human Drugs—GUIDANCE DOCUMENT Rev.1. 2021. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/141720/download (accessed on 5 April 2023).
- European Chemicals Agency (ECHA). Nitrosamines-Substance Infocard. Available online: https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.305.347 (accessed on 5 April 2023).
- European Commission (EC). Directorate-General for Health and Food Safety (DG SANTE), SANCO/10597/2003—Rev. 10.1: Guidance Document on the Assessment of the Equivalence of Technical Materials of Substances Regulated Under Regulation (EC) No 1107/2009. 2012. Available online: https://food.ec.europa.eu/system/files/2016-10/pesticides_guidance_equivalence-chem-substances_en.pdf (accessed on 5 April 2023).
- Europol. 122 Tons of Illegal or Counterfeit Pesticides Seized during Operation Silver Axe II. 2017. Available online: https://www.europol.europa.eu/media-press/newsroom/news/record-number-of-1-346-tonnes-of-illegal-pesticides-taken-market-in-2020-global-operation-silver-axe#:~:text=Email-,A%20record%20number%20of%201%20346%20tonnes%20of%20illegal%20pesticides,2020%20global%20operation%20Silver%20Axe&text=Europol%20coordinated%20the%20fifth%20edition,compared%20to%20last%20year’s%20operation, (accessed on 5 April 2023).
- Plonka, M.; Walorczyk, S.; Miszczyk, M. Chromatographic methods for the determination of active substances and characterization of their impurities in pesticide formulations. Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 85, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plonka, M.; Walorczyk, S.; Miszczyk, M.; Kronenbach-Dylong, D. Simultaneous gas chromatographic determination of chlorpyrifos and its impurity sulfotep in liquid pesticide formulations. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2016, 51, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badawy, M.E.I. Development and validation of HPLC methods for analysis of chlorantraniliprole insecticide in technical and commercial formulations. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2018, 53, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.; Prusnick, T. Application of Raman microscopy in pesticide formulation analysis. Abstr. Pap. Am. Chem. S 2018, 256. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.Q.; Xie, J.C.; Zhang, J.X.; Yan, H.; Xiong, Y.M.; Liu, W.; Min, S.G. A global model for the determination of prohibited addition in pesticide formulations by near infrared spectroscopy. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2020, 105, 103191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maragou, N.C.; Balayiannis, G. Determination of Ethephon in Pesticide Formulations by Ion Exchange Chromatography with Indirect Spectrophotometric Detection. Anal. Lett. 2020, 53, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission (EC). Directorate-General for Health and Food Safety, SANCO/3030/99 rev.5: Technical Active Substance and Plant Protection Products: Guidance for Generating and Reporting Methods of Analysis in Support of Pre- and Post-Registration Data Requirements for Annex (Section 4) of Regulation (EU) No 283/2013 and Annex (Section 5) of Regulation (EU) No 284/2013. Available online: https://food.ec.europa.eu/system/files/2019-03/pesticides_ppp_app-proc_guide_phys-chem-ana_3030.pdf (accessed on 5 April 2023).
- European Union (EU). Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) No 540/2011 of 25 May 2011 Implementing Regulation (EC) No 1107/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council as Regards the List of Approved Active Substances. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A32011R0540 (accessed on 5 April 2023).
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO)—World Health Organization (WHO). Manual on the Development and Use of FAO and WHO Specifications for Chemical Pesticides, 2nd ed.; FAO: Rome, Italy; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH). Draft ICH Guideline Q14 Analytical Procedure Development. 2022. Available online: https://database.ich.org/sites/default/files/ICH_Q14_Document_Step2_Guideline_2022_0324.pdf (accessed on 5 April 2023).
- Anagnostopoulos, C.; Charalampous, A.; Balayiannis, G. EI and NCI GC-MS and GC-MS/MS: Comparative Study of Performance Characteristics for the Determination of Pesticide Residues in Plant Matrix. Chromatographia 2015, 78, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magee, P.N.; Barnes, J.M. The production of malignant primary hepatic tumors in the rat by feeding dimethylnitrosamine. Br. J. Cancer 1956, 10, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality: Fourth Edition Incorporating the First and Second Addenda. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240045064 (accessed on 5 April 2023).
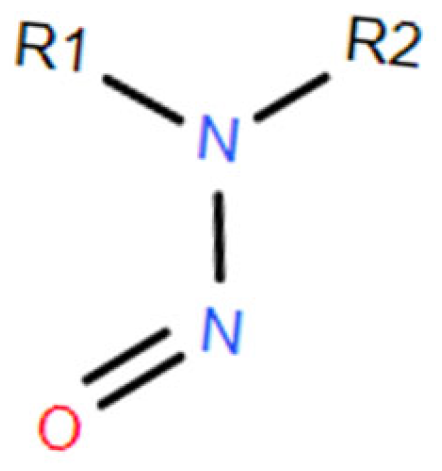


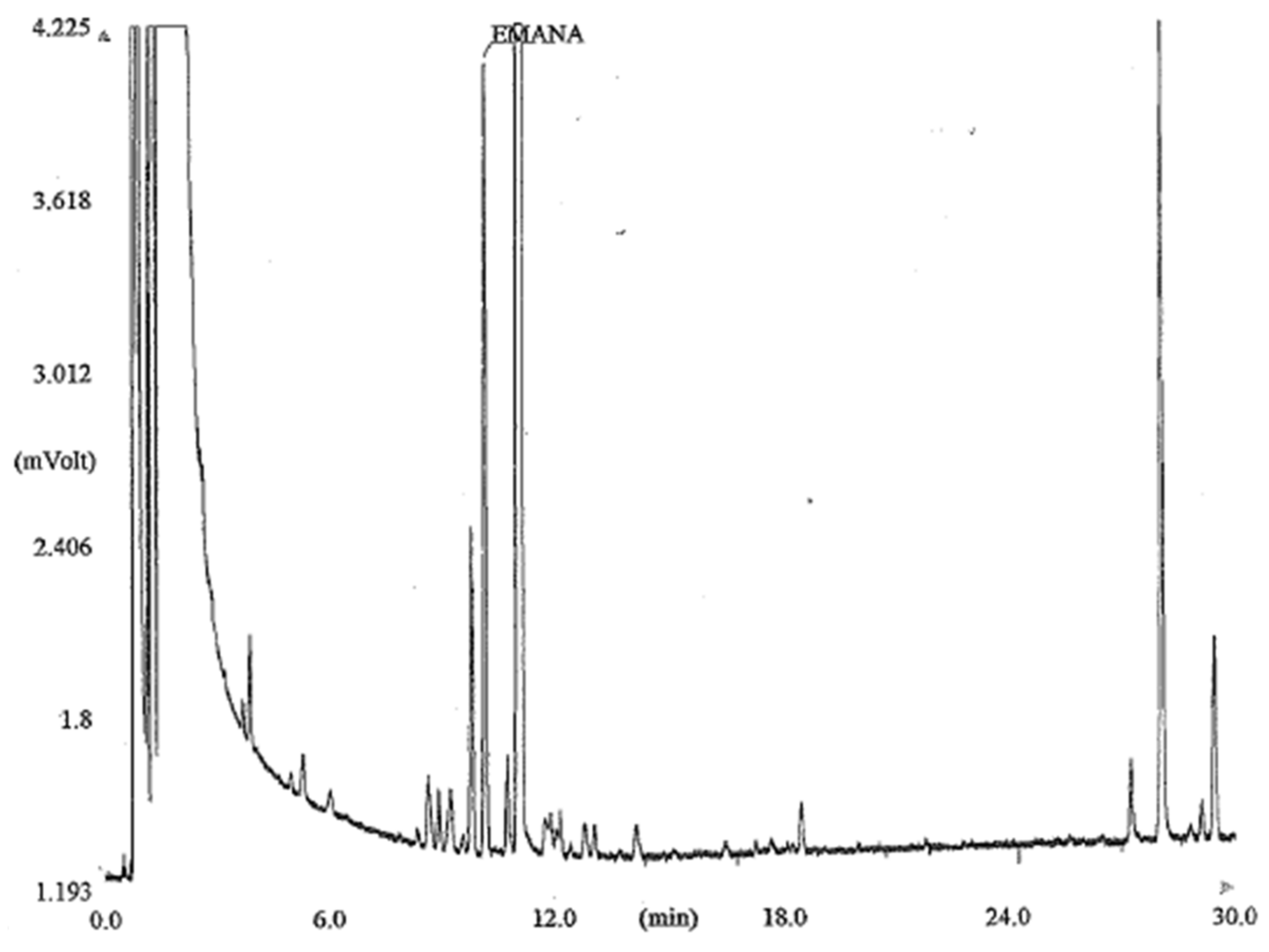
| GC-SIM | GC-EI-MS/MS | GC-PCI-MS/MS | GC-FID | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linearity of response * | Concentration range * | 10–300 μg g−1 | 1–10 μg g−1 | 0.05–180 μg g−1 | 1–110 μg g−1 |
| Correlation coefficient | 0.9979 | 0.9999 | 0.9998 | 0.9997 | |
| Slope | 7.6943 × 105 | 1356.4 | 1.8895 × 105 | 6653.9 | |
| Intercept | −2.2331 × 104 | −5455.36 | 1.4769 × 104 | −2971.52 | |
| Sensitivity | Limit of Quantification (LOQ) ** | 90 μg g−1 | 1 μg g−1 *** | 0.33 μg g−1 *** | 1 μg g−1 *** |
| System Precision * | RSD of Peak Area | 8 @ 0.1 μg mL−1 (n = 5) | 2.9 @0.1 μg mL−1 (n = 3) | [email protected] μg mL−1 (n = 3) | 0.21@10 μg mL−1 (n = 5) |
| Horwitz RSDr | 10.7@ 0.1 μg mL−1 (HorRat 0.75) | 10.7 @0.1 μg mL−1 (HorRat 0.27) | 10.7@ μg mL−1 (HorRat 1.29) | 7.48 @10 μg mL−1 (HorRat 0.03) | |
| Method precision | RSD | 4.89 @0.3 μg g−1 (n = 5) | 27.6 @10 μg/g (n = 5) | [email protected] μg g−1 (n = 10) | 8@20 μg g−1 (n = 3) |
| Horwitz RSDr | [email protected] μg g−1 (HorRat 0.54) | 30.321@10 μg/g (HorRat 0.91) | [email protected] μg g−1 (HorRat 0.05) | 0.14@20 μg g−1 (HorRat 0.91) | |
| Accuracy | Low concentration | @90 μg g−1 (n = 3) recovery:91.75% | @1 μg g−1 (n = 3) recovery:121.2% | @0.33 μg g−1 (n = 10) recovery:110.67% | @20μg g−1 (n = 3) recovery:101.49% |
| RSD 2.88 Horwitz 1.88 | RSD 44.56 Horwitz 30.32 | RSD 0.68 Horwitz 12.66 | RSD 0.14 Horwitz 6.83 | ||
| High concentration | @300 μg g−1 (n = 3) recovery:103.01% | @10 μg g−1 (n = 3) recovery: 95.21% | @180 μg g−1 (n = 3) recovery:97.44 | @40 μg g−1 (n = 3) recovery:100.54% | |
| RSD 2.35 Horwitz 1.60 | RSD 17.21 Horwitz 21.44 | RSD 1.74 Horwitz 4.906 | RSD 1.13 Horwitz 6.15 | ||
| GC-SIM | GC-MS/MS (EI) | GC-MS/MS (PCI) | GC-FID | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Column | VF-5 MS 30 m × 0.25 mm, 0.25 μm film thickness | DB1 30 m × 0.53 mm, 1.5 μm film thick | |||||||
| Injection Port | 250 °C split 100 | 250 °C, split 30 | |||||||
| Oven Program | Temp (°C) | Rate (°C/min) | Hold (min) | Temp (°C) | Rate (°C/min) | Hold (min) | Temp (°C) | Rate (°C/min) | Hold (min) |
| 80 | 0.00 | 50 | 0.50 | 60 | 5 | ||||
| 220 | 12 | 0.00 | 135 | 10 | 0.00 | 180 | 5 | 10 | |
| 290 | 25 | 30.00 | 290 | 70 | 30.00 | 270 | 70 | 20 | |
| Detector Temperatures | Transfer Line/Source: 280 °C/200 °C | Detector (FID): 250 °C | |||||||
| Mass filtering parameters | * m/z: 55, 82, 128 | ** m/z: 111 > 83, 128 > 111 | *** m/z: 129 > 55, 129 > 70, 129 > 84, 129 > 99 | ||||||
| Q2 pressure (Argon) | 1.5 mTorr | ||||||||
| Source pressures | 47 mTorr | 5 Torr CH4 (ion source) | |||||||
| Electron multiplier (V) | 1300 | ||||||||
| Sample Code | Concentration of ΕΜAΝA in the PPP (μg g−1) | ΕΜAΝA in the Technical Active Substance (μg g−1) | Sample Code | Concentration of ΕΜAΝA in the PPP (μg g−1) | ΕΜAΝA in the Technical Active Substance (μg g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | <LOQ | <LOQ | S14 | <LOQ | <LOQ |
| S2 | <LOQ | <LOQ | S15 | <LOQ | <LOQ |
| S3 | <LOQ | <LOQ | S16 | <LOQ | <LOQ |
| S4 | 68.4 | 203.1 | S17 | <LOQ | <LOQ |
| S5 | <LOQ | <LOQ | S18 | <LOQ | <LOQ |
| S6 | <LOQ | <LOQ | S19 | <LOQ | <LOQ |
| S7 | <LOQ | <LOQ | S20 | <LOQ | <LOQ |
| S8 | 72.8 | 216.3 | S21 | <LOQ | <LOQ |
| S9 | <LOQ | <LOQ | S22 | <LOQ | <LOQ |
| S10 | 72.1 | 214.2 | S23 | 137.2 | 406.9 |
| S11 | <LOQ | <LOQ | S24 | 136.1 | 403.9 |
| S12 | <LOQ | <LOQ | S25 | <LOQ | <LOQ |
| S13 | <LOQ | <LOQ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Balayiannis, G.P.; Karasali, H. N-Nitrosamine Impurities in Ethalfluralin: Determination of an Overlooked Deleterious Source in Pesticides. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13051104
Balayiannis GP, Karasali H. N-Nitrosamine Impurities in Ethalfluralin: Determination of an Overlooked Deleterious Source in Pesticides. Agriculture. 2023; 13(5):1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13051104
Chicago/Turabian StyleBalayiannis, George P., and Helen Karasali. 2023. "N-Nitrosamine Impurities in Ethalfluralin: Determination of an Overlooked Deleterious Source in Pesticides" Agriculture 13, no. 5: 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13051104
APA StyleBalayiannis, G. P., & Karasali, H. (2023). N-Nitrosamine Impurities in Ethalfluralin: Determination of an Overlooked Deleterious Source in Pesticides. Agriculture, 13(5), 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13051104







