Abstract
In this study we explored the methods and effects of spectral resistance reduction for soil-engaging surface of self-excited resonant bulldozing plates with a plane base on the basis of resonance effects. In the acquisition of the low-order vibration frequency f0 of the bin soil, centering around frequency point f0, eight spatial geometric wave frequency points ni of soil-engaging surfaces and three amplitudes were selected; by superimposing with soil-engaging surfaces of plane-based bulldozing plates, 24 spectral structures of the soil-engaging surface of bulldozing plates and model samples were combinatorically designed. Resistance reduction characteristics of each model sample were tested using an indoor soil bin test. Near the resonance point f0, the structures of the self-excited vibrating frequency spectrum of the soil-engaging surface obtain a preferable inhibitory effect on working resistance. At a 4 mm amplitude resonance point, model samples achieved the best resistance reduction effect, with a maximum relative resistance reduction rate of 22.67%, and the soil desorption effect of the relevant model sample was also good. On the other hand, away from the resonance point, whether the frequency increased or decreased, the corresponding working resistance of the model sample surfaces increased relatively. This is in good agreement with the law that the resonance point amplitude of the theoretical resonance curve is higher and the amplitude on both sides is lower. This paper provides a reference for the parameter design and related product development for various forced or self-excited vibration soil cutting tools.
1. Introduction
Applications of vibration technology in soil cutting tools are effective means to reduce soil cutting resistance [1]. Operations on soil cutting include not only the various forms of soil tillage in agricultural fields, but also soil excavation, shoveling and other operation methods in construction projects, and even soil exploration and development in the fields of oceans and outer space [2,3,4]. The reduction of working resistance and energy consumption in the soil cutting process is of great significance. In all the researches and applications of resistance reduction designs of various soil cutting tools, various methods have been tried and applied, such as geometric structure modification of soil cutting tools [5,6], material modification [7,8], soil-engaging interface lubrication [9], bionic design [10,11], vibration technology [12,13] and others. Among them, vibration technology has achieved better effects on resistance reduction and soil loosening on specific soil cutting conditions. To further explore the principles and method of soil vibration cutting resistance reduction, and to improve the efficiency and application scope of resistance reduction in soil vibration cutting, this study aimed to materialize the methods of soil vibrating cutting and the law of resistance reduction by employing a self-excited vibration form generated by a soil-engaging surface spectrum, in combination with the resonance effect.
In the theories and technical applications of resistance reduction design of vibrating soil cutting tools, there are mainly two forms: forced vibration [14,15] and self-excited vibration [16,17]. Forced vibration is mainly implemented by adding extra excitation devices such as eccentric shafts, eccentric blocks, cams, crank rods or hydraulic mechanisms to soil cutting tools [18,19,20], which can achieve considerable resistance reduction effects under specific frequencies, amplitudes, soil conditions and working modes [21,22,23]. This approach, due to the addition of additional excitation devices, makes its structure more complex, at a relatively high cost. When soil conditions and working modes change, the system power consumption may increase if the vibration parameters of the tool are not adjusted [24,25]. Self-excited vibration has no extra excitation mechanisms, and the occurrence of vibration is mainly achieved by a periodic balance between energy supply and dissipation of the system. By employing the principle of self-excited vibration, the effect of resistance reduction [26] and soil loosening [27] during soil tillage can also be achieved. Additionally, there are two mature methods of self-excited vibration: using a spring tooth with a cutting tools hinge, and using additional springs, both of which present the problems of relatively fixed vibration parameters and weak adaptability to complex soil conditions and tool operation modes [28]. Zhou Hua et al. [29] and Cui Tao et al. [30] explored ways by which to improve the adaptive capacity of vibration resistance reduction to soil conditions and operation modes by setting multi-stage springs. Whatever forms of vibration is to be adopted, how to achieve the optimal matching effect among tool operation modes, tool vibration parameters and soil parameters, so as to improve the vibration resistance reduction effect and the adaptive capacity to complex working conditions, is an urgent problem to be solved in the designs and applications of various vibratory soil cutting tools.
Unlike the abovementioned two self-excited vibration forms, which either make use of self-resilience or add extra springs, this study was designed to materialize the idea of resistance reduction via self-excited resonance by combining tool geometry modification and vibration technology. Specifically, soil self-excited vibration tillage conditions are constructed by superimposing spatial geometric waves with particular frequency on the base of a soil-engaging surface [31]. This method not only enhances the cutting process and improves cutting efficiency, but also has certain adaptability to complex soil conditions. Taking a plane bulldozing plate soil-engaging surface as the base, the simplest soil-engaging surface spectrum structure is constructed by superimposing geometric waves of a single frequency ni on it. The product of this frequency ni and the tool working speed u forms the self-excited oscillation frequency ft of the tool to the soil in front of the soil-engaging surface, and the resonance conditions of the cultivated soil are created by making this oscillation frequency ft close to the soil vibration frequency f0. Because of the granular characteristics of soil materials, it will be easily broken in a resonance state, so it is conducive to obtain lower cutting resistance. On the basis of obtaining the low-order vibration frequency f0 of indoor bin soil, centering around frequency point f0, 24 spectrum structures and model samples of the soil-engaging surface were combinatorically designed and manufactured, mainly by combining 8 spatial geometric wave frequencies with 3 amplitudes. Through comprehensive soil bin tests and comparisons with the plane bulldozing plate, this study explored the resistance reduction characteristics and cases of soil adhesion of each model sample under different frequencies and amplitude. The feasibility of the resistance reduction methods of the self-excited vibrating bulldozing plate soil-engaging surface spectrum based on the resonance effect was further verified, which provides a reference for the efficient resistance reduction design and development of various types of vibratory soil cutting systems or components.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil-Engaging Components-Soil Vibration Cutting Model
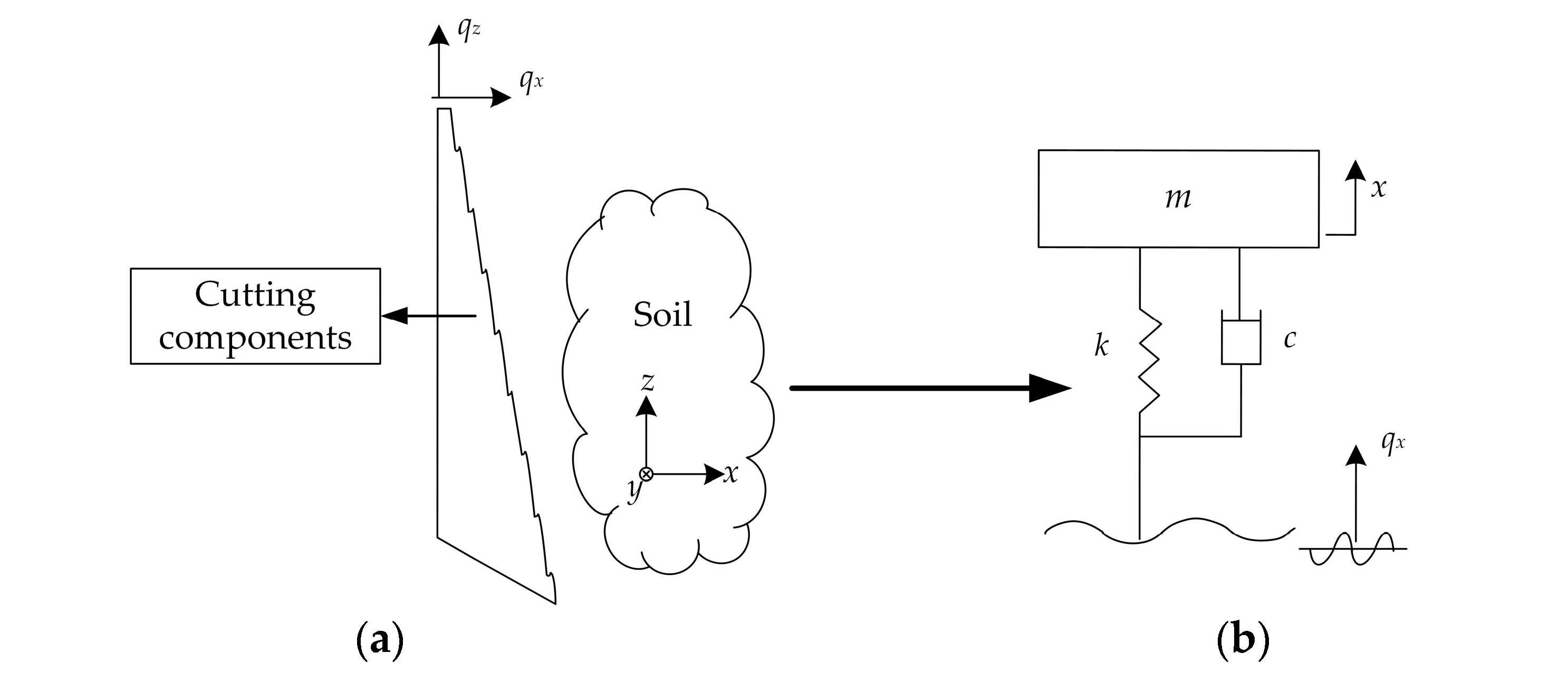
The impact cutting effect of soil-engaging components on soil can also be understood reversely as the process where the tool is fixed, and the soil slides over the soil-engaging surface at a certain speed u (m/s). In the cutting component–soil two-dimensional cutting model shown in Figure 1a, taking the cutting marching direction, i.e., the horizontal +x direction, as an example, the simplest single-degree-of-freedom soil vibration cutting model can be approximately established, as shown in Figure 1b. In it, the soil mass is m (kg), the stiffness is k (N/m), the damping coefficient is c (N∙s/m), qx represents the horizontal excitation displacement of the cutting component and x represents the horizontal displacement of the soil. The differential equation of the system motion in Figure 1b is:
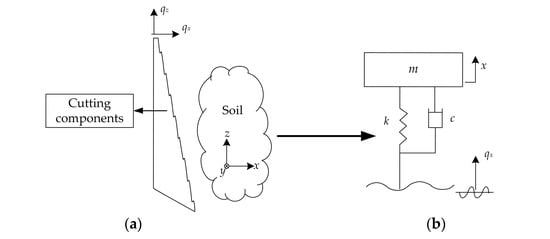
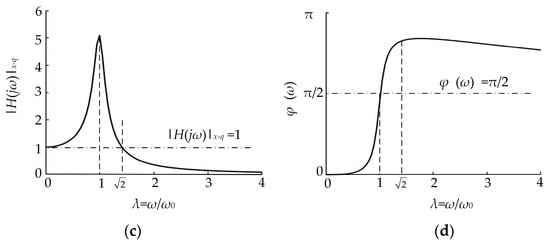
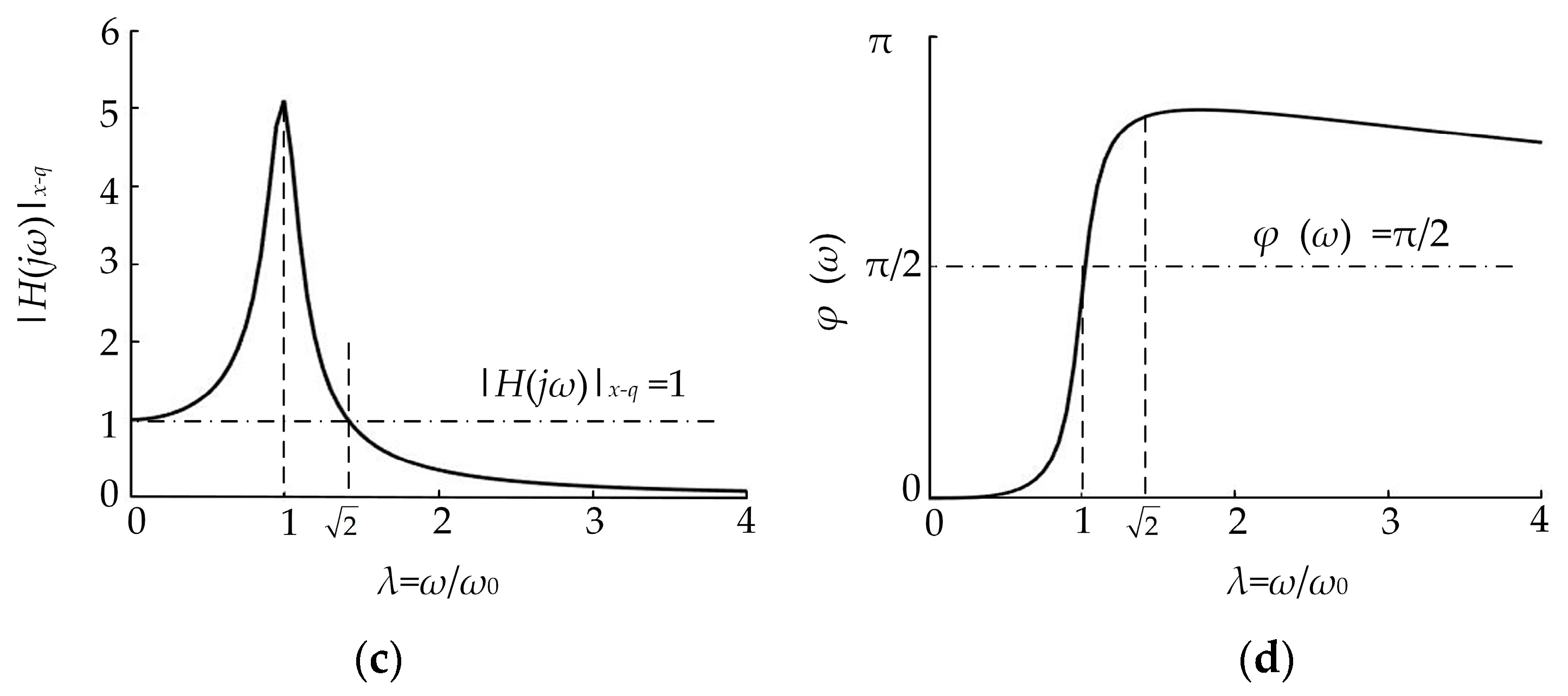
Figure 1.
Single-degree-of-freedom soil vibration cutting theoretical model. (a) A schematic diagram of soil vibration cutting; (b) the simplified vibration model; (c) the amplitude-frequency characteristics; (d) the phase-frequency characteristics.
It is easy to know that the amplitude–frequency characteristic equation of the system is:
The phase–frequency characteristic equation is:
where ξ is the system damping ratio, λ = ω/ω0 is the system frequency ratio, ω is the excitation frequency of the tool to the soil (rad/s) and ω0 = 2πf0 is the natural circular frequency of soil (rad/s).
Taking the damping ratio ζ = 0.1 as an example, the amplitude–frequency and phase–frequency characteristic curves of this system are shown in Figure 1c,d, respectively. When the impact frequency of the soil-engaging component is equal to the natural vibration frequency of soil, that is, the system frequency ratio λ in Figure 1c,d is close to 1, the system amplitude–frequency characteristic curve obtains the maximum point, namely, the system resonance point. In addition, the interval of 0.75 < λ < 1.25 is often taken as the resonance region in engineering [32]. In the resonance region, especially the resonance point, the impact frequency is relatively close to the natural vibration frequency of the soil, and according to the amplitude–frequency characteristic curve, the impact action of tool on the soil shows the phenomenon of resonance amplification. At this time, the soil in front of the soil-engaging surface is easily broken due to the resonance phenomenon, and accordingly a lower soil cutting resistance may be obtained.
In Figure 1c, when , the abscissas λ of the intersection point of the corresponding amplitude–frequency characteristic curve are 0 and , respectively, and the values of the ordinate and abscissa of these two points do not vary with the damping ratio. When , the figure corresponds to , that is, the tool oscillation or excitation frequency is in the interval , the vibration displacement signal input by the tool to the soil is in an amplified state, and the soil being cut is vulnerable to stronger disturbance. When the oscillation frequency of the designed tool is in this interval, a better vibration resistance reduction effect will be achieved. Accordingly, the better vibration resistance reduction effect will be obtained near the resonance point or in the resonance region. Here, this interval is called the theoretical expected resistance reduction region. When , the frequency ratio of the corresponding abscissa is . At this time, the tool oscillation frequency or excitation frequency is greater than , and the vibration signal amplitude of the tool input to the soil is theoretically attenuated. When the oscillation frequency of the tool is located in this interval, it is relatively difficult to obtain a better vibration resistance reduction effect. Here, this interval is called the theoretical expected poor resistance reduction region. These abovementioned principle predictions are the starting point of this study in this paper.
2.2. Soil Natural Vibration Frequency
To verify the abovementioned ideas, the accurate measurement of natural vibration fundamental frequency f0 of soil is the first and foremost problem to be solved. The soil constituents, density, moisture content, firmness and other soil physical parameters in production actually show great indeterminacy, which makes the natural vibration frequency of the actual soil more complex, and the distribution range is relatively wide [33]. To obtain the relatively stable natural vibration fundamental frequency of soil, relevant studies were conducted in relatively controllable soil conditions of an indoor soil bin. The soil in the soil bin was cinnamon soil with yellow sandy characteristics, available in wheat fields in Luoyang, China [34]. Before the test, all impurities, such as broken stones and grass roots in the soil, were removed first, and then the soil was completely broken loose, stirred, scraped and compacted. The length × width × height dimensions of the effective soil after preparation were 1.5 m × 0.8 m × 0.35 m, respectively, which was shortened only by 4.5 m in length, compared with the actual soil bin size of this bulldozing test. The mean value of the soil firmness test was 1.006 MPa, the standard deviation being 0.198. The mean value of the moisture content test was 12.45%, the standard deviation being 0.398. Poisson’s ratio, shear modulus and other parameters of soil were also measured during the test, and the measurement results are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
The parameters of soil physical characteristic.
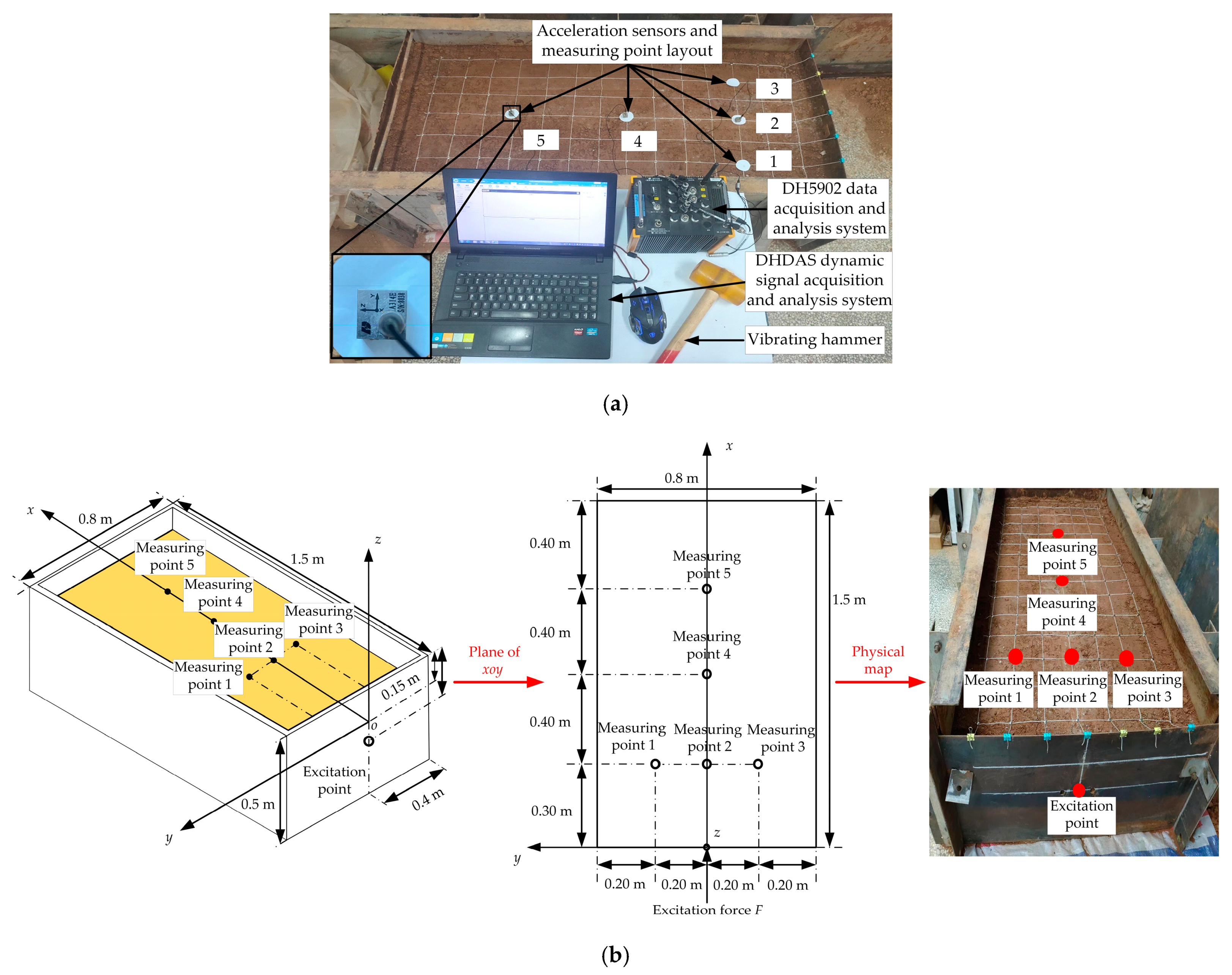
The method of hammering pulse-excitation was employed to complete the test of natural vibration parameters of the bin soil shown in Figure 2. For clarification, by taking into consideration cutting conditions of the shovel blade in the soil bin, a three-dimensional coordinate system was established for the soil of the soil bin according to Ampere’s rule. The upper surface of the soil mass shown in Figure 2a was the xoy plane surface, and the intersection point of the longitudinal centerline of the upper surface of the soil bin soil mass and the right-hand surface of the steel plate was the origin of the coordinates. The cutting march direction of the shovel blade was the +x direction (Figure 2a, the soil bin pointing to the left), perpendicular to the soil mass surface upwards was the +z direction, and the left side was the +y direction. The excitation position of the rubber hammer was located on the intersection line between the longitudinal section of the soil bin and the right end face in Figure 2a. The excitation point was 0.1 m away from the upper surface of the soil, the excitation direction was the +x direction, and the specific coordinate position was (0, 0, −0.1) m; see Figure 2b. To select the location and direction of the excitation point was to comprehensively consider the working depth and marching direction of the model shovel blade during the soil bin test. Distribution of measuring points for all tests was composed of grid intersections of 100 mm × 100 mm shown in Figure 2a, 98 in all. It was found through testing that the response amplitude of each measuring point close to the right end of the soil bin in Figure 2a was relatively strong, while those that marched along the longitudinal centerline, i.e., in the cutting direction, decreased successively. Due to space limitations, five representative measuring points were selected for elaboration; see Figure 2. The sensor positions of each measuring point Nos. 1~5 in the two figures correspond correspondingly, and the specific coordinates in the xoy plane were (0.3, 0.2), (0.3, 0), (0.3, −0.2), (0.7, 0) and (1.1, 0), respectively, with unit being m. The receiving directions of the vibration signal by all the acceleration sensors were all in the +x direction. Shovel blade size, working direction and signal response strength were all taken into consideration in the layout position of the sensors [35]. In terms of shovel blade size, shovel blade width (300 mm) was mainly taken into consideration, to ensure that the area of the impact oscillation force on the excited soil can be covered by sensors. In terms of working direction, the existence and clarity of vibration parameters were mainly considered, which were determined according to the law that the soil vibration parameters’ amplitudes attenuate as the excitation point extends. In an actual tillage or bulldozing test, the topsoil gets the maximum disturbance and displacement; therefore, only the vibration signals of the topsoil were tested in this study.
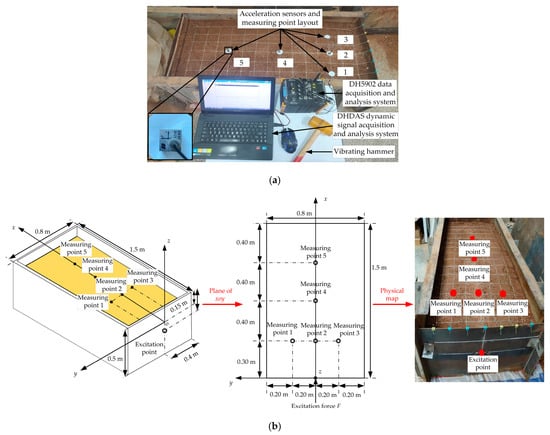
Figure 2.
Soil natural frequency testing system. (a) Site diagram of soil natural frequency test; (b) position schematic diagram of measuring points and excitation point.
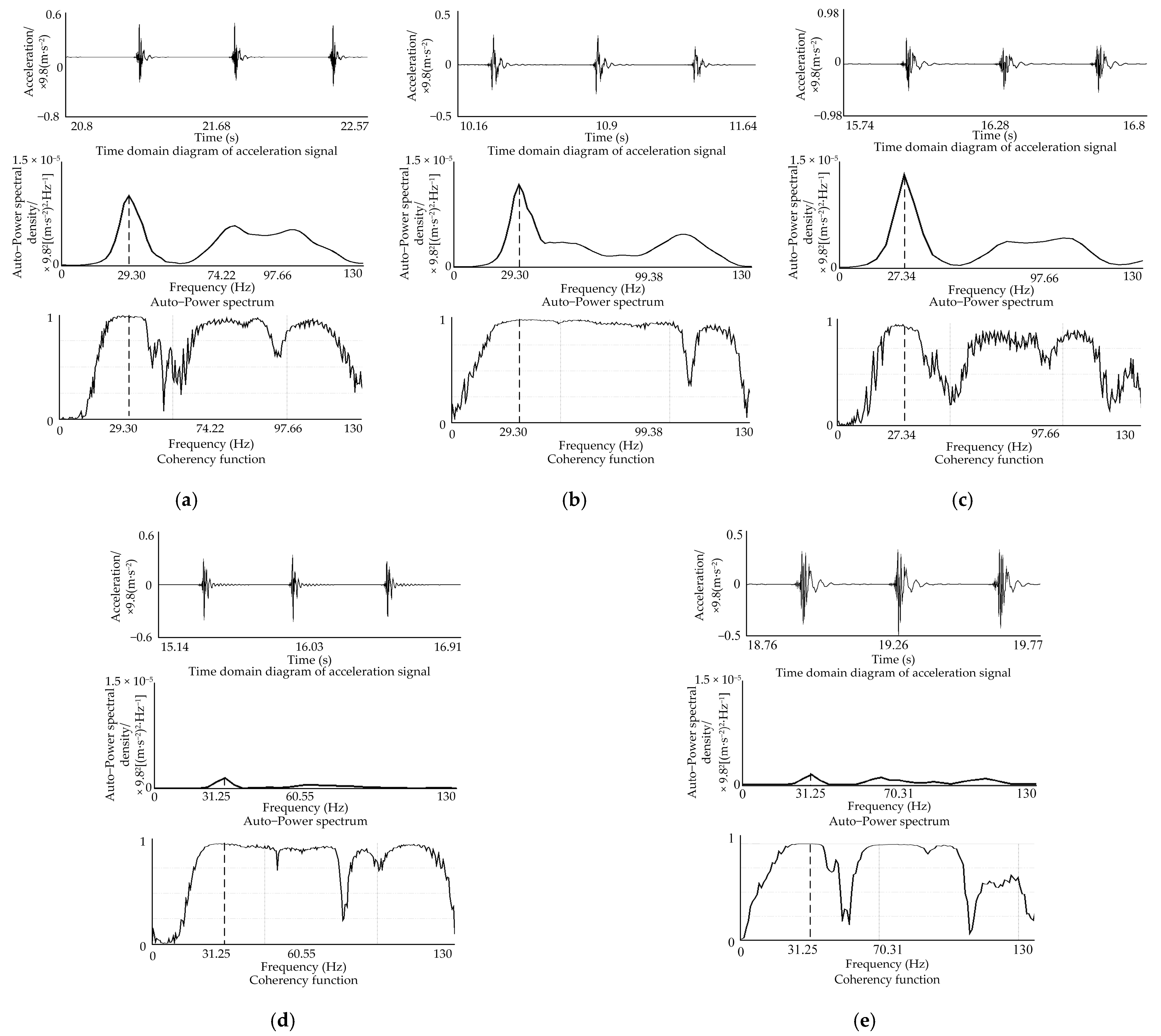
The test of soil vibration signals of each measuring point was replicated more than three times, and the test results were relatively close. Additionally, the representative time history profiles, auto-power spectrum, and coherence function curves of the acceleration signals of the five measuring points are shown in Figure 3. The first-order natural vibration frequencies of the five measuring points in the x-direction were 29.30, 29.30, 27.34, 31.25 and 31.25 Hz, with a mean value 29.69 Hz and a standard deviation 1.46. Among them, measuring points 1, 2 and 3 were close to the excitation position; as a result, their amplitude response signals were also strong. The corresponding coherence function values of the first-order vibration frequency positions of soil at these three measuring points were 0.981, 0.983 and 0.964, respectively, and the vibration characteristics were obvious. Measuring points 4 and 5 were farther and farther away from the excitation point, and despite a higher value of coherence function near the 29.69 Hz vibration frequency, the measured signal amplitudes were weaker and weaker, which was consistent with the signal transmission and attenuation of actual soil vibration. The second-order vibration frequency of each measuring point was located near 70~110 Hz, the vibration amplitude was relatively weak, the coherence function value was also relatively small, and the peak point was not clear enough; it was especially not readily excited by a relatively low soil cutting speed and oscillation frequency. Therefore, a further study will be conducted only on the first-order vibration frequency.
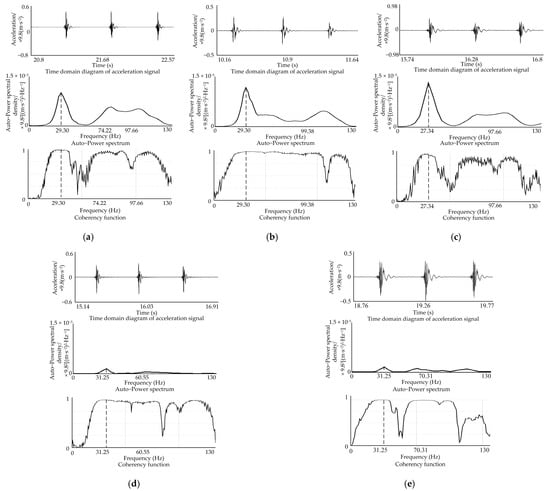
Figure 3.
Time history, auto-power spectrum and coherence function curve of acceleration signals of five measuring points. (a) Measuring point 1; (b) measuring point 2; (c) measuring point 3; (d) measuring point 4; (e) measuring point 5.
2.3. Model Bulldozing Plate for Test
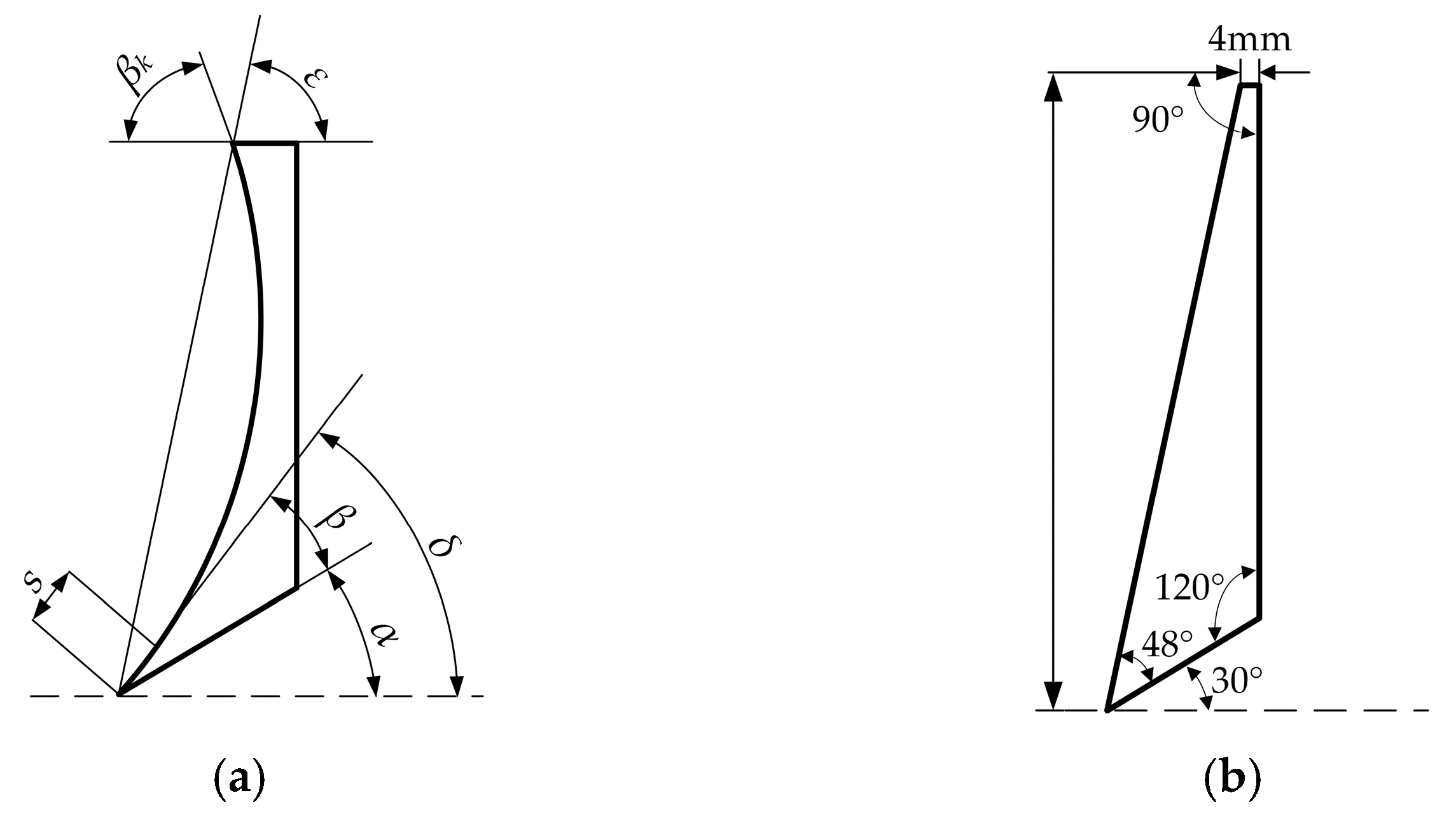
Referring to Figure 4a, the structural parameters of the typical bulldozing plate mainly include the directrix of the soil-engaging surface of the bulldozing plate, the cutting angle δ, the clearance angle α, the shovel point closed angle β, the front roll angle βk, the skew angle ε and the shovel lip length S [36]. The soil-engaging surface of the bulldozing plate is generally formed by the parallel translation of the generatrix along the directrix. The generatrix is usually a straight line, which forms as a result of the directrix exerting an essential influence on the working characteristics of the bulldozing plate [37]. In this study, the related principle research was conducted by taking the plane bulldozing plate as the base, and the spatial frequency spectrum geometric structure of the self-excited vibrating soil-engaging surface was formed by superimposing a spatial geometric wave on the basis of the plane base directrix.
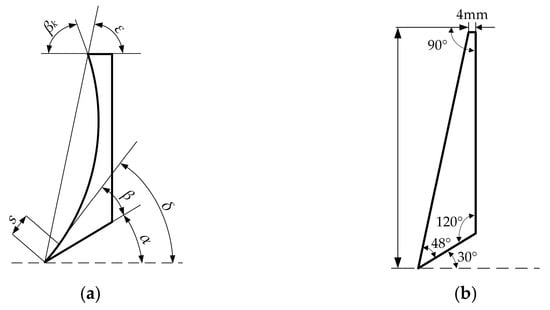
Figure 4.
Schematic diagram of structural parameters of bulldozing plate, longitudinal section. (a) The curved bulldozing plate; (b) the plane bulldozing plate.
The general equation expression of the directrix of the designed self-excited vibration soil-engaging surface spectrum this time is:
Therefore, the system vibration equation is:
where C1k’x is the thrust generated by the base surface-ruled surface, and is the vibration excitation force generated by the soil-engaging surface spectrum. Since ωi = 2πfi = 2πuni = 2πnix/t, Equation (5) can be written as:
where k’ is the slope of the base plane, Ai is the amplitude of spatial geometric wave (mm), ωi is the excitation frequency of the spatial spectrum to soil (rad/s), φi is the phase of the spatial spectrum (°), ni is the geometric frequency of the spatial geometric wave (m−1), and C1 and C2i are the stiffness coefficients of soil-engaging surface (N/mm).
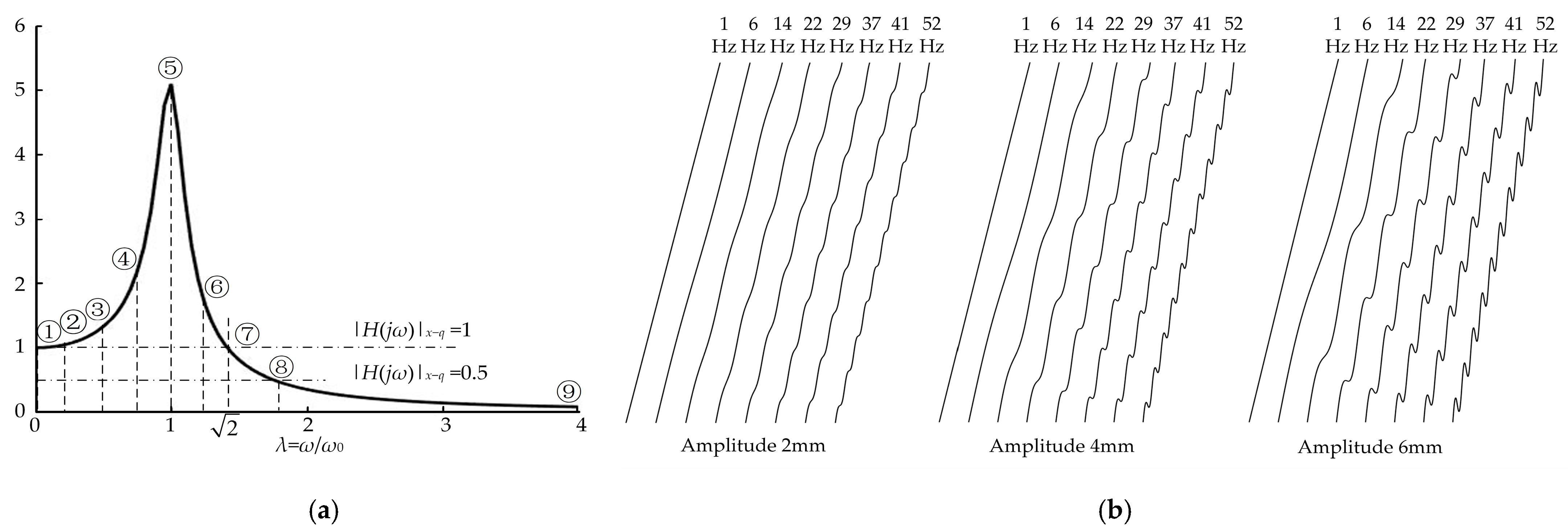
The skew angle of each model is 78°, and the corresponding straight line equation in Equation (4) is f1(x) = k’x = tan(78°)x = 4.7x. The sine equation in Equation (4) needs to determine three parameters, namely the excitation frequency ωi (namely geometric frequency ni), amplitude Ai and phase φi. Only the single-frequency spectrum was studied; therefore, i = 1 in above formula. With reference to the analysis results of the resonance point and resonance region in Figure 1c, based on the measured vibration frequency f0 of soil in the indoor soil bin, a series of geometric frequency points ni were selected around this resonance point as test points. Altogether, eight impact frequency ft test points were selected from the three regions, i.e., the theoretical expected resistance reduction region, the expected point of transition and the expected poor resistance reduction region. They were 1 Hz (near zero frequency), 0.205 f0, 0.47 f0, engineering experience method lower limit corresponding frequency 0.75 f0, the resonance point f0, the engineering experience method upper limit corresponding frequency 1.25 f0, corresponding upper limit frequency 1.414 f0 and corresponding frequency 1.758 f0. The locations and sizes of each frequency point are shown in Figure 5a and Table 2, respectively. Vibration fundamental frequency f0 of the soil in Table 2 was taken for an integer 29 Hz as a result of the convenience of the structural parameterization design of the bulldozing plate as well as the complexity of soil parameters in each test.
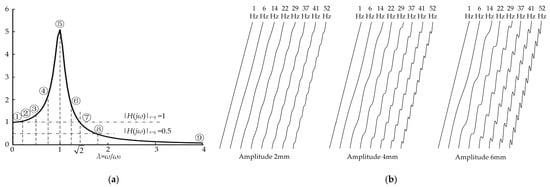
Figure 5.
Directrix design of self-excited vibration bulldozing plate soil-engaging surface spectrum. (a) Single-degree-of-freedom theoretical amplitude-frequency characteristic curve and test model frequency points; (b) directrix collection of 24 soil-engaging surface spectrum test models.

Table 2.
Directrix equation of model bulldozing plate soil-engaging surface spectrum.
The amplitude value of the spatial geometric wave superimposed on the soil-engaging surface was based on the selection principle of a relatively coordinated geometric structure, and was determined by the contour dimensions and scaling ratio of the selected model samples. By comparison of the three-dimensional simulation designs, three levels of 2, 4 and 6 mm were selected to complete the specific structure design of spatial geometric spectrum of the soil-engaging surface.
Changes of phase will affect the cutting angles of the corresponding shovel tip or cutting edge, and selections of the phase have an effect on both the penetrability and resistance reduction performance of the soil-engaging surface. To simplify the work, φi = 0 was selected for all phase angles to complete the design of the soil-engaging surface model sample.
After determining the values of the working speed u of the bulldozing plate (set as 0.16 m/s based on the speed of the traction motor of the soil bin), impact frequency ft of the tool on the soil (eight points selected in Figure 5a), amplitude Ai (2, 4, 6 mm), initial phase angle φi (0°) and cutting angle δ (78°) of the bulldozing plate, values of the spatial geometric frequency ni (reciprocal relationship with spatial geometric wave wavelength λi) or excitation frequency ωi could be calculated. Taking impact frequency 29 Hz and amplitude 4 mm as an example, when ni = ft/u = 29/0.16 = 181.25 m−1 = 0.18125 mm−1, 2πni = 1.138 mm−1, so the directrix equation of the soil-engaging surface spectrum is F(x) = 4.7x + 4 × sin(1.138 × x), x∈(0, 153.8 × cos(1.3607)). All the directrix equations of the soil-engaging surface spectrum of bulldozing plates are shown in Table 2, and the directrix collections of soil-engaging surface spectrum of the self-excited vibrating bulldozing plate are shown in Figure 5b.
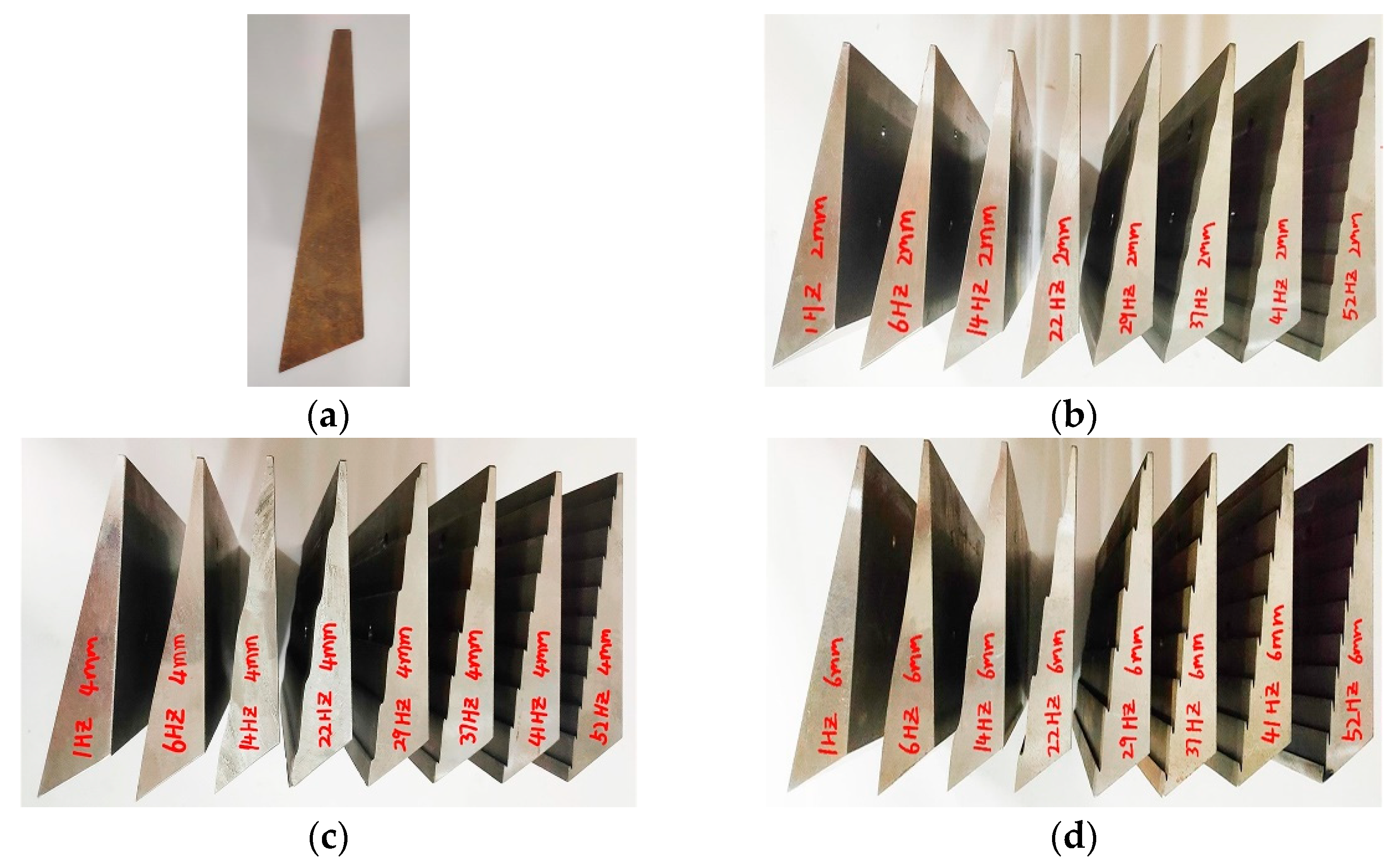
The test bulldozing plate model was designed as a fixed shovel blade. Referring to similarity theory [38], differences in resistance reduction effects caused by the directrix form, which function as the only variable, were investigated, while other geometric factors in the bulldozing plate model remained unchanged. Referring to empirical values [39], the angle parameters of the test model were: cutting angle δ 78°, clearance angle α 30°, shovel point closed angle β 48°, and skew angle ε 78°. The actual ratio of height to width of the bulldozing plate was approximately between 1:2~1:3 [40]. The height–width ratio of each model bulldozing plate had taken the upper limit and was designed as 150 mm × 300 mm. This was mainly in order to consider that the soil was likely to overflow the upper end of the size-reduced bulldozing plate during the test, which might affect the sensors arranged behind it, as well as the fact that the model bulldozing plate design process in the lower part of the straight cutting edge is canceled. Specific dimension parameters are shown in Figure 4b. The material of the bulldozing plate was Q235 steel, and the bulldozing plate after processing is shown in Figure 6.
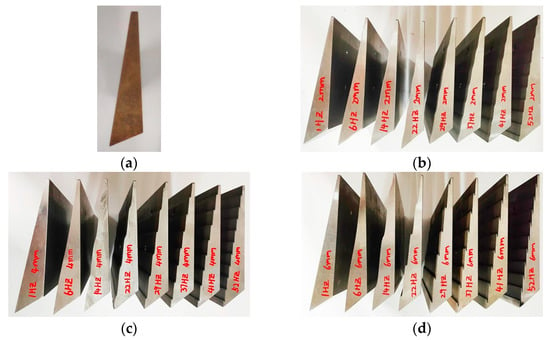
Figure 6.
25 experiment bulldozing plate samples. (a) Plane bulldozing plate; (b) self-excited vibration bulldozing plate of plane base with 2 mm amplitude; (c) self-excited vibration bulldozing plate of plane base with 4 mm amplitude; (d) self-excited vibration bulldozing plate of plane base with 6 mm amplitude.
2.4. Soil Bin Test
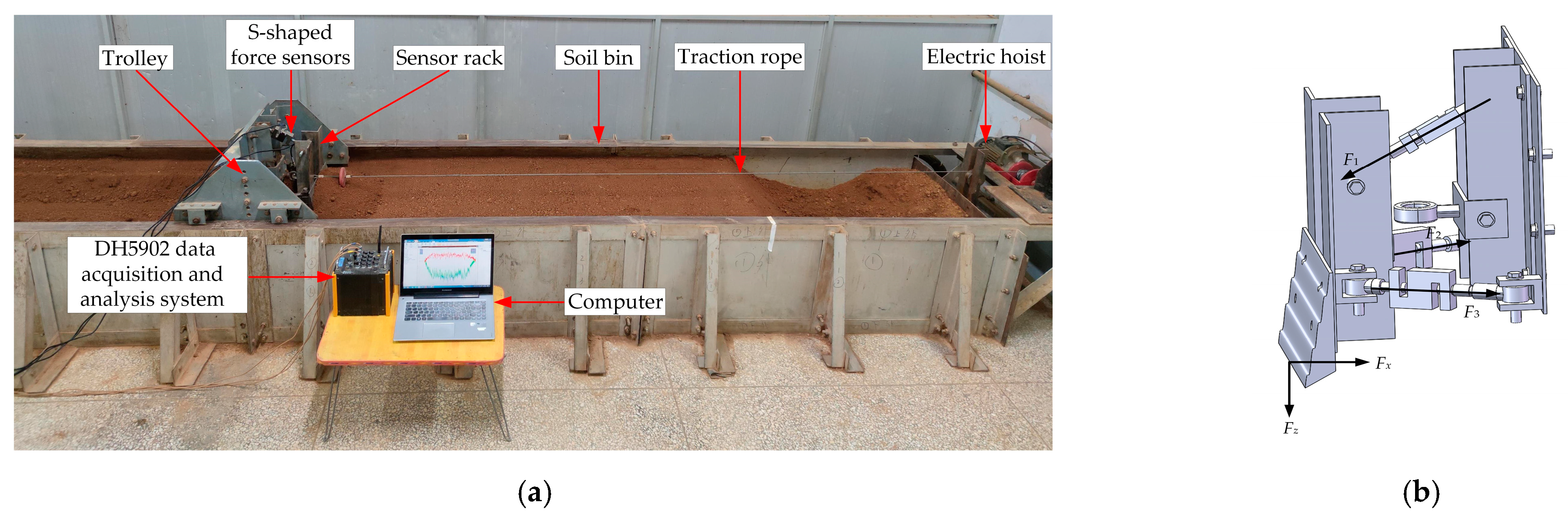
Basic parameters of the valid soil length, width and height of the test soil bin were 6 m × 1.2 m × 0.6 m, and deep turning and water sprinkling of the soil were performed before each experiment, by means of which the soil moisture content, firmness, vibration frequency and other parameters in each soil cutting test were kept consistent as far as possible, and also consistent with the soil parameters in the soil frequency test as shown in Table 1, and the comparability of the test data were thus enhanced. The tested sample bulldozing plate was driven by a trolley, and the trolley system was pulled by a PA600 electric hoist (Wanhua Lifting Machinery Co., Ltd., Renqiu, China, rated power 1.15 kW) through wire rope to achieve horizontal movement, at a pulling speed of 0.16 m/s. Generally, the operating speed of the bulldozers did not to exceed 0.7 m/s, and a slightly lower test speed was used. This was limited by the length of soil bin, or by the need to facilitate effective observation and control during the test process. The cutting depth was controlled to be 30 mm, about 20% of the height of the model bulldozing plate (actual designed tillage depth less than 40% of the height of the bulldozing plate).
The resistance signal, when converted into an electrical signal by the S-shaped force sensor, was transmitted to the DH5902 data acquisition instrument, by which the data were processed, and then recorded and analyzed by DHDAS. Figure 7a show live photography of the test work. The test bulldozing plate model was connected to the trolley by three S-shaped force sensors, both ends of which were ball-and-hinge structures, and a three-dimensional force system was thus formed, as shown in Figure 7b. The horizontal resistance Fx, vertical resistance Fz, and resultant force F under different working circumstances could be obtained by trigonometric-function calculations shown in Equations (7) and (8) of the three force signals. The horizontal resistance Fx, vertical resistance Fz and resultant force F under different working circumstances could be obtained by trigonometric-function calculations of the three force signals. This study focused on the impact on the working resistance of the spatial geometric frequency and amplitude of the soil-engaging surface directrix. The frequency factor was set as eight levels, and amplitude as three levels; see Table 3.
where Fx is the horizontal resistance (N), Fy is the vertical resistance (N), F1 is the force on sensor S1 (N), F2 is the force on sensor S2 (N), F3 is the force on sensor S3 (N), ϕ1 is the angle between F1 and the installation plate of the test trolley equipment (°), ϕ2 is the angle between F2 and the installation plate of the test trolley equipment (°) and ϕ3 is the angle between F3 and the installation plate of the test trolley equipment (°); in this paper, ϕ1, ϕ2 and ϕ3 all take 60°.
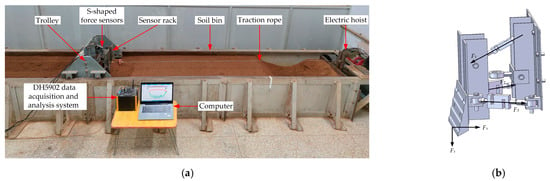
Figure 7.
Testing system of soil bin and soil working resistance. (a) Live photo of test work; (b) schematic diagram of the force measuring device.

Table 3.
Table of test factor levels.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Law of Resistance Reduction
Comprehensive tests were conducted for each factor and level in Table 3, each working condition repeated three times. Table 4 shows the test results of the working resistance under various working conditions, all of which are the mean value of the three repeated tests. The horizontal working resistance of the tested model bulldozing plate amounted to over 99% of the total working resistance, both of which were exactly similar in variation tendency, only slightly differing in values. Variations of the horizontal resistance Fx basically represent laws of resistance reduction of the bulldozing plate.

Table 4.
Results of working resistance test.
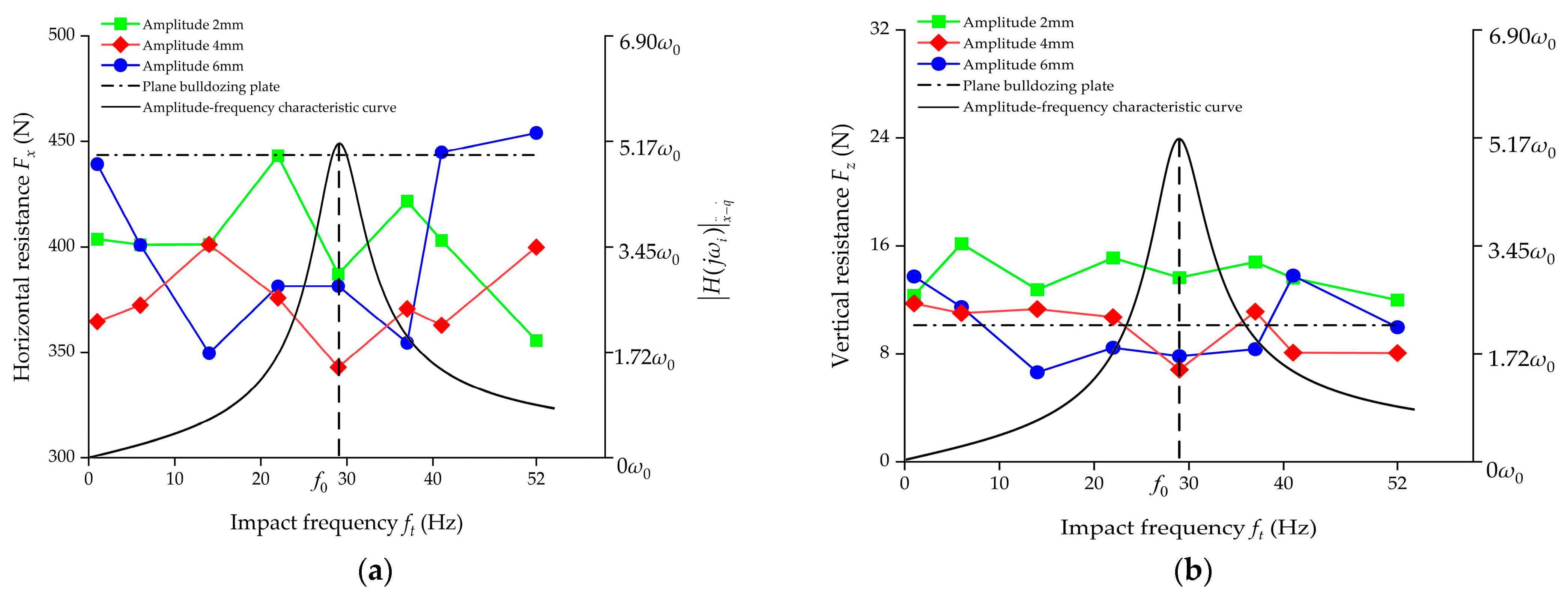
The test results in Table 4 were drawn into line charts of working resistance, as shown in Figure 8, in which theoretical resonance curves of acceleration–velocity amplitude–frequency characteristics are also provided for references. Since the law of acceleration–velocity amplitude–frequency characteristics approximates variations of the impacted oscillation force of the excited object, soil, the curves can approximately reflect the variations law of the vibration energy of the excited soil [41].
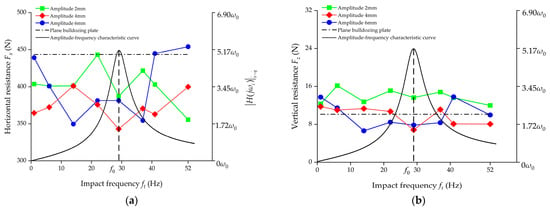
Figure 8.
Working resistance test results and theoretical amplitude–frequency characteristic curve. (a) Horizontal resistance; (b) vertical resistance.
As can be seen in Figure 8a, both frequency and amplitude had an impact on resistance reduction effects of the bulldozing plate sample. Additionally, most self-excited vibrating bulldozing plate models exerted considerable inhibiting effects on the horizontal working resistance in the expected resistance reduction region 0~41 Hz. At the resonance point of 29 Hz, the resistance values of the self-excited vibrating bulldozing plate models with geometric wave amplitudes of 2, 4 and 6 mm were 387.08, 342.89 and 381.37 N, respectively, decreased by 12.71%, 22.67% and 13.99% compared with those of the plane bulldozing plates. Additionally, at other frequency points for expected possible resistance reduction, including levels 2, 3, 4 and 6 in Table 3, that is, working points 2, 3, 4 and 6 in Figure 5a, the horizontal working resistance values of the bulldozing plate models with corresponding frequency values of 6, 14, 22 and 37 Hz were also lower than those of the plane bulldozing plates. The above test results are basically consistent with the theoretical expectations, namely, the conditions for resistance reduction due to amplifications of vibration intensity were met in wider frequency bands (0 < ft < 1.414 f0), and the closer to the resonance zone (22 Hz = 0.75 f0 < ft < 1.25 f0 = 37 Hz), the more obvious the resistance-reduction effect. However, working resistance values of the model bulldozing plates at expected transition points (1 Hz, 41 Hz) and the expected poor resistance reduction points (ft = 1.758 f0 = 52 Hz) all exceeded those at their respective corresponding resonance points. Horizontal working resistance values of the 52 Hz, 6 mm bulldozing plate even exceeded those of the plane bulldozing plate. These subtle differences in experimental results at the theoretical expected poor resistance reduction point might be caused by the slight differences in resistance reduction bandwidth in the resonance zone, due to the uneven soil composition and its natural frequency. In general, trends of the horizontal working resistance varying with frequency were basically consistent with the theoretical analysis, and also consistent with the research results of Zhang Pangang [32]. In other words, centered on the resonance point, the law of the variations with the resistance with the frequency presented obvious concave characteristics, whose trend was in good agreement with the theoretical resonance curve of the convex. Comparatively, the average resistance reduction rates of the bulldozing plate models with amplitudes of 2 and 6 mm were not much different, at 9.34% and 9.63%, respectively. There are two reasons for this phenomenon. First, due to the relatively small amplitude of 2 mm, the vibration energy transfer of the self-excited vibration bulldozing plate in the process of cutting soil is relatively weak, and the working resistance is relatively large. Second, due to the relatively large amplitude of 6 mm, the soil adhesion degree of the bulldozing plate is relatively severe, resulting in a relatively high working resistance. The 4 mm amplitude is between the two, which can ensure a certain degree of vibration energy transmission while also preventing excessive soil adhesion. Therefore, 4 mm amplitude bulldozing plate models obtained lower horizontal working resistance in relatively wider frequency bands around the resonance point. Among them, the bulldozing plate model with an amplitude of 4 mm and a frequency of 29 Hz obtained the minimum value of horizontal working resistance among all the test models.
As can be seen from Figure 8b, the vertical resistance of each self-excited vibrating bulldozing plate was slightly larger than that of the plane bulldozing plate (its absolute value being relatively small). The slight increase in vertical resistance is beneficial to increase the vertical upward disturbance and crushing effect of the soil in front of the soil-engaging surface, and to improve the frictional state between the soil and the soil-engaging surface. This slight increase in vertical resistance, in turn, resulted in a much lower horizontal and overall working resistance.
3.2. Law of Soil Adhesion
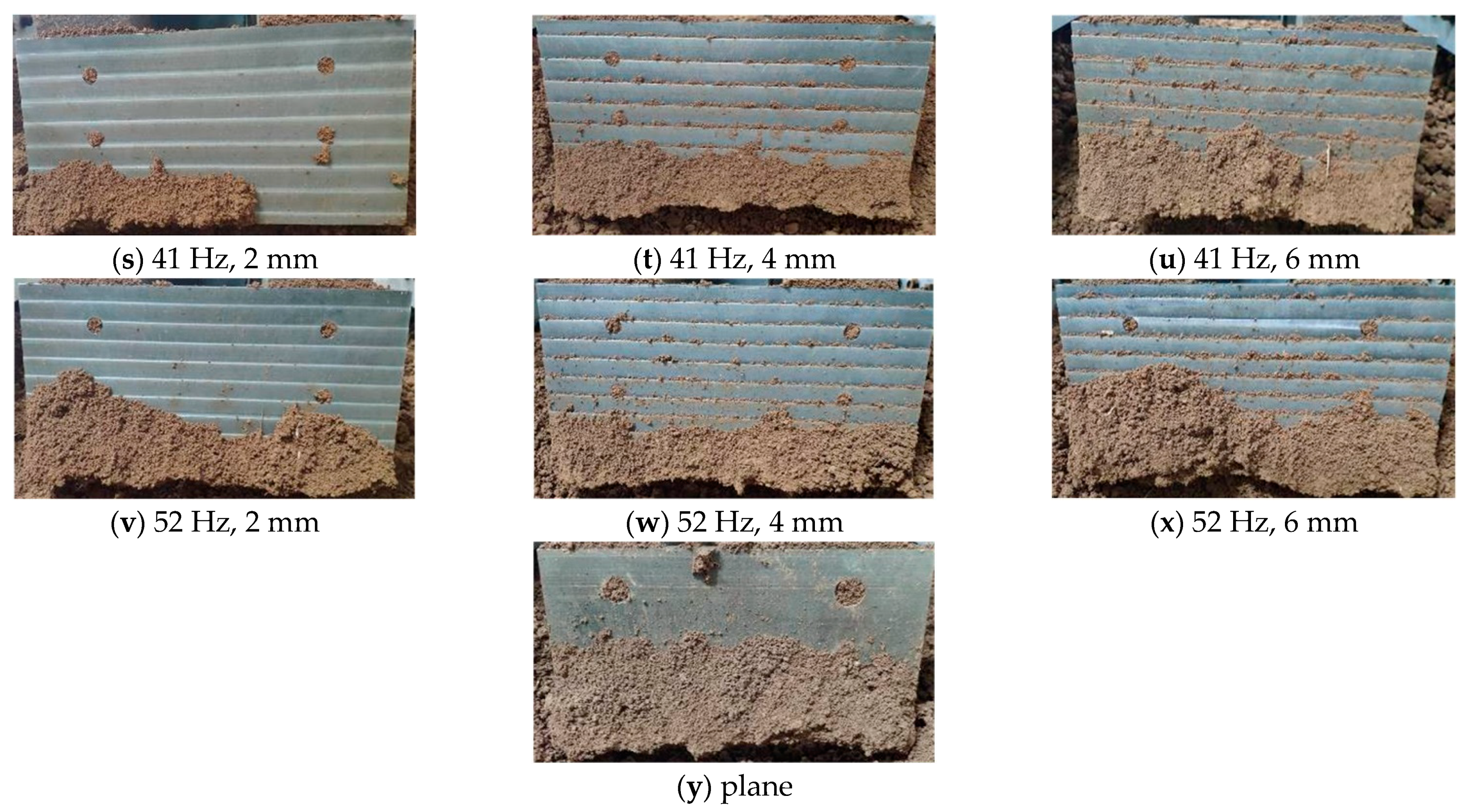
Figure 9 shows all of the soil adhesion on the soil-engaging surface of the tested bulldozing plate samples. The bulldozing plates shown in each column in Figure 9 are consistent with Nos. 1~8, 9~16, 25 and 17~24 in Table 4, respectively. The amount of soil adhesion on soil-engaging surfaces of the bulldozing plate model was relatively smaller at the resonance points corresponding to three different amplitudes in Figure 9m–o. By comparison of these photos of soil adhesion effects, it can be concluded that the bulldozing plate model in the resonance region obtained relatively good effects of soil desorption and loosening by means of a self-excited vibrated frequency spectrum structure of the soil-engaging surface. Additionally, as a result, these models obtained relatively lower working resistance. Referring to Figure 8, the working resistance of most measuring points deviating from the resonance region was relatively higher, and the soil adhesion degree shown in Figure 9 was also relatively severe. Plane bulldozing plates, or self-excited vibrating bulldozing plates whose expected resistance reduction is poor, in the process of cutting soil, were not conducive to the desorption of soil on the soil-engaging surface, and would produce relatively large working resistance. This is basically consistent with the theoretical expectation and results of the resistance test in terms of the variation trend.
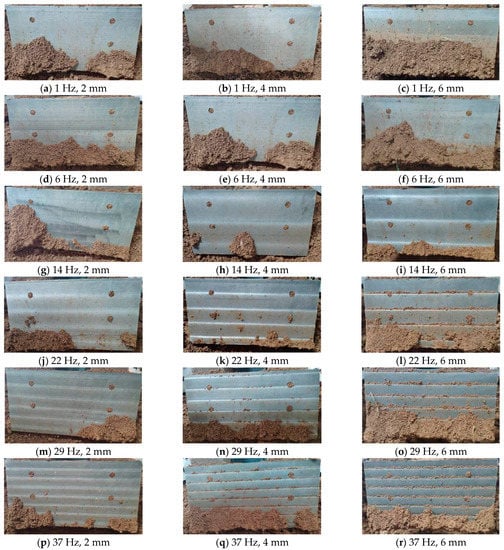


Figure 9.
Soil adhesion on the soil-engaging surface of bulldozing plate with different frequencies and amplitudes.
To sum up, by constructing spatial geometric waves of soil-engaging surfaces on the basis of self-excited vibration and the resonance effect, modifying geometrical configurations of soil-engaging surfaces reasonably, soil adhesion to the soil-engaging surface will be greatly reduced, lower working resistance will be obtained, and expected resistance reduction effects will be achieved, at a given working speed.
3.3. Adaptive Law of Resonance Resistance Reduction
Since there is a f0 = uni relationship among the working speed u of the bulldozing plate, the spatial geometric frequency ni and the natural frequency f0 of the soil, the third parameter can be determined, given any other two. Once the spatial geometry frequency ni of the soil-engaging surface is given, it is difficult to change, while variable ranges of the tool working speed u and the soil natural frequency f0 are relatively open to vary in practice.
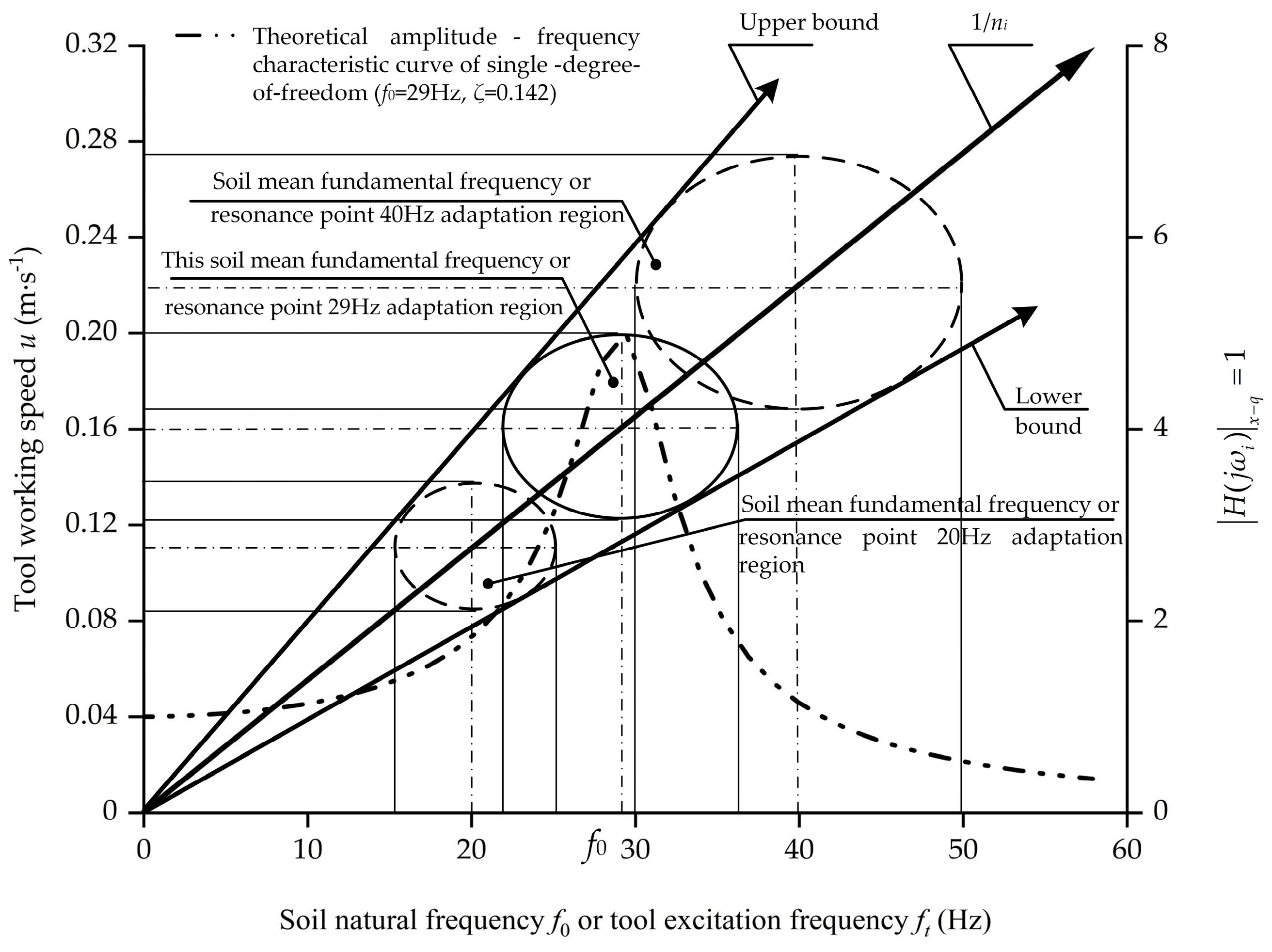
Figure 10 illustrates theoretical mutual adaptation ranges between the working speed of the bulldozing plate u and inherent frequency of the soil f0 or excitation frequency of the equipment ft, when the self-excited resonance resistance reduction phenomenon occurs for a single soil-engaging surface frequency spectrum structure. In the above study, at the resonance point ft = f0 = 29 Hz and when the test speed 0.16 m/s, the required spatial geometric frequency of the soil-engaging surface was ni = ft/u = 29/0.16 = 181.25 m−1. When the working speed remained unchanged (0.16 m/s in the figure), and when the effective resonance resistance reduction conditions recommended by the engineering experience was met, and the permittable variation range of the natural frequency of soil was 22 Hz = 0.75, f0~1.25 and f0 = 37 Hz. Similarly, given ni = 181.25 m−1, if the soil parameters stable or natural frequency remain constant, the working speed u of the tool is also allowed to have a certain change range. As shown in the figure, when the natural frequency of the soil was constant at 29 Hz, the allowable variation range of the working speed of the tool was 22/181.25 = 0.121 m/s~37/181.25 = 0.204 m/s, and considerable resonance resistance reduction effect could still be maintained within this range. In this vein, referring to the requirements of the theoretical resonance curve and engineering empirical resonance zone, coordinated by ft = f0 = uni, the permittable soil natural frequency (or tool excited frequency) and working speed of the tool form an approximate elliptical region, which means that even the constant single geometric frequency of the soil-engaging surface is adaptable to a certain range of physical parameters of soil and the working speed of the tool. Additionally, within this range, a considerable resonance resistance reduction effect could be maintained. This feature makes the technique adaptable to intricate production and application requirements.
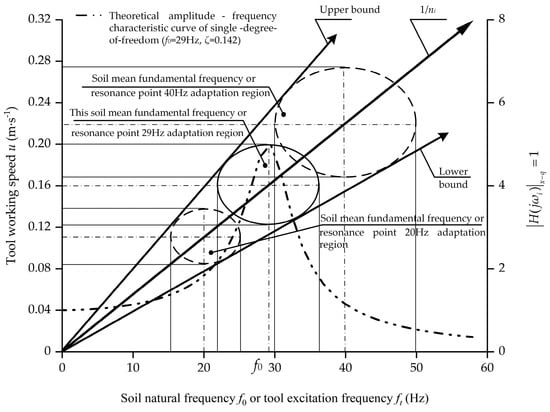
Figure 10.
Self-excited resonance resistance reduction region diagram between bulldozing plate’s working speed u, spatial geometric frequency ni, soil natural frequency f0 and machine excitation frequency ft determined by the engineering experience resonance region.
The ray with slope 1/ni shown in Figure 10 consists of serialized elliptical center points, which theoretically show that when the natural frequency of soil varies from low to high, the working speed must increase according to the corresponding law to ensure the realization of the self-excited resonance soil cutting effect. Additionally, as the natural frequency of the soil varies from low to high, the ellipse area corresponding to each point of the ray in Figure 10 also gradually changes from small to large, which means that in order to ensure the realization of the resistance reduction effect of self-excited resonance soil cutting, variation in the soil natural frequency (or tool excitation frequency) and working speed is allowed to increase as the mean soil natural frequency increases. Additionally, this law can also be interpreted as follows: for harder plots, or land masses with larger soil stiffness or higher natural frequencies, the resistance reduction structure of the soil-engaging surface spectrum whose fixed frequency is designed on the principle of self-excited resonance has relatively stronger adaptability to the actual soil natural frequency, excitation frequency of tools, or fluctuations of the working speed of the tool, and vice versa.
This study verified the feasibility of using the resonance effect to achieve resistance reduction by superimposing a single excitation frequency on a planar substrate. Due to the narrow resonance zone generated by a single excitation on the soil, a good resistance reduction effect was achieved only near the natural vibration frequency of the soil. Once the soil vibration frequency changes, the single excitation frequency of the soil-engaging surface space designed according to the initial test soil fundamental frequency can easily deviate from the actual soil natural frequency, and the resonance state of the cultivated soil cannot be excited properly, thus making the final resistance reduction effect worse. At a later stage, the theory will be expanded by setting multiple excitation frequencies on the soil-engaging surface to further explore the complete multi-spectral result design and resistance reduction theory of the soil-engaging surface.
4. Conclusions
Forms of self-excited vibration tillage of soil were implemented by means of constructing a spatial geometric frequency spectrum on soil-engaging surfaces; by coupling the resonance effect, the effects of soil desorption, loosening and resistance reduction during the cutting process might largely improve near the resonance point. Under study conditions, the bulldozing plate model at the 4 mm amplitude 29 Hz resonant point achieved the best effect on soil desorption and resistance reduction, with a maximum relative resistance reduction rate of 22.67%, in comparison to the base plane bulldozing plate. In this vein, by reasonably matching the working speed, the frequency bandwidth and variation ranges of the working speed could be widened in the effective resistance reduction region near the resonance point, which would enable this soil self-excited vibration cutting resistance reduction method to obtain certain adaptability to soil conditions and the working mode. This research, as an attempt to materialize patterns of self-excited vibration and specific designed structures of resistance reduction by modifying spectrums of soil-engaging surfaces, is of essential significance to the resistance reduction design of related agricultural or engineering vibrating soil cutting tools.
These conclusions were obtained in an indoor soil bin with relatively homogeneous and consistent soil composition. As for real and complex soil conditions in which there are rock particles, grass roots, etc., the components of their inherent vibration frequencies are relatively complex. At this time, the self-excited vibration resistance reduction method only by superimposing a single frequency geometric wave on the soil-engaging surface will be limited. As for field soil conditions, the actual natural vibration frequency of soil could be matched by superimposing multiple geometric spectrum structures of frequency values on the soil-engaging surface simultaneously, in accordance with the actual soil vibration parameters test and statistical results, and eventually the resistance reduction effect in a wider frequency band would be obtained, greatly improving the adaptability of the resistance reduction methods to soil conditions and the working modes of tools.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.Q. and Z.G.; methodology, Y.Q.; software, J.W. validation, Z.G. and X.Y. formal analysis, P.Z.; investigation, Y.Z.; resources, F.Z.; data curation, Y.Q.; writing—original draft, Y.Q.; writing—review and editing, Y.Q.; visualization, Y.Q.; supervision, Z.G.; project administration, Z.G.; funding acquisition, Z.G., J.W. and F.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 51675163, 52075149 and 51905155).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our sincere thanks to the members of the study group for their hard work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Awuah, E.; Zhou, J.; Liang, Z.; Aikins, K.A.; Gbenontin, B.V.; Mecha, P.; Makange, N.R. Parametric analysis and numerical optimization of Jerusalem artichoke vibrating digging shovel using discrete element method. Soil Till. Res. 2022, 219, 105344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manuwa, S.I. Performance evaluation of tillage tines operating under different depths in a sandy clay loam soil. Soil Till. Res. 2009, 103, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanpour, J.; Rostami, J.; Azali, S.T.; Zhao, J. Introduction of an empirical TBM cutter wear prediction model for pyroclastic and mafic igneous rocks; a case history of Karaj water conveyance tunnel, Iran. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2014, 43, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvidsson, J.; Keller, T.; Gustafsson, K. Specific draught for mouldboard plough, chisel plough and disc harrow at different water contents. Soil Till. Res. 2004, 79, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, H.; Ji, J. Effect of Mounting Angle on Bending Subsoiling Tool–Soil Interactions Using DEM Simulations. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godwin, R.J. A review of the effect of implement geometry on soil failure and implement forces. Soil Till. Res. 2007, 92, 331–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.D.; Guo, J.Y.; Hu, J.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H.L.; Dai, H.Q. Research status of wear resistance and drag reduction treatment of soil cultivation components. Surf. Technol. 2017, 46, 119–126. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Z.W.; Mu, Z.Z.; Yin, W.; Niu, S.; Zhang, J.Q.; Ren, L.Q. Biomimetic multifunctional surfaces inspired from animals. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 234, 27–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, X.B.; Zhang, R.H.; Shan, X.; Ye, W.W.; Shi, Y.J.; Ma, G.L.; Tao, D.Q. Optimization of gas explosion subsoiling parameters based on soil fissure trace equation and soil disturbance model. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 15–24. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.; Ni, X.; Song, K.; Wen, N.; Wang, J.; Fu, Q.; Na, M.; Tang, H.; Wang, Q. Bionic Optimization Design and Discrete Element Experimental Design of Carrot Combine Harvester Ripping Shovel. Processes 2023, 11, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Ma, Y.; Wang, S.; Xu, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Qi, H.; Han, L.; Zhuang, J. 3D finite element simulation and experimental validation of a mole rat’s digit inspired biomimetic potato digging shovel. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, H.; Chen, Y.; Lin, P.; Zhang, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, Z.; Huang, G. Research on Ditching Mechanism of Self-Excited Vibration Ditching Machine. Agronomy 2023, 13, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.M.; Wang, T.Y.; Guo, B.; Chen, X.; Zhou, F.J. Design and experiment of key components of rotary cultivator based on vibration reducing resistance principle. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2019, 50, 35–45. [Google Scholar]
- Gholamhossein, S.; Chris, S.; Jacky, D.; John, F. The effect of oscillation angle on the performance of oscillatory tillage. Soil Till. Res. 2009, 104, 97–105. [Google Scholar]
- Gholamhossein, S.; John, F.; Jacky, D.; Chris, S. Optimising oscillation frequency in oscillatory tillage. Soil Till. Res. 2010, 106, 202–210. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Chen, Y. Soil disturbance and cutting forces of four different sweeps for mechanical weeding. Soil Till. Res. 2017, 169, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisowski, A.; Klonowski, J.; Green, O.; Swietochowski, A.; Sypula, M.; Struzyk, A.; Nowakowski, T.; Chlebowski, J.; Kamiński, J.; Kostyra, K.; et al. Duckfoot tools connected with flexible and stiff tines: Three components of resistances and soil disturbance. Soil Till. Res. 2016, 158, 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niyamapa, T.; Salokhe, V.M. Soil distribution and force mechanics of vibrating tillage tool. J. Terramech. 2000, 37, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.X.; Zhang, D.; Li, Y.; Cui, T.; Jing, H.; Zhong, X.J. Modeling the interaction of soil and a vibrating subsoiler using the discrete element method. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2000, 174, 105518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.; Zhong, X.J. Optimized design and field experiment of a staggered vibrating subsoiler for conservation tillage. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2019, 174, 59–65. [Google Scholar]
- Niyamapa, T.; Salokhe, V.M. Force and pressure distribution under vibratory tillage tool. J. Terramech. 2000, 37, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahay, C.S.; Thomas, E.V.; Satapathy, K.K.; Anthonis, J. Performance evaluation of a novel power-tiller-operated oscillatory tillage implement for dry land tillage. Biosyst. Eng. 2009, 102, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elyas, R.; Yuness, S. Vibratory soil cutting a new approach for the mathematical analysis. Soil Till. Res. 2016, 159, 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Sakai, K.; Hata, S.I.; Takai, M.; Nambu, S. Design parameters of four-shank vibrating subsoiler. Trans. Amer. Soc. Agric. Eng. 1993, 36, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.W.; Wang, J.S.; Shang, S.Q. Experimental research on soil digging resistance and energy consumption based on vibration. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2020, 51, 267–272. [Google Scholar]
- Berntsen, R.; Bere, B.; Torp, T.; Aasen, H. Tine forces established by a two-level model and the draught requirement of rigid and flexible tines. Soil Till. Res. 2006, 90, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouazen, A.M.; Duerinckx, K.; Ramon, H.; Anthonis, J. Soil influences on the mechanical actions of a flexible spring tine during selective weed harrowing. Biosyst. Eng. 2007, 96, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berntsen, R.; Bere, B. Soil fragmentation and the efficiency of tillage implements. Soil Till. Res. 2002, 64, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, W.L.; Yang, Q.J.; Li, D.D.; Xia, J.F. Design and experiment of sliding cutting self-excited vibration drag reduction subsoiling device. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2019, 50, 71–78. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, T.; Shi, Z.D.; Yang, L.; Wang, Y.X.; Han, D.D.; Zhang, D.X. Design and experiment of vibration subsoiler with adjustable spring pre-tightening force. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2016, 47, 96–102. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P. Design and Experiment of Drag Reduction on Self-Exciting Vibrating Soil-engaging Surface of Bulldozing Plates with Parabolic Basement. Master’s Thesis, Henan University of Science and Technology, Luoyang, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.M. Forced vibration of single degree of freedom systems. In Mechanical Vibration; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2007; pp. 38–39. [Google Scholar]
- Zong, Q.; Wang, H.B.; Zhou, S.B. Research on monitoring and controlling techniques considering effects of seismic shock. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2008, 27, 938–945. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Y.Q.; Guo, Z.J.; Jin, X.; Zhang, P.G.; Si, S.J.; Guo, F.G. Calibration and verification test of cinnamon soil simulation parameters based on discrete element method. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, L.Z.; Tong, J.; Zeng, B.G.; Chen, D.H. Finite element mode analysis and experiment of cornstubble harvester. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2011, 27, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.J.; Xing, Y.S.; Du, G.; Zhang, S. Influence of intrinsic geometrical quantity of soil-engaging surface on working resistance of bulldozing plate. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2014, 45, 328–333. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.J.; Zhou, D.Y.; Zhou, Z.L. Simulation research on mechanical performances of several kinds of cultivating components with different soil-engaging surfaces. J. Mech. Eng. 2010, 46, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.J. Similar concepts and definitions. In Similitude Theory and Structural Model Test; Wuhan University of Technology Press: Wuhan, China, 2005; pp. 10–12. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.J.; Du, G.; Li, Z.L.; Li, X.P. Orthogonal experiment on resistance reduction by soil-engaging surfaces of bulldozer blade. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2015, 46, 372–378. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, L.Q.; Han, Z.W.; Li, J.Q.; Tong, J. Experimental investigation of bionic rough curved soil cutting blade surface to reduce soil adhesion and friction. Soil Till. Res. 2006, 85, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.S. The comfort of a car. In Automobile Theory, 6th ed.; China Machine Press: Beijing, China, 2019; pp. 246–247. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).