Environmental and Human Health Hazards from Chlorpyrifos, Pymetrozine and Avermectin Application in China under a Climate Change Scenario: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Selection of Literature Review
2.1. Literature Search Terms
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.2.1. Inclusion Criteria
2.2.2. Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Selection of Relevant Articles, Data Extraction, and Data Quality Analysis
3. Behavior of the Legacy and Currently Used Pesticides and Their Risk in Both Environment and Biological Routes in China
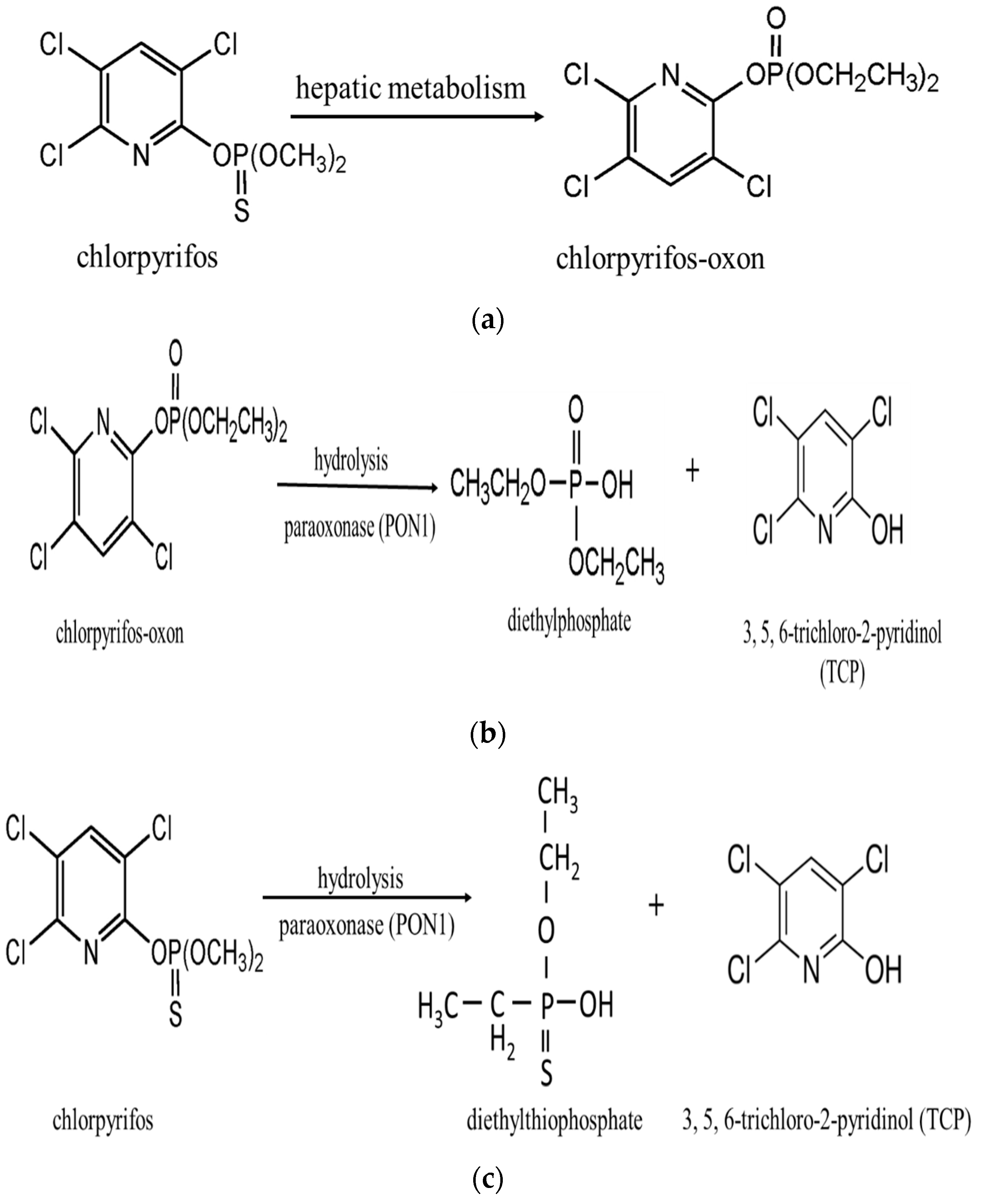
3.1. Chlorpyrifos
3.1.1. Soil Monitoring
3.1.2. Water Monitoring
3.1.3. Crop Monitoring
3.1.4. Air Monitoring
3.1.5. Biological Monitoring
3.2. Pymetrozine
3.3. Avermectin (Abamectin)
4. Climate Factors and Their Possible Impact on Pesticide Use
4.1. Impact of the Climate Change Factors on Pesticide Application and Its Health Risk
4.1.1. Impact on Social and Economic Factors Related to Pesticide Application
4.1.2. Impact of Environmental Factors on Pesticide Application
4.2. Climate Change and Its Expected Impact on Pymetrozine and Avermectin Use and Behavior in Chinese Crop Cultivation
5. Conclusions and New Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tudi, M.; Daniel Ruan, H.; Wang, L.; Lyu, J.; Sadler, R.; Connell, D.; Chu, C.; Phung, D.T. Agriculture development, pesticide application and its impact on the environment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brovini, E.M.; Moreira, F.D.; Martucci, M.E.P.; de Aquino, S.F. Water treatment technologies for removing priority pesticides. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 53, 103730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nas, B.; Yel, E.; Argun, M.; Dinç, S.; Kara, M.; Koyuncu, S.; Dolu, T.; Ateş, H. Fate and removal of pesticides in solid and liquid phases of metropolitan, urban and rural-scale wastewater treatment plants. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 53, 103680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phung, D.; Miller, G.; Connell, D.; Chu, C. Is the World Health Organization predicted exposure assessment model for space spraying of insecticides applicable to agricultural farmers? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 896–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Liu, E.; Zhang, E.; Luo, W.; Chen, L.; Wang, C.; Lin, Q. Historical records and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in sediment from a representative plateau lake, China. Chemosphere 2017, 173, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, G.C.; Tang, J.H.; Xie, Z.Y.; Mi, W.Y.; Chen, Y.J.; Moller, A.; Sturm, R.; Zhang, G.; Ebinghaus, R. Selected current-use pesticides (CUPs) in coastal and offshore sediments of Bohai and Yellow seas. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 1653–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.F.; Luo, J.H.; Li, S.H.; Liu, C.H. Evaluation of nine pesticide residues in three minor tropical fruits from southern China. Food Control 2016, 60, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuqin, J.; Fang, Z. Zero growth of chemical fertilizer and pesticide use: China’s objectives, progress and challenges. J. Resour. Ecol. 2018, 9, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Guanming, S.; Jian, S.; Hu, R.-f. Productivity effect and overuse of pesticide in crop production in China. J. Integr. Agric. 2015, 14, 1903–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Jiang, F.; Ou, J. Global pesticide consumption and pollution: With China as a focus. Proc. Int. Acad. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2011, 1, 125. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Chu, M.; Ma, Y. Measuring rice farmer’s pesticide overuse practice and the determinants: A statistical analysis based on data collected in Jiangsu and Anhui Provinces of China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W. Global pesticide use: Profile, trend, cost/benefit and more. Proc. Int. Acad. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2018, 8, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, R.; Luo, X.; Li, Q.X.; Wang, T.; Zheng, X.; Peng, P.; Mai, B. Legacy and emerging organohalogenated contaminants in wild edible aquatic organisms: Implications for bioaccumulation and human exposure. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Luo, Y.; Li, Q. Burden and depth distribution of organochlorine pesticides in the soil profiles of Yangtze River Delta Region, China: Implication for sources and vertical transportation. Geoderma 2009, 153, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zhou, H.; Pan, G.; Wang, J.; Chen, B. Factors influencing the persistence of organochlorine pesticides in surface soil from the region around the Hongze Lake, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 443, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Z.; Baležentis, T.; Chen, X.; Valdmanis, V. Green growth and structural change in Chinese agricultural sector during 1997–2014. China Econ. Rev. 2018, 51, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Z.; Sun, B.Q.; Lydy, M.J.; You, J. Sediment-Associated pesticides in an urban stream in guangzhou, China: Implication of a shift in pesticide use patterns. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2013, 32, 1040–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Sun, J.; Li, Z.; Zhan, Y.; Xu, S.; Zhu, L. Organophosphate pesticide in agricultural soils from the Yangtze River Delta of China: Concentration, distribution, and risk assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.Y.; Zhu, F.X.; Wang, F.W.; Gao, J.A.; Fan, G.P.; Zhou, D.M.; Fang, G.D. Comparison of Persulfate Activation and Fenton Reaction in Remediating an Organophosphorus Pesticides-Polluted Soil. Pedosphere 2017, 27, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudi, M.; Atabila, A.; Ruan, H.D.; Wang, L.; Lyu, J.; Tong, S.; Yu, Q.J.; Sadler, R.; Phung, D.T.; Connell, D. Natural dynamics and residues of pymetrozine for typical rice-growing areas of China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 232, 113230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudi, M.; Wang, L.; Ruan, H.D.; Tong, S.; Atabila, A.; Sadler, R.; Yu, Q.J.; Connell, D.; Phung, D.T. Environmental monitoring and potential health risk assessment from Pymetrozine exposure among communities in typical rice-growing areas of China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 59547–59560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.X.; Feng, X.X.; Cao, M.; Zhang, S.W.; Huang, Y.F.; Xu, T.H.; Jing, J.; Zhang, H.Y. Determination and distribution of pesticides and antibiotics in agricultural soils from northern China. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 15686–15693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, G.F.; Zeng, L.R.; Zhao, S.; Ge, S.J.; Long, X.F.; Zhang, Y.P.; Hu, D.Y. Monitoring residue levels and dietary risk assessment of pymetrozine for Chinese consumption of cauliflower. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2019, 33, e4455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.F.; Zhang, L.; Xu, P.; Li, J.Z.; Wang, H.L. Dissipation and residue of pymetrozine in rice field ecosystem. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.L.; Li, H.Z.; Zhang, J.J.; Xiong, J.J.; Yi, X.Y.; You, J. Legacy and Current-Use Insecticides in Agricultural Sediments from South China: Impact of Application Pattern on Occurrence and Risk. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 4247–4254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.P.; Zhang, S.Q.; Chen, Z.L.; Du, H.X.; Zhu, Q.; Dong, Z.; Li, H.D. Risk assessment of pesticide residues in dietary intake of celery in China. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 73, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.S.; Miao, J.; Liu, M.; Liu, X.T.; Bao, L.Q.; Jiang, Y.G.; Wang, D.M.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, L.X. Different fates of avermectin and artemisinin in China. Sci. China-Life Sci. 2016, 59, 634–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.Q.; Wu, X.H.; Xu, J.; Dong, F.S.; Shi, Y.C.; Li, Y.B.; Liu, X.G.; Zheng, Y.Q. Different residue behaviors of four pesticides in mushroom using two different application methods. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 8377–8387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamsan, H.; Ho, Y.B.; Zaidon, S.Z.; Hashim, Z.; Saari, N.; Karami, A. Occurrence of commonly used pesticides in personal air samples and their associated health risk among paddy farmers. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 603, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marasinghe, J.; Yu, Q.; Connell, D. Assessment of health risk in human populations due to chlorpyrifos. Toxics 2014, 2, 92–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phung, D.T.; Connell, D.; Chu, C. A new method for setting guidelines to protect human health from agricultural exposure by using chlorpyrifos as an example. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2015, 22, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atabila, A.; Phung, D.T.; Sadler, R.; Connell, D.; Chu, C. Comparative evaluation of chlorpyrifos exposure estimates from whole-body dermal dosimetry and urinary trichloro-2-pyridinol (TCP) methods. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 172, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tudi, M.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Lyu, J.; Yang, L.; Tong, S.; Yu, Q.J.; Ruan, H.D.; Atabila, A. Exposure Routes and Health Risks Associated with Pesticide Application. Toxics 2022, 10, 335. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Connell, D.W.; Miller, G.J.; Anderson, S.M. Persistent organic pollutants: Occurrence and health risks in Australia. Dev. Environ. Sci. 2007, 7, 753–770. [Google Scholar]
- Li, A.J.; Kannan, K. Profiles of urinary neonicotinoids and dialkylphosphates in populations in nine countries. Environ. Int. 2020, 145, 106120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.D.; Zhang, H.J.; Li, F.M.; Zhou, Z.L.; Wang, W.L.; Ma, D.K.; Yang, L.; Zhou, P.G.; Huang, Q.L. Potential dermal and inhalation exposure to imidacloprid and risk assessment among applicators during treatment in cotton field in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 624, 1195–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, W.; Jing, R.; Wheeler, K.; Smith, G.A.; Stallones, L.; Xiang, H. Work-related pesticide poisoning among farmers in two villages of Southern China: A cross-sectional survey. BMC Public Health 2011, 11, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Fang, X.; Zhou, L.; Su, L.; Zheng, J.; Jin, M.; Zou, H.; Chen, G. Pesticide poisoning in Zhejiang, China: A retrospective analysis of adult cases registration by occupational disease surveillance and reporting systems from 2006 to 2010. BMJ Open 2013, 3, e003510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azari, A.; Nabizadeh, R.; Nasseri, S.; Mahvi, A.H.; Mesdaghinia, A.R. Comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis of dyes adsorption by carbon-based adsorbent materials: Classification and analysis of last decade studies. Chemosphere 2020, 250, 126238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atabila, A.; Phung, D.T.; Hogarh, J.N.; Fobil, J.N.; Sadler, R.; Connell, D.; Chu, C. Probabilistic health risk assessment of chlorpyrifos exposure among applicators on rice farms in Ghana. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 67555–67564. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.L.; Fang, H.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.Q.; Fan, D.F. Dissipation of chlorpyrifos on pakchoi inside and outside greenhouse. J. Environ. Sci. 2005, 17, 503–505. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Wei, W.; He, L.; Hao, L.L.; Ji, X.F.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Q. Chlorpyrifos Residual Behaviors in Field Crops and Transfers during Duck Pellet Feed Processing. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 10215–10221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atabila, A.; Sadler, R.; Phung, D.T.; Hogarh, J.N.; Carswell, S.; Turner, S.; Patel, R.; Connell, D.; Chu, C. Biomonitoring of chlorpyrifos exposure and health risk assessment among applicators on rice farms in Ghana. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 20854–20867. [Google Scholar]
- Sang, C.H.; Yu, Z.Y.; An, W.; Sorensen, P.B.; Jin, F.; Yang, M. Development of a data driven model to screen the priority control pesticides in drinking water based on health risk ranking and contribution rates. Environ. Int. 2022, 158, 106901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Wu, C.H.; Chang, X.L.; Qi, X.J.; Zheng, M.L.; Zhou, Z.J. Assessment of chlorpyrifos exposure and absorbed daily doses among infants living in an agricultural area of the Province of Jiangsu, China. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2014, 87, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atabila, A.; Phung, D.T.; Hogarh, J.N.; Sadler, R.; Connell, D.; Chu, C. Health risk assessment of dermal exposure to chlorpyrifos among applicators on rice farms in Ghana. Chemosphere 2018, 203, 83–89. [Google Scholar]
- Atabila, A.; Phung, D.T.; Hogarh, J.N.; Osei-Fosu, P.; Sadler, R.; Connell, D.; Chu, C. Dermal exposure of applicators to chlorpyrifos on rice farms in Ghana. Chemosphere 2017, 178, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phung, D.T.; Connell, D.; Miller, G.; Rutherford, S.; Chu, C. Needs assessment for reducing pesticide risk: A case study with farmers in Vietnam. J. Agromed. 2013, 18, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.W.; Dou, X.W.; Lu, Q.; Qin, J.A.; Luo, J.Y.; Yang, M.H. Comprehensive assessment for the residual characteristics and degradation kinetics of pesticides in Panax notoginseng and planting soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 714, 136718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zou, W.B.; Cui, G.L.; Tian, J.C.; Wang, Y.C.; Ma, L.M. Ecological risk assessment of current-use pesticides in an aquatic system of Shanghai, China. Chemosphere 2020, 257, 127222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.P.; Zheng, L.G.; Yu, W.T.; Cao, X.M.; Yang, R.B. Dissipation behavior of chlorpyrifos residues and risk assessment in sugarcane fields. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2019, 33, e4424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.X.; Mo, R.H.; Yuan, X.Y.; Zhong, D.L.; Tang, F.B.; Ye, C.F.; Liu, Y.H. Pesticide residues in nut-planted soils of China and their relationship between nut/soil. Chemosphere 2017, 180, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.Z.; Wei, Y.L.; Lydy, M.J.; You, J. Inter-compartmental transport of organophosphate and pyrethroid pesticides in South China: Implications for a regional risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 190, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Yang, C.L.; Gong, M.B.; Zhao, Y.F.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, C.X.; Jiang, J.D.; Li, S.P. Adsorption and degradation of triazophos, chlorpyrifos and their main hydrolytic metabolites in paddy soil from Chaohu Lake, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 2229–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, N.D.; Li, F.S.; Hou, H.; Li, B.W. Occurrence of endocrine-disrupting pesticide residues in wetland sediments from Beijing, China. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2008, 27, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.Y.; Wang, K.; Zhang, B. Applying a network data envelopment analysis model to quantify the eco-efficiency of products: A case study of pesticides. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 69, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.L.; Wang, C.; Niu, W.P.; Huan, Q.; Tian, T.T.; Zou, S.J.; Huang, D.Y. Occurrence and risk assessment of currently used organophosphate pesticides in overlying water and surface sediments in Guangzhou urban waterways, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 48194–48206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.D.; Zhang, H.J.; Wu, C.Y.; Wang, C.A.M.; Li, Q.F. Pesticides in surface waters of tropical river basins draining areas with rice-vegetable rotations in Hainan, China: Occurrence, relation to environmental factors, and risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 283, 117100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, C.H.; Sorensen, P.B.; An, W.; Andersen, J.H.; Yang, M. Chronic health risk comparison between China and Denmark on dietary exposure to chlorpyrifos. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 257, 113590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, X.M.; Liu, L.; Wang, X.M.; Zhong, G.C.; Tang, J.H. Fates and ecological effects of current-use pesticides (CUPs) in a typical river-estuarine system of Laizhou Bay, North China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.Y.; Yang, Y.; Tam, N.F.Y.; Tao, R.; Dai, Y.N. Pesticides in three rural rivers in Guangzhou, China: Spatiotemporal distribution and ecological risk. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 3569–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Tang, J.H.; Zhong, G.C.; Zhen, X.M.; Pan, X.H.; Tian, C.G. Spatial distribution and seasonal variation of four current-use pesticides (CUPs) in air and surface water of the Bohai Sea, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.X.; Shi, W.; Yu, N.Y.; Jiang, X.; Wang, S.H.; Giesy, J.P.; Zhang, X.W.; Wei, S.; Yu, H.X. Bioassay-directed identification of organic toxicants in water and sediment of Tai Lake, China. Water Res. 2015, 73, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, G.C.; Tang, J.H.; Xie, Z.Y.; Moller, A.; Zhao, Z.; Sturm, R.; Chen, Y.J.; Tian, C.G.; Pan, X.H.; Qin, W.; et al. Selected current-use and historic-use pesticides in air and seawater of the Bohai and Yellow Seas, China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 1073–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.C.; Xu, X.M.; Hou, J.; Gong, Z.Y.; Cheng, Z.P.; Fan, W.Z.; Fu, T.; Wang, S.S.; Ye, X.J.; Wu, Y.P.; et al. Dengue Fever Vector Composition and Pesticide Residues in Yiwu, Zhejiang Province, China. J. Entomol. Sci. 2012, 47, 309–315. [Google Scholar]
- Ping, H.; Wang, B.H.; Li, C.; Li, Y.; Ha, X.J.; Jia, W.S.; Li, B.R.; Ma, Z.H. Potential health risk of pesticide residues in greenhouse vegetables under modern urban agriculture: A case study in Beijing, China. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 105, 104222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Liao, X.F.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, L.C.; Zhou, L.D.; Zhao, H.P.; Kong, W.J. An orthogonal experimental design and QuEChERS based UFLC-MS/MS for multi-pesticides and human exposure risk assessment in Honeysuckle. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 164, 113384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.D.; Li, Q.F.; Zhang, H.J.; Wu, C.Y.; Zhao, S.Q.; Deng, X.; Li, Y. Pesticide residues in agricultural topsoil from the Hainan tropical riverside basin: Determination, distribution, and relationships with planting patterns and surface water. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 722, 137856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.G.; Yuan, L.; Chen, M.L.; Zheng, X.Q.; Liu, X.W.; Zhao, Y.J.; Liu, A.F.; Jia, J.J.; Xu, M.M.; Zhao, Z.S. Detection of Frequently Used Pesticides in Apple Orchard Soil in China by High Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2020, 29, 1341–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.X.; Zhang, Y.H.; Zhao, Q.Y.; Wang, C.Q.; Cui, Y.L.; Li, J.; Chen, A.H.; Liang, G.L.; Jiao, B.N. Occurrence, temporal variation, quality and safety assessment of pesticide residues on citrus fruits in China. Chemosphere 2020, 258, 127381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khammanee, N.; Qiu, Y.L.; Kungskulniti, N.; Bignert, A.; Meng, Y.; Zhu, Z.L.; Teffera, Z.L. Presence and Health Risks of Obsolete and Emerging Pesticides in Paddy Rice and Soil from Thailand and China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.M.; Huang, H.L.; Chen, Z.J.; Wei, J.; Deng, C.; Tan, H.H.; Li, X.S. Representative Commodity for Six Leafy Vegetables Based on the Determination of Six Pesticide Residues by Gas Chromatography. Acta Chromatogr. 2019, 31, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.W.; Liu, F.M.; Ge, J.; Ma, L.L.; Wu, L.M.; Xue, X.F. Changes in eleven pesticide residues in jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill.) during drying processing. Dry. Technol. 2018, 36, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Z.; Duan, J.S.; Wu, Y.C.; Liu, Q.Q.; He, Q.B.; Shi, Y.H.; Yu, L.S.; Cao, H.Q. A survey of multiple pesticide residues in pollen and beebread collected in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 640, 1578–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.P.; Zhou, X.L.; Zhao, D.Y.; Feng, T.; Zhou, J.; Sun, T.; Wang, J.M.; Wang, C. Seasonal variation and exposure risk assessment of pesticide residues in vegetables from Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region of China during 2010–2014. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2017, 58, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Jiang, W.W.; Jian, Q.; Song, W.C.; Zheng, Z.T.; Wang, D.L.; Liu, X.J. Changes of Field Incurred Chlorpyrifos and Its Toxic Metabolite Residues in Rice during Food Processing from-RAC-to-Consumption. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.H.; Mo, R.H.; Tang, F.B.; Fu, Y.; Guo, Y.R. Influence of different formulations on chlorpyrifos behavior and risk assessment in bamboo forest of China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 20245–20254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; He, L.; Wei, W.; Hao, L.L.; Ji, X.F.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Q. Chlorpyrifos residue levels on field crops (rice, maize and soybean) in China and their dietary risks to consumers. Food Control 2015, 51, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Liu, F.F.; Zhao, C.L.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.H.; Zhu, G.N. Distribution of chlorpyrifos in rice paddy environment and its potential dietary risk. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 35, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.W.; Chen, C.; Zheng, C.M.; Wang, X.L.; Yang, G.L.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Z.H. Residue of chlorpyrifos and cypermethrin in vegetables and probabilistic exposure assessment for consumers in Zhejiang Province, China. Food Control 2014, 36, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.M.; Wang, Z.L.; Zhang, Y.B.; Wang, J.; Guo, R. Pesticide residues in market foods in Shaanxi Province of China in 2010. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 2016–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Qian, Y.Z.; Liu, X.J.; Tao, C.J.; Liang, Y.; Li, Y. Risk assessment of chlorpyrifos on rice and cabbage in China. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2012, 62, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Shan, W.L.; Song, W.C.; Gong, Y.; Liu, X.J. Phytotoxicity and uptake of chlorpyrifos in cabbage. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2011, 9, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, E.S.J.; Cao, S.G.; Littlefield, B.A.; Craycroft, J.A.; Scholten, R.; Kaptchuk, T.; Fu, Y.L.; Wang, W.Q.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.B.A.; et al. Heavy metal and pesticide content in commonly prescribed individual raw Chinese Herbal Medicines. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 4297–4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Li, Y.; Chen, M.X.; Chen, Z.J.; Qian, Y.Z. Organophosphorus pesticide residues in milled rice (Oryza sativa) on the Chinese market and dietary risk assessment. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2009, 26, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.L.; Wang, P.S.; Gu, M.Y.; Xue, J.; Wu, X.L. Human health risk assessment of pesticide residues in honeysuckle samples from different planting bases in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 142747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.Z.; Ma, H.Z.; Lydy, M.J.; You, J. Occurrence, seasonal variation and inhalation exposure of atmospheric organophosphate and pyrethroid pesticides in an urban community in South China. Chemosphere 2014, 95, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, X.H.; Ji, X.F.; Wu, M.; Hu, X.Q.; Yu, R.X.; Zhao, X.P.; Cai, L.M. Risk Assessment of Applicators to Chlorpyrifos through Dermal Contact and Inhalation at Different Maize Plant Heights in China. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 7072–7077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, B.B.; Tao, C.J.; Ye, J.M.; Ning, J.; Mei, X.D.; Jiang, Z.F.; Chen, S.; She, D.M. Measurement of operator exposure to chlorpyrifos. Pest Manag. Sci. 2014, 70, 636–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.B.; Li, H.Z.; Xiong, J.J.; You, J. Target and Suspect Screening of Urinary Biomarkers for Current-use Pesticides: Application of a Simple Extraction Method. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2022, 41, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.J.; Kannan, K. Urinary concentrations and profiles of organophosphate and pyrethroid pesticide metabolites and phenoxyacid herbicides in populations in eight countries. Environ. Int. 2018, 121, 1148–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.K.; Liu, W.L.; Wu, C.C.; She, D.M. Effect of spraying direction on the exposure to handlers with hand-pumped knapsack sprayer in maize field. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 170, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Huang, M.Y.; Guo, X.Y.; Lin, P. Urinary Metabolites of Organophosphate and Pyrethroid Pesticides and Neurobehavioral Effects in Chinese Children. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 9627–9635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Han, S.; Liang, D.H.; Shi, X.Z.; Wang, F.Z.; Liu, W.; Zhang, L.; Chen, L.X.; Gu, Y.Z.; Tian, Y. Prenatal Exposure to Organophosphate Pesticides and Neurobehavioral Development of Neonates: A Birth Cohort Study in Shenyang, China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J.J.; Wu, Y.H.; Sun, H.W. Chlorpyrifos exposure in farmers and urban adults: Metabolic characteristic, exposure estimation, and potential effect of oxidative damage. Environ. Res. 2016, 149, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phung, D.T. Assessing and Reducing Risk Due to Chlorpyrifos Use among Rice Farmers in Vietnam: From Probabilistic Risk Assessment to Safety Strategy Development; Griffith University: Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Atabila, A. Health Risk Assessment and Management of Chlorpyrifos Exposure among Rice Farmers in Ghana; Griffith University: Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.H.; Tai, L.Y.; Liu, J.X.; Gai, Z.K.; Ding, G.T. Monitoring of pesticide residues levels in fresh vegetable form Heibei Province, North China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 6341–6349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phung, D.T.; Connell, D.; Yu, Q.; Chu, C. Health Risk Characterization of Chlorpyrifos Using Epidemiological Dose-Response Data and Probabilistic Techniques: A Case Study with Rice Farmers in Vietnam. Risk Anal. 2013, 33, 1596–1607. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, G.D.; Wang, P.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, J.; Gao, Y.; Wang, X.J.; Shi, R.; Wang, G.Q.; Shen, X.M. Organophosphate Pesticide Exposure and Neurodevelopment in Young Shanghai Children. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 2911–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phung, D.T.; Connell, D.; Miller, G.; Rutherford, S.; Chu, C. Pesticide regulations and farm worker safety: The need to improve pesticide regulations in Viet Nam. Bull. World Health Organ. 2012, 90, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phung, D.T.; Connell, D.; Miller, G.; Chu, C. Probabilistic assessment of chlorpyrifos exposure to rice farmers in Viet Nam. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2012, 22, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phung, D.T.; Connell, D.; Miller, G.; Hodge, M.; Patel, R.; Cheng, R.; Abeyewardene, M.; Chu, C. Biological monitoring of chlorpyrifos exposure to rice farmers in Vietnam. Chemosphere 2012, 87, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Harrewijn, P.; Kayser, H. Pymetrozine, a fast-acting and selective inhibitor of aphid feeding. In-situ studies with electronic monitoring of feeding behaviour. Pestic. Sci. 1997, 49, 130–140. [Google Scholar]
- Tudi, M. Pesticide Contamination and Environmental Health Risk Assessment in Typical Rice Growing Areas of China; Griffith University Queensland: Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Yang, T.; Huangfu, W.; Wu, Y. Residues and dynamics of pymetrozine in rice field ecosystem. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Hu, X.; Hu, Y. Kinetic study of the degradation of the insecticide pymetrozine in a vegetable-field ecosystem. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Sun, H.; Wang, X.; Liang, Y.; Guo, M.; Yu, J.; Yang, M.; Zhang, X.; Luo, F.; Zhou, L. Residue behavior and safety evaluation of pymetrozine in tea. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 4118–4124. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Zheng, K.; Yang, G.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, K.; Hu, D. Determination, residue analysis, risk assessment and processing factor of pymetrozine and its metabolites in Chinese kale under field conditions. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2019, 36, 141–151. [Google Scholar]
- Authority, E.F.S. Pesticide risk assessment for the active substance pymetrozine in light of negligible exposure data submitted. EFSA J. 2017, 15, e04678. [Google Scholar]
- Connell, D.W. Environmental routes leading to the bioaccumulation of lipophilic chemicals. In Bioaccumulation of Xenobiotic Compounds; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 59–74. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, H.L.; Garthwaite, D.G.; Ramwell, C.T.; Brown, C.D. Assessment of exposure of professional agricultural operators to pesticides. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619, 874–882. [Google Scholar]
- Abhilash, P.; Singh, N. Pesticide use and application: An Indian scenario. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 165, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-H.; Kabir, E.; Jahan, S.A. Exposure to pesticides and the associated human health effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 525–535. [Google Scholar]
- Sugeng, A.J.; Beamer, P.I.; Lutz, E.A.; Rosales, C.B. Hazard-ranking of agricultural pesticides for chronic health effects in Yuma County, Arizona. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 463, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, X.; Zhang, W.; Xie, J.; Wang, W.; Lu, T.; Dong, Q.; Yang, H. Monitoring and risk assessment of pesticide residue in plant-soil-groundwater systxem about medlar planting in Golmud. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 26413–26426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, D.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Wan, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Q. Assessing Pesticide Residue and Spray Deposition in Greenhouse Eggplant Canopies to Improve Residue Analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 11920–11927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, M.; Abbas, R.Z.; Mehmood, K.; Hussain, R.; Shah, S.; Faheem, M.; Zaheer, T.; Abbas, A.; Morales, B.; Aneva, I. Assessment of avermectins-induced toxicity in animals. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 332. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rajendra, K.; Pachauri., A.R. Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Miraglia, M.; Marvin, H.; Kleter, G.; Battilani, P.; Brera, C.; Coni, E.; Cubadda, F.; Croci, L.; De Santis, B.; Dekkers, S. Climate change and food safety: An emerging issue with special focus on Europe. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 1009–1021. [Google Scholar]
- Pachauri, R.K.; Allen, M.R.; Barros, V.R.; Broome, J.; Cramer, W.; Christ, R.; Church, J.A.; Clarke, L.; Dahe, Q.; Dasgupta, P. Climate change 2014: Synthesis report. In Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Field, C.B.; Barros, V.R. Climate Change 2014—Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability: Regional Aspects; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hiraishi, T.; Krug, T.; Tanabe, K.; Srivastava, N.; Baasansuren, J.; Fukuda, M.; Troxler, T. 2013 Supplement to the 2006 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories: Wetlands; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Yan, X. Temporal change of climate zones in China in the context of climate warming. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2014, 115, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Yang, R.; Wu, T.; Wu, C.; Sun, S.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, B.; Tian, S.; Liu, X.; Han, T. Analyzing the effects of climate factors on soybean protein, oil contents, and composition by extensive and high-density sampling in China. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 4121–4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, C.C.; Chan, J.C. Simulating seasonal tropical cyclone intensities at landfall along the South China coast. Clim. Dyn. 2018, 50, 2661–2672. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Li, W.; Tang, Q.; Zhang, P.; Liu, Y. Warm season heavy rainfall events over the Huaihe River Valley and their linkage with wintertime thermal condition of the tropical oceans. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 46, 71–82. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.; Wu, P.; Zhou, S.; Han, Z.; Tu, H.; Zhang, S. Seasonal variability of oxygen and hydrogen isotopes in a wetland system of the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau, southwest China: A quantitative assessment of groundwater inflow fluxes. Hydrogeol. J. 2018, 26, 215–231. [Google Scholar]
- Bodansky, D. The United Nations framework convention on climate change: A commentary. Yale J. Int. L. 1993, 18, 451. [Google Scholar]
- Delcour, I.; Spanoghe, P.; Uyttendaele, M. Literature review: Impact of climate change on pesticide use. Food Res. Int. 2015, 68, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, L.; Shan, B.; Xu, Z.; Niu, Q.; Cheng, L.; Liu, X.; Xu, Z. Spatiotemporal variation of drought and associated multi-scale response to climate change over the Yarlung Zangbo River Basin of Qinghai–Tibet Plateau, China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Ding, Y.; Han, T.; Liu, Y. Identification of the factors influencing the baseflow in the permafrost region of the northeastern qinghai-tibet plateau. Water 2017, 9, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Xu, Y.-P.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H. Understanding the impact of climatic variability on terrestrial water storage in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau of China. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2022, 67, 963–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, R.; Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Niu, Z. Less sensitive of urban surface to climate variability than rural in Northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 628, 650–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K.; Yu, B.; Klik, A.; Jae Lim, K.; Yang, J.E.; Ni, J.; Miao, C.; Chattopadhyay, N. Global rainfall erosivity assessment based on high-temporal resolution rainfall records. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ruby Leung, L.; Zhao, N.; Zhao, C.; Qian, Y.; Hu, K.; Liu, X.; Chen, B. Contribution of urbanization to the increase of extreme heat events in an urban agglomeration in east China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 6940–6950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Meyers, P.A.; Liu, X.; Wang, G.; Ma, X.; Li, X.; Yuan, Y.; Wen, B. Holocene climate changes in the central Asia mountain region inferred from a peat sequence from the Altai Mountains, Xinjiang, northwestern China. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2016, 152, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y. Climate-driven ground-level ozone extreme in the fall over the Southeast United States. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 10025–10030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-m.; Li, Y.-j.; Cheng, S.-j.; Yang, F.-t.; Chen, Y.-t. Effects of spatial-temporal imperviousness on hydrological responses of various areas in an urbanized watershed. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 3551–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, P.; Sokhansanj, S.; Bi, X.; Lim, C.; Naimi, L.; Hoque, M.; Mani, S.; Womac, A.R.; Narayan, S.; Ye, X. Bulk density of wet and dry wheat straw and switchgrass particles. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2008, 24, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardes, M.F.F.; Pazin, M.; Pereira, L.C.; Dorta, D.J. Impact of pesticides on environmental and human health. In Toxicology Studies—Cells, Drugs and Environment; InTech: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Handford, C.E.; Elliott, C.T.; Campbell, K. A review of the global pesticide legislation and the scale of challenge in reaching the global harmonization of food safety standards. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2015, 11, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, M.; Longstreth, J.; Johnson, A.; Rosenberg, N. Dust Bowl Migration as an Analog for Possible Global Warming-Induced Migration from Mexico; Pacific Northwest Lab.: Richland, WA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Eid, H.M.; El-Marsafawy, S.M.; Ouda, S.A. Assessing the economic impacts of climate change on agriculture in Egypt: A Ricardian approach. World Bank Policy Research Working Paper, 2007. Available online: https://elibrary.worldbank.org/doi/abs/10.1596/1813-9450-4293 (accessed on 14 July 2023).
- Uram, C. International regulation of the sale and use of pesticides. Nw. J. Int. L. Bus. 1989, 10, 460. [Google Scholar]
- Dworak, V.; Selbeck, J.; Dammer, K.-H.; Hoffmann, M.; Zarezadeh, A.A.; Bobda, C. Strategy for the development of a smart NDVI camera system for outdoor plant detection and agricultural embedded systems. Sensors 2013, 13, 1523–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzluebbers, A.J.; Haney, R.L.; Honeycutt, C.W.; Arshad, M.; Schomberg, H.H.; Hons, F.M. Climatic influences on active fractions of soil organic matter. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2001, 33, 1103–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melillo, J.M.; Steudler, P.; Aber, J.D.; Newkirk, K.; Lux, H.; Bowles, F.; Catricala, C.; Magill, A.; Ahrens, T.; Morrisseau, S. Soil warming and carbon-cycle feedbacks to the climate system. Science 2002, 298, 2173–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobell, D.B.; Gourdji, S.M. The influence of climate change on global crop productivity. Plant Physiol. 2012, 160, 1686–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challinor, A.J.; Watson, J.; Lobell, D.B.; Howden, S.; Smith, D.; Chhetri, N. A meta-analysis of crop yield under climate change and adaptation. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasannakumar, N.; Chander, S.; Pal, M. Assessment of impact of climate change with reference to elevated CO2 on rice brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stal.) and crop yield. Curr. Sci. 2012, 103, 1201–1205. [Google Scholar]
- Ghini, R.; Bettiol, W.; Hamada, E. Diseases in tropical and plantation crops as affected by climate changes: Current knowledge and perspectives. Plant Pathol. 2011, 60, 122–132. [Google Scholar]
- Alford, L.; Burel, F.; Van Baaren, J. Improving methods to measure critical thermal limits in phloem-feeding pest insects. Entomol. Exp. Et Appl. 2016, 159, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Huang, D.; Nachman, G.; Ahmed, N.; Begum, M.A.; Rabbi, M. Will climate change affect outbreak patterns of planthoppers in Bangladesh? PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babenko, A. The agricultural pests of West Siberia in a changing climate. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 2009, 66, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, D.; Westbrook, J.; Joyce, R.; Lingren, P.; Rogasik, J. Weeds, insects, and diseases. Clim. Chang. 1999, 43, 711–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakala, K.; Hannukkala, A.; Huusela-Veistola, E.; Jalli, M.; Peltonen-Sainio, P. Pests and diseases in a changing climate a major challenge for Finnish crop production. Agric. Food Sci. 2011, 20, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschi, M.; Stoeckli, S.; Dubrovsky, M.; Spirig, C.; Calanca, P.; Rotach, M.; Fischer, A.; Duffy, B.; Samietz, J. Downscaling climate change scenarios for apple pest and disease modeling in Switzerland. Earth Syst. Dyn. 2012, 3, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Tardif, J.C.; Bergeron, Y.; Denneler, B.; Berninger, F.; Girardin, M.P. Radial growth response of four dominant boreal tree species to climate along a latitudinal gradient in the eastern Canadian boreal forest. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2010, 16, 711–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, M.; van Sprundel, G.-J.; Turvey, C.G.; Meuwissen, M.P. Applying weather index insurance to agricultural pest and disease risks. Int. J. Pest Manag. 2016, 62, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.N.; Jones, T.H. Global Climate Change and Terrestrial Invertebrates; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Luck, J.; Spackman, M.; Freeman, A.; Trebicki, P.; Griffiths, W.; Finlay, K.; Chakraborty, S. Climate change and diseases of food crops. Plant Pathol. 2011, 60, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juroszek, P.; von Tiedemann, A. Climate change and potential future risks through wheat diseases: A review. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2013, 136, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenzweig, C.; Iglesius, A.; Yang, X.-B.; Epstein, P.R.; Chivian, E. Climate Change and Extreme Weather Events-Implications for Food Production, Plant Diseases, and Pests; National Aeronautics and Space Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Kremer, P.; Schlüter, J.; Racca, P.; Fuchs, H.-J.; Lang, C. Possible impact of climate change on the occurrence and the epidemic development of cercospora leaf spot disease (Cercospora beticola sacc.) in sugar beets for Rhineland-Palatinate and the southern part of Hesse. Clim. Chang. 2016, 137, 481–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrève, A.; Duveiller, E. Preventing potential diseases and pest epidemics under a changing climate. Clim. Chang. Crop Prod. 2010, 1, 50–70. [Google Scholar]
- Sadler, R.; Gabric, A.; Shaw, G.; Shaw, E.; Connell, D. An opinion on the distribution and behavior of chemicals in response to climate change, with particular reference to the Asia-Pacific region. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2011, 93, 3–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Devkota, B.R.; Yu, J.s.; Oh, K.c.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.J. Effects of global warming on mosquitoes & mosquito-borne diseases and the new strategies for mosquito control. Entomol. Res. 2014, 44, 215–235. [Google Scholar]
- West, J.S.; Townsend, J.A.; Stevens, M.; Fitt, B.D. Comparative biology of different plant pathogens to estimate effects of climate change on crop diseases in Europe. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2012, 133, 315–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, A.C.; Johnson, S.N.; Gregory, P.J. Implications of climate change for diseases, crop yields and food security. Euphytica 2011, 179, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Megías, C.; Mentzel, S.; Fuentes-Edfuf, Y.; Moe, S.J.; Rico, A. Influence of climate change and pesticide use practices on the ecological risks of pesticides in a protected Mediterranean wetland: A Bayesian network approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 878, 163018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-C.; McCarl, B.A. An investigation of the relationship between pesticide usage and climate change. Clim. Chang. 2001, 50, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.-S.; Zhang, W.; Peng, Y.; Zhao, F.; Chang, X.-Q.; Xing, K.; Zhu, L.; Ma, G.; Yang, H.-P.; Rudolf, V.H. Climate warming promotes pesticide resistance through expanding overwintering range of a global pest. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noyes, P.D.; McElwee, M.K.; Miller, H.D.; Clark, B.W.; Van Tiem, L.A.; Walcott, K.C.; Erwin, K.N.; Levin, E.D. The toxicology of climate change: Environmental contaminants in a warming world. Environ. Int. 2009, 35, 971–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloomfield, J.; Williams, R.; Gooddy, D.; Cape, J.; Guha, P. Impacts of climate change on the fate and behaviour of pesticides in surface and groundwater—A UK perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 369, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagnon, P.; Sheedy, C.; Rousseau, A.N.; Bourgeois, G.; Chouinard, G. Integrated assessment of climate change impact on surface runoff contamination by pesticides. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2016, 12, 559–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B. Climate Change and Pesticide Loss in Watershed Systems: A Simulation Modeling Study. J. Environ. Inform. 2007, 10, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marvin, H.J.; Kleter, G.A.; Noordam, M.Y.; Franz, E.; Willems, D.J.; Boxall, A. Proactive systems for early warning of potential impacts of natural disasters on food safety: Climate-change-induced extreme events as case in point. Food Control 2013, 34, 444–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennon, J.J. Potential impacts of climate change on agriculture and food safety within the island of Ireland. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 44, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staudinger, J.; Roberts, P.V. A critical compilation of Henry’s law constant temperature dependence relations for organic compounds in dilute aqueous solutions. Chemosphere 2001, 44, 561–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Cao, Y.; Tang, T.; Qian, K.; Chen, W.L.; Li, J. Biodegradation and chiral stability of fipronil in aerobic and flooded paddy soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 407, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xu, X.; Li, C.; Zhang, H.; Fu, Q.; Shao, X.; Ye, Q.; Li, Z. Degradation of chiral neonicotinoid insecticide cycloxaprid in flooded and anoxic soil. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, C.J. Soil erosion, climate change and global food security: Challenges and strategies. Sci. Prog. 2014, 97, 97–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sistla, S.A.; Moore, J.C.; Simpson, R.T.; Gough, L.; Shaver, G.R.; Schimel, J.P. Long-term warming restructures Arctic tundra without changing net soil carbon storage. Nature 2013, 497, 615–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| CGA128632 | 3-pyridinemethanol |  |
| CGA180777 (Nicotinic acid) | 3-pyridinecarboxylic acid |  |
| CGA180778 (Nicotinamide) | 3-pyridinecarboxamide |  |
| CGA313124 | 4,5-dihydro-6-hydroxymethyl-4-((3-pyridinylmethylene)amino)-1,2,4-triazine-3(2H)-one |  |
| U5/IA2 | 4,5-dihydro-6-carboxy-4-((3-pyridinyl methylene)- amino)-1,2,4-triazine-3(2H)-one |  |
| IA7 | 4,5-dihydro-6-methyl-4-(3-(1-methyl-6-oxo-1,6- dihydropyridinylmethylene)- amino)-1,2,4-triazine- 3(2H)-one |  |
| IA17 | hydroxylated 3-pyridinecarboxaldehyde |  |
| CGA259168 | N-(4,5-dihydro-6-methyl-3,5-dioxo-1,2,4-triazine-4(2H)-yl)-acetamide |  |
| CGA294849 | 4-amino-6-methyl-1,2,4-triazine-3,5(2H,4H)-dione |  |
| CGA96956 (Trigonelline) | 1-methyl-3-pyridinecarboxylic acid |  |
| GS23199 | 6-methyl-1,2,4-triazine-3,5(2H,4H)-dione |  |
| CGA359009 | 4,5-dihydro-5-hydroxy-6-methyl-4-((3-pyridinylmethylene)-amino)-1,2,4-triazine-3(2H)-one |  |
| CGA215525 | 4-amino-6-methyl-1,2,4-triazine-3(2H)-one |  |
| CGA300407 (Nicotinealdehyde) | 3-pyridinecarboxaldehyde |  |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tudi, M.; Yang, L.; Wang, L.; Lv, J.; Gu, L.; Li, H.; Peng, W.; Yu, Q.; Ruan, H.; Li, Q.; et al. Environmental and Human Health Hazards from Chlorpyrifos, Pymetrozine and Avermectin Application in China under a Climate Change Scenario: A Comprehensive Review. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1683. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13091683
Tudi M, Yang L, Wang L, Lv J, Gu L, Li H, Peng W, Yu Q, Ruan H, Li Q, et al. Environmental and Human Health Hazards from Chlorpyrifos, Pymetrozine and Avermectin Application in China under a Climate Change Scenario: A Comprehensive Review. Agriculture. 2023; 13(9):1683. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13091683
Chicago/Turabian StyleTudi, Muyesaier, Linsheng Yang, Li Wang, Jia Lv, Lijuan Gu, Hairong Li, Wei Peng, Qiming (Jimmy) Yu, Huada (Daniel) Ruan, Qin Li, and et al. 2023. "Environmental and Human Health Hazards from Chlorpyrifos, Pymetrozine and Avermectin Application in China under a Climate Change Scenario: A Comprehensive Review" Agriculture 13, no. 9: 1683. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13091683
APA StyleTudi, M., Yang, L., Wang, L., Lv, J., Gu, L., Li, H., Peng, W., Yu, Q., Ruan, H., Li, Q., Sadler, R., & Connell, D. (2023). Environmental and Human Health Hazards from Chlorpyrifos, Pymetrozine and Avermectin Application in China under a Climate Change Scenario: A Comprehensive Review. Agriculture, 13(9), 1683. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13091683







