Phosphate Fertilizer Type and Liming Affect the Growth and Phosphorus Uptake of Two Maize Cultivars
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
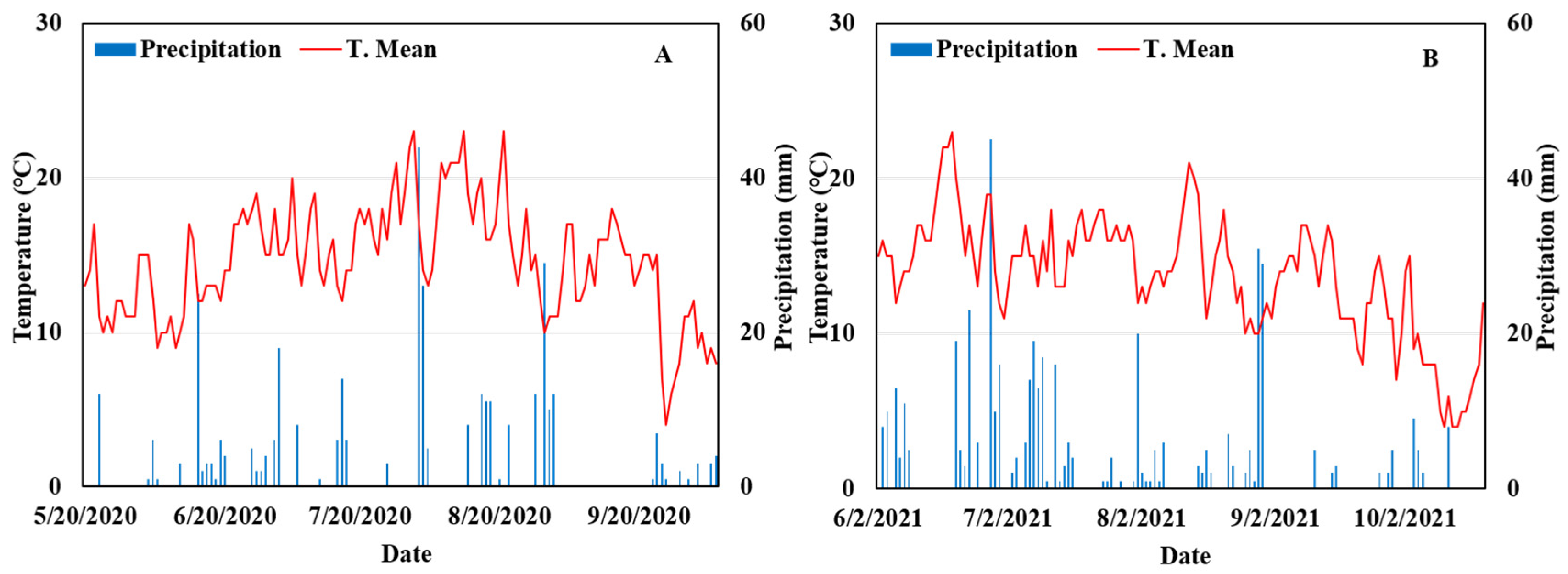
2.2. Field Experiments
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Leaf Area Index and Light Interception
3.2. Biomass Accumulation
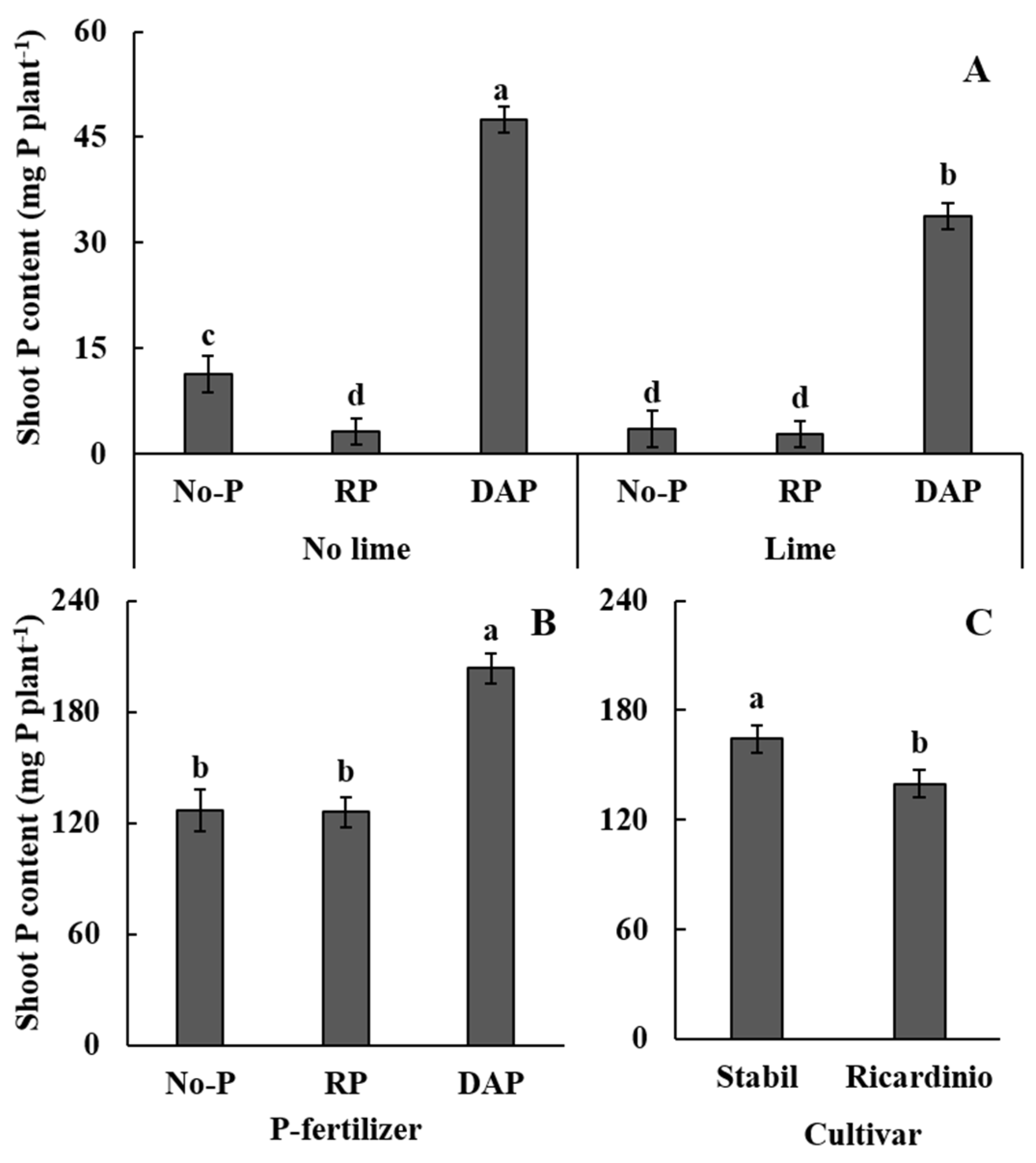
3.3. P Concentration, P Content, and PUE
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Phosphate Fertilizer Type on the Growth and P Uptake of Maize
4.2. Effect of Soil Liming on Growth and P Uptake of Maize
4.3. Maize Cultivar and PUE
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Colomb, B.; Kiniry, J.R.; Debaeke, P. Effect of soil phosphorus on leaf development and senescence dynamics of field-grown maize. Agron. J. 2000, 92, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzotsi, K.A.; Jones, J.W.; Adiku, S.G.K.; Naab, J.B.; Singh, U.; Porter, C.H.; Gijsman, A.J. Modeling soil and plant phosphorus within DSSAT. Ecol. Model. 2010, 221, 2839–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alewell, C.; Ringeval, B.; Ballabio, C.; Robinson, D.A.; Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P. Global phosphorus shortage will be aggravated by soil erosion. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, J.; Lombardi, R.; Boardman, D.; Carliell-Marquet, C. The future distribution and production of global phosphate rock reserves. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2011, 57, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, A.E.; Poulton, P.R.; Fixen, P.E.; Curtin, D. Phosphorus: Its efficient use in agriculture. Adv. Agron. 2014, 123, 177–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, M.K.; Musa, N.; Manzoor, M. Mineralization of soluble P fertilizers and insoluble rock phosphate in response to phosphate-solubilizing bacteria and poultry manure and their effect on the growth and P utilization efficiency of chilli (Capsicum annuum L.). Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 4607–4619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolland, M.; Barrow, N. Effect of level of application on the relative effectiveness of rock phosphate. Fertil. Res. 1988, 15, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.Q.; Meng, F.L.; Wang, G.H.; Hartmann, T.E.; Feng, G.; Wu, J.C.; Jiao, X.Q.; Zhang, F.S. Toward the sustainable use of mineral phosphorus fertilizers for crop production in China: From primary resource demand to final agricultural use. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 804, 150183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.H.; Hartmann, T.E.; Wang, X.H.; Cui, Z.L.; Hou, Y.; Meng, F.L.; Yu, X.C.; Wu, J.C.; Zhang, F.S. Phosphorus flow analysis in the maize based food-feed-energy systems in China. Environ. Res. 2020, 184, 109319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freiling, M.; von Tucher, S.; Schmidhalter, U. Factors influencing phosphorus placement and effects on yield and yield parameters: A meta-analysis. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 216, 105257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkebiwe, P.M.; Weinmann, M.; Bar-Tal, A.; Müller, T. Fertilizer placement to improve crop nutrient acquisition and yield: A review and meta-analysis. Field Crops Res. 2016, 196, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, J.; Rui, Y.; Zhang, F.; Rengel, Z.; Shen, J. Localized application of phosphorus and ammonium improves growth of maize seedlings by stimulating root proliferation and rhizosphere acidification. Field Crops Res. 2010, 119, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouten, M.; Meinel, T.; Kath-Petersen, W. Effects of precise fertilizer placement in corn. Landtechnik 2020, 75, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minasny, B.; Hong, S.Y.; Hartemink, A.E.; Kim, Y.H.; Kang, S.S. Soil pH increase under paddy in South Korea between 2000 and 2012. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 221, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, R.J. Effects of liming on phosphate availability in acid soils. Plant Soil 1982, 68, 289–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, J.E.; Bennett, A.E.; Newton, A.C.; White, P.J.; McKenzie, B.M.; George, T.S.; Pakeman, R.J.; Bailey, J.S.; Fornara, D.A.; Hayes, R.C. Liming impacts on soils, crops and biodiversity in the UK: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610–611, 316–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, R., Jr.; Quader, M.A.; Truog, E. Rock phosphate availability as influenced by soil pH. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1955, 19, 484–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.H.; Barber, S.A. Soil pH and phosphorus and potassium uptake by maize evaluated with an uptake model. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1990, 54, 1032–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, E.A.; Silva, U.C.; Marriel, I.E.; Oliveira, C.A.; Lana, U.G.P. Rock phosphate solubilizing microorganisms isolated from maize rhizosphere soil. Rev. Bras. Milho Sorgo 2014, 13, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.N.; Li, R.K.; Huang, Y.F.; Sun, X.M.; Qin, W.; Wei, F.F.; Ye, Y.L. Effects of various phosphorus fertilizers on maize yield and phosphorus uptake in soils with different pH values. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2022, 68, 1746–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrow, N.J. The effects of pH on phosphate uptake from the soil. Plant Soil 2017, 410, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buczko, U.; van Laak, M.; Eichler-Löbermann, B.; Gans, W.; Merbach, I.; Panten, K.; Peiter, E.; Reitz, T.; Spiegel, H.; von Tucher, S. Re-evaluation of the yield response to phosphorus fertilization based on meta-analyses of long-term field experiments. Ambio 2018, 47, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usuda, H.; Shimogawara, K. Phosphate deficiency in maize. I. leaf phosphate status, growth, photosynthesis and carbon Partitioning. Plant Cell Physiol. 1991, 32, 497–504. [Google Scholar]
- Timlin, D.J.; Naidu, T.C.M.; Fleisher, D.H.; Reddy, V.R. Quantitative effects of phosphorus on maize canopy photosynthesis and biomass. Crop Sci. 2017, 57, 3156–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; Mang, M.; Piepho, H.P.; Melchinger, A.; Ludewig, U. Decline of seedling phosphorus use efficiency in the heterotic pool of flint maize breeding lines since the onset of hybrid breeding. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2021, 207, 857–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; Quan, X.H.; Mang, M.; Neumann, G.; Melchinger, A.; Ludewig, U. Flint maize root mycorrhization and organic acid exudates under phosphorus deficiency: Trends in breeding lines and doubled haploid lines from landraces. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2021, 184, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciarelli, D.M.; Furlani, A.M.C.; Dechen, A.R.; Lima, M. Genetic variation among maize genotypes for phosphorus-uptake and phosphorus-use efficiency in nutrient solution. J. Plant Nutr. 1998, 21, 2219–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.M.; Guo, Z.H.; He, L.Y.; Li, J.S. Identification of maize genotypes with high tolerance or sensitivity to phosphorus deficiency. J. Plant Nutr. 2011, 34, 1290–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiß, T.M.; Leiser, W.L.; Reineke, A.J.; Li, D.D.; Liu, W.X.; Hahn, V.; Würschum, T. Optimizing the P balance: How do modern maize hybrids react to different starter fertilizers? PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.D.; Chen, Z.; Wang, M.; Leiser, W.L.; Weiß, T.M.; Zhao, Z.; Cheng, S.; Chen, S.J.; Chen, F.J.; Yuan, L.X.; et al. Dissecting the phenotypic response of maize to low phosphorus soils by field screening of a large diversity panel. Euphytica 2021, 217, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesler, F.; Appel, T.; Dittert, K.; Ebertseder, T.; Müller, T.; Nätscher, L.; Olfs, H.W.; Rex, M.; Schweitzer, K.; Steffens, D.; et al. Phosphordüngung nach Bodenuntersuchung und Pflanzenbedarf. Standpunkt des VDLUFA 2018, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Nguy-Robertson, A.L.; Gitelson, A.A. Algorithms for estimating green leaf area index in C3 and C4 crops for MODIS, Landsat TM/ETM+, MERIS, Sentinel MSI/OLCI, and Venµs sensors. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 6, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.W.; Wang, D.L.; Zhou, J.; Du, Y.; Luo, M.; Zhang, Y.J.; Guo, W.S. Remotely assessing fraction of photosynthetically active radiation (FPAR) for wheat canopies based on hyperspectral vegetation indexes. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piepho, H.P. A SAS macro for generating letter displays of pairwise mean comparisons. Commun. Biometry Crop Sci. 2012, 7, 4–13. [Google Scholar]
- Graffitti, M.S.; Umburanas, R.C.; Fontana, D.C.; Pilau, F.G.; Reichardt, K.; Dourado Neto, D. Performance of maize hybrids as a function of spatial arrangements during second growth season under irrigation. Bragantia 2021, 80, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, X.X.; Liu, Y.M.; Liu, D.Y.; Du, Y.F.; Chen, X.P.; Zou, C.Q. The role of phosphorus supply in maximizing the leaf area, photosynthetic rate, coordinated to grain yield of summer maize. Field Crops Res. 2018, 219, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.W.; Klein, J.; Hartmann, T.E.; Nkebiwe, P.M.; Yang, H.Y.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X.P.; Müller, T. Producing superphosphate with sewage sludge ash: Assessment of phosphorus availability and potential Toxic Element Contamination. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Reddy, M.S. Effects of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria, rock phosphate and chemical fertilizers on maize-wheat cropping cycle and economics. Pedosphere 2015, 25, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qarni, A.; Billah, M.; Hussain, K.; Shah, S.H.; Ahmed, W.; Alam, S.; Sheikh, A.A.; Jafri, L.; Munir, A.; Malik, K.M.; et al. Isolation and Characterization of Phosphate Solubilizing Microbes from Rock Phosphate Mines and Their Potential Effect for Sustainable Agriculture. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, W.D.; Cleveland, C.C.; Halada, Ĺ.; Hreško, J.; Baron, J.S. Negative impact of nitrogen deposition on soil buffering capacity. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 767–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.G.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Cai, J.P.; Zhu, P.; Gao, H.J.; Jiang, Y. Variation in available micronutrients in black soil after 30-year fertilization treatment. Plant Soil Environ. 2014, 60, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.E.; Gaudin, A.C.M. What is the agronomic potential of biofertilizers for maize? A meta-analysis. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2018, 94, fiy094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ström, L.; Owen, A.; Godbold, D.; Jones, D. Organic acid mediated P mobilization in the rhizosphere and uptake by maize roots. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2002, 34, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfaye, F.; Liu, X.; Zheng, J.; Cheng, K.; Bian, R.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Drosos, M.; Joseph, S.; Pan, G. Could biochar amendment be a tool to improve soil availability and plant uptake of phosphorus? A meta-analysis of published experiments. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 34108–34120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrow, N.J.; Hartemink, A.E. The effects of pH on nutrient availability depend on both soils and plants. Plant Soil 2023, 487, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemu, E.; Selassie, Y.G.; Yitaferu, B. Effect of lime on selected soil chemical properties, maize (Zea mays L.) yield and determination of rate and method of its application in Northwestern Ethiopia. Heliyon 2022, 8, e08657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opala, P.A. Influence of lime and phosphorus application rates on growth of maize in an acid soil. Adv. Agric. 2017, 2017, 7083206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Cho, C.M.; Racz, G.J.; Chang, C. Chemical retardation of phosphate diffusion in an acid soil as affected by liming. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2002, 64, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, J. Root architecture and plant productivity. Plant Physiol. 1995, 109, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Year | Depth | Clay | Silt | Sand | Bulk Density | pH | Nmin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cm | % | % | % | g cm−3 | kg N ha−1 | ||
| 2020 | 0–30 | 32.6 | 60.9 | 6.5 | 1.3 | 5.3 | 23.4 |
| 30–60 | 35.3 | 59.3 | 5.4 | 1.3 | 5.5 | 13.1 | |
| 60–90 | 34.9 | 54.5 | 10.6 | 1.4 | 6.0 | 29.9 | |
| 2021 | 0–30 | - | - | - | - | 4.7 | 23.9 |
| 30–60 | - | - | - | - | 4.8 | 21.3 | |
| 60–90 | - | - | - | - | 4.3 | 33.4 |
| Trait | Shoot Biomass at Six-Leaf Stage | Silage Yield at Harvest | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit | kg DM ha−1 | |||
| Year | 2020 | 2021 | 2020 | 2021 |
| Pf | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Cul | ns | 0.035 | ns | <0.001 |
| Lime | ns | 0.002 | ns | <0.001 |
| Pf × Cul | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| Pf × Lime | ns | 0.033 | ns | 0.002 |
| Cul × Lime | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| Pf × Cul × Lime | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| Six-Leaf Stage | Harvest | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trait | P Concentration | P Content | PUE | P Concentration | P Content | PUE | ||||
| Unit | g P kg−1 | mg P Plant−1 | % | g P kg−1 | mg P Plant−1 | % | ||||
| Year | 2020 | 2021 | 2020 | 2021 | 2021 | 2020 | 2021 | 2020 | 2021 | 2021 |
| Pf | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ns | ns | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Cul | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | 0.025 | 0.016 |
| Lime | ns | ns | ns | <0.001 | 0.003 | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| Pf × Cul | ns | ns | ns | ns | 0.003 | ns | ns | 0.010 | ns | ns |
| Pf × Lime | ns | ns | ns | 0.004 | 0.018 | ns | ns | 0.026 | ns | ns |
| Cul × Lime | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| Pf × Cul × Lime | ns | ns | ns | ns | 0.004 | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| P Fertilizer | P Concentration | |
|---|---|---|
| g P kg−1 | ||
| 2020 | 2021 | |
| No-P | - | 2.15 b |
| RP | 2.53 b | 2.05 b |
| DAP | 3.37 a | 4.11 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ning, F.; Nkebiwe, P.M.; Hartung, J.; Munz, S.; Huang, S.; Zhou, S.; Graeff-Hönninger, S. Phosphate Fertilizer Type and Liming Affect the Growth and Phosphorus Uptake of Two Maize Cultivars. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1771. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13091771
Ning F, Nkebiwe PM, Hartung J, Munz S, Huang S, Zhou S, Graeff-Hönninger S. Phosphate Fertilizer Type and Liming Affect the Growth and Phosphorus Uptake of Two Maize Cultivars. Agriculture. 2023; 13(9):1771. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13091771
Chicago/Turabian StyleNing, Fangfang, Peteh Mehdi Nkebiwe, Jens Hartung, Sebastian Munz, Shoubing Huang, Shunli Zhou, and Simone Graeff-Hönninger. 2023. "Phosphate Fertilizer Type and Liming Affect the Growth and Phosphorus Uptake of Two Maize Cultivars" Agriculture 13, no. 9: 1771. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13091771
APA StyleNing, F., Nkebiwe, P. M., Hartung, J., Munz, S., Huang, S., Zhou, S., & Graeff-Hönninger, S. (2023). Phosphate Fertilizer Type and Liming Affect the Growth and Phosphorus Uptake of Two Maize Cultivars. Agriculture, 13(9), 1771. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13091771






