Effects of Tillage Depth and Lime Application on Acidification Reduction and Nutrient Availability in Vertisol Soil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site and Sampling Description
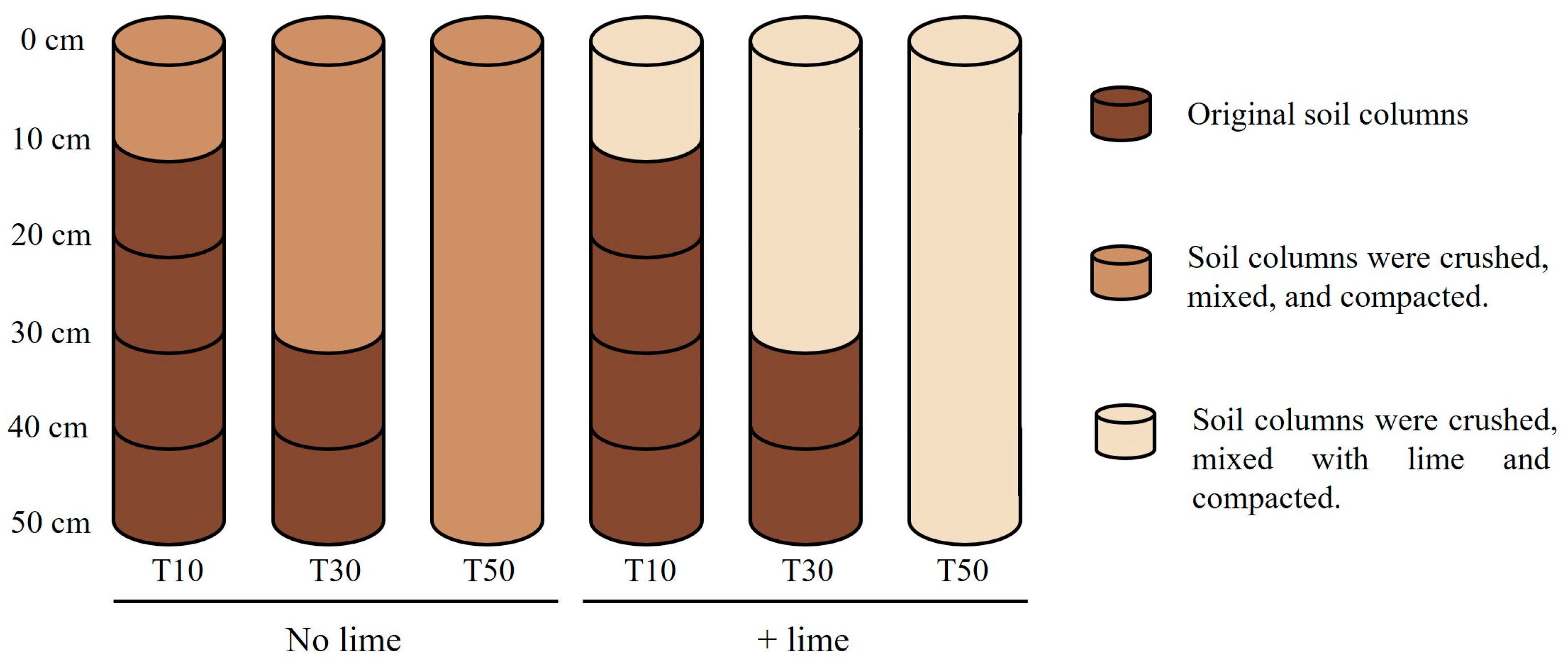
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Soil Sample Collection
2.4. Measurement of Soil Parameters
2.5. PLFA Extraction and Analysis
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
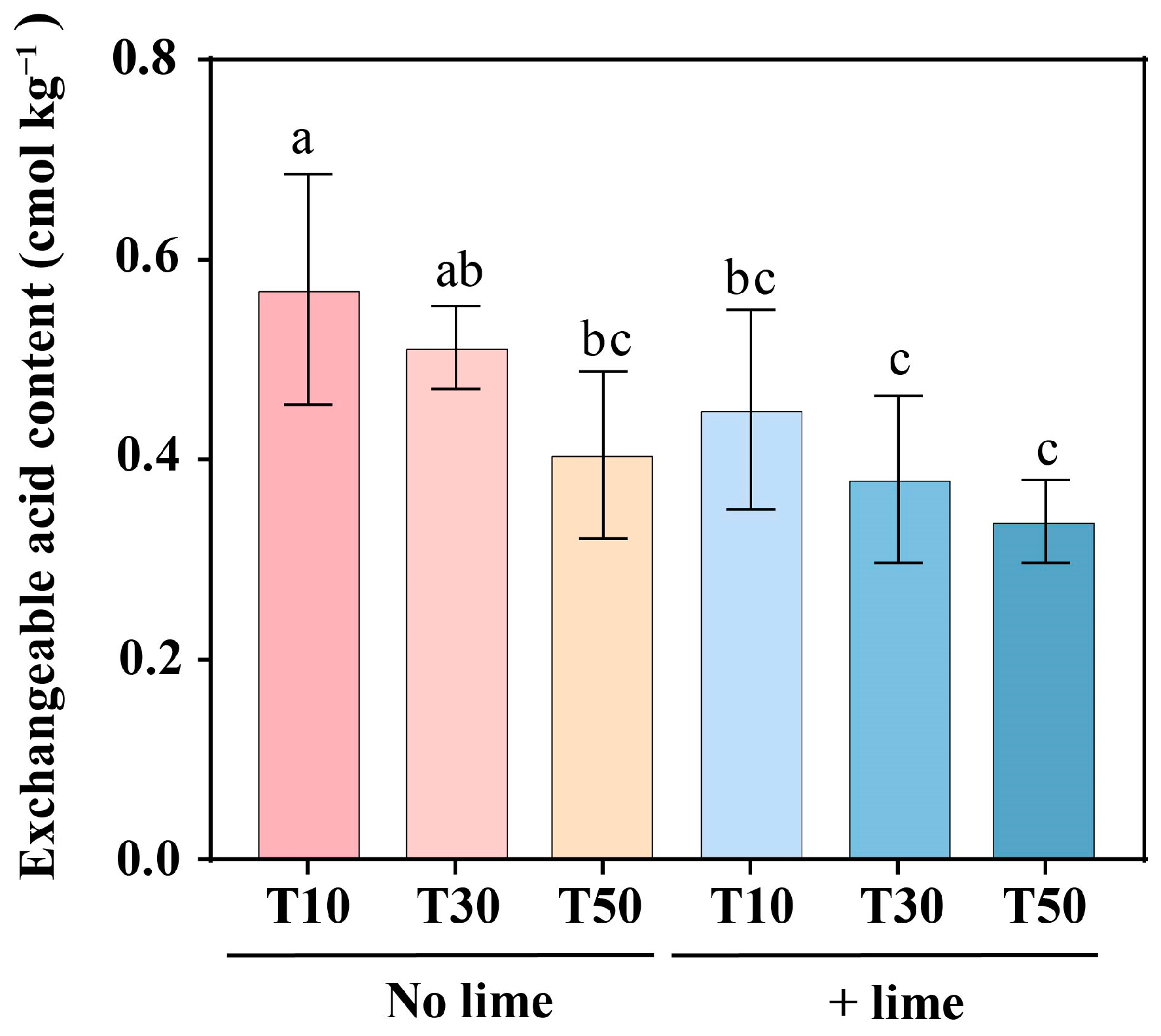
3.1. Effects of Tillage and Lime Addition on the pH and Soil Exchangeable Acidity of the Topsoil (0–20 cm)
3.2. Effects of Tillage and Lime Addition on the Soil Available N and P
3.2.1. Effects of Tillage and Lime Addition on NH4+-N Content (0–20 cm) and Accumulation (0–50 cm)
3.2.2. Effects of Tillage and Lime Addition on NO3−-N Content (0–20 cm) and Accumulation (0–50 cm)
3.2.3. Effects of Tillage and Lime Addition on AP Content (0–20 cm) and Accumulation (0–50 cm)
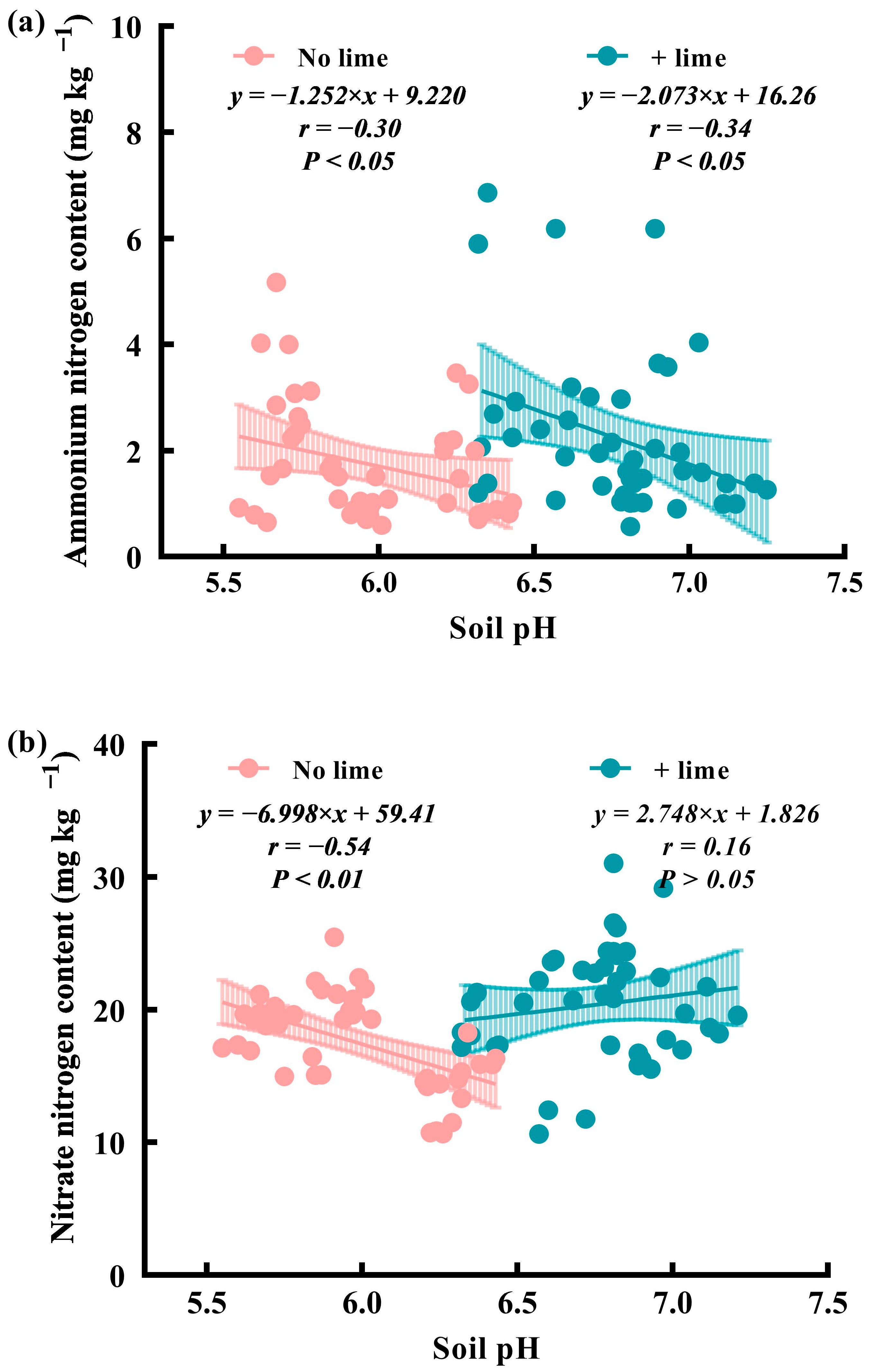
3.3. The Relationship between Available Soil N and P and Soil pH
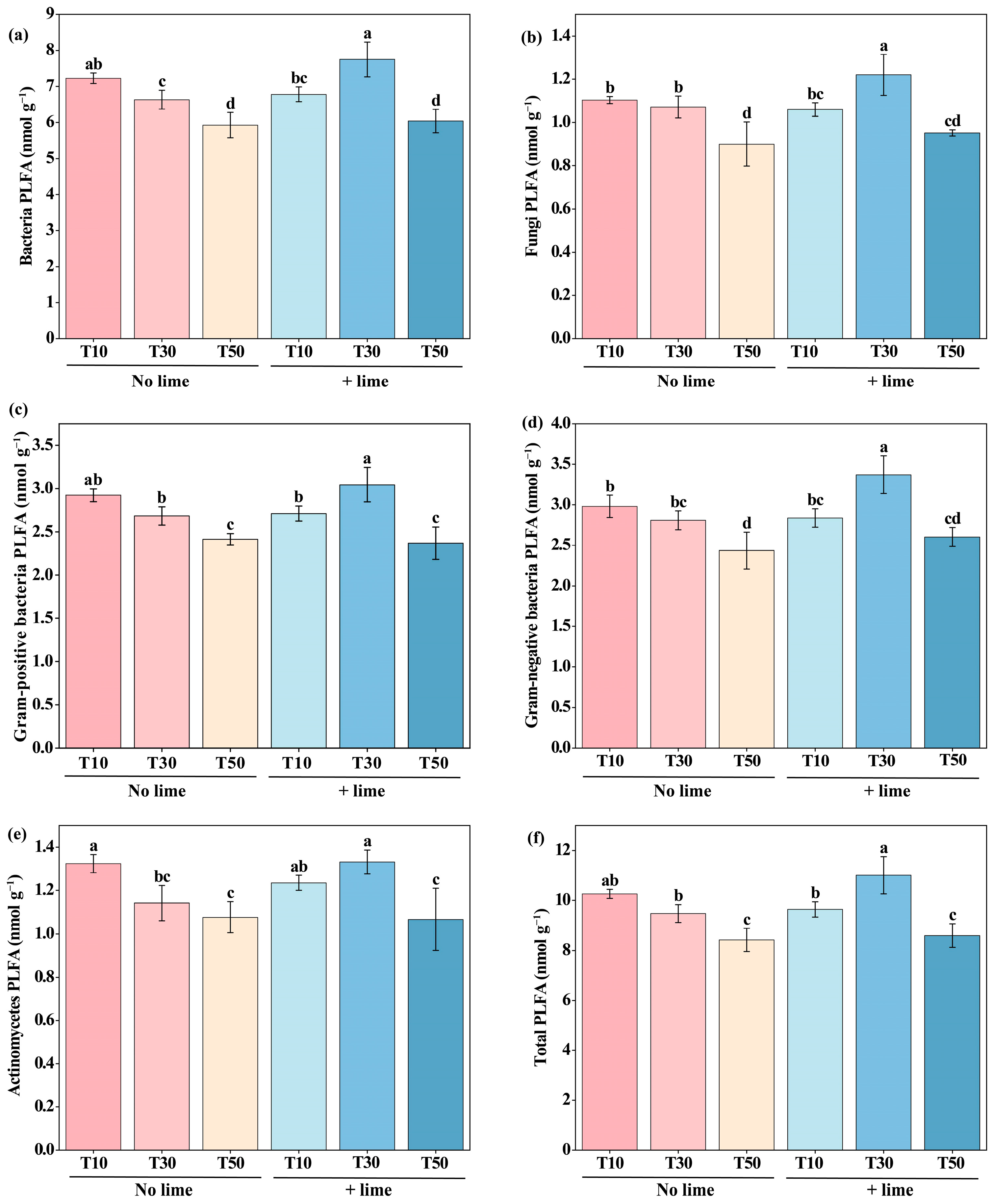
3.4. Effects of Tillage and Lime Addition on Topsoil (0–20 cm) Microbial Community Structure and Diversity
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Tillage and Lime Addition on the Soil Acidity
4.2. Effects of Tillage and Lime on the Available N and P
4.3. Effects of Tillage and Lime on Soil Microbial Community
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yadav, D.S.; Jaiswal, B.; Gautam, M.; Agrawal, M. Soil Acidification and Its Impact on Plants. In Plant Responses to Soil Pollution; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.H.; Liu, X.J.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.L.; Han, W.X.; Zhang, W.F.; Christie, P.; Goulding, K.W.T.; Vitousek, P.M.; Zhang, F.S. Significant Acidification in Major Chinese Croplands. Science 2010, 327, 1008–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, T.; Zhu, Q.; Zeng, M.; Shen, J.; Shi, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, F.; de Vries, W. Quantification of the Contribution of Nitrogen Fertilization and Crop Harvesting to Soil Acidification in a Wheat-Maize Double Cropping System. Plant Soil 2019, 434, 167–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, T.; Liu, X.; Zhu, Q.; Zeng, M.; Chen, X.; Yang, L.; Shen, J.; Shi, X.; Zhang, F.; de Vries, W. Quantifying Drivers of Soil Acidification in Three Chinese Cropping Systems. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 215, 105230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Sun, X.; Sun, Y.; Yan, J.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, J. Soil Acidification and Factors Controlling Topsoil PH Shift of Cropland in Central China from 2008 to 2018. Geoderma 2022, 408, 115586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; de Vries, W.; Liu, X.; Hao, T.; Zeng, M.; Shen, J.; Zhang, F. Enhanced Acidification in Chinese Croplands as Derived from Element Budgets in the Period 1980–2010. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 1497–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, Q.; Fang, H.; Zhao, B.; Ran, M.; Song, L.; Xue, J.; Tao, Q.; et al. The Driving Factors and Buffering Mechanism Regulating Cropland Soil Acidification across the Sichuan Basin of China. CATENA 2023, 220, 106688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Baquy, M.A.-A.; Guan, P.; Yan, J.; Wang, R.; Xu, R.; Xie, L. Effect of Soil Acidification on the Growth and Nitrogen Use Efficiency of Maize in Ultisols. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 1435–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaswar, M.; Dongchu, L.; Jing, H.; Tianfu, H.; Ahmed, W.; Abbas, M.; Lu, Z.; Jiangxue, D.; Khan, Z.H.; Ullah, S.; et al. Interaction of Liming and Long-Term Fertilization Increased Crop Yield and Phosphorus Use Efficiency (PUE) through Mediating Exchangeable Cations in Acidic Soil under Wheat–Maize Cropping System. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Tan, J.; Wang, Y.; Qin, Y.; He, H.; Wu, H.; Zuo, W.; He, D. Responses of the Rhizosphere Bacterial Community in Acidic Crop Soil to PH: Changes in Diversity, Composition, Interaction, and Function. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 700, 134418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Lu, H.; Nkoh, J.N.; Hong, Z.; Xu, R. Aluminum Mobilization as Influenced by Soil Organic Matter during Soil and Mineral Acidification: A Constant PH Study. Geoderma 2022, 418, 115853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.K.; Zhang, Z.B.; Jiang, F.H.; Guo, Z.C.; Peng, X.H. Evaluating Soil Physical Quality Indicators of a Vertisol as Affected by Different Tillage Practices under Wheat-Maize System in the North China Plain. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 209, 104970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.J.; Li, P.P.; Wen, Q.; Huang, K.M.; Wang, M.Y.; Xu, H.; Hua, D.L.; Han, Y.L. Characteristics of Acidification and the Distribution of Available Phosphorus along Soil Depths in Heavy Clay Soils in Southern Henan Province, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2022, 33, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Guo, H.; Wang, L.; Cheng, D. Suitable Tillage Depth Promotes Maize Yields by Changing Soil Physical and Chemical Properties in A 3-Year Experiment in the North China Plain. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, J.E.; Bennett, A.E.; Newton, A.C.; White, P.J.; McKenzie, B.M.; George, T.S.; Pakeman, R.J.; Bailey, J.S.; Fornara, D.A.; Hayes, R.C. Liming Impacts on Soils, Crops and Biodiversity in the UK: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610–611, 316–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Luan, L.; Luo, Y.; Fan, J.; Xu, Q.; Sun, B.; Jiang, Y. Biochar and Lime Amendments Promote Soil Nitrification and Nitrogen Use Efficiency by Differentially Mediating Ammonia-Oxidizer Community in an Acidic Soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 180, 104619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Talukder, M.M.H.; Hoque, M.A.; Uddin, S.; Hoque, T.S.; Rea, R.S.; Alorabi, M.; Gaber, A.; Kasim, S. Lime and Manure Amendment Improve Soil Fertility, Productivity and Nutrient Uptake of Rice-Mustard-Rice Cropping Pattern in an Acidic Terrace Soil. Agriculture 2021, 11, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, A.; Ding, L.; Tang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Duan, G. Microbial Response to CaCO3 Application in an Acid Soil in Southern China. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 79, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Ji, X.; Chao, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, J.; Peng, H. Effects of Increasing Lime Application Rates on Microbial Diversity and Community Structure in Paddy Soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 161, 103837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cui, S.; Chang, S.X.; Zhang, Q. Liming Effects on Soil PH and Crop Yield Depend on Lime Material Type, Application Method and Rate, and Crop Species: A Global Meta-Analysis. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 1393–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gascho, G.J.; Parker, M.B. Long-Term Liming Effects on Coastal Plain Soils and Crops. Agron. J. 2001, 93, 1305–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Pan, W.L.; Carter, P.; Wang, K. Addition of Lignin to Lime Materials for Expedited PH Increase and Improved Vertical Mobility of Lime in No-till Soils. Soil Use Manag. 2019, 35, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellissier, J.P.; Swanepoel, P.A.; Hardie, A.G.; Labuschagne, J. Strategies to Alleviate PH Stratification and Subsurface Acidity in a No-Tillage System. Agron. J. 2024, 116, 777–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frostegård, Å.; Bååth, E.; Tunlio, A. Shifts in the Structure of Soil Microbial Communities in Limed Forests as Revealed by Phospholipid Fatty Acid Analysis. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1993, 25, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Sun, J.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H. Changes in the soil microbial Phospholipid Fatty Acid Profile with depth in three soil types of paddy fields in China. Geoderma 2017, 290, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources. In International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps, 4th ed.; International Union of Soil Sciences (IUSS): Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Q.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.X.; Liu, G.B.; Zhang, C. Effects of different meadow use types on the fractal characteristics of soil particle in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 1716–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaffar, M.; Zong, Y.; Lu, S.; Ghulam, H.A.; Shafaqat, A.; Muhammad, I.K.; Muhammad, K.; Moazzam, J.; Mohammad, A.W.; Muhammad, R. Effect of Biochar and Quicklime on Growth of Wheat and Physicochemical Properties of Ultisols. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, S.R.; Sommers, L.E. Phosphorus. In Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 2. Chemical and Microbiological Properties; SSSA: Madison, MI, USA, 1982; Volume 9, pp. 403–430. [Google Scholar]
- Han, C.; Chen, L.; Xin, X.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, C.; Ma, D.; Li, Y.; Ma, L.; Zhang, J. Long-Term Fertilization Affects Microbial Necromass Accumulation by Regulating Nutrient and Enzymatic Stoichiometry in a Calcareous Fluvisol. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 194, 105169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossio, D.A.; Scow, K.M.; Gunapala, N.; Graham, K.J. Determinants of Soil Microbial Communities: Effects of Agricultural Management, Season, and Soil Type on Phospholipid Fatty Acid Profiles. Microb. Ecol. 1998, 36, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niroshika, K.; Zhou, Y.; An, Z.; Cai, Y.; Chang, X. Science of the Total Environment Microplastics Affect the Ecological Stoichiometry of Plant, Soil and Microbes in a Greenhouse Vegetable System. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 924, 171602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Sun, S.; Xing, F.; Mu, X.; Bai, Y. Nitrogen Addition Interacted with Salinity-Alkalinity to Modify Plant Diversity, Microbial PLFAs and Soil Coupled Elements: A 5-Year Experiment. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 137, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, J. Effects of Tillage Method on Soil Physical Properties, Infiltration and Yield in an Olive Orchard. Soil Tillage Res. 1999, 52, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, F.; Don, A.; Hennings, I.; Schmittmann, O.; Seidel, S.J. The Effect of Deep Tillage on Crop Yield—What Do We Really Know? Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 174, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auler, A.C.; Pires, L.F.; dos Santos, J.A.B.; Caires, E.F.; Borges, J.A.R.; Giarola, N.F.B. Effects of Surface-Applied and Soil-Incorporated Lime on Some Physical Attributes of a Dystrudept Soil. Soil Use Manag. 2017, 33, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakwoya, M.B.; Woldeyohannis, W.H.; Yimamu, F.K. Effects of Minimum Tillage and Liming on Maize (Zea mays L.) Yield Components and Selected Properties of Acid Soils in Assosa Zone, West Ethiopia. J. Agric. Food Res. 2022, 8, 100301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzluebbers, A.J.; Schomberg, H.H.; Endale, D.M. Surface-Soil Responses to Paraplowing of Long-Term No-Tillage Cropland in the Southern Piedmont USA. Soil Tillage Res. 2007, 96, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tan, C.; Wang, R.; Li, J.; Wang, X. Conservation Tillage Rotation Enhanced Soil Structure and Soil Nutrients in Long-Term Dryland Agriculture. Eur. J. Agron. 2021, 131, 126379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Gong, L.; Yang, L.; He, S.; Liu, X. Dynamics in C, N, and P Stoichiometry and Microbial Biomass Following Soil Depth and Vegetation Types in Low Mountain and Hill Region of China. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Zhu, C.; Jiang, G.; Yang, J.; Zhu, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, R.; Liu, F.; Jie, X.; Liu, S. Differentiation in Nitrogen Transformations and Crop Yield as Affected by Tillage Modes in a Fluvo-Aquic Soil. Plants 2023, 12, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Hu, Y.; Wang, T.; Yuan, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, Q.; Ge, T.; Wu, J. Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Biologically-based Phosphorus Fractions in the Farmland Soil. Environ. Sci. 2017, 38, 1606–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Cerozi, B.; Fitzsimmons, K. The Effect of PH on Phosphorus Availability and Speciation in an Aquaponics Nutrient Solution. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 219, 778–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Ma, W.; Zhang, X.; Ping, J.; Yan, X.; Liu, J.; Yuan, J.; Wang, L.; Ren, J. Effect of Subsoil Tillage Depth on Nutrient Accumulation, Root Distribution, and Grain Yield in Spring Maize. Crop J. 2014, 2, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Islam, M.U.; Jiang, F. The Effect of Deep-Tillage Depths on Crop Yield: A Global Meta-Analysis. Plant Soil Environ. 2023, 69, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, R.; Zhu, C.; Jiang, G.; Yang, J.; Zhu, X.; Li, L.; Shen, F.; Jie, X.; Liu, S. Variations in Soil Nitrogen Availability and Crop Yields under a Three-Year Annual Wheat and Maize Rotation in a Fluvo-Aquic Soil. Plants 2023, 12, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejigu, W.; Selassie, Y.G.; Elias, E.; Molla, E. Effect of Lime Rates and Method of Application on Soil Properties of Acidic Luvisols and Wheat (Triticum aestivum, L.) Yields in Northwest Ethiopia. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Liu, H.; Wang, T.; Gong, P.; Li, P.; Li, L.; Bai, Z. Deep Vertical Rotary Tillage Depths Improved Soil Conditions and Cotton Yield for Saline Farmland in South Xinjiang. Eur. J. Agron. 2024, 156, 127166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Zheng, B.; Liu, Y.; Peng, S.; Gong, J.; Li, J.; Qin, T.; Liang, J.; Xiong, K.; Shao, L.; et al. Deep Tillage Enhances the Spatial Homogenization of Bacterial Communities by Reducing Deep Soil Compaction. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 239, 106062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, B.; Hu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Mu, X.; Liu, K.; Li, C. Effects of Deep Tillage and Straw Returning on Soil Microorganism and Enzyme Activities. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 451493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Yu, W.; Dutta, S.; Gao, H. Geoderma Soil Microbial Community Composition and Function Are Closely Associated with Soil Organic Matter Chemistry along a Latitudinal Gradient. Geoderma 2021, 383, 114744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, L.; Kate, A.M.; Sharon, A.E.; Warren, J.; Podrebarac, F.A.; Ziegler, S.E. Microbial Inputs at the Litter Layer Translate Climate into Altered Organic Matter Properties. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2021, 27, 435–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Shao, Y.; Zou, X.; Liu, T.; Zhou, L.; Wan, S.; Rao, X.; Li, Z.; et al. Invariant Community Structure of Soil Bacteria in Subtropical Coniferous and Broadleaved Forests. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Depths | pH | NH4+-N (mg kg−1) | NO3−-N (mg kg−1) | TN (g kg−1) | AP (mg kg−1) | SOM (mg kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–10 cm | 5.41 ± 0.18 d | 3.37 ± 1.96 a | 6.14 ± 1.73 a | 1.20 ± 0.10 a | 19.67 ± 3.98 a | 30.67 ± 2.06 a |
| >10–20 cm | 5.86 ± 0.10 c | 4.93 ± 1.60 a | 5.62 ± 2.50 ab | 0.90 ± 0.20 b | 17.06 ± 2.30 a | 24.29 ± 0.98 b |
| >20–30 cm | 5.92 ± 0.08 c | 4.30 ± 1.28 a | 4.10 ± 1.82 abc | 0.72 ± 0.03 bc | 17.26 ± 6.45 a | 14.84 ± 1.18 c |
| >30–40 cm | 6.85 ± 0.20 b | 5.27 ± 1.52 a | 2.55 ± 1.46 bc | 0.51 ± 0.08 cd | 8.61 ± 2.95 b | 10.31 ± 0.90 d |
| >40–50 cm | 7.18 ± 0.22 a | 4.13 ± 1.04 a | 1.78 ± 0.29 c | 0.49 ± 0.11 d | 4.46 ± 0.89 b | 9.21 ± 1.50 d |
| Treatment | 7 Days | 14 Days | 21 Days | 28 Days | 35 Days |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T10 | 5.60 ± 0.05 e | 5.65 ± 0.03 f | 5.69 ± 0.04 d | 5.95 ± 0.09 d | 5.93 ± 0.06 d |
| T30 | 5.81 ± 0.06 d | 5.74 ± 0.04 e | 5.78 ± 0.08 d | 5.97 ± 0.06 d | 5.95 ± 0.03 d |
| T50 | 6.24 ± 0.02 c | 6.25 ± 0.05 d | 6.24 ± 0.06 c | 6.39 ± 0.06 c | 6.35 ± 0.03 c |
| T10+Lime | 6.33 ± 0.02 bc | 6.39 ± 0.05 c | 6.73 ± 0.21 b | 6.81 ± 0.01 b | 6.82 ± 0.03 b |
| T30+Lime | 6.52 ± 0.25 ab | 6.59 ± 0.08 b | 6.75 ± 0.04 b | 6.85 ± 0.10 b | 6.83 ± 0.02 b |
| T50+Lime | 6.63 ± 0.08 a | 6.91 ± 0.02 a | 6.97 ± 0.07 a | 7.17 ± 0.07 a | 7.12 ± 0.09 a |
| Factor means | For incubation time: 7 days = 6.19; 14 days = 6.25; 21 days = 6.36; 28 days = 6.52; 35 days = 6.50 | ||||
| For lime application: Unlimed soils = 5.97; Limed soils = 6.76 | |||||
| For soil depth: T10 = 5.76; T30 = 5.85; T50 = 6.29 | |||||
| Incubation time (T) | 0.000 *** | ||||
| Lime application (L) | 0.000 *** | ||||
| Tillage depth (D) | 0.000 *** | ||||
| T×L | 0.000 *** | ||||
| T×D | 0.024 * | ||||
| L×D | 0.000 *** | ||||
| T×L×D | 0.288 | ||||
| Treatment | 7 Days | 14 Days | 21 Days | 28 Days | 35 Days |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T10 | 0.79 ± 0.14 b | 4.02 ± 1.16 a | 1.84 ± 0.41 a | 1.23 ± 0.55 a | 1.06 ± 0.03 bc |
| T30 | 1.96 ± 0.45 ab | 3.40 ± 0.52 a | 2.13 ± 0.57 a | 0.96 ± 0.11 a | 0.76 ± 0.05 d |
| T50 | 1.57 ± 0.60 ab | 4.52 ± 2.01 a | 2.06 ± 0.10 a | 0.88 ± 0.12 a | 0.81 ± 0.09 cd |
| T10+Lime | 1.55 ± 0.46 ab | 4.16 ± 2.34 a | 2.58 ± 0.61 a | 1.33 ± 0.67 a | 1.19 ± 0.18 ab |
| T30+Lime | 3.26 ± 2.31 a | 3.87 ± 2.03 a | 2.36 ± 0.54 a | 0.99 ± 0.07 a | 1.33 ± 0.26 ab |
| T50+Lime | 1.43 ± 0.42 ab | 4.47 ± 1.49 a | 2.57 ± 1.29 a | 1.09 ± 0.16 a | 1.46 ± 0.12 a |
| Factor means | For incubation time: 7 days = 1.76; 14 days = 4.07; 21 days = 2.26; 28 days = 1.08; 35 days = 1.1 | ||||
| For lime application: Unlimed soils = 1.87; Limed soils = 2.24 | |||||
| For soil depth: T10 = 1.98; T30 = 2.10; T50 = 2.09 | |||||
| Incubation time (T) | 0.000 *** | ||||
| Lime application (L) | 0.068 | ||||
| Tillage depth (D) | 0.856 | ||||
| T×L | 0.916 | ||||
| T×D | 0.289 | ||||
| L×D | 0.850 | ||||
| T×L×D | 0.976 | ||||
| Treatment | 7 Days | 14 Days | 21 Days | 28 Days | 35 Days |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T10 | 17.14 ± 0.21 b | 20.19 ± 0.82 a | 19.00 ± 0.25 c | 22.04 ± 0.41 b | 20.25 ± 1.15 b |
| T30 | 15.52 ± 0.82 c | 19.53 ± 0.43 a | 18.25 ± 2.75 c | 20.05 ± 1.00 b | 22.05 ± 2.98 ab |
| T50 | 10.75 ± 0.11 d | 13.52 ± 1.74 c | 14.63 ± 0.33 d | 15.19 ± 1.62 c | 16.51 ± 1.56 c |
| T10+Lime | 18.20 ± 0.11 a | 19.75 ± 2.11 a | 25.51 ± 3.16 a | 26.49 ± 3.94 a | 23.60 ± 1.31 a |
| T30+Lime | 17.25 ± 0.07 b | 21.14 ± 0.91 a | 22.27 ± 0.99 b | 22.16 ± 1.18 b | 25.19 ± 2.00 a |
| T50+Lime | 11.62 ± 0.92 d | 15.87 ± 0.36 b | 17.16 ± 0.52 cd | 19.37 ± 2.04 b | 19.33 ± 0.58 bc |
| Factor means | For incubation time: 7 days = 15.08; 14 days = 18.33; 21 days = 19.47; 28 days = 20.88; 35 days = 21.15 | ||||
| For lime application: Unlimed soils = 17.64; Limed soils = 20.33 | |||||
| For soil depth: T10 = 21.22; T30 = 20.34; T50 = 15.40 | |||||
| Incubation time (T) | 0.000 *** | ||||
| Lime application (L) | 0.000 *** | ||||
| Tillage depth (D) | 0.000 *** | ||||
| T×L | 0.008 ** | ||||
| T×D | 0.028 * | ||||
| L×D | 0.811 | ||||
| T×L×D | 0.324 | ||||
| Treatment | 7 Days | 14 Days | 21 Days | 28 Days | 35 Days |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T10 | 15.20 ± 1.86 b | 16.71 ± 3.86 b | 13.85 ± 0.75 bc | 20.44 ± 3.90 a | 21.75 ± 0.77 a |
| T30 | 12.39 ± 0.74 b | 22.85 ± 1.08 b | 12.58 ± 2.77 bc | 15.49 ± 0.53 b | 20.49 ± 0.80 a |
| T50 | 19.97 ± 0.81 a | 9.44 ± 1.61 c | 10.92 ± 1.26 c | 21.91 ± 2.07 a | 15.27 ± 1.66 b |
| T10+Lime | 20.73 ± 3.75 a | 34.43 ± 1.14 a | 20.58 ± 3.89 a | 20.85 ± 3.51 a | 20.24 ± 0.25 a |
| T30+Lime | 19.45 ± 2.07 a | 22.07 ± 3.99 b | 16.77 ± 3.48 ab | 21.3 ± 1.61 a | 21.08 ± 0.60 a |
| T50+Lime | 12.13 ± 0.11 b | 35.95 ± 5.49 a | 20.44 ± 1.33 a | 18.78 ± 2.35 ab | 16.62 ± 1.46 b |
| Factor means | For incubation time: 7 days = 16.65; 14 days = 22.62; 21 days = 16.58; 28 days = 20.04; 35 days = 19.01 | ||||
| For lime application: Unlimed soils = 16.62; Limed soils = 21.43 | |||||
| For soil depth: T10 = 20.48; T30 = 18.45; T50 = 18.14 | |||||
| Incubation time (T) | 0.000 *** | ||||
| Lime application (L) | 0.000 *** | ||||
| Tillage depth (D) | 0.001 ** | ||||
| T×L | 0.000 ** | ||||
| T×D | 0.070 | ||||
| L×D | 0.135 | ||||
| T×L×D | 0.000 *** | ||||
| Treatment | F/B | G+/G− | Shannon–Wiener Index (H) | Pielou Index (J) | Simpson Index (D) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T10 | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 0.98 ± 0.04 ab | 1.74 ± 0.02 | 0.83 ± 0.01 | 0.79 ± 0.00 |
| T30 | 0.16 ± 0.00 | 0.96 ± 0.04 ab | 1.73 ± 0.00 | 0.83± 0.00 | 0.79 ± 0.00 |
| T50 | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 1.00 ± 0.03 a | 1.73 ± 0.01 | 0.83 ± 0.00 | 0.79± 0.00 |
| T10+Lime | 0.16 ± 0.00 | 0.96 ± 0.02 ab | 1.73 ± 0.00 | 0.83 ± 0.00 | 0.79 ± 0.00 |
| T30+Lime | 0.16 ± 0.00 | 0.90 ± 0.00 b | 1.72 ± 0.00 | 0.83 ± 0.00 | 0.79 ± 0.00 |
| T50+Lime | 0.16 ± 0.01 | 0.91± 0.03 b | 1.72 ± 0.01 | 0.84 ± 0.01 | 0.79 ± 0.01 |
| Lime application (L) | 0.481 | 0.003 ** | 0.225 | 0.225 | 0.418 |
| Tillage depth (D) | 0.235 | 0.127 | 0.247 | 0.247 | 0.459 |
| L×D | 0.259 | 0.290 | 0.801 | 0.801 | 0.851 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shang, Y.; Chen, W.; Li, F.; Li, S.; Han, Y.; Li, P. Effects of Tillage Depth and Lime Application on Acidification Reduction and Nutrient Availability in Vertisol Soil. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14101728
Shang Y, Chen W, Li F, Li S, Han Y, Li P. Effects of Tillage Depth and Lime Application on Acidification Reduction and Nutrient Availability in Vertisol Soil. Agriculture. 2024; 14(10):1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14101728
Chicago/Turabian StyleShang, Yuanyi, Wenju Chen, Fang Li, Shiying Li, Yanlai Han, and Peipei Li. 2024. "Effects of Tillage Depth and Lime Application on Acidification Reduction and Nutrient Availability in Vertisol Soil" Agriculture 14, no. 10: 1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14101728
APA StyleShang, Y., Chen, W., Li, F., Li, S., Han, Y., & Li, P. (2024). Effects of Tillage Depth and Lime Application on Acidification Reduction and Nutrient Availability in Vertisol Soil. Agriculture, 14(10), 1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14101728






