Infiltration Characteristics and Hydrodynamic Parameters in Response to Topographic Factors in Bare Soil Surfaces, Laboratory Experiments Based on Cropland Fields of Purple Soil in Southwest China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Experimental Procedure
2.3. Parameter Calculation
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
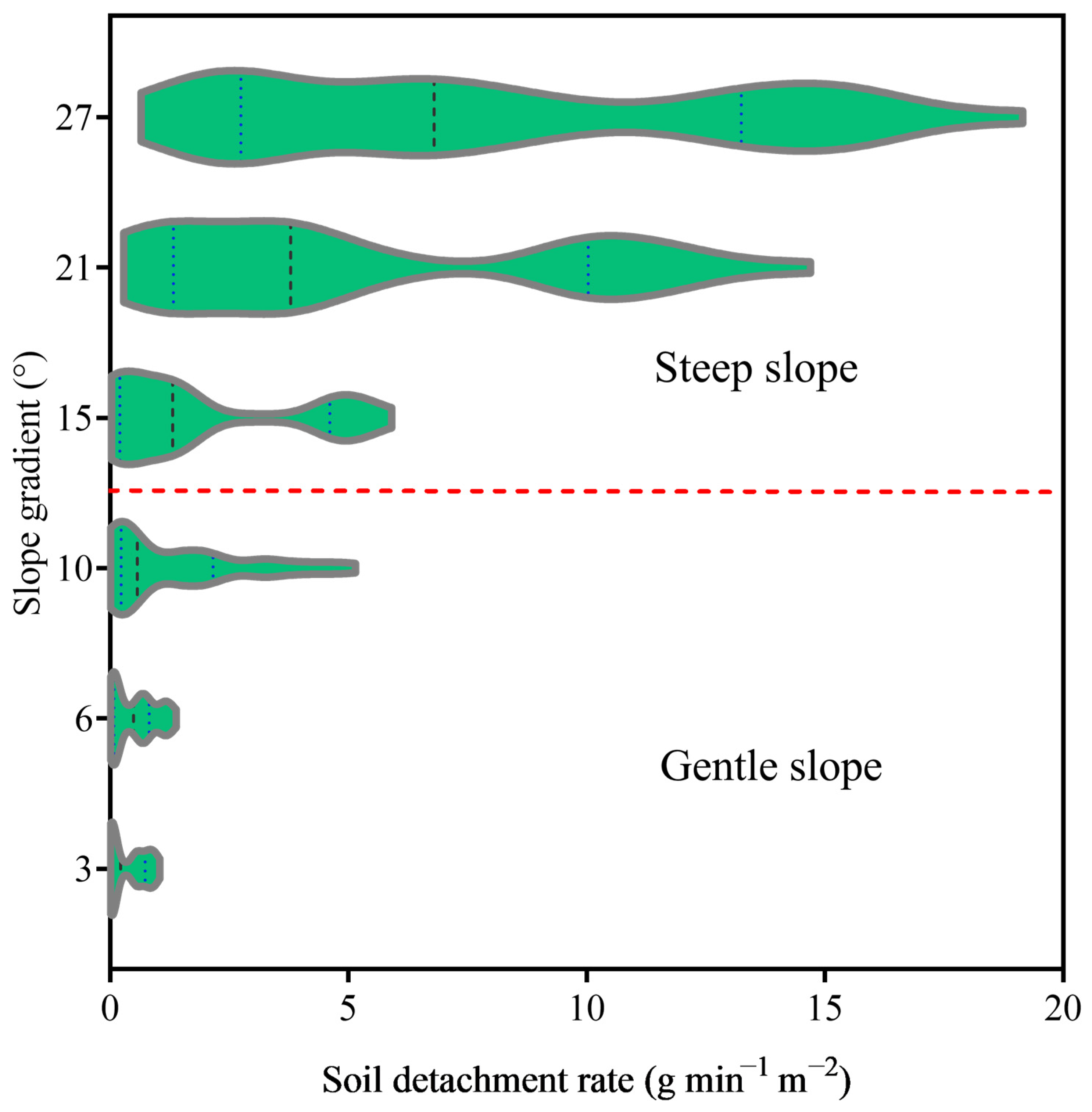
3.1. Infiltration Characteristics under Different Slope Gradients
3.2. Hydrodynamic Parameters under Different Slope Gradients and Slope Positions
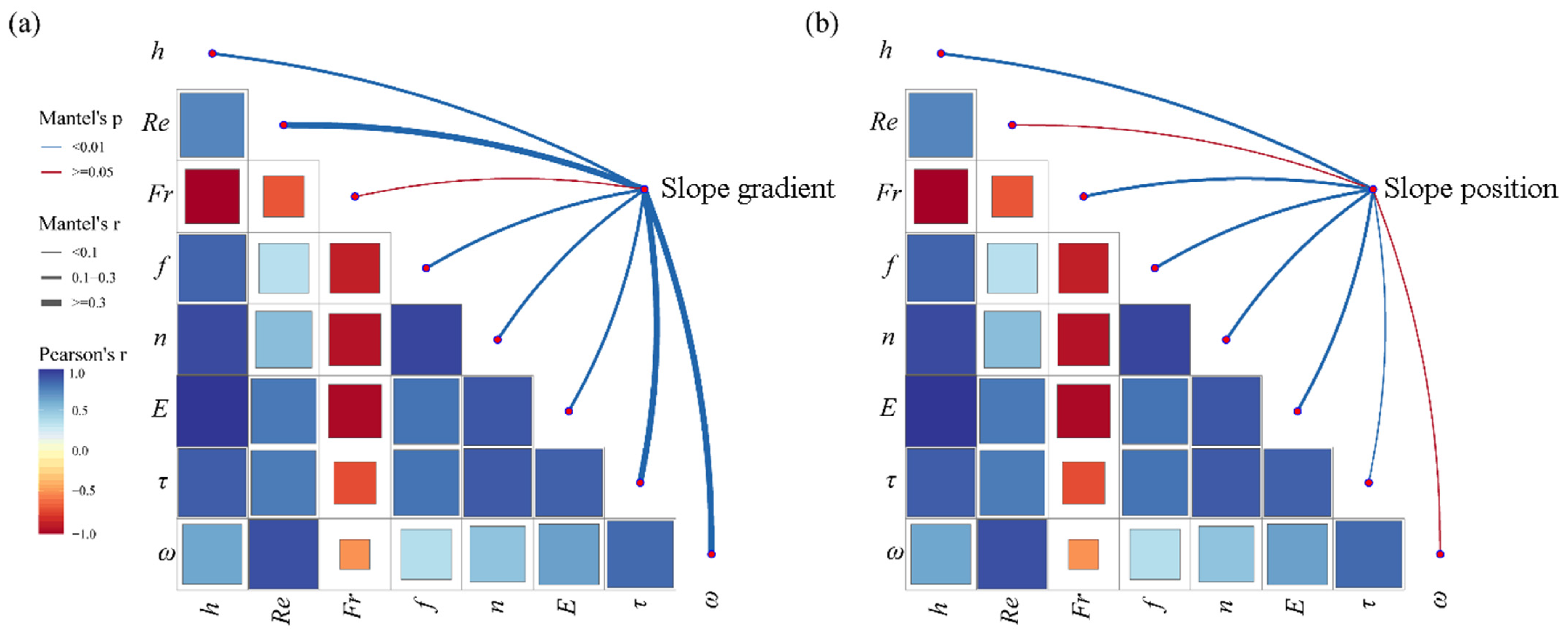
3.3. Hydrodynamic Parameters in Response to Topographic Factors
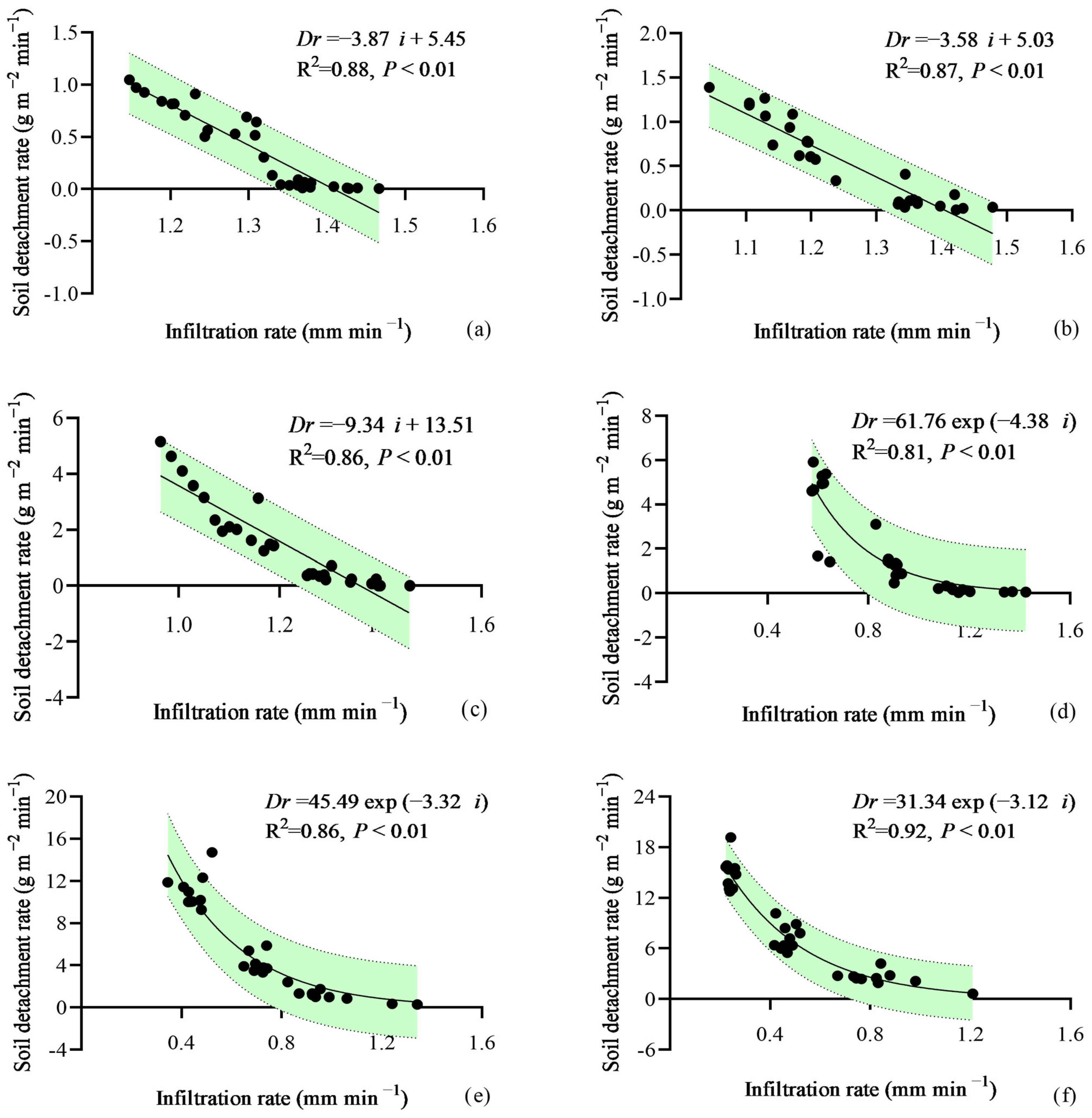
3.4. Relationship between the Hydrodynamic Parameter and the Soil Detachment Rate
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ribolzi, O.; Patin, J.; Bresson, L.M.; Latsachack, K.O.; Mouche, E.; Sengtaheuanghoung, O.; Silvera, N.; Thiebaux, J.P.; Valentin, C. Impact of slope gradient on soil surface features and infiltration on steep slopes in northern Laos. Geomorphology 2011, 127, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, A.K.; Garg, A.; Coo, J.L.; Ng, C.W.W.; Hau, B.C.H. Effects of the roots of cynodon dactylon and schefflera heptaphylla on water infiltration rate and soil hydraulic conductivity. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 3342–3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.D.; Reardon, C.; Wuest, S.B.; Long, D.S. Soil water infiltration after oil seed crop introduction into a Pacific Northwest winter wheat-fallow rotation. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 75, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lei, T.W.; Zhao, J.; Yuan, C.P.; Fan, Y.T.; Qu, L.Q. Effects of rainfall intensity and antecedent soil water content on soil infiltrability under rainfall conditions using the run off-on-out method. J. Hydrol. 2011, 396, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harden, C.P.; Scruggs, P.D. Infiltration on mountain slopes: A comparison of three environments. Geomorphology 2003, 55, 5–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, X.M.; Zhu, Q.K.; Ma, L.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y.; Hao, W.J. Effect of stand origin and slope position on infiltration pattern and preferential flow on a Loess hillslope. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 1353–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Wu, G.L.; Huang, Z.; Liu, Y. Fine roots determine soil infiltration potential than soil water content in semi-arid grassland soils. J. Hydrol. 2019, 578, 124023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaplot, V.; Le Bissonnais, Y. Field measurements of interrill erosion under different slopes and plot sizes. Earth Surf. Proc. Landf. 2000, 25, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.P.; Lei, T.W.; Guo, S.Y.; Jiang, D.S. Study on spatial variation of infiltration rates for small watershed in loess plateau. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2001, 10, 88–92, (In Chinese with English Abstracts). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janeau, J.L.; Briquet, J.P.; Planchon, O.; Valentin, C. Soil crusting and infiltration on steep slopes in northern Thailand. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2003, 54, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assouline, S.; Ben-Hur, M. Effects of rainfall intensity and slope gradient on the dynamics of interrill erosion during soil surface sealing. Catena 2006, 66, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdà, A.; García-Fayos, P. The influence of slope angle on sediment, water and seed losses on badland landscapes. Geomorphology 1997, 18, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mah, M.G.C.; Douglas, L.A.; Ringrose-Voase, A.J. Effects of crust development and surface slope on erosion by rainfall. Soil Sci. 1992, 154, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wu, P.; Zhao, X. Effects of rainfall intensity, underlying surface and slope gradient on soil infiltration under simulated rainfall experiments. Catena 2013, 104, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Wu, Y.; Li, T.; Fu, Q.; Wei, Y. Mid-and long-term effects of biochar on soil improvement and soil erosion control of sloping farmland in a black soil region, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 320, 115902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, S.; Lewandowski, J.; Grimm, N.B.; Hannah, D.M.; Pinay, G.; McDonald, K.; Martí, E.; Argerich, A.; Pfister, L.; Klaus, J.; et al. Ecohydrological interfaces as hot spots of ecosystem processes. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 6359–6376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costabile, P.; Cea, L.; Barbaro, G.; Costanzo, C.; Llena, M.; Vericat, D. Evaluation of 2D hydrodynamic-based rainfall/runoff modelling for soil erosion assessment at a seasonal scale. J. Hydrol. 2024, 632, 130778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, M.; Mengoni, B.; Luppi, L.; Darby, S.E.; Mosselman, E. Numerical simulation of hydrodynamics and bank erosion in a river bend. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, W09428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Li, B.; Zhang, F.; Shen, N.; Yang, M. Exploring the relationship between soil erosion and hydraulic parameters on slopes with clipped herbaceous vegetation through Bayesian network modeling. Land Degrad. Dev. 2024, 35, 3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Qin, Q.; Geng, H.; Zheng, F.; Zhang, X.J.; Li, G.; Xu, X.; Zhang, J. Effects of upslope inflow rate, tillage depth, and slope gradients on hillslope erosion processes and hydrodynamic mechanisms. Catena 2023, 228, 107189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahams, A.D.; Li, G.; Krishnan, C.; Atkinson, J.F. A sediment transport equation for interrill overland flow on rough surfaces. Earth Surf. Proc. Landf. 2001, 26, 1443–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarpoor, A.; Sadeghi, S.H.; Darki, B.Z.; Homaee, M. Changes in morphologic, hydraulic, and hydrodynamic properties of rill erosion due to surface inoculation of endemic soil cyanobacteria. Catena 2022, 208, 105782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todisco, F.; Vergni, L.; Iovino, M.; Bagarello, V. Changes in soil hydrodynamic parameters during intermittent rainfall following tillage. Catena 2023, 226, 107066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhou, Z.C.; Zhang, X.J. Impacts of sediment load and size on rill detachment under low flow discharges. J. Hydrol. 2019, 570, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, N.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, B.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, J. Quantifying the contribution of sediment load to soil detachment rate by sediment-laden rill flow. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2017, 81, 1526–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Liu, G.; Liu, P.; Zheng, P.; Zhang, J.Q.; Hu, F.N. Response of soil detachment rate to the hydraulic parameters of concentrated flow on steep loessial slopes on the Loess Plateau of China. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 2613–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimenez, R.; Govers, G. Flow detachment by concentrated flow on smooth and irregular beds. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2002, 66, 1475–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Y.; Huang, Y.H.; Zhao, Y.; Mo, B.; Mi, H.X. Comparison of loess and purple rill erosions measured with volume replacement method. J. Hydrol. 2015, 530, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Xu, M.; Wu, J.; Yang, G.; Zhang, X.; Song, C.; Long, l.; Chen, C.; Xu, C.; Wang, Y. Effects of variable-sized polyethylene microplastics on soil chemical properties and functions and microbial communities in purple soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 868, 161642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jin, Y.; Wang, J.; Ma, Z.; Liu, X.; Liang, X. Laboratory-Scaled Investigation into Combined Impacts of Temporal Rainfall Patterns and Intensive Tillage on Soil and Water Loss. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.H.; Ma, B.; Wu, F.Q. Infiltration characteristics in sloping farmland at different growth stages of soybean (Glycine max L.) in loess area. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2015, 13, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aru, S.; Chang, S.L.; Zhang, Y.T. Comparative analysis and simulation of soil moisture infiltration characteristics in different communities in the forests of Tianshan Mountains, China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 9111–9118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Mu, X.; Gao, P.; Zhao, G.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chiew, F. Landscape patches influencing hillslope erosion processes and flow hydrodynamics. Geoderma 2019, 353, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, K. Hydrodynamic characteristics of rill flow on steep slopes. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 3677–3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.Q.; Singh, V.P. Effect of microtopography, slope length and gradient, and vegetative cover on overland flow through simulation. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2004, 9, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.Q.; Chen, L.; Li, J.C. Influences of slope gradient on soil erosion. Appl. Math. Mech. 2001, 22, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Yu, M.; Chen, L. Nonmonotonic and spatial-temporal dynamic slope effects on soil erosion during rainfall-runoff processes. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 1369–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdić, I.; Safner, T.; Rubinić, V.; Rutić, F.; Husnjak, S.; Filipović, V. Effect of slope position on soil properties and soil moisture regime of Stagnosol in the vineyard. J. Hydrol. Hydromech. 2022, 70, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Zhang, L.; Song, X.; Zhang, S.; Liu, X.; Liang, Y.; Zheng, S. Runoff and sediment loss responses to rainfall and land use in two agricultural catchments on the Loess Plateau of China. Hydrol. Process. 2001, 15, 977–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famiglietti, J.S.; Rudnicki, J.W.; Rodell, M. Variability in surface moisture content along a hillslope transect: Rattlesnake Hill. Texas. J. Hydrol. 1998, 210, 259–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Fu, B.J.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.D. Soil moisture variation in relation to topography and land use in a hillslope catchment of the Loess Plateau, China. J. Hydrol. 2001, 240, 243–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Soil erosion and the global carbon budget. Environ. Int. 2003, 29, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, D.; Xu, R.; Gao, P.; Mu, X. Effect of vegetation restoration type and topography on soil water storage and infiltration capacity in the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2024, 241, 108079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Yang, Y.; He, T.; Wang, Y.; Wendroth, O.; Liu, B. Mechanical sowing alters slope-scale spatial variability of saturated hydraulic conductivity in the black soil region of Northeast China. Catena 2022, 212, 106115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Soil Texture | pH | Bulk Density (g cm−3) | Soil Moisture (%) | Wet Aggregate Stability (mm) | Organic Carbon (g kg−1) | CaCO3 (g kg−1) | Particle Size (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sand | Silt | Clay | |||||||
| Clay loam | 8.11 | 1.44 | 15.72 | 1.39 | 6.21 | 93.97 | 29.05 | 28.33 | 42.62 |
| Slope Gradient (°) | Kostiakov | Horton | Philip | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | b | R2 | MSE | Ii | If | c | R2 | MSE | A | B | R2 | MSE | |
| 3 | 1.623 | 0.068 | 0.765 | 0.002 | 1.453 | 1.178 | 0.028 | 0.822 | 0.001 | 1.186 | 0.551 | 0.591 | 0.003 |
| 6 | 1.686 | 0.092 | 0.791 | 0.003 | 1.456 | 1.111 | 0.032 | 0.830 | 0.002 | 1.094 | 0.743 | 0.632 | 0.005 |
| 10 | 1.713 | 0.108 | 0.756 | 0.005 | 1.429 | 1.007 | 0.026 | 0.826 | 0.003 | 1.026 | 0.853 | 0.592 | 0.008 |
| 15 | 1.982 | 0.253 | 0.807 | 0.013 | 1.398 | 0.604 | 0.038 | 0.877 | 0.008 | 0.510 | 1.744 | 0.715 | 0.020 |
| 20 | 1.855 | 0.308 | 0.854 | 0.009 | 1.291 | 0.419 | 0.042 | 0.907 | 0.006 | 0.317 | 1.778 | 0.797 | 0.012 |
| 27 | 1.816 | 0.411 | 0.828 | 0.012 | 1.095 | 0.237 | 0.045 | 0.905 | 0.007 | 0.088 | 1.905 | 0.803 | 0.014 |
| Mean | 1.779 | 0.207 | 0.800 | 0.007 | 1.354 | 0.759 | 0.035 | 0.861 | 0.005 | 0.704 | 1.262 | 0.688 | 0.010 |
| Slope Gradient (°) | Slope Position | Re | Fr | f | n | τ (Pa) | h (10−3 m) | w (W m−2) | E (10−4 m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | Upper | 124.54 ± 64.33 a | 0.08 ± 0.03 a | 72.99 ± 37.71 a | 0.41 ± 0.15 a | 3.87 ± 1.99 a | 7.61 ± 3.96 a | 0.08 ± 0.04 a | 76.22 ± 39.51 a |
| Middle | 124.88 ± 64.63 a | 0.14 ± 0.05 b | 26.41 ± 13.67 b | 0.24 ± 0.09 b | 2.76 ± 1.43 b | 5.41 ± 2.82 b | 0.08 ± 0.04 a | 54.53 ± 28.13 b | |
| Lower | 125.15 ± 64.86 a | 0.25 ± 0.09 c | 8.63 ± 4.47 c | 0.12 ± 0.05 c | 1.91 ± 0.98 c | 3.72 ± 1.94 c | 0.08 ± 0.04 a | 38.14 ± 19.36 b | |
| Average | 124.86 ± 64.61 | 0.16 ± 0.06 | 36.01 ± 18.62 | 0.26 ± 0.09 | 2.85 ± 1.47 | 5.59 ± 2.90 | 0.08 ± 0.04 | 56.30 ± 29.00 | |
| 6 | Upper | 139.91 ± 82.05 a | 0.16 ± 0.08 a | 51.79 ± 31.14 a | 0.33 ± 0.14 a | 5.93 ± 3.52 a | 5.82 ± 3.47 a | 0.17 ± 0.10 a | 58.34 ± 34.53 a |
| Middle | 139.98 ± 83.12 a | 0.17 ± 0.09 a | 42.39 ± 25.17 ab | 0.29 ± 0.13 a | 5.54 ± 3.29 a | 5.45 ± 3.25 a | 0.18 ± 0.11 a | 54.67 ± 32.29 a | |
| Lower | 140.05 ± 82.18 a | 0.18 ± 0.10 a | 34.88 ± 20.72 b | 0.26 ± 0.11 a | 5.20 ± 3.09 a | 5.10 ± 3.04 a | 0.18 ± 0.10 a | 51.33 ± 30.26 a | |
| Average | 139.98 ± 83.12 | 0.17 ± 0.09 | 43.02 ± 25.55 | 0.30 ± 0.13 | 5.56 ± 3.30 | 5.46 ± 3.26 | 0.18 ± 0.11 | 54.78 ± 32.36 | |
| 10 | Upper | 152.36 ± 77.60 a | 0.22 ± 0.08 a | 57.93 ± 29.48 a | 0.26 ± 0.08 a | 6.38 ± 3.25 a | 5.57 ± 2.84 a | 0.38 ± 0.20 a | 56.11 ± 28.13 a |
| Middle | 152.43 ± 77.66 a | 0.26 ± 0.11 ab | 43.89 ± 22.43 b | 0.23 ± 0.07 ab | 5.81 ± 2.96 a | 5.07 ± 2.59 a | 0.38 ± 0.15 a | 51.35 ± 25.59 a | |
| Lower | 152.52 ± 77.74 a | 0.32 ± 0.14 b | 29.19 ± 14.92 c | 0.17 ± 0.07 c | 5.07 ± 2.58 a | 4.42 ± 2.26 a | 0.39 ± 0.20 a | 45.39 ± 22.33 a | |
| Average | 152.43 ± 77.67 | 0.27 ± 0.11 | 43.67 ± 22.27 | 0.22 ± 0.08 | 5.75 ± 2.93 | 5.02 ± 2.57 | 0.38 ± 0.20 | 50.95 ± 25.35 | |
| 15 | Upper | 359.82 ± 171.64 a | 0.17 ± 0.10 a | 113.59 ± 54.18 a | 0.54 ± 0.20 a | 26.40 ± 12.59 a | 9.66 ± 5.06 a | 1.13 ± 0.54 a | 102.59 ± 48.81 a |
| Middle | 360.88 ± 172.41 a | 0.25 ± 0.16 ab | 51.66 ± 24.68 b | 0.35 ± 0.13 b | 20.34 ± 9.72 bc | 7.42 ± 3.89 bc | 1.14 ± 0.55 a | 79.69 ± 37.50 bc | |
| Lower | 361.51 ± 172.87 a | 0.33 ± 0.21 c | 28.58 ± 13.66 c | 0.25 ± 0.09 c | 16.72 ± 7.99 c | 6.09 ± 3.18 c | 1.14 ± 0.54 a | 66.45 ± 30.76 c | |
| Average | 360.74 ± 172.31 | 0.25 ± 0.16 | 64.61 ± 30.84 | 0.38 ± 0.14 | 21.15 ± 10.10 | 7.72 ± 4.04 | 1.14 ± 0.54 | 82.91 ± 39.02 | |
| 21 | Upper | 453.15 ± 174.36 a | 0.13 ± 0.06 a | 213.36 ± 82.09 a | 0.79 ± 0.22 a | 47.20 ± 18.16 a | 13.63 ± 5.30 a | 1.98 ± 0.76 a | 128.16 ± 49.42 a |
| Middle | 454.21 ± 175.01 a | 0.17 ± 0.07 ab | 130.26 ± 50.19 b | 0.60 ± 0.17 b | 40.10 ± 15.45 ab | 11.56 ± 4.49 ab | 1.99 ± 0.77 a | 109.13 ± 41.90 ab | |
| Lower | 456.58 ± 176.48 a | 0.35 ± 0.16 c | 28.70 ± 11.09 c | 0.26 ± 0.07 c | 24.30 ± 9.39 c | 6.97 ± 2.71 c | 2.00 ± 0.77 a | 68.49 ± 25.26 c | |
| Average | 454.65 ± 175.28 | 0.21 ± 0.09 | 124.11 ± 47.79 | 0.55 ± 0.16 | 31.09 ± 11.99 | 8.95 ± 3.47 | 1.99 ± 0.77 | 101.93 ± 38.86 | |
| 27 | Upper | 532.71 ± 172.17 a | 0.10 ± 0.03 a | 393.39 ± 127.13 a | 1.12 ± 0.26 a | 75.47 ± 24.39 a | 17.27 ± 5.64 a | 2.96 ± 0.95 a | 154.64 ± 50.31 a |
| Middle | 537.93 ± 174.90 a | 0.31 ± 0.09 b | 44.02 ± 14.31 bc | 0.33 ± 0.09 b | 36.61 ± 11.90 bc | 7.96 ± 2.71 bc | 2.98 ± 0.97 a | 77.30 ± 24.17 bc | |
| Lower | 539.06 ± 175.50 a | 0.46 ± 0.14 c | 19.98 ± 6.50 c | 0.21 ± 0.05 c | 28.17 ± 9.17 c | 6.11 ± 2.08 c | 2.99 ± 0.97 a | 62.50 ± 18.56 c | |
| Average | 536.57 ± 174.19 | 0.29 ± 0.09 | 152.47 ± 49.31 | 1.08 ± 0.25 | 46.75 ± 15.16 | 10.21 ± 3.48 | 2.97 ± 0.97 | 98.15 ± 31.01 |
| Factors | Re | h | Fr | f | n | τ | ω | E |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slope gradient | 153.01 ** | 79.22 ** | 0.914 ** | 117.02 ** | 197.27 ** | 348.26 ** | 440.68 ** | 78.82 ** |
| Slope position | 0.01 | 74.15 ** | 68.623 ** | 354.86 ** | 318.56 ** | 79.67 ** | 0.01 | 52.93 ** |
| Interaction | 0.01 | 15.65 ** | 6.11 ** | 82.19 ** | 81.40 ** | 37.68 ** | 0.01 | 10.40 ** |
| Hydrodynamic Parameter | Slope Gradient (°) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 6 | 10 | 15 | 21 | 27 | |
| Re | 0.893 ** | 0.804 ** | 0.898 ** | 0.916 ** | 0.912 ** | 0.836 ** |
| Fr | –0.744 ** | –0.556 * | –0.640 ** | –0.517 * | –0.521 * | –0.643 ** |
| f | 0.897 ** | 0.802 ** | 0.897 ** | 0.961 ** | 0.912 ** | 0.861 ** |
| τ | 0.953 ** | 0.814 ** | 0.897 ** | 0.940 ** | 0.912 ** | 0.869 ** |
| n | 0.871 ** | 0.794 ** | 0.868 ** | 0.871 ** | 0.868 ** | 0.837 ** |
| h | 0.946 ** | 0.824 ** | 0.891 ** | 0.907 ** | 0.913 ** | 0.897 ** |
| ω | 0.951 ** | 0.804 ** | 0.896 ** | 0.827 ** | 0.912 ** | 0.852 ** |
| E | 0.493 * | 0.813 ** | 0.897 ** | 0.917 ** | 0.913 ** | 0.857 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Li, D.; Hou, G.; Zheng, J. Infiltration Characteristics and Hydrodynamic Parameters in Response to Topographic Factors in Bare Soil Surfaces, Laboratory Experiments Based on Cropland Fields of Purple Soil in Southwest China. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1820. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14101820
Wang Y, Ma Z, Li D, Hou G, Zheng J. Infiltration Characteristics and Hydrodynamic Parameters in Response to Topographic Factors in Bare Soil Surfaces, Laboratory Experiments Based on Cropland Fields of Purple Soil in Southwest China. Agriculture. 2024; 14(10):1820. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14101820
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yong, Ziting Ma, Dandan Li, Guirong Hou, and Jiangkun Zheng. 2024. "Infiltration Characteristics and Hydrodynamic Parameters in Response to Topographic Factors in Bare Soil Surfaces, Laboratory Experiments Based on Cropland Fields of Purple Soil in Southwest China" Agriculture 14, no. 10: 1820. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14101820
APA StyleWang, Y., Ma, Z., Li, D., Hou, G., & Zheng, J. (2024). Infiltration Characteristics and Hydrodynamic Parameters in Response to Topographic Factors in Bare Soil Surfaces, Laboratory Experiments Based on Cropland Fields of Purple Soil in Southwest China. Agriculture, 14(10), 1820. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14101820







