Deep Simple Epicotyl Morphophysiological Dormancy in Seeds of Endemic Chinese Helleborus thibetanus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Seed Materials
2.2. Seed Properties
2.3. Embryo Morphology Observations and Index Determination
2.4. Effects of Temperature and GA3 on Radicle Emergence
2.5. Epicotyl Dormancy Release Test
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Helleborus thibetanus Seeds
3.2. Seed Embryo Growth during the Morphological Post-Ripening Process
3.3. Effect of the Incubation Temperature on Radicle Emergence
3.4. Effect of GA3 on Radicle Emergence
3.5. Effects of Root Length and GA3 on the Epicotyl Dormancy of Seeds with Emerged Radicles
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, W.C. Flora Republicae Popularis Sinicae; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1979; Volume 27, p. 106. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.J.; Wang, J.X.; Su, Y.F.; Wei, Y.X.; Zhu, Y.H. Shaanxi Qiyao; Shaanxi Science and Technology Press: Xi’an, China, 2003; p. 35. [Google Scholar]
- Meiners, J.; Debener, T.; Schweizer, G.; Winkelmann, T. Analysis of the taxonomic subdivision within the genus Helleborus by nuclear DNA content and genome-wide DNA markers. Sci. Hortic. 2011, 128, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zonneveld, B.J.M. Nuclear DNA contents of all species of Helleborus (Ranunculaceae) discriminate between species and sectional divisions. Plant Syst. Evol. 2001, 229, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.Y.; Su, Y.F.; Wang, Y.; Chai, X.; Han, X.; Wu, Z.H.; Gao, X.M. Bufadienolides and phytoecdystones from the rhizomes of Helleborus thibetanus (Ranunculaceae). Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2010, 38, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Miao, F.; Zhou, L.; Sun, W. Two new bufadienolides from the rhizomes of Helleborus thibetanus Franch. Fitoterapia 2010, 81, 636–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Su, Y.F.; Yang, F.Y.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Gao, X.M. Two new bufadienolides and one new pregnane from Helleborus thibetanus. Phytochem. Lett. 2014, 10, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Su, Y.F.; Yang, F.Y. Three new steroidal saponins from Helleborus thibetanus. Nat. Prod. Res. 2016, 30, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Su, Y.F.; Yang, F.Y. Four new minor spirostanol glycosides from Helleborus thibetanus. Phytochem. Lett. 2016, 18, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xue, B.; Chen, W.; Xu, W.; Jiang, R. The co-occurrence of bufadienolides and podophyllotoxins from Helleborus thibetanus. Biochem. Syst. Ecolo. 2020, 90, 104042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, P.; Che, X.F.; Wang, W.; Ren, Y. Floral organogenesis of Helleborus thibetanus and Nigella damascena (Ranunculaceae) and its systematic significance. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2011, 166, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.H.; Zou, Q.C.; Jin, L.; An, X.; Zhou, J.H.; Ma, G.Y. Comparative research on pollen fertility and morphology of Helleborus thibetanus. Mol. Plant Breed. 2018, 16, 1690–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Song, L.; Ren, Y.; Tian, X.H.; Zhang, X.H. Vegetative organ structures and their phylogenic significance of Helleborus thibetanus franch. (Ranunculaceae). Acta Bot. Boreal.-Occident. Sin. 2006, 26, 2208–2213. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.H.; Ma, G.Y.; Zou, Q.C.; Tian, D.Q. Preliminary analysis of transcriptome information and SSR markers in young leaves of Helleborus thibetanus. Mol. Plant Breed. 2019, 17, 3297–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonogaki, H. Seed germination and dormancy: The classic story, new puzzles, and evolution. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2019, 61, 541–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskin, J.M.; Baskin, C.C. Some considerations for adoption of Nikolaeva’s formula system into seed dormancy classification. Seed Sci. Res. 2008, 18, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskin, C.C.; Baskin, J.M. Seeds: Ecology, Biogeography, and Evolution of Dormancy and Germination, 2nd ed.; Elsevier/Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2014; pp. 33–77. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, F.Y.; Zhou, Y.F.; Li, Y. Anatomical study of Helleborus thibetanus seed embryo during the morphological post-ripening process. Shaanxi J. Agr. Sci. 2021, 67, 56–58. [Google Scholar]
- Niimi, Y.; Han, D.; Abe, S. Temperature affecting embryo development and seed germination of Christmas rose (Helleborus niger) after sowing. Sci. Hortic. 2006, 107, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, B.K.; Park, K.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, H.; Song, S.K.; Kim, J.; Lee, C.H.; Cho, J.S. Comparison of the seed dormancy and germination characteristics of six Clematis species from South Korea. Sci. Hortic. 2023, 307, 11488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finch-Savage, W.E.; Leubner-Metzger, G. Seed dormancy and the control of germination. New Phytol. 2006, 171, 501–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.E.; Peng, D.L.; Li, Z.M.; Huang, L.; Yang, J.; Sun, H. Cold stratification, temperature, light, GA3, and KNO3 effects on seed germination of Primula beesiana from Yunnan, China. Plant Divers. 2020, 42, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, M.; Chu, L.Y.; Li, Q.F.; Yu, J.W.; Yang, Y.H.; Zhou, P.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, C.Q.; Fan, X.L.; Zhao, D.S.; et al. Brassinosteroid and gibberellin coordinate rice seed germination and embryo growth by regulating glutelin mobilization. Crop J. 2021, 9, 1039–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Lv, B.; Wang, X.; Gao, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; He, S. Effects of exogenous hormone GA3, 6-BA and root length on breaking of epicotyls dormancy of Paeonia ostii ‘Fengdanbai’ mature embryo. J. Henan Agr. Sci. 2015, 44, 122–126. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, A.; Zhang, M.; Yuan, Q.; Wan, Y. Dormancy breaking technologies of Paeonia emodi seeds. Seed 2023, 42, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonogaki, H. Seed dormancy and germination-emerging mechanisms and new hypotheses. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Ji, Y.; Song, X.; Yao, L.; Liu, H.; Tao, J. Deep complex morphophysiological dormancy in seeds of Clematis hexapetala Pall. (Ranunculaceae). Sci. Hortic. 2021, 286, 110247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qiu, Y.P.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J. Dormancy breaking and storage behavior of Garcinia cowa Roxb. (Guttiferae) seeds: Implications for ecological function and germplasm conservation. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2005, 47, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Yang, L.; Wang, Y.; Shen, S. Physiological epicotyl dormancy and its alleviation in seeds of Yunnanopilia longistaminea: The first report of physiological epicotyl dormancy in China. Peer J. 2017, 5, e3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaganathan, G.K. Ecological insights into the coexistence of dormancy and desiccation-sensitivity in Arecaceae species. Ann. For. Sci. 2021, 78, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskin, C.C.; Baskin, J.M. Deep complex morphophysiological dormancy in seeds of the mesic woodland herb Delphinium tricorne (Ranunculaceae). Int. J. Plant Sci. 1994, 155, 738–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomizu, T.; Niimi, Y.; Watanabe, E. Embryo development and seed germination of Hepatica nobilis Schreber var. japonica as affected by temperature after sowing. Sci. Hortic. 2004, 99, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandelook, F.; Van Assche, J.A. Temperature conditions control embryo growth and seeds germination of Corydalis solida (L.) Clairv., a temperate forest spring geophyte. Plant Biol. 2009, 11, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Rhie, Y.H.; Kim, K.S. Non-deep simple morphophysiological dormancy in seeds of Thalictrum rochebrunianum, an endemic perennial herb in the Korean peninsula. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2015, 56, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Ji, Y.; Fu, G.; Yao, L.; Liu, H.; Tao, J. Dormancy-breaking and germination requirements of Thalictrum squarrosum Stephan ex Willd. seeds with underdeveloped embryos. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2021, 24, 100311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Rhie, Y.H.; Kim, K.S. Dormancy breaking and germination requirements of seeds of Thalictrum uchiyamae (Ranunculaceae) with underdeveloped embryos. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 231, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskin, C.C.; Baskin, J.M. Germination ecophysiology of herbaceous plant species in a temperate region. Am. J. Bot. 1988, 75, 286–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawłowski, T.A.; Bujarska-Borkowska, B.; Suszka, J.; Tylkowski, T.; Chmielarz, P.; Klupczyńska, E.A.; Staszak, A.M. Temperature Regulation of Primary and Secondary Seed Dormancy in Rosa canina L.: Findings from Proteomic Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhie, Y.H.; Lee, S.Y. Seed dormancy and germination of Epimedium koreanum Nakai. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 272, 109600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.L.; Luo, X.P.; Yuan, Z.; Bai, M.J.; Hu, X.W. Seed dormancy release of Halenia elliptica in response to stratification temperature, duration and soil moisture content. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaeim, H.; Kende, Z.; Balla, I.; Gyuricza, C.; Eser, A.; Tarnawa, A. Temperature and water stresses on seed germination and seedling growth of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Sustainability 2022, 14, 3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahdati, K.; Aslamarz, A.A.; Rahemi, M.; Hassani, D.; Leslie, C. Mechanism of seed dormancy and its relationship to bud dormancy in Persian walnut. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2012, 75, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassankhah, A.; Vahdati, K.; Rahemi, M.; Hassani, D.; Khorami, S.S. Persian walnut phenology: Effect of chilling and heat requirements on budbreak and flowering date. Int. J. Hort. Sci. Technol. 2017, 4, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Shi, X.; Du, L. Effects of temperature and gibberellin on seed germination of Helleborus foetidus. Seed 2022, 41, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.H.; Yu, P.; Song, C.H.; Wu, J.J.; Tian, Y.; Wu, X.F.; Zhang, X.W.; Liu, Y.M. Differential protein analysis of Heracleum moellendorffii Hance seeds during Stratification. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 145, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurgül, E.; Muhammed, F.K.; Mehmet, D.K. GA3 acts as a germination promoter in wild castor bean (Ricinus communis L.). Seed Sci. Technol. 2022, 50, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, N.; Jia, J.S.; Yang, L.; Huang, R.; Wang, Q.; Chen, C.; Meng, Z.; Li, L.; Chen, J. Exogenous gibberellic acid shortening after-ripening process and promoting seed germination in a medicinal plant Panax notoginseng. BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Yao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Baskin, J.M.; Baskin, C.C.; Xiong, Z.; Tao, J. A review of the seed biology of Paeonia species (Paeoniaceae), with particular reference to dormancy and germination. Planta 2019, 249, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhie, Y.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, K.S. Seed dormancy and germination in Jeffersonia dubia (Berberidaceae) as affected by temperature and gibberellic acid. Plant Biol. 2015, 17, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Chen, X.; Guo, B. Identification of genes involved in metabolism and signalling of abscisic acid and gibberellins during Epimedium pseudowushanense B.L. Guo seed morphophysiological dormancy. Plant Cell Rep. 2018, 37, 1061–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhyani, A.; Phartyal, S.S.; Nautiyal, B.P.; Nautiyal, M.C. Epicotyl morphophysiological dormancy in seeds of Lilium polyphyllum (Liliaceae). J. Biosci. 2013, 38, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhie, Y.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, K.S. Deep simple epicotyl morphophysiological dormancy in seeds of Gymnospermium microrrhynchum (S. Moore) Takht., a rare species in Korea. Hortic. Sci. Techol. 2019, 37, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copete, E.; Herranz, J.M.; Ferrandis, P.; Baskin, C.C.; Baskin, J.M. Physiology, morphology and phenology of seed dormancy break and germination in the endemic Iberian species Narcissus hispanicus (Amaryllidaceae). Ann. Bot. 2011, 107, 1003–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.P.; He, Z.; Li, H.; Shi, L.; Tang, Y.D. Effect of root length on epicotyl dormancy release in seeds of Paeonia ludlowii, Tibetan peony. Ann. Bot. Lond. 2014, 113, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Van Staden, J. Seedling establishment characteristics of Paeonia ostii var. lishizhenii. S Afr. J. Bot. 2002, 68, 382–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Pan, H.; Baskin, C.C.; Baskin, J.M.; Xiong, Z.; Cao, W.; Yao, L.; Tang, B.; Zhang, C.; Tao, J. Epicotyl morphophysiological dormancy in seeds of Paeonia ostii (Paeoniaceae): Seasonal temperature regulation of germination phenology. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2022, 194, 104742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koornneef, M.; Bentsink, L.; Hilhorst, H. Seed dormancy and germination. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2002, 5, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
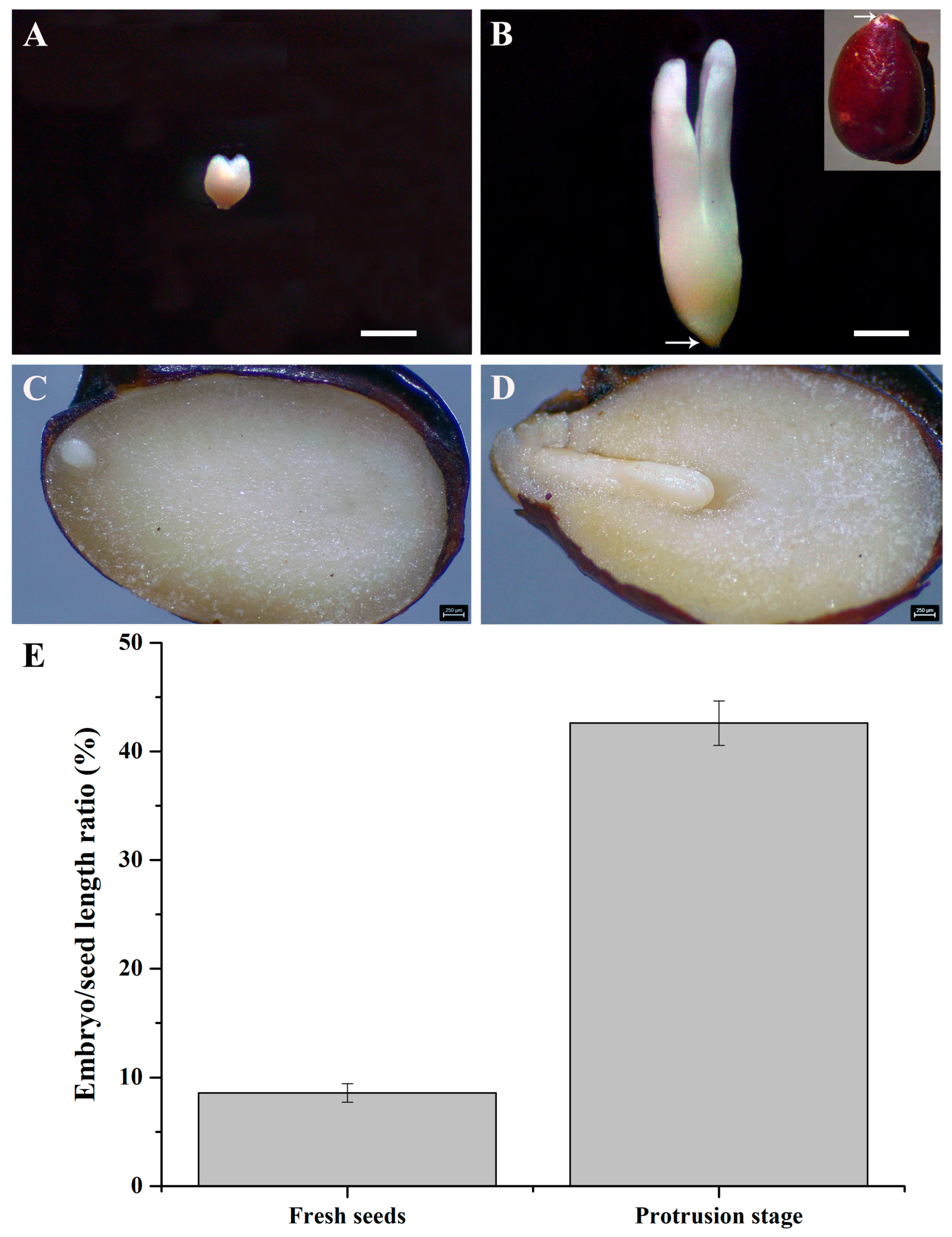
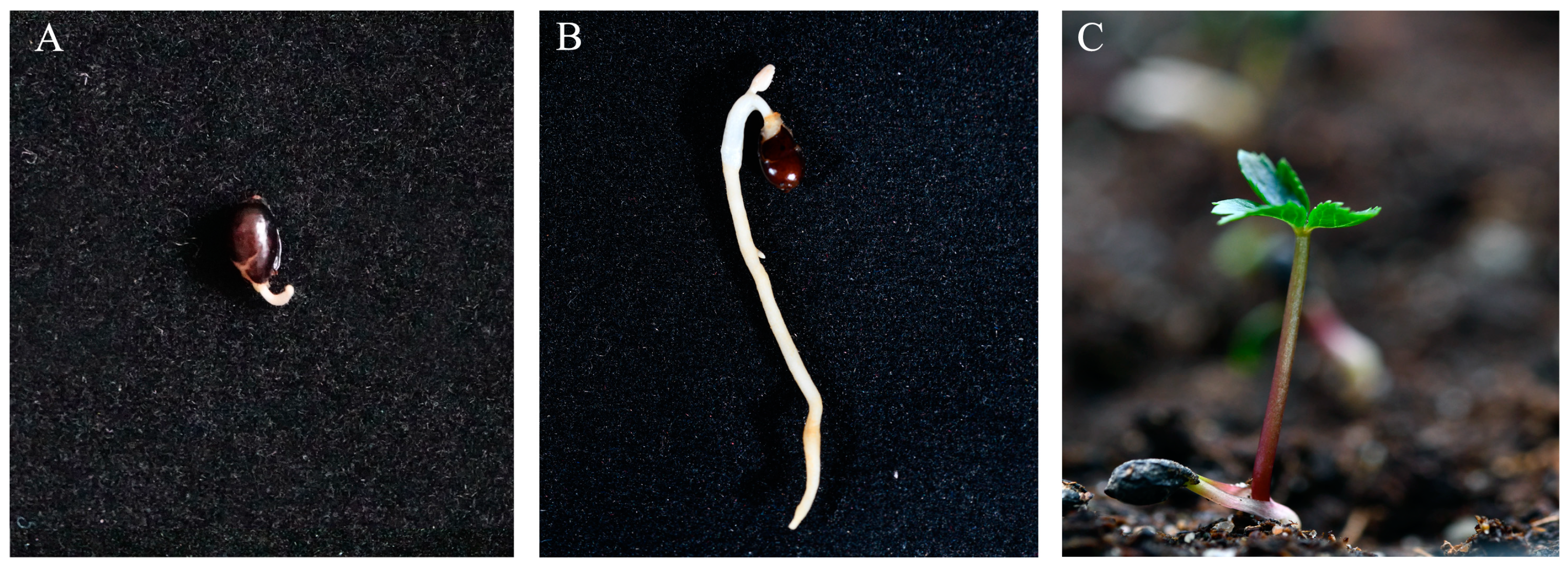
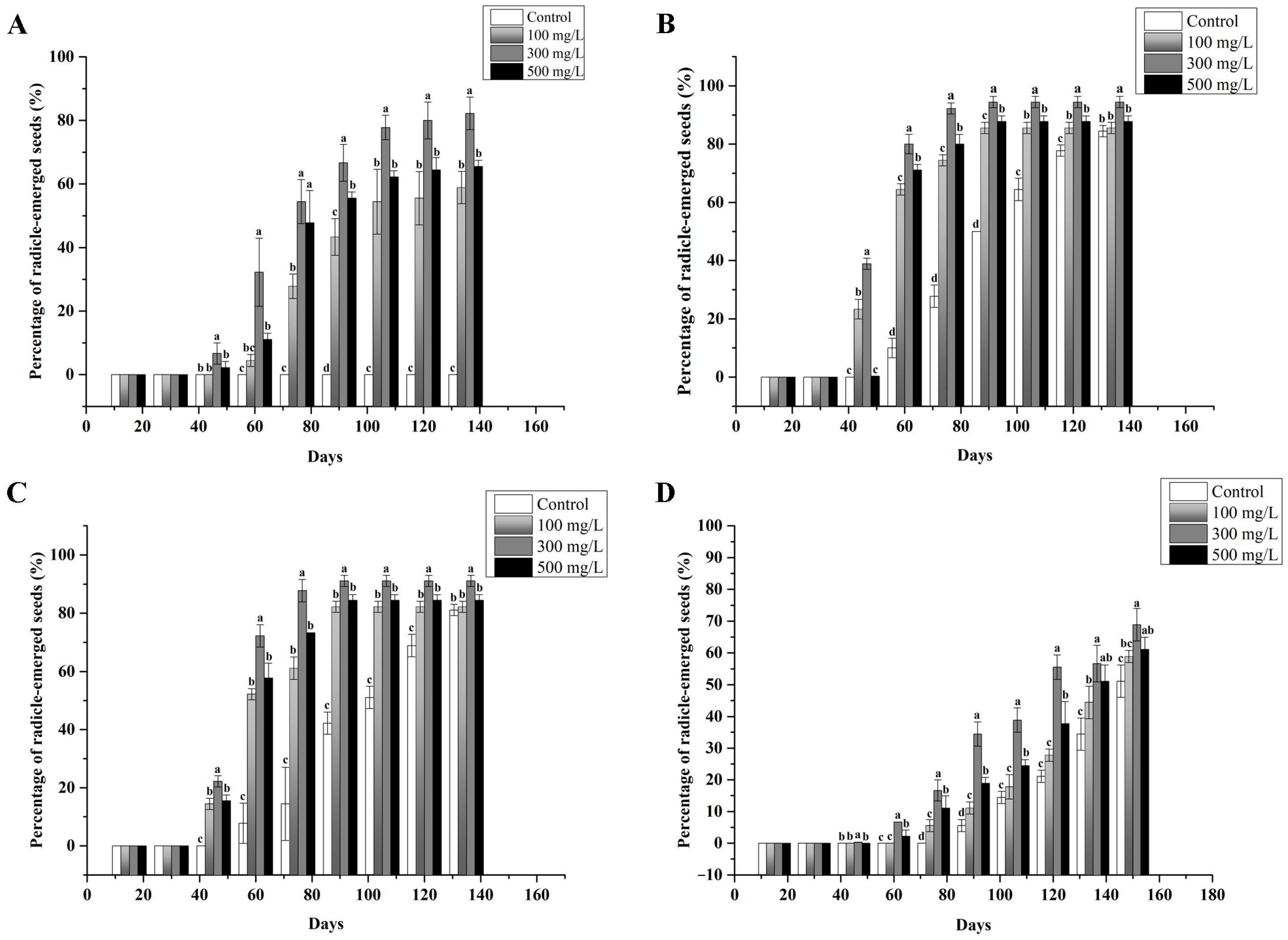

| Temperature (°C) | Radicle Emergence Starting Time (d) | Radicle Emergence Duration (d) | Radicle Emergence Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| 15 | 58.33 ± 1.53 C | 75.33 ± 0.58 A | 84.44 ± 1.93 A |
| 20 | 79.33 ± 2.89 A | 70.67 ± 2.89 A | 51.11 ± 5.09 B |
| 15/20 | 62.67 ± 1.15 B | 74.67 ± 4.51 A | 81.11 ± 1.92 A |
| 25 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| 30 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| Source of Variations | SS | df | MS | F | p | R2 | CV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 24,073.659 | 15 | 1604.911 | 135.89 | <0.01 | ||
| Error | 377.934 | 32 | 11.810 | ||||
| Corrected total | 24,451.593 | ||||||
| Incubation temperature | 11,686.696 | 3 | 3895.565 | 329.84 | <0.01 | ||
| GA3 | 5647.907 | 3 | 1882.636 | 159.40 | <0.01 | ||
| Interactions | 6739.056 | 9 | 748.784 | 63.40 | <0.01 | 0.985 | 4.833 |
| Source of Variations | SS | df | MS | F | p | R2 | CV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Root length of 0.5 cm | |||||||
| Model | 46,314.149 | 9 | 5146.017 | 217.003 | <0.01 | ||
| Error | 474.282 | 20 | 23.714 | ||||
| Corrected total | 46,788.431 | 29 | |||||
| GA3 | 20,453.530 | 1 | 20,453.530 | 862.506 | <0.01 | ||
| Cold stratification time | 18,519.727 | 4 | 4629.932 | 195.240 | <0.01 | ||
| GA3 × Cold stratification time | 7340.893 | 4 | 1835.223 | 77.390 | <0.01 | 0.990 | 11.267 |
| Root length of 1.5 cm | |||||||
| Model | 46,742.276 | 9 | 5193.586 | 292.157 | <0.01 | ||
| Error | 355.534 | 20 | 17.777 | ||||
| Corrected total | 47,097.809 | 29 | |||||
| GA3 | 3413.120 | 1 | 3413.120 | 192.000 | <0.01 | ||
| Cold stratification time | 36,598.098 | 4 | 9149.524 | 514.693 | <0.01 | ||
| GA3 × Cold stratification time | 6731.058 | 4 | 1682.764 | 94.661 | <0.01 | 0.992 | 6.588 |
| Root length of 2.5 cm | |||||||
| Model | 45,703.852 | 9 | 5078.206 | 274.113 | <0.01 | ||
| Error | 370.519 | 20 | 18.526 | ||||
| Corrected total | 46,074.371 | 29 | |||||
| GA3 | 1920.320 | 1 | 1920.320 | 103.656 | <0.01 | ||
| Cold stratification time | 40,614.807 | 4 | 10,513.702 | 548.080 | <0.01 | ||
| GA3 × Cold stratification time | 3168.724 | 4 | 792.181 | 42.761 | <0.01 | 0.992 | 6.053 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, X.; Wang, F.; Wang, L.; Wang, Q.; Liu, A.; Li, Y. Deep Simple Epicotyl Morphophysiological Dormancy in Seeds of Endemic Chinese Helleborus thibetanus. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1041. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14071041
Zhao X, Wang F, Wang L, Wang Q, Liu A, Li Y. Deep Simple Epicotyl Morphophysiological Dormancy in Seeds of Endemic Chinese Helleborus thibetanus. Agriculture. 2024; 14(7):1041. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14071041
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Xueyan, Fangyuan Wang, Li Wang, Qing Wang, Ancheng Liu, and Yan Li. 2024. "Deep Simple Epicotyl Morphophysiological Dormancy in Seeds of Endemic Chinese Helleborus thibetanus" Agriculture 14, no. 7: 1041. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14071041
APA StyleZhao, X., Wang, F., Wang, L., Wang, Q., Liu, A., & Li, Y. (2024). Deep Simple Epicotyl Morphophysiological Dormancy in Seeds of Endemic Chinese Helleborus thibetanus. Agriculture, 14(7), 1041. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14071041





