Abstract
The color features of strawberries at different growth stages vary slightly and occluded during growth. To address these challenges, this study proposes a lightweight multi-stage detection method based on You Only Look Once version 7-tiny (YOLOv7-tiny) for strawberries in complex environments. First, the size of the model is reduced by replacing the ordinary convolution of the neck network used for deep feature extraction and fusion with lightweight Ghost convolution. Then, by introducing the Coordinate Attention (CA) module, the model’s focus on the target detection area is enhanced, thereby improving the detection accuracy of strawberries. The Wise Intersection over Union (WIoU) loss function is integrated to accelerate model convergence and enhance the recognition accuracy of occluded targets. The advanced Adaptive nesterov momentum algorithm (Adan) is utilized for gradient descent, processing averaged sample data. Additionally, considering the small size of strawberry targets, a detection head specifically for small targets is added, performing detection on a 160 × 160 × 64 feature map, which significantly improves the detection performance for small strawberries. Experimental results demonstrate that the improved network model achieves an of 88.2% for multi-stage strawberry detection, which is 2.44% higher than the original YOLOv7-tiny algorithm. Meanwhile, and are reduced by 1.54% and 12.10%, respectively. In practical detection and inference, the improved model outperforms current mainstream target detection models, enabling a quicker and more accurate identification of strawberries at different growth stages, thus providing technical support for intelligent strawberry picking.
1. Introduction
China ranks first in the world in terms of strawberry planting area and output, and the trend is increasing year by year [1]. At present, strawberries are still mainly picked manually, which is labor-intensive [2,3]. Meanwhile, strawberries are densely planted and have a relatively short maturity period. Untimely collection can easily cause the fruit to rot, resulting in economic losses. This makes the use of autonomous picking robots for strawberry harvesting of great significance and development prospects [4]. Fruit target detection and positioning is a key technology for fruit-picking robots [5,6,7,8], which has a direct impact on fruit picking success rates and efficiency. However, the density of commercial strawberry planting is very high, and it is easy for branches to block or overlap in the robot’s field of view [1], resulting in inaccurate detection results. In addition, the fruits on the strawberry plant are usually at different growth stages, and the color characteristics of the fruits change greatly during the color change period, which can easily lead to false detection.
1.1. Related Work
Currently, deep learning [1,6] and conventional recognition [9,10,11] techniques are the main mehods of fruit detection research. Conventional methods mainly recognize fruits by their color, shape and texture features. Conventional image recognition techniques have long been applied to fruit recognition. For example, Li et al. [12] distinguished pineapples from complex backgrounds based on the color features of fruits. Balano et al. [13] employed apple color differences to segment and recognize fruit within the ideal threshold, hence increasing fruit identification accuracy. However, variations in light intensity can easily impact extraction based on color feature information. In addition, it is difficult to maintain the recognition accuracy for different types of fruits, maturity and background complexity. To this end, Zhou et al. [14] employed RGB and HIS color spaces to enhance apple images and weaken the impact of maturity differences on recognition results. Simultaneously, the saturation channel threshold of the HIS color space was utilized to segment and identify ripe apples in order to lessen the effect of uneven illumination. In [15], the skin texture characteristics of pineapples and bitter melons were retrieved for identification and segmentation. The recognition accuracy of pineapples and bitter melons in a laboratory environment reached 85% and 100%, respectively. In summary, it is difficult to use traditional image processing technology to identify fruits. The limitations of individual features make it difficult to fulfill the visual system demands of strawberry-picking robots operating in natural surroundings.
Deep learning [16,17] has recently enjoyed popularity in fruit target detection research. Deep learning-based detection methods frequently break down into two types: one-stage methods and two-stage methods. The two-stage algorithm needs to extract the object area first and then classify and identify the area with a neural network. It mainly includes Region-based Convolutional Network method (R-CNN) [18], Fast R-CNN [18], spatial pyramid pooling networks (SPPNet) [19], etc. The one-stage approach eliminates the need for generating candidate regions and directly predicts the object’s category probability and position coordinates, such as You Look Only Once (YOLO) [20], SSD [21] and other algorithms. In conventional practice, the two-stage target detection technique often has a slower detection rate than the one-stage approach, yet it demonstrates superior detection efficacy. In addressing the challenge of sluggish detection pace, Fu et al. [22] amalgamated ZFNet with backpropagation for feature extraction and incorporated gradient random descent to expedite model convergence. Concurrently, Parvathi et al. [23] devised an enhanced algorithm rooted in Fast R-CNN for coconut detection. Despite preserving elevated precision, there was a discernible enhancement in detection velocity. Nevertheless, the detection velocity and scale of the two-stage algorithm continue to pose constraints on fulfilling the real-time detection requisites of robotic systems.
In contrast to the two-stage algorithm, the one-stage detection network [24,25] demonstrates superior real-time performance at the expense of diminished detection accuracy. Nonetheless, with iterative refinements, the single-stage approach has progressively ascended as the primary methodology for fruit target detection. For instance, Zhang et al. [26] introduced the RC-YOLOv4 model, which revamped the backbone network to R-CSPDarknet53, thereby attenuating fruit feature loss and enhancing tomato detection accuracy. Addressing the challenge of detecting small target fruits, Gai et al. [27] proposed an enhanced YOLOv4-densenet model, substituting the original backbone network with densenet and integrating the leak ReLu activation function to facilitate fruit feature fusion. In the pursuit of model deployment convenience, Zhang et al. [2] devised an RTSD-net model to streamline and optimize the convolutional layer on the YOLOv4 backbone network. Despite these advancements, achieving high-precision real-time detection in intricate environments remains elusive, rendering it unsuitable for the multi-stage detection of strawberries.
1.2. Motivation and Contributions
Based on prior discussions, this paper introduces a YOLO-GCWA lightweight strawberry detection network designed for strawberry-picking robots. Firstly, we update the convolution method in the neck network of the classic original network, employing a simple Ghost convolution technique to reduce computational complexity and model parameters. Secondly, a CA module is added to the final layer of the backbone network to minimize redundant background features and increase the network’s focus on the detection target area. The original model’s CIoU loss function does not account for the orientation between the true box and the predicted box, leading to slow convergence. Therefore, we introduce the WIoU loss function to decrease the weight of anchor boxes for simple samples, mitigate the impact of complex samples, and enhance the algorithm’s accuracy for strawberries in various conditions. Lastly, the advanced Adan optimizer is implemented to improve the gradient descent algorithm for the dataset and network. Considering the complex agricultural environment in which the picking robot operates, the dataset is enhanced to boost the detection model’s generalization and robustness. The improved detection model is successfully deployed on a low-performance microcomputer, achieving the real-time and accurate detection of strawberries at different stages in a complex agricultural setting.
The primary contributions of this article are outlined below:
- A real-time lightweight detection network YOLO-GCWA is investigated for strawberry detection on the agricultural robot. A lightweight Ghost convolution is used in the neck network. The CA attention module is embedded into the backbone network CSP-Darknet, and a detection head is added to detect small strawberries on the 160 × 160 × 64 feature map, optimizing the performance of the model.
- The advanced WIoU loss function is employed to enhance the model’s focus on anchor boxes of normally distributed samples, thereby improving object localization. Additionally, the introduction of the advanced Adan optimizer addresses the issue of high model training costs.
- Extensive experiments on a mixed strawberry dataset under various conditions (directions, lighting, and backgrounds) demonstrate that the proposed YOLO-GCWA algorithm achieves an impressive performance of 88.2% . Additionally, and are reduced by 1.54% and 12.10%, respectively, significantly outperforming other popular object detection networks.
The remainder of this paper is structured as follows. Section 2 provides a detailed explanation of the methodology for establishing a multi-stage strawberry dataset under various conditions along with the improvement process on the network framework. Section 3 presents a comparative analysis and discussions of the data derived from both simulations and experiments. Finally, Section 4 presents the conclusion.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Acquisition
In this study, strawberry fruits in the strawberry park in Maoming, Guangdong Province are selected as the dataset. The dataset contains 1332 images of strawberry fruit at different growth stages. The acquisition device is an iPhone original camera, which simulates the perspective of the strawberry-picking robot. The camera ’s angle is set between 90° and 45°, and the shooting distance is 5–30 cm when the image of the strawberry is taken. When obtaining the dataset, the situation of strawberry-picking robot operation is fully considered, and the fruit images were collected under the conditions of sunlight, dim light, fruit overlap and fruit occlusion, as shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1.
Images of strawberries under different conditions. (a) Sunny; (b) Dusky; (c) Occluded and small target; (d) Overlapped.
2.2. Dataset Establishment
Currently, a predominant approach in fruit-picking research relies on depth cameras for positional data acquisition. However, the resolution of images captured by depth cameras notably lags behind that of conventional mobile phones or cameras. Consequently, models trained on high-definition images often exhibit suboptimal detection efficacy in practical settings. To better align the trained dataset with real-world application scenarios, image resolution is uniformly adjusted to 640 × 480 pixels prior to annotation. Strawberry images are annotated utilizing LabelImg v1.8.0, encompassing various stages such as mature, young fruit, turning and flower, as depicted in Figure 2. The label files are stored in txt format. To mitigate overfitting, this study employs data augmentation techniques, including spatial blurring, brightness adjustments, and histogram equalization, thereby expanding the dataset to encompass 5328 images. Subsequently, the dataset is partitioned into training, validation, and test sets in an 8:1:1 ratio.
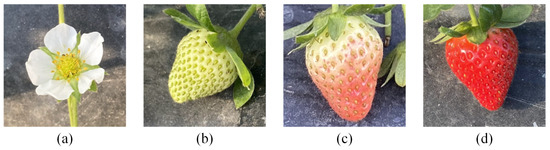
Figure 2.
The label classes of multi-stages strawberry dataset. (a) Sunny; (b) Young fruit; (c) Turning; (d) Mature.
2.3. YOLOv7-Tiny Model
Wang et al. [28] initially proposed the YOLOv7 model, which encompasses variants tailored to diverse application scenarios, such as YOLOv7-tiny, YOLOv7 and YOLOv7x. This investigation prioritizes deployment convenience and balances detection speed and accuracy, choosing YOLOv7-Tiny as the foundational network for enhancement and experimentation. The architecture of YOLOv7-tiny comprises three pivotal components: the backbone network for extracting features, the neck network for combining features, and the head for detection. Within the backbone component, the Efficient Length Aggregation Network (ELAN) [28] is deployed, optimizing gradient path length to facilitate more efficient learning in deeper network modules and bolster network convergence.The Path Aggregation Network (PANet) [29] is utilized in the neck network to amalgamate shallow and deep feature information, thereby enriching feature representation. In the Head component, channel counts are adjusted via standard convolution operations, yielding detection outputs for large, medium, and small targets with corresponding feature map sizes of 80 × 80, 40 × 40, and 20 × 20, culminating in the derivation of final detection results.
Nevertheless, YOLOv7-tiny exhibits limitations in accurately detecting strawberry fruits across various growth stages within intricate agricultural settings. Owing to its lightweight design, the network’s depth of detection is constrained, thereby impeding its ability to discern intricate features. This limitation directly impacts strawberry detection tasks, leading to diminished accuracy, particularly when identifying occluded, small targets, as well as mature and turning strawberries sharing similar feature characteristics. To solve these challenges, this study suggests targeted improvements on YOLOv7-tiny, with the goal of increasing the efficiency of strawberry-picking robots while lowering picking expenses.
2.4. Improvement of YOLOv7-Tiny
This paper proposes an improved YOLOv7-tiny network framework, which includes a backbone network with enhanced feature extraction capabilities, a lightweight feature fusion network, and a head network with a small target detection head. Lightweight Ghost convolution [30] is used in the neck network to reduce the amount of calculation. After that, to enhance the distinction between the background and target fruit features, we integrated a Coordinate Attention (CA) module [31] into the backbone network. This addition increases the model’s focus on the target area’s feature information, thereby improving the detection accuracy of occluded or overlapped strawberries from the perspective of the strawberry-picking robot. In addition, a convolutional layer for detecting 160 × 160 feature maps is added to the head part to increase the detection accuracy of small target strawberries. Furthermore, an advanced WIoU [32] loss function is substituted for the CIoU [33] loss function. In WIoU, the anchor box’s quality is assessed using a dynamic, non-monotonic process, which helps the model identify the target by making it more aware of anchor boxes of average quality. Finally, the Adan optimizer is used to address the challenges of unsatisfactory convergence speed of averaged data and high model training time consumption. Figure 3 describes the network structure of the improved YOLOv7-tiny model.
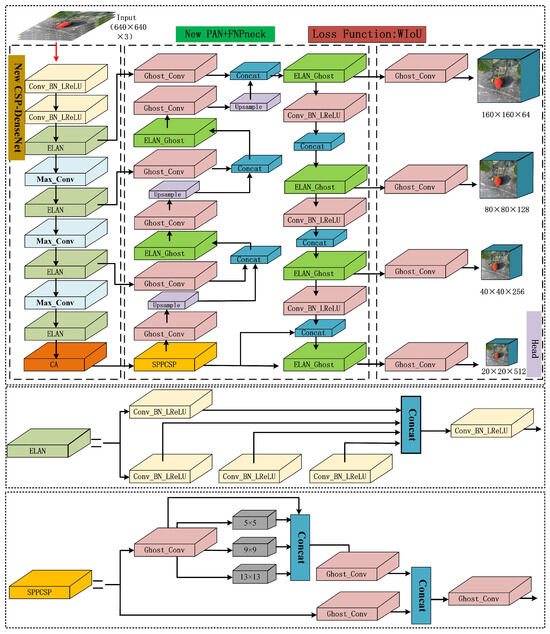
Figure 3.
The YOLO-GCWA network framework.
2.4.1. Ghost Convolution Module
Traditional convolution methods often produce a significant amount of redundancy in intermediate feature maps. This is addressed by the Ghost structure, which uses fewer parameters to create more redundant feature maps. The Ghost convolution module comprises three parts: first, it uses a 1 × 1 convolution to minimize the number of channels in the input feature map. Second, it creates redundant feature maps through grouped linear operations. Finally, it merges the map of features in the first part with the redundant feature maps in the second part to produce the output feature map with the required amount of channels. The structure is illustrated in Figure 4. Firstly, the input feature X is convolved using conventional convolution to acquire the intrinsic feature map. The process is described by Equation (1) [30].
where is the convolution kernel used for convolution.
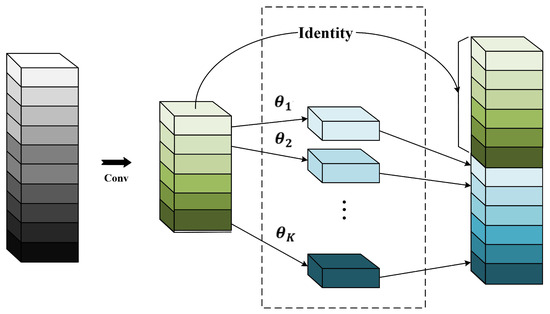
Figure 4.
Ghost convolution module.
In order to acquire a feature map with an output channel number of n, the Ghost convolution module needs to generate s redundant feature maps, which can be specifically described as shown below:
where is the ith input feature map, is the jth linear operation utilized to produce the jth redundant feature map , and the sth linear operation is used as the identity mapping.
Finally, the output feature map is created by concatenating the intrinsic feature map from the first step with the Ghost feature map from the second phase.
2.4.2. Coordinate Attention Mechanism
During the YOLOv7-tiny feature extraction process, many key intermediate and shallow layer texture and contour information are not properly recovered, which has an influence on the recognition of strawberry fruit regions at various stages, resulting in missing and incorrect target detection. To this purpose, we incorporate the Coordinate Attention (CA) mechanism into the YOLOv7-tiny model for detecting strawberries at various growth stages.
The CA module encodes long-range dependence and location information from both horizontal and vertical spatial directions before fusing the features. Figure 5 depicts the structural diagram of CA, consisting of two parts: coordinate information embedding and coordinate attention creation. Coordinate information embedding allows the model to better comprehend and use the spatial connection of the input picture, boosting detection performance. The CA module applies global average pooling to the input feature map in the horizontal and vertical directions, yielding feature maps in the horizontal and vertical directions and avoiding the disadvantage of single global average pooling, which does not retain position information. The input feature tensor encodes the information in both the horizontal and vertical dimensions using a pooling kernel. Equations (3) and (4) [31] provide the height h and width w of the cth channel, respectively.
where W and H represent the width and height of the pooling kernel.
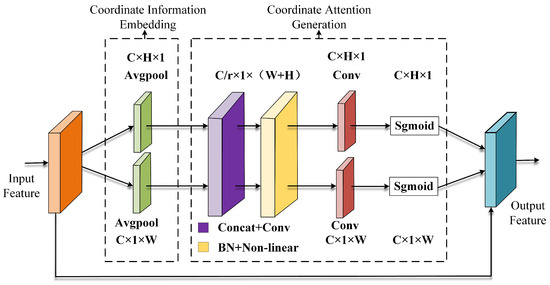
Figure 5.
Schematic diagram of CA module.
These two transformations aggregate data in two distinct spatial directions, resulting in a pair of feature maps depending on direction perception. CA may extract long-range dependencies in a feature map along one spatial dimension while retaining precise location information along another. In the spatial dimension, two transformations of Equations (3) and (4) are used, and 1 × 1 convolution is used to compress the channel dimension. Subsequently, following the encoding of the spatial information in both vertical and horizontal directions using batch norm and nonlinear activation function, the encoded data are divided by the 1 × 1 convolution transformation function to produce two tensors with the same number of channels by breaking the encoded data into two distinct feature maps along the horizontal and vertical spatial dimensions. The final output is represented by f, and the calculation formula of f is as follows:
where denotes a nonlinear activation function, is the intermediate feature map that is utilized to encode spatial information in both the horizontal and vertical directions, and represents the channel connection operation along the spatial dimension. f should be divided along the spatial dimension into two separate tensors, and . The input X is transformed into two tensors, and , with the same number of channels, and , which are two 1 × 1 convolution transformations. The equations for the calculating procedure are shown in (6) and (7).
where the sigmoid activation function is represented by , and the attention weights and are boosted as a result. The coordinate attention block’s output, , may be represented using Equation (8).
where represents the input feature map. and represent the attention weights in the horizontal and vertical spatial directions, respectively.
Different from the classic channel attention mechanism, the CA module not only adopts the re-weighting method but also encodes the spatial information. The introduction of the CA module can more accurately locate the exact position of the recognition target, so that the improved YOLOv7-tiny network can more accurately identify the strawberry fruit area, weakening the influence of the background information, which enhances the detection accuracy of the model.
2.4.3. WIoU Loss Function
The multi-stage strawberry detection task has many overlapping and occluded fruits. The regression box may be successfully made to resemble the real box, and the model’s detection performance can be enhanced by a fair design of the loss function of the detection network. The original model uses the CIoU loss function as the regression loss of the bounding box. The calculation process is described by Equations (9)–(11) [33].
where the intersection ratio between the genuine box and the predicted box is denoted by Intersection over Union (IoU). denotes the Euclidean separation between the genuine box’s centroid and the predicted box’s centroid. The height and width of the genuine box are represented by and , whereas the height and breadth of the predicted box are described by h and w. The minimal rectangular box produced by the genuine box and the forecast box has width and height , respectively.
The CIoU loss function has poor detection performance on samples with substantial overlap and disregards the balance between challenging and easy-to-detect samples. Furthermore, one of the loss function’s penalty elements in CIoU is the aspect ratio. The penalty term is unable to capture the true difference between the two boxes, leading to a detection failure, if the width and height values of the real box and the projected box have different aspect ratios.
To this end, the CIoU loss function is replaced in this study with the WIoU loss function. In order to improve the detection model’s overall performance, the WIoU loss function offers a sensible gradient gain allocation strategy and a dynamic non-monotonic adjustment mechanism that can lower the weight of the anchor box of simple samples while simultaneously lessening the influence of complex samples on the model. First, the initial WIoU function containing the two-layer attention mechanism of and is constructed. The specific calculation process is described by Equations (12)–(14).
where the typical quality anchor box is substantially enlarged by using . High-quality anchor boxes may be greatly decreased by using , and the distance between the ground truth box and the detection box’s center can be given more consideration. Also, as Equation (15) [32] illustrates, a dynamic non-monotonic focusing mechanism is added.
where the non-monotonic focal factors are represented by r, are the monotonic focal coefficients, the outliers are represented by , and hyperparameters and are modifiable to fit various models.
The utilization of a dynamic non-monotonic method to assess anchor frame quality is taken into consideration by WIoU in comparison to the CIoU loss function. This enhances the model’s object location capabilities by forcing it to focus more on anchor frames of average quality. For the detection task of multi-stage strawberries in complex environments, the proportion of complex samples with severe overlap, occlusion, and similar features is high. WIoU can dynamically optimize its loss weight and enhance the detection performance of the network.
2.4.4. Adan Optimizer
Adan is used as the optimizer in the original network. Its design is simple and effective. To estimate the first and second moments of the gradient, it uses the heavy ball acceleration technology in conjunction with the moving average concept, adopting a single common learning rate for all gradient coordinates. However, the training period is lengthy and the convergence speed is frequently not optimal in the issue of averaging data. This study will present the Adan optimizer as a result. To estimate the stable and precise first and second moments in the adaptive acceleration gradient algorithm, it provides a method based on the estimation of Nesterov momentum. Theoretically, heavy ball acceleration is slower to converge than Nesterov acceleration. On account of employing the gradient at the present solution’s extrapolation point, it strengthens the optimizer’s ability to make greater use of the dynamic training trajectory’s curve information and strengthens its robust to deep neural network architecture.
For the Adan optimizer, first set the initialization , the basic learning rate , the momentum , the stability parameter > 0, the weight decay >0, the output average value, where k∈[1,K], k is an integer, and the stochastic gradient , which is estimated at , where [34]
where = , = 0, = −, = . is the accumulation of gradients, is the second-order moment estimate (second-order derivative plus gradient), is the correction of the second-order moment estimate, is the basic learning rate, is the stochastic gradient, and finally the variable is updated. In the experiment, , , and are 0.98, 0.92, and 0.99, respectively, and the learning rate is .
2.5. Model Evaluation Metrics
This investigation primarily assesses the proposed model’s efficacy in multi-stage strawberry fruit detection through five metrics: Precision (P), Recall (R), Mean Average Precision (), Giga Floating-point Operations Per Second (), and Parameters (). Precision denotes the likelihood of correctly identifying strawberry as positive samples among all actual positive samples. Recall represents the ratio of correctly identified positive samples to the total number of samples. signifies the average precision across four categories: flower, young fruit, transitioning and mature. quantifies the computational workload required for detection by the model, while indicates the model’s size. Equations (21)–(26) delineate the computational procedures for computing these evaluation metrics.
where (True Positive) denotes the count of accurately identified strawberries, whereas (False Positive) represents the number of incorrect predictions for images lacking strawberry labels. (False Negative) refers to the missed strawberry targets, and (True Negative) indicates the instances where strawberries are present in the image but not detected. The variable N signifies the total number of detection categories. The constant denotes the order, K signifies the size of the convolution kernel, C represents the number of channels, M refers to the input image size, and i indicates the iteration count.
3. Experiments and Results
The computing equipment and algorithm environment configuration used in this study are shown in Table 1. After hyperparameter adjustment, the initial learning rate is uniformly set to 0.001, and cosine annealing is used to adjust the learning rate. The decay coefficient is 0.0005, the number of iterations is 300, and the batch size is 8.

Table 1.
Experimental configuration.
3.1. Comparative Experiment of Attention Mechanism
In order to verify the effectiveness of the CA module, the multi-stage strawberry image dataset constructed in this paper is used as a training set to compare the CA module with other attention mechanisms. The CA, Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks (SEnet) [35], Efficient Channel Attention (ECA) [36], Convolutional Block Attention Module (CBAM) [37] and Simple Attention Module (SimAM) [38] module are embedded in the same position of the feature extraction network of the model to train and evaluate the model. The results of the comparative validation are shown in Table 2. Compared with the original YOLOv7-tiny model, after adding SEnet, ECA, CBAM, simAM and CA modules, respectively, although the network and increased slightly, the was improved by 0.81%, 0.58%, 0.35%, 0.47% and 0.93%, respectively. In summary, the improved YOLOv7-tiny model after introducing the CA module is superior and can improve the accuracy of multi-stage strawberry detection in complex environments.

Table 2.
Result comparison of different attention mechanisms in the backbone.
3.2. Ablation Experiments
In this experiment, Ghost convolution is used to replace the traditional convolution method in the neck network, reducing the model’s and . In the backbone network, a built-in CA attention mechanism module enhances the model’s focus on the target area. Additionally, a 160 × 160 detection head is added to improve the performance on small targets. The WIoU loss function is integrated to accelerate convergence, and the Adan optimizer is introduced to enhance the model’s ability to process averaged sample data. Nine groups of experiments are conducted to ensure the feasibility of the optimization scheme with the results presented in Table 3. Group 0 serves as the evaluation of the baseline network, functioning as a control experiment. Groups 1–5 assess each enhancement method independently to confirm the efficacy of the respective improvements introduced in this study. Groups 6–8 evaluate the enhancement methods in various random combinations to determine their compatibility. Finally, Group 9 integrates all enhancement methods to validate the overall feasibility of the proposed approach.

Table 3.
Ablation experiment results.
As shown in Table 3, replacing the neck network with Ghost lightweight convolution decreases the and by 16.92% and 27.77%, respectively, though the detection accuracy decreases by 0.58%. The standalone addition of the CA module improves detection accuracy by 0.92% due to the better utilization of positional relationships in the image. Integrating the WIoU loss function improves detection accuracy by 1.28% due to enhanced sensitivity to overlapping targets and accelerates model convergence, resulting in more stable detection. The standalone addition of the Adan optimizer also improves model accuracy by better handling homogenized samples. Adding the detection head alone slightly improves the model’s detection accuracy for small targets, increasing the mean average accuracy by 1.16%. However, this addition also increases the and by 18.4% and 1.70%, respectively, compared to the original model. Observing the combined effects, the improved model achieves the best detection performance.
3.3. Comparison Detection Experiment of Original Model and Proposed Model
In order to verify the multi-stage strawberry detection performance of the network proposed in this paper under complex planting conditions, strawberry detection experiments under different conditions were carried out, and the detection results were compared with those of the original model, as shown in Figure 6 and Figure 7. As can be seen from Figure 6b, in the case of insufficient light, the original model has missed detection, but our proposed model does not miss. The original model also missed detection when the fruit was too small, as shown in Figure 7. Our model achieves a perfect detection of small targets by adding a small target detection head. Comparing (c) and (d) of the two figures, it can be seen that even when the strawberry fruit is heavily obscured or overlapped, the strawberry in these difficult situations can be achieved due to the increased CA attention mechanism of our network.
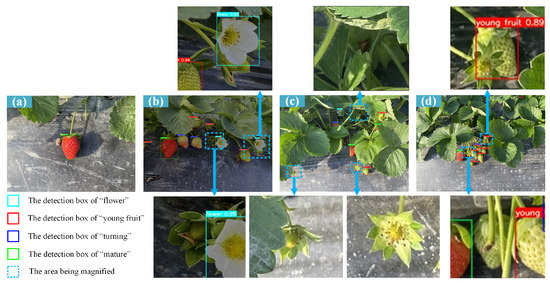
Figure 6.
The strawberry detection results of YOLOv7-tiny in different conditions. (a) Sunny; (b) Dusky; (c) Occluded and small target; (d) Overlapped.
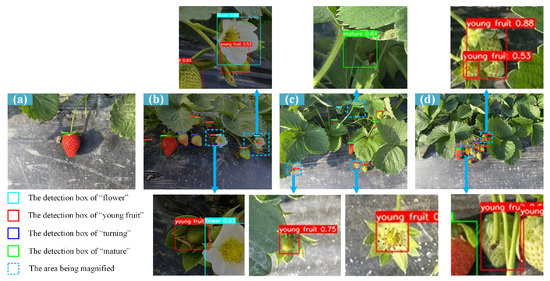
Figure 7.
The strawberry detection results of YOLO-GCWA in different conditions. (a) Sunny; (b) Dusky; (c) Occluded and small target; (d) Overlapped.
3.4. Comparison of Different Algorithms
In order to demonstrate the superiority of the algorithm proposed in this study, YOLOv5s, YOLOv6n, the original YOLOv7-tiny, YOLOv7, YOLOv8s and Faster R-CNN are selected as comparison algorithms. All algorithms were trained with the same parameters, such as 300 epochs and eight batch sizes. The evaluation indicators in the validation set are shown in Table 4. YOLO-GCWA achieves 88.2% , which is 2.44% higher than the original YOLOv7-tiny. Meanwhile, and are reduced by 1.54% and 12.10%, respectively. Compared to the popular models YOLOv5s, YOLOv6n, YOLOv7, YOLOv8s, and Faster R-CNN, the is higher by 2.32%, 1.73%, 1.03%, 1.15%, and 4.38%, respectively. The and Params of our model are the smallest among the tested models. Therefore, the proposed model can outperform both the lightweight network YOLOv5s and the larger YOLOv7. In summary, the model proposed in this study has the best detection performance in multi-stage strawberry detection and matches the requirement of convenient deployment on the strawberry-picking robot. Figure 8 describes the changes in the P-R values of different algorithms during training, which more intuitively illustrates the differences between different algorithms.

Table 4.
Comparison of experimental results of different models.
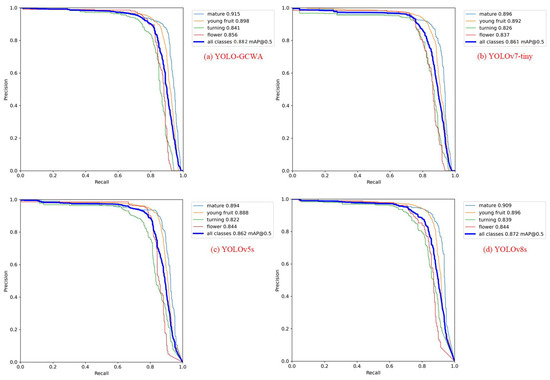
Figure 8.
The PR curves of different detection models.
Different Model Detection Analysis
The growing environment of strawberries is complex, and there are many different situations in robot vision. For example, the fruit is blocked by branches and leaves, the fruit is densely overlapped, the fruit is sparse and obvious, and the fruit image is small. YOLO-GCWA adds the CA module to enhance the ability to extract strawberry features. As can be seen from Figure 9, even if the fruit is blocked, overlapped, or the fruit target is small, YOLO-GCWA can detect the strawberries perfectly. From Figure 9c,d, when the color of the environment is similar to the color characteristics of the fruit, YOLOv5s and YOLOv6n make incorrect detections, which detect the background as “young fruit”. When the strawberry is too small or the feature information is lost due to severe occlusion, YOLOv5s, YOLOv7-tiny, YOLOv8s and Faster R-CNN miss the detection. Fast R-CNN is the most serious. The YOLO-GCWA is the most accurate and comprehensive for multi-stage strawberry detection in complex environments. As a result, when compared to other algorithms, our suggested approach maximizes the ability to identify obstructed or overlapping strawberries and can finish the real-time strawberry recognition assignment in intricate agricultural settings.
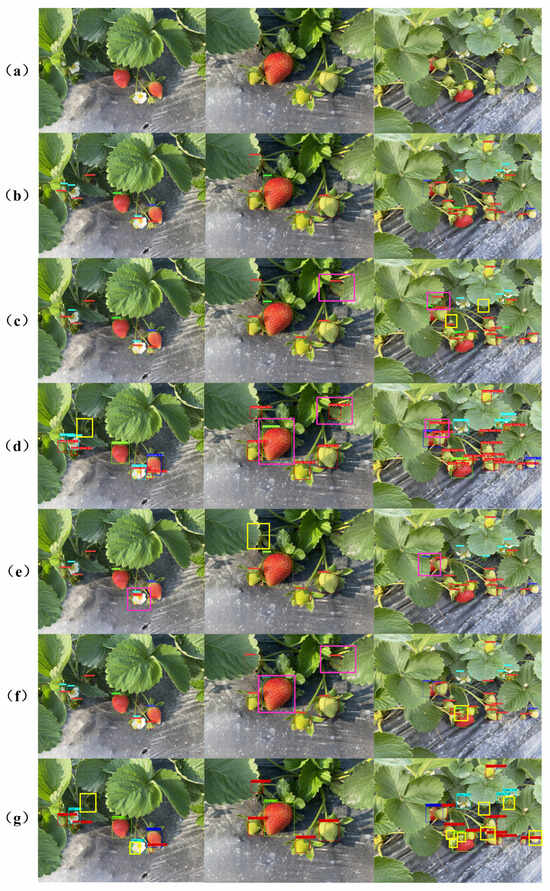

Figure 9.
Detection results of different models: (a) Original image. (b) YOLO-GCWA. (c) YOLOv5s (d) YOLOv6n. (e) YOLOv7-tiny. (f) YOLOv8. (g) Faster R-CNN. Notes: The red box is the correct detection box of “young fruit”. The green box is the correct detection box of “mature”. The cyan box is the correct detection box of “flower”. The blue box is the correct detection box of “turning”. The yellow box is the missed detection box. The pink box is the wrong detection box.
3.5. Model Visualization Analysis
The network model based on deep learning often only shows predicted results and lacks interpretability during processing. To address this, we apply Gradient-weighted Class Activation Mapping (Grad-CAM) [39] to both the proposed model and YOLOv7-tiny to generate heat map visualizations using strawberry images from the test set. Grad-CAM is a visualization method that uses gradients to determine the importance of spatial positions in a convolutional layer. Since gradients are calculated with respect to a specific class, Grad-CAM results can clearly highlight the regions involved in the prediction through heat maps. Figure 10 and Figure 11 show these visualization results. The darker the red region in the image, the greater the influence of that region on the prediction results, indicating higher model attention.
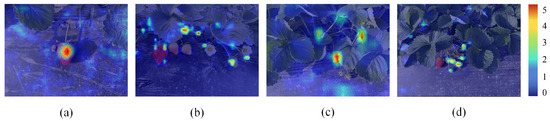
Figure 10.
The heat map of YOLO-GCWA. (a) Sunny; (b) Dusky; (c) Occluded and small target; (d) Overlapped.
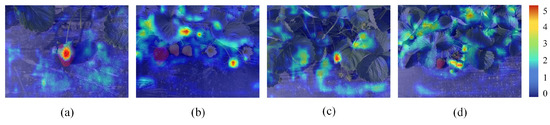
Figure 11.
The heat map of YOLOv7-tiny. (a) Sunny; (b) Dusky; (c) Occluded and small target; (d) Overlapped.
Comparing Figure 10 and Figure 11, it is evident that the Grad-CAM mask of our proposed model better covers the strawberry regions compared to the original YOLOv7-tiny. Our model’s heat map shows less mask coverage on background interferences. This indicates that the model integrated with the CA module effectively mines and learns information from the fruit region, performs feature aggregation, and enhances the model’s focus on strawberry characteristics. As a result, it achieves an accurate detection of strawberries in complex environments.
4. Conclusions
In this study, a real-time multi-stage strawberry detection method is proposed, utilizing an improved YOLOv7-tiny model within the context of complex agricultural environments. The traditional convolution of the neck network is replaced by Ghost convolution, which has less computational complexity. The Coordinate Attention (CA) module is integrated after the backbone to enhance the extraction of strawberry image features, thereby improving detection accuracy under conditions of occlusion, background-feature similarity, and dense fruit clusters. The CIoU loss function in the detection layer is replaced with the WIoU loss function to accelerate model convergence and reduce detection time. The adoption of the advanced Adan optimizer for gradient descent is used to process the averaged sample data. Additionally, a detection head specifically designed for small targets is incorporated, performing detection on a 160 × 160 × 64 feature map, significantly improving the detection performance for small strawberries. A comprehensive multi-stage strawberry fruit dataset is utilized for experimentation. On this dataset, the YOLO-GCWA model achieved an of 88.2% on the validation set, outperforming the YOLOv5s, YOLOv6n, YOLOv7, YOLOv8s and Faster R-CNN models. Compared to the original YOLOv7-tiny, the is improved by 2.44%. At the same time, the average detection time of our proposed method for each image in the test set is 6.1 ms, which fully meets the requirement of real-time detection. In summary, the proposed YOLO-GCWA model effectively meets the requirements of a vision system for a strawberry-picking robot, providing robust and accurate multi-stage automatic strawberry detection under complex environments.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.L. (Jiehao Li); Data curation, J.L. (Jiahuan Lu); Formal analysis, T.Z.; Funding acquisition, J.L. (Jiehao Li); Investigation, C.L. and H.W.; Methodology, C.L.; Project administration, J.L. (Jiehao Li); Resources, H.W. and T.Z.; Software, T.Z.; Supervision, J.L. (Jiahuan Lu); Validation, H.W.; Visualization, C.L. and H.W.; Writing—original draft, C.L. and J.L. (Jiehao Li). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supporyed by the Young Talent Support Project of Guangzhou Association for Science and Technology under Grant QT2024-006, 2024 Basic and Applied Research Project of Guangzhou Science and Technology Plan under Grant 2024A04J4140, and the State Key Laboratory of Robotics and Systems (HIT) under Grant SKLRS-2024-KF-08.
Data Availability Statement
This paper has not available data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Du, X.; Cheng, H.; Ma, Z.; Lu, W.; Wang, M.; Meng, Z.; Jiang, C.; Hong, F. DSW-YOLO: A detection method for ground-planted strawberry fruits under different occlusion levels. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 214, 108304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, J.; Chen, Y.; Yang, W.; Zhang, W.; He, Y. Real-time strawberry detection using deep neural networks on embedded system (rtsd-net): An edge AI application. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 192, 106586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; NAGATA, M.; Guo, F.; Hiyoshi, K.; Kinoshita, O.; Mitarai, M. Study on strawberry harvesting robot using machine vision for strawberry grown on annual hill top (Part 2) Ripeness judgment and recognition of peduncle using picking camera, and fabrication of the picking hand. J. Jpn. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2007, 69, 60–68. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, G.; Li, Z. Design and test of tomatoes harvesting robot. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Information and Automation, Lijiang, China, 8–10 August 2015; pp. 949–952. [Google Scholar]
- He, F.; Zhang, Q.; Deng, G.; Li, G.; Yan, B.; Pan, D.; Luo, X.; Li, J. Research Status and Development Trend of Key Technologies for Pineapple Harvesting Equipment: A Review. Agriculture 2024, 14, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J. A dragon fruit picking detection method based on YOLOv7 and PSP-Ellipse. Sensors 2023, 23, 3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wang, B.; Xue, J. YOLO-P: An efficient method for pear fast detection in complex orchard picking environment. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 13, 1089454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, Y.; Zheng, J.; Ge, Y. Intelligent detection of Multi-Class pitaya fruits in target picking row based on WGB-YOLO network. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 208, 107780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, S.; Hayashi, S.; Yoshida, H.; Kobayashi, K. Development of a stationary robotic strawberry harvester with a picking mechanism that approaches the target fruit from below. Jpn. Agric. Res. Q. JARQ 2014, 48, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, S.; Yamamoto, S.; Saito, S.; Ochiai, Y.; Kamata, J.; Kurita, M.; Yamamoto, K. Field operation of a movable strawberry-harvesting robot using a travel platform. Jpn. Agric. Res. Q. JARQ 2014, 48, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiping, T.; Wangming, H.; Anguo, H.; Weiyang, W. Design and experiment of intelligentized tea-plucking machine for human riding based on machine vision. Nongye Jixie Xuebao/Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2016, 47. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Wang, M.; Wang, N. Development of a Real-Time Fruit Recognition System for Pineapple Harvesting Robots; American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2010; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Bulanon, D.M.; Kataoka, T.; Ota, Y.; Hiroma, T. AE—automation and emerging technologies: A segmentation algorithm for the automatic recognition of Fuji apples at harvest. Biosyst. Eng. 2002, 83, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Damerow, L.; Sun, Y.; Blanke, M.M. Using colour features of cv.‘Gala’apple fruits in an orchard in image processing to predict yield. Precis. Agric. 2012, 13, 568–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaivivatrakul, S.; Dailey, M.N. Texture-based fruit detection. Precis. Agric. 2014, 15, 662–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Dai, Y.; Su, X.; Wu, W. Efficient Dual-Branch Bottleneck Networks of Semantic Segmentation Based on CCD Camera. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Li, J. URTSegNet: A real-time segmentation network of unstructured road at night based on thermal infrared images for autonomous robot system. Control Eng. Pract. 2023, 137, 105560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girshick, R. Fast r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1440–1448. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 37, 1904–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.Y.; Berg, A.C. Ssd: Single shot multibox detector. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Proceedings, Part I 14. Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, L.; Feng, Y.; Majeed, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Karkee, M.; Zhang, Q. Kiwifruit detection in field images using Faster R-CNN with ZFNet. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2018, 51, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvathi, S.; Selvi, S.T. Detection of maturity stages of coconuts in complex background using Faster R-CNN model. Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 202, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, J.; Zhao, X.; Su, X.; Wu, W. Lightweight detection networks for tea bud on complex agricultural environment via improved YOLO v4. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 211, 107955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Zhang, K.; Zhong, H.; Xie, J.; Xue, X.; Yan, M.; Wu, W.; Li, J. Efficient Tobacco Pest Detection in Complex Environments Using an Enhanced YOLOv8 Model. Agriculture 2024, 14, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Jiang, M.; Li, Y.; Feng, M. Research on tomato detection in natural environment based on RC-YOLOv4. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 198, 107029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, R.; Chen, N.; Yuan, H. A detection algorithm for cherry fruits based on the improved YOLO-v4 model. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 13895–13906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Liao, H.Y.M. YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 7464–7475. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Qi, L.; Qin, H.; Shi, J.; Jia, J. Path aggregation network for instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 8759–8768. [Google Scholar]
- Han, K.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Q.; Guo, J.; Xu, C.; Xu, C. Ghostnet: More features from cheap operations. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 1580–1589. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Q.; Zhou, D.; Feng, J. Coordinate attention for efficient mobile network design. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 13713–13722. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, Z.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Z.; Yu, R. Wise-IoU: Bounding box regression loss with dynamic focusing mechanism. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.10051. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Wang, P.; Liu, W.; Li, J.; Ye, R.; Ren, D. Distance-IoU loss: Faster and better learning for bounding box regression. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 12993–13000. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.; Zhou, P.; Li, H.; Lin, Z.; Yan, S. Adan: Adaptive nesterov momentum algorithm for faster optimizing deep models. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2208.06677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, B.; Zhu, P.; Li, P.; Zuo, W.; Hu, Q. ECA-Net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11534–11542. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, R.Y.; Li, L.; Xie, X. Simam: A simple, parameter-free attention module for convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Vienna, Austria, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 11863–11874. [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-cam: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).