Abstract
Straw returning has gradually been adopted as an effective approach to address the serious degradation of farmland. However, the carbon/nitrogen (C/N) ratio of rice straw is generally too high for microorganisms to decompose the organic materials and release nutrients, which may minimize the benefits of straw returning to the agricultural production system. This study aimed to investigate the effects of straw returning on rice production and propose optimum nitrogen (N) management for early rice production under a straw returning system. The total N fertilizer that was evaluated was 165 kg N ha-1, urea (46% N), applied in different proportions in three stages of rice cultivation: basal, tillering, and panicle. Using no straw returning with the N fertilizer ratio of basal:tillering:panicle = 5:2:3 treatment (T1) as the control, four different N fertilizer ratios of basal:tillering:panicle, including 5:2:3 (T2), 5:2:2 (T3), 5:4:1 (T4), and 5:5:0 (T5) were set under straw returning. The return of straw decreased the available N in the soil at the tillering stage, and impeded root growth and the crop canopy from establishing, which decreased the effective panicles by 10.1% compared with that of T1, limiting the increases in rice grain yield. Increasing the N fertilizer ratio 10–20% (T3 and T4) at the tillering stage effectively increased the content of soil ammonium and nitrate nitrogen, improved the root growth, and increased the root activities by 16.0–40.5% at the tillering stage. As a result, the effective panicle number increased by 5.1–16.2%. Among these, T4 treatment maximized the benefits of straw returning the most. Additionally, increasing the N fertilizer ratio at the tillering stage increased the shoot uptake across the early rice growing season and synchronized crop N uptake with the accumulation of carbon assimilates, which enhanced the crop growth rate and increased the rice yield by 13.5–25.1%. It is concluded that increasing the N fertilizer ratio by 20% at the tillering stage is a promising strategy to increase the availability of N in the phases of high demand for this nutrient.
1. Introduction
Rice is a staple food for humanity, with great social and economic importance. The demand for rice continues to grow with the rapidly expanding population. The south of the Yangtze River, as the major double rice-growing region, produces about one-third of the total rice in China [1]. Thus, it is of great significance to ensure the high-yielding and sustainable production of rice in this region. However, the degradation of paddy soil in this region is increasing under intensive agriculture, which greatly restricts crop production [2,3].
Crop straws, as one of the main by-products of agricultural production, are important carbon-rich energy sources, containing abundant organic and mineral nutrients that are necessary for crop growth and development [4,5]. China is one of the top agricultural-producing countries, with annual straw production ranking first in the world. According to statistics, the total amount of straw in China in 2022 was 9.77 × 108 t. Therefore, using crop straws appropriately and efficiently plays a crucial role in environmentally friendly, efficient, and sustainable agricultural production. Crop straw is a high-quality organic matter, which can be used as a resource to fertilize the soil [6,7,8]. It has been proven that straw returning was able to ensure progressive increase in carbon sequestered in the soil over time, improving the soil quality, biodiversity, functioning, and also contributing significantly to adaptation and mitigation of climate change [9,10,11]. Additionally, crop residue contains abundant nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium nutrients. Generally, the amounts of N, P, and K in rice straw at harvest are 5–8, 0.7–1.2, and 12–17 kg, respectively, per ton of straw on a dry weight basis [12,13]. Therefore, straw returning theoretically can offset part of the P2O5, K2O, and N fertilizers consumption [3]. Reducing the N rate by 20% with straw returning significantly improved the soil structure and no significant losses of maize grain yield were observed [14]. Encouraged by national policies, straw returning has been widely recognized and accepted as a crucial farmland management measure to improve soil fertility and crop yields [10]. The most significant increases in rice yield were obtained in the northeast region, while less pronounced yield improvements were observed in regions at low latitudes, compared to those at higher latitudes [15]. However, as the decomposition processes of crop straw are complicated and affected by a lot of factors, straw returning can also have some negative impacts on crop growth and the agricultural ecological environment [16,17]. For some nutrient-deprived soils, excessive application of nitrogen fertilizer is relatively common, which generally diminishes both microbial biomass and activity, exacerbates soil acidification and disrupts soil nutrient equilibrium [18,19]. In such circumstances, incorporating straw back into the soil will further exacerbate nutrient imbalances and adversely affect crop growth [20,21,22,23]. Additionally, due to the C/N ratio of crop straw being much higher than the appropriate C/N ratio for soil microorganisms to decompose organic materials, soil N is heavily utilized by microorganisms for straw degradation, leading to native soil N and from fertilizer N immobilization, thereby decreasing the crop yield [24,25,26,27,28]. With varying climate and soil texture factors, straw return could also have negative effects on soil organic carbon (SOC) sequestration [15,29]. In some counties of the northeast China, SOC continues to be lost due to excessively high initial SOC levels [15]. Thus, inappropriate straw returning may deteriorate soil structure and increase nutrient loss, further inhibiting crop production [17,30].
Rice straws are rich in lignins, tannins, and waxes; such substances are difficult for microorganisms to decompose, restricting the nutrition-releasing processes. Additionally, the C/N ratio of rice straw is about 60~100:1, and is rich in carbon, which causes the competition for N between microorganisms and crop plants, especially at the early growth stage, adversely affecting crop growth. The C/N ratio is the key factor determining the N mineralization rate of straws during the early stage of straw decomposition [31]. Some studies have suggested that increasing the N rate could promote the degradation of straws, enhancing the soil N contents, labile organic carbon components, and microbial ecological functions [10,32,33,34]. Appropriately increasing the basal topdressing N ratio with straw returning could effectively alleviate the competition between microorganisms and rice crops, significantly increasing the richness and diversity of soil bacteria, and the N fertilizer utilization efficiency of crops, thus the grain yield [35]. Undoubtedly, optimizing N management is an effective way to maximize the advantages and minimize the disadvantages of straw returning to the crop production system [36]. However, how to optimize the N management strategies and what the underlying mechanisms are still need further study. This study innovatively explored the connections between nitrogen content, root growth, and crop N uptake, putting forward a new optimum nitrogen management to match up the soil nitrogen supply with crop requirements, which addressed a very current research issue regarding sustainable nitrogen fertilization. Based on the fact that the N fertilizer ratio of basal:tillering:panicle = 5:2:3 is widely recognized as the optimum N management strategy under a no straw returning system, the optimum N fertilizer ratio at the tillering stage under a straw returning system should be higher, concerning the competitive effects for nitrogen between microorganisms and rice crops at the early growth stage. To verify this hypothesis, we conducted an experiment with an increasing N fertilizer ratio at the tillering stage in the early rice growth season from 2017 to 2022 in a double-rice cropping system with the following main objectives: (1) to investigate the effects of various N ratios in the early growth stage of rice on the soil nutrients; (2) to explore the impacts of various N ratios in the early growth stage of rice on root growth and activities; (3) to elucidate whether optimizing the N ratio in the early growth stage of rice can match up the crop N uptake with the plant N requirement for growth, thus enhancing crop yields.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Set-Up
This field experiment was conducted across the early rice growing season from 2017 in Jinxian County, Jiangxi province, China (116°20′24″ E, 28°15′30″ N). The hybrid of Xiangzaoxian45 was planted in a density of 25×104 hill ha−1. The trail was arranged in a randomized complete block design with three replicates. The area of each plot was 6 m × 8 m. Five treatments were set up including no straw returning with the N fertilizer ratio of basal:tillering:panicle = 5:2:3 treatment (T1), straw returning with the N fertilizer ratio of basal:tillering:panicle = 5:2:3 treatment (T2), straw returning with the N fertilizer ratio of basal:tillering:panicle = 5:3:2 treatment (T3), straw returning with the N fertilizer ratio of basal:tillering:panicle = 5:4:1 treatment (T4), and straw returning with the N fertilizer ratio of basal:tillering:panicle = 5:5:0 treatment (T5), using T1 as the control. The total N was applied at 165 kg N ha−1 as urea (46% N). In total, 75 kg P2O5 ha−1 was applied as calcium magnesium phosphate (15.0% P2O5) prior to seeding, and 75 kg K2O ha−1 as potassium chloride (60% K2O) were applied equally at basal and panicle initiation stages. The soil types were acrisols. Before the establishment of the experiment platform, the soil organic matter was 20.50 g kg−1, TN was 1.03 g kg−1, total P was 0.43 g kg−1, available N was 127.21 mg kg−1, available P was 7.88 mg kg−1, available K was 5.97 g kg−1, and the buck density was 1.06g cm−3. The data used in this manuscript was obtained in 2021 and 2022. The details are described in Table 1.

Table 1.
Details of the experimental design and the dose of N applied in three phases to a rice crop.
2.2. Measurements
2.2.1. Rice Yield and Yield Components
At maturity, six hills from each plot were randomly sampled to determine the yield and yield components according to Liao et al. [37]. The rice kernel was determined with 14% moisture content.
Yield (kg ha−1) = Effective panicles (ha−1) × Spikelets (per panicle) × 1000-kernel weight (g 1000−1 kernels) × 10−6.
2.2.2. The Content of Soil Ammonium N and Nitrate N
The soil samples were collected from the surface layer of 0–20 cm, using a 5-point sampling method. The fresh soil sample was passed through a 2 mm sieve and then preserved at −80 °C in the freezer for later measurement of soil nitrate N and ammonium N according to the method described by Rock et al. [38]. A total of2 mol/L KCl was used to extract 5 g fresh soil for 60 min. Then, the supernatants were collected and analyzed by AA3 continuous-flow analysis (AutoAnalyzer 3, Bran + Luebbe GmbH, Norderstedt, Germany).
2.2.3. Rice Root Characteristics
Rice roots were sampled at tillering, heading, and maturation stages following the same approach as Huang et al. [39]. Each plot was replicated three times. The root activities were determined using methylene blue solution. The length, surface area, and volume of roots were determined using a scanner (Epson Expression 12000XL, Shanghai Zequan Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) and a WinRHIZO Root Analyzer System (Regent Instruments Inc., Québec City, QC, Canada). Then, the root samples were oven-dried at 105 °C for 30 min and then at 70 °C to a constant weight to determine root biomass.
2.2.4. The N Uptake of Rice Aboveground Biomass
The plant was digested using the H2SO4-H2O2 method for determining plant total nitrogen. Then, the plant N concentration (mg N g−1 DW) was determined by the micro Kjeldahl method [40], and then N uptake of aboveground biomass was calculated according to the equation as follows:
The N uptake of aboveground biomass = plant N concentration in plants × aboveground biomass dry weight. Three plants per plot were sampled as one replicate for the measurement, and each treatment was replicated three times.
2.2.5. Rice Crop Biomass Accumulation and Translocation
Three plants of rice were sampled from each plot at the tillering, heading stage, and maturation stages. Above-ground plant samples were separated into the leaf, stem, and spikelet (from the heading). The plant samples were oven-dried at 75°C to a constant weight and then weighed separately. The proportion of crop biomass in panicles was calculated. The crop growth rate (CGR) was calculated by the equation of CGR (g m−2 d−1) = (W2 − W1)/(t2 − t1), where W1 and W2 are the above-ground biomass (g m−2) measured at the time t1 and t2, respectively [41].
2.3. Data Analysis
Microsoft Excel 2016 (Microsoft, Redmond, WA, USA) and SigmaPlot 12.5 (Systat Software, Inc., Richmond, CA, USA) were used for data processing and plotting, IBM SPSS Statistics 25.0 (IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY, USA) was used for data statistics and analysis. Comparisons among groups were tested by one-way ANOVA and LSD tests at a 0.05 probability level.
3. Results
3.1. Rice Grain Yield
Straw returning slightly increased the spikelets per panicle, but decreased the effective panicle number, leading to no obvious increases in the grain yield of rice compared with no straw returning treatments. Increasing the N fertilizer ratio at the tillering stage with straw returning could increase the effective panicle number of rice, and keep the stability of seed setting rate and 1000-grain weight, thus enhancing the spikelets number and the grain yield. Among these, increasing the N fertilizer ratio of basal:tillering:panicle from 5:2:3 to 5:4:1 increased the yield the most. The grain yield of the T4 (with N applied in the proportion of 5:4:1, respectively, in the basal:tillering:panicle phases) treatment increased by 24.1% (p < 0.05) and 25.1% (p < 0.05), respectively, in 2021 and 2022 compared with that of the T2 (with N applied in the proportion of 5:2:3, respectively, in the basal:tillering:panicle phases) treatment (Table 2). These results suggest that straw returning may reduce the soil available nitrogen content at the tillering stage, which affects the rice yield formation. In contrast, increasing the nitrogen ration at the tillering stage could offset the negative effects of straw returning on rice yield.

Table 2.
The effects of increasing the tillering fertilization ratio on rice yield.
3.2. Rice Biomass Accumulation and Translocation
Straw returning significantly increased the crop biomass of rice at the heading and maturation stages but decreased it at the tillering stage. Increasing the N fertilizer ratio at the tillering stage with straw returning increased the crop growth rate across the rice growing season, thus increasing the total crop biomass accumulation. Among these, the crop biomass increased mostly in T4 treatment (with N applied in the proportion of 5:4:1, respectively, in basal:tillering:panicle phases), which significantly (p < 0.05) increased by 14.14%, 19.52%, and 15.71%, respectively, compared with that of T2 (with N applied in the proportion of 5:2:3, respectively, in basal:tillering:panicle phases). Additionally, increasing N fertilizer ratio at the tillering stage with straw returning promoted the crop biomass translocation to panicles. The proportion of crop biomass in panicles of T4 (5:4:1) treatment was significantly increased by 5.35% (p < 0.05), on average, compared with that of T2 (5:2:3) (Figure 1). These results suggest that an insufficient supply of nitrogen at the tillering stage may adversely affect the rice shoot establishment and function, thus decreasing the carbon assimilation and translocation processes.
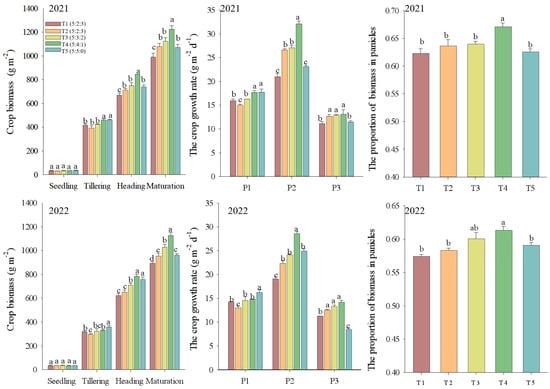
Figure 1.
Effects of increasing N fertilizer ratio at the rice tillering stage on crop biomass accumulation and translocation. Note: T1 (5:2:3), no straw returning with the N fertilizer ratio of basal:tillering:panicle = 5:2:3 treatment. T2 (5:2:3), straw returning with four different N fertilizer ratios of basal:tillering:panicle = 5:2:3 treatment. T3 (5:3:2), straw returning with four different N fertilizer ratios of basal:tillering:panicle = 5:3:2 treatment. T4 (5:4:1), straw returning with four different N fertilizer ratios of basal:tillering:panicle = 5:4:1 treatment. T5 (5:5:0), straw returning with four different N fertilizer ratios of basal:tillering:panicle = 5:5:0 treatment. P1: The periods during the seedling to tillering stage. P2: The periods during the tillering to heading stage. P3: The periods during the heading to maturation stage. Values followed by a different small letter are significantly different at 5% probability level. The same as follow.
3.3. Rice N Uptake
Straw returning decreased the crop N uptake at the tillering stage, however, straw returning promoted the N translocation to panicles. Increasing the N fertilizer ratio at the tillering stage significantly enhanced the N uptake rate of rice shoots at the tillering and heading stage, and increased the shoot N content across the rice growing season. Furthermore, it promoted N translocation to panicles. Among these, the T4 (5:4:1) treatment increased the most. The N content of T4 (5:4:1) treatment at tillering, heading, and maturation stages increased by 14.53%, 8.96%, and 6.19% (p < 0.05), respectively, on average compared with T2 (5:2:3). The proportions of N in panicles of the T4 (5:4:1) treatment were increased by 6.90% (p < 0.05) compared with that of T2 (5:2:3) treatment (Figure 2). These results suggest that properly adjusting nitrogen management could optimize the nitrogen uptake and translocation of rice under a straw returning system.
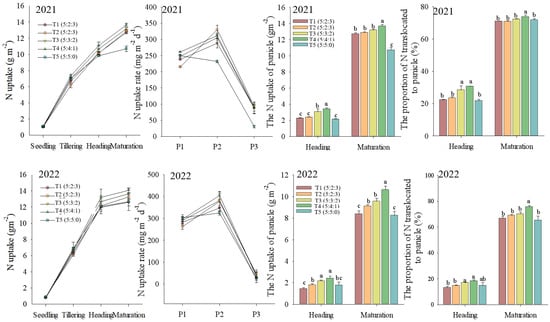
Figure 2.
Effects of increasing N fertilizer ratio at tillering stage on the rice N uptake and translocation of rice. Note: T1 (5:2:3), no straw returning with the N fertilizer ratio of basal:tillering:panicle = 5:2:3 treatment. T2 (5:2:3), straw returning with four different N fertilizer ratios of basal:tillering:panicle = 5:2:3 treatment. T3 (5:3:2), straw returning with four different N fertilizer ratios of basal:tillering:panicle = 5:3:2 treatment. T4 (5:4:1), straw returning with four different N fertilizer ratios of basal:tillering:panicle = 5:4:1 treatment. T5 (5:5:0), straw returning with four different N fertilizer ratios of basal:tillering:panicle = 5:5:0 treatment. P1: The periods during the seedling to tillering stage. P2: The periods during the tillering to heading stage. P3: The periods during the heading to maturation stage. Values followed by a different small letter are significantly different at 5% probability level.
3.4. Rice Root Weigh and Root Characteristics
Straw returning decreased the root growth rate of rice in the early growth stages, affecting the rice root architecture significantly. At the tillering stage, the dry matter weight, length, surface area, and volume of the roots were significantly (p < 0.05) decreased in the T2 (5:2:3) treatment, compared with that of the T1 (5:2:3) treatment. These results suggest that rice root establishment was impeded by the insufficient supply of nitrogen. Increasing the N fertilizer ratio at the tillering stage improved the root growth significantly (p < 0.05). The root dry matter weight, length, surface area, volume, and active absorption area at the tillering stage of T4 (5:4:1) treatment were 17.6%, 15.4%, 17.3%, 14.6%, and 40.5% higher than that of T2 (5:2:3) (Figure 3).
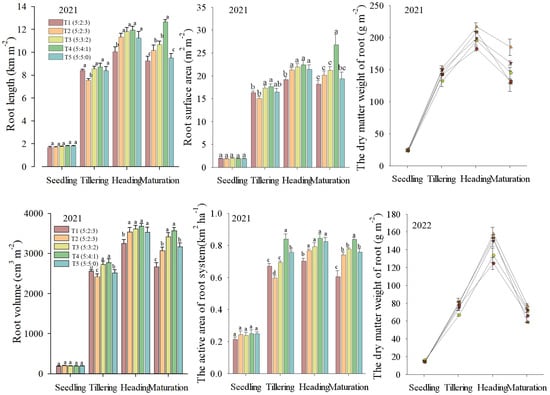
Figure 3.
Effects of increasing N fertilizer ratio at the tillering stage on rice root characteristics. Note: T1 (5:2:3), no straw returning with the N fertilizer ratio of basal:tillering:panicle = 5:2:3 treatment. T2 (5:2:3), straw returning with four different N fertilizer ratios of basal:tillering:panicle = 5:2:3 treatment. T3 (5:3:2), straw returning with four different N fertilizer ratios of basal:tillering:panicle = 5:3:2 treatment. T4 (5:4:1), straw returning with four different N fertilizer ratios of basal:tillering:panicle = 5:4:1 treatment. T5 (5:5:0), straw returning with four different N fertilizer ratios of basal:tillering:panicle = 5:5:0 treatment. Values followed by a different small letter are significantly different at the 5% probability level.
3.5. Soil Nitrate and Ammonium Nitrogen Content
Straw returning significantly decreased the content of soil ammonium and nitrate N at the rice tillering stage. For example, the content of ammonium and nitrate N at the tillering stage in T2 (5:2:3) treatment of 2021 and 2022 decreased on average by 11.25% and 11.16% (p < 0.05), compared with that of T1 (5:2:3). This may because the microorganisms competed for the available N in the soil to decompose straw. Increasing the N fertilizer ratio at the tillering stage could not only increase the soil N content at the tillering stage but also maintain a relatively high level at the later growth stages. Among these, the content of soil ammonium and nitrate N in T4 (5:4:1) treatments increased the most, which were 19.29% and 28.91% (p < 0.05) higher at the rice tillering stage, respectively, compared with that of T2 (5:2:3) treatment (Figure 4).
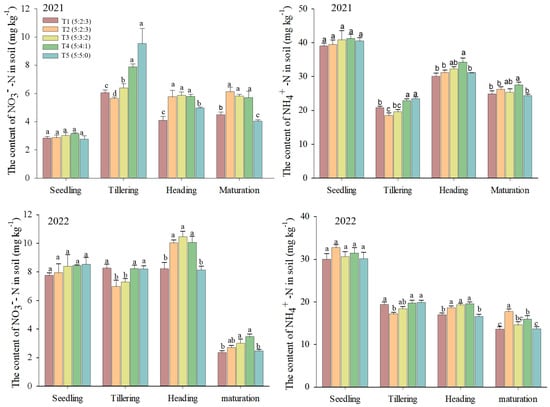
Figure 4.
Effects of increasing N fertilizer ratio at the rice tillering stage on the soil available N content. Note: T1 (5:2:3), no straw returning with the N fertilizer ratio of basal:tillering:panicle = 5:2:3 treatment. T2 (5:2:3), straw returning with four different N fertilizer ratios of basal:tillering:panicle = 5:2:3 treatment. T3 (5:3:2), straw returning with four different N fertilizer ratios of basal:tillering:panicle = 5:3:2 treatment. T4 (5:4:1), straw returning with four different N fertilizer ratios of basal:tillering:panicle = 5:4:1 treatment. T5 (5:5:0), straw returning with four different N fertilizer ratios of basal: tillering: panicle = 5:5:0 treatment. Values followed by a different small letter are significantly different at the 5% probability level.
3.6. Relationships among Rice Yield, Root Characteristics, and Soil Available Nitrogen
Correlation analysis showed that the rice yield and yield components were mainly determined by the root characteristics, nitrogen uptake, and crop biomass. The root characteristics including root volume, root surface area, and root active area at the tillering stage were mainly correlated with the effective panicle number and yield. Meanwhile, the root characteristics, nitrogen uptake, and crop biomass at heading and maturation stages were significantly correlated with the grain yield suggesting that root establishment was crucial for rice yield formation. Additionally, the root characteristics, nitrogen uptake, and crop biomass were closely correlated with the soil available nitrogen (Figure 5).
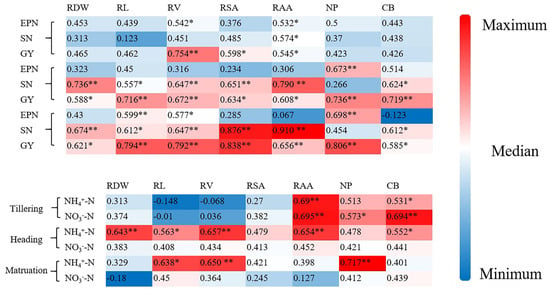
Figure 5.
Person correlation analysis. Note: * Significant at the 0.05 probability level. ** Significant at the 0.01 probability level; RDW: root dry matter weight, RL: root length, RV: root volume, RSA: root surface area, RAA: root active area, NP: nitrogen uptake, CB: crop biomass; EPN: effective panicle number, SN: spikelet number, GY: rice grain yield.
4. Discussion
4.1. Increasing the N Fertilizer Ratio at the Rice Tillering Stage with Straw Returning Increased the Grain Yields of Rice
Among rice yield components, effective panicle number and spikelet number per panicle have great potential for increase. Due to their large variability and adjustability, many agronomy measures have been adapted to enhance the effective panicle number and spikelet number per panicle for a higher grain yield in rice production [42,43,44,45]. In this study, straw returning increased the spikelet setting rate, enhancing the spikelet number per panicle. This may because of a higher supply of available N around the heading stage, which ensured sufficient nutrition for kernel growth and development as reported in Li et al. [8]. However, straw returning reduced the effective panicle number, which offset the increase in the spikelet number per panicle. Thus, no significant increase in grain yield was observed in the T2 (5:2:3) treatment, compared with that of T1 (5:2:3) (Table 2). Consistently, previous studies have suggested that straw returning might inhibit the rice seedling growth, offsetting the benefits of straw returning on increasing yield or even reducing the rice yield slightly [11]. As straw decomposition at the early stages consumed the nitrogen from the soil, the soil available nitrogen for rice growth decreased. This could be the reason for the negative effects of straw returning on rice seedling growth. It could also be proven by the results that increasing the N fertilizer ratio of basal:tillering:panicle from 5:2:3 to 5:4:1 could significantly increase the panicle number and spikelet number per panicle synchronously, therefore, effectively increasing the grain yield of early rice. However, further increasing the N fertilizer ratio at the tillering stage reduced the effective panicle number and rice yield. Thus, only increasing the tillering fertilizer ratio properly could maximize the benefits of straw returning to obtain a high grain yield. Our results support the idea that increasing the N ratio in the early growth stages of rice is an effective approach to obtaining a higher grain yield in a straw-returning agricultural system.
4.2. Increasing the N Fertilizer Ratio at the Tillering Stage with Straw Returning Synchronized the Soil Available Nutrients and Crop Demand
Synchronizing the supply of soil available N and the demand of rice plants is the key for achieving high grain yield under a straw returning agricultural system. The C/N ratio of rich straw is too high for microorganisms to decompose, causing the competition for soil available N between crop roots and microorganisms, which results in insufficient N application for root growth [8,26]. Consistently, in this study, rice straw returning significantly decreased the contents of ammonium and nitrate N at the rice tillering stage. The tillering stage is a crucial stage to establish a robust root system, ensuring effective acquisition of soil available nutrition and the formation of a high-yielding canopy structure [39,46,47]. Correlation analysis results showed that the effectively panicle number was largely determined by the root volume and root active area at the tillering stage. The reduced soil available N supply at the tillering stage inhibited root growth, resulting in the significant reductions of root length, root surface area, and root volume, which may account for the decreases in the effective panicle number of T2 (5:2:3). The addition of N fertilizer could alleviate the negative effects of straw returning by supplying the soil with available N to weaken the nutrition competition [13,48]. In this study, increasing the N fertilizer ratio at tillering from 20% to 40% significantly increased the length, surface area, active absorption area, and volume of roots at the tillering stage and maintained a relatively high level at the later growth stages. Roots, serving as the primary interface between plants and their soil environment, are responsible for the absorption of water and nutrients from the soil, which are essential for plant growth and development [45,49,50]. Straw returning with an increasing N ratio at the tillering stage, not only increased the available soil N at the tillering stage but also ensured a higher N supply at the panicle stage, which created a healthy and highly efficient root system. Accordingly, the N uptake rate was increased across the rice growth season, especially at the tillering and panicle stages.
5. Conclusions
Straw returning might cause competition for N between crops and microorganisms, resulting in insufficient available soil N for rice plant growth, offsetting some of the benefits of straw returning on crop production. Increasing the N fertilizer ratio 20% (with N applied in the proportion of 5:4:1, respectively, in the basal:tillering:panicle phases) at tillering ratio with straw returning effectively increased the availability of soil N at the tillering stage, and ensured sufficient N supply at rice later growth stages, which promoted robust root establishment and rice growth, thus gaining more effective panicles and rice grain yield.
After conducting the research, we noticed that there existed a research gap in nitrogen management to match up the soil nitrogen supply with the rice demanding in consideration with various soil texture, straw management, climate conditions, cropping patterns, and such factors that affect the “supply–demand” relationship. Therefore, researchers should focus on closing this research gap. The variations in rice straw management measures undoubtedly changed the nitrogen “supply–demand” relationship in the cropping system, which call for new optimum nitrogen management for rice production. The agricultural policy-makers should combine the actual situation of agricultural production and scientific studies to guide farmers in agricultural management. In this study, we found that straw returning reduced the nitrogen supply for rice growth at the early stages, thus decreased the effective panicle number. Therefore, we suggest that the policy-makers should encourage farmers to properly increase the nitrogen rate at the rice early growth stage, thus ensuring effective tillers and panicle number, maximizing the benefit of straw returning on rice production.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.Z. and J.C. (Jin Chen); Software, J.H., X.G. and X.L. (Xihuan Liang); Validation, X.L. (Xihuan Liang), B.W., X.C., X.H., J.X., G.D., J.C. (Ji Chen), X.L. (Xiuxiu Li) and C.Q.; Formal analysis, B.W., X.C., X.H., J.X., G.D., J.C. (Ji Chen), X.L. (Xiuxiu Li) and C.Q.; Investigation, C.Q., K.Z. and J.C. (Jin Chen); Data curation, B.W., X.C., X.H., J.X., G.D., J.C. (Ji Chen) and X.L. (Xiuxiu Li); Writing–original draft, J.H., X.G. and X.L. (Xihuan Liang); Writing–review and editing, Y.Q., C.P., K.Z. and J.C. (Jin Chen); Funding acquisition, K.Z. and J.C. (Jin Chen). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Nature Science Funds (32060431; 32360530); The Science and Technology Special Grant for Jinggangshan Agricultural Hi-Tech Zone (20222-051246); Basic research and talent training special project of Jiangxi Academy of Agricultural Science (JXSNKYJCRC202426); National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFD0300901); Jiangxi Province Key Laboratory of Arable Land Improvement and Quality Enhancement (2024SSY04221); Danish Independent Research Foundation (1127-00015B).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
References
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.Z.; Niu, B.; Liu, D.L.; He, J.Q.; Meng, Q.T. Impact of climate change and planting date shifts on growth and yields ofdouble cropping rice in southeastern China in future. Agric. Syst. 2023, 205, 103581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.H.; Liu, X.J.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.L.; Han, W.X.; Zhang, W.F.; Christie, P.; Goulding, K.W.T.; Vitousek, P.M.; Zhang, F.S. Significant Acidification in Major Chinese Croplands. Science 2010, 327, 1008–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, H.J.; Zhao, W.Q.; Li, T.; Cheng, X.Y.; Liu, Q. Balancing straw returning and chemical fertilizers in China: Role of straw nutrient resources. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 2695–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comino, E.; Rosso, M.; Riggio, V. Investigation of increasing organic loading rate in the co-digestion of energy crops and cow manure mix. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 3013–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.D.; Liu, Y.; Jiao, X.Y.; Li, J.; Liu, K.H.; Wu, T.N.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Luo, D.H. Response of soil nutrients retention and rice growth to biochar in straw returning paddy fields. Chemosphere 2023, 312, 137244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Cao, Y.; Wang, X.M.; Ge, X.; Li, B.Q.; Jin, C.Q. Evaluation on the Production of Food Crop Straw in China from 2006 to 2014. Bioenergy Res. 2017, 10, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, H.; Yao, Z.; Zhao, L.; Meng, H.; Wang, J.; Huo, L.; Yuan, Y.; Jia, J.; Xie, T.; Wu, Y. Distribution of crop straw resources and its industrial system and utilization path in China. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2019, 35, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.K.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, W.Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L.J.; Wang, Z.Q.; Gu, J.F.; Yang, J.C. Effects of long-term straw returning on rice yield and soil properties and bacterial community in a rice-wheat rotation system. Field Crop. Res. 2023, 291, 108800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deligios, P.A.; Farina, R.; Tiloca, M.T.; Francaviglia, R.; Ledda, L. C-sequestration and resilience to climate change of globe artichoke cropping systems depend on crop residues management. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 41, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Xia, H.; Jiang, C.; Riaz, M.; Yang, L.; Chen, Y.; Fan, X.; Xia, X. 14 year applications of chemical fertilizers and crop straw effects on soil labile organic carbon fractions, enzyme activities and microbial community in rice-wheat rotation of middle China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 841, 156608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.Y.; Liu, T.Q.; Ding, H.N.; Li, C.F.; Yu, M.; Liu, J.; Cao, C.G. The effects of straw returning and nitrogen fertilizer application on soil labile organic carbon fractions and carbon pool management index in a rice–wheat rotation system. Pedobiol.-J. Soil Ecol. 2023, 101, 150913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witt, C.; Cassman, K.G.; Olk, D.C.; Biker, U.; Liboon, S.P.; Samson, M.I.; Ottow, J.C.G. Crop rotation and residue management effects on carbon sequestration, nitrogen cycling and productivity of irrigated rice systems. Plant Soil 2000, 225, 263–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.Z.; Nie, L.X.; Buresh, R.J.; Huang, J.L.; Cui, K.H.; Xu, B.; Gong, W.H.; Peng, S.B. Agronomic performance of late-season rice under different tillage, straw, and nitrogen management. Field Crop. Res. 2010, 115, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Li, B.; Ren, B.; Zhao, B.; Liu, P.; Zhang, J.W. Achieve simultaneous increase in straw resources efficiency and nitrogen efficiency under crop yield stabilization—A case study of NCP in China for up to 8 years. Field Crop. Res. 2022, 278, 108431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.C.; Ti, Y.G.; Wang, F.; Sun, Y.F.; Lin, B.J.; Dang, Y.P.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, H.L.; Xu, Z.Y. Optimizing the rate of straw returning to balance trade-offs between carbon emission budget and rice yield in China. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2024, 47, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Liu, T.; Jiang, S.; Cao, C.; Li, C.; Chen, B.; Liu, J. Combined Effects of Straw Returning and Chemical N Fertilization on Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Yield from Paddy Fields in Northwest Hubei Province, China. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2020, 20, 392–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.C.; Zhang, R.Y.; Li, H.C.; Tan, J.L.; Song, W.J.; Wen, X.; Lu, B.L.; Hu, Z.R. The combination of different nitrogen fertilizer types could promote rice growth by alleviating the inhibition of straw decomposition. Food Energy Secur. 2021, 10, e298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Wang, M.; Feng, X.; Li, Q.; Qin, Y.; Sun, B.; Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer on nitrospira- and nitrobacter-like nitrite-oxidizing bacterial microbial communities under mulched fertigation system in semi-arid area of Northeast China. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Su, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. Comparisons between diversified multicropping systems in terms of crop productivity, economic benefits and carbon footprint in the Pearl River Delta region of South China. Farming Syst. 2023, 1, 100051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossuyt, H.; Denef, K.; Six, J.; Frey, S.D.; Merckx, R.; Paustian, K. Influence of microbial populations and residue quality on aggregate stability. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2001, 16, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soon, K.Y.; Lupwayi, Z.N. Straw management in a cold semi-arid region: Impact on soil quality and crop productivity. Field Crop. Res. 2012, 139, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Lam, S.K.; Wolf, B.; Kiese, R.; Chen, D.; Butterbach-Bahl, K. Trade-offs between soil carbon sequestration and reactive nitrogen losses under straw return in global agroecosystems. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, 5919–5932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, J.; Gao, C.; Afi, S.P.; Xie, J.; Zhao, L.; Bi, Y.; Wang, Y. Analysis of the available straw nutrient resources and substitution of chemical fertilizers with straw returned directly to the field in China. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiland, F.; Klamer, M.; Lind, A.M.; Leth, M.; Baath, E. Influence of initial C/N ratio on chemical and microbial compositionduring long term composting of straw. Microb. Ecol. Int. J. 2001, 41, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, D.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Teng, Y.; Christie, P. Nitrogen and phosphorus leaching losses from intensively managed paddy fields with straw retention. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 141, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvaro-Fuentes, J.; Morell, F.J.; Madejon, E.; Lampurlanes, J.; Arrue, J.L.; Cantero-Martinez, C. Soil biochemical properties in a semiarid Mediterranean agroecosystem as affected by long-term tillage and N fertilization. Soil Tillage Res. 2013, 129, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Zhang, Q.; Ai, C.; Liang, G.; He, P.; Zhou, W. Nitrogen enrichment regulates straw decomposition and its associated microbial community in a double-rice cropping system. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Huang, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, C.; Xu, L. Mapping the distribution, trends, and drivers of soil organic carbon in China from 1982 to 2019. Geoderma 2023, 429, 116232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poeplau, C.; Kätterer, T.; Bolinder, M.A.; Börjesson, G.; Berti, A.; Lugato, E. Low stabilization of aboveground crop residue carbon in sandy soils of Swedish long-term experiments. Geoderma 2015, 237, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Sun, Y.; Hui, X.; Jiang, M.; Xiang, K.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Sun, Y. The effect of straw mulch on nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium uptake and use in hybrid rice. Paddy Water Environ. 2019, 17, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksen, T.M.; Breland, T.A. Nitrogen availability effects on carbon mineralization, fungal and bacterial growth, and enzyme activities during decomposition of wheat straw in soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1999, 31, 1121–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.W.; Ge, Y.X.; Zhu, Q.; Yu, J.H.; Zhou, Q.; Cai, J.; Jiang, D.; Cao, W.X.; Dai, T.B. Soil nitrogen balance and nitrogen utilization of winter wheat affected by straw management and nitrogen application in the Yangtze river basin of China. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2019, 65, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, L.C.; Xu, P.; Zhang, Z.B.; Wei, B.H.; Jia, X.L.; Zhang, L.H. Improvements in Grain Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency of Summer Maize by Optimizing Tillage Practice and Nitrogen Application Rate. Agron. J. 2019, 111, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, H.H.T.; Marschner, P. Plant Growth and Nutrient Uptake in Soil Amended with Mixes of Organic Materials Differing in C/N Ratio and Decomposition Stage. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2019, 19, 512–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.; Cai, Y.; Zuo, W.; Hai-Tao, Z.; Yang, H.; Mao, W.; Yu-Hua, S.; Ke, F. Effects of Nitrogen Management on Soil Nitrogen Content and Rice Grain Yield in Double Cropping Rice Production Area with Continuous Full Amount of Straw Returning. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2019, 50, 2655–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.S.; Xu, M.M.; Koide, R.T.; Liu, Q.; Dai, Y.J.; Liu, L.; Bian, X.M. Effects of ditch-buried straw return on water percolation, nitrogen leaching and crop yields in a rice-wheat rotation system. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, P.; Huang, S.; van Gestel, N.C.; Zeng, Y.; Wu, Z.; van Groenigen, K.J. Liming and straw retention interact to increase nitrogen uptake and grain yield in a double rice-cropping system. Field Crop. Res. 2018, 219, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rock, L.; Ellert, B.; Mayer, B. Tracing sources of soil nitrate using the dual isotopic composition of nitrate in 2 M KCl-extracts. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 2397–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Chen, J.N.; Cao, F.B.; Jiang, L.G.; Zou, Y.B. Rhizosphere processes associated with the poor nutrient uptake in no-tillage rice (Oryza sativa L.) at tillering stage. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 163, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.K. Analysis Method of Soil Agricultural Chemistry; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M.; Fang, S.L.; Cao, F.B.; Chen, J.N.; Shan, S.L.; Liu, Y.; Lei, T.; Tian, A.L.; Tao, Z.; Zou, Y.B. Early sowing increases grain yield of machine-transplanted late-season rice under single-seed sowing. Field Crop. Res. 2020, 253, 107832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, J. Grain-filling problem in ‘super’ rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cécile, V.; Eugenia, R.; Christophe, R. Boosting crop yields with plant steroids. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 842–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.Y.; Fu, L.D.; Men, C.B.; Yu, J.X.; Yao, J.Y.; Sheng, J.Y.; Xu, Y.J.; Wang, Z.Q.; Liu, L.J.; Yang, J.C.; et al. Response of brassinosteroids to nitrogen rates and their regulation on rice spikelet degeneration during meiosis. Food Energy Secur. 2020, 9, e201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Guo, M.; Li, Y.; Ruan, W.; Mo, X.; Wu, Z.; Sturrock, C.J.; Yu, H.; Lu, C.; Peng, J. Large root ANGLE1,encoding OsPIN2, is involved in root system architecture in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, R.F.; Chen, Y.J.; Jiang, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, Z.M.; Pan, S.G.; Zhang, M.H.; Tang, X.R.; Mo, Z.W. Deep placement of liquid fertilizer at tillering stage influences grain quality, 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline synthesis, and antioxidant response of fragrant rice. Field Crop. Res. 2022, 289, 108716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ashraf, U.; Mo, Z.; Tian, H.; Duan, M.; Li, Y.; Tang, X.; Pan, S. Precise delivery of nitrogen at tillering stage enhances grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency in double rice cropping systems of South China. Field Crop. Res. 2022, 289, 108736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Yang, G.H.; Feng, Y.Z.; Ren, G.X.; Han, X.H. Optimizing feeding composition and carbon–nitrogen ratios for improved methane yield during anaerobic co-digestion of dairy, chicken manure and wheat straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 120, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafi, S.; Shafi, I.; Zaffar, A.; Zargar, S.M.; Shikari, A.B.; Ranjan, A.; Prasad, P.V.; Sofi, P.A. The resilience of rice under water stress will be driven by better roots: Evidence from root phenotyping, physiological, and yield experiments. Plant Stress 2023, 10, 100211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, J.P. Harnessing root architecture to address global challenges. Plant J. 2022, 109, 415–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).