Enhancing Maize Yield and Nutrient Utilization through Improved Soil Quality under Reduced Fertilizer Use: The Efficacy of Organic–Inorganic Compound Fertilizer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
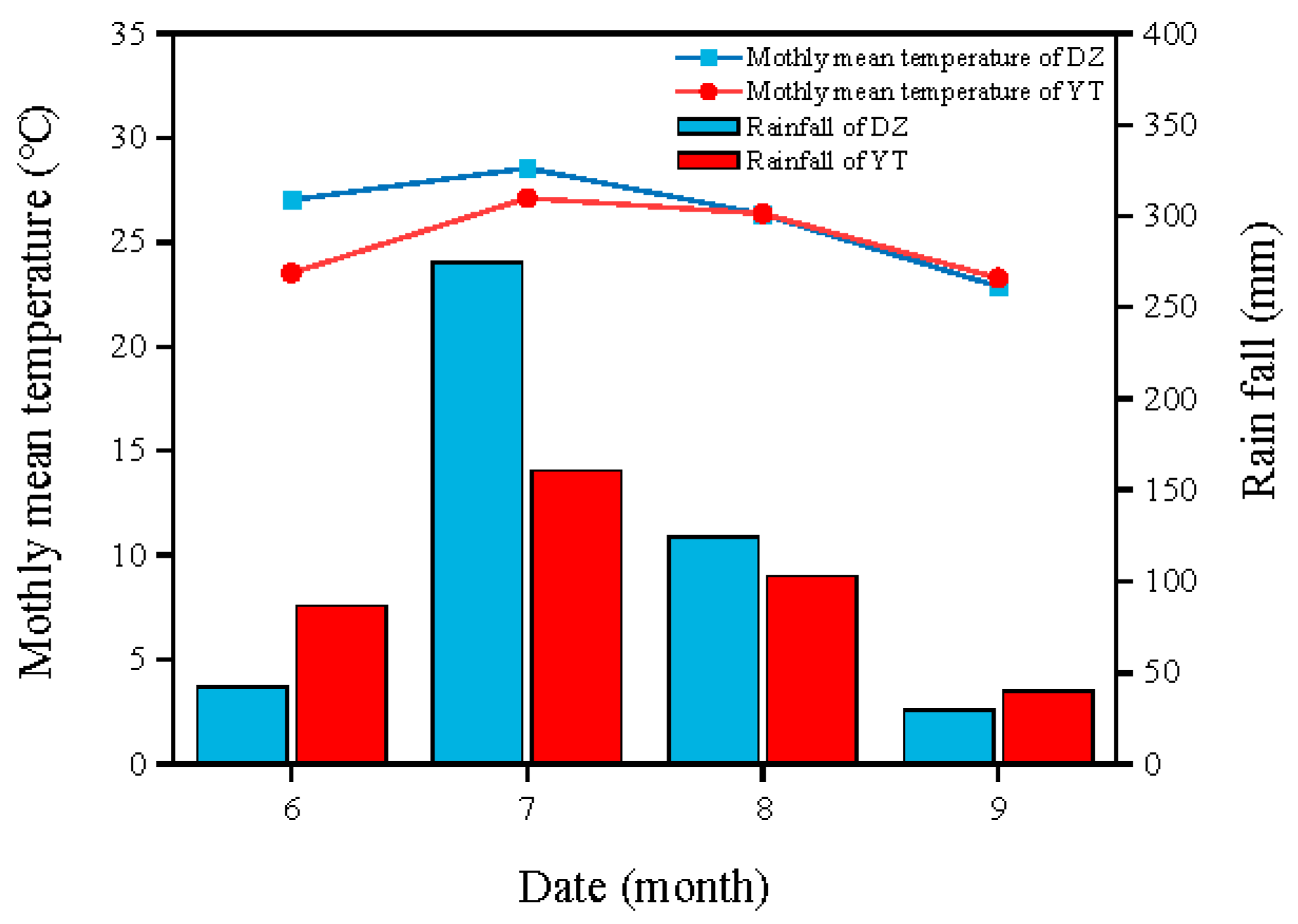
2.1. Experimental Site Parameters
2.2. Sample Collection and Measurements
2.2.1. Biomass, Grain Yield, and Nutrient Content
2.2.2. Soil Properties
2.3. Soil Quality Measurement
2.4. NUE
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
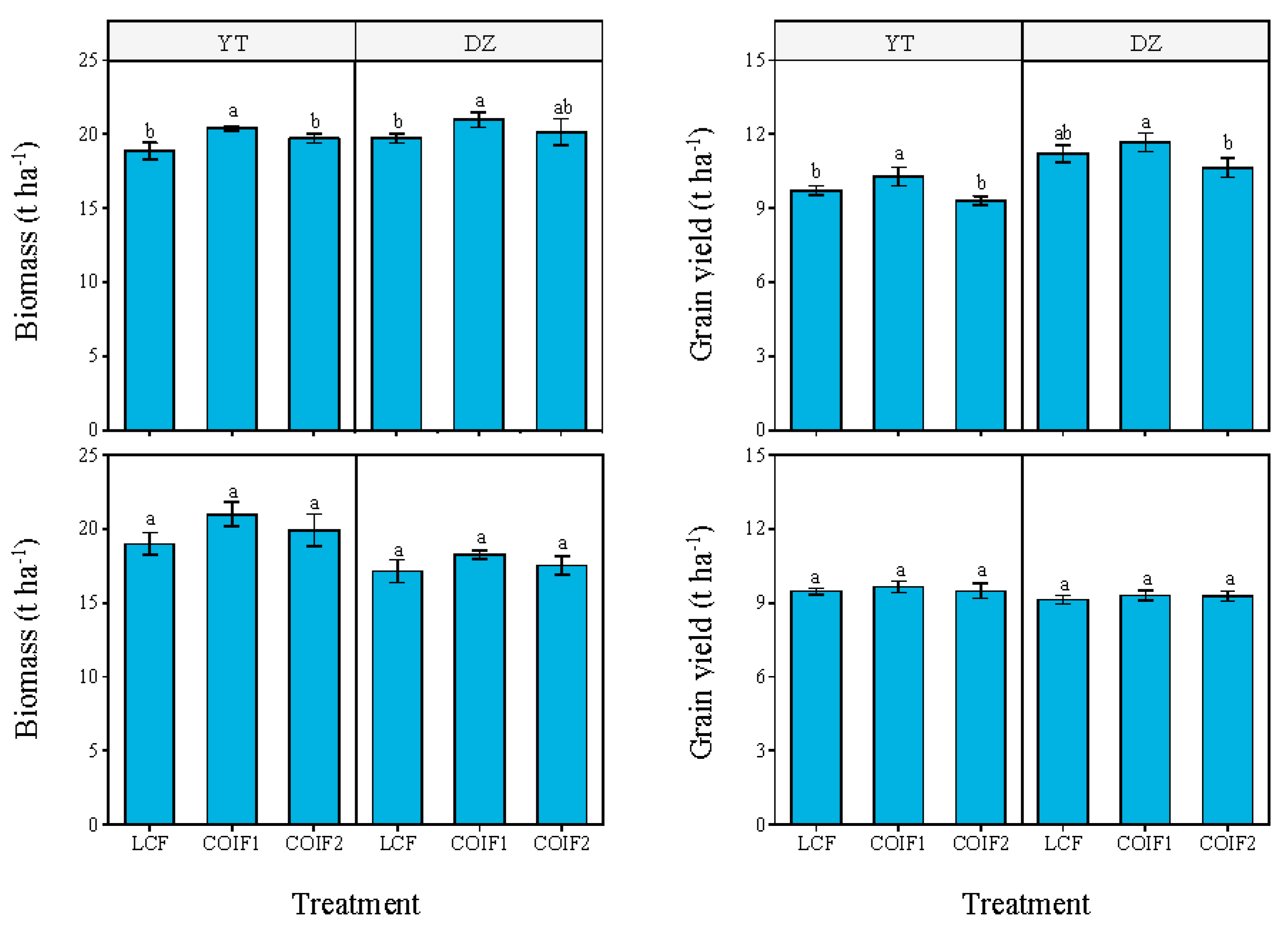
3.1. Biomass and Grain Yield
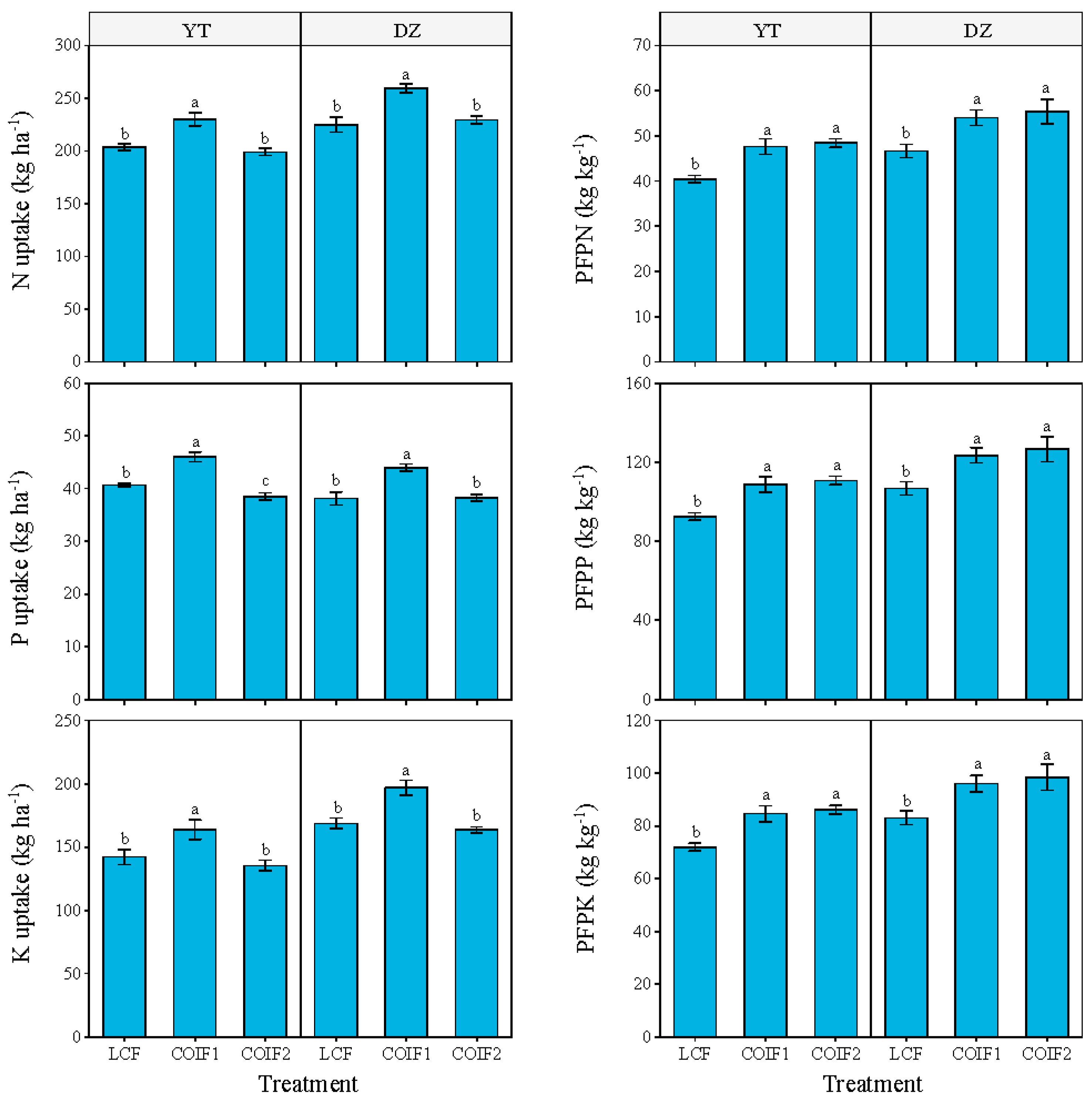
3.2. Nutrient Uptake and NUE
3.3. Soil Properties
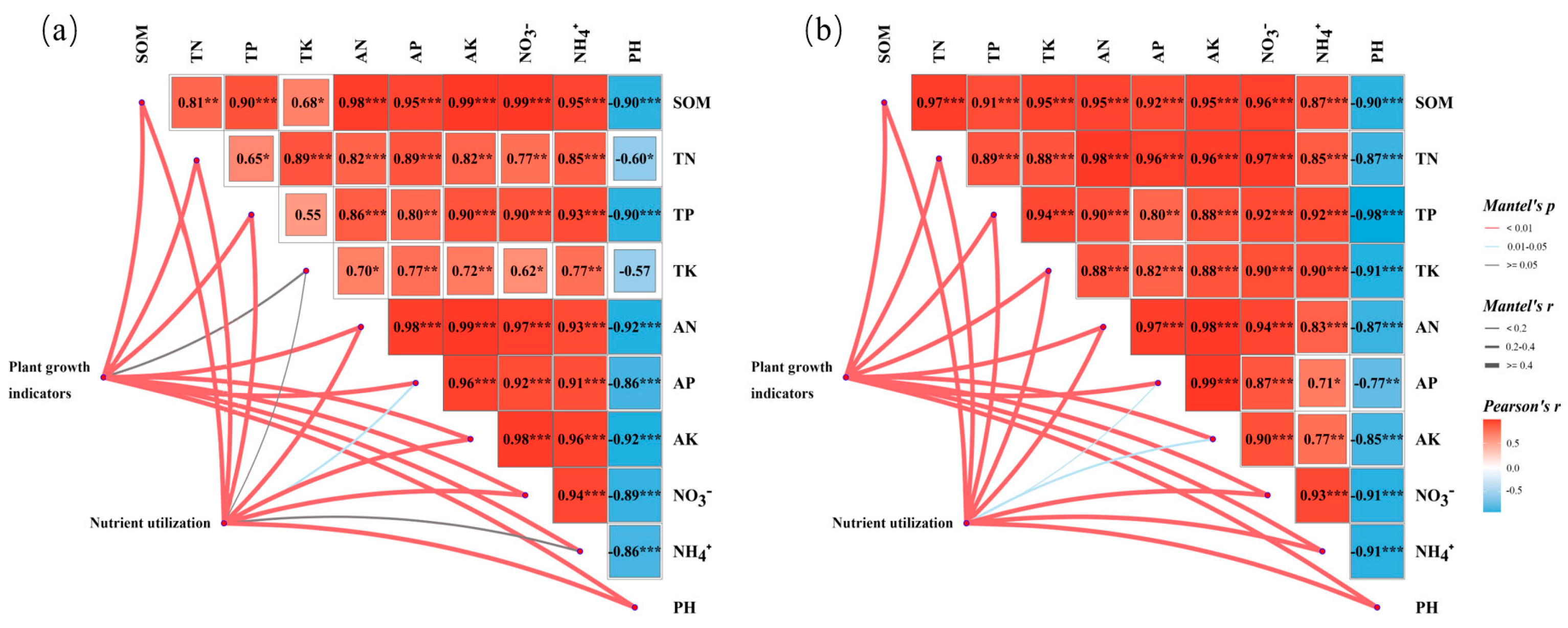
3.4. Correlation Analysis of Soil Properties, Plant Characteristics, and NUE
3.5. Evaluation of Soil Quality and Its Relation to Grain Yield
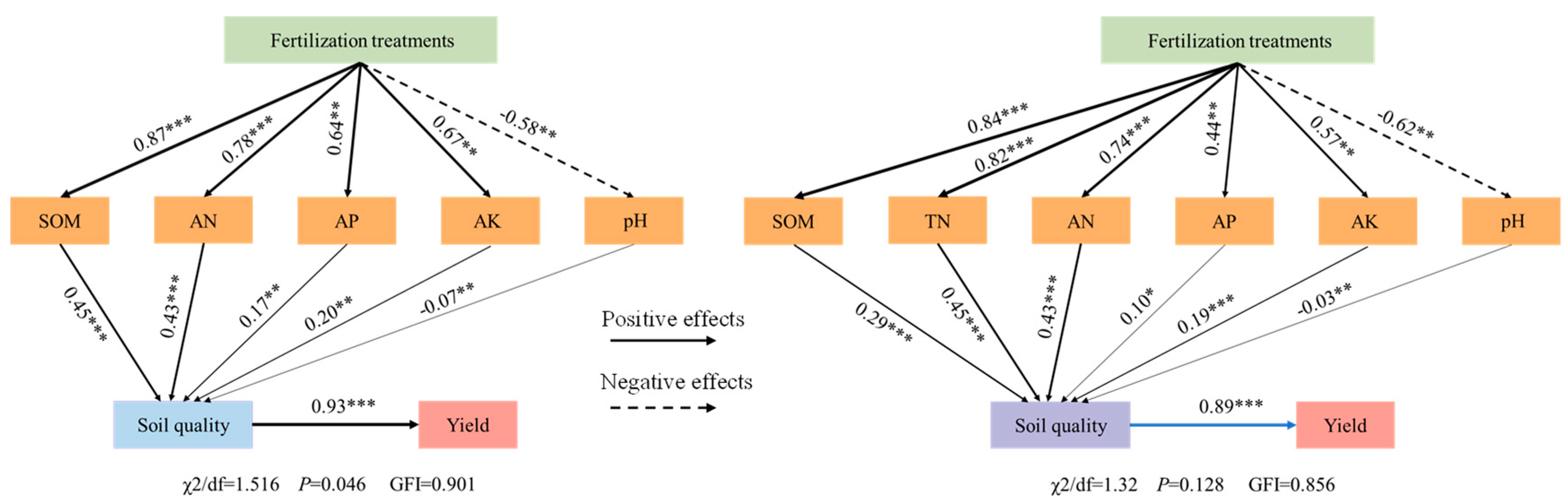
3.6. Analysis of SEM
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of COIF on Maize Biomass, Grain Yield, and Nutrient Utilization
4.2. Effect of COIF on Soil Properties
4.3. Effect of Soil Quality on Grain Yield under COIF
4.4. The Benefits and Development Prospects of COIF
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- China Statistical Yearbook. 2023. Available online: http://www.stats.gov.cn/sj/ndsj/2023/indexch.htm (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- Omonode, R.A.; Halvorson, A.D.; Gagnon, B.; Vyn, T.J. Achieving lower nitrogen balance and higher nitrogen recovery efficiency reduces nitrous oxide emissions in North America’s maize cropping systems. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagnon, B.; Ziadi, N.; Bélanger, G.; Parent, G. Validation and use of critical phosphorus concentration in maize. Eur. J. Agron. 2020, 120, 126147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Wei, K.; Pu, J.H.; Huang, W.J.; Bao, H.X.; Chen, L.J. A balanced reduction in mineral fertilizers benefits P reserve and inorganic P-solubilizing bacterial communities under residue input. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 159, 103833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassaletta, L.; Billen, G.; Grizzetti, B.; Anglade, J.; Garnier, J. 50 year trends in nitrogen use efficiency of world cropping systems: The relationship between yield and nitrogen input to cropland. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 105011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, C.D.; Cade-Menun, B.J.; Liu, C.W.; Hill, J.E. The short-term transport and transformation of phosphorus species in a saturated soil following poultry manure amendment and leaching. Geoderma 2015, 257, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Bom, F.; Nunes, I.; Raymond, N.S.; Hansen, V.; Bonnichsen, L.; Magid, J.; Nybroe, O.; Jensen, L.S. Long-term fertilisation form, level and duration affect the diversity, structure and functioning of soil microbial communities in the field. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 122, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.W.; Du, X.F.; Li, Y.B.; Han, X.; Li, B.; Zhang, X.K.; Li, Q.; Liang, W.J. Organic substitutions improve soil quality and maize yield through increasing soil microbial diversity. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 347, 131323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanick, B.; Choudhary, S.; Kumar, M.; Singh, S.K.; Jha, R.K.; Singh, A.K.; Salmen, S.H.; Ansari, M.J.; Hossain, A. Can site-specific nutrient management improve the productivity and resource use efficiency of climate-resilient finger millet in calcareous soils in India? Heliyon 2024, 10, e32774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pareek, A.; Dhankher, O.P.; Foyer, C.H. Mitigating the impact of climate change on plant productivity and ecosystem sustainability. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.C.; Niu, W.Q.; Ma, L.; Du, Y.D.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, J.; Siddique, K.H.M. Legacy effects of wheat season organic fertilizer addition on microbial co-occurrence networks, soil function, and yield of the subsequent maize season in a wheat-maize rotation system. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 347, 119160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saudy, H.S.; Hamed, M.F.; Abd El-Momen, W.R.; Hussein, H. Nitrogen use rationalization and boosting wheat productivity by applying packages of humic, amino acids and microorganisms. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2020, 51, 1036–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaswar, M.; Jing, H.; Ahmed, W.; Li, D.C.; Liu, S.J.; Lu, Z.; Cai, A.D.; Liu, L.S.; Xu, Y.M.; Gao, J.S.; et al. Yield sustainability, soil organic carbon sequestration and nutrients balance under long-term combined application of manure and inorganic fertilizers in acidic paddy soil. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 198, 104569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elrahman, S.H.; Saudy, H.S.; Abd El-Fattah, D.A.; Hashem, F.A. Effect of irrigation water and organic fertilizer on reducing nitrate accumulation and boosting lettuce productivity. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2022, 22, 2144–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Peng, M.W.; Lu, W.D.; Hou, Z.N.; Li, J.H. Commercial organic fertilizer substitution increases wheat yield by improving soil quality. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 158132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, L.; Ni, K.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yi, X.; Yang, X.; Ling, N.; You, Z.; Guo, S.; Ruan, J. Effect of organic substitution rates on soil quality and fungal community composition in a tea plantation with long-term fertilization. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2020, 56, 633–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, F.L.; Song, J.S.; Giltrap, D.; Feng, Y.T.; Yang, X.Y.; Zhang, S.L. Crop yield and N2O emission affected by long-term organic manure substitution fertilizer under winter wheat-summer maize cropping system. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 732, 139321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.D.; Jiao, Y.Q.; Yin, J.; Li, D.; Wang, B.B.; Zhang, K.L.; Zheng, X.X.; Hong, Y.; Zhang, H.X.; Xie, C.; et al. Productivity and quality of banana in response to chemical fertilizer reduction with bio-organic fertilizer: Insight into soil properties and microbial ecology. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 322, 107659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Ni, T.; Lia, J.; Lua, Q.; Fang, Z.; Huang, Q.W.; Zhang, R.F.; Li, R.; Shen, B.; Shen, Q.R. Effects of organic–inorganic compound fertilizer with reduced chemical fertilizer application on crop yields, soil biological activity and bacterial community structure in a rice–wheat cropping system. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 99, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, H.L.; Huang, Y.Y.; Yang, H.Z.; Bei, M.R.; Lin, Q.H. Effects of application of organic-inorganic compound fertilizers on microbial communities and enzyme activities in tropical paddy soil. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2021, 27, 619–629. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Hu, T.T.; Cao, S.F.; Wang, M.D.; Fang, J.; Wang, Q.Y. Present situation and research progress of organic and inorganic compound fertilizer. Agric. Sci. 2023, 10, 890–895. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lu, S.; Luo, X.G.; Liu, Q.W.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, H.Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.L. Effect of organic-inorganic compound fertilizer on wheat growth, nutrients and heavy metal content of soil and wheat. Acta Agric. Zhejiangensis 2023, 35, 922–930. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dai, L.; Hu, C.; Wan, J.H.; Xu, H.L.; Liu, M.J.; Guo, H.W.; Qiao, Y. Effects of organic and inorganic compound fertilizers on yield and nutrient uptake and utilization of rice. Soil Fertil. Sci. China 2024, 2, 111–119. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.; Li, Y.B.; Du, X.F.; Li, Y.H.; Wang, Z.W.; Jiang, S.W.; Li, Q. Effect of grassland degradation on soil quality and soil biotic community in a semi-arid temperate steppe. Ecol. Process. 2020, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.L.; Wang, C.; Li, X.L.; Li, H.; Dong, M.M.; Jin, S.J.; Liu, L.; Zhu, C.; Xue, R. Long-term effect of integrated fertilization on maize yield and soil fertility in a calcaric fluvisol. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2021, 67, 1400–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.L.; Zhang, H.Y.; Li, X.L.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.L.; Jiang, R.F.; Feng, G.; Liu, X.J.; Zuo, Y.M.; Yuan, H.M.; et al. Field management practices drive ecosystem multifunctionality in a smallholder-dominated agricultural system. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 313, 107389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diacono, M.; Montemurro, F. Long-term effects of organic amendments on soil fertility. A Review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2010, 30, 401–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czachor, H.; Charytanowicz, M.; Gonet, S.; Niewczas, J.; Jozefaciuk, G.; Lichner, L. Impact of long-term mineral and organic fertilizer application on the water stability, wettability and porosity of aggregates obtained from two loamy soils. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2015, 66, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Fang, H.; Mooney, S.J.; Peng, X. Effects of long-term inorganic and organic fertilizations on the soil micro and macro structures of rice paddies. Geoderma 2016, 266, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.W.; Rensing, C.; Chen, H.; Liu, M.Q.; Wang, M.; Guo, S.W.; Ling, N.; Shen, Q.R. Deciphering the associations between soil microbial diversity and ecosystem multifunctionality driven by long-term fertilization management. Funct. Ecol. 2018, 32, 1103–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Redmile-Gordon, M.; Li, J.W.; Zhang, J.B.; Xin, X.L.; Zhang, C.Z.; Ma, D.H.; Zhou, Y.F. Linking cropland ecosystem services to microbiome taxonomic composition and functional composition in a sandy loam soil with 28-year organic and inorganic fertilizer regimes. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 139, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.L.; Ding, J.; Zhu, D.; Hu, H.W.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Ma, Y.B.; He, J.Z.; Zhu, Y.G. Rare microbial taxa as the major drivers of ecosystem multifunctionality in long-term fertilized soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 141, 107686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, A.D.; Xu, M.G.; Wang, B.R.; Zhang, W.J.; Liang, G.P.; Hou, E.Q.; Luo, Y.Q. Manure acts as a better fertilizer for increasing crop yields than synthetic fertilizer does by improving soil fertility. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 189, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.D.; Cui, B.J.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Sun, J.; Niu, W.Q. Effects of manure fertilizer on crop yield and soil properties in China: A meta-analysis. CATENA 2020, 193, 104617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bünemann, E.K.; Bongiorno, G.; Bai, Z.; Creamer, R.E.; De Deyn, G.; de Goede, R.; Fleskens, L.; Geissen, V.; Kuyper, T.W.; Mäder, P.; et al. Soil quality—A critical review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 120, 105–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Zhou, D. Selecting the minimum data set and quantitative soil quality indexing of alkaline soils under different land uses in northeastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Shi, K.; Wang, Y.Y.; Kong, D.N.; Liu, T.; Jiao, J.G.; Liu, M.Q.; Li, H.X.; Hu, F. Soil quality assessment of wheat-maize cropping system with different productivities in China: Establishing a minimum data set. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 190, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boafo, D.K.; Kraisornpornson, B.; Panphon, S.; Owusu, B.E.; Amaniampong, P.N. Effect of organic soil amendments on soil quality in oil palm production. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 147, 103358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, B.T.; Le, L.B.; Pham, L.P.; Nguyen, H.T.; Tran, T.D.; Van Thai, N. The effects of biochar on the biomass yield of elephant grass (Pennisetum purpureum Schumach) and properties of acidic soils. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 161, 113224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, Y.; Guo, L.Y.; Liu, M.Z.; Gu, X.; Li, C.H.; Jiang, G.M. Using organic fertilizers to increase crop yield, economic growth, and soil quality in a temperate farmland. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.W.; Yuan, J.P.; Li, X.H.; Zhang, S.L.; Ren, X.J.; Wang, F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ou, X.Q.; Chen, X.L. Improving winter wheat N utilization efficiency and soil fertility through replacement of chemical N by 20% organic manure. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2020, 26, 1395–1406. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bao, S.D. Soil and Agriculture Chemistry Analysis, 3rd ed.; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, M.W.; He, H.; Wang, Z.K.; Li, G.F.; Lv, X.H.; Pu, X.Z.; Zhuang, L. Responses and comprehensive evaluation of growth characteristics of ephemeral plants in the desert–oasis ecotone to soil types. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 316, 115288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adekiya, A.O.; Ejue, W.S.; Olayanju, A.; Dunsin, O.; Aboyeji, C.M.; Aremu, C.; Akinpelu, O. Different organic manure sources and NPK fertilizer on soil chemical properties, growth, yield and quality of okra. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.J.; Lei, T.; Du, W.; Liang, C.L.; Li, H.D.; Lv, J.L. Substituting chemical fertilizer nitrogen with organic manure and comparing their nitrogen use efficiency and winter wheat yield. J. Agric. Sci. 2020, 158, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Li, B.; Chen, L.; Liang, J.Y.; Huang, R.; Tang, X.Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C.Q. Partial substitution of chemical fertilizer with organic fertilizer over seven years increases yields and restores soil bacterial community diversity in wheat-rice rotation. Eur. J. Agron. 2022, 133, 126445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Q.; Yang, Y.D.; Zhao, J.; Nie, J.W.; Zang, H.D.; Zeng, Z.H.; Olesen, J.E. Yield benefits from replacing chemical fertilizers with manure under water deficient conditions of the winter wheat-summer maize system in the North China Plain. Eur. J. Agron. 2020, 119, 126118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.H.; Cao, G.J.; Wang, L.C.; Wang, S.H. Effects of equal chemical fertilizer substitutions with organic manure on yield, dry matter, and nitrogen uptake of spring maize and soil nitrogen distribution. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, H.Q.; Liu, P.; Dong, S.T.; Zhang, J.W.; Zhao, B.; Ren, B.Z. Nitrogen placement at sowing affects root growth, grain yield formation, N use efficiency in maize. Plant Soil 2020, 457, 355–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Arb, C.; Bünemann, E.K.; Schmalz, H.; Portmann, M.; Adamtey, N.; Musyoka, M.W.; Frossard, E.; Fliessbach, A. Soil quality and phosphorus status after nine years of organic and conventional farming at two input levels in the Central Highlands of Kenya. Geoderma 2020, 362, 114112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.L.; Song, D.L.; Zhou, W.; Liu, G.R.; Liang, G.Q.; He, P.; Sun, G.; Yuan, F.S.; Liu, Z.B.; Yao, Y.K.; et al. Partial substitution of chemical nitrogen with organic nitrogen improves rice yield, soil biochemical indictors and microbial composition in a double rice cropping system in south China. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 205, 104753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.H.; Wang, X.J.; Xu, M.G.; Feng, G.; Zhang, W.J.; Lu, C.A. Crop yield and soil organic matter after long-term straw return to soil in China. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2015, 102, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Li, C.H.; Wang, Y.W.; Hu, Y.M.; Christie, P.; Zhang, J.L.; Li, X.L. Maize yield and soil fertility with combined use of compost and inorganic fertilizers on a calcareous soil on the North China Plain. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 155, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wu, M.C.; Kang, G.D.; Zhu, B.J.; Li, H.X.; Hu, F.; Jiao, J.G. Soil quality response to organic amendments on dryland red soil in subtropical China. Geoderma 2020, 373, 114416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.A.; Shu, A.P.; Song, W.F.; Shi, W.C.; Li, M.C.; Zhang, W.X.; Li, Z.Z.; Liu, G.R.; Yuan, F.S.; Zhang, S.X.; et al. Long-term organic fertilizer substitution increases rice yield by improving soil properties and regulating soil bacteria. Geoderma 2021, 404, 115287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, C.C.; Gao, P.D.; Wang, B.Q.; Lin, W.P.; Jiang, N.H.; Cai, K.Z. Impacts of chemical fertilizer reduction and organic amendments supplementation on soil nutrient, enzyme activity and heavy metal content. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 1819–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.H.; Guo, J.J.; Fan, L.Y.; Ji, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, F.; Pu, Z.X.; Ling, N.; Shen, Q.R.; Guo, S.W. The source–sink balance during the grain filling period facilitates rice production under organic fertilizer substitution. Eur. J. Agron. 2022, 134, 126468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Qu, J.; Li, H.; La, S.; Tian, Y.; Gao, L. Biochar addition combined with daily fertigation improves overall soil quality and enhances water-fertilizer productivity of cucumber in alkaline soils of a semi-arid region. Geoderma 2020, 363, 114170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.L.; Wang, C. Multiple soil quality assessment methods for evaluating effects of organic fertilization in wheat-maize rotation system. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 150, 126929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denardin, L.G.D.; Carmona, F.D.; Veloso, M.G.; Martins, A.P.; de Freitas, T.F.S.; Carlos, F.S.; Marcolin, E.; Camargo, F.A.D.; Anghinoni, I. No-tillage increases irrigated rice yield through soil quality improvement along time. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 186, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.Y.; Liu, Z.J.; Zhou, J.B.; Xu, X.P.; Zhu, Y.J. Long-term straw mulching with nitrogen fertilization increases nutrient and microbial determinants of soil quality in a maize-wheat rotation on China’s Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 775, 145930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Liu, Y.L.; Du, W.C.; Li, C.L.; Xu, M.L.; Xie, T.C.; Yin, Y.; Guo, H. Response of soil bacterial communities, antibiotic residuals, and crop yields to organic fertilizer substitution in North China under wheat-maize rotation. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 785, 147248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, C.P.; Kumar, N.; Das, K.; Hazra, K.K.; Praharaj, C.S.; Singh, N.P. Impact of variable tillage based residue management and legume based cropping for seven years on enzymes activity, soil quality index and crop productivity in rice ecology. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2021, 10, 100107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.X.; Shang, Y.W.; Zhang, W.J.; Chen, X.P.; Cui, Z.L. Improving soil quality for higher grain yields in Chinese wheat and maize production. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 1125–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asrade, D.A.; Kulhánek, M.; Balík, J.; Černý, J.; Sedlář, O. Side effect of organic fertilizing on the phosphorus transformation and balance over 27 years of maize monoculture. Field Crops Res. 2023, 295, 108902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Locations | SOM (g kg−1) | TN (g kg−1) | TP (g kg−1) | TK (g kg−1) | AN (mg kg−1) | AP (mg kg−1) | AK (mg kg−1) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YT | 9.30 | 0.60 | 0.49 | 30.99 | 60.43 | 22.63 | 145.33 | 6.23 |
| DZ | 8.07 | 0.45 | 0.76 | 18.26 | 28.48 | 7.73 | 97.32 | 8.62 |
| Treatments | Chemical Fertilizer (kg ha−1) | Organic–Inorganic Compound Fertilizer (kg ha−1) | Total Nutrients (kg ha−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | P2O5 | K2O | N | P2O5 | K2O | ||
| LCF | 240 | 105 | 135 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 480 |
| COIF1 | 27.75 | 31.75 | 0 | 188.25 | 62.75 | 121.5 | 432 |
| COIF2 | 30 | 30 | 0 | 162 | 54 | 108 | 384 |
| Locations | Treatments | SOM (g kg−1) | TN (g kg−1) | TP (g kg−1) | TK (g kg−1) | AN (mg kg−1) | AP (mg kg−1) | AK (mg kg−1) | NO3− (mg kg−1) | NH4+ (mg kg−1) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YT | LCF | 10.82 c | 0.66 c | 0.51 a | 32.99 ab | 87.43 c | 24.63 b | 156.00 b | 7.93 b | 2.48 b | 7.04 a |
| COIF1 | 12.21 a | 1.04 a | 0.61 a | 36.14 a | 134.27 a | 46.39 a | 288.83 a | 22.19 a | 3.64 a | 6.38 b | |
| COIF2 | 11.39 b | 0.74 b | 0.57 a | 30.95 b | 106.07 b | 30.03 b | 209.00 b | 14.86 ab | 2.82 a | 6.54 b | |
| DZ | LCF | 8.63 c | 0.46 c | 0.97 b | 18.38 b | 34.02 c | 8.05 b | 110.33 b | 24.95 c | 2.21 b | 9.44 a |
| COIF1 | 10.89 a | 0.72 a | 1.12 a | 19.25 a | 53.66 a | 13.61 a | 133.17 a | 58.20 a | 2.92 a | 9.22 b | |
| COIF2 | 9.68 b | 0.57 b | 1.07 ab | 18.86 ab | 41.03 b | 8.97 b | 115.77 b | 45.77 b | 2.81 a | 9.29 ab |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Zhao, H.; Li, Y.; Wei, J.; Ma, L.; Zheng, F.; Tan, D. Enhancing Maize Yield and Nutrient Utilization through Improved Soil Quality under Reduced Fertilizer Use: The Efficacy of Organic–Inorganic Compound Fertilizer. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14091482
Chen X, Li Z, Zhao H, Li Y, Wei J, Ma L, Zheng F, Tan D. Enhancing Maize Yield and Nutrient Utilization through Improved Soil Quality under Reduced Fertilizer Use: The Efficacy of Organic–Inorganic Compound Fertilizer. Agriculture. 2024; 14(9):1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14091482
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xiaoying, Zishuang Li, Huanyu Zhao, Yan Li, Jianlin Wei, Lei Ma, Fuli Zheng, and Deshui Tan. 2024. "Enhancing Maize Yield and Nutrient Utilization through Improved Soil Quality under Reduced Fertilizer Use: The Efficacy of Organic–Inorganic Compound Fertilizer" Agriculture 14, no. 9: 1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14091482
APA StyleChen, X., Li, Z., Zhao, H., Li, Y., Wei, J., Ma, L., Zheng, F., & Tan, D. (2024). Enhancing Maize Yield and Nutrient Utilization through Improved Soil Quality under Reduced Fertilizer Use: The Efficacy of Organic–Inorganic Compound Fertilizer. Agriculture, 14(9), 1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14091482






