Integrated Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Analysis of Antimony (Sb) Stress Response in Common Bermudagrass (Cynodon dactylon [L.] Pers.)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Experimental Treatments
2.2. Measurement of Physiological Indexes
2.2.1. Measurement of Chlorophyll Pigments and Fluorescence
2.2.2. Determination of Antioxidant Enzyme Activity, Malondialdehyde (MDA), and Soluble Protein Content
2.3. Metabolite Extraction and GC-TOF-MS Analysis
2.4. RNA Extraction, cDNA Library Construction, and Transcriptome Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
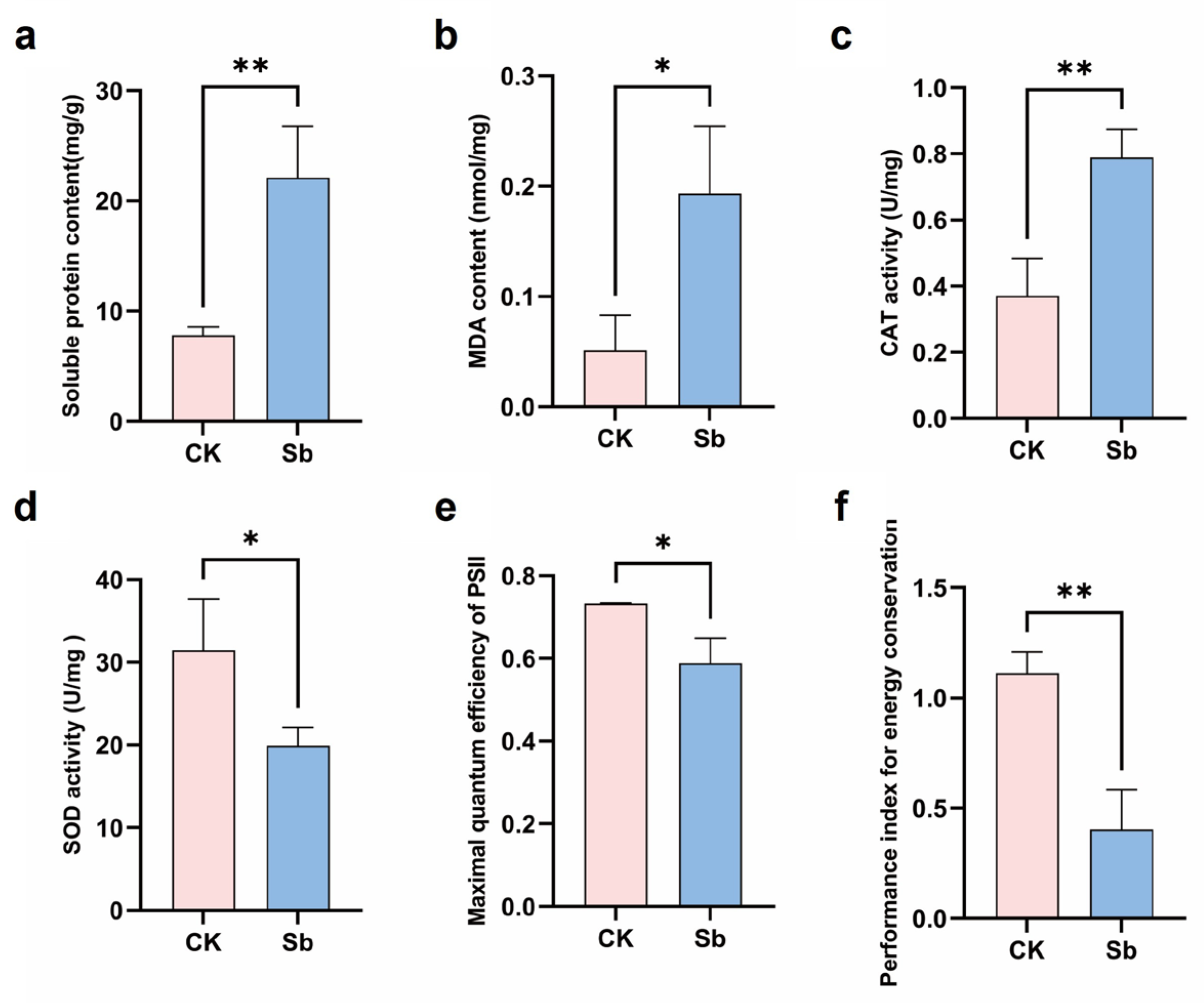
3.1. Physiological Indicators of Bermudagrass Under Sb Stress
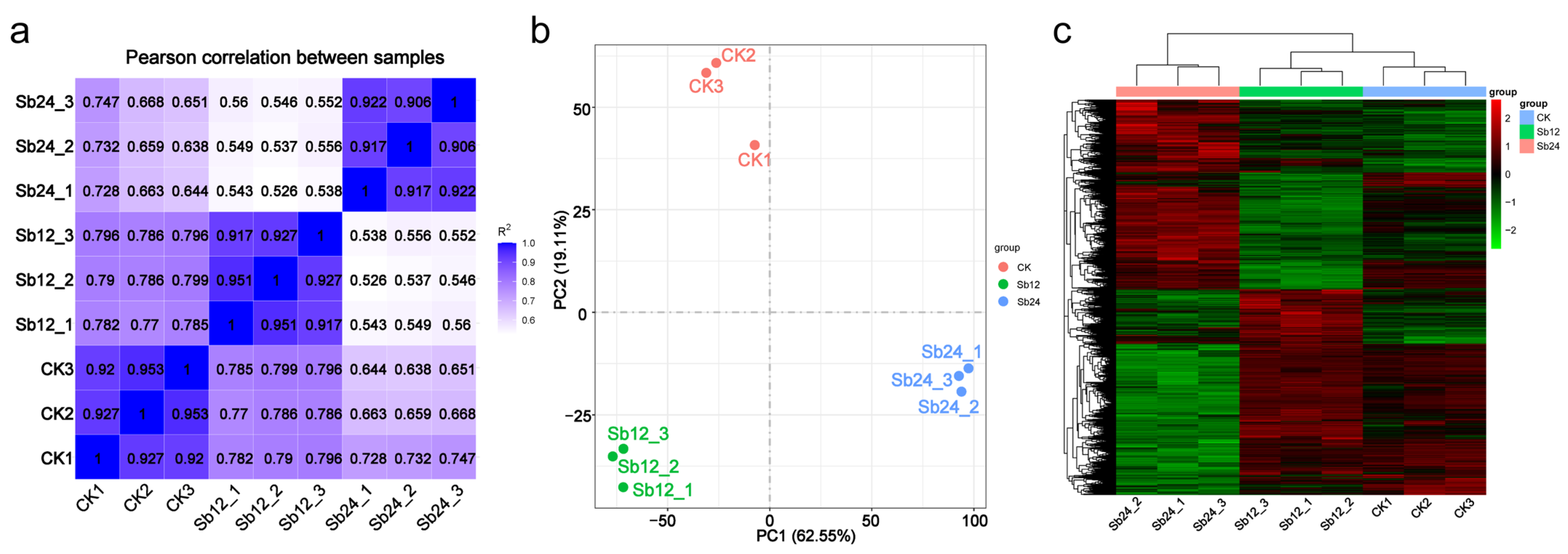
3.2. Transcriptomic Analysis
3.2.1. Sequence Assembly, Generation, and Correlation Analysis
3.2.2. Differentially Expressed Gene (DEG) Analysis
3.2.3. Gene Ontology (GO) and KEGG Pathway Analysis
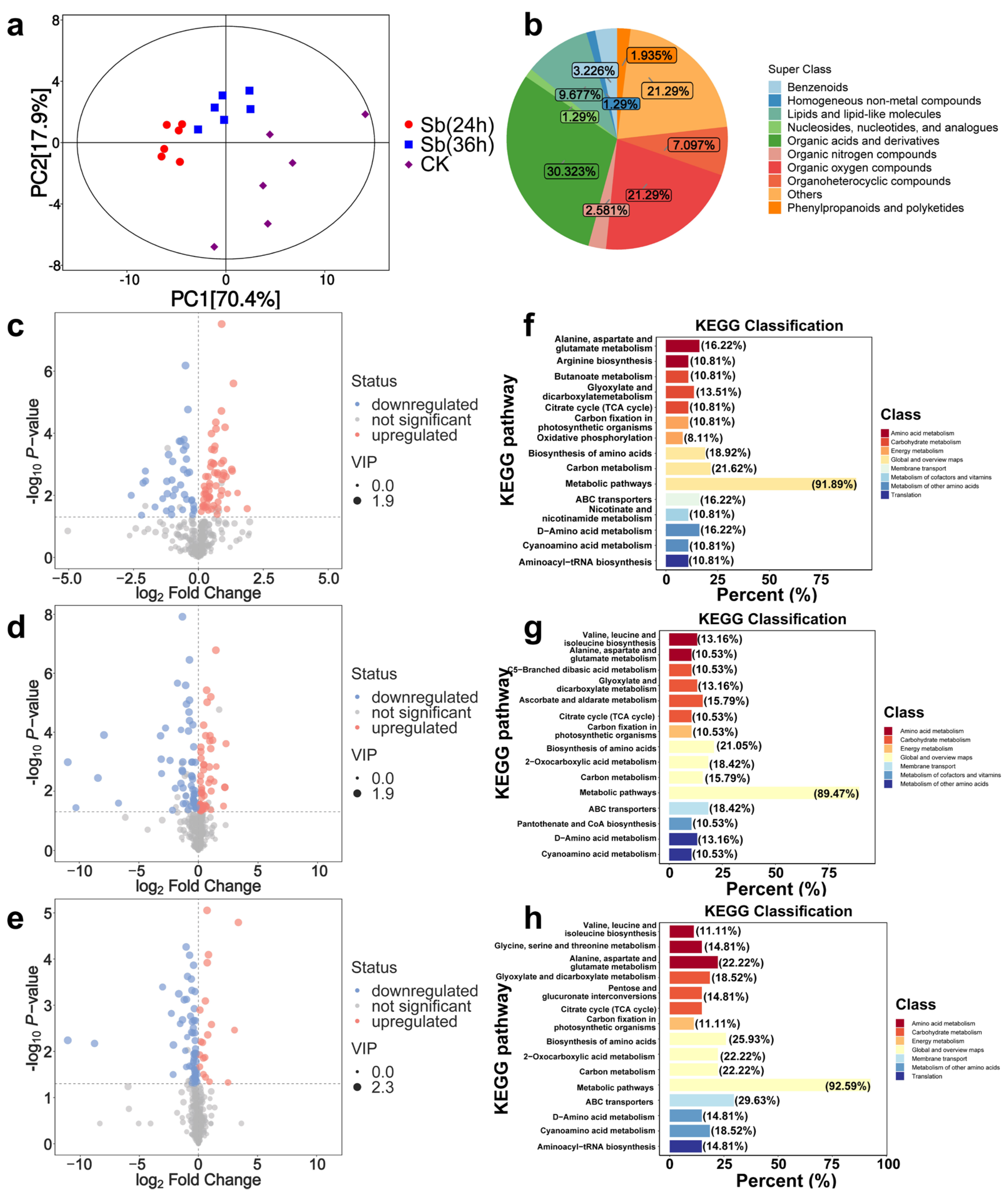
3.3. Metabolomics Analysis
3.3.1. Metabolite Accumulation
3.3.2. Differentially Accumulated Metabolite (DAMs) Analysis
3.3.3. KEGG Pathway Analysis
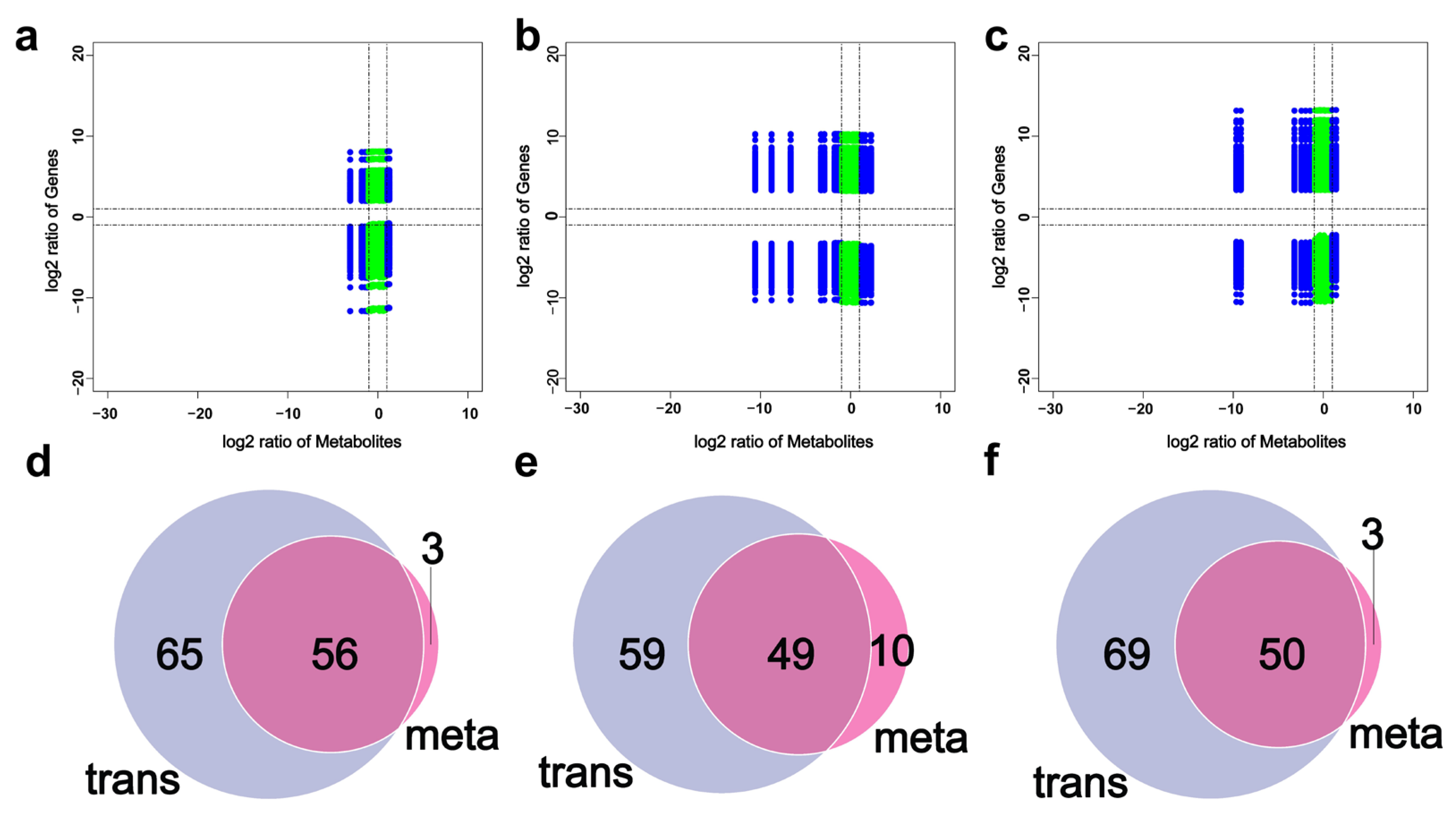
3.4. Integrated Analysis of Transcriptomics and Metabolomics
4. Discussion
4.1. Sb Stress-Induced Physiological Change in Bermudagrass
4.2. Photosystem Was Involved in Sb Stress Response of Bermudagrass
4.3. Sb Stress Affected the Synthesis of Polypeptides in Bermudagrass
4.4. Bermudagrass Response to Sb Stress Through Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Regulation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karagas, M.R.; Wang, A.; Dorman, D.C.; Hall, A.L.; Pi, J.; Sergi, C.M.; Symanski, E.; Ward, E.M.; Arrandale, V.H.; Azuma, K.; et al. Carcinogenicity of cobalt, antimony compounds, and weapons-grade tungsten alloy. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 577–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filella, M.; Williams, P.A. Antimony biomethylation in culture media revisited in the light of solubility and chemical speciation considerations. Environ. Toxicol. 2010, 25, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschan, M.; Robinson, B.H.; Nodari, M.; Schulin, R. Antimony uptake by different plant species from nutrient solution, agar and soil. Environ. Chem. 2009, 6, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wu, Z.; He, M. Removal of antimony (V) and antimony (III) from drinking water by coagulation–flocculation–sedimentation (CFS). Water Res. 2009, 43, 4327–4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Liu, G.; Kang, Y.; Lam, P.K.S.; Chou, C. Assessment and distribution of antimony in soils around three coal mines, Anhui, China. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2011, 61, 850–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boreiko, J.C.; Rossman, G.T. Antimony and its compounds: Health impacts related to pulmonary toxicity, cancer, and genotoxicity. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2020, 403, 115156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Fu, Z.; Liu, B.; Mo, C.; Chen, B.; Corns, W.; Liao, H. Health risk associated with dietary co-exposure to high levels of antimony and arsenic in the world’s largest antimony mine area. Sci. Total. Environ. 2011, 409, 3344–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Wei, C.; Tu, S.; Ding, Y.; Wang, R.; Guo, J. The uptake and detoxification of antimony by plants: A review. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2013, 96, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.K.; Mishra, A.; Jha, B. Non-targeted metabolite profiling and scavenging activity unveil the nutraceutical potential of psyllium (Plantago ovata Forsk). Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saharan, B.S.; Brar, B.; Duhan, J.S.; Kumar, R.; Marwaha, S.; Rajput, V.D.; Minkina, T. Molecular and physiological mechanisms to mitigate abiotic stress conditions in plants. Life 2022, 12, 1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, R.; Ge, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, R. Plants’ response to abiotic stress: Mechanisms and strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batista, R.; Saibo, N.; Lourenço, T.; Oliveira, M.M. Microarray analyses reveal that plant mutagenesis may induce more transcriptomic changes than transgene insertion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 3640–3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walia, H.; Wilson, C.; Condamine, P.; Liu, X.; Ismail, A.M.; Zeng, L.; Wanamaker, S.I.; Mandal, J.; Xu, J.; Cui, X.; et al. Comparative transcriptional profiling of two contrasting rice genotypes under salinity stress during the vegetative growth stage. Plant Physiol. 2005, 139, 822–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Yu, Y.; Snesrud, E.C.; Moy, L.P.; Linford, L.D.; Haas, B.J.; Nierman, W.C.; Quackenbush, J. Transcriptional divergence of the duplicated oxidative stress-responsive genes in the Arabidopsis genome. Plant J. 2005, 41, 212–220. [Google Scholar]
- Puglia, G.D.; Prjibelski, A.D.; Vitale, D.; Bushmanova, E.; Schmid, K.J.; Raccuia, S.A. Hybrid transcriptome sequencing approach improved assembly and gene annotation in Cynara cardunculus (L.). BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Duan, Y.; Liu, D.; Zong, Y.; Zhang, D.; Shi, X.; Hao, X.; Li, P. Physiological and transcriptome analysis of response of soybean (Glycine max) to cadmium stress under elevated CO2 concentration. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 448, 130950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, L.W.; Mendes, P.; Dixon, R.A. Plant metabolomics: Large-scale phytochemistry in the functional genomics era. Phytochemistry 2003, 62, 817–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, H.; Sun, H.; Wang, X. The application of metabolomics in traditional Chinese medicine opens up a dialogue between Chinese and Western medicine. Phytother. Res. 2015, 29, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Yun, E.J.; Hossain, M.A.; Lee, H.; Kim, K.H. Global profiling of ultraviolet-induced metabolic disruption in Melissa officinalis by using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 404, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, M.Y.; Yano, M.; Goodenowe, D.B.; Kanaya, S.; Kimura, T.; Awazuhara, M.; Arita, M.; Fujiwara, T.; Saito, K. Integration of transcriptomics and metabolomics for understanding of global responses to nutritional stresses in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 10205–10210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Schumaker, K.S.; Zhu, J.K. Cell signaling during cold, drought, and salt stress. Plant Cell 2002, 14 (Suppl. 1), S165–S183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taliaferro, C.M. Diversity and vulnerability of Bermuda turfgrass species. Crop Sci. 1995, 35, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Liu, C.; Ye, T.; Huang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chan, Z. Integrated transcriptome and proteome analyses provide insight into abiotic stress crosstalks in bermudagrass. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2022, 199, 104864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, M.; Fan, J.; Kaleem, M.; Akhtar, M.T.; Jin, S.; Nazir, U.; Zhang, C.J.; Yan, X. Assessment of the changes in growth, photosynthetic traits and gene expression in Cynodon dactylon against drought stress. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, C.; Peng, L. Antimony’s environmental impact in China. Science 2024, 386, 280–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Fan, J.; Zhu, W.; Amombo, E.; Lou, Y.; Chen, L.; Fu, J. Effect of heavy metals pollution on soil microbial diversity and bermudagrass genetic variation. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, K.H.; Huang, M.Y.; Huang, W.D.; Hsu, M.H.; Yang, Z.W.; Yang, C.M. The effects of red, blue, and white light-emitting diodes on the growth, development, and edible quality of hydroponically grown lettuce (Lactuca sativa L. var. capitata). Sci. Hortic. 2013, 150, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.M.; Li, Z.F.; Shen, J.; Wu, K.; Zhao, P.; Wu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Yang, J.; Liu, H.; Rensing, C.; et al. Toxicity of different forms of antimony to rice plants: Photosynthetic electron transfer, gas exchange, photosynthetic efficiency, and carbon assimilation combined with metabolome analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 437, 129433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.X.; Chen, J.Y.; Hu, C.Y.; Han, R.; Dai, Z.H.; Guan, D.X.; Ma, L.Q. Uptake, speciation and detoxification of antimonate and antimonite in As-hyperaccumulator Pteris Cretica L. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 308, 119653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.J.; Sun, C.Y.; Zhu, P.F.; Liu, F. Effects of antimony stress on photosynthesis and growth of Acorus calamus. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.L.; Ullah, F.; Zhou, D.X.; Yi, M.; Zhao, Y. Mechanisms of ROS regulation of plant development and stress responses. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbdElgawad, H.; Zinta, G.; Hamed, B.A.; Selim, S.; Beemster, G.; Hozzein, W.N.; Wadaan, M.A.M.; Asard, H.; Abuelsoud, W. Maize roots and shoots show distinct profiles of oxidative stress and antioxidant defense under heavy metal toxicity. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Cai, J.S.; Li, J.J.; Lu, G.Y.; Li, C.S.; Fu, G.P.; Zhang, X.K.; Ma, H.Q.; Liu, Q.Y.; Zou, X.L.; et al. Exogenous application of a low concentration of melatonin enhances salt tolerance in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) seedlings. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, S.N.; Bao, Q.L.; Chu, Y.; Sun, H.; Huang, Y. Jasmonic acid alleviates cadmium toxicity through regulating the antioxidant response and enhancing the chelation of cadmium in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environ. Pollut. 2022, 304, 119178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Pan, X.; Mu, G.; Wang, J. Toxic effects of antimony on photosystem II of Synechocystis sp. as probed by in vivo chlorophyll fluorescence. J. Appl. Phycol. 2010, 22, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Lv, C.; Xu, M.; Chen, G.; Lv, C.; Gao, Z. Photosynthesis performance, antioxidant enzymes, and ultrastructural analyses of rice seedlings under chromium stress. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 1768–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasulu, P.; Murthy, S.D.S. Action of selected heavy metal on photosynthetic electron transport activities of maize thylakoid membranes. Int. J. Plant Anim. Environ. Sci. 2015, 5, 90–93. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Wufuer, R.; Duo, J.; Li, W.; Pan, X. Cadmium caused different toxicity to photosystem I and photosystem II of freshwater unicellular algae Chlorella pyrenoidosa (Chlorophyta). Toxics 2022, 10, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.Y.; Choi, Y.H.; Lee, J.I.; Kim, I.H.; Nam, T.J. Antioxidant activity of Oxygen Evolving Enhancer Protein 1 purified from Capsosiphon fulvescens. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, H1412–H1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaskulak, M.; Rostami, S.; Zorena, K.; Vandenbulcke, F. Transcriptome sequencing of Brassica napus highlights the complex issues with soil supplementation with sewage sludge. Chemosphere 2022, 298, 134321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Sun, S.; Zhao, W.; Yang, X.; Mao, H.; Sheng, L.; Chen, Z. Utilizing transcriptomics and proteomics to unravel key genes and proteins of Oryza sativa seedlings mediated by selenium in response to cadmium stress. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Hong, H.; Zhao, J.; Fang, R.; Chen, S.; Tang, C. Metabolome analysis to investigate the effect of heavy metal exposure and chemoprevention agents on toxic injury caused by a multi-heavy metal mixture in rats. Sci. Total. Environ. 2024, 906, 167513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, W.; Guo, G.; Cui, L.; Rashid, M.A.R.; Jiang, L.; Sun, G.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y. Combined transcriptome and metabolome analysis reveals the effects of light quality on maize hybrids. BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, G.; Zhao, J.; Wang, W.; Hong, X. Integrated analysis of transcriptome and metabolome reveals insights for low-temperature germination in hybrid rapeseeds (Brassica napus L.). J. Plant Physiol. 2023, 291, 154120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Q.; Noor, M.; Xiang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gao, S.; Wu, F.; Li, X.; Hu, X.; Yan, X.; Wen, B.; et al. Integrated Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Analysis of Antimony (Sb) Stress Response in Common Bermudagrass (Cynodon dactylon [L.] Pers.). Agriculture 2025, 15, 2221. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15212221
Liu Q, Noor M, Xiang Y, Chen Y, Gao S, Wu F, Li X, Hu X, Yan X, Wen B, et al. Integrated Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Analysis of Antimony (Sb) Stress Response in Common Bermudagrass (Cynodon dactylon [L.] Pers.). Agriculture. 2025; 15(21):2221. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15212221
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Qian, Maryam Noor, Yuanhang Xiang, Yao Chen, Shang Gao, Fangming Wu, Xiaoqin Li, Xutong Hu, Xuebing Yan, Bing Wen, and et al. 2025. "Integrated Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Analysis of Antimony (Sb) Stress Response in Common Bermudagrass (Cynodon dactylon [L.] Pers.)" Agriculture 15, no. 21: 2221. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15212221
APA StyleLiu, Q., Noor, M., Xiang, Y., Chen, Y., Gao, S., Wu, F., Li, X., Hu, X., Yan, X., Wen, B., & Fan, J. (2025). Integrated Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Analysis of Antimony (Sb) Stress Response in Common Bermudagrass (Cynodon dactylon [L.] Pers.). Agriculture, 15(21), 2221. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15212221