Abstract
The dichotomy of striking a balance between sustainable food crop production for the skyrocketing human population and ensuring agricultural practices that mitigate environmental degradation has prompted much research into sustainable crop production methods. The application of amendments has become an integral part of arable soil management in restoring declining soil fertility for sustainable and high-quality crop production. This study was conducted on lettuce and carrot cultivated on soil treated with three different amendments: cow dung, sewage sludge, and nitrogen–phosphorus–potassium (NPK) mineral fertilizer. The vegetables were harvested at maturity at 60 and 110 days for lettuce and carrot, respectively, dried in a hot air oven, crushed, and then digested to obtain an aliquot sample. The level of macronutrients was quantified from the aliquots using inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES), Avio 550 Max, PerkinElmer, USA. It was observed that both soil treatment and types of vegetables significantly impacted the level of mineral contents in the vegetables. The highest values of 58.00 ± 8.36 mg/kg and 72.97 ± 12.53 mg/kg were recorded for Na and P in carrots from soil treated with sewage sludge, respectively. The highest values of 247.97 ± 17.07 mg/kg and 104.72 ± 4.12 mg/kg were recorded for Ca and Mg in lettuce from sewage sludge-treated soil, respectively. Similarly, the highest value of 546.75 ± 76.44 mg/kg for K was also recorded in lettuce, but from cow dung-treated soil. The overall pattern of mineral accumulation by vegetables shows that carrots accumulate more Na than lettuce, and lettuce accumulates more Mg, Ca, and K than carrots, while there was no significant difference in the level of P in both lettuce and carrots. The findings reveal that lettuce and carrots from soil treated with organic manure cow dung and sewage sludge accumulated higher mineral contents of most of the investigated minerals. It was also observed that lettuce accumulated higher contents of most of the minerals investigated. This study therefore concludes that organic manures are better alternatives to mineral fertilizers for vegetable production, which supports the effort to strike a balance between sustainable and ecofriendly agriculture.
1. Introduction
Over the years, the adoption of sustainable agricultural practices that mitigate environmental degradation has continued to gain traction all over the world. The dichotomy of striking a balance between sustainable food crop production for the skyrocketing human population and ensuring agricultural practices with minimal to no negative environmental consequences has prompted much research into various methods of crop production. Proffering solutions to this complexity includes agricultural practices like soil management methods for quality crop production. Soil is an essential non-renewable resource with potentially rapid degradation rates, but an extremely slow formation and regeneration process [1]. Arable soil management is multidimensional, but in the purview of this study, our focus was on the application of soil amendments in food crop production. The application of amendments has become an integral part of arable soil management in restoring declining soil fertility for sustainable crop production. Proper soil management ensures that essential nutrients do not become deficient or toxic to plants, and that appropriate nutrients enter the food chain [2].
Soil amendments are substances containing one or more naturally occurring or synthetically manufactured elements that are added to the soil to supply deficient nutrients, improving soil fertility and the overall quality of the crops [3]. Soil amendments are broadly classified into two main groups of organic manures and inorganic fertilizers, depending on the method of production [4]. Organic manures are made up of materials of natural origin, such as crop residues, green plants, food wastes, and human and animal feces [5], with examples such as compost, sewage sludge, livestock and poultry dung, and human urine and feces [6,7]. Inorganic fertilizers, commonly referred to as mineral or chemical fertilizers, on the other hand, are industrially synthesized compounds or substances containing one or more elements that are chemically combined, with examples including the nitrogen–phosphorus–potassium (NPK), granular triple superphosphate, and anhydrous ammonia fertilizers, and so on [4,8].
There are few factors that influence the choices of amendments that are used by farmers in soil treatments. Characteristics such as nutrient specificity have made synthetic fertilizers the preferred choice of commercial or intensive food crop producers [9,10]. Organic manures, on the other hand, are mostly preferred by subsistence farmers due to their cheap availability and accessibility. More importantly, there is a misconception that crops from organic manure are nutritionally superior to their counterparts from synthetic fertilizers [11]. Whether this perspective holds true has become a genuine topical issue in research, with contrasting reports in the literature.
Whatever informs the choices of amendments used in soil treatments for crop production, it must be noted that the uptake of nutrients (both major and trace minerals) from the soil by plants depends on many factors, including the type of plant and the plant’s physiological demands [12,13,14]. For instance, in the soil–plant system, the electrochemical gradient plays a significant role in the mobilization of ions in the soil and their adsorption by plant roots and subsequent uptake to plant tissues. The surfaces of plant roots are negatively charged under normal conditions due to dissociating carboxyl, hydroxyl, and phosphate functional groups from the cell wall and cell membrane of plant roots [15]. The interaction of these negatively charged functional groups on the surface of plant roots significantly influences the uptake of nutrients from the soil by plants [16].
Vegetables are popular components of diets all over the world because of their wide range of nutritional and health benefits. They provide essential nutrients, such as amino acids, fibers, proteins, vitamins, and minerals, which are beneficial to human health [12,13,14,15]. Vegetables are rich sources of major minerals like calcium (Ca), potassium (K), magnesium (Mg), sodium (Na), and phosphorus (P), which have been associated with numerous health benefits such as a lower risk of cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases, as well as certain types of cancer [17,18,19,20,21]. Na is a principal cation of extracellular fluid and plays a major role in body fluid homeostasis, which helps in the transmission of nerve impulses, muscle contraction, and regulation of blood pressure [22]. A deficiency in Na, in very rare circumstances, causes hyponatremia with symptoms such as nausea, headache, and confusion, while Na toxicity causes dehydration, restlessness, poor concentration, sleep disruption, and high blood pressure [23]. K is the principal intracellular cation that helps maintain the fluid and electrolyte balance, as well as nerve impulse transmission and muscle contraction [24]. A low level of K in the blood can result in metabolic alkalosis with symptoms like excessive sweating, burns, and diarrhea [25]. Ca is the most abundant mineral in the body and is involved in bone formation in early life, as well as preventing the loss of bone mass in later life [26]. A deficiency in Ca causes hypocalcemia, a medical condition with symptoms such as numbness and tingling in the fingers, spasms, and osteoporosis in later life [27]. P is the second most abundant mineral in the body, and in combination with Ca forms the hydroxyapatite crystals of bone and teeth [28]. Other major roles include lipid transport in the blood, being a structural component of cell membranes, and assisting in energy metabolism [29]. Mg is found in bones, muscles, soft tissues, and extracellular fluid, and plays significant roles in muscle contraction, blood clotting, ATP production, normal function of the immune system, and energy metabolism [30]. Magnesium deficiency can cause illnesses such as loss of appetite, fatigue, muscle weakness, and its toxicity can cause gastrointestinal distress, stomach cramps, and diarrhea [31].
Fresh vegetables such as Lactuca sativa and Daucus carrota, commonly known as lettuce and carrot, respectively, are very popular and commonly consumed vegetables globally [32,33]. Due to their richness in the aforementioned minerals, the numerous nutritional and health benefits of these vegetables include improvements in gastrointestinal health and a reduced risk of heart disease, strokes, diabetes, anemia, gastric ulcers, rheumatoid arthritis, and other cardiovascular and chronic diseases [34,35]. Vegetable production contributes substantially to the global economy and plays a crucial role in reducing unemployment and alleviating poverty in developing countries. In addition to their health benefits, characteristics like their short cycle production period have been attributed to the massive production of vegetables around the world [36]. Therefore, the aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of different soil amendments on the major mineral contents of commonly consumed vegetables like lettuce and carrot. The objective was to compare the levels of five major minerals (Ca, Mg, Na, K, and P) in two types of vegetables.
2. Materials and Methodology
2.1. Study Area
This study was conducted at the Sefako Makgatho Health Sciences University, located in the northern part of Pretoria, one of the cities in the Tshwane Metropolitan Municipality in South Africa with coordinates 250 37′8″ S and 280 1′22″ E. Pretoria, the administrative capital of South Africa, has a monsoon-influenced humid subtropical climate with long, hot, rainy summers, and short, dry, and mild winters. Pretoria experiences an average annual temperature of 18.7 °C (65.7 °F) and 675 mm (26.6 in) average annual rain [37]. The planting experiment was conducted at the production unit of the university, in a net-fenced enclosure to prevent intrusions from animals and unauthorized people. This area is used for a lot of experimental planting and some other research activities in the university.
2.2. Experimental Design and Planting
This study was conducted on Lactuca sativa var. capitata and Daucus carota, commonly known as butterhead lettuce and carrot, respectively. The butterhead lettuce has soft, loose, green or reddish-purple leaves, and the chantenay carrot variety develops a short, conical orange carrot, tapering towards blunt, rounded tip roots. These two vegetables were cultivated on soil treated with three different amendments: cow dung, sewage sludge, and nitrogen–phosphorus–potassium (NPK) mineral fertilizer. The sewage sludge was collected from Daspoort Marabastad, a governmental sewage treatment plant, situated at the city central of Tshwane, South Africa. The cow dung was collected from the livestock farm at De-Wilt, Brits Road Ga-Rankuwa, located in the northern region of the city of Tshwane, South Africa. The nitrogen–phosphorus–potassium fertilizer, with a weight distribution of N2P3K2, i.e., 40% nitrogen, 60% phosphorus, and 40% potassium, manufactured by Omina Fertilizers Johannesburg, South Africa, was purchased from a registered nursery marketer (Plantland Nursery), Longmore and Old Brits Road, Akasia–Pretoria South Africa.
The planting was carried out using a total of 96 pots divided into two equal numbers for each vegetable and further subdivided into 12 pots per treatment (sewage sludge-treated soil, SS; cow dung-treated soil, CD; NPK-treated soil, NPK; and untreated soil, UNTRD). The soil quantity and manure dry weight used in this study was adapted from previous studies [13,38]. The pots from the treatment groups were each filled with 5 kg of thoroughly mixed sandy and loamy soil and 0.15 kg of amendment, while the pots from the untreated group were filled with just 5.15 kg of sandy and loamy soil. Also, the 0.15 kg weight of amendments used was comparative to the recommended dose of NPK fertilizer for vegetable cultivation, and the amendments were only applied once at the beginning of the planting [39,40,41]. The lettuce and carrot seedlings, which were raised at a self-propagated nursery, were introduced into the pot two weeks after germination. The plants were exposed to the same normal environmental condition and irrigated with the same quantity of portable water enough to moisten the soil and to prevent nutrients runoff and NO3− leaching [28,29]. The experimental design used for this study has been peer-reviewed and published [42].
2.3. Soil Properties Analysis
The method described by [43] was followed to determine the relevant physicochemical properties such as pH, electrical conductivity, organic matter, and texture of the soil used in this experiment. About 10 g of the oven-dried soil samples were weighed into 100 mL falcon tubes containing 25 mL of distilled water and were placed in a stirrer for 30 min. After stirring, the falcon tubes containing the mixture were centrifuged for 2 min and allowed to settle, after which the soil pH and electrical conductivity (EC) were measured using a pH and conductivity multi-probe HQ 440D HACH benchtop meter. The wet combustion method was used to determine the percentage of organic matter. The soil organic carbon (SOC) and total nitrogen (TN) were determined using a standard potassium dichromate digestion method and Kjeldahl method, respectively [44]. The cation-exchange (Ca2+, K+, Mg2+) capacity of the soil was extracted using 1 M ammonium acetate. Subsequently, the total contents of Ca2+ and Mg2+ from the extracts were determined using the EDTA complexometric titration method, while that of K+ was determined using the flame photometric absorption method [45].
2.4. Sample Preparation and Digestion Process
The vegetables were harvested at maturity, at 60 and 110 days for lettuce and carrot, respectively. The samples were rinsed with distilled water, and the carrots were shredded; then, both samples were dried in a hot air oven at 50 °C for 24 and 48 h for lettuce and carrot, respectively. The dried samples were homogenized with a ceramic mortar and pestle. The method described by [46,47], with slight modifications, was used for the digestion of the samples. The acid (i.e., wet) digestion included a mixture of 10 mL of 69% nitric acid, 5 mL of 65% perchloric acid, and 4 mL of hydrogen peroxide pipetted into an Erlenmeyer flask containing 0.5g of the finely ground sample, and the mixture was heated for 20 min on a hot stove until a very clear solution was observed. The digested sample was transferred into a 50 mL volumetric flask and made up to the 50 mL mark with deionized water. The solution was then filtered with a Whatman No. 1 filter paper, Whatman Ltd., Maidstone, UK. The level of macronutrients was subsequently quantified from the aliquots using inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES), Avio 550 Max, PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, USA. The final value for each macronutrient was calculated as the average of triplicate readings and the results were expressed as mg/100 g of plant weight.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
The data were statistically analyzed using statistical package for social sciences (IBM-SPSS 28.0). A general linear model multivariate analysis was conducted to determine differences in the mean concentrations of the major minerals of the vegetables between treatments. Tukey’s LSD post hoc test was used for the separation of means, at a 5% significance level (p < 0.05).
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Experimental Soil
The analyses of the physicochemical properties of the experimental soil and the amendments for this study, before planting and after harvesting, are presented in Table 1. The soil was neutral to slightly alkaline, but there was no noticeable difference in soil pH across all treatments. The application of cow dung and sewage sludge increased the OM contents of the soil, while the application of sewage sludge and NPK had a significant effect on the EC of the soil. The application of all treatments increased the exchangeable cation content of the soil. The experimental soil for this study was classified as calcareous, as observed in the result of the analysis of the available mineral contents of the experimental soil, where Ca was significantly higher than the remaining minerals (see Table 2).

Table 1.
The physical and chemical properties of the experimental soil and the amendments.

Table 2.
Available mineral contents of the experimental soil.
3.2. The Level of Mineral Contents in Lettuce and Carrot
The results of the mean concentrations of the major minerals (Ca, K, Mg, Na, and P) in lettuce and carrot from different soil amendments are presented in Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5. The overall pattern of mineral accumulation by vegetables shows that carrots accumulate more Na than lettuce, and lettuce accumulates more Mg, Ca, and K than carrots, but there was no significant difference in the P contents of both the lettuce and carrots. Also, the relative abundance of these minerals (in descending order), as observed in the current study, was K > Ca > Mg > P > Na.
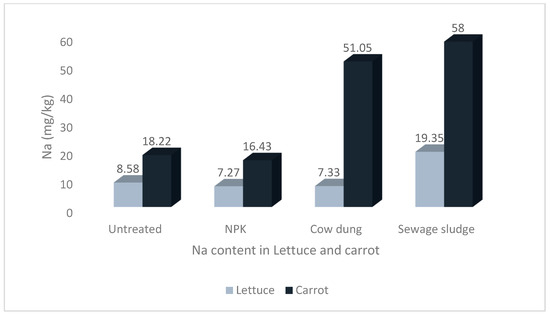
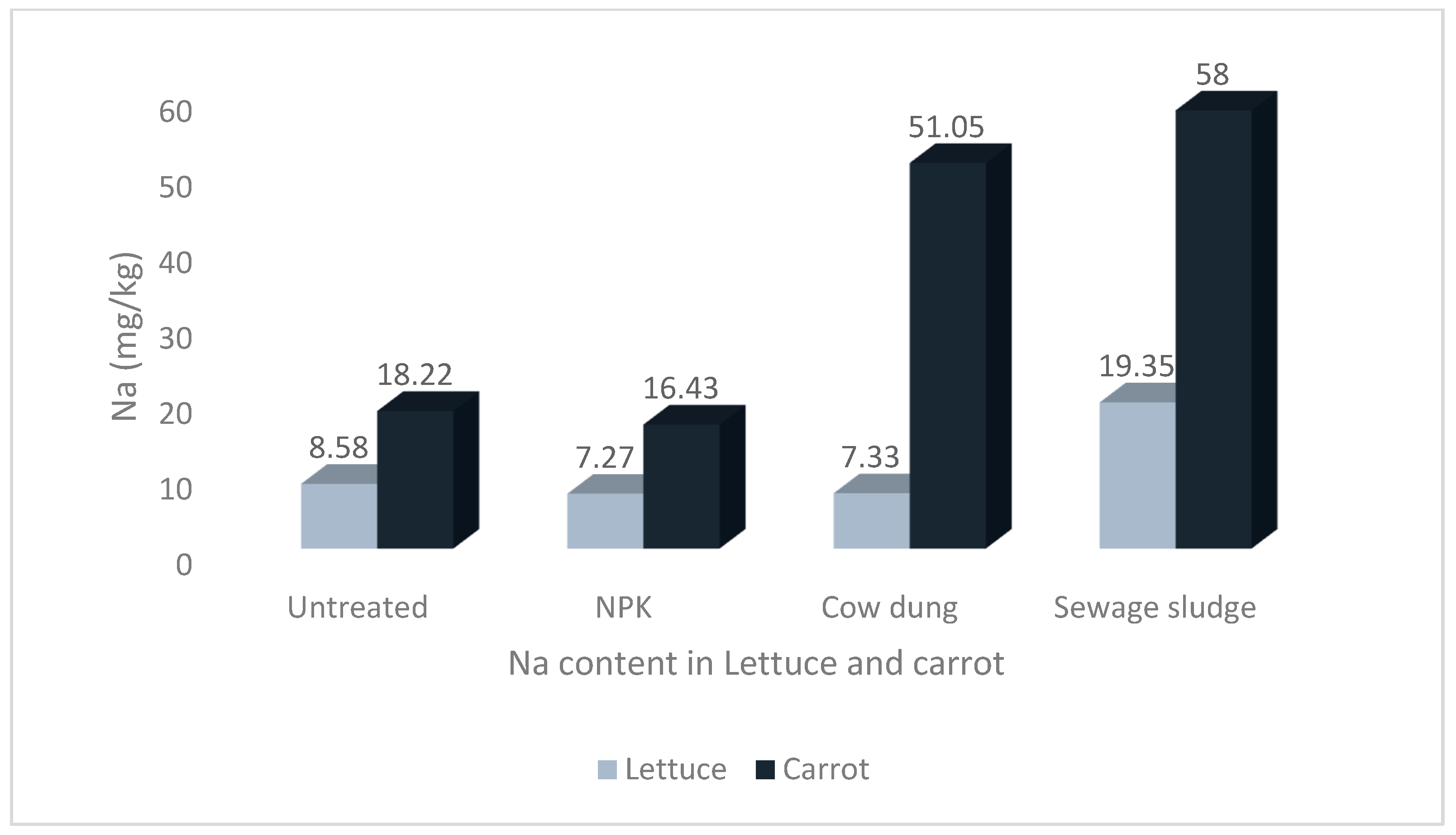
Figure 1.
Levels of sodium in lettuce and carrot from different soil treatments.
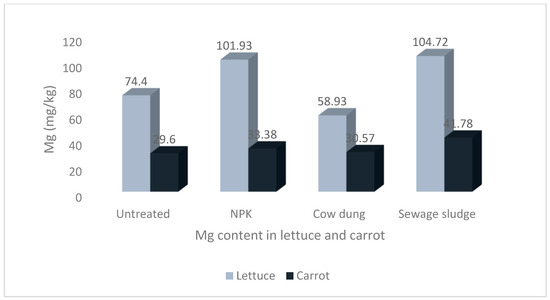
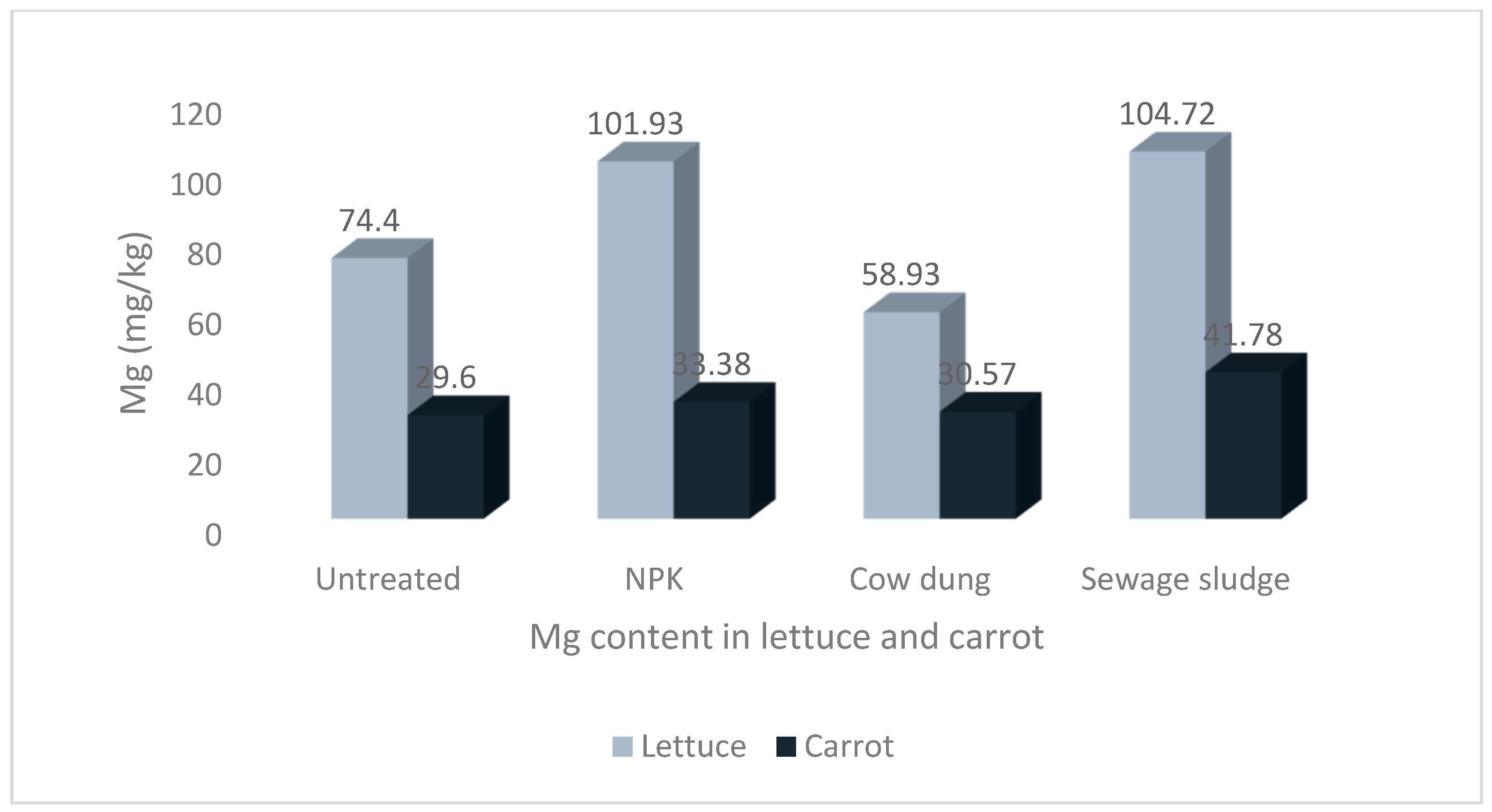
Figure 2.
Levels of magnesium in lettuce and carrot from different soil treatments.
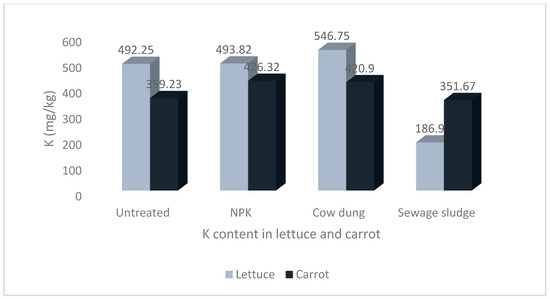
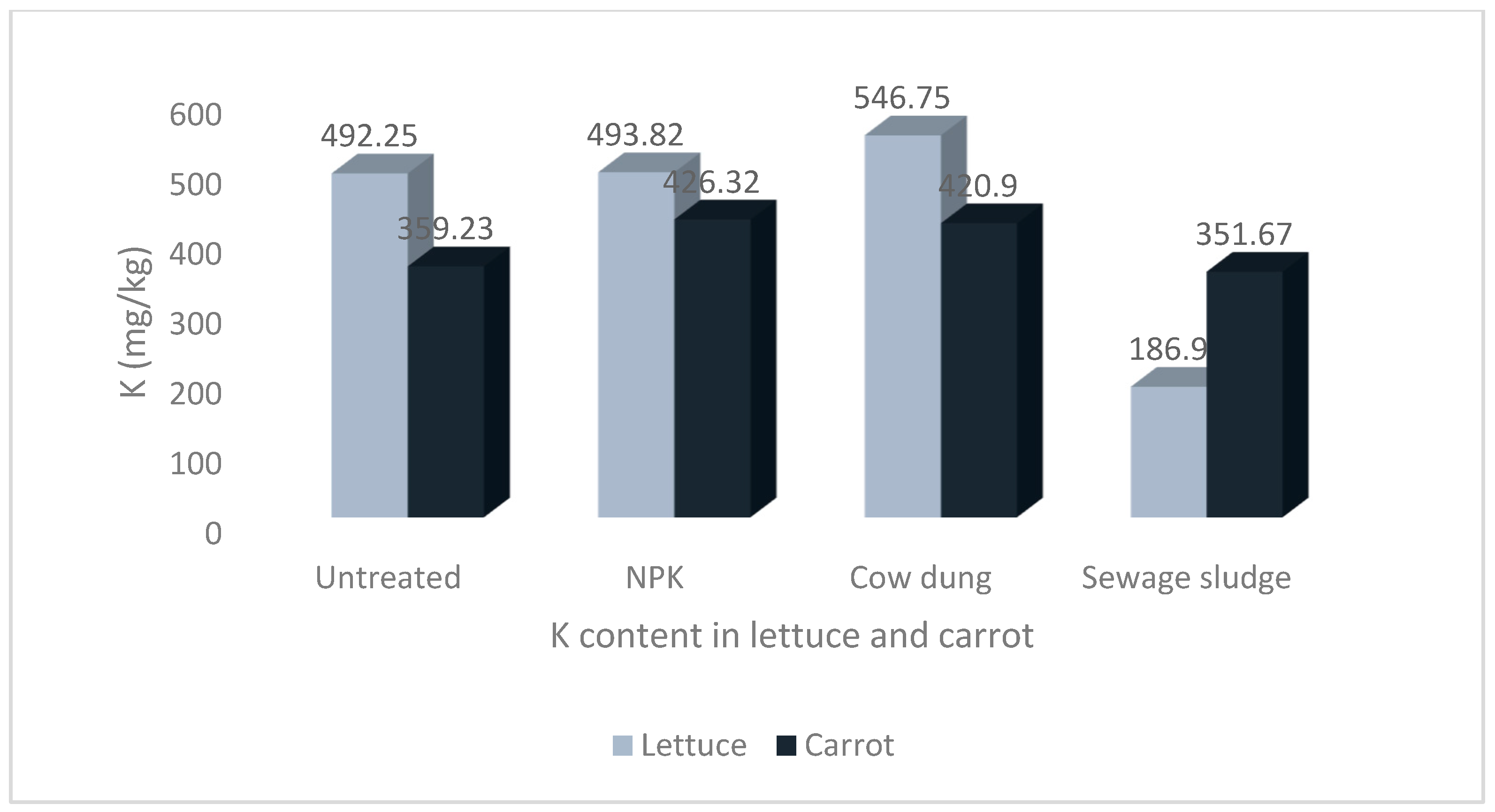
Figure 3.
Levels of potassium in lettuce and carrot from different soil treatments.
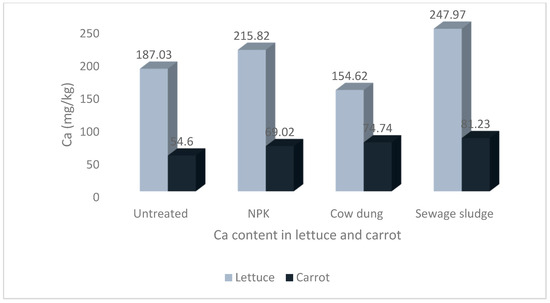
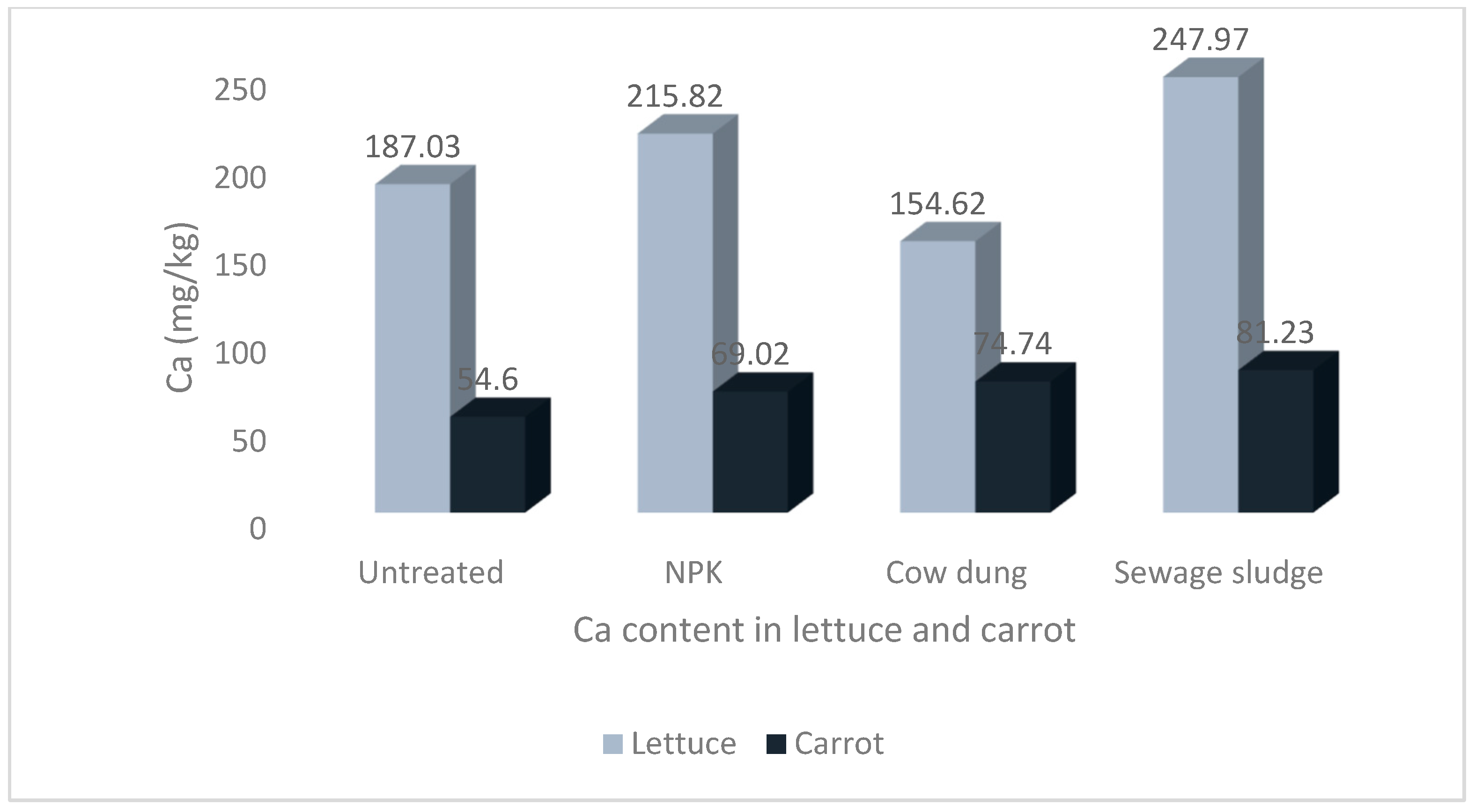
Figure 4.
Levels of calcium in lettuce and carrot from different soil treatments.
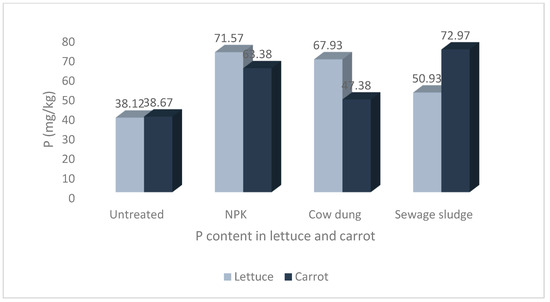
Figure 5.
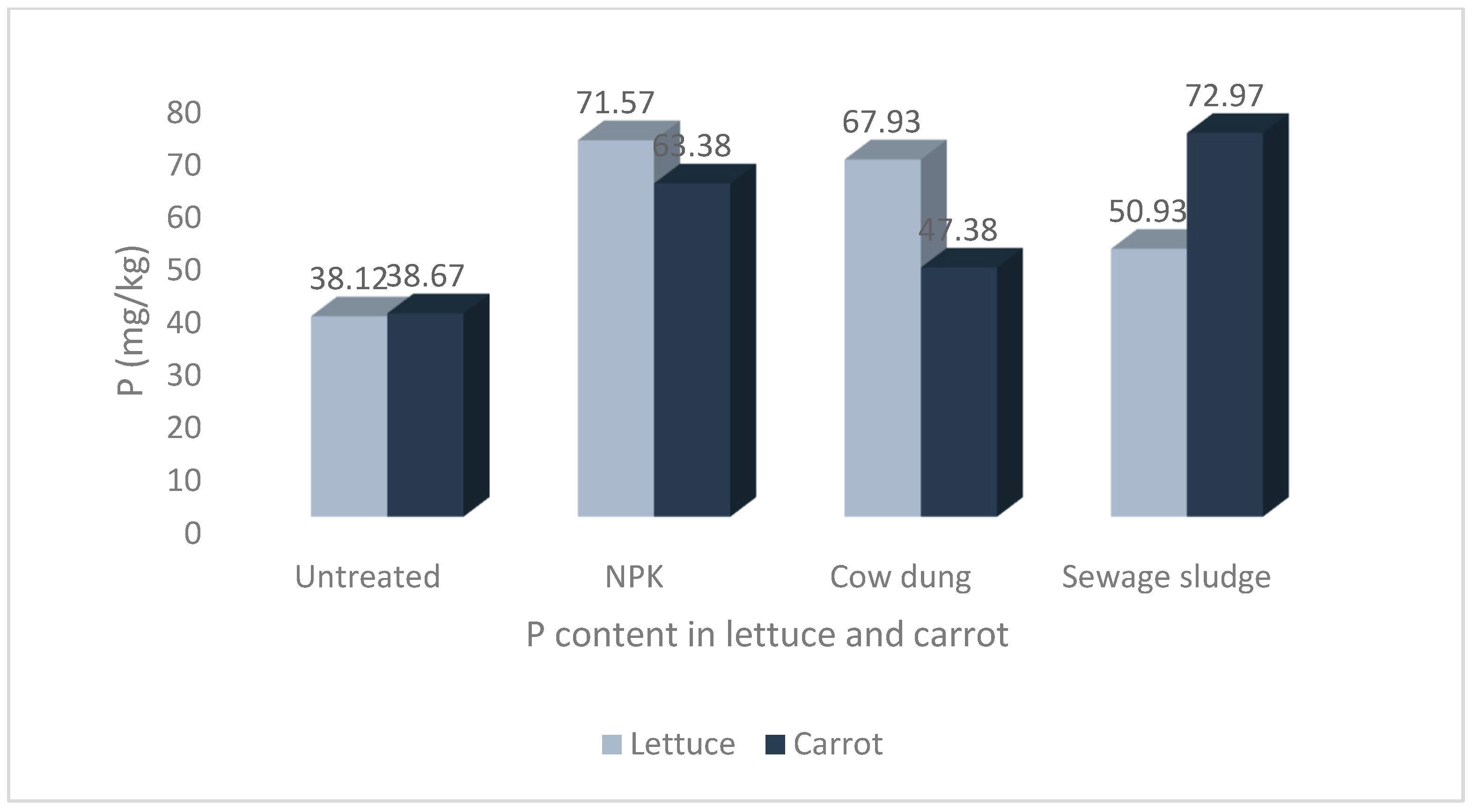
Levels of phosphorus in lettuce and carrot from different soil treatments.
The results show that the soil treatments and vegetable type significantly impacted the mineral contents of the studied vegetables. The highest Na and P values of 58.00 ± 8.36 mg/kg and 72.97 ± 12.53 mg/kg, respectively, were recorded in carrots grown in soil treated with sewage sludge. The highest Ca and Mg values of 247.97 ± 17.07 mg/kg and 104.72 ± 4.12 mg/kg, respectively, were recorded in lettuce grown in sewage sludge-treated soil. Similarly, the highest value for K, 546.75 ± 76.44 mg/kg, was also recorded in lettuce but from cow dung-treated soil.
The difference in the Na content of lettuce and carrot was statistically significant, at p < 0.05. Although there was no significant difference in the Na contents of carrots grown in soil treated with sewage sludge and those grown in cow dung-treated soil (p > 0.05), the values were significantly higher than the values from other soil treatments Figure 1. Furthermore, although there was no significant difference between the Mg contents of lettuce from the NPK and sewage sludge treatments, the values were significantly higher than the lettuce grown in the other treatments and those of carrots (see Figure 2).
Additionally, the values of K in lettuce were significantly higher than the corresponding values in carrots. Although the values of K in the lettuce from the NPK and cow dung treatments were higher than the values recorded for carrots from the same soil treatments, the differences were not statistically significant at p > 0.05 (Figure 3).
There was no statistical difference in the Ca contents in carrots across all treatments. The Ca values were significantly higher in lettuce compared to carrots, and the differences were statistically significant (p < 0.05) Figure 4.
Finally, there were no significant differences in the P contents of lettuce and carrots. However, the differences were significant within treatments, with lettuce and carrot from NPK, cow dung, and sewage sludge treatments having significantly higher P contents than their counterparts grown in untreated soil (Figure 5).
This study observed that the highest mineral contents of the studied minerals were recorded in vegetables cultivated in soil treated with organic manure. For instance, the Na and P contents were highest in carrots from the sewage sludge treatment, the Ca and Mg contents were highest in lettuce from the sewage sludge treatment, and K was highest in lettuce from the cow dung treatment. The mean values of the major mineral contents in the lettuce and carrot samples are summarized in Table 3.

Table 3.
The mean values of the mineral contents in vegetables.
4. Discussion
Accumulation of Minerals in Vegetables
The organic matter (OM) content of soil is derived from decomposed plant materials and microbial activity [48]. The high contents of OM in the soil treated with cow dung and sewage sludge indicate a high level of microbial activity and decomposed plant materials, which are readily present in animal biota and sewage sludge. Even though the application of organic manure has been shown to improve the physical and biological characteristics of soil, including its microbial activity [49], its role in nutrient uptake by plants are still somewhat unclear. It has, however, been reported that soils with low CEC are more likely to develop deficiencies and are susceptible to those minerals [43]. It is plausible that the application of organic manure, which typically has high levels of CEC, is able to influence the soil nutrient quantity and its availability to plants. This study observed that, in comparison with the untreated and NPK-treated soils, vegetables grown with the addition of organic manure (i.e., the cow dung and sewage sludge soil treatments) accumulated higher amounts of the investigated minerals (Ca in lettuce from the sewage sludge treatment, K in lettuce from the cow dung treatment, Na in carrots from the cow dung and sewage sludge treatments, and P in carrots from the cow dung and sewage sludge treatments).
According to the literature, the nutrient contents of various plant parts might be useful predictors of the plant’s response to nutrients supplied via fertilizers [50]. The available N, P, and K were significantly higher in the soils treated with amendments compared to the untreated soil (Table 2), which is an indication that the amendments might have contributed to the available nutrient pool of these minerals upon mineralization. It has been reported that a low C:N ratio favors a quick mineralization and release of nutrients to the soil, which makes them readily available for plant uptake [51]. This is evident in this study, as observed in the soil treated with NPK, which had the lowest C:N ratio (Table 1). This suggests that the rate of mineralization might have been faster in the NPK treatments, but the levels of the mineral contents is unclear.
We also observed that the differences in mineral contents were statistically significant between the types of vegetables, which suggests that the plants might have also played a crucial role in the nutrient uptake profile. Even though organic manure is believed to be better than inorganic fertilizers in the management of soil fertility [52], it has been argued that if there is an adequate and balanced supply of nutrients, and no deficiencies or excesses of a nutrient that cause excessive consumption are observed, then the plant will take the nutrients in proportion to their needs [50]. This study, however, observed that the application of amendments significantly increased the CEC of the soil (Table 1) and other chemical properties, which can significantly influence the availability of nutrients to plants. It has been reported that soil with a low CEC is most likely to be nutrient deficient, and a high CEC can also cause nutrient leaching [53]. Moderately high CEC (below the critical point of 3 cmolkg−1) is known to improve soil fertility through greater nutrient availability, and prevents the nutrients from leaching [54]. There were no recorded differences in CEC for all of the treated soils in this study, except in the sewage sludge treatments where CEC values were relatively higher than the rest of the soils. This might be a contributory factor to the level of P contents observed in the lettuce from the cow dung and NPK treatments and in the carrots from the sewage sludge and NPK treatments, respectively, with no noticeable differences. A comprehensive literature review of crops produced in various farming systems reported no significant differences in mineral contents such as Ca, K, and Mg between organically and inorganically grown crops [55]. This suggests that plants will take up nutrients in proportion to their needs.
The relative abundance of major minerals reported in this study is consistent with the literature. It has been reported that K is the second-most abundant mineral (after N) in plants [56]. Numerous studies have also reported higher concentrations of K relative to minerals such as Ca, Mg, Na, and P, in vegetables such as onions, potato, butternut, beetroot, carrot, lettuce, and so on [57,58,59].
Plants generally maintain high a cytosolic K+/Na+ ratio and a negative electrical potential difference across the plasma membrane under normal physiological states [60]. However, under saline conditions which result in a Na+-saturated solution, the pathway for K+/Na+ reportedly shows a high affinity for Na+ movement into the root from the external media [61]. It is then transported by the xylem to the aerial part of the plant in a process regulated by some apoplastic barriers, in order to prevent chlorosis from the high concentration of Na+ and Cl− due to transpiration [62,63,64,65]. This mechanism ensures that the concentration of Na is always higher in the root than any other part of the plant. It is therefore understandable why we recorded higher concentrations of Na in the carrots, which is a root vegetable, compared to lettuce, a leafy vegetable.
The accumulation of Mg in plants is influenced by factors such as species, plant demand, and plant type, and is reportedly more concentrated in the aboveground parts of the plants in comparison to the roots because of the significant role they play in photosynthesis and carbohydrate portioning [66]. This role includes the transport of photoassimilates from the aerial parts of the plant to the sink organs, and therefore requires more concentration to augment the shortages. This is evident in our study, as the values recorded for lettuce were significantly higher than those for carrots.
Potassium is absorbed from the soil as a monovalent cation (K+) [56], determined by a genetic expression response to stimuli to ensure cytosolic homeostasis [67]. It is then transported by phloem tissues to other plant parts where it plays numerous functions, including cell volume growth, turgor regulation, and is heavily involved in photosynthesis and the transportation of photosynthates to storage organs [67,68,69,70]. Considering K plays a significant role in photosynthesis, it is more concentrated in plant parts with a high level of photosynthetic activity. This is evident in our study, where a significantly higher concentration of K was recorded in lettuce compared to carrots.
The uptake of Ca by plants is reportedly affected by factors like the species or type of plant, root structures, and plant transpiration [71]. Due to its structural role in cell walls and cell membranes, Ca is often more concentrated in developing tissues and plant parts that undergo high transpiration activity [72]. It has also been reported that Ca2+ plays a signal role in protective response processes in plants that are exposed to biotic stresses like attacks from fungi and bacteria [73]. This would explain why we recorded a higher concentration of Ca in lettuce, which is more exposed to light and undergoes higher transpiration activity.
Phosphorus is absorbed as an orthophosphate ion, and its uptake is heavily influenced by soil pH [56]. The function of P in plants includes cell division, plant growth, root lengthening, fruit development, energy production, and storage and transportation in the forms of adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) [74,75,76]. These crucial roles of P across every plant part ensure that it is proportionately distributed according to the requirement, and this may explain why there is little to no difference in the observed P concentrations of both lettuce and carrots in this study.
The current study reveals that the application of fertilizers, irrespective of type, may not be the only determinant factor for nutrient accumulation in plants. Evidence from the literature has shown that organic manure and other materials of natural origin used as soil treatments supply more nutrients to the soil because of the wide range of their material composition, unlike mineral or chemical fertilizers, which are often nutrient-specific [14]. However, the slow release of these nutrientsm due to their crude form in organic manure as opposed to the already mineralized nature of nutrients in chemical fertilizers, significantly influences their availability to crops [77,78,79]. Nevertheless, even if the nutrients are available to the plants in equal proportions, other factors such as the plant species, type, and physiological demand may also play a significant role in nutrient uptake, as evidenced in the current study.
5. Conclusions
This study observed that the highest concentrations of all of the investigated minerals were recorded in vegetables cultivated in the soil treated with sewage sludge and cow dung. It was also observed that lettuce, a leafy vegetable in comparison to carrots, a root vegetable, accumulated more of the investigated minerals, in total. The findings of this study suggest that organic manure in the form of cow dung and sewage sludge, as well as the type or variety of the plant and a plant’s demand for nutrients, are major factors that significantly influence the uptake and accumulation of nutrients in plants. This study therefore concludes that in an effort to strike a balance between sustainable and ecofriendly agricultural practices, organic manures might be better alternatives to mineral fertilizers in vegetable production.
Author Contributions
O.E.A.: conceptualization, investigation, design methodology, formal analysis, data curation, and writing original draft. L.L.M., J.O.O. and L.C.O.: conceptualization, design methodology, supervision, resources, validation, review, and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was partially funded by the National Research Foundation in collaboration with Sefako Makgatho Health Sciences University (NRF: N006=UID118704).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article. Should any raw data files be needed in another format, they are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the instrumental scientists at the Analytical Facility, University of Johannesburg, for their assistance with the laboratory analysis of the samples.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Nest, T.V.; Vandecasteele, B.; Ruysschaert, G.; Cougnon, M.; Merckx, R.; Reheul, D. Effect of organic and mineral fertilizers on soil P and C levels, crop yield and P leaching in a long term trial on a silt loam soil. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 197, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neina, D. The Role of Soil pH in Plant Nutrition and Soil Remediation. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2019, 2019, 5794869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Kumar, A.; Prakash, O. The Impact of Chemical Fertilizers on Our Environment and Ecosystem. 2019. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Randeep-Kumar/publication/331132826_The_Impact_of_Chemical_Fertilizers_on_our_Environment_and_Ecosystem/links/5c66ebe492851c1c9de446eb/The-Impact-of-Chemical-Fertilizers-on-our-Environment-and-Ecosystem.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2024).
- Hazra, G. Different Types of Eco-Friendly Fertilizers: An Overview. Sustain. Environ. 2016, 1, 54. Available online: www.scholink.org/ojs/index.php/se54 (accessed on 8 February 2025). [CrossRef]
- Bokhtiar, S.; Sakurai, K. Effects of organic manure and chemical fertilizer on soil fertility and productivity of plant and ratoon crops of sugarcane. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2005, 51, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goss, M.J.; Tubeileh, A.; Goorahoo, D. A Review of the Use of Organic Amendments and the Risk to Human Health. Adv. Agron. 2013, 120, 275–379. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, S.; Pradhan, S.S.; Singh, A.; Kushuwaha, M. Effect of Organic Manure on Different Soil Properties: A Review. Int. J. Plant Soil Sci. 2024, 36, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbowski, T.; Garbowski, T.; Bar-Michalczyk, D.; Bar-Michalczyk, D.; Charazińska, S.; Charazińska, S.; Grabowska-Polanowska, B.; Grabowska-Polanowska, B.; Kowalczyk, A.; Kowalczyk, A.; et al. An overview of natural soil amendments in agriculture. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 225, 105462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Bueren, E.L.; Jones, S.; Tamm, L.; Murphy, K.; Myers, J.; Leifert, C.; Messmer, M. The need to breed crop varieties suitable for organic farming, using wheat, tomato and broccoli as examples: A review. NJAS Wagening. J. Life Sci. 2011, 58, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Pieniak, Z.; Verbeke, W. Consumers’ attitudes and behaviour towards safe food in China: A review. Food Control. 2013, 33, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonne, A.; Ozores-Hampton, M.; Treadwell, D.; House, L. Organic and Conventional Produce in the U.S.: Examining Safety and Quality, Economic Values, and Consumer Attitudes. Horticulturae 2016, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Reid, B.J.; Li, G.; Zhu, Y.-G. Application of biochar to soil reduces cancer risk via rice consumption: A case study in Miaoqian village, Longyan, China. Environ. Int. 2014, 68, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aina, O.E.; Amoo, S.O.; Mugivhisa, L.L.; Olowoyo, J.O. EEffect of Organic and Inorganic Sources of Nutrients on the Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Activity of Tomato. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2019, 17, 3681–3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Ballesta, M.C.; Dominguez-Perles, R.; Moreno, D.A.; Muries, B.; Alcaraz-López, C.; Bastías, E.; García-Viguera, C.; Carvajal, M. Minerals in plant food: Effect of agricultural practices and role in human health. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2010, 30, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.-L.; Nkoh, J.N.; Baquy, M.A.-A.; Dong, G.; Li, J.-Y.; Xu, R.-K. Plants alter surface charge and functional groups of their roots to adapt to acidic soil conditions. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhangi-Abriz, S.; Ghassemi-Golezani, K. Improving electrochemical characteristics of plant roots by biochar is an efficient mechanism in increasing cations uptake by plants. Chemosphere 2023, 313, 137365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, M.; De Roma, A.; Cavallo, S.; Miedico, O.; Chiaravalle, E.; Soprano, V.; Baldi, L.; Gallo, P. Trace elements in vegetables and fruits cultivated in Southern Italy. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2019, 84, 103302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guadie, A.; Yesigat, A.; Gatew, S.; Worku, A.; Liu, W.; Ajibade, F.O.; Wang, A. Evaluating the health risks of heavy metals from vegetables grown on soil irrigated with untreated and treated wastewater in Arba Minch, Ethiopia. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 761, 143302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rempelos, L.; Almuayrifi, M.S.B.; Baranski, M.; Tetard-Jones, C.; Barkla, B.; Cakmak, I.; Ozturk, L.; Cooper, J.; Volakakis, N.; Hall, G.; et al. The effect of agronomic factors on crop health and performance of winter wheat varieties bred for the conventional and the low input farming sector. Field Crop. Res. 2020, 254, 107822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, N.-U.; Hussain, A.; Alamzeb, S.; Begum, S. Accumulation of heavy metals in edible parts of vegetables irrigated with waste water and their daily intake to adults and children, District Mardan, Pakistan. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 1515–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahia, E.M.; García-Solís, P.; Celis, M.E.M. Contribution of fruits and vegetables to human nutrition and health. In Postharvest Physiology and Biochemistry of Fruits and Vegetables; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 19–45. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, A.A.H. Overview of the vital roles of macro minerals in the human body. J. Trace Elements Miner. 2023, 4, 100076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehra, A.; Grover, S. Catatonia Associated with Hypernatremia. Indian J. Psychol. Med. 2019, 41, 293–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpe, S.L. Micronutrient Requirements for Athletes. Clin. Sports Med. 2007, 26, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarnowski, A.; Gama, R.M.; Dawson, A.; Mason, H.; Banerjee, D. Hyperkalemia in Chronic Kidney Disease: Links, Risks and Management. Int. J. Nephrol. Renov. Dis. 2022, 15, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciosek, Ż.; Kot, K.; Kosik-Bogacka, D.; Łanocha-Arendarczyk, N.; Rotter, I. The Effects of Calcium, Magnesium, Phosphorus, Fluoride, and Lead on Bone Tissue. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe, J.; Colangelo, L.; Biamonte, F.; Sonato, C.; Danese, V.C.; Cecchetti, V.; Occhiuto, M.; Piazzolla, V.; De Martino, V.; Ferrone, F.; et al. Diagnosis and management of hypocalcemia. Endocrine 2020, 69, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serna, J.; Bergwitz, C. Importance of Dietary Phosphorus for Bone Metabolism and Healthy Aging. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elser, J.J. Phosphorus: A limiting nutrient for humanity? Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2012, 23, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, L.; Hamza, M.; Iqbal, E.; Kaleem, Z. Role of Micronutrients (Vitamins & Minerals). Int. J. Multidiscip. Sci. Arts 2024, 3, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Laecke, S. Hypomagnesemia and hypermagnesemia. Acta Clin. Belg. 2018, 74, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansorena, M.R.; Agüero, M.V.; Goñi, M.G.; Roura, S.; Ponce, A.; Moreira, M.D.R.; Di Scala, K. Assessment of lettuce quality during storage at low relative humidity using Global Stability Index methodology. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 32, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, R.; Gomes, T.; Ferreira, A.; Mendes, E.; Baptista, P.; Cunha, S.; Pereira, J.A.; Ramalhosa, E.; Casal, S. Antioxidant activity and bioactive compounds of lettuce improved by espresso coffee residues. Food Chem. 2014, 145, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keatinge, J.D.H.; Waliyar, F.; Jamnadas, R.H.; Moustafa, A.; Andrade, M.; Drechsel, P.; Hughes, J.D.; Kadirvel, P.; Luther, K. Relearning Old Lessons for the Future of Food—By Bread Alone No Longer: Diversifying Diets with Fruit and Vegetables. Crop. Sci. 2010, 50, S-51–S-62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, J.S. Nutritional Quality and Health Benefits of Vegetables: A Review. Food Nutr. Sci. 2012, 03, 1354–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Głąbska, D.; Guzek, D.; Groele, B.; Gutkowska, K. Fruit and Vegetable Intake and Mental Health in Adults: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beraki, A.F.; Landman, W.A.; DeWitt, D.G.; Olivier, C.; Mathole, K.; Ndarana, T. Modelled Sea-Surface Temperature Scenario Considerations and Southern African Seasonal Rainfall and Temperature Predictability: Report to the Water Research Commission; Water Research Commission: Pretoria, South Africa, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bloem, E.; Albihn, A.; Elving, J.; Hermann, L.; Lehmann, L.; Sarvi, M.; Schaaf, T.; Schick, J.; Turtola, E.; Ylivainio, K. Contamination of organic nutrient sources with potentially toxic elements, antibiotics and pathogen microorganisms in relation to P fertilizer potential and treatment options for the production of sustainable fertilizers: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607–608, 225–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammad, H.M.; Khaliq, A.; Abbas, F.; Farhad, W.; Fahad, S.; Aslam, M.; Shah, G.M.; Nasim, W.; Mubeen, M.; Bakhat, H.F. Comparative Effects of Organic and Inorganic Fertilizers on Soil Organic Carbon and Wheat Productivity under Arid Region. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2020, 51, 1406–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daliakopoulos, I.; Tsanis, I.; Koutroulis, A.; Kourgialas, N.; Varouchakis, A.; Karatzas, G.; Ritsema, C. The threat of soil salinity: A European scale review. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 727–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.B.; Incrocci, L.; van Ruijven, J.; Massa, D. Reducing contamination of water bodies from European vegetable production systems. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 240, 106258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aina, O.E.; Mugivhisa, L.L.; Olowoyo, J.O.; Obi, C.L. Heavy metals and potential health risk assessment of Lactuca sativa and Daucus carrota from soil treated with organic manures and chemical fertilizer. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agegnehu, G.; Nelson, P.N.; Bird, M.I. Crop yield, plant nutrient uptake and soil physicochemical properties under organic soil amendments and nitrogen fertilization on Nitisols. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 160, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhao, N.; Huang, F.; Lv, Y. Long-term effects of different organic and inorganic fertilizer treatments on soil organic carbon sequestration and crop yields on the North China Plain. Soil Tillage Res. 2014, 146, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinichenko, V.P.; Glinushkin, A.P.; Sokolov, M.S.; Zinchenko, V.E.; Minkina, T.M.; Mandzhieva, S.S.; Sushkova, S.N.; Makarenkov, D.A.; Bakoyev, S.Y.; Il’ina, L.P. Impact of soil organic matter on calcium carbonate equilibrium and forms of Pb in water extracts from Kastanozem complex. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 19, 2717–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimohammadi, M.; Younesian, M.; Madihi-Bidgoli, S.; Nodehi, R.N.; Khaniki, G.R.J.; Hadi, M.; Ghanbari, F. Heavy metal(oid)s concentration in Tehran supermarket vegetables: Carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic health risk assessment. Toxin Rev. 2018, 39, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, S.; Bahiraei, A. Ultra trace quantification of chromium(VI) in food and water samples by highly sensitive catalytic adsorptive stripping voltammetry with rubeanic acid. Food Chem. 2012, 133, 1075–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, K.T. Soil Organic Matter. In Soils; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, W.; Wang, Q.; Wu, L.; Luo, Y.; Christie, P. Soil properties and microbial ecology of a paddy field after repeated applications of domestic and industrial sewage sludges. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 8619–8628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herencia, J.F.; Maqueda, C. Effects of time and dose of organic fertilizers on soil fertility, nutrient content and yield of vegetables. J. Agric. Sci. 2016, 154, 1343–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adekiya, A.O. Legume Mulch Materials and Poultry Manure Affect Soil Properties, and Growth and Fruit Yield of Tomato. Agric. Conspec. Sci. 2018, 83, 161–167. Available online: https://hrcak.srce.hr/203014 (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- Singh, R.; Agrawal, M. Effects of sewage sludge amendment on heavy metal accumulation and consequent responses of Beta vulgaris plants. Chemosphere 2007, 67, 2229–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okhumata, D.S. Comparative effects of mineral fertilizer, compost and compost—Mineral fertilizer on biological, chemical and physical properties of soil. J. Wastes Biomass-Manag. 2022, 4, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Lv, Y.; Sun, J.; Shao, H.; Wei, L. Recent Advances in Biochar Applications in Agricultural Soils: Benefits and Environmental Implications. CLEAN Soil Air Water 2012, 40, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangour, A.D.; Dodhia, S.K.; Hayter, A.; Allen, E.; Lock, K.; Uauy, R. Nutritional quality of organic foods: A systematic review. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 90, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, R.N.; Finck, A.; Blair, G.J.; Tandon, H.L.S. Tandon, Plant Nutrition for Food Security: A Guide for Integrated Nutrient Management; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Knap, M.; Nečemer, M.; Kump, P.; Potočnik, K.; Vidrih, R. The content of minerals in Slovenian organic and conventional produced fruits, herbs and vegetables. Acta Agric. Slov. 2014, 103, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popović-Djordjević, J.B.; Kostić, A.Ž.; Rajković, M.B.; Miljković, I.; Krstić, Đ.; Caruso, G.; Moghaddam, S.S.; Brčeski, I. Organically vs. Conventionally Grown Vegetables: Multi-elemental Analysis and Nutritional Evaluation. Biol. Trace Element Res. 2021, 200, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armesto, J.; Rocchetti, G.; Senizza, B.; Pateiro, M.; Barba, F.J.; Domínguez, R.; Lucini, L.; Lorenzo, J.M. Nutritional characterization of Butternut squash (Cucurbita moschata D.): Effect of variety (Ariel vs. Pluto) and farming type (conventional vs. organic). Food Res. Int. 2020, 132, 109052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keisham, M.; Mukherjee, S.; Bhatla, S.C. Mechanisms of Sodium Transport in Plants—Progresses and Challenges. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apse, M.P.; Blumwald, E. Na+ transport in plants. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 2247–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plett, D.C.; Møller, I.S. Na+ transport in glycophytic plants: What we know and would like to know. Plant Cell Environ. 2010, 33, 612–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, E.; Shin, R. Transport, signaling, and homeostasis of potassium and sodium in plants. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2014, 56, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrt, C.S.; Zhao, M.; Kourghi, M.; Bose, J.; Henderson, S.W.; Qiu, J.; Gilliham, M.; Schultz, C.; Schwarz, M.; Ramesh, S.A.; et al. Non-selective cation channel activity of aquaporin AtPIP2;1 regulated by Ca2+ and pH. Plant Cell Environ. 2016, 40, 802–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munns, R.; Tester, M. Mechanisms of Salinity Tolerance. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 651–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhat, N.; Elkhouni, A.; Zorrig, W.; Smaoui, A.; Abdelly, C.; Rabhi, M. Effects of magnesium deficiency on photosynthesis and carbohydrate partitioning. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2016, 38, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardans, J.; Peñuelas, J. Potassium Control of Plant Functions: Ecological and Agricultural Implications. Plants 2021, 10, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tränkner, M.; Tavakol, E.; Jákli, B. Functioning of potassium and magnesium in photosynthesis, photosynthate translocation and photoprotection. Physiol. Plant. 2018, 163, 414–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrés, Z.; Pérez-Hormaeche, J.; Leidi, E.O.; Schlücking, K.; Steinhorst, L.; McLachlan, D.H.; Schumacher, K.; Hetherington, A.M.; Kudla, J.; Cubero, B.; et al. Control of vacuolar dynamics and regulation of stomatal aperture by tonoplast potassium uptake. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E1806–E1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sustr, M.; Soukup, A.; Tylova, E. Potassium in Root Growth and Development. Plants 2019, 8, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Głodowska, M.; Krawczyk, J. Difference in the Concentration of Macro Elements between Organically and Conventionally Grown Vegetables. Agric. Sci. 2019, 10, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thor, K. Calcium—Nutrient and Messenger. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudla, J.; Batistič, O.; Hashimoto, K. Calcium Signals: The Lead Currency of Plant Information Processing. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 541–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Arredondo, D.L.; Leyva-González, M.A.; González-Morales, S.I.; López-Bucio, J.; Herrera-Estrella, L. Phosphate Nutrition: Improving Low-Phosphate Tolerance in Crops. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2014, 65, 95–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preuss, C.P.; Huang, C.Y.; Tyerman, S.D. Proton-coupled high-affinity phosphate transport revealed from heterologous characterization in Xenopus of barley-root plasma membrane transporter, HvPHT1;1. Plant Cell Environ. 2011, 34, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambers, H. Phosphorus Acquisition and Utilization in Plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2022, 73, 17–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zare, L.; Ronaghi, A. Comparison of N Mineralization Rate and Pattern in Different Manure- and Sewage Sludge-Amended Calcareous Soil. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2019, 50, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisseler, D.; Smith, R.; Cahn, M.; Muramoto, J. Nitrogen mineralization from organic fertilizers and composts: Literature survey and model fitting. J. Environ. Qual. 2021, 50, 1325–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosling, P.; Shepherd, M. Long-term changes in soil fertility in organic arable farming systems in England, with particular reference to phosphorus and potassium. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2004, 105, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).