Abstract
Dissolved biochar (DBC) can make a significantly impact on soil ecosystems and the associated biota due to its high environmental bioavailability. However, the impact of DBC on the adaptability of entomopathogenic nematodes (EPNs), such as Steinernema feltiae, remains uncertain. This study investigates the impact of DBC on oxidative stress, antioxidant enzyme activity, virulence, and gene expression in EPNs through culture assays and RNA-seq analysis. Results showed that DBC exposure significantly increased the accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation. The nematodes treated with DBC700 exhibited 64.34% higher ROS levels, while those treated with DBC400 had 51.13% higher levels compared to the control. Superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT) activities were significantly suppressed, with a stronger inhibition observed in the DBC700 group. As revealed by virulence assays, DBC treatment reduced the infectivity of EPNs against Galleria mellonella larvae. Transcriptome analysis revealed that DBC primarily affected oxidative stress response, membrane transport, and longevity regulation pathways. Moreover, DBC400 predominantly inhibited carbohydrate metabolism, whereas DBC700 significantly impacted oxidative metabolism, protein processing, and neuronal signaling pathways, suggesting the presence of distinct metabolic adaptation mechanisms between the two DBCs. Overall, this study suggests that DBC may impair the biocontrol efficacy of S. feltiae through oxidative stress and genetic perturbations, providing new insights into its long-term ecological impacts on soil ecosystems.
1. Introduction
Biochar is a porous carbon material produced by pyrolyzing biomass under oxygen-limited conditions [1,2]. Over the past decades, biochar and other carbon-based materials have been extensively utilized for soil improvement, nutrient retention, and pollutant adsorption [3]. As the most reactive and bioavailable fraction of biochar, dissolved biochar (DBC)—consisting of micro- and nanoparticles particles (<1 μm) with a large surface area (400–500 m2/g)—has garnered increasing attention due to its enhanced mobility, greater surface reactivity, and potential ecological interactions [4,5]. Studies suggest that DBC plays a crucial role in carbon cycling, nutrient transport, and pollutant dynamics in soil ecosystems, highlighting its significance in both agricultural productivity and environmental remediation [6,7,8]. Nevertheless, several studies have identified the ecological risks posed by dissolved biochar to soil organisms, possibly due to chemical toxicity–induced oxidative stress [9,10,11], although the precise mechanisms remain unclear.
Nematodes are the crucial bioindicators of soil health, with their community structure serving as a reliable proxy of soil health status and nutrient cycling efficiency [12,13]. Studies have shown that biochar significantly enhances the abundance of bacterivorous nematodes by increasing soil organic matter and microbial diversity while suppressing the relative abundance of herbivore nematodes through interspecies competition [14]. However, due to the vast diversity of soil nematodes and the challenges of culturing them in the laboratory, research on the direct effects of biochar on specific nematode groups remains limited. Current studies have focused on the model nematode (C. elegans) and certain root-knot nematodes [15]. For instance, it was observed that C. elegans showed a clear attraction to peanut shell biochar, with genes exhibiting differential expression mainly linked to collagen synthesis and eggshell formation during development [16]. Additionally, the mechanism by which wood biochar confers resistance to root-knot nematodes in rice was investigated, and it was found that biochar enhanced plant resistance by increasing hydrogen peroxide accumulation and the expression of genes in the ethylene signaling pathway [17]. Despite these findings, the direct impact of biochar on entomopathogenic nematodes (EPNs) remains poorly understood, especially concerning the regulatory mechanisms that control their infection rates, representing a significant gap in the current literature.
Entomopathogenic nematodes (EPNs), regarded as a promising biocontrol agent, are capable of exterminating soil pests rapidly via a symbiotic bacterial co-infection mechanism [18]. Due to its broad host adaptability and its cold tolerance, Steinernema feltiae is one of the most widely distributed species of EPNs, making it particularly suitable for crop protection in temperate regions [19]. Early studies primarily focused on the field dispersal and distribution patterns of EPNs, with dispersal being significantly influenced by soil management practices. These practices, in turn, affect the environmental factors that modulate EPN dispersal patterns and aggregation [20,21]. Moreover, the third-stage infective juveniles (IJs) constitute the sole free-living life stage of EPNs, actively seeking hosts in the soil [22,23]. Upon host infection, IJs release their symbiotic bacteria, which utilize the host’s nutrients for reproduction, suppress the host’s immune responses, and induce septicemia, ultimately resulting in the host’s mortality [24]. After leaving the host, IJs can survive for months in the soil without a host, during which they may encounter soluble biochar. Recent studies by Yaman et al. (2023) have indicated that the effects of biochar on EPNs are highly dependent on their physicochemical properties [25]. Specifically, carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus content, porosity, and pH can influence the survival, dispersal, and infectivity of EPNs to varying degrees. However, the precise mechanisms by which dissolved biochar influences EPN development and pathogenicity remain poorly understood, with significant gaps in research. This knowledge gap is a critical area that requires further investigation to fully understand how biochar modulates EPN behaviors and biocontrol efficacy.
Biochar, due to its unique physiochemical properties, may influence the survival, infectivity, and overall biocontrol efficacy of EPNs. Steinernema feltiae is one of the most widely distributed strains among EPNs, having been detected in various habitats such as forests, farmland, etc. It has been successfully commercialized and is widely used in agricultural production [26]. Current research primarily focuses on the symbiosis relationship between Steinernema nematodes and Xenorhabdus bacteria, utilizing the bioactive compounds produced by Xenorhabdus to suppress insect pests, plant pathogens, and other nematodes [27,28]. However, the fundamental mechanisms by which dissolved biochar influences S. feltiae are still inadequately understood. This study aims to: (1) assess the impact of micro/nano biochar on the infectivity, pathogenicity, and development of Steinernema feltiae larvae; (2) examine the regulatory effects of micro/nano biochar on the gene expression of entomopathogenic nematodes using transcriptomic techniques; and (3) detect the pathway for Steinernema feltiae exposed to micro/nano biochar. The significance of this research lies in addressing the critical knowledge gap regarding the influence of micro/nano biochar on EPN survival and infectivity, which could enhance their biocontrol efficacy. Moreover, the results may offer significant insights for enhancing biochar utilization in sustainable pest management approaches.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation and Characterization of Dissolved Biochar
Corn straw was selected as the raw material for biochar production. The straw was first crushed and compressed before being placed in pyrolysis in a muffle furnace (HBYQ 2200). The pyrolysis process was conducted under a nitrogen atmosphere, with the temperature being increased at a rate of 10 °C/min to the final temperatures of 400 °C and 700 °C. The corn straw was pyrolyzed at these target temperatures to produce bulk biochar, denoted as BC400 and BC700 (Table S1).
After pyrolysis, the biochar samples (BC400 and BC700) were ground and passed through a 100-mesh (0.15 mm) sieve. The sieved biochar was then further pulverized in a planetary ball mill with a ball-to-powder ratio of 20:1. The milling process was carried out at a constant speed of 350 RPM for 12 h, with periodic reversals of every 15 min and a 5-min cooling interval to prevent overheating. Following milling, the biochar was mixed with deionized water (DI) at a ratio of 1 g of biochar per 50 mL of water. After that, the mixture was stirred at 150 RPM at room temperature for 24 h to facilitate the dissolution process. Ultrasonic treatment (100 W, 2 h) was subsequently applied to further improve the dissolution. The resulting suspension was then filtered through a 0.65 μm membrane. A portion of the filtrate was extracted for the measurement of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) content, while the remaining filtrate was freeze-dried at −70 °C to obtain solid dissolved biochar particles. The concentration of the DBC exposure solution in this experiment was calibrated to 500 mg/L based on the previous studies [29,30,31]. The DBC samples were reconstituted in deionized water to a final concentration of 1000 mg/L and were subsequently mixed with an equal volume of nematode suspension, achieving a final dissolved biochar concentration of 500 mg/L. Additionally, the CK group, serving as the untreated control, received only deionized water to establish a baseline. The experimental design comprised three groups: CK (control), DBC400, and DBC700, all of which were maintained under identical experimental protocols to ensure comparability.
The characterization of the biochar and dissolved biochar samples was performed using several analytical techniques. Three-dimensional excitation-emission matrix (EEM) fluorescence spectra were recorded using a fluorescence spectrophotometer (F-700, Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan) to assess the fulvic acid-like and humic acid-like substances properties of the dissolved biochar. The functional groups of the biochar were analyzed by Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) in the wavenumber range of 4000 to 400 cm−1. Additionally, the Environmental Persistent Free Radicals (EPFRs) of the biochar were detected using an Electron Paramagnetic Resonance (EPR) spectrometer (BRUKER EMXPLUS, Karlsruhe, Germany).
2.2. Measurement of Virulence in EPNs Post-Infection Nematodes Treated with DBC
2.2.1. Acquisition of Steinernema feltiae and Galleria mellonella
The entomopathogenic nematode strain Steinernema feltiae (Sf) was purchased from Jiyuan Baiyun Industrial Co., Ltd. (Jiyuan, China) and was maintained through in vivo culturing under controlled laboratory conditions for preservation and experimental purposes [32]. Galleria mellonella larvae were purchased from Tianjin Huiyude Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Tianjin, China), and were stored at 4 °C in a refrigerator for low-temperature preservation.
2.2.2. The Mortality Rate of EPNs During the Infective Stage After DBC Treatment
Before the mortality tests were conducted, the viability of the EPNs was assessed by selecting only those exhibiting clear movement and excluding non-motile individuals. After that, the viable EPNs were carefully transferred into centrifuge tubes. The supernatant was gently removed, and the EPNs were washed three times with sterile deionized water. The EPN suspension was then diluted to a final concentration of 50–60 nematodes per 200 µL and added to a 24-well culture plate. Each well was supplemented with 200 µL of the exposure solution containing 500 mg/L of either DBC400 or DBC700. The control group (CK) was treated with sterile deionized water. The 24-well plates were sealed with a sealing film and incubated at 25 °C. After incubation, the total number of EPNs in each well was counted under a microscope, and mortality was recorded at 48, 72, and 84 h post-treatment. The EPNs with a rigid body posture and no signs of movement were classified as dead. The mortality rate was calculated as the proportion of dead EPNs relative to the total number of EPNs in each well. Each experimental setup included one control group and two treatment groups, with 12 biological replicates per group.
2.2.3. CAT/SOD/ROS Test
The SOD, CAT, and ROS concentrations in the samples (CK, DBC400, and DBC700) were quantified using commercially available ELISA kits. The subsequent operation was executed in accordance with the manufacturer’s guidelines.
(1) Reagent Preparation and Sample Addition: Before the assay, all reagents were prepared, and both standards and test samples were loaded in duplicate onto the microtiter plate to ensure accuracy. A volume of 50 μL of the standard solutions was added to the designated standard wells, while 10 μL of each test sample (CK, DBC400, and DBC700) was added to the corresponding sample wells. Then, 40 μL of sample diluent was added to each sample well, while the blank well was left empty.
(2) Incubation and Washing: Following sample addition, 100 μL of HRP-conjugate reagent was added to each well. The plate was then covered with an adhesive strip and incubated at 37 °C for 60 min. Following incubation, the well contents were aspirated, and the plate was rinsed five times with 400 μL of washing solution per well to remove unbound substances. After the final wash, the residual liquid was carefully removed by blotting the plate against clean paper towels.
(3) Chromogen Reaction and Color Development: Subsequently, 50 μL of Chromogen Solution A and 50 μL of Chromogen Solution B were added to each well, and the plate was gently mixed. The plate was incubated at 37 °C for 15 min in the dark to allow for color development. Following this incubation, 50 μL of Stop Solution was added to each well, resulting in a color change from blue to yellow. To ensure uniformity, the plate was gently tapped to facilitate consistent color development across the wells.
Optical Density Measurement: The optical density (O.D.) at 450 nm was assessed within 15 min of the addition of the Stop Solution utilizing a microtiter plate reader. The SOD, CAT, and ROS concentrations in the test samples were determined by comparing their O.D. Each treatment group (CK, DBC400, DBC700) included three independent biological replicates (separately cultured nematode populations). For each biological replicate, two technical duplicate measurements were performed. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD) of biological replicate values with those derived from the standard curve constructed in line with the calibration standards.
2.2.4. The Virulence of EPNs During the Infective Stage After DBC Treatment
The exposure experiment was conducted as described in Section 2.2.2 to assess the virulence of entomopathogenic nematodes (EPNs) during the infective stage after DBC treatment. EPNs were treated with 500 mg/L of DBC400 and DBC700, while in the control group (CK), EPNs were treated with deionized water (DI). After exposure, the nematodes were washed and their concentration was adjusted to 50–60 EPNs per 40 µL.
Filter paper discs were placed in each well of a 24-well plate, and one Galleria mellonella larva was added to each well. Using a pipette, 40 µL of the EPN suspension was introduced into each well, ensuring proper contact between the nematodes and larvae. The plates were then incubated at a constant temperature of 25 °C in an incubator. Beginning at the point of EPN addition, the survival status of each larva was monitored at four-hour intervals. The time of death for each was recorded until complete mortality was observed in all treatments. Mortality was defined as the absence of movement or other signs of life. Each treatment group (CK, DBC400, DBC700) included 25 biological replicates, represented by independent wells in 24-well plates. Each well contained 50–60 EPNs and was processed separately.
2.3. Transcriptome Sequencing
After 48 h of exposure, the EPNs from each treatment group were collected, treated with liquid nitrogen, and stored at −80 °C for RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) and transcriptomic analysis.
Total RNA was extracted from the tissue using TRIzol® Reagent according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Then, RNA quality was determined by 5300 Bioanalyser (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA) and quantified using the ND-2000 (NanoDrop Technologies, Wilmington, DE, USA). Only high-quality RNA sample [OD 260/280 = 1.8~2.2, OD 260/230 ≥ 2.0, RQN ≥ 6.5, 28S: 18S ≥ 1.0, >1 μg. OR OD 260/280 = 1.8~2.2, RIN > 6.5, >10 ng] was used to construct sequencing library.
RNA purification, reverse transcription, library creation, and sequencing were performed at Shanghai Majorbio Bio-pharm Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China), adhering to the manufacturer’s protocols for the utilized kits and instruments. The RNA-seq transcriptomic library was prepared using 1 μg of total RNA and the Illumina® Stranded mRNA Prep, Ligation protocol (San Diego, CA, USA). Briefly, messenger RNA was isolated using the poly(A) selection method with oligo(dT) beads and then fragmented with a fragmentation buffer. Subsequently, double-stranded cDNA was synthesized with random hexamer primers using a SuperScript Double-Stranded cDNA Synthesis Kit (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). The synthesized cDNA underwent end repair, phosphorylation, and adapter ligation following the library construction protocol. The libraries were size-selected for 300 bp cDNA target fragments using 2% Low Range Ultra Agarose, followed by amplification for 15 PCR cycles with Phusion DNA polymerase (NEB). After quantification using a Qubit 4.0, sequencing was performed on a NovaSeq X Plus platform (PE150) with the NovaSeq Reagent Kit or on a DNBSEQ-T7 platform (PE150) with the DNBSEQ-T7RS Reagent Kit (FCL PE150), version 3.0.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
The statistical significance of the changes was assessed using R tools (ggplot2, DescTools) and one-way ANOVA accompanied by Duncan’s test. Data were tested for homogeneity of variance to validate the ANOVA assumptions and were presented as means ± SDs. The mortality rate of EPNs after 48 h of DBC treatment was assessed using Kaplan-Meier survival curves and log-rank tests.
The raw paired-end reads were trimmed and quality-controlled using fastp software v0.23.4 (using default parameters). The processed reads were subsequently matched to the reference genome in a stranded mode utilizing HISAT2 [33]. Transcript assembly was performed for each sample using StringTie [34] based on the reference genome.
To identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between the two samples, the expression levels were calculated based on the transcripts per million (TPM) value for each transcript. Gene abundance was quantified using RSEM [35]. Differential expression analysis was primarily carried out using DESeq2 [36] or DEGseq [37]. DEGs were classified as significantly differentially expressed when |log2FC| ≥ 1 and FDR < 0.05 (DESeq2) or FDR < 0.001 (DEGseq). Additionally, functional enrichment analysis, including GO and KEGG, was performed to identify significantly enriched DEGs in GO terms and metabolic pathways, with a Bonferroni-corrected p-value < 0.05 compared to the whole transcriptome background. GO functional enrichment and KEGG pathway analyses were conducted using Goatools v1.4.4 and Python scipy v1.9.3 respectively.
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Dissolved Biochar
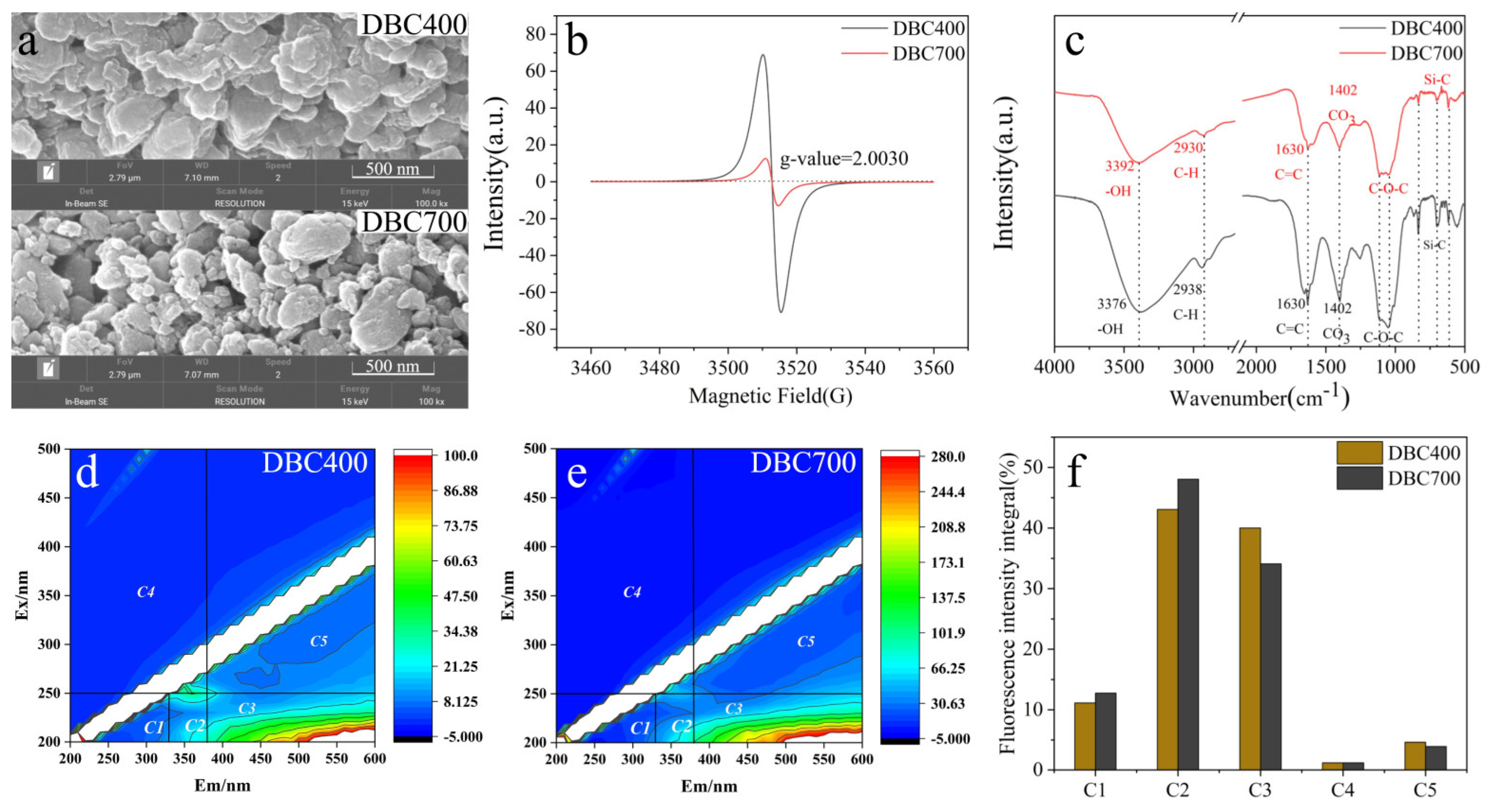
To investigate the impact of dissolved biochar (DBC) on entomopathogenic nematodes (EPNs) and evaluate the differential effects of DBC prepared at different temperatures (DBC400 and DBC700), the physical and chemical properties of DBC400 and DBC700 were first analyzed. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) pictures demonstrated that both dissolved biochar particles displayed uneven forms, diverse particle sizes, and rough surfaces (Figure 1a). Under identical ball-milling conditions, DBC700 particles were ground into smaller, spherical structures with an average particle size of 0.10 μm, whereas DBC400 exhibited larger, sheet-like structures with a particle size of 7.36 μm. Additionally, DBC700 contained less dissolved organic carbon (DOC) (17.63 mg/L) and a higher ash content (69.62%) compared to DBC400, which had a DOC concentration of 66.34 mg/L and an ash content of 57.38%. However, there were no significant differences between DBC400 and DBC700 in terms of pH, zeta potential, and electrical conductivity (EC) (Table 1).
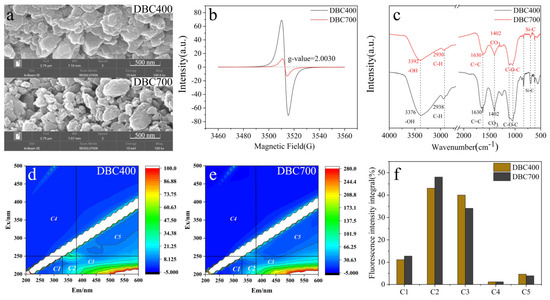
Figure 1.
SEM images (a), EPFRs (b), FTIR spectra (c), EEM images of DBC400/DBC700 (d,e), and the fluorescence intensity integral (f). C1 denotes low-molecular-weight aromatic compounds, C2 denotes fulvic acid, C3 denotes humic acid, C4 denotes highly condensed aromatic compounds, and C5 denotes complex organic substances.

Table 1.
Properties of dissolved biochar are made at different temperatures.
Environmental Persistent Free Radicals (EPFRs) are stable pollutants with long half-lives, with the potential to induce cellular damage in EPNs. EPFRs analysis revealed that the radicals associated with DBC were primarily oxygen-centered. Moreover, the signal intensity of DBC400 was higher than that of DBC700, suggesting a higher abundance of oxygen-containing functional groups on the surface of DBC400 compared to DBC700 (Figure 1b). Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy further confirmed the presence of polar functional groups in both DBC400 and DBC700. The spectra displayed -OH stretching vibrations at 3400 cm−1, CO3 vibrations at 1400 cm−1, and C-O stretching vibrations in the range of 1000–1250 cm−1 (Figure 1c). Therefore, DBC400 exhibited significantly stronger absorption peaks than DBC700, indicating a higher concentration of certain functional groups on its surface.
Additionally, the primary components of both DBC400 and DBC700 were identified as fulvic acid-like and humic acid-like substances (Figure 1d,e). These components accounted for 83.06% of the total components in DBC400 and 82.14% in DBC700. Notably, DBC400 had a higher humic acid-like content than DBC700, whereas DBC700 had a higher fulvic acid-like content than DBC400 (Figure 1f).
3.2. DBC Effect on ROS and Antioxidant Enzyme Activity in S. feltiae During Infection
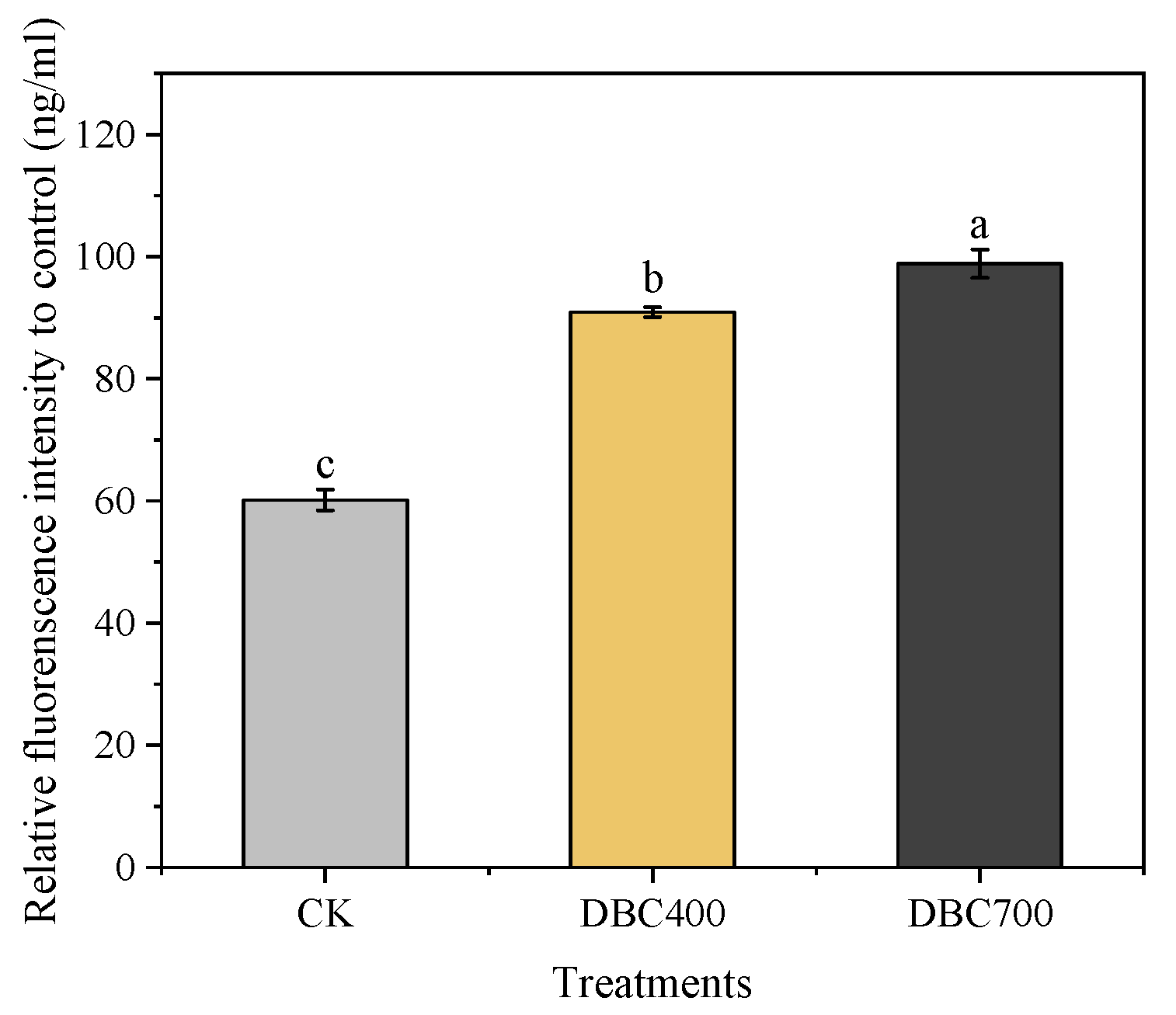
The exposure to dissolved biochar (DBC) significantly increased the levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in S. feltiae (Figure 2). Specifically, the ROS concentrations in the DBC700 and DBC400 groups were elevated by 64.34% and 51.13% (p < 0.05), respectively, compared to the control group (CK). These results suggested that DBC treatment can enhance ROS production in S. feltiae, thereby inducing oxidative stress during the infection process.
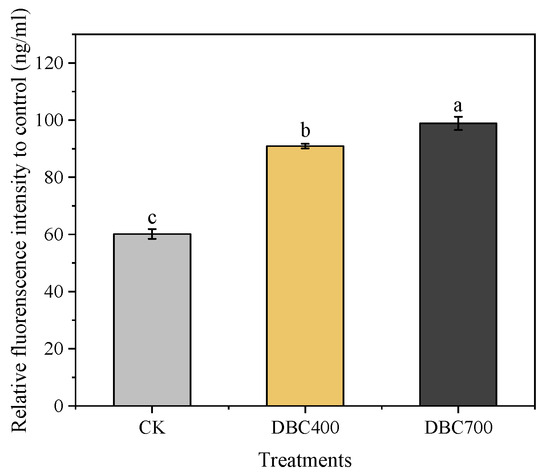
Figure 2.
The relative fluorescence intensity of S. feltiae infective juveniles after being exposed to DBC. (Different lowercase letters indicated significant differences between treatments according to Duncan’s multiple range test (p < 0.05)).
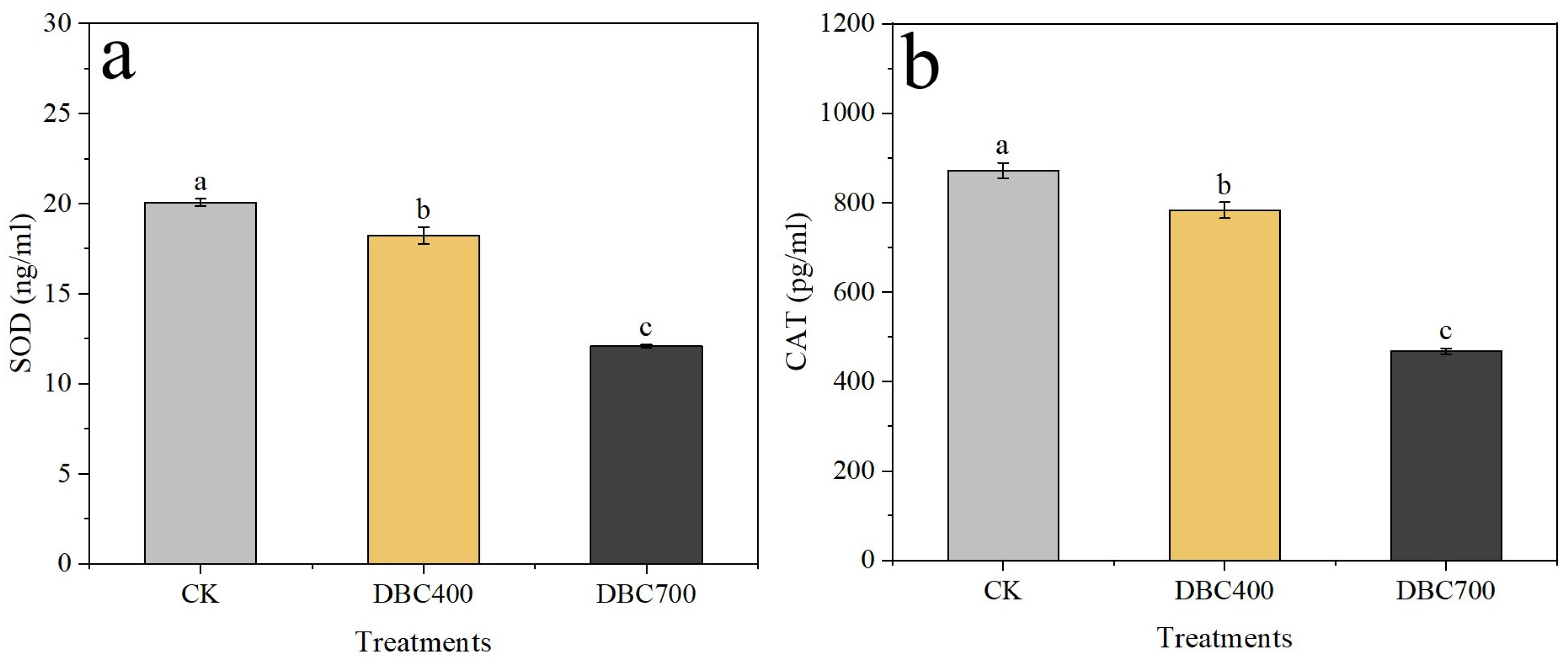
Moreover, the antioxidant enzyme activities were significantly reduced in both DBC–treated groups (Figure 3). Superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity in S. feltiae decreased to 18.23 ± 0.46 ng/mL and 12.09 ± 0.08 ng/mL for the DBC400 and DBC700 treatments, respectively, compared to 20.06 ± 0.20 ng/mL in the control group (Figure 3a, p < 0.05). Similarly, catalase (CAT) activity dropped to 783 ± 18.01 pg/mL and 467.77 ± 6.28 pg/mL in the DBC400 and DBC700 groups, respectively, both of which were significantly lower than the value of 872.27 ± 17.00 pg/mL in the control group (Figure 3b, p < 0.05). These findings indicated that DBC exposure not only increased ROS production but also impaired the antioxidant defenses in S. feltiae, suggesting a potentially toxic effect during the infection period.
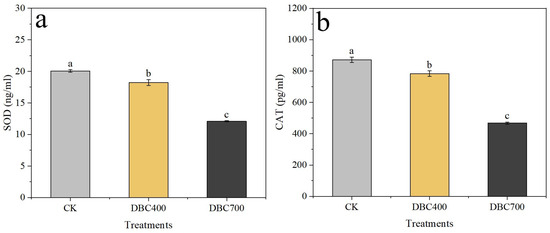
Figure 3.
Superoxide dismutase (SOD) activities (a) and Catalase (CAT) activities (b) in S. feltiae infective juveniles after being exposed to DBC. (Different lowercase letters indicated significant differences between treatments according to Duncan’s multiple range test (p < 0.05)).
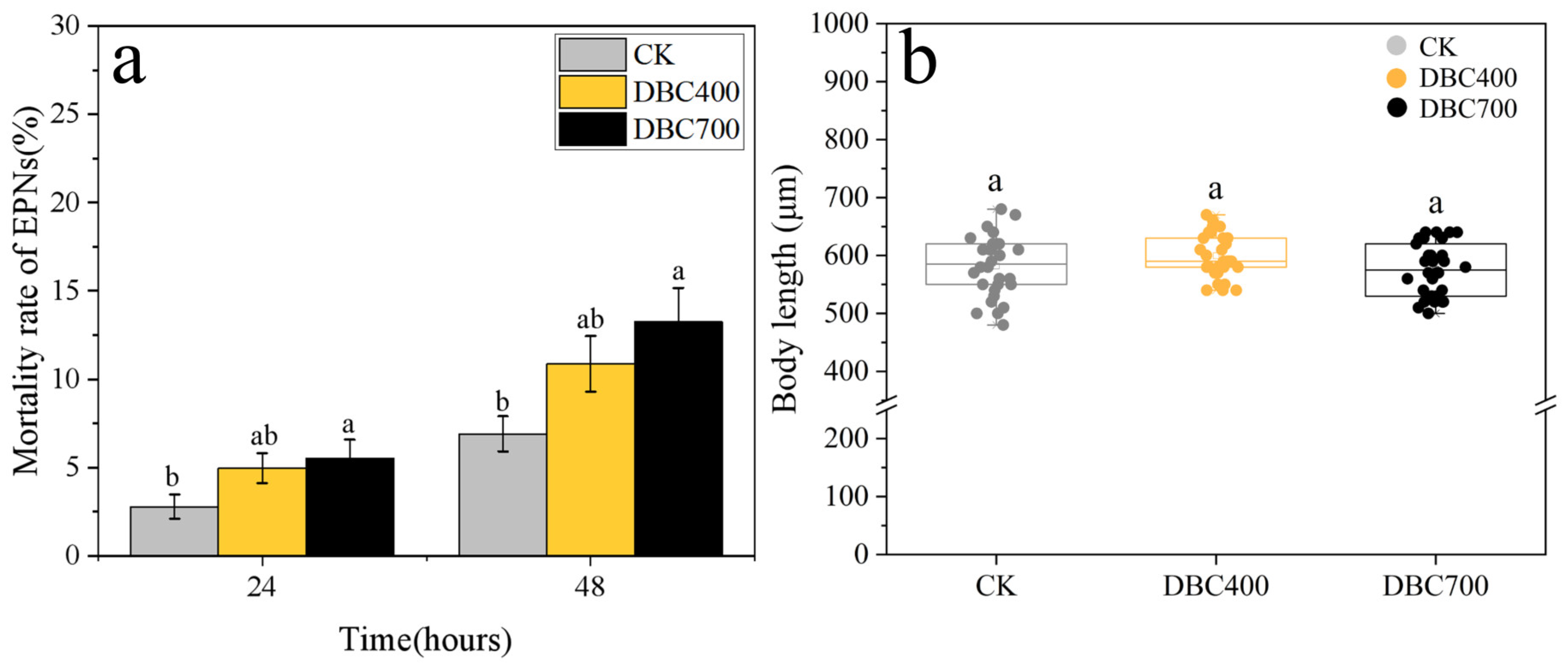
Additionally, Figure 4a demonstrated that exposure to DBC700 significantly increased the EPN mortality rate. Within 48 h of exposure, the mortality rate of S. feltiae treated with DBC700 (5.53 ± 1.07%) was significantly higher than that of the control group (2.80 ± 0.69%) (p < 0.05). However, the mortality rate in the DBC400 group was found not significantly different from the control. Moreover, no significant differences in the body length of S. feltiae were detected among the DBC treatments (Figure 4b). These results further indicated that DBC may initially induce oxidative stress in S. feltiae without affecting their growth parameters under the test conditions.
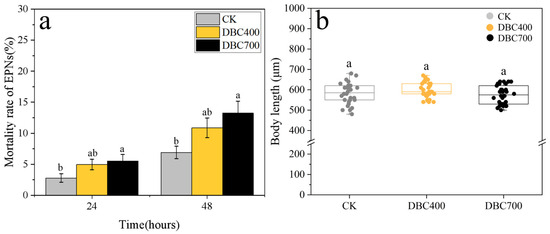
Figure 4.
The mortality rate (a) and body length (b) of S. feltiae infective juveniles after being exposed to DBC treatments (Different lowercase letters indicated significant differences between treatments at p < 0.05).
3.3. DBC Effect on S. feltiae Virulence During Infection
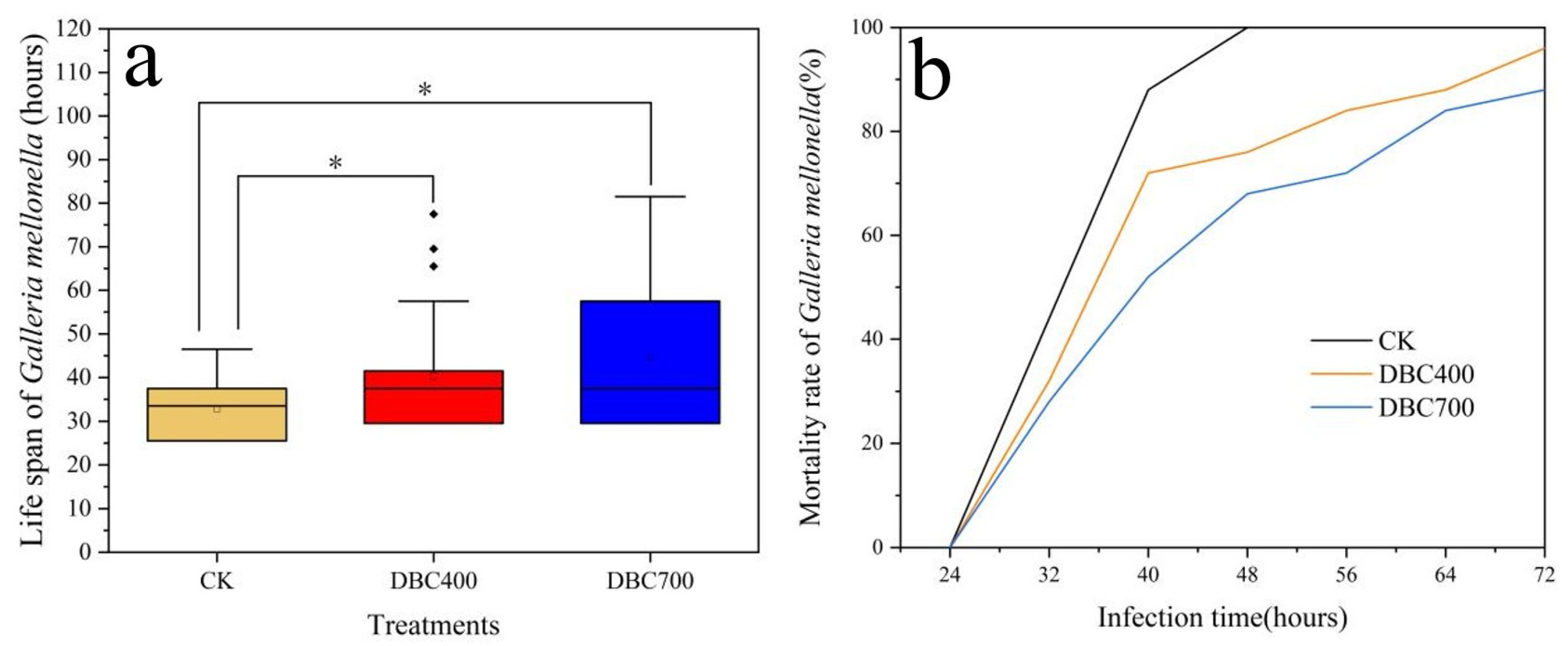
The exposure to DBC significantly reduced the virulence of EPNs. The virulence of of EPNs was assessed by measuring the mortality rate of Galleria mellonella larvae after infection. A shorter larval survival time indicates a higher EPN virulence, while a longer survival time suggests a lower virulence of EPNs.
According to Figure 5a, the mean survival time of Galleria mellonella larvae infected with S. feltiae that was exposed to DBC400 and DBC700 significantly increased to 40.36 ± 2.76 h and 44.53 ± 3.43 h (p < 0.05), respectively, compared to 32.78 ± 1.32 h in the control group (S. feltiae without DBC exposure). This indicated that DBC exposure prolonged larval survival, thereby weakening the virulence of S. feltiae.
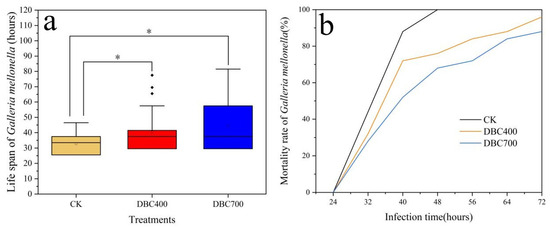
Figure 5.
The Time-to-death of Galleria mellonella after being infected with the S. feltiae, that exposed to DBC400, DBC700, or the control (a). Trends in mortality rate of G. mellonella larvae after 72 h post-infection (b). (The asterisk (*) indicated the statistically significant difference between treatments at p < 0.05).
Furthermore, Figure 5b demonstrated temporal trends in the mortality rate of Galleria mellonella larvae within 72 h post-infection. The results showed that DBC may impact the infection process of S. feltiae, thereby affecting larval mortality. After 24 h infection, the mortality rate of Galleria mellonella larvae increased rapidly across all groups. By 40-h, the mortality rate in the control group reached 88%, whereas the mortality rates of the Galleria mellonella larvae infected with DBC400 and DBC700 treated S. feltiae were significantly lower at 72% and 52%, respectively. After 48 h, the larval mortality in the CK group reached 100%, while in the DBC400 and DBC700 groups, mortality remained below 80% (DBC 400 vs. CK: HR = 2.18, 95% CI 1.22–3.91, p < 0.05; DBC 700 vs. CK: HR = 1.85, 95% CI 1.02–3.37, p < 0.05) (Figure S1). These findings indicated that DBC exposure effectively reduced the virulence of S. feltiae, leading to a lower mortality rate in Galleria mellonella larvae. This indicated that DBC may diminish the infectiveness of EPNs, potentially affecting their efficacy as biological control agents.
3.4. Statistical Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes
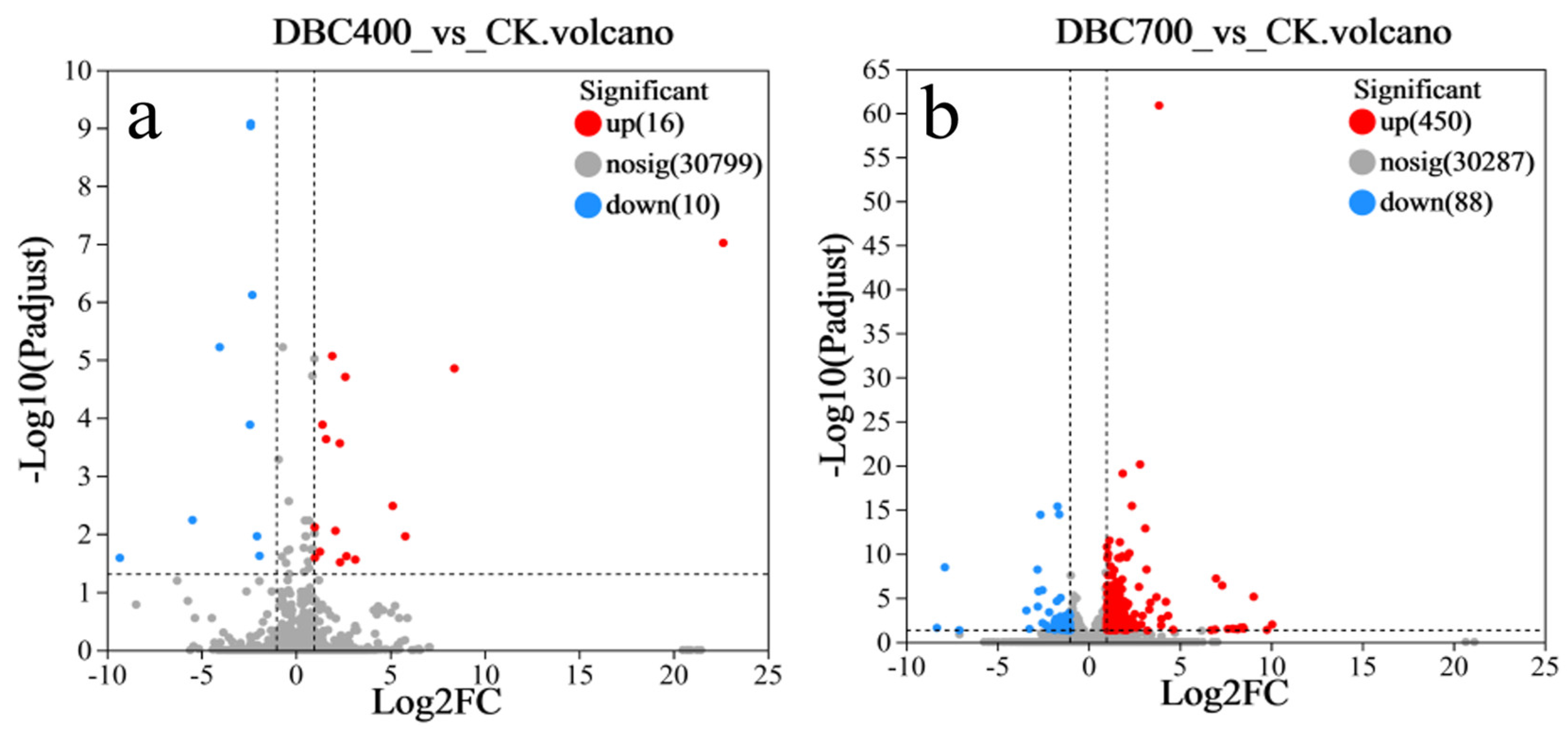
In this study, transcriptome sequencing was performed on three treatment groups of S. feltiae, with three biological replicates per group. The DBC400 treatment group exhibited relatively modest transcriptional changes, with 26 identified DEGs compared to the control group (FC ≥ 2, p adjust < 0.05), consisting of 16 upregulated (61.5%) and 10 downregulated (38.5%) genes (Figure 6a). In contrast, the DBC700 treatment showed a substantially more extensive transcriptional response, with 538 identified DEGs, of which 450 (83.6%) were upregulated and 88 were (16.4%) downregulated (Figure 6b). These results indicated a strong molecular response to the higher temperature of DBC preparation.
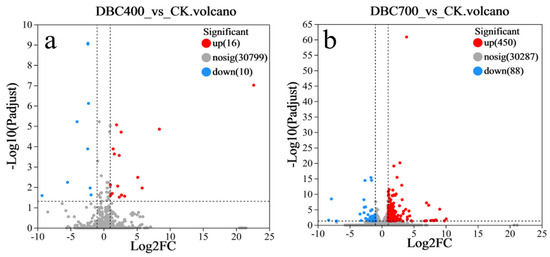
Figure 6.
The volcano plot of differentially expressed genes in S. feltiae during infection treated with DBC400 (a) and DBC700 (b) exposure.
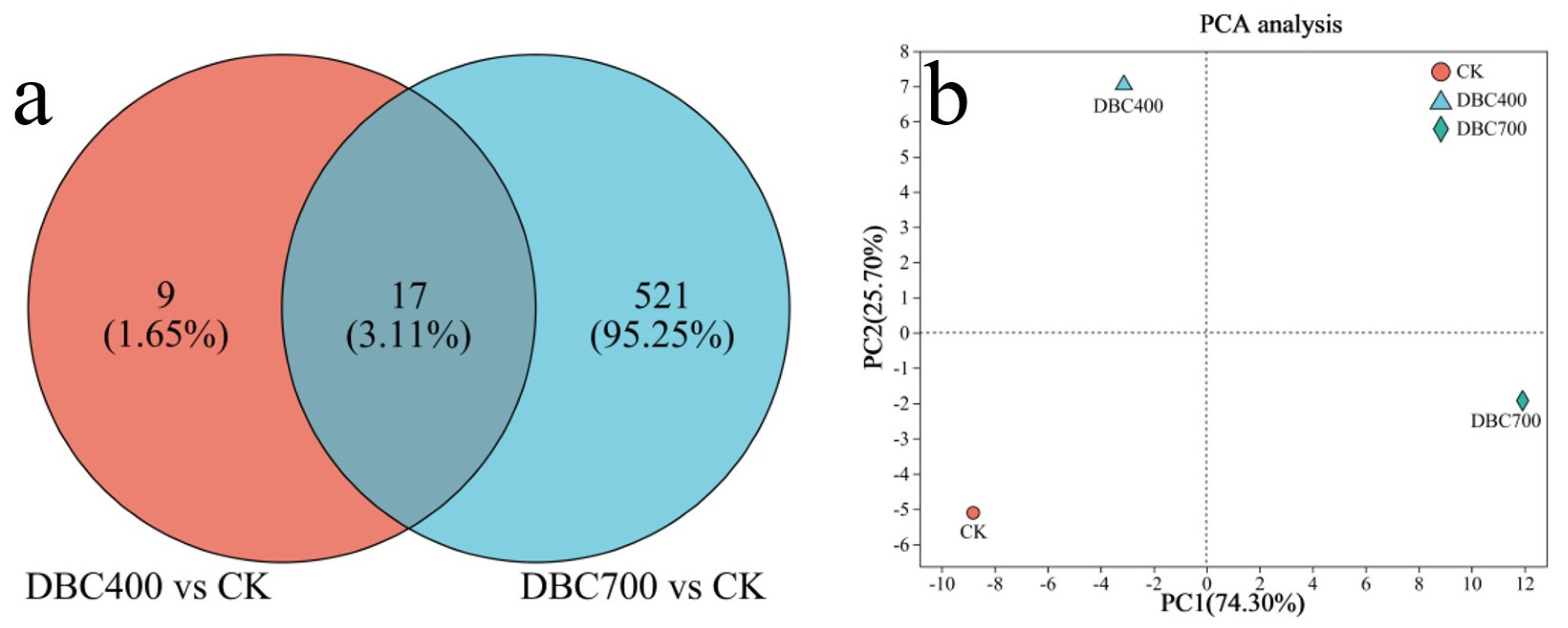
A Venn diagram revealed 17 DEGs commonly expressed between the DBC400 and DBC700 treatment groups, suggesting a core set of genes responsive to DBC treatment regardless of preparation temperature. Statistical analysis was conducted to confirmed that these DEGs were significantly different from the control group, with 95.23% of DEGs in the DBC700 treatment group showing obvious differences compared to the controls (Figure 7a). Principal Component Analysis (PCA) further validated the distinctions between the DBC400 and DBC700 treatments compared to the control group (Figure 7b). The first two principal components explained 74.30% and 25.70% of the variation, respectively. These results indicate that the nematodes were more sensitive to the DBC that prepared at higher temperatures.
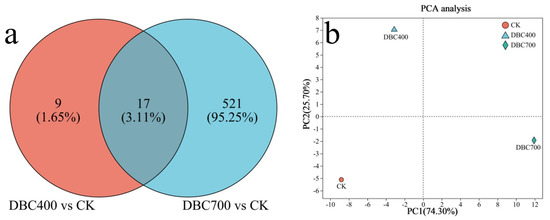
Figure 7.
(a) The venn diagram of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in S. feltiae during infection exposed to DBC. (b) Principal component analysis for DEGs of S. feltiae under different treatments.
The differentially expressed genes (DEGs) identified by DBC400 and DBC700 were further annotated through Gene Ontology (GO) analysis. The identified functional process terms included the following categories: Biological Process (BP), Cellular Component (CC), and Molecular Function (MF).
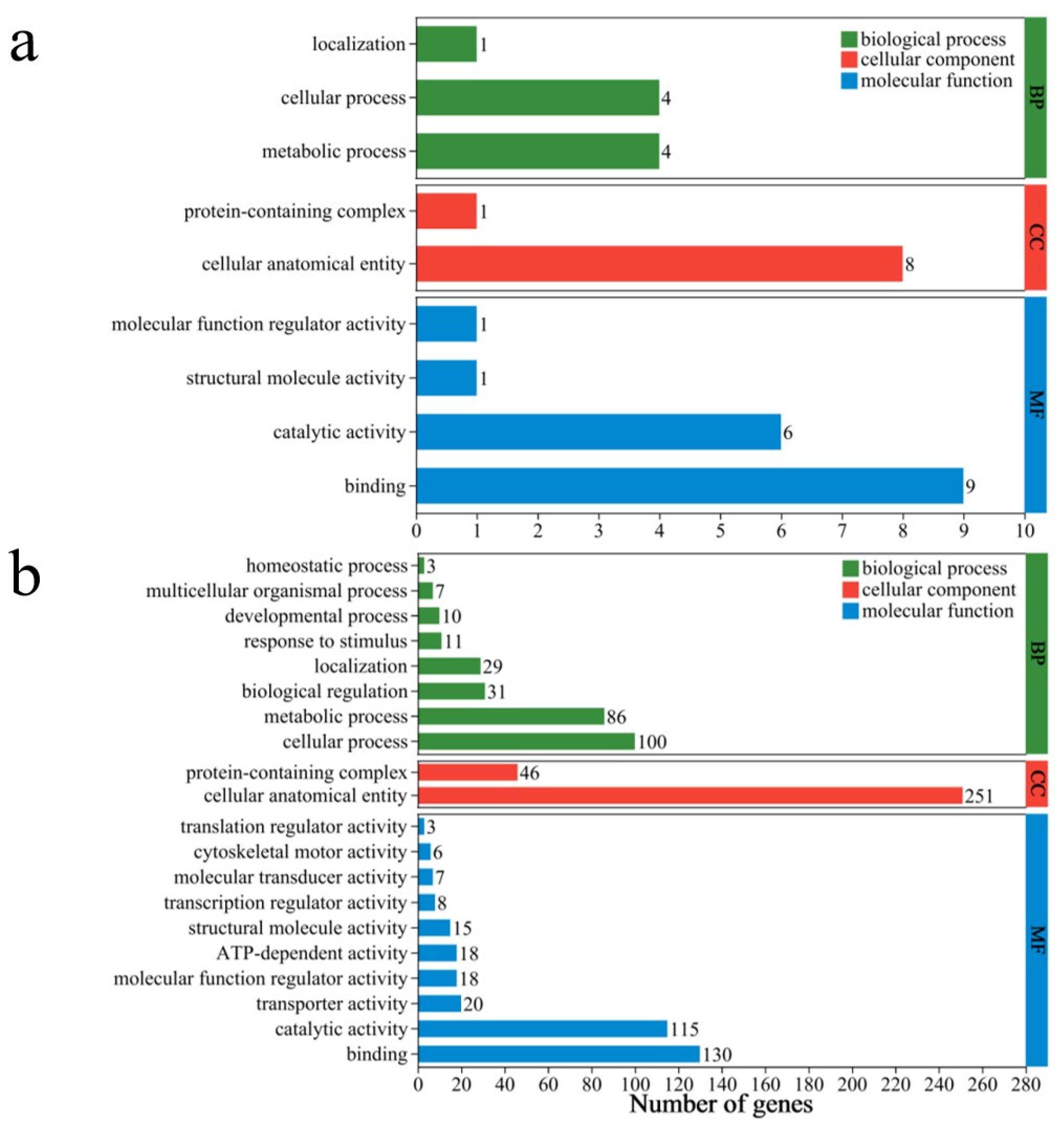
For the DBC400 treatment group, the DEGs were predominantly associated with 9 key biological processes, 9 cellular components, and 17 molecular functions. In the biological process category, the majority of annotations were related to “metabolic processes” (4 genes) and “cellular processes” (4 genes), indicating the fundamental biological activities related to cell growth, maintenance, and response to environmental changes. In the cellular component category, the most significant annotation was “cellular anatomical structure” (8 genes), reflecting the importance of cellular structures or organelles in specific biological processes. In terms of the molecular function category, “binding activity” was associated with 9 genes, suggesting that the proteins encoded by these genes were involved in various crucial cellular processes such as cell signaling, substance transport, and structural maintenance. Additionally, “catalytic activity” was noted in 6 genes, which may be involved in various biochemical reactions and metabolic pathways (Figure 8a).
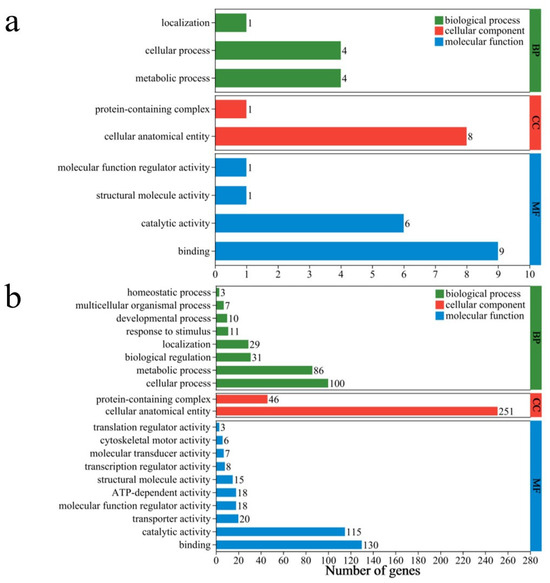
Figure 8.
The major gene ontology (GO) terms for the DEGs identified in S. feltiae exposed to DBC400 (a) and DBC700 (b).
For the DBC700 treatment group, GO analysis revealed that the biological processes (BP) primarily involved metabolic processes (86 genes) and cellular processes (100 genes), indicating significant changes in cellular and metabolic activities. These processes are crucial for maintaining cellular homeostasis and responding to the environmental changes induced by DBC700. As further suggested by other biological processes such as “biological regulation” (31 genes) and “response to stimuli” (11 genes), the nematodes may be undergoing adaptive responses to the altered environmental conditions induced by the DBC700. In the cellular components category (CC), a large proportion of DEGs were associated with “cellular anatomical structures” (251 genes) and “protein complexes” (46 genes), implying potential reorganization or regulation of cellular structure. For molecular functions (MF), “binding activities” were the predominant feature (115 genes), followed by “catalytic activities” (46 genes). These molecular functions are essential for numerous biochemical pathways, suggesting that enzymatic and binding activities play key roles in the nematode’s response to DBC700 treatment. Additionally, “transporter activity” (20 genes) and “transcriptional regulator activity” (8 genes) were also observed, highlighting the importance of gene expression regulation and substance transport in the adaptation of EPNs to DBC700 (Figure 8b).
3.5. Functional Enrichment and Pathway Analysis of DBC-Exposed Steinernema feltiae
Functional enrichment and KEGG pathway analysis revealed significant alterations in gene expression in Steinernema feltiae following exposure to DBC400 and DBC700, highlighting key metabolic and regulatory pathways affected by DBC treatment.
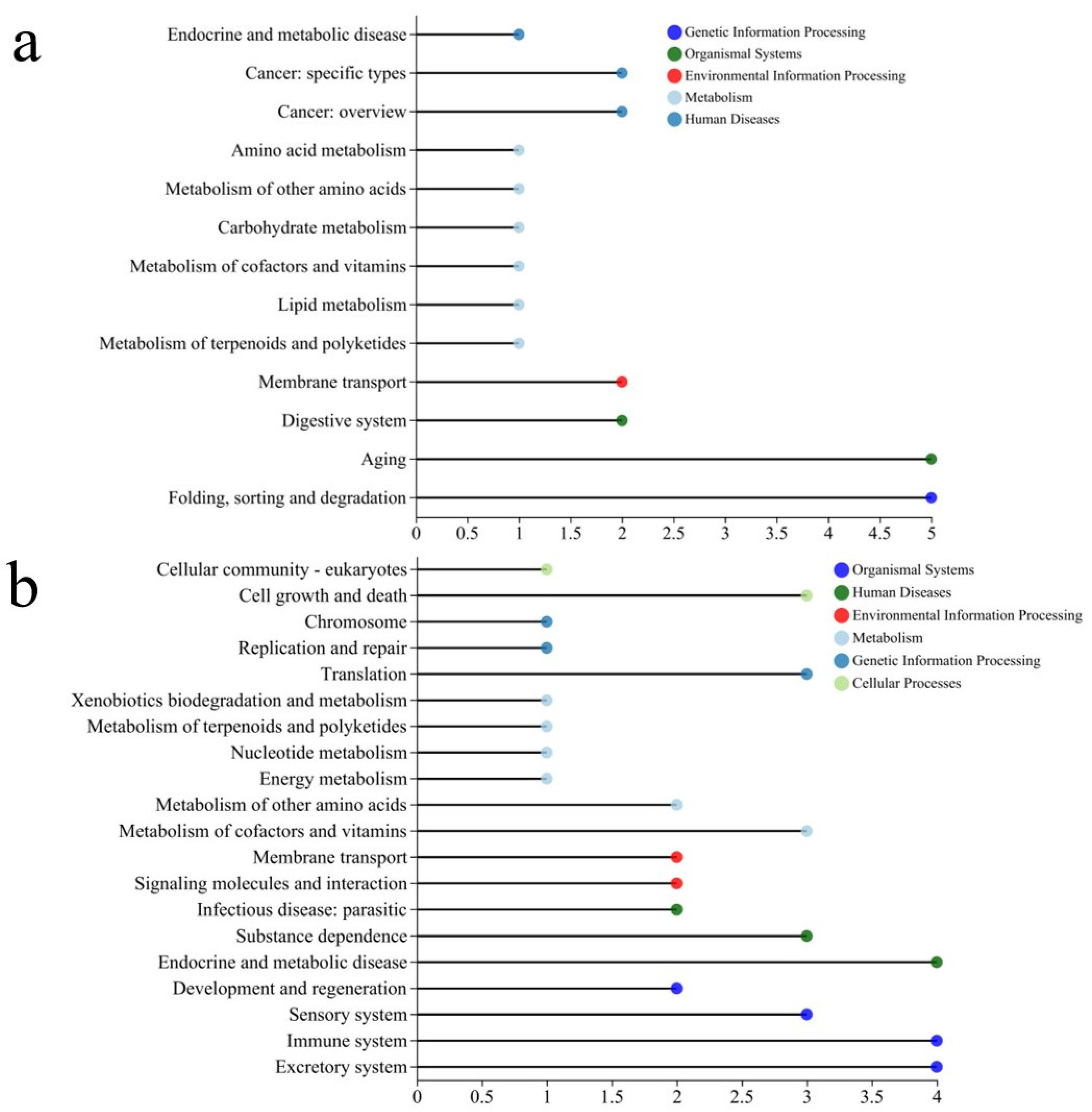
According to Figure 9a, DBC400 treatment significantly modulated several critical biological pathways. Within the environmental information processing category, significant changes were observed in membrane transport and digestive system pathways. These findings suggest that DBC400 may impact membrane-associated and digestive system functions, potentially influencing nutrient uptake and metabolic efficiency in nematodes. Moreover, DBC400 is likely to influence cellular energy homeostasis and material conversion through different metabolic pathways, such as “Lipid metabolism” and “Carbohydrate metabolism”. Differences in the expression of genes related to folding, sorting, degradation, and aging were also observed, which may be involved in protein stability and cellular aging processes, crucial for maintaining cellular function and preventing disease progression. Additionally, differential expression was noted in genes related to protein folding, sorting, and degradation, as well as aging-related pathways. These processes are essential for maintaining protein stability and cellular function, which in turn play a crucial role in cellular longevity and stress response adaptation. Enrichment analysis identified the Longevity Regulating Pathway (LRP-Multiple Species) as significantly enriched, suggesting a strong association between DBC400 exposure and potential lifespan-regulating mechanisms. The protein processing pathway in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) was also significantly affected, an essential pathway involved in protein folding and misfolded protein degradation. Dysregulation of this pathway is commonly associated with cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and cellular stress responses.
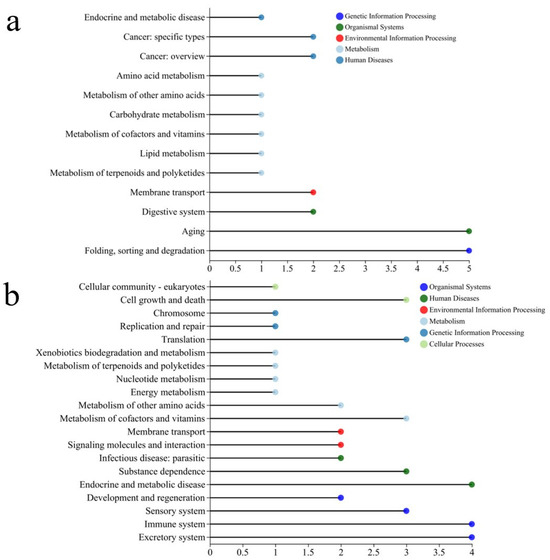
Figure 9.
The KEGG pathway classification analysis of DEGs in the treated group with DBC400 (a), and DBC700 (b).
Furthermore, KEGG pathway annotation also revealed more pronounced gene expression differences in the DBC700 treatment group compared to the control (Figure 9b). Membrane transport was among the most significantly altered pathways, suggesting substantial modifications in transmembrane transport mechanisms, which could influence cellular communication, signaling, and homeostasis. Signaling molecules and interaction pathways also exhibited significant changes, indicating that cellular signaling networks may be either upregulated or suppressed in response to DBC700 exposure. In the organismal systems category, genes associated with immune system regulation and sensory functions were significantly enriched in the DBC700-treated group. This suggests that DBC700 exposure may alter host defense mechanisms and sensory perception in nematodes. The enrichment of the ABC transporters pathway, which is responsible for the transmembrane transport of various molecules, suggesting possible implications for drug resistance, metabolite clearance, or responses to environmental toxins.
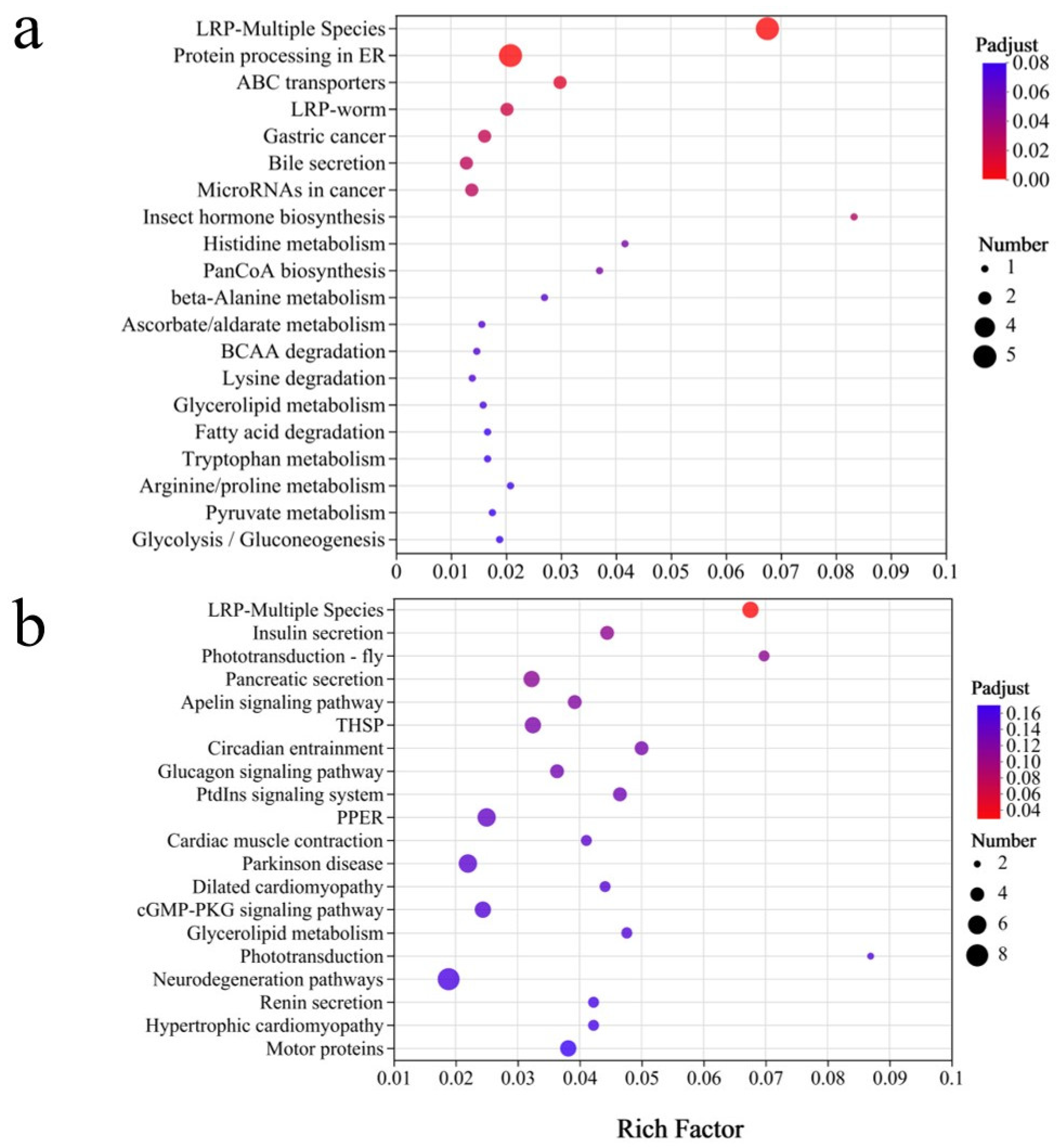
The KEGG enrichment pathway diagram (Figure 10) shows varying levels of enrichment for several key pathways across treatment groups. Pathways such as neurodegeneration, phototransduction, and glycerolipid metabolism showed moderate enrichments, suggesting potential effects on lipid metabolism, visual signal transduction, and nervous system integrity. In contrast, pathways such as the cGMP-PKG signaling pathway, dilated cardiomyopathy, and Parkinson’s disease-related pathways showed higher enrichment levels, suggesting potential impacts on neuromuscular function, cardiac physiology, and neurodegenerative processes.
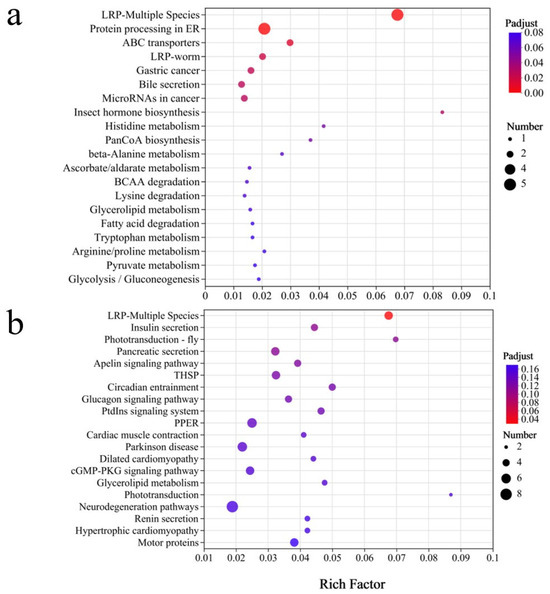
Figure 10.
The KEGG pathway enrichment for the DEGs identified in Steinernema feltiae exposed to DBC400 (a) and DBC700 (b).
In addition, THSP (Tetraspanin Signaling Pathway), Apelin signaling, pancreatic secretion, and phototransduction pathways displayed distinct alterations, suggesting potential modifications in metabolic secretion, intercellular communication, and sensory processing. Notably, insulin secretion and the LRP-Multiple Species pathway exhibited the highest enrichment factor values and the lowest P-adjust values, reinforcing the hypothesis that DBC exposure can significantly influence lifespan regulation and aging-related processes. These findings indicate that both DBC400 and DBC700 treatments have substantial effects on lifespan-associated regulatory pathways, with potential implications for organism health, metabolic adaptation, and stress resistance.
4. Discussion
4.1. DBC-Induced Oxidative Stress and Its Impact on EPNs Antioxidant Defense System
Dissolved biochar (DBC) has attracted attention due to its high specific surface area, abundant surface functional groups, and the generation of environmentally persistent free radicals (EPFRs), which potentially influence soil organisms. The characterization of DBC can provide deep insights into its potential applications in soil improvement. Previous studies have indicated that DBC may have biotoxic effects on microorganisms and animals [38,39]. Liu (2023) further noted that DBC properties depend on a series of factors such as raw material type and pyrolysis temperature, with the latter being the most crucial factor in determining the dissolved biochar properties [40]. In our study, significant differences were found between DBC400 and DBC700 in elemental composition, surface functional groups, and EPFRs. These properties may directly influence the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in EPNs.
The attributes of DBC provide significant insights into its prospective applications for soil enhancement. Our study indicated that EPFR signal intensity was stronger in DBC400 than in DBC700, suggesting a greater potential for oxidative stress induction. Furthermore, FTIR analysis confirmed that DBC400 contained more polar functional groups such as -OH, C-O, and CO3, which can further promote ROS accumulation in EPNs through redox reactions. Zhao et al. (2023) reported that the dissolved biochar derived from 300 °C pyrolysis could exert more hazardous effects on earthworms than the biochar derived from higher temperatures (500 °C and 700 °C), indicating that biochar prepared at lower temperatures may have a greater toxicological potential for organisms [41]. In contrast to the prior study, our results indicate that, despite lower EPFR signals, DBC700 generated substantially greater oxidative stress in EPNs. This higher oxidative stress in DBC700 may be linked to its particle size. After ball milling, DBC700 particles tend to form smaller spherical structures, with 50% of the particles being less than 0.1 μm in diameter. Smaller particles have higher surface areas, which enhance interactions with the cell membranes of EPNs, possibly exacerbating oxidative damage and inducing ROS accumulation [42]. Although numerous studies endorse the idea that elevated EPFR values in biochar result in increased oxidative stress [43,44], our research indicates that the induction of oxidative stress by various DBCs may be influenced not solely by their EPFRs but also by particle size, which accounts for the discrepancies observed in prior investigations. Therefore, future studies are needed to investigate the relationship between the physicochemical properties of DBC and oxidative stress in soil biota.
Typically, nematodes rely on antioxidant enzyme systems, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT), to eliminate excess ROS and maintain cellular redox balance. However, a significant reduction in SOD and CAT activities in EPNs was observed after DBC exposure, with the inhibitory effect being more pronounced in the DBC700 treatment. This could be attributed to oxidative damage directly inhibiting enzyme activity and also to gene expression regulation, which suppresses the synthesis of antioxidant enzymes. Prior research indicates that excessive ROS might oxidize the active sites of SOD and CAT, resulting in enzyme inactivation and suppressed catalytic activity [45,46]. Additionally, oxidative stress induced by environmental pollutants can activate stress signaling pathways, thereby inhibiting the transcription of antioxidant enzyme genes [47]. Our analysis of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) also revealed that DBC700 treatment significantly downregulated the expression of genes related to antioxidant enzymes, suggesting that DBC may suppress antioxidant enzyme synthesis through gene regulation. Furthermore, DBC’s colloidal stability may indirectly affect the functionality of the antioxidant system by altering the availability of metal elements [48]. Studies have indicated that metal chelation may reduce the availability of essential metal cofactors like Cu2+ and Zn2+, which are crucial for SOD activity [49,50], thereby impairing antioxidant enzyme function.
Moreover, KEGG pathway analysis further revealed the physiological effects of DBC-induced oxidative stress on EPNs. Changes in the membrane transport system (Figure 9) may result in altered expression of membrane transport proteins, thus affecting ion balance and exacerbating oxidative stress. Additionally, the enrichment of the protein processing pathway in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) suggests that ROS-induced oxidative stress may lead to protein misfolding, causing EPNs to expend considerable energy on protein repair and degradation, which in turn disrupts their metabolic balance. Furthermore, the significant enrichment of the Longevity Regulating Pathway (LRP) in the KEGG analysis suggests that oxidative stress may reduce the survival rate of EPNs, shortening their lifespan. This finding is consistent with previous research on the oxidative stress caused by high-dose biochar in zebrafish [15]. Overall, our findings suggest that DBC exposure could reduce the survival rate of EPNs in the environment, potentially undermining their effectiveness as biological control agents. Therefore, future studies should be conducted to explore how DBC-induced oxidative stress impacts EPNs’ metabolic adaptation strategies, and to investigate the long-term effects of DBC on EPNs, their host interactions, and the soil microbial communities in agricultural ecosystems.
Differences in dissolved organic carbon (DOC) content may also play a crucial role in mediating the oxidative stress of DBC on EPNs. Compared to DBC400 (66.34 mg/L), DBC700 had significantly lower DOC content (17.63 mg/L). Therefore, its oxidative damage is likely driven by direct physicochemical interactions rather than soluble organic compounds. In previous studies, DOC has been reported to mediate redox reactions and promote microbial growth [51]. While DOC has been shown to mitigate oxidative stress in bacteria by acting as a labile carbon source, its effect on EPNs appears to be different. High DOC levels in DBC400 may have promoted redox cycling, leading to increased ROS accumulation. In contrast, oxidative stress in DBC700 was likely intensified by particle-membrane interactions and reduced membrane stability. Biochar produced at low pyrolysis temperatures has been shown to promote beneficial soil microbial communities [52]. This raises the possibility that DBC400 could indirectly support Xenorhabdus, the symbiotic bacteria essential for EPN virulence. Conversely, the lower DOC content in DBC700 may provide fewer microbial growth resources, leading to decreased bacterial stability and reduced nematode infectivity. Future research should explore whether DOC-mediated changes in the soil microbiome indirectly influence EPN virulence by modulating symbiotic bacterial populations.
4.2. Mechanisms of EPN Virulence Reduction and Adaptation via DBC Regulation
Our study revealed that a 48-h exposure to DBC resulted in increased levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in entomopathogenic nematodes (EPNs). A significant correlation was found between these elevated ROS levels and reduced survival rates after 48 h (p < 0.05, Table S2). It is suggested that high ROS levels may detrimentally affect EPN survival, thereby diminishing their pathogenicity. Supporting this, Maleita et al. demonstrated that ROS generation induced by 1,4-NTQ contributed to rapid mortality in root-knot nematodes, reinforcing the notion that increased ROS can heighten mortality across nematode species [53]. The virulence of EPNs is likely to be weakened by the excessive accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Several studies have indicated that the exposure to micro- or nano materials can trigger oxidative stress in EPNs, leading to increased ROS levels, compromised mitochondrial membrane potential, and enhanced antioxidant enzyme activity, ultimately hindering EPN pathogenicity [32]. Moreover, Devi (2023) reported that elevated oxidative stress could disrupt the stability of EPNs’ symbiotic bacteria, such as Xenorhabdus, thereby reducing toxin secretion and weakening virulence [54]. The ability of EPNs to manage oxidative stress is critical for their infectivity. Excessive ROS accumulation can cause cellular damage and disrupt symbiotic bacterial stability, ultimately reducing their capacity to infect and kill hosts [23].
DBC may also affect the survival capacity of EPNs by interfering with key metabolic pathways, particularly carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. In this study, it was found that DBC exposure significantly impacted the glycolysis and lipid metabolism pathways of EPNs, potentially disrupting energy supply and membrane stability. Similarly, M. Shamim Hasan et al. (2024) demonstrated that under oxidative stress conditions, organisms tend to reduce energy metabolism and allocate resources to protein repair and ROS detoxification mechanisms [55]. This aligns with the study of Li and Chen et al. (2020), who found that biochar exposure triggered metabolic reprogramming in nematodes, reducing glycolysis and lipid synthesis for adaptation to the high oxidative stress environments [15]. Furthermore, our results indicated that the effects of DBC400 and DBC700 on EPNs’ virulence varied, with DBC700 inducing a more significant reduction in virulence. It is suggested that DBC400 and DBC700 may influence EPNs’ metabolic adaptation through distinct mechanisms. Specifically, DBC400 primarily suppressed carbohydrate metabolism, thereby restricting energy availability, and leading to a decrease in pathogenic activity. DBC700 likely disrupted lipid metabolism and increased oxidative stress, reducing membrane stability and making EPNs more vulnerable to oxidative damage (Table 2).

Table 2.
Comparison of the differential effects of DBC400 vs. DBC700 on S. feltiae.
In addition to affecting metabolic pathways, DBC may regulate EPNs’ membrane transport systems, which in turn modulate their adaptability and survival. This aligns with previous studies that examined nematode adaptation to environmental stresses. Shi et al. (2005) proposed that the downregulation of membrane transport proteins might serve as a protective mechanism under oxidative stress, reducing external pressure on cellular function [56]. Furthermore, Jiang et al. (2023), performed full-length transcriptome sequencing, found that nematodes under high pH and salt stress exhibited significant activation of transmembrane receptors, ion channels, and transporter-related signaling pathways [57]. It is suggested that nematodes may modulate membrane potential, ion homeostasis, and signal transduction to counteract environmental stress. Similarly, François-Xavier Gillet et al. (2017) discovered that under extreme environmental conditions, nematodes tend to downregulate transmembrane protein expression to prevent excessive ROS accumulation [58]. In this study, DBC400 exposure resulted in a reduction of ATP-related transmembrane protein expression, potentially limiting energy availability and metabolic activity. Exposure to DBC700 may have altered membrane permeability, destabilizing cell membranes and increasing the vulnerability of nematodes to oxidative damage. These changes could impair nematode motility and ultimately compromise their ability to locate and infect hosts.
In summary, this study provides strong evidence that DBC exposure induces oxidative stress, disrupts metabolic pathways, and affects membrane transport regulation, ultimately reducing the virulence and adaptability of EPNs. The differential effects of DBC400 and DBC700 suggest distinct metabolic adaptation mechanisms. DBC400 primarily impairs carbohydrate metabolism, while DBC700 induces more severe oxidative stress and membrane destabilization. However, it is important to acknowledge that this research was conducted under controlled laboratory conditions, which may not fully capture the complexity of natural soil ecosystems. The dissolution and migration of biochar in the environment necessitate field studies to evaluate the effects of varying DBC concentrations on EPN populations under realistic conditions. Additionally, advancements in efficient nano-biochar production techniques and the development of related products, such as nano-carbon-based fertilizers and soil amendments, could play a pivotal role in exploring the broader impacts of DBC on soil health. Future research should focus on identifying oxidative stress thresholds, assessing long-term adaptive responses, and evaluating the implications of nano-biochar applications to gain a comprehensive for understanding the effects of DBC on EPN-based biological control strategies.
5. Conclusions
This study systematically investigated the effects of dissolved biochar (DBC400 and DBC700) on the entomopathogenic nematode Steinernema feltiae, revealing that DBC can impair nematode survival and pathogenicity through oxidative stress, antioxidant enzyme inhibition, and genetic regulation. Exposure to DBC significantly increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation, particularly in the DBC700 group, indicating a stronger oxidative stress. Furthermore, antioxidant enzyme activities (SOD and CAT) were markedly suppressed likely due to the direct oxidative damage to enzyme active sites or the transcriptional downregulation of antioxidant enzyme genes. Transcriptomic analysis identified multiple metabolic adaptation pathways affected by DBC, including membrane transport, energy metabolism, protein processing, and longevity regulation. Virulence assays demonstrated that DBC exposure reduced EPN infectivity against host insects, suggesting that oxidative stress might disrupt the interactions between EPNs and their symbiotic bacteria, thereby weakening their pathogenic mechanisms. Overall, this study provides evidence that DBC can negatively affect EPN adaptability through multiple mechanisms, potentially compromising their biocontrol efficacy. Future research should further explore the oxidative stress threshold induced by different DBC types and conduct soil ecosystem experiments to evaluate the long-term impact of DBC on EPN-host-microbe interactions. These findings offer critical insights into the rational application of biochar in agricultural ecosystems.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agriculture15070772/s1, Figure S1: Kaplan-Meier survival curves of Galleria mellonella larvae infected with S. feltiae exposed to DBC400 and DBC700 treatments; Table S1: Properties of bulk biochar (BC) made at different temperatures; Table S2: The Pearson correlation coefficients between the mortality rate of EPNs and ROS, SOD, and CAT.
Author Contributions
All the authors contributed to the study’s conception and design, material preparation, data collection, and analysis. X.W.: Wrote the first draft of the manuscript. J.L. (Jie Li): Contributed to writing, review, and editing, and finalized the manuscript; also provided funding support. J.L. (Jing Li): Responsible for software development and application of related tools. L.L.: Responsible for the visualizations in the manuscript. G.L.: In charge of data curation and cleaning. W.R.: Provided resources for the study. G.Z.: Responsible for project administration and conceptualization. X.W. wrote the manuscript’s first draft. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the Young Scientists Fund, National Science Foundation of China (grant number 42207048).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data were added as Supplementary Material.
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their appreciation to the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences Innovation Program (Agro-Environmental Protection Institute).
Conflicts of Interest
Author Jing Li was employed by the company Cucumber Research Institute of Tianjin Kernel Agricultural Science and Technology Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- El-Naggar, A.; El-Naggar, A.H.; Shaheen, S.M.; Sarkar, B.; Chang, S.X.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Rinklebe, J.; Ok, Y.S. Biochar Composition-Dependent Impacts on Soil Nutrient Release, Carbon Mineralization, and Potential Environmental Risk: A Review. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 241, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczyk, A.; Sokolowska, Z.; Boguta, P. Biochar Physicochemical Properties: Pyrolysis Temperature and Feedstock Kind Effects. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio-Technol. 2020, 19, 191–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Joseph, S. Biochar for Environmental Management: Science, Technology and Implementation, 2nd ed.; Earthscan from Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Kaushik, G.; Masto, R.E. Evaluation of the Fuel Value and Soil Application Potential of the Cadmium Contaminated Biochar Obtained after Water Treatment. Solid Fuel Chem. 2020, 54, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, F.; Xing, B.S. From Bulk to Nano: Formation, Features, and Functions of Nano-Black Carbon in Biogeochemical Processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 15910–15925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sani, M.N.H.; Amin, M.; Siddique, A.; Nasif, S.O.; Ghaley, B.B.; Ge, L.Y.; Wang, F.; Yong, J.W.H. Waste-Derived Nanobiochar: A New Avenue Towards Sustainable Agriculture, Environment, and Circular Bioeconomy. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 166881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Kumar, M. Cycling of Black Carbon and Black Nitrogen in the Hydro-Geosphere: Insights on the Paradigm, Pathway, and Processes. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 770, 144711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hameed, R.; Li, G.L.; Son, Y.; Fang, H.J.; Kim, T.; Zhu, C.D.; Feng, Y.F.; Zhang, L.H.; Abbas, A.; Zhao, X.; et al. Structural Characteristics of Dissolved Black Carbon and Its Interactions with Organic and Inorganic Contaminants: A Critical Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 872, 162210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Zhang, R.J.; He, Z.; Su, P.J.; Wang, L.K.; Yao, Y.Z.; Zhang, X.J.; Liu, X.Y.; Yang, F.S. Biochar Alters the Soil Fauna Functional Traits and Community Diversity: A Quantitative and Cascading Perspective. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 477, 135302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, Q.; Yousaf, B.; Ullah, H.; Ali, M.U.; Ok, Y.S.; Rinklebe, J. Environmental Transformation and Nano-Toxicity of Engineered Nano-Particles (ENPs) in Aquatic and Terrestrial Organisms. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 50, 2523–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Han, M.; Si, X.H.; Bai, L.L.; Zhang, C.X.; Quan, X. Toxicity of Biochar Influenced by Aging Time and Environmental Factors. Chemosphere 2022, 298, 134262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongers, T.; Ferris, H. Nematode Community Structure as a Bioindicator in Environmental Monitoring. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1999, 14, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.F.; Liu, T.T.; Wang, N.Q.; Dou, Z.C.; Wang, K.G.; Zuo, Y.M. A Review of Soil Nematodes as Biological Indicators for the Assessment of Soil Health. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng. 2020, 7, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.D.; Zhang, D.X.; Li, H.X.; Qi, X.X.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.B.; Han, Y.L.; Jiang, Y.; Li, H. Soil Nematode Community and Crop Productivity in Response to 5-Year Biochar and Manure Addition to Yellow Cinnamon Soil. BMC Ecol. 2020, 20, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikram, M.; Singh, S.; Bano, N.; Alahmadi, T.A.; Shariq, M.; Siddiqui, M.A.; Islam, J. Biochar and Oil Cakes Act as Antagonists Towards Meloidogyne incognita in Tomato: A Sustainable Approach. Plant Stress 2024, 11, 100320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, Y.X.; Zhang, G.L.; Ruan, W.B.; Shan, S.J.; Lai, X.; Yang, D.L.; Yu, Z.G. Integration of Behavioural Tests and Transcriptome Sequencing of C. elegans Reveals How the Nematode Responds to Peanut Shell Biochar Amendment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 707, 136024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.K.; Ji, H.L.; Gheysen, G.; Debode, J.; Kyndt, T. Biochar-Amended Potting Medium Reduces the Susceptibility of Rice to Root-Knot Nematode Infections. BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, S.; Kakouli-Duarte, T. The Behaviour of the Nematode, Steinernema feltiae (Nematoda: Steinernematidae) in Sand Contaminated with the Industrial Pollutant Chromium VI. Ecotoxicology 2018, 27, 590–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askary, T.H.; Bhat, A.H.; Ahmad, M.J.; Chaubey, A.K.; Spiridonov, S.E. Steinernema feltiae (Rhabditida: Steinernematidae) from Hilly Areas of Kashmir Valley, India with a Note on Its Geographical Distribution. Russ. J. Nematol. 2020, 28, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bal, H.K.; Acosta, N.; Cheng, Z.Q.; Grewal, P.S.; Hoy, C.W. Effect of Habitat and Soil Management on Dispersal and Distribution Patterns of Entomopathogenic Nematodes. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 121, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herren, G.L.; Binnemans, I.; Joos, L.; Viaene, N.; Ehlers, R.U.; Vandecasteele, B.; Bert, W.; Steel, H. Compost as a Carrier Medium for Entomopathogenic Nematodes—The Influence of Compost Maturity on Their Virulence and Survival. Biol. Control 2018, 125, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.H.; Macchietto, M.; Chang, D.; Barros, M.M.; Baldwin, J.; Mortazavi, A.; Dillman, A.R. Activated Entomopathogenic Nematode Infective Juveniles Release Lethal Venom Proteins. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maushe, D.; Ogi, V.; Divakaran, K.; Mogena, A.M.V.; Himmighofen, P.A.; Machado, R.A.R.; Towbin, B.D.; Ehlers, R.U.; Molina, C.; Parisod, C.; et al. Stress Tolerance in Entomopathogenic Nematodes: Engineering Superior Nematodes for Precision Agriculture. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2023, 199, 107953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleftherianos, I.; Shokal, U.; Yadav, S.; Kenney, E.; Maldonado, T. Insect Immunity to Entomopathogenic Nematodes and Their Mutualistic Bacteria. In Molecular Biology of Photorhabdus Bacteria; Ffrench-Constant, R.H., Ed.; Springer International Publishing AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 123–156. [Google Scholar]
- Yaman, E.; Ulu, T.C.; Özbay, N. Characterization of Different Biochars and Their Impacts on Infectivity of Entomopathogenic Nematode Heterorhabditis bacteriophora. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2023, 13, 10177–10190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, A.H.; Chaubey, A.K.; Askary, T.H. Global Distribution of Entomopathogenic Nematodes, Steinernema and Heterorhabditis. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control. 2020, 30, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elgawad, M.M.M. Xenorhabdus spp.: An Overview of the Useful Facets of Mutualistic Bacteria of Entomopathogenic Nematodes. Life 2022, 12, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awori, R.M. Nematophilic Bacteria Associated with Entomopathogenic Nematodes and Drug Development of Their Biomolecules. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 993688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.A.; Naqvi, S.R.; Mehran, M.T.; Khoja, A.H.; Niazi, M.B.K.; Juchelková, D.; Atabani, A. A Performance Evaluation Study of Nano-Biochar as a Potential Slow-Release Nano-Fertilizer from Wheat Straw Residue for Sustainable Agriculture. Chemosphere 2021, 285, 131382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, B.; Niu, A.P.; Cheng, N.; Chen, M.; Zhang, X.Y.; Yu, Z.B.; Wang, S.S. Application of Biochar Immobilized Microorganisms for Pollutants Removal from Wastewater: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 837, 155563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mod, B.; Baskar, A.V.; Bahadur, R.; Tavakkoli, E.; Van Zwieten, L.; Singh, G.; Vinu, A. From Cane to Nano: Advanced Nanomaterials Derived from Sugarcane Products with Insights into Their Synthesis and Applications. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2024, 25, 2393568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.G.; Ha, B.; Li, Y.C.; Vrieling, K.; Fu, Z.; Yu, Q.L.; Rasmann, S.; Wei, X.Q.; Ruan, W.B. Toxicological Impacts of Microplastics on Virulence, Reproduction, and Physiological Processes of Entomopathogenic Nematodes. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 273, 116153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Landmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A Fast Spliced Aligner with Low Memory Requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertea, M.; Pertea, G.M.; Antonescu, C.M.; Chang, T.C.; Mendell, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. StringTie Enables Improved Reconstruction of a Transcriptome from RNA-seq Reads. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate Transcript Quantification from RNA-Seq Data with or without a Reference Genome. BMC Bioinformatics 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated Estimation of Fold Change and Dispersion for RNA-seq Data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Feng, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X. DEGseq: An R Package for Identifying Differentially Expressed Genes from RNA-seq Data. Bioinformatics 2009, 26, 136–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.R.; Hatcher, P.G.; Kumar, S.; Lee, J.W. Investigation into the Sources of Biochar Water-Soluble Organic Compounds and Their Potential Toxicity on Aquatic Microorganisms. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2550–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.L.; Hu, A.B.; Wang, Q.D.; Ai, J.; Zhang, W.J.; Liang, Y.; Cao, M.X.; Wu, H.J.; Wang, D.S. Molecular Composition and Biotoxicity Effects of Dissolved Organic Matters in Sludge-Based Carbon: Effects of Pyrolysis Temperature. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Z.; Zhou, S.S.; Fu, Y.; Sun, X.M.; Li, T.J.; Yang, C.H. Characterization of Dissolved Organic Matter in Biochar Derived from Various Macroalgae (Phaeophyta, Rhodophyta, and Chlorophyta): Effects of Pyrolysis Temperature and Extraction Solution pH. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 869, 161786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, X.; Nan, J. Systematic Assessment of the Ecotoxicological Effects and Mechanisms of Biochar-Derived Dissolved Organic Matter (DOM) on the Earthworm Eisenia fetida. Environ. Res. 2023, 236, 116855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.C.; Qian, S.F.; Chen, L.; Guan, Y.; Zheng, L.; Liu, S.H.; Chen, W.L.; Cai, P.; Huang, Q.Y. Size-Dependent Bacterial Toxicity of Hematite Particles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 8147–8156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfei, S.; Pandoli, O.G. Biochar-Derived Persistent Free Radicals: A Plethora of Environmental Applications in a Light and Shadows Scenario. Toxics 2024, 12, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odinga, E.S.; Waigi, M.G.; Gudda, F.O.; Wang, J.; Yang, B.; Hu, X.J.; Li, S.Y.; Gao, Y.Z. Occurrence, Formation, Environmental Fate and Risks of Environmentally Persistent Free Radicals in Biochars. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matés, J.M. Erratum to ‘Effects of antioxidant enzymes in the molecular control of reactive oxygen species toxicology’: [Toxicology 153 (2000) 83–104]. Toxicology 2001, 163, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Signorella, S.; Palopoli, C.; Ledesma, G. Rationally Designed Mimics of Antioxidant Manganoenzymes: Role of Structural Features in the Quest for Catalysts with Catalase and Superoxide Dismutase Activity. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 365, 75–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limón-Pacheco, J.; Gonsebatt, M.E. The Role of Antioxidants and Antioxidant-Related Enzymes in Protective Responses to Environmentally Induced Oxidative Stress. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen 2009, 674, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.G.; Lian, F.; Han, Y.R.; Wang, Z.Y.; Xing, B.S. Effect of Root Exudates on the Release, Surface Property, Colloidal Stability, and Phytotoxicity of Dissolved Black Carbon. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 239, 113687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selkirk, M.E.; Smith, V.P.; Thomas, G.R.; Gounaris, K. Resistance of Filarial Nematode Parasites to Oxidative Stress. Int. J. Parasitol. 1998, 28, 1315–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Gao, F.F.; Ge, R.T.; Liu, R.; Ma, S.M.; Liu, X.D. Metal Ions Overloading and Cell Death. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2024, 40, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Song, T.; Lai, X.; Zhang, G.; Ruan, W. The effects of different biochars on Caenorhabditis elegans and the underlying transcriptomic mechanisms. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0284348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budai, A.; Rasse, D.P.; Lagomarsino, A.; Lerch, T.Z.; Paruch, L. Biochar persistence, priming and microbial responses to pyrolysis temperature series. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2016, 52, 749–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleita, C.; Esteves, I.; Braga, M.E.M.; Figueiredo, J.; Gaspar, M.C.; Abrantes, I.; de Sousa, H.C. Juglone and 1,4-Naphthoquinone—Promising Nematicides for Sustainable Control of the Root Knot Nematode Meloidogyne luci. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 867803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, G. Entomopathogenic Nematodes and Their Symbiotic Bacteria: Microorganism-Host Interactions: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Clim. Change 2023, 13, 3443–3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.S.; Lin, C.J.; Marhavy, P.; Kyndt, T.; Siddique, S. Redox Signalling in Plant-Nematode Interactions: Insights into Molecular Crosstalk and Defense Mechanisms. Plant Cell Environ. 2024, 47, 2811–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.Y.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y.D.; Zhang, L.G.; Zhang, L.X. Protective Effect of Nitric Oxide against Oxidative Stress under Ultraviolet-B Radiation. Nitric Oxide-Biol. Chem. 2005, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Huang, M.H.; Qin, R.F.; Jiang, D.; Chang, D.D.; Xie, Y.F.; Li, C.J.; Wang, C.L. Full-Length Transcriptome Analysis of Soybean Cyst Nematode (Heterodera glycines) Reveals an Association of Behaviors in Response to Attractive pH and Salt Solutions with Activation of Transmembrane Receptors, Ion Channels, and Ca2+ Transporters. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 8778–8796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillet, F.X.; Bournaud, C.; de Souza, J.D.A.; Grossi-de-Sa, M.F. Plant-Parasitic Nematodes: Towards Understanding Molecular Players in Stress Responses. Ann. Bot. 2017, 119, 775–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).