Predicting the Sound Speed of Seafloor Sediments in the East China Sea Based on an XGBoost Algorithm
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data Source
2.1. Location of the Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
3. Methods
3.1. Data Preprocessing
3.1.1. Data Noise Removal
3.1.2. Normalization Processing
3.1.3. Physical Parameter Extraction
- Geospatial information of the seafloor sediment sampling stations—longitude (Log), latitude (Lat), and depth (D);
- Basic physical parameters—density (), water content (), and void ratio ();
- Grain composition—sand (S), silt (T), clay contents (Y);
- Grain size coefficient—average grain size (Mz).
3.1.4. Data Division
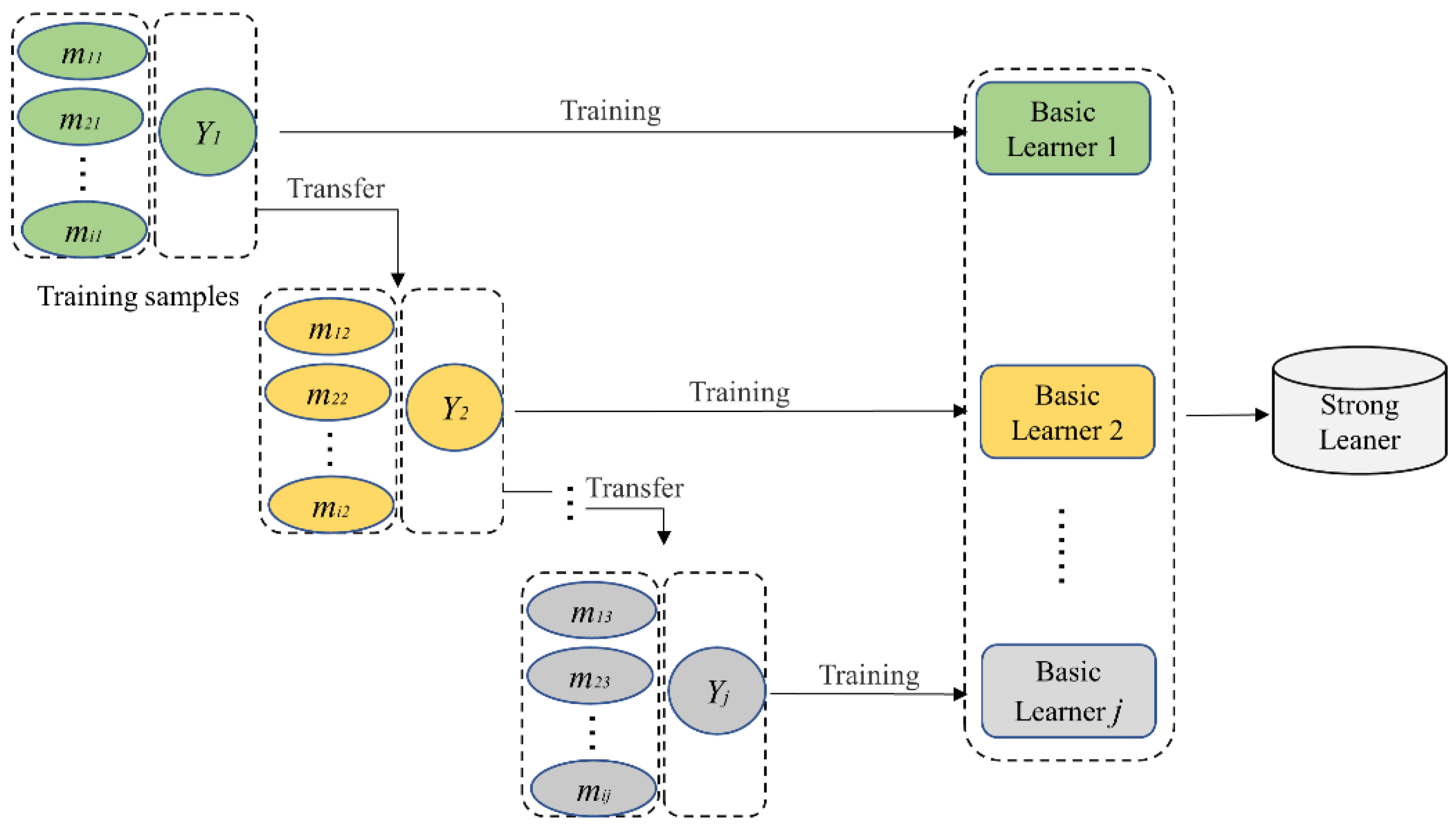
3.2. XGBoost Algorithm
3.2.1. Loss Function
3.2.2. Regularization
4. Results
4.1. Training and Validation of Seafloor Sediment Prediction Model
4.2. Model Interpretation
5. Discussion
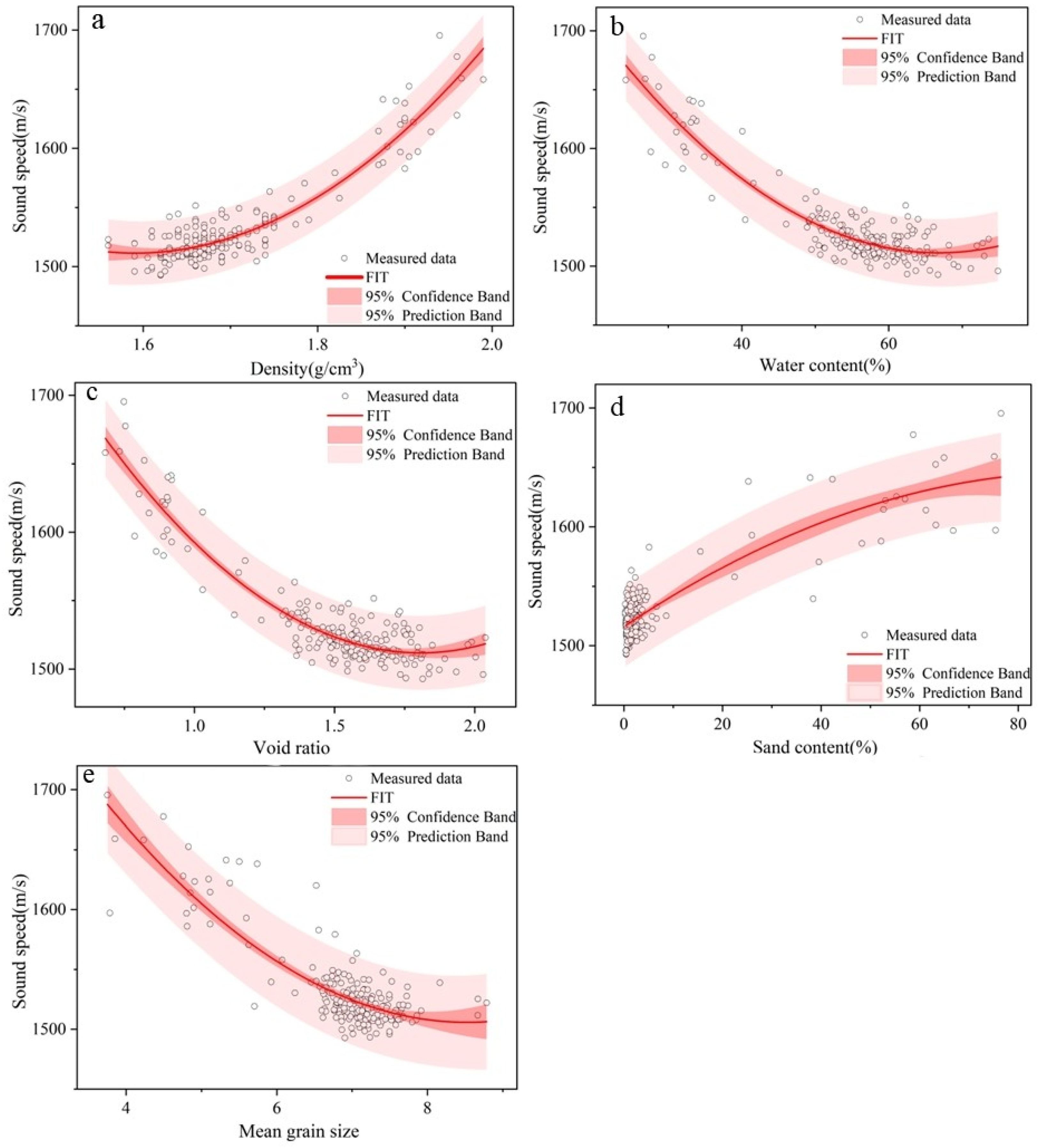
5.1. Single-Parameter Prediction Equation
5.2. Two-Parameter Prediction Equation
5.3. Comparison of XGBoost Prediction Models with Predictions of Single-and Two-Parameter Equations
6. Conclusions
- The XGBoost machine learning method exhibited high prediction accuracy and generalization ability when applied to the prediction of the sound speed of sediments in the East China Sea. When the n_estimator of the model was 75 and the max_depth was 5, the performance of the model was excellent, the goodness of fit (R2) was 0.923, the MAE of the training results and true values was 7.79 m/s, and the MAE of the validation results and true values was 8.96 m/s.
- Compared with the traditional single- and two-parameter models, the seafloor sediment model exhibited a higher goodness-of-fit and prediction accuracy. The MAE, MAPE, max absolute error, and max absolute percentage error of the prediction results were 7.99 m/s, 0.51% and 29.27 m/s, 1.73%, respectively, which were 2.47–7.73 m/s, 0.16–0.49%, 6.54 m/s–19.56 m/s, and 0.47–1.06% lower than those of the traditional single- and two-parameter equations. It is proven that the model has better performance in controlling error and the prediction accuracy of the sound speed of the seafloor sediment improved.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pan, G. Research on the Acoustic Characteristics of Seafloor Sediments in the Northern South. China Sea; Tongji University: Shanghai, China, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.L. The development of research in marine geophysics and acoustic technology for submarine exploration. Prog. Geophys. 2007, 22, 1243–1249. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, D.D.; Wang, N.; Zhou, X.H. Interdisciplinary study of acoustics and marine sedimentology. Adv. Mar. Sci. 2006, 24, 392–396. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.Y.; Wang, D.; Zhou, J.P.; Wang, X.M. Acoustic wave dispersion and attenuation in marine sediment based on partially gas-saturated Biot-Stoll model. Chin. J. Geophys. 2012, 55, 180–188. [Google Scholar]
- Biot, M.A. Theory of propagation of elastic waves in a fluid-saturated porous solid: II. Higher frequency range. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1956, 28, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckingham, M.J. Wave propagation, stress relaxation, and grain-to-grain shearing in saturated, unconsolidated marine sediments. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2000, 108, 2796–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckingham, M.J. Theory of acoustic attenuation, dispersion, and pulse propagation in unconsolidated granular materials including marine sediments. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1997, 102, 2579–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckingham, M.J. Theory of compressional and shear waves in fluidlike marine sediments. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1998, 103, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoll, R.D. Sediments Acoustics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Stoll, R.D. Acoustic waves in ocean sediments. Geophysics 1977, 42, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, A.B.; Lindsay, R.B. A Textbook of Sound. Phys. Today 1956, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.S.; Tao, C.H.; Prasad, M.; Wilkens, R.H.; Frazer, L.N. Acoustic properties of coral sands, Waikiki, Hawaii. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2004, 115, 2013–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.S.; Wilkens, R.H.; Frazer, L.N. In situ velocity profiles in gassy sediments: Kiel Bay. Geo-Mar. Lett. 1996, 16, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, E.L.; Bachman, R.T. Sound velocity and related properties of marine sediments. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1982, 72, 1891–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, E.L. Prediction of in-situ acoustic and elastic properties of marine sediments. Geophysics 1971, 36, 266–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, E.L. Geoacoustic modeling of the sea floor. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1980, 68, 1313–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guangming, K.; Yuexia, Z.; Guanbao, L.; Guozhong, H.; Xiangmei, M. Comparison on the sound speeds of seafloor sediments measured by in-situ and laboratorial technique in Southern Yellow Sea. Ocean. Technol. 2011, 30, 52–56. [Google Scholar]
- Kan, G.; Su, Y.; Li, G.; Liu, B.; Meng, X. The correlations between in-situ sound speeds and physical parameters of seafloor sediments in the middle area of the southern Huanghai Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2013, 35, 166–171. [Google Scholar]
- Dapeng, Z.; Baihai, W.; Bo, L. Analysis and study on the sound velocity empirical equations of seafloor sediments. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2007, 29, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Orsi, T.H.; Dunn, D.A. Sound velocity and related physical properties of fine grained abyssal sediments from the Brazil Basin (South Atlantic Ocean). J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1990, 88, 1536–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsi, T.H.; Dunn, D.A. Correlations between sound velocity and related properties of glacio-marine sediments: Barents Sea. Geo-Mar. Lett. 1991, 11, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, M.D.; Briggs, K.B. In situ and laboratory geoacoustic measurements in soft mud and hard-packed sand sediments: Implications for high-frequency acoustic propagation and scattering. Geo-Mar. Lett. 1996, 16, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, A.; Dong, J.; Lu, J.; Huang, J.; Wan, S. Provenance discrimination of sediments in the Zhejiang-Fujian mud belt, East China Sea: Implications for the development of the mud depocenter. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2018, 151, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.J.; Li, A.C.; Huang, J.L. Research progress in the mud deposits along the Zhemin coast of the East China Sea continental shelf. Mar. Sci. Bull. 2021, 31, 97–104. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Shi, X.; Fang, X.; Dou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X. Spatial and temporal distributions of clay minerals in mud deposits on the inner shelf of the East China Sea: Implications for paleoenvironmental changes in the Holocene. Quat. Intern. 2014, 349, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Li, A.; Huang, P.; Lu, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J. Sedimentary responses to the cross-shelf transport of terrigenous material on the East China Sea continental shelf. Sediment. Geolog. 2019, 384, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, D.I.; Choi, J.Y.; Jung, H.S.; Rho, K.C.; Ahn, K.S. Recent sediment accumulation and origin of shelf mud deposits in the Yellow and East China Seas. Prog. Oceanogr. 2007, 73, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.M.; Liu, B.H.; Kan, G.M.; Li, G.B. An experimental study on acoustic properties and their influencing factors of marine sedi-ment in the southern Huanghai Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2012, 34, 74–83. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.H.; Liu, L. An improved ID3 algorithm based on correlation coefficients. Comput. Eng. Sci. 2016, 38, 2342–2347. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, N.; Wang, X.; Fu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, J.; Chen, J. Predicting heat transfer of oscillating heat pipes for machining processes based on extreme gradient boosting algorithm. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2020, 164, 114521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Zhang, J. Load forecasting based on multi-model by stacking ensemble learning. Proc. CSEE 2019, 39, 4032–4042. [Google Scholar]








| ρ/ | w/ | S/ % | T/ % | Y/ % | Mz/ Φ | (m/s) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max | 2.00 | 74.85 | 2.04 | 76.30 | 79.30 | 73.10 | 8.78 | 1695.38 |
| Min | 1.56 | 24.25 | 0.68 | 0.10 | 10.70 | 34.50 | 6.71 | 1492.86 |
| Ave | 1.72 | 52.07 | 1.43 | 10.34 | 55.15 | 7.60 | 5.9 | 1540.96 |
| Related Parameters | Prediction Equation | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| 0.86 | ||
| 0.85 | ||
| 0.86 | ||
| Mz | 0.76 | |
| S | 0.76 |
| Related Parameters | Prediction Equation | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| 0.87 | ||
| 0.87 | ||
| 0.86 | ||
| Mz | 0.87 |
| Prediction Model | Max Absolute Error (m/s) | Max Absolute Percentage Error (%) | MAE (m/s) | MAPE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 41.29 | 2.49 | 10.53 | 0.67 | |
| 42.03 | 2.79 | 12.30 | 0.79 | |
| 37.88 | 2.52 | 11.97 | 0.77 | |
| Mz | 48.83 | 2.65 | 10.57 | 0.67 |
| S | 37.24 | 2.20 | 15.72 | 1.00 |
| 39.36 | 2.38 | 13.89 | 0.89 | |
| 35.81 | 2.37 | 10.46 | 0.67 | |
| 39.39 | 2.62 | 14.36 | 0.93 | |
| Mz | 41.42 | 2.75 | 14.77 | 0.95 |
| XGBoost | 29.27 | 1.73 | 7.99 | 0.51 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, M.; Meng, X.; Kan, G.; Wang, J.; Li, G.; Liu, B.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lu, J. Predicting the Sound Speed of Seafloor Sediments in the East China Sea Based on an XGBoost Algorithm. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10101366
Chen M, Meng X, Kan G, Wang J, Li G, Liu B, Liu C, Liu Y, Liu Y, Lu J. Predicting the Sound Speed of Seafloor Sediments in the East China Sea Based on an XGBoost Algorithm. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2022; 10(10):1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10101366
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Mujun, Xiangmei Meng, Guangming Kan, Jingqiang Wang, Guanbao Li, Baohua Liu, Chenguang Liu, Yanguang Liu, Yuanxu Liu, and Junjie Lu. 2022. "Predicting the Sound Speed of Seafloor Sediments in the East China Sea Based on an XGBoost Algorithm" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 10, no. 10: 1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10101366
APA StyleChen, M., Meng, X., Kan, G., Wang, J., Li, G., Liu, B., Liu, C., Liu, Y., Liu, Y., & Lu, J. (2022). Predicting the Sound Speed of Seafloor Sediments in the East China Sea Based on an XGBoost Algorithm. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 10(10), 1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10101366






