Identifying Hydraulic Characteristics Related to Fishery Activities Using Numerical Analysis and an Automatic Identification System of a Fishing Vessel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Target Waters and Underwater Reef
2.2. AIS Information Phase
2.2.1. FV Assumption
2.2.2. FV Tracking Using Automatic Identification System Information
2.3. Numerical Analysis Phase
2.3.1. Framework of Numerical Analysis
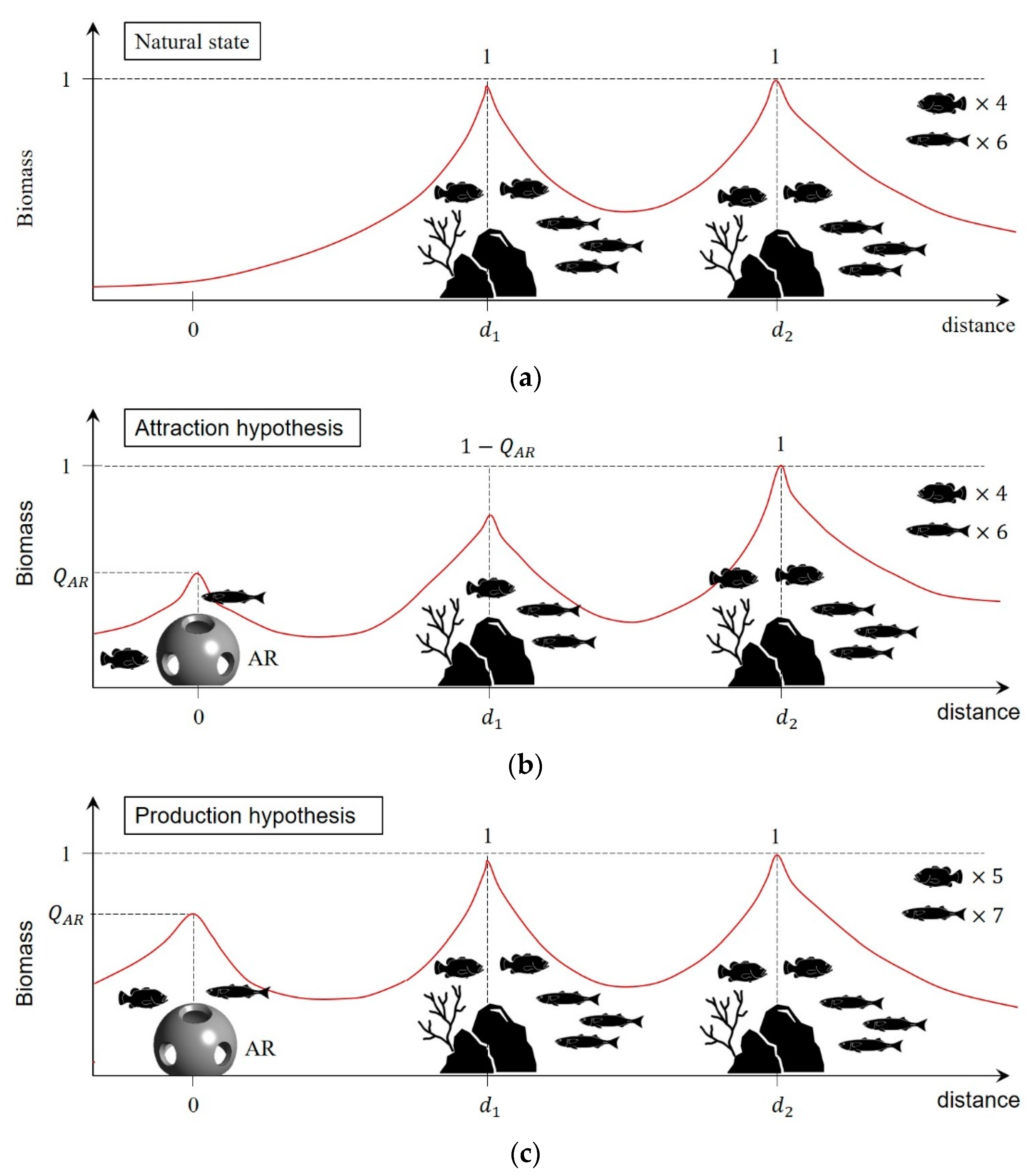
2.3.2. Identification of Hydraulic Features Related to Fish Attraction
3. Results
3.1. Quantification of Two Candidates Related Fish Attraction Using Mumerical Analysis
3.2. Superimposition of AIS Information-Based FV Path and Numerical Analysis Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A


References
- De Troch, M.; Reubens, J.T.; Heirman, E.; Degraer, S.; Vincx, M. Energy profiling of demersal fish: A case-study in wind farm artificial reefs. Mar. Environ. Res. 2013, 92, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrose, R.F.; Swarbrick, S.L. Comparison of fish assemblages on artificial and natural reefs off the coast of southern California. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1989, 44, 718–733. [Google Scholar]
- Bohnsack, J.A. Are high densities of fishes at artificial reefs the result of habitat limitation or behavior preference? Bull. Mar. Sci. 1989, 44, 631–645. [Google Scholar]
- Bohnsack, J.A.; Harper, D.E.; McClellan, D.B.; Hulsbeck, M. Effects of reef size on colonization and assemblage structure of fishes at artificial reefs off southeastern Florida, USA. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1994, 55, 796–823. [Google Scholar]
- Bombace, G.; Fabi, G.; Fiorentini, L.; Speranza, S. Analysis of the efficacy of artificial reefs located in five different areas of the Adriatic Sea. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1994, 55, 559–580. [Google Scholar]
- Frazer, T.K.; Lindberg, W.J. Refuge spacing similarly affects reef-associated species from three phyla. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1994, 55, 388–400. [Google Scholar]
- Charbonnel, E.; Serre, C.; Ruitton, S.; Harmelin, J.-G.; Jensen, A. Effects of increased habitat complexity on fish assemblages associated with large artificial reef units (French Mediterranean coast). ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2002, 59, S208–S213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bortone, S.A. Resolving the Attraction-Production Dilemma in Artificial Reef Research: Some Yeas and Nays. Fisheries 2001, 23, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gove, J.M.; McManus, M.A.; Neuheimer, A.B.; Polovina, J.J.; Drazen, J.C.; Smith, C.R.; Merrifield, M.A.; Friedlander, A.M.; Ehses, J.S.; Young, C.W.; et al. Near-island biological hotspots in barren ocean basins. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.; Woo, J.; Yoon, H.-S.; Na, W.-B. Efficiency, tranquillity and stability indices to evaluate performance in the artificial reef wake region. Ocean Eng. 2016, 122, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowden, A.A.; Dower, J.F.; Schlacher, T.; Consalvey, M.; Clark, M.R. Paradigms in seamount ecology: Fact, fiction and future. Mar. Ecol.-Evol. Perspect. 2010, 31, 226–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, K.L.; Mowles, S.L.; Foggo, A. Mounting evidence: Near-slope seamounts are faunally indistinct from an adjacent bank. Mar. Ecol. 2010, 31, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morato, T.; Hoyle, S.D.; Allain, V.; Nicol, S.J. Seamounts are hotspots of pelagic biodiversity in the open ocean. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 9707–9711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Danovaro, R.; Company, J.B.; Corinaldesi, C.; D’Onghia, G.; Galil, B.; Gambi, C.; Gooday, A.J.; Lampadariou, N.; Luna, G.M.; Morigi, C.; et al. Deep-Sea Biodiversity in the Mediterranean Sea: The Known, the Unknown, and the Unknowable. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liao, J.C.; Beal, D.N.; Lauder, G.V.; Triantafyllou, M.S. Fish Exploiting Vortices Decrease Muscle Activity. Science 2003, 302, 1566–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beal, D.N.; Hover, F.S.; Triantafyllou, M.S.; Liao, J.C.; Lauder, G.V. Passive propulsion in vortex wakes. J. Fluid Mech. 2006, 549, 385–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hockley, F.A.; Wilson, C.A.M.E.; Brew, A.; Cable, J. Fish responses to flow velocity and turbulence in relation to size, sex and parasite load. J. R. Soc. Interface 2014, 11, 20130814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marine Traffic. Available online: https://www.marinetraffic.com/en/ais/home/centerx:-12.0/centery:25.0/zoom:4 (accessed on 8 August 2022).
- Ha, K.-J.; Nam, S.; Jeong, J.-Y.; Moon, I.-J.; Lee, M.; Yun, J.; Jang, C.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Byun, D.-S.; Heo, K.-Y.; et al. Observations Utilizing Korea Ocean Research Stations and their Applications for Process Studies. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 100, 2061–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, D.-S.; Jeong, J.-Y.; Kim, D.-J.; Hong, S.; Lee, K.-T.; Lee, K. Ocean and Atmospheric Observations at the Remote Ieodo Ocean Research Station in the Northern East China Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 618500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocean Data in Grid Framework. Available online: http://www.khoa.go.kr/oceangrid/gis/category/observe/observeSearch.do?type=EYS (accessed on 1 August 2022).
- Kim, D. Evaluation of Turbulence Models for Computational Fluid Dynamics of Artificial Reef. Ph.D. Thesis, Pukyong National University, Busan, Korea, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.E. Numerical Experiment of Artificial Upwelling by Ocean Submerged Structure. Master’s Thesis, Pukyong National University, Busan, Korea, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.; Jung, S.; Na, W.-B. Evaluation of turbulence models for estimating the wake region of artificial reefs using particle image velocimetry and computational fluid dynamics. Ocean Eng. 2021, 223, 108673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Woo, J.; Na, W.-B. Intensively Stacked Placement Models of Artificial Reef Sets Characterized by Wake and Upwelling Regions. Mar. Technol. Soc. J. 2017, 51, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.; Yan-Xuan, Z.; Pi-Hai, G.; Chang-Tao, G. Numerical simulation and PIV experimental study of the effect of flow fields around tube artificial reefs. Ocean Eng. 2017, 134, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.-L.; Su, D.-T. Numerical analysis of the influence of reef arrangements on artificial reef flow fields. Ocean Eng. 2013, 74, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wan, R.; Wang, X.; Zhao, F.; Lan, X.; Cheng, H.; Tang, W.; Guan, Q. Study on the influence of cut-opening ratio, cut-opening shape, and cut-opening number on the flow field of a cubic artificial reef. Ocean Eng. 2018, 162, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Woo, J.; Yoon, H.-S.; Na, W.-B. Wake lengths and structural responses of Korean general artificial reefs. Ocean Eng. 2014, 92, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Jung, S.; Kim, J.; Na, W.-B. Efficiency and unit propagation indices to characterize wake volumes of marine forest artificial reefs established by flatly distributed placement models. Ocean Eng. 2019, 175, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, S.; Kaiser, M.J.; Reynolds, J.D. Marine Fisheries Ecology; Blackwell Science: Oxford, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Yanagi, T.; Nakajima, M. Change of oceanic condition by the man-made structure for upwelling. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1991, 23, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakimoto, M.; Okubo, H.; Itano, H.; Arai, K. Distribution pattern of zooplankton around the fish reef. J. Fish. Eng. 1983, 19, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.R. Determining vertical velocities during upwelling off the Oregon coast. Deep Sea Res. 1977, 24, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawaragi, T. Coastal Engineering-Waves, Beaches, Wave-Structure Interactions; Elsevier Science, B.V.: Amsterdam, The Nether-lands, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Ono, M.; Deguchi, I. Relation between Aggregating Effect of Artificial Fish Reef and Flow Pattern around Reef. Coast. Struct. 2003, 2004, 1164–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, S.; Porter, J.; Wilding, T.A. Artificial reef design affects benthic secondary productivity and provision of functional habitat. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 2122–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.; Jung, S.; Na, W.-B. Wake Region Estimation of Artificial Reefs using Wake Volume Diagrams. J. Fishries Mar. Sci. Educ. 2016, 28, 1042–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Code | LON | LAT | Timestamp (GMT) | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FV1 | 125.1871 | 32.13589 | 11 March 2022 19:41 | P1 |
| 125.1873 | 32.13599 | 11 March 2022 21:53 | P2 | |
| 125.1854 | 32.13173 | 11 March 2022 22:11 | P3 | |
| 125.1790 | 32.13143 | 11 March 2022 22:13 | P4 | |
| 125.1812 | 32.13128 | 11 March 2022 22:21 | P5 | |
| 125.1811 | 32.12952 | 11 March 2022 22:23 | P6 | |
| 125.1791 | 32.12979 | 11 March 2022 22:25 | P7 | |
| 125.1730 | 32.13166 | 11 March 2022 22:40 | P8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jang, S.-C.; Jeong, J.-Y.; Lee, S.-W.; Kim, D. Identifying Hydraulic Characteristics Related to Fishery Activities Using Numerical Analysis and an Automatic Identification System of a Fishing Vessel. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1619. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10111619
Jang S-C, Jeong J-Y, Lee S-W, Kim D. Identifying Hydraulic Characteristics Related to Fishery Activities Using Numerical Analysis and an Automatic Identification System of a Fishing Vessel. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2022; 10(11):1619. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10111619
Chicago/Turabian StyleJang, Sung-Chul, Jin-Yong Jeong, Seung-Woo Lee, and Dongha Kim. 2022. "Identifying Hydraulic Characteristics Related to Fishery Activities Using Numerical Analysis and an Automatic Identification System of a Fishing Vessel" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 10, no. 11: 1619. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10111619
APA StyleJang, S.-C., Jeong, J.-Y., Lee, S.-W., & Kim, D. (2022). Identifying Hydraulic Characteristics Related to Fishery Activities Using Numerical Analysis and an Automatic Identification System of a Fishing Vessel. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 10(11), 1619. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10111619







