Investigating Spatial Distribution of Green-Tide in the Yellow Sea in 2021 Using Combined Optical and SAR Images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
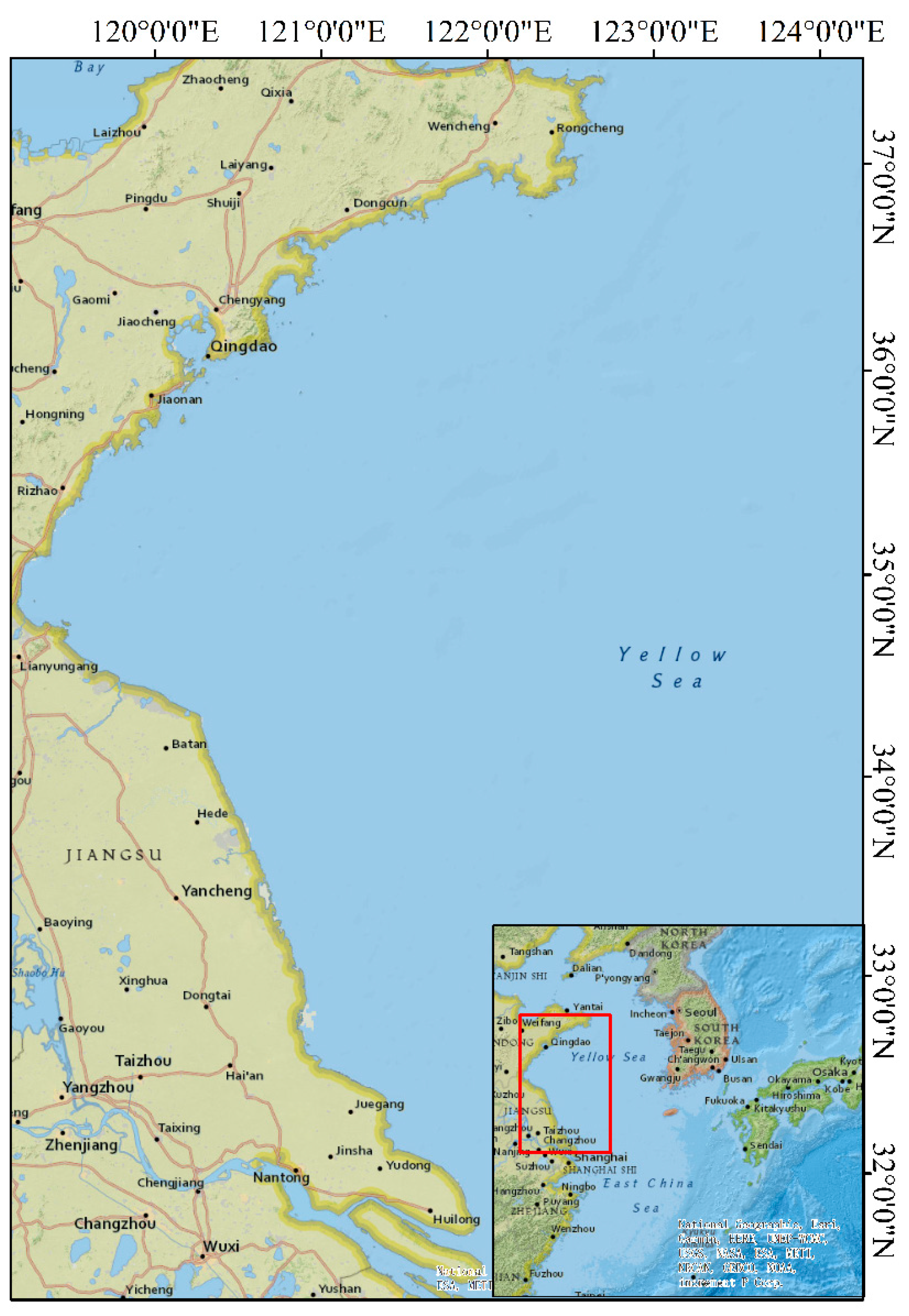
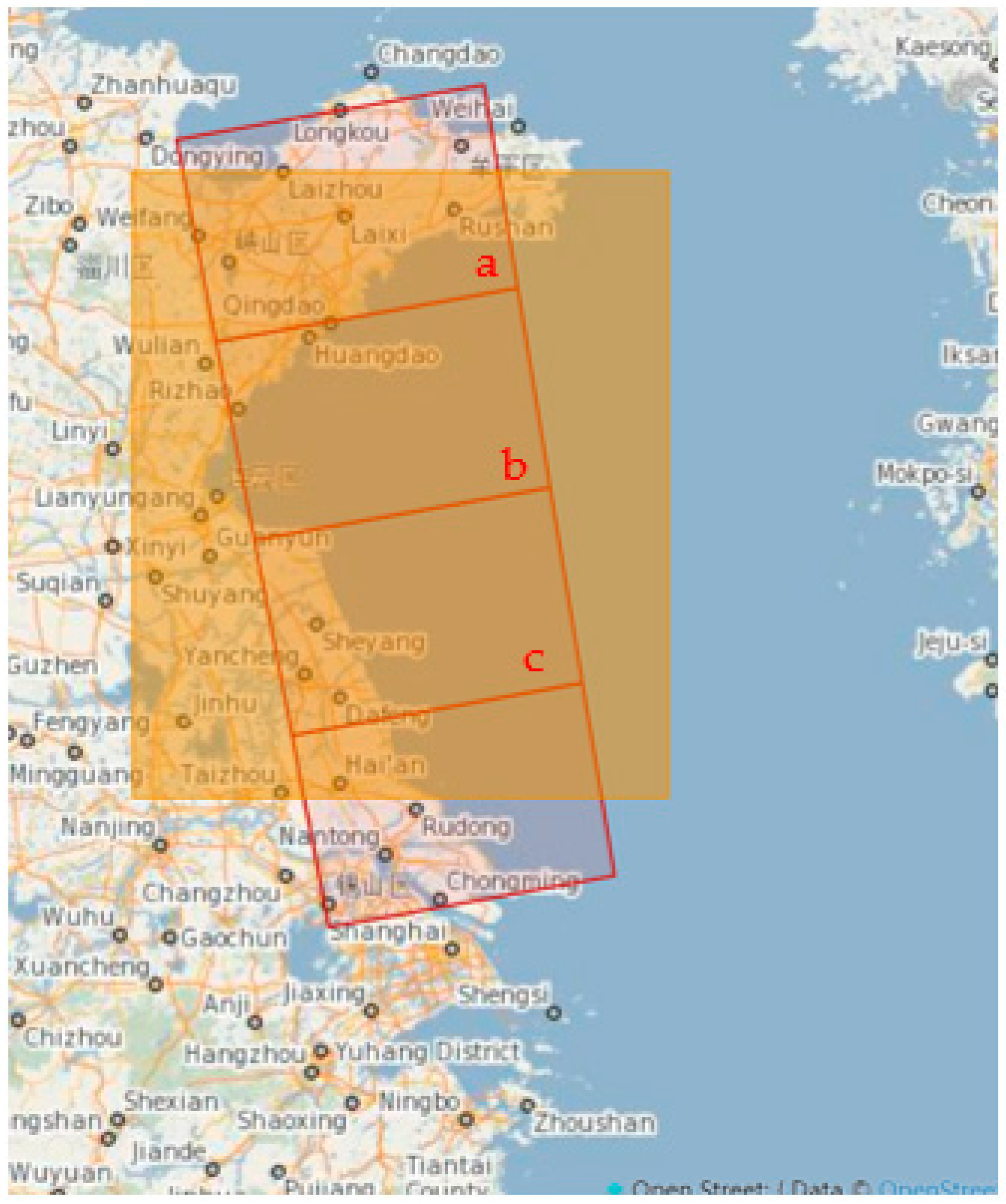
2.1. Study Area and Data
2.2. Research Methods and Data Processing
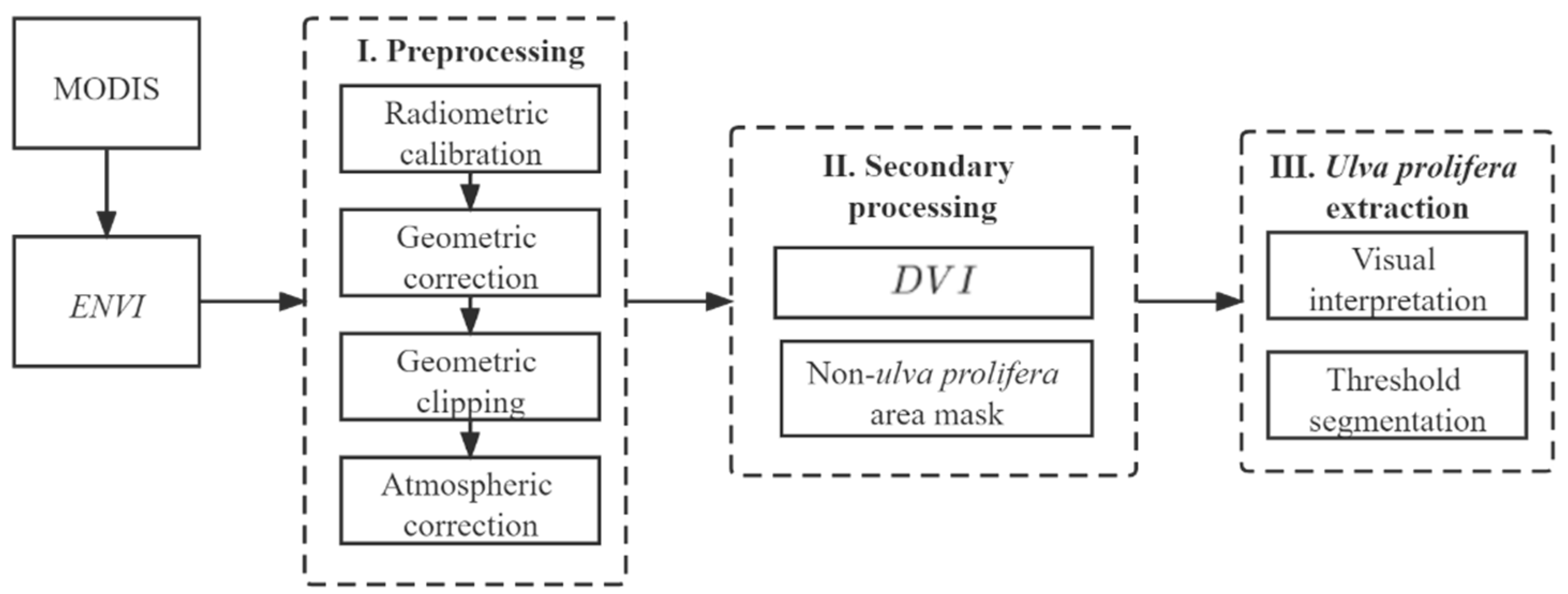
2.2.1. MODIS Image Preprocessing
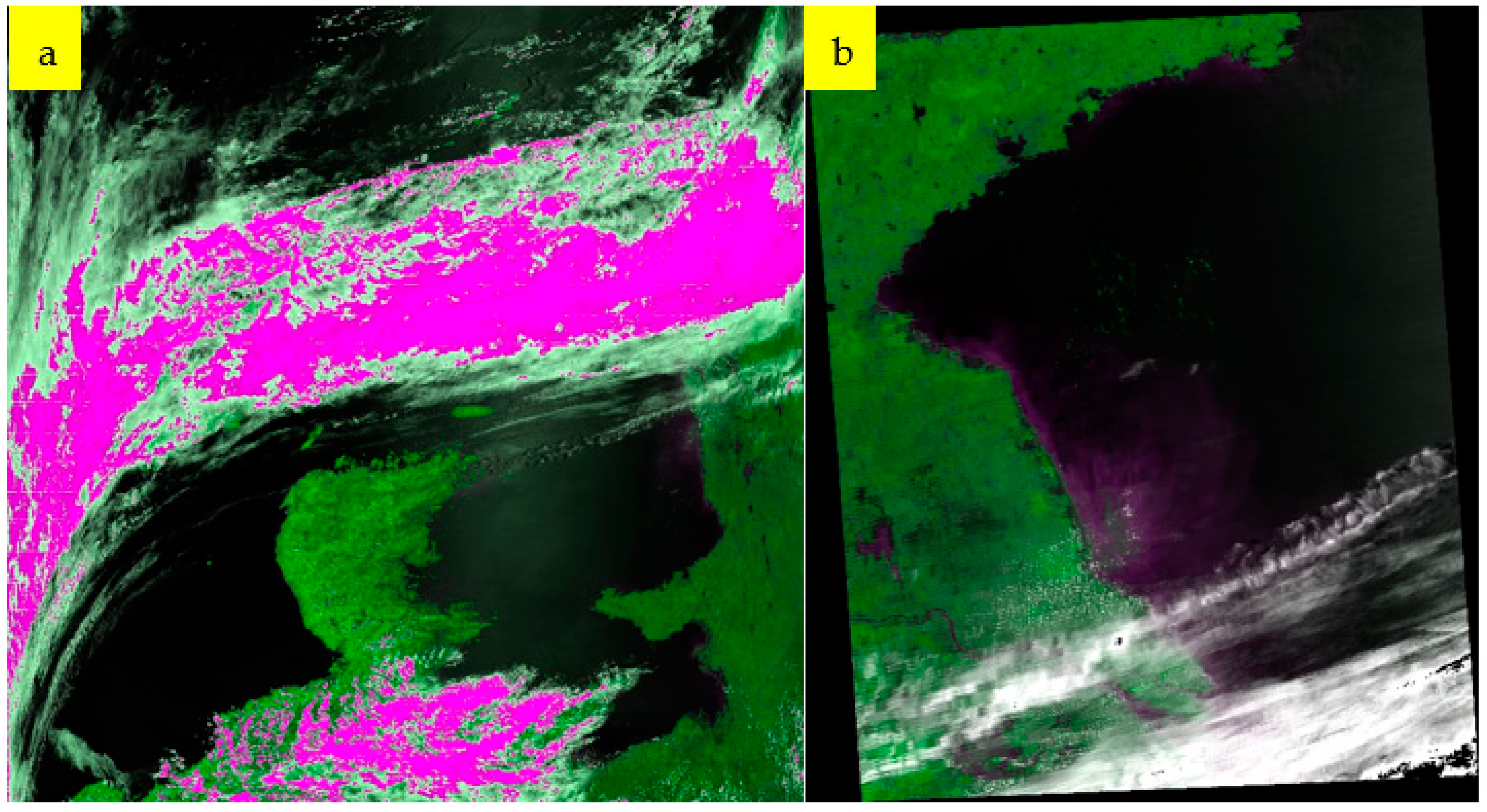
2.2.2. Ulva prolifera Extraction Based on MODIS Images
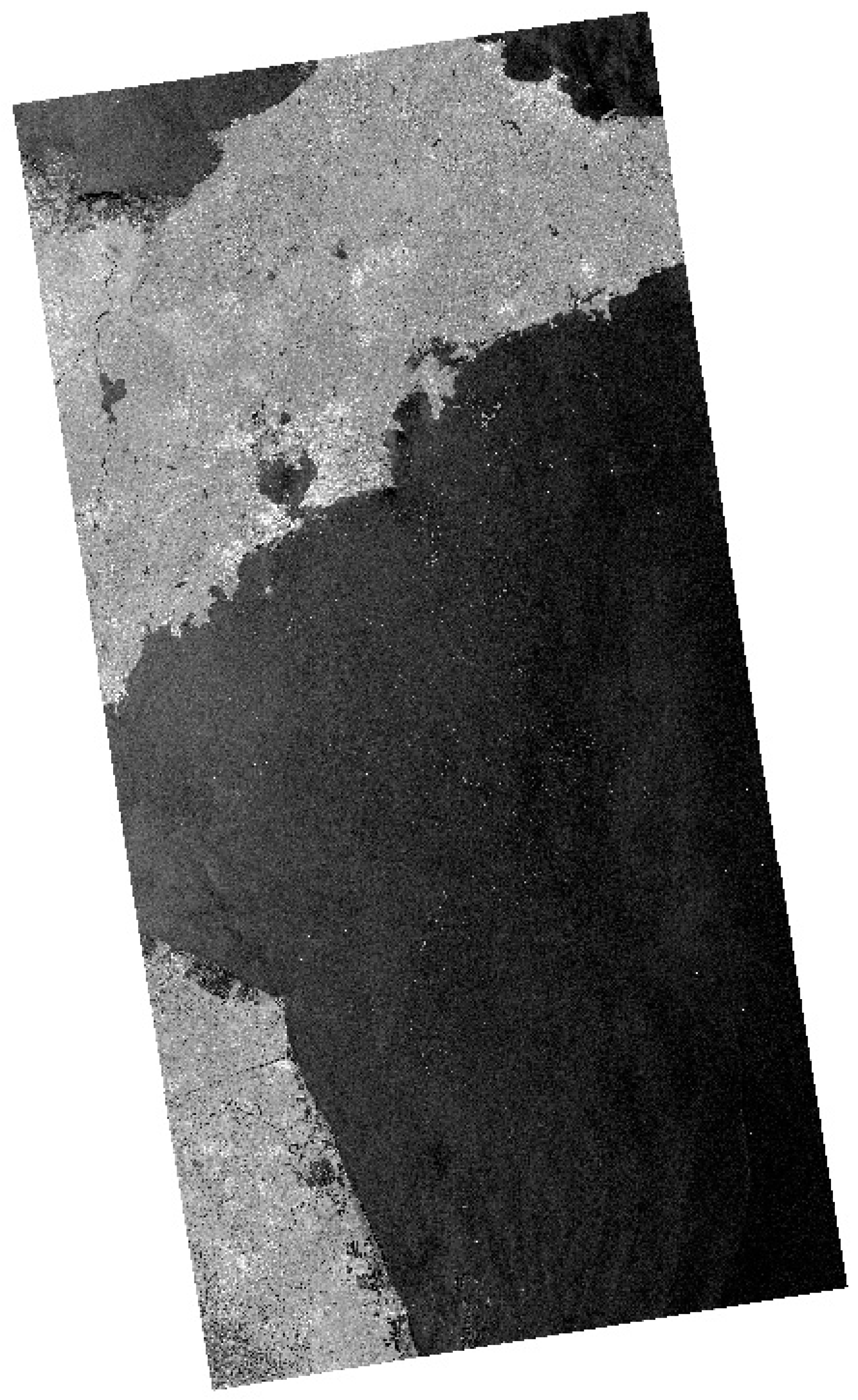
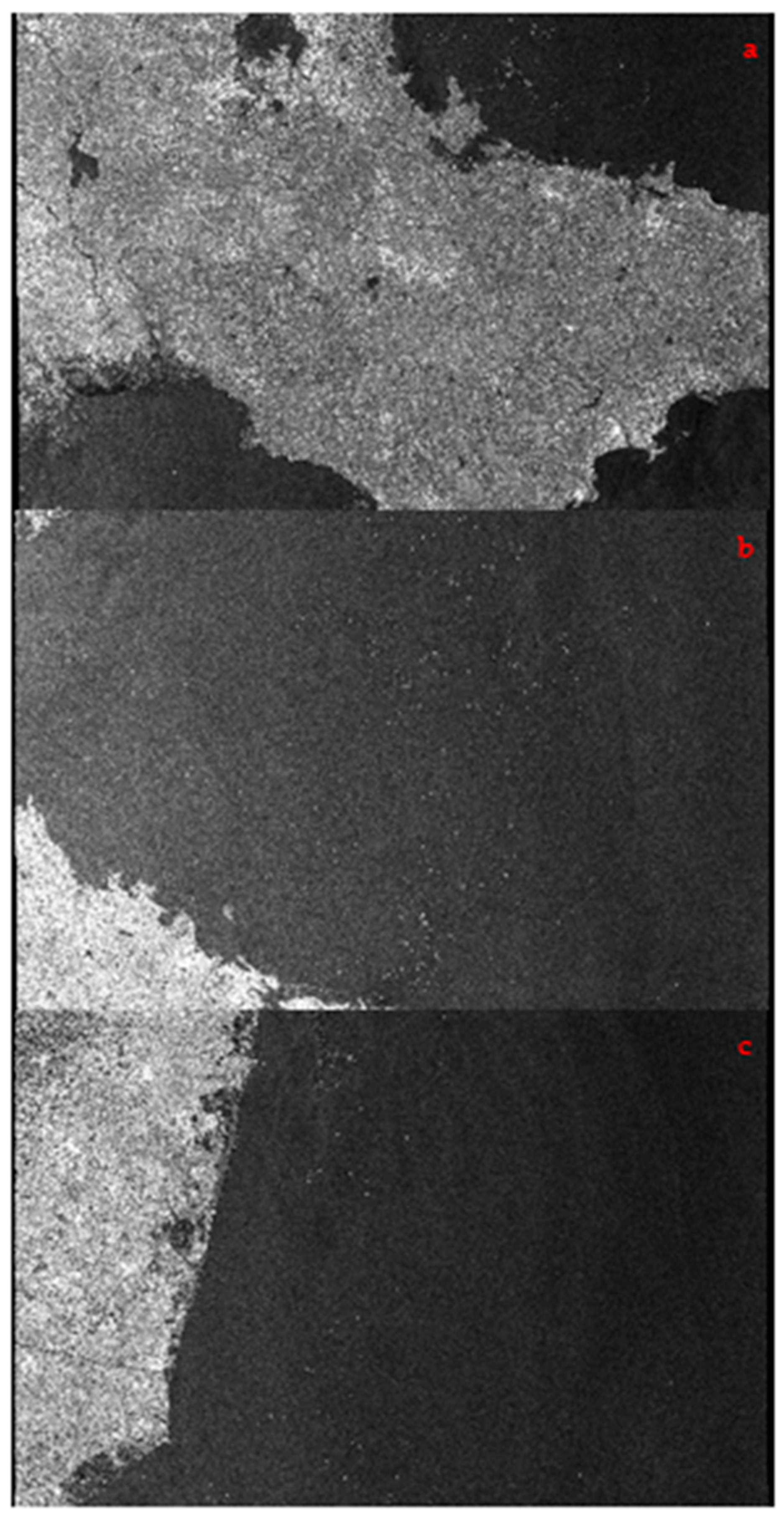
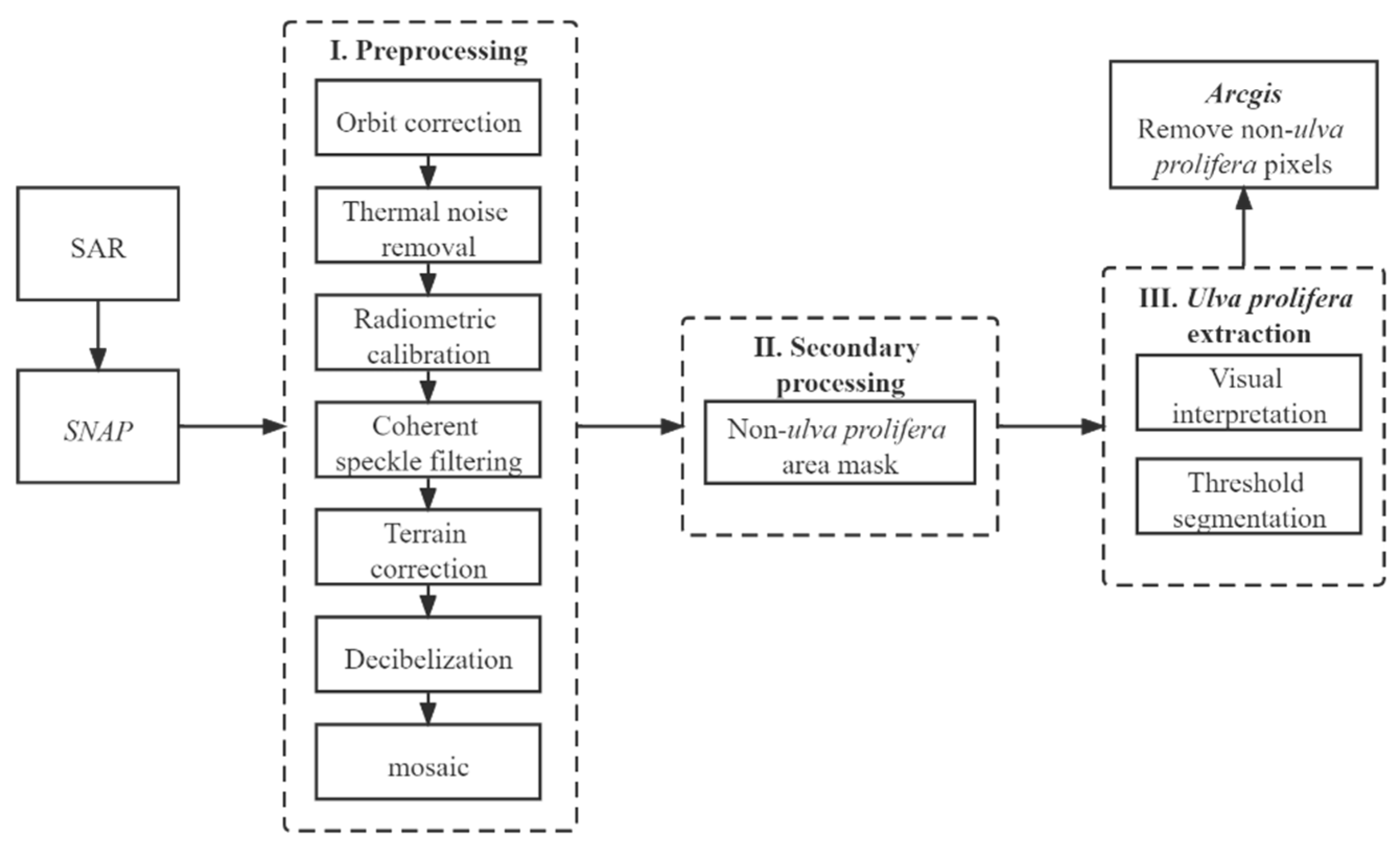
2.2.3. SAR Image Preprocessing
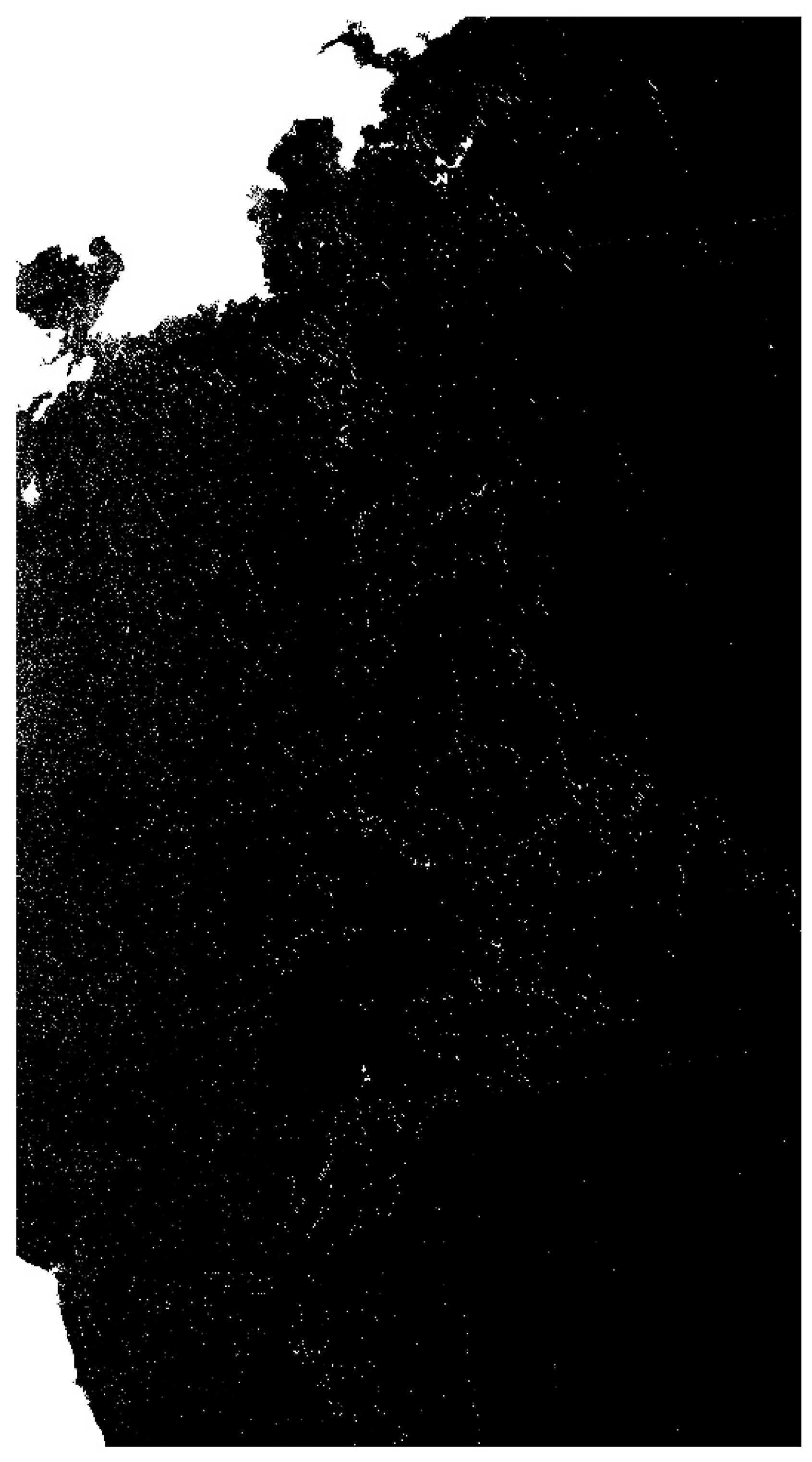
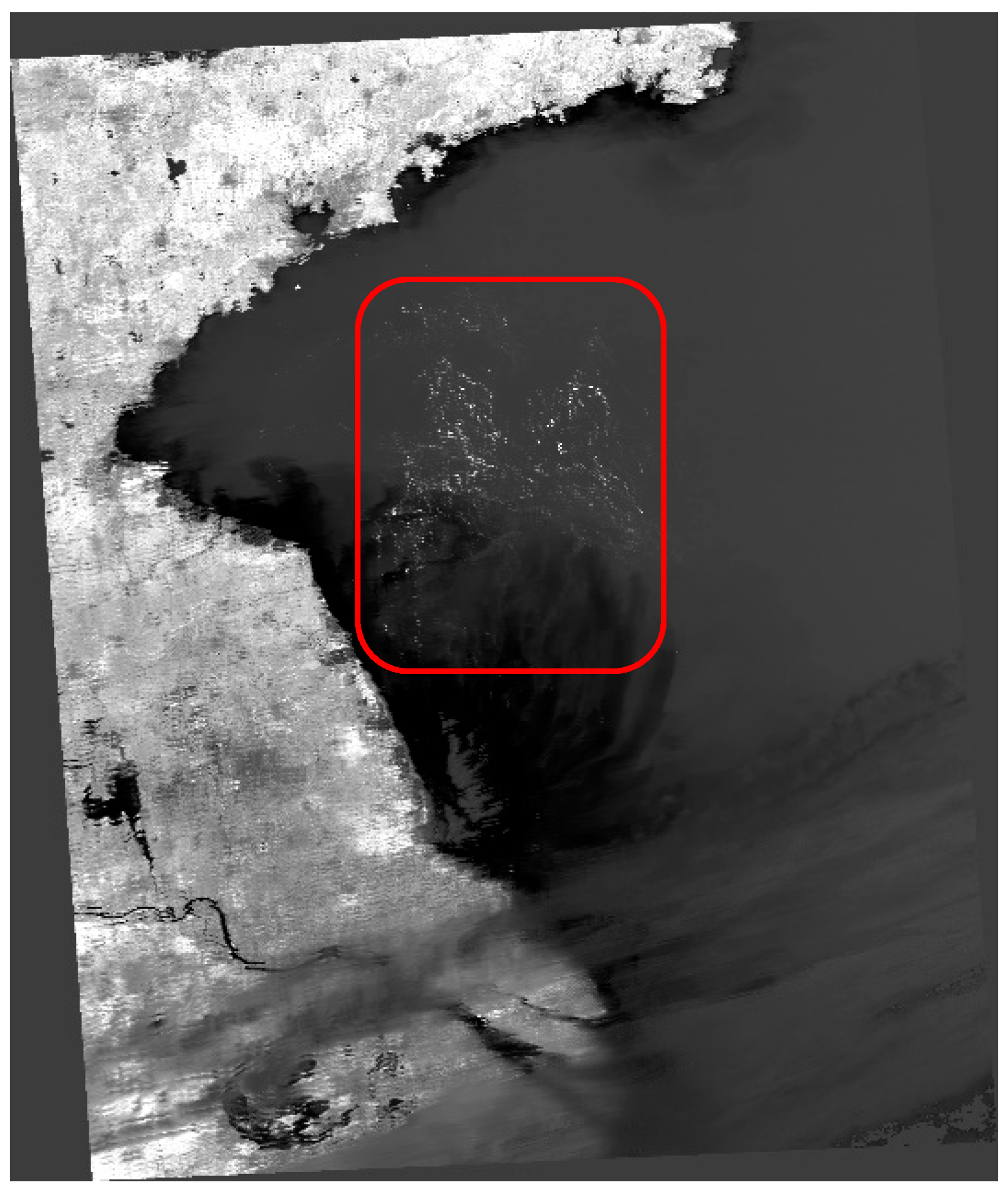
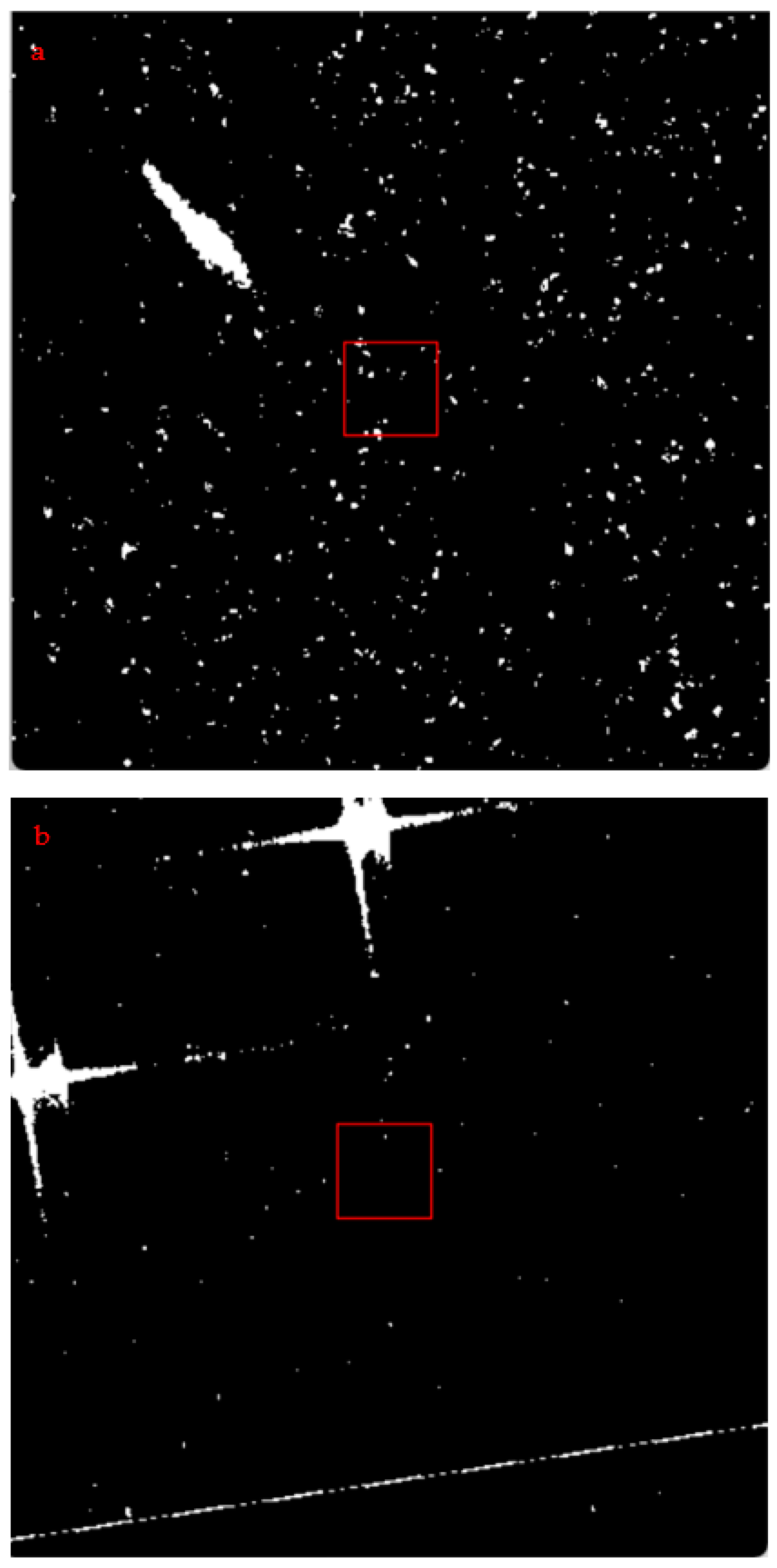
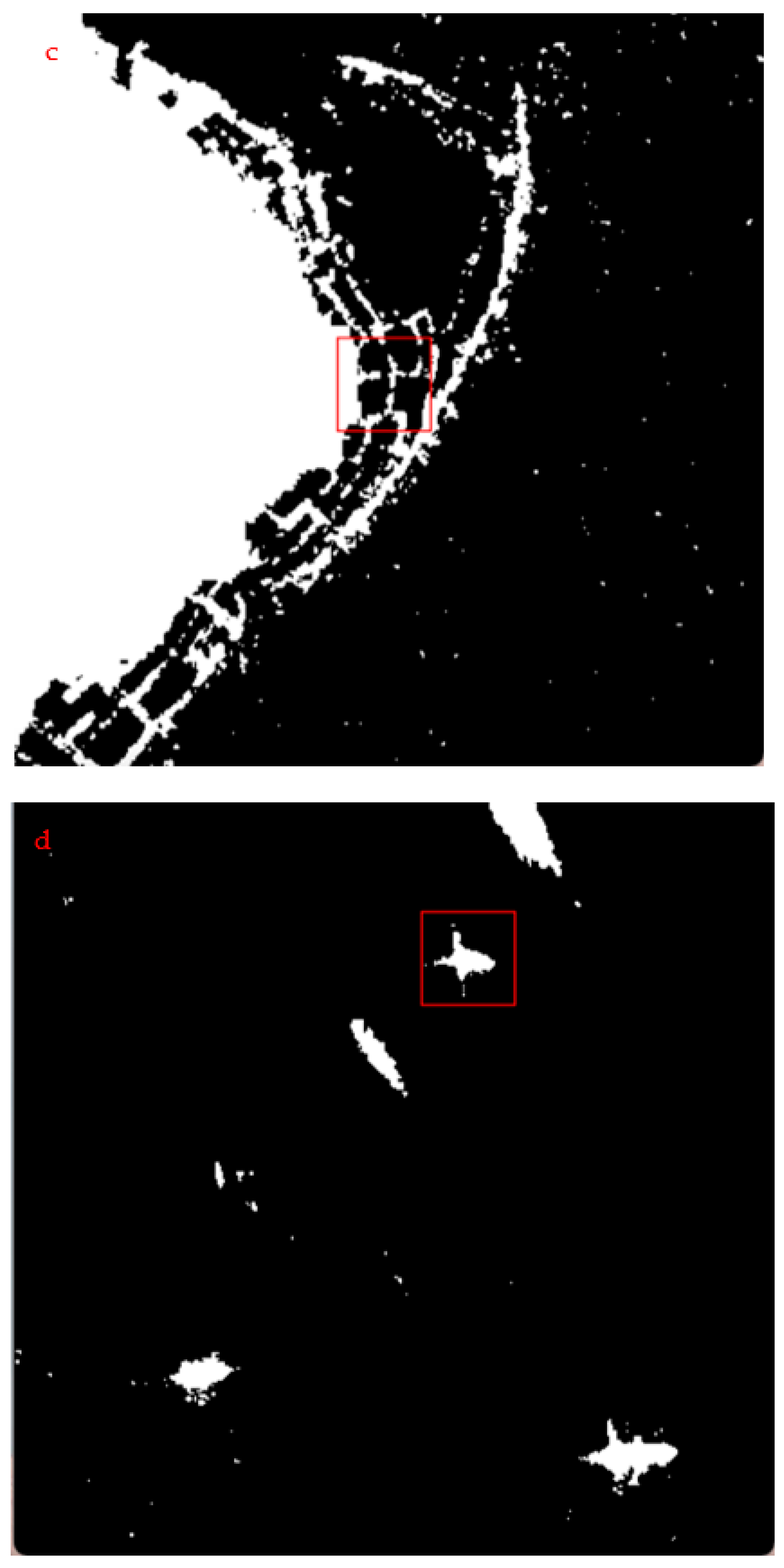
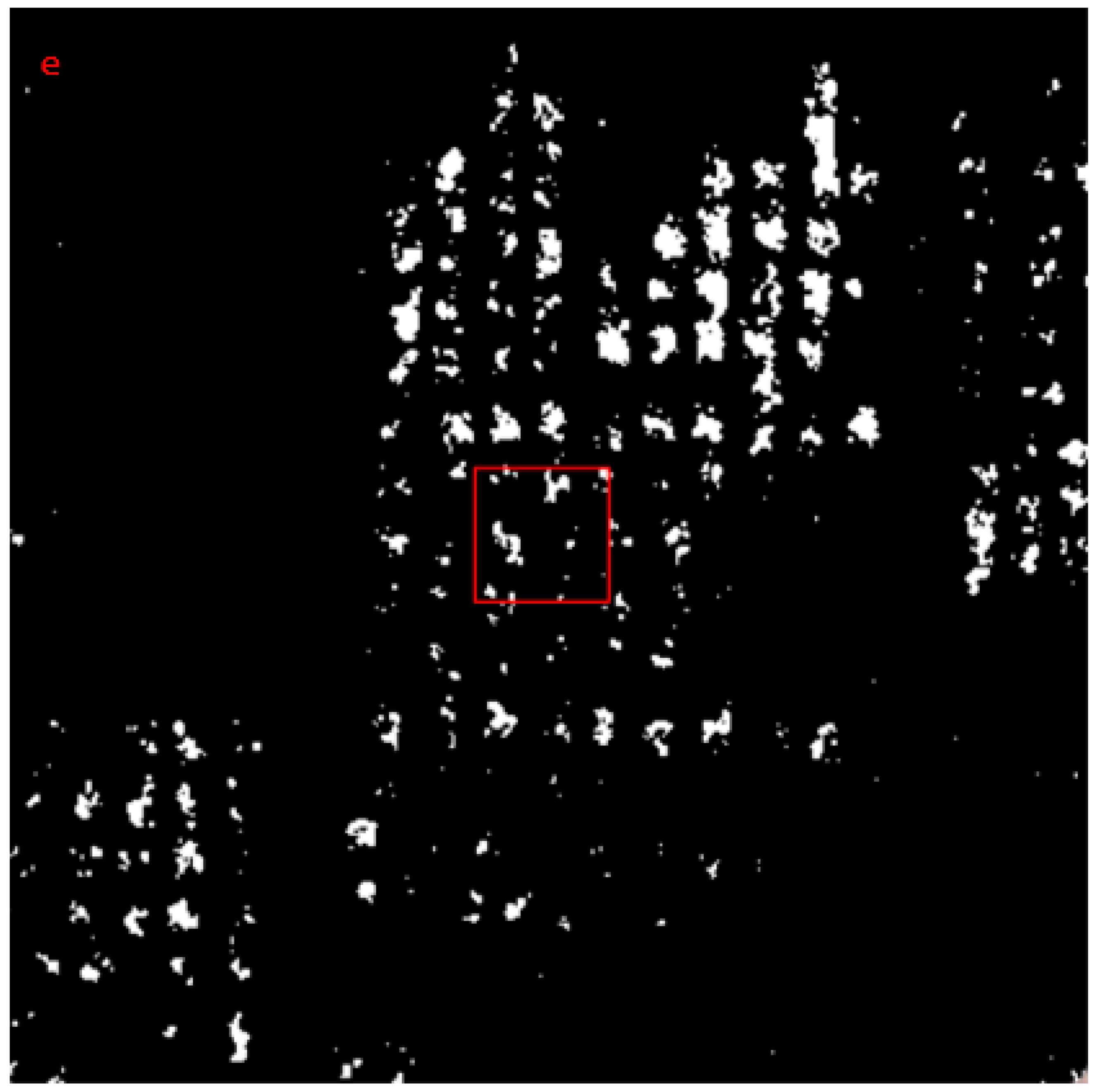
2.2.4. Ulva prolifera Extraction Based on SAR Images
2.2.5. Ulva prolifera Drift Path and Influence Range
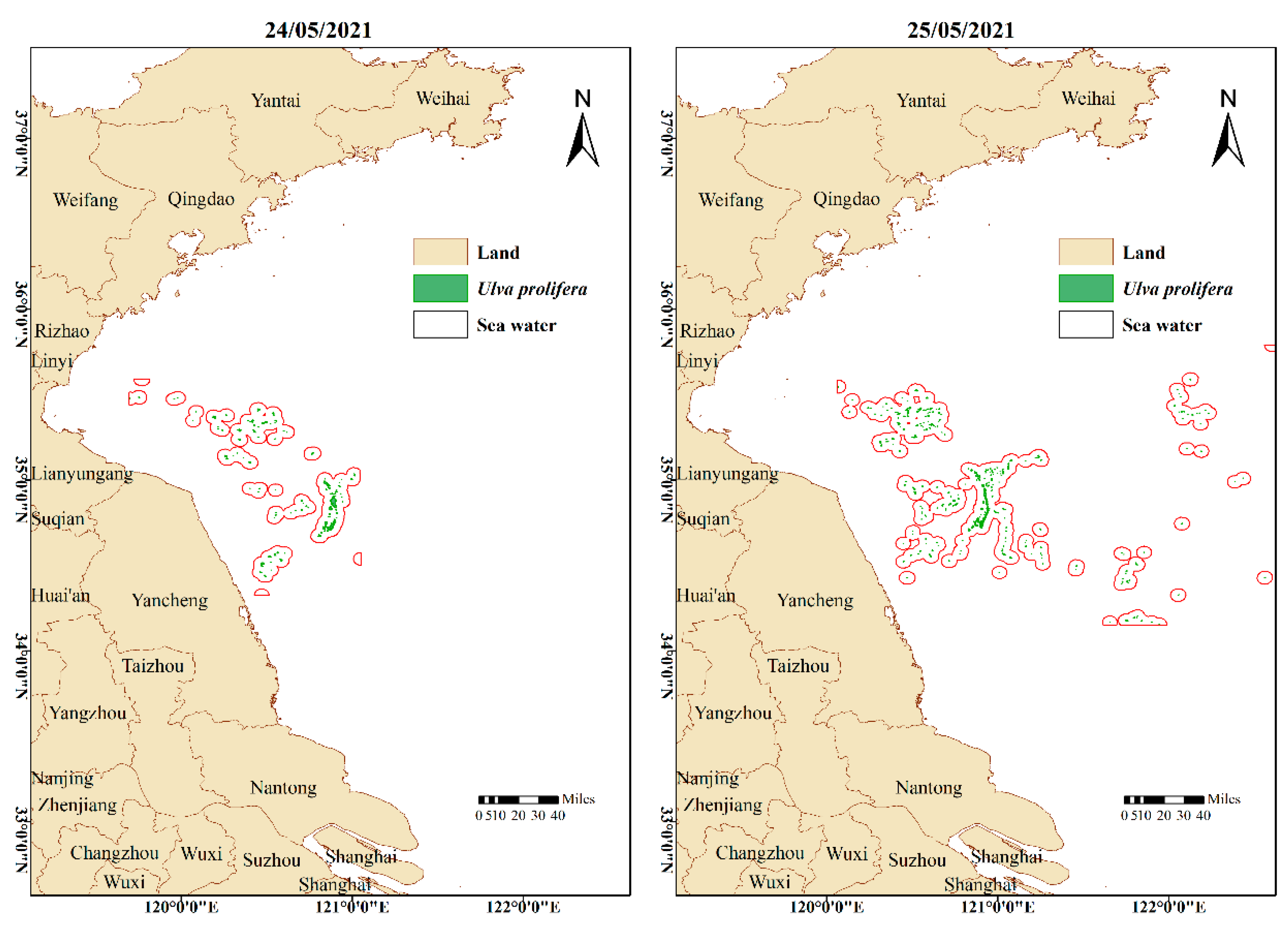
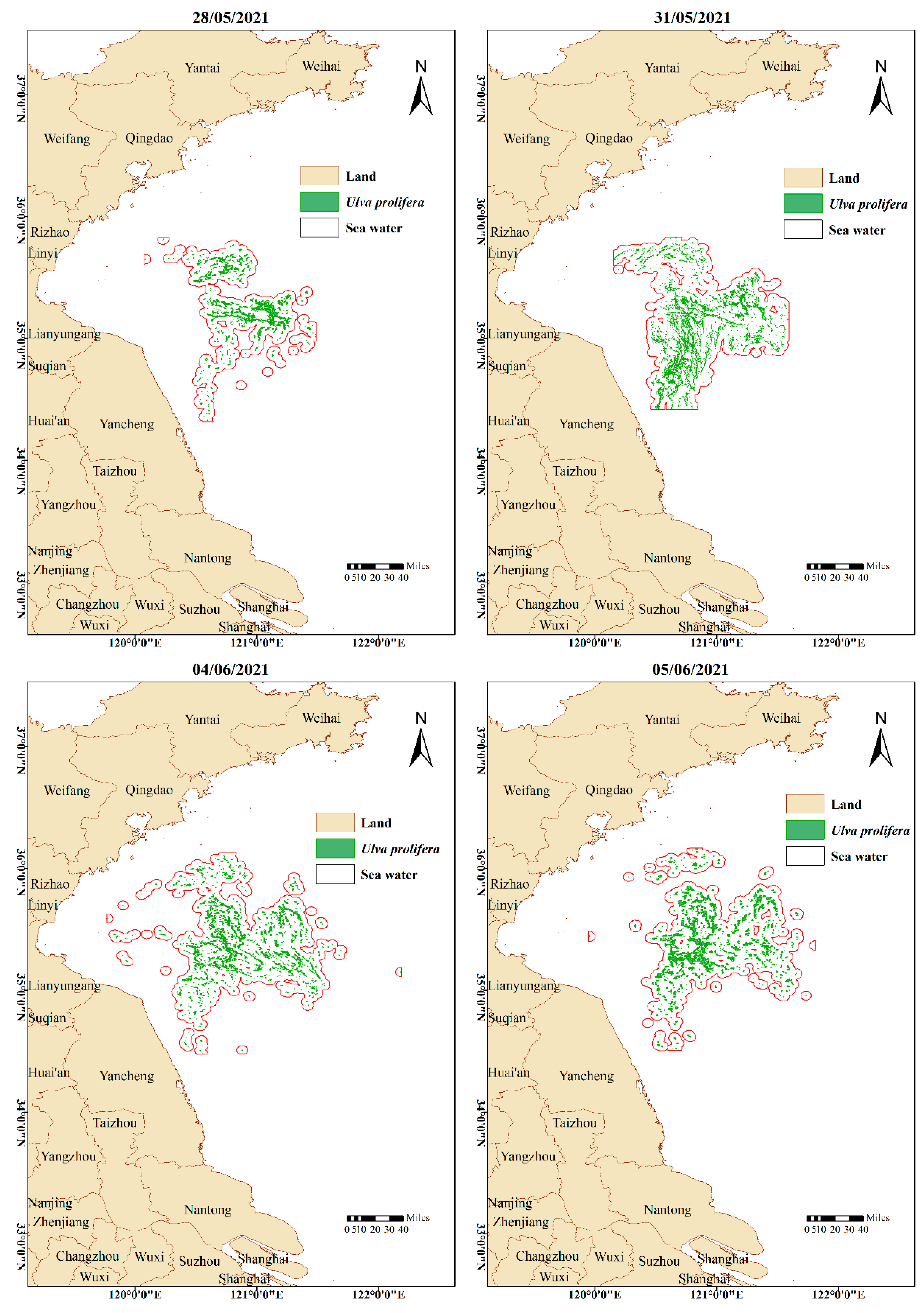
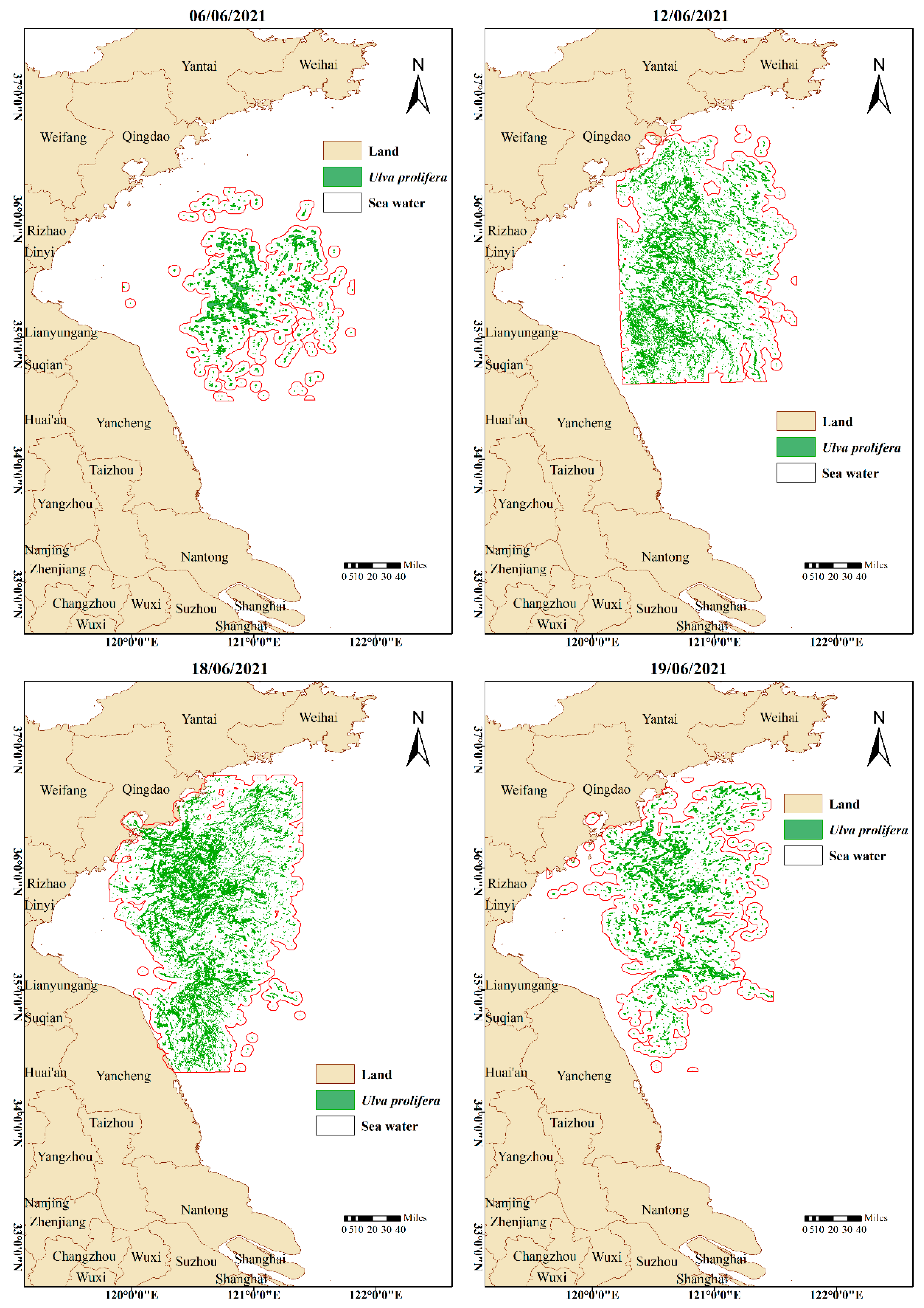
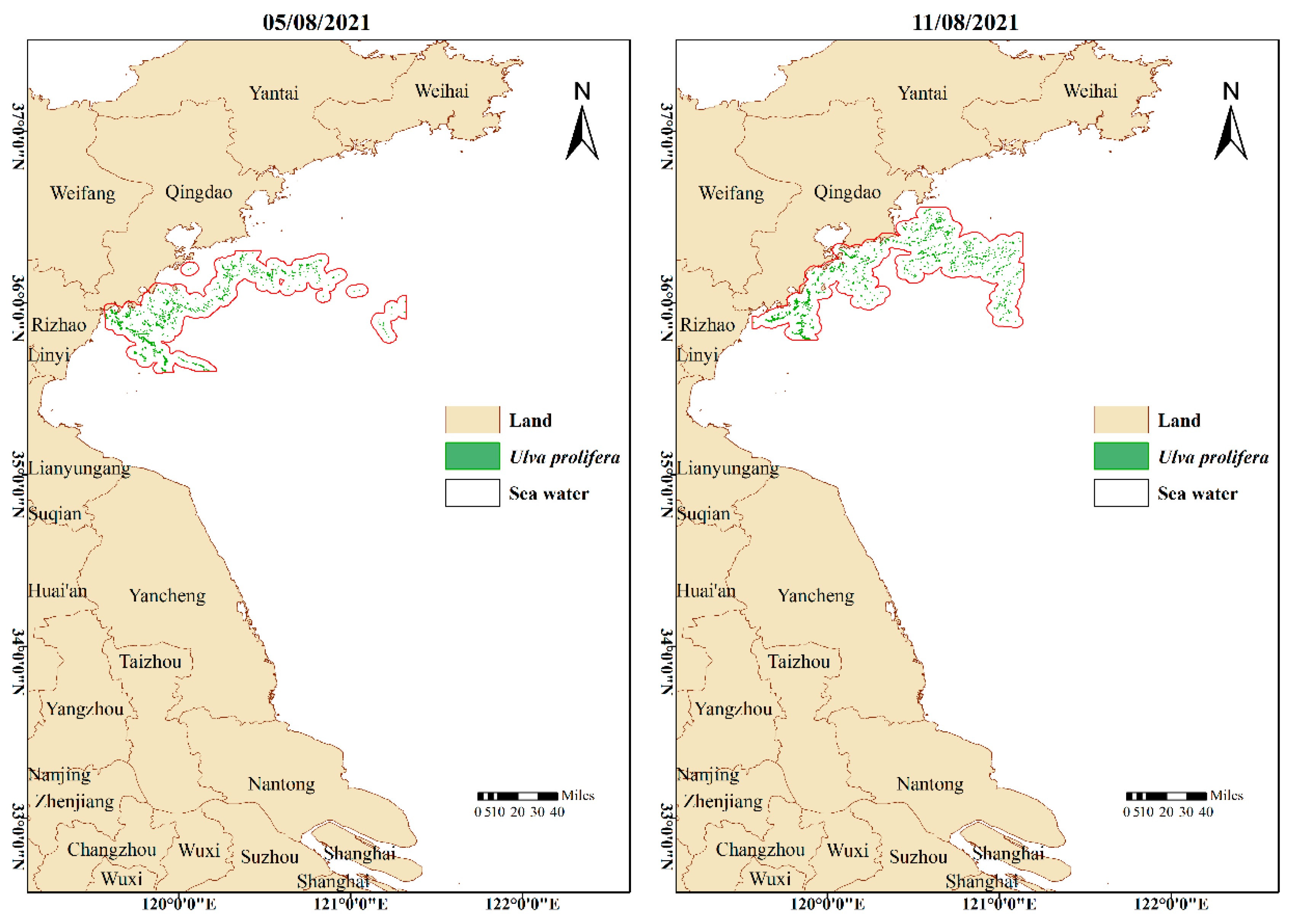
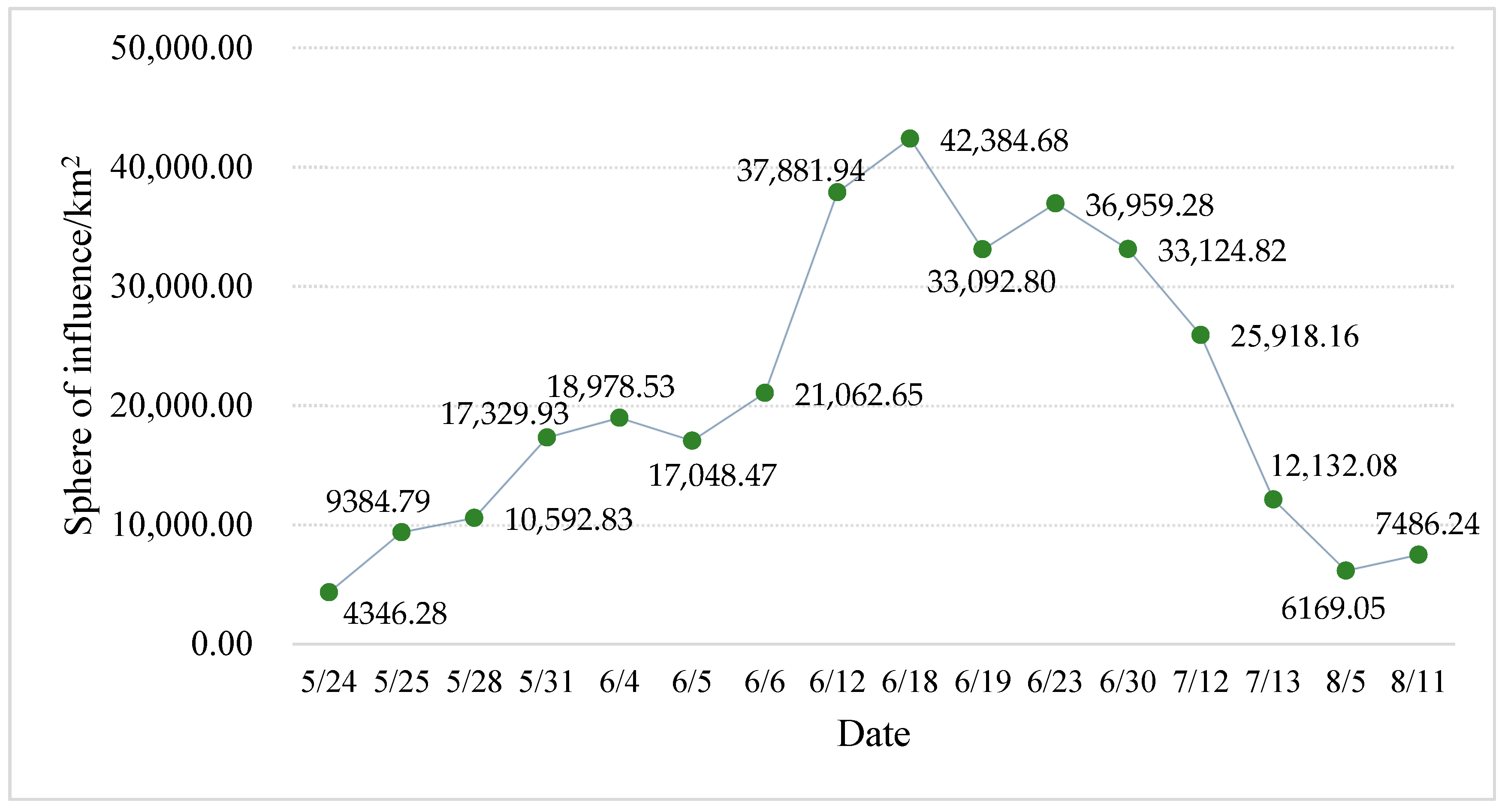
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leliaert, F.; Zhang, X.; Ye, N.; Malta, E.; Engelen, A.H.; Mineur, F.; Verbruggen, H.; De Clerck, O. Research note: Identity of the Qingdao algal bloom. Psychol. Res. 2009, 57, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, D.; Fu, M.; Yuan, C.; Yan, T. Harmful macroalgal blooms (HMBs) in China’s coastal water: Green and golden tides. Harmful Algae 2021, 107, 102061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, N.; Zhang, X.; Mao, Y.; Liang, C.; Xu, D.; Zou, J.; Zhuang, Z.; Wang, Q. ‘Green tides’ are overwhelming the coastline of our blue planet: Taking the world’s largest example. Environ. Res. 2011, 26, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.-J.; Liu, D.-Y.; Anderson, D.M.; Valiela, I. Introduction to the Special Issue on green tides in the Yellow Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 163, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pang, S.J.; Liu, F.; Shan, T.F.; Xu, N.; Zhang, Z.H.; Gao, S.Q.; Chopin, T.; Sun, S. Tracking the algal origin of the Ulva bloom in the Yellow Sea by a combination of molecular, morphological and physiological analyses. Mar. Environ. Res. 2010, 69, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, F.; Pang, S.J.; Zhao, X.B.; Hu, C.M. Quantitative, molecular and growth analyses of Ulva microscopic propagules in the coastal sediment of Jiangsu province where green tides initially occurred. Mar. Environ. Res. 2012, 74, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, L. A Preliminary Study of the Enteromorpha prolifera Drift Gathering Causing the Green Tide Phenomenon. Period. Ocean Univ. China 2008, 38, 601–604. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, D.; Mao, Y.; Li, Y.; Xue, S.; Zou, J.; Lian, W.; Liang, C.; Zhuang, Z.; Wang, Q.; et al. Settlement of vegetative fragments of Ulva prolifera confirmed as an important seed source for succession of a large-scale green tide bloom. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 2010, 56, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Keesing, J.K.; Dong, Z.; Zhen, Y.; Di, B.; Shi, Y.; Fearns, P.; Shi, P. Recurrence of the world’s largest green-tide in 2009 in Yellow Sea, China: Porphyra yezoensis aquaculture rafts confirmed as nursery for macroalgal blooms. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Keesing, J.K.; He, P.; Wang, Z.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Y. The world’s largest macroalgal bloom in the Yellow Sea, China: Formation and implications. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 129, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xiao, J.; Fan, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, D. Who made the world’s largest green tide in China?—An integrated study on the initiation and early development of the green tide in Yellow Sea. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2015, 60, 1105–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Sha, J.; Wen, R.; Li, J.; Pan, Y.; Wei, M.; Wang, H.; Wang, T.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, S. Present situation and prospect of green tide monitoring technology. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 769, 032043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.H.; Lu, J.B. Advances in the monitoring of Enteromorpha prolifera using remote sensing. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 4977–4985. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.; He, M.X. Origin and offshore extent of floating algae in olympic sailing area. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2008, 89, 302–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Zhang, A.; Wu, M. Spatial and temporal distribution characteristic of Enteromorpha in Shandong Peninsula in 2013 on the Basis of MODIS Data. Yantai Teach. Univ. J. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2015, 2, 172–177. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, H.; Lu, R.; Li, D. Remote sensing of the Yellow Sea green tide evolution in 2015. Mar. Sci. 2016, 40, 134–142. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Huang, H.; Zhang, W.; Lin, W. Distribution characteristics and dynamic mechanism of Enteromorpha prolifera in the Yellow Sea in 2018. Mar. Sci. 2020, 44, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Song, D.-B.; Gao, Z.-Q.; Xu, F.-X.; Ai, J.-Q.; Ning, J.-C.; Shang, W.-T.; Jiang, X.-P. Spatial and temporal variability of the green tide in the south Yellow Sea in 2017 deciphered from the GOCI image. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2018, 49, 1068–1074. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Sun, D.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S.; Qiu, Z.; He, Y. Remote-sensing monitoring of green tide and its drifting trajectories in Yellow Sea Based on observation data of geostationary ocean color imager. Acta Opt. Sin. 2020, 40, 7–19. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.Q.; Ma, W.D.; Wang, X.L.; Yao, Y.J.; Wu, D. Remote Sensing Monitoring Hab in Yellow Sea by HJ1-CCD. Environ. Monit. China 2015, 31, 161–165. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, D.; Li, J.; Qiu, Z.; Wang, S.; He, Y. Remote sensing algorithm for detecting green tide in china coastal waters based on GF1-WFV and HJ-CCD data. Acta Opt. Sin. 2016, 36, 0601004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Wu, C.; Lu, L.; Wang, X. A new algorithm predicting the end of growth at five evergreen conifer forests based on nighttime temperature and the enhanced vegetation index. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 144, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Fang, Z.; Cui, X.; Liang, J.; Song, X. Spatiotemporal patterns and morphological characteristics of ulva prolifera distribution in the Yellow Sea, China in 2016–2018. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, R.K.; Prasad, S.; Nadham, T.S.V.; Rao, G.H. Relative sensitivity of district mean RVI and NDVI over an agrometeorological zone. Adv. Space Res. 1993, 13, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Fang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Liang, J.; Song, X. Multi-source evidence data fusion approach to detect daily distribution and coverage of Ulva prolifera in the Yellow Sea, China. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 115214–115228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C. A novel ocean color index to detect floating algae in the global oceans. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2118–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q.; Hu, C. Mapping macroalgal blooms in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea using HJ-1 and Landsat data: Application of a virtual baseline reflectance height technique. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 178, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Wang, M. Green macroalgae blooms in the Yellow Sea during the spring and summer of 2008. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ciappa, A.; Pietranera, L.; Coletta, A.; Jiang, X. Surface transport detected by pairs of COSMO-SkyMed ScanSAR images in the Qingdao region (Yellow Sea) during a macro-algal bloom in July 2008. J. Mar. Syst. 2010, 80, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Zou, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhu, H. Application study on quick extraction of Entermorpha prolifera information using SAR data. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2009, 31, 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, H.; Perrie, W.; Liu, Q.; He, Y. Detection of macroalgae blooms by complex SAR imagery. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 78, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xing, Q.; An, D.; Meng, L.; Zheng, X.; Jiang, B.; Liu, H. Effects of Spatial Resolution on the Satellite Observation of Floating Macroalgae Blooms. Water 2021, 13, 1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Satellite | Sensor | Resolution/m | Band | Product | Revisit Cycle/d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TERRA/AQUA | MODIS | 250 | red/near-infrared | L1-B | 1 |
| Sentinel-1A/B | SAR | 5 × 20 | C | L1-GRD (VV) | 12 |
| Data Time | |||||
| Optics | 24/5/2021 25/5/2021 28/5/2021 4/6/2021 5/6/2021 6/6/2021 19/6/2021 23/6/2021 | ||||
| Microwave | 31/5/2021 12/6/2021 18/6/2021 30/6/2021 12/7/2021 24/7/2021 5/8/2021 11/8/2021 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Y.; Wong, K.; Tsou, J.Y.; Zhang, Y. Investigating Spatial Distribution of Green-Tide in the Yellow Sea in 2021 Using Combined Optical and SAR Images. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10020127
Ma Y, Wong K, Tsou JY, Zhang Y. Investigating Spatial Distribution of Green-Tide in the Yellow Sea in 2021 Using Combined Optical and SAR Images. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2022; 10(2):127. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10020127
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Yufei, Kapo Wong, Jin Yeu Tsou, and Yuanzhi Zhang. 2022. "Investigating Spatial Distribution of Green-Tide in the Yellow Sea in 2021 Using Combined Optical and SAR Images" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 10, no. 2: 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10020127
APA StyleMa, Y., Wong, K., Tsou, J. Y., & Zhang, Y. (2022). Investigating Spatial Distribution of Green-Tide in the Yellow Sea in 2021 Using Combined Optical and SAR Images. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 10(2), 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10020127








