Study on Buried Depth Protection Index of Submarine Cable Based on Physical and Numerical Modeling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Damage Mechanism of Anchoring to Submarine Cable
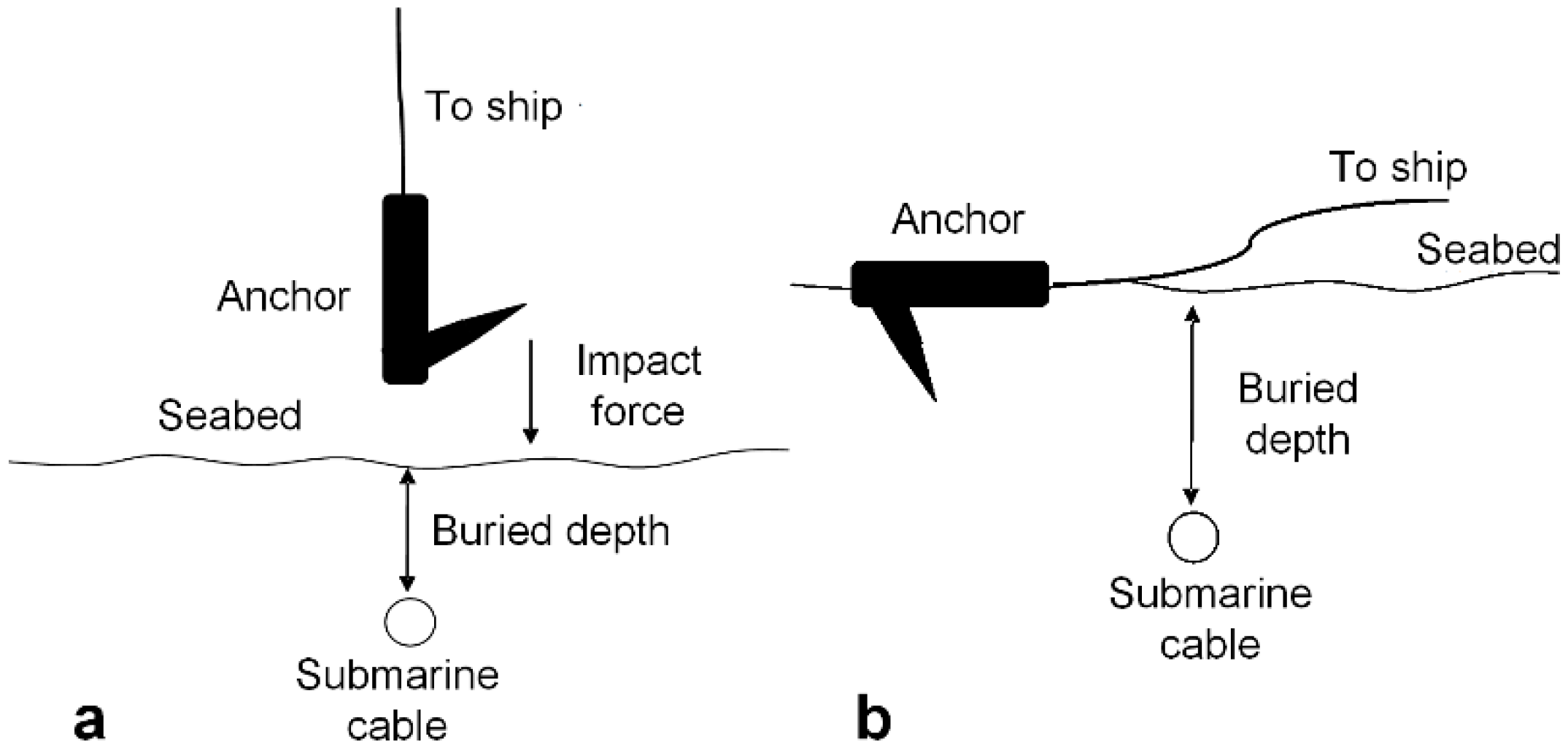
2.1. Impact Damage Analysis
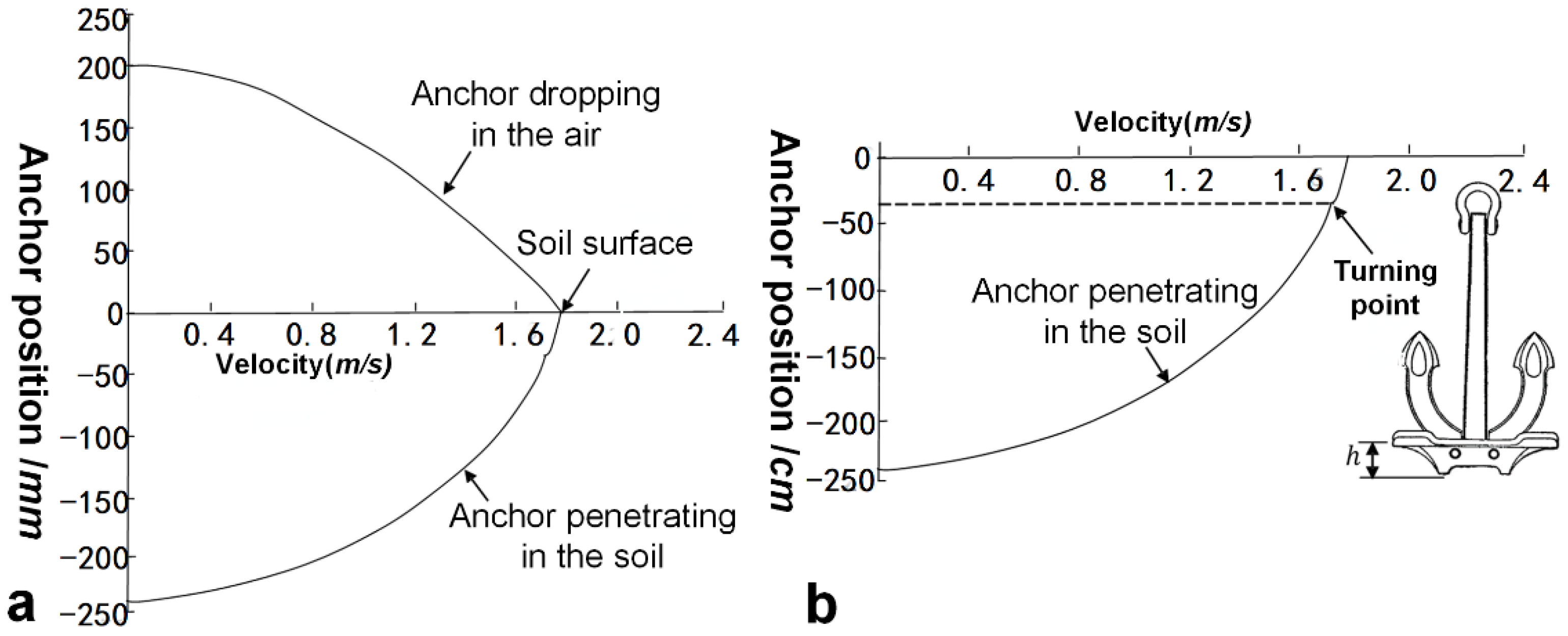
2.1.1. Analysis of the Dropping Velocity of an Anchor
2.1.2. Analysis the Impact Energy of an Anchor
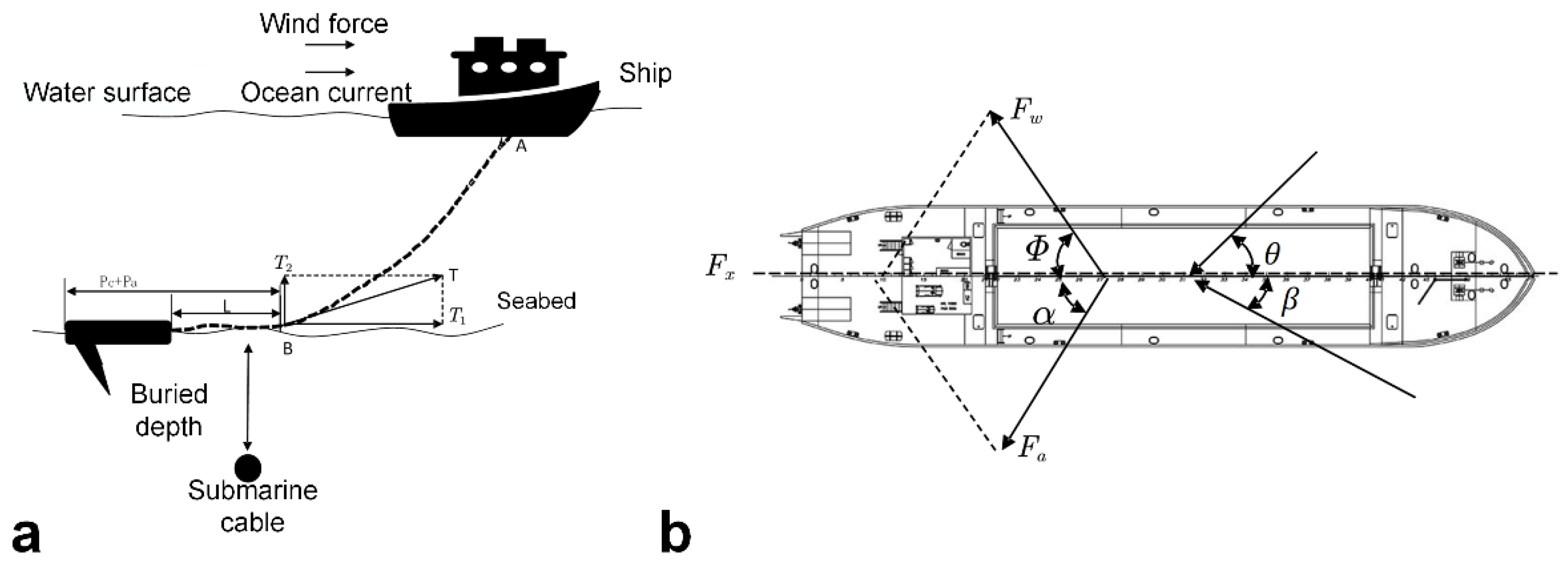
2.2. Drag Damage Analysis
2.2.1. Drag Force
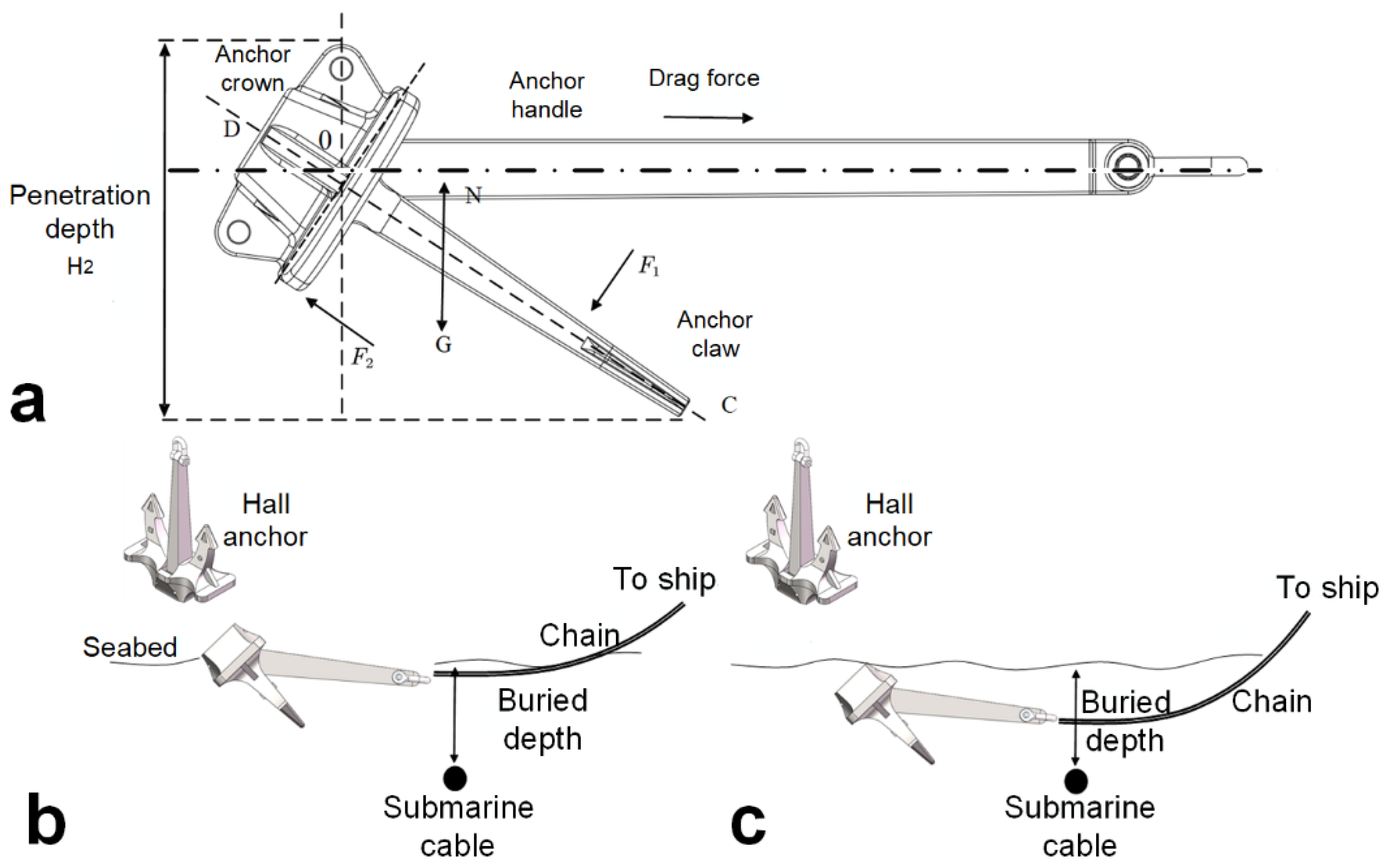
2.2.2. Penetration Depth of Anchor Dragging
- (1)
- The anchor claw is fully inserted into the soil: .
- (2)
- The anchor crown is fully inserted into the soil:
2.3. Comparison of the Impact Damage and Drag Damage on Submarine Cable
3. Numerical Simulation Analysis
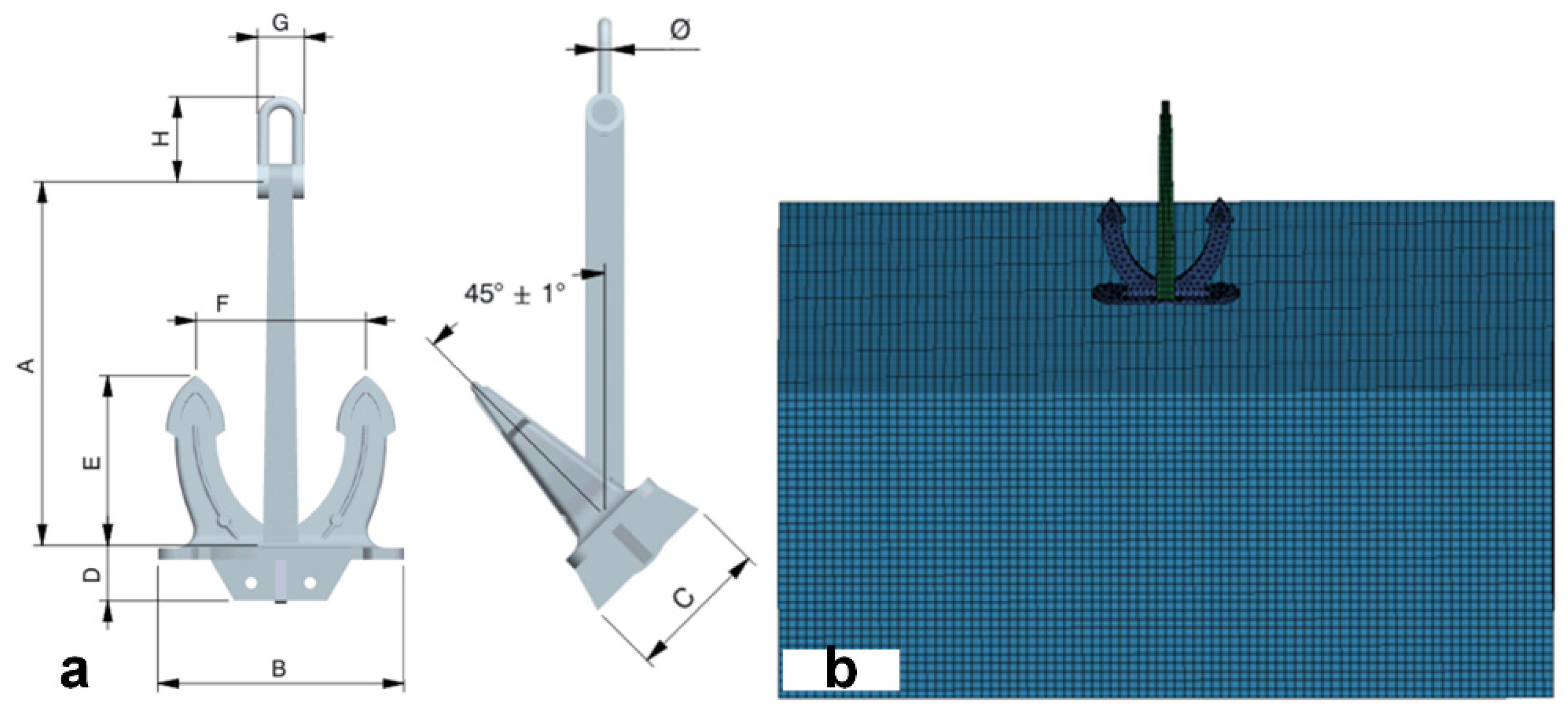
3.1. Finite Element Method
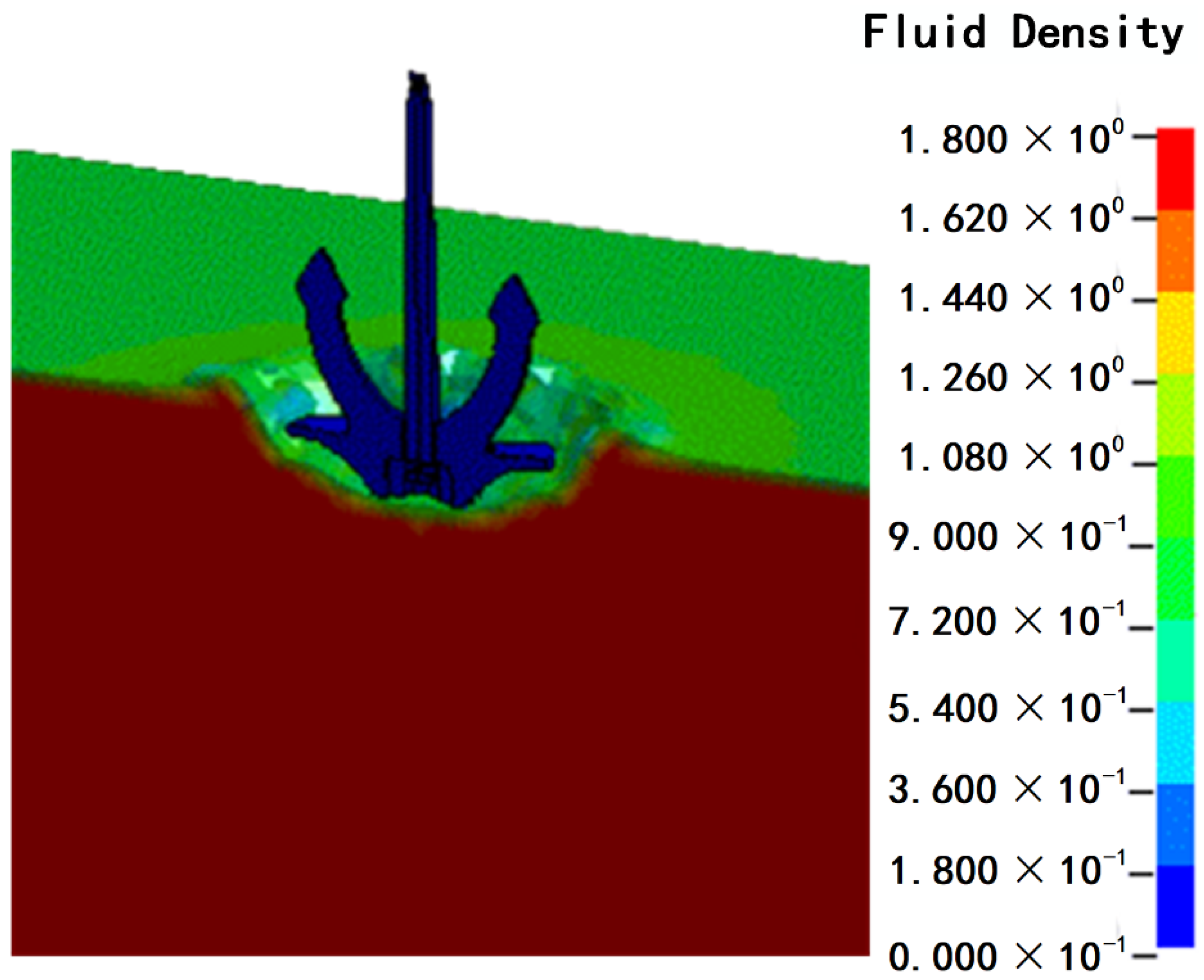
3.2. Simulation Results
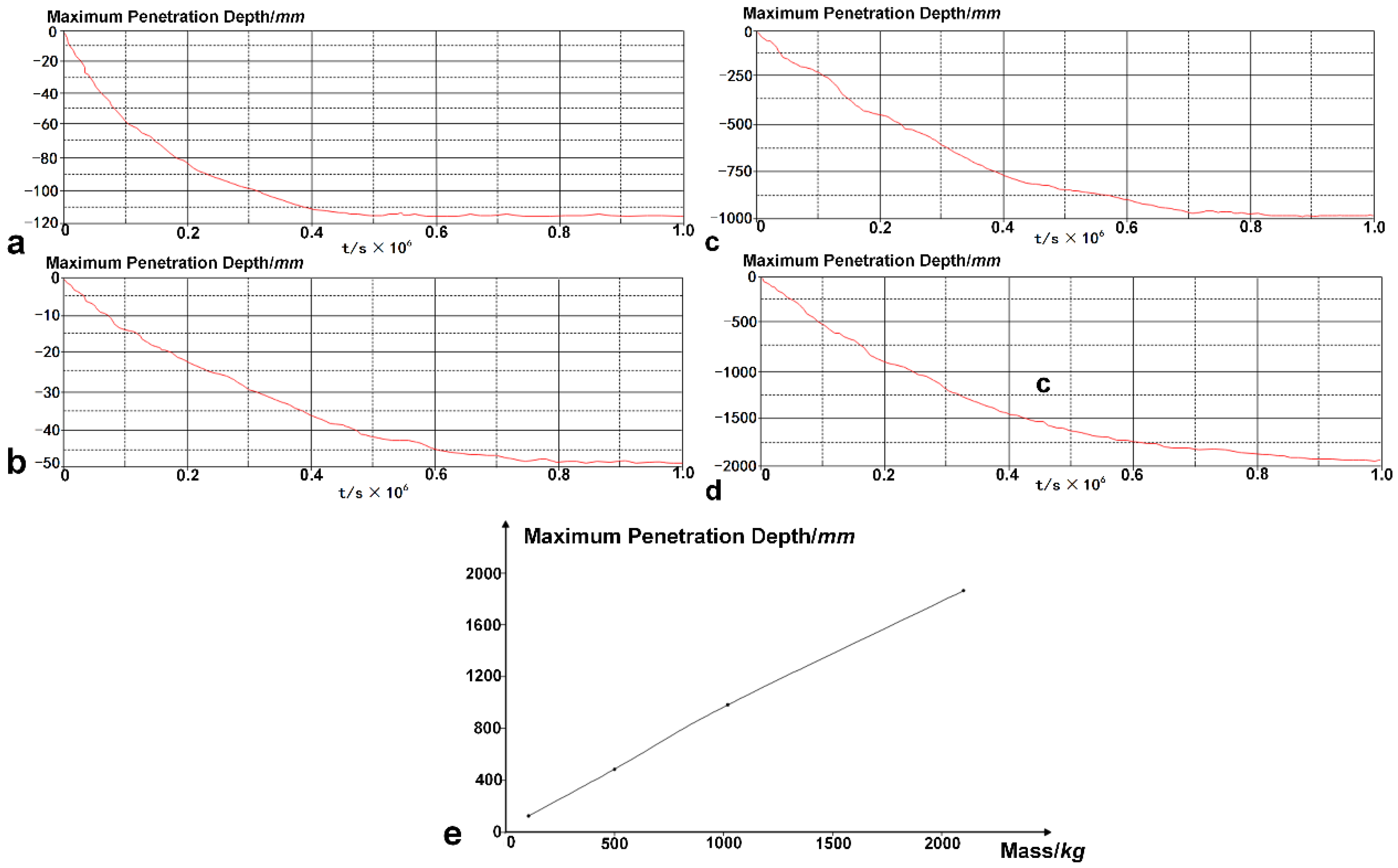
3.2.1. Influence of Anchor Weight on The Penetration Depth of the Anchor
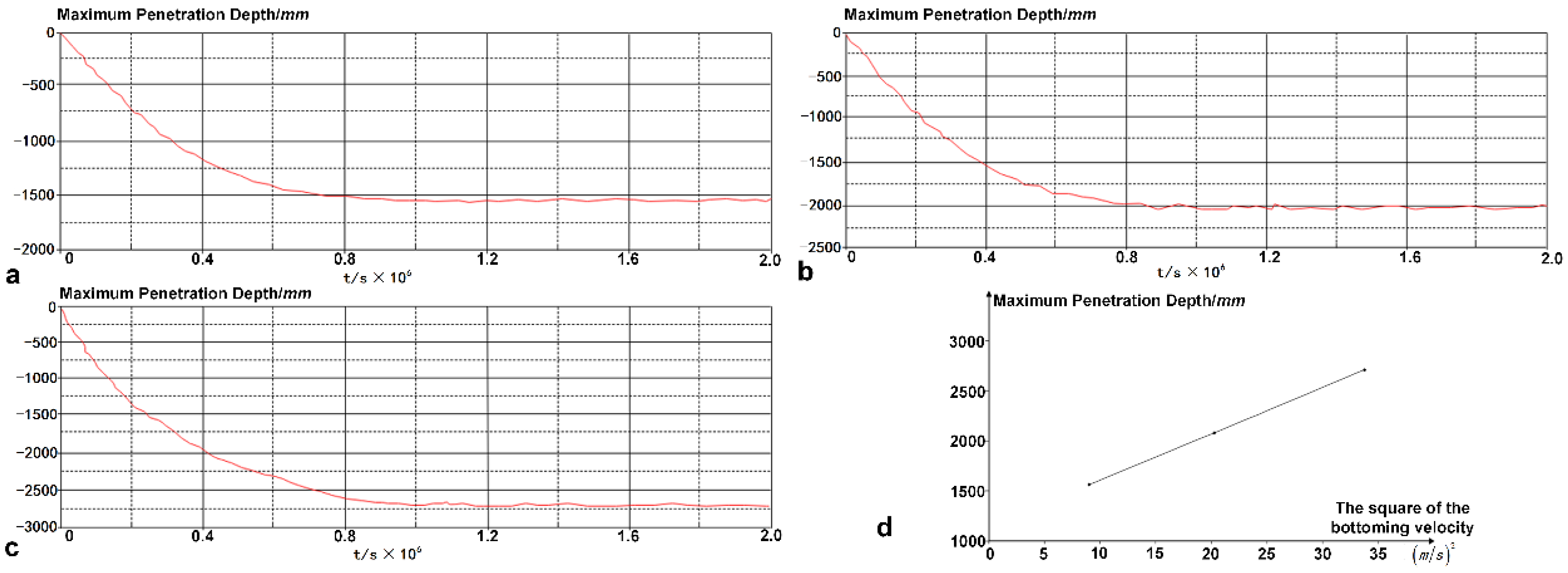
3.2.2. Influence of Bottoming Velocity on the Penetration Depth of the Anchor
4. Experiment and Results
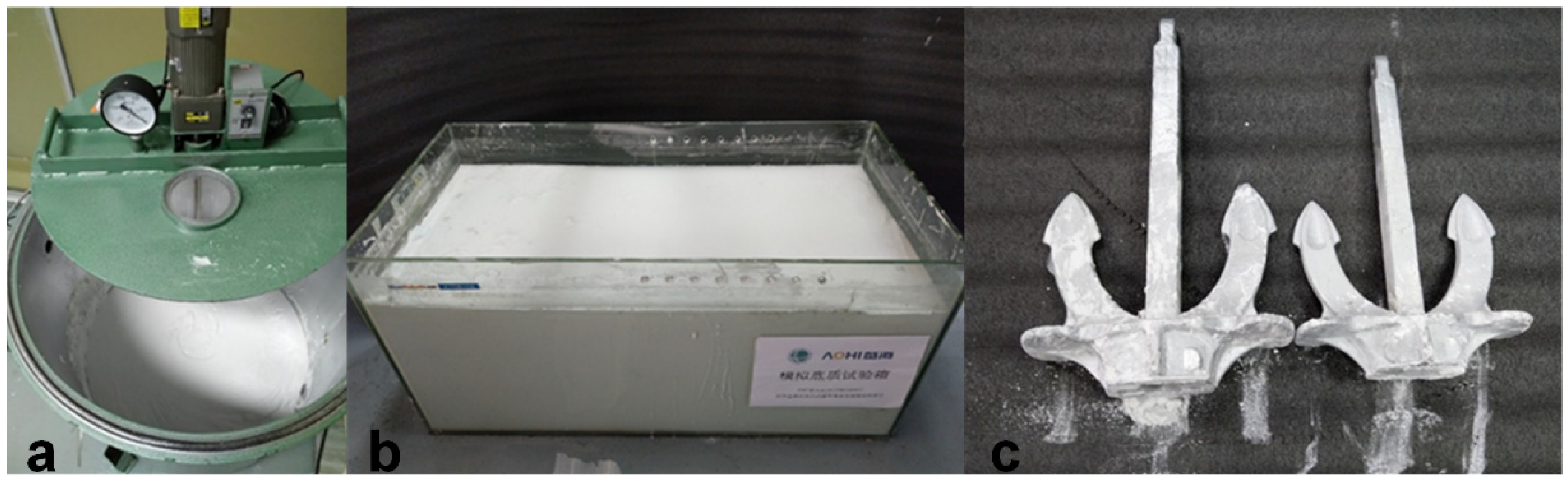
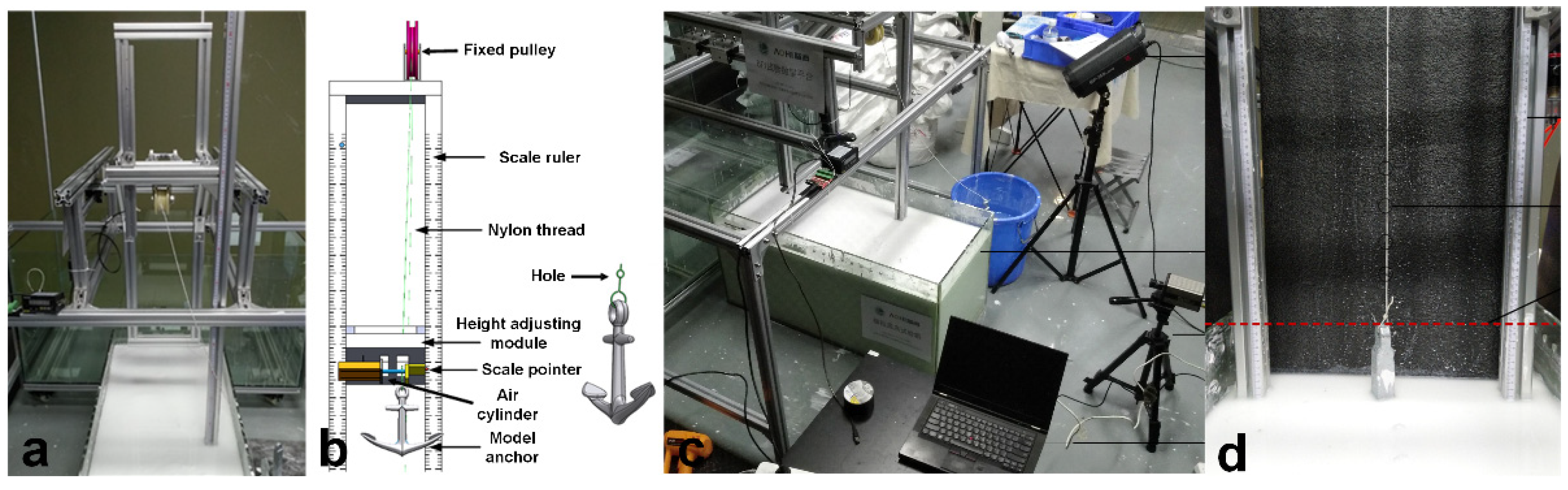
4.1. Design of Experiment Platform
4.1.1. Soil and Anchor Model
- (1)
- Soil preparation
- (2)
- Model anchor
4.1.2. Experiment Platform
4.2. Experimental Cases
4.3. Experimental Results
4.3.1. Static Scouring Experiment
4.3.2. The Penetration Depth Versus the Anchor Weight
4.3.3. Results Analysis
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The parametric study from the model tests and numerical simulation indicates that the anchor penetration depth is affected by the bottom velocity, impact energy, and anchor mass.
- (2)
- The analytical model based on impact and drag mechanism, which is put forward based on Energy conservation law and Newton’s second law, can help to analyze each force subjected by the anchor when dropping and dragging in the soil.
- (3)
- The maximum penetration depth of the 2100 kg anchor in the test and the simulation analysis is 2.53 m and 2.77 m, respectively. Therefore, the buried depth protection index of the submarine cable in Zhoushan Island is recommended to be 3 m.
- (4)
- In future research, the influence of different anchors (e.g., types, size, etc.) on the penetration depth of the seabed soil should be considered, and the penetration depth of the anchor should be studied in the actual submarine cable project in Zhoushan area.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Randolph, M.F.; Gaudin, C.; Gourvenec, S.M.; White, D.J.; Boylan, N.; Cassidy, M.J. Recent advances in offshore geotechnics for deep water oil and gas developments. Ocean Eng. 2011, 38, 818–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Osthoff, D.; Heins, E.; Grabe, J. Impact on submarine cables due to anchor-soil interaction. Geotechnik 2017, 40, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, E. CNN. Vandals Cut San Francisco Area Fiber Optic Lines for 11th Time in a Year. 1 July 2015. Available online: https://edition.cnn.com/2015/07/01/tech/california-fiber-optic-cable-cuts/index.html (accessed on 10 December 2021).
- Wu, A.-G.; Yuan, Z.-L.; Gong, Y.-Q. Overview of Construction Technology for Deep-buried Laying of Submarine Cables in China. Zhejiang Electr. Power 2015, 3, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Det Norske Veritas. DNVGL-RP-F107 Risk Assessment of Pipeline Protection. May 2017 ed. Available online: https://oilgas.standards.dnvgl.com/download/dnvgl-rp-f107-risk-assessment-of-pipeline-protection (accessed on 10 December 2021).
- Luger, D.; Harkes, M. Anchor Tests German Bight: Test Setup and Results; Project Rep., 1207052-002-GEO-0003; Deltares: Delft, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Grabe, J.; Qiu, G.; Wu, L. Numerical simulation of the penetration process of ship anchors in sand. Geotechnik 2015, 38, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabe, J.; Wu, L. Coupled-Eulerian-Lagrangian simulation of the penetration and braking behaviour of ship anchors in clay. Geotechnik 2016, 39, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Hossain, M.S.; Lee, J. Dynamic Installation of a Torpedo Anchor in Two-layered Clays. Can. Geotech. J. 2017, 55, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.-H.; Hossain, M.S.; Wang, D.; Randolph, M.F. Numerical investigation of dynamic installation of torpedo anchors in clay. Ocean Eng. 2015, 108, 820–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Yu, G. Penetration depth of torpedo anchor in cohesive soil by free fall. Ocean Eng. 2016, 116, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xu, K.; Zhao, Y. Numerical investigation on the penetration of gravity installed anchors by a coupled Eulerian–Lagrangian approach. Appl. Ocean Res. 2016, 60, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Duan, M.; Gao, Q.; Jia, X.; Huang, J. A prediction method for anchor penetration depth in clays. Ships Offshore Struct. 2016, 11, 782–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, M.-X.; Yu, G.-L. Penetration depth of torpedo anchor in two-layered cohesive soil bed by free fall. China Ocean Eng. 2018, 32, 706–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Chen, F.; Xu, W. Experimental study and calculation method of falling anchor depth under sand soil. South. Energy Constr. 2018, 5, 222–227. [Google Scholar]
- Zha, M.; Wang, Y.-J.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Fan, X.-M. The Burial Depth of Submarine Cable. Opt. Fiber Electr. Cable Appl. 2015, 2, 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.-S. Study on the Depth of Penetration of Anchors. Master’s Thesis, Dalian Maritime University, Dalian, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.-P. Submarine Cable Mechanical Impact Structural Damage Analysis. Master’s Thesis, China University of Petroleum, Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Katteland, L.H.; Oygarden, B. Risk analysis of dropped objects for deep water development. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Offshore Mechanics & Arctic Engineering, Copenhagen, Denmark, 18–22 June 1995; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 1995; Volume 2, pp. 443–450. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.-S.; Yan, S.-W.; Yan, Y.; Chen, G.; He, X.-Q. Numerical Analysis on Dragging Anchors in Soil Based on CEL. Chin. J. Undergr. Space Eng. 2017, 13, 1573–1578. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, D.; Pan, L. Application of integral hoisting technology of VindebyTunoeKnob in Zhoushan sea area. Ocean Dev. Manag. 2018, 35, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.H.; Liu, F.; Jiang, J.; Liu, P.; Cui, Z.M. Continuous arc-shaped laying technique for large diameter flexible pipeline in complicated sea conditions. Pet. Eng. Constr. 2018, 44, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Xuan, K. The Study on Anchoring Damage to Subsea Pipelines. Master’s Thesis, Dalian Maritime University, Dalian, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Wang, J.-Y.; Zheng, Z.-Y.; Li, Y.-Y. Influence of Dragging Anchor upon the Buried Depth of Submarine Cable. Ship Ocean Eng. 2018, 1, 147–150. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, X.-B. Research on Settlement Characteristics and Calculation of Immersed Tube Tunnel with Soft Foundation and High Siltation. Ph.D Thesis, Chang’an University, Xi’an, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, K.-B.; Yang, T.; Shan, T.-K.; Meng, Q.-J.; Li, Z.-G. Study on the Adsorption Forces of Seabed Platform on Muddy Seafloor Based on ANSYS. J. Ocean Technol. 2017, 36, 58–62. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.-H.; Pan, Y.-J.; Pan, G.-F.; Chen, P.-X. Statistic analysis of physical and mechanical indices of quaternary marine sediments in the western sea area between Zhoushan and Daishan Island. Mar. Sci. Bull. 2011, 30, 557–561. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, B.-L. Research on the Jetting Arm of Jetting Propelled ROV Trencher and Its Jetting Process. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Han, C.-C.; Liu, J. Model tests on the penetration depth of gravity installed plate anchors. Ocean Eng. 2016, 5, 92–100. [Google Scholar]
- Han, C.-C.; Chen, X.-J.; Liu, J. Model tests on penetration depth of hall anchor. Ocean Eng. 2018, 5, 90–98. [Google Scholar]





| Anchor Mass/t | Horizontal Projection Area/m2 | Aerial Height/m | Water Depth/m | Measured Velocity/ms−1 | Calculated Velocity/ms−1 | Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.26 | 0.6 | 0 | 17.7 | 4.5 | 5.39 | 19.8% |
| 1.26 | 0.6 | 1.6 | 17.7 | 4.5 | 5.39 | 19.8% |
| 6.84 | 1.9 | 0 | 17 | 6 | 7.01 | 16.8% |
| 6.84 | 1.9 | 3.4 | 17 | 6.8 | 7.07 | 4% |
| 6.84 | 1.9 | 6.5 | 17 | 6.9 | 7.12 | 3.2% |
| Parameters | Value | Parameters | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1025 kg/m3 | 1469.53 m2 | ||
| 1.29 kg/m3 | d | 19 m | |
| v | 4 m/s | 40° | |
| 0.5 m/s | 0.15 | ||
| L | 313 m | 1.733 | |
| 348.47 m2 |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| 18.9 mm2 | |
| 35 kN | |
| 51 | |
| 0.25 |
| Mass/kg | A/mm | E/mm | D/mm | B/mm | F/mm | C/mm | H/mm | G/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2100 | 2093 | 1136 | 249 | 1614 | 1136 | 628 | 340 | 256 |
| Density | Shear Modulus (MPa) | Poisson’s Ratio | Cohesion (MPa) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.920 | 4.445 | 0.340 | 0.477 | 0.010 |
| Water Content (W%) | Porosity Ratio | Liquid Limit (WL/%) | Plasticity Index (IP/%) | Compression Modulus (MPa) |
| 40.7% | 1.163 | 36.300 | 15.800 | 2.810 |
| Case | Mass (kg) | Simulation Velocity (m/s) | Limit Dropping Velocity (m/s) | Maximum Penetration Depth (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1-1 | 10 | 4 | 4.982 | 116.85 |
| F1-2 | 500 | 4 | 5.235 | 484.58 |
| F1-3 | 1020 | 4 | 5.421 | 982.11 |
| F1-4 | 2100 | 4 | 5.812 | 1863.01 |
| Case | Mass (kg) | Bottoming Velocity (m/s) | Maximum Penetration Depth (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| F2-1 | 2100 | 3 | 1564.83 |
| F2-2 | 2100 | 4.5 | 2082.15 |
| F2-3 | 2100 | 5.812 | 2712.64 |
| Parameter | Length | Area | Weight | Velocity | Penetration Depth | Shear Strength |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scale | ||||||
| Similarity | ||||||
| Test model |
| Parameter | Test Model | Original Model |
|---|---|---|
| scale | 1 | 6.54 |
| Anchor weight | 5.1 kg, 7.5 kg | 1440 kg, 2100 kg |
| Penetration velocity | 2.268 m/s | 5.8 m/s |
| Shear strength | 4.59 kPa | 30 kPa |
| Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|
| Proportion | 2.61 |
| Liquid limit | 65% |
| Plastic limit | 33% |
| Mass (kg) | A (mm) | E (mm) | D (mm) | B (mm) | F (mm) | C (mm) | H (mm) | G (mm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2100 kg anchor | 2100 | 2093 | 1136 | 249 | 1614 | 1136 | 628 | 340 | 256 |
| 7.5 kg model anchor | 322 | 175 | 38 | 252 | 175 | 96 | 52 | 39 | 322 |
| Group | Case | Mass (kg) | Dropping Height (mm) | Bottoming Velocity (m/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | P1-1 | 7.5 | 13.0 | 0.5 |
| P1-2 | 7.5 | 51.0 | 1.0 | |
| P1-3 | 7.5 | 114.8 | 1.5 | |
| P1-4 | 7.5 | 204.1 | 2.0 | |
| P1-5 | 7.5 | 262.0 | 2.268 | |
| II | P2-1 | 7.5 | 114.8 | 1.5 |
| P2-2 | 7.5 | 262.0 | 2.268 | |
| P2-3 | 5.1 | 114.8 | 1.5 | |
| P2-4 | 5.1 | 262.0 | 2.268 |
| Case | Bottoming Velocity (m/s) | Simulation Velocity (m/s) | Dropping Height (mm) | Modified Dropping Height (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1-1 | 0.5 | 1.279 | 13.0 | 29.0 |
| P1-2 | 1.0 | 2.557 | 51.0 | 69.0 |
| P1-3 | 1.5 | 3.836 | 114.8 | 133.0 |
| P1-4 | 2.0 | 5.115 | 204.1 | 219.0 |
| P1-5 | 2.268 | 5.8 | 262.0 | 282.0 |
| Case | Average Penetration Depth in Model Tests (mm) | Penetration Depth in Prototype (m) | Penetration Depth in Simulation (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| P1-1 | 119.3 | 0.78 | 0.98 |
| P1-2 | 123.3 | 0.81 | 1.92 |
| P1-3 | 164.6 | 1.078 | 1.34 |
| P1-4 | 243.0 | 1.59 | 2.28 |
| P1-5 | 387.3 | 2.53 | 2.71 |
| Case | Average Penetration Depth in Model Tests (mm) | Penetration Depth in Prototype (m) | Penetration Depth in Simulation (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| P2-1 | 164.67 | 1.078 | 0.98 |
| P2-2 | 387.33 | 2.53 | 2.71 |
| P2-3 | 107.00 | 0.70 | 0.81 |
| P2-4 | 183.67 | 1.20 | 1.41 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, X.; Ge, Y.; Lu, Z.; Cao, C.; Zhou, P.; Li, S.; Chen, J. Study on Buried Depth Protection Index of Submarine Cable Based on Physical and Numerical Modeling. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10020137
Zheng X, Ge Y, Lu Z, Cao C, Zhou P, Li S, Chen J. Study on Buried Depth Protection Index of Submarine Cable Based on Physical and Numerical Modeling. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2022; 10(2):137. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10020137
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Xinlong, Yongqiang Ge, Zhifei Lu, Chen Cao, Peng Zhou, Shiqiang Li, and Jiawang Chen. 2022. "Study on Buried Depth Protection Index of Submarine Cable Based on Physical and Numerical Modeling" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 10, no. 2: 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10020137
APA StyleZheng, X., Ge, Y., Lu, Z., Cao, C., Zhou, P., Li, S., & Chen, J. (2022). Study on Buried Depth Protection Index of Submarine Cable Based on Physical and Numerical Modeling. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 10(2), 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10020137








