Abstract
To investigate tetrodotoxin (TTX) retention by the toxic goby Yongeichthys criniger, rearing experiments feeding nontoxic diets were conducted using 12 (Group I) and 17 (Group II) specimens collected from a natural environment. The specimens were reared in an aquarium with aeration and fed a diet lacking TTX for 60 days. Specimens were removed at 0, 20, 40, and 60 days (Group I) or 0, 30, and 60 days (Group II) after initiation of rearing. Liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry revealed that whole-body concentrations and amounts of TTX decreased with increasing rearing duration in Group I. There were similar decreases in Group II, but the trend differed among tissues; the concentrations and amounts of TTX in the skin exhibited the greatest decreases. The results imply that Y. criniger has low TTX retention ability.
1. Introduction
Tetrodotoxin (TTX) is a potent neurotoxin long thought to be unique to pufferfish. However, it is present in diverse marine phyla; among fish, the goby Yongeichthys criniger and pufferfish have TTX [1]. In Japan, Y. criniger inhabits estuarine areas of the Nansei Islands, which have mature mangrove forests [2,3]. In the Okinawa/Amami region, the goby has long been known to be toxic [4], and its toxin was confirmed to be TTX by Noguchi and Hashimoto [5]. Like the marine pufferfish, the goby takes up TTX by ingesting benthic TTX-bearing organisms and accumulates it in certain tissues [1], but it is unclear whether the goby accumulates and retains or eliminates TTX by the same or a different mechanism as the pufferfish. Therefore, the absorption, transportation, accumulation, retention, and elimination of TTX in Y. criniger and pufferfish warrant investigation.
Like marine pufferfish of the genus Takifugu, Y. criniger accumulates a large amount of TTX in the skin and ovary, the latter increasing with maturation [6,7,8,9]. Y. criniger accumulates TTX in muscle and testis, where it is rarely detected in Takifugu [6,7,8,9,10]. This is similar to the brackish water pufferfish, Chelonodon patoca [11]. Elimination of TTX in Y. criniger has been reported via the skin and ovaries. A toxicity equivalent to 3.1–187 µg of TTX was detected in gauze used to wipe the skin of Y. criniger [8,9,12]. Marine pufferfish also eliminate TTX from their skin [13,14]. Toxicity has been detected in the ovulated eggs of Y. criniger [15], indicating that TTX in ovary is retained in eggs and eliminated by ovulation. This is the case in pufferfish [16,17].
TTX retention has been examined using nontoxic Takifugu alboplumbeus and T. rubripes cultured from hatching with nontoxic feeding. That is, in these studies nontoxic individuals of both species were fed a toxic diet to accumulate TTX and switched to a nontoxic diet to investigate TTX retention. The two species retained toxin for 170–210 and 45 days after switching to a nontoxic diet, respectively [18,19,20]. However, no study has evaluated TTX retention in Y. criniger.
We investigated TTX retention by Y. criniger by rearing individuals collected from a natural environment on a nontoxic diet as part of a study to clarify differences in TTX absorption, transportation, accumulation, and retention/elimination between Y. criniger and pufferfish.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Goby Specimens
In June 2010 (Group I) and 2015 (Group II), wild specimens of Y. criniger were collected from the Fukido River, Okinawa Prefecture, Japan, and transported live to Nagasaki University. The body sizes of Groups I and II are shown in Table 1 and Table 2, respectively. As a control, 3 of 12 specimens in Group I and 6 of 17 specimens in Group II were used for TTX quantification without rearing. The remaining specimens were subjected to the rearing experiments. Because the gonads were not of sufficient size (≤0.06 g), the specimens were used without distinguishing between females and males.

Table 1.
Body size of the Y. criniger specimens of Group I.

Table 2.
Body size of the Y. criniger specimens of Group II.
2.2. Rearing Experiments
The specimens were reared in an aerated aquarium (60 L) and fed a commercial diet without TTX until the end of the experiment. In Group I, three specimens were randomly collected at 20, 40, and 60 days after initiation of rearing. In Group II, five or six specimens were randomly collected at 30 and 60 days after initiation of rearing. These specimens, together with the non-reared specimens (rearing period day 0), were subjected to TTX quantification.
2.3. TTX Quantification
The specimens in Group I were small, making it difficult to remove tissues, whereas we were able to dissect four specific tissues from Group II specimens: skin, muscle, liver, and gonads. Whole-body (Group I) or specific tissues (Group II) were homogenized and added to three to five volumes of 0.1% acetic acid. The mixtures were heated in boiling water for 10 min and centrifuged at 3000× g for 15 min [21]. The extracts were passed through an HLC-DISK membrane filter (0.45 µm, Kanto Chemical Co., Inc., Tokyo, Japan).
Filtrates of Group I were analyzed by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry (LC/MS) for TTX according to Nakashima et al. [22]. Briefly, LC/MS was performed using an Alliance system equipped with a Zspray™ MS 2000 detector (Waters Alliance, Milford, MA, USA). A Mightysil RP-18 GP column (2.0 × 250 mm, Kanto Chemical Co., Inc., Tokyo, Japan) was used with a mobile phase of 30 mmol/L heptafluorobutyric acid in 1 mmol/L ammonium acetate buffer (pH 5.0). The flow rate was set at 0.2 mL/min, and the eluate was introduced into the ion source of the MS detector for electrospray ionization of TTX in positive-ion mode. The desolvation temperature, source-block temperature, and cone voltage were 350 °C, 120 °C, and 30 V, respectively. A precursor ion (m/z 320) was monitored using the MassLynx™ NT operating system. A TTX standard (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd. [purity > 90%], Osaka, Japan) was dissolved in distilled water at 0.05, 0.1, 0.2, and 0.4 µg/mL and used for quantification.
Filtrates of Group II were submitted to liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) analysis of TTX according to Gao et al. [23]. LC was performed on an Alliance 2690 Separations Module (Waters Alliance). The column and mobile phase conditions were as for Group I. TTX was ionized using a Quattro Micro™ API Detector (Waters), and a product ion (m/z 162) with a collision voltage of 38 V and a precursor ion (m/z 320) were monitored. A TTX standard (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd. [purity > 90%]) was dissolved in distilled water at 0.01, 0.02, and 0.04 µg/mL and used for quantification.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
The Kruskal-Wallis test was used to compare the concentrations and amounts of TTX in the whole body (Group I) or skin, muscle, liver, and gonads (Group II) among the four (Group I) and three (Group II) rearing periods. Significant differences were analyzed using the Wilcoxon rank-sum test with Bonferroni correction.
3. Results
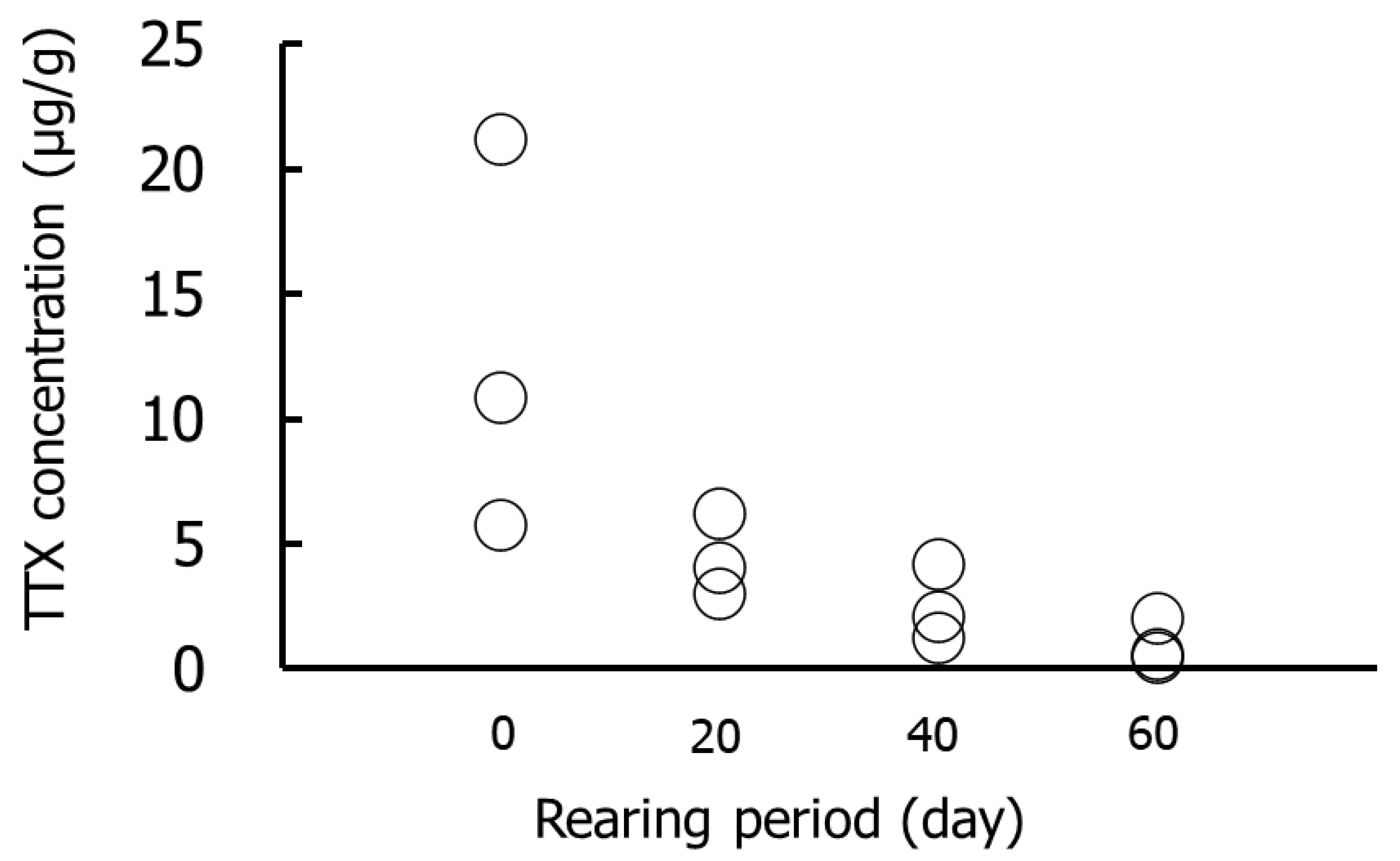
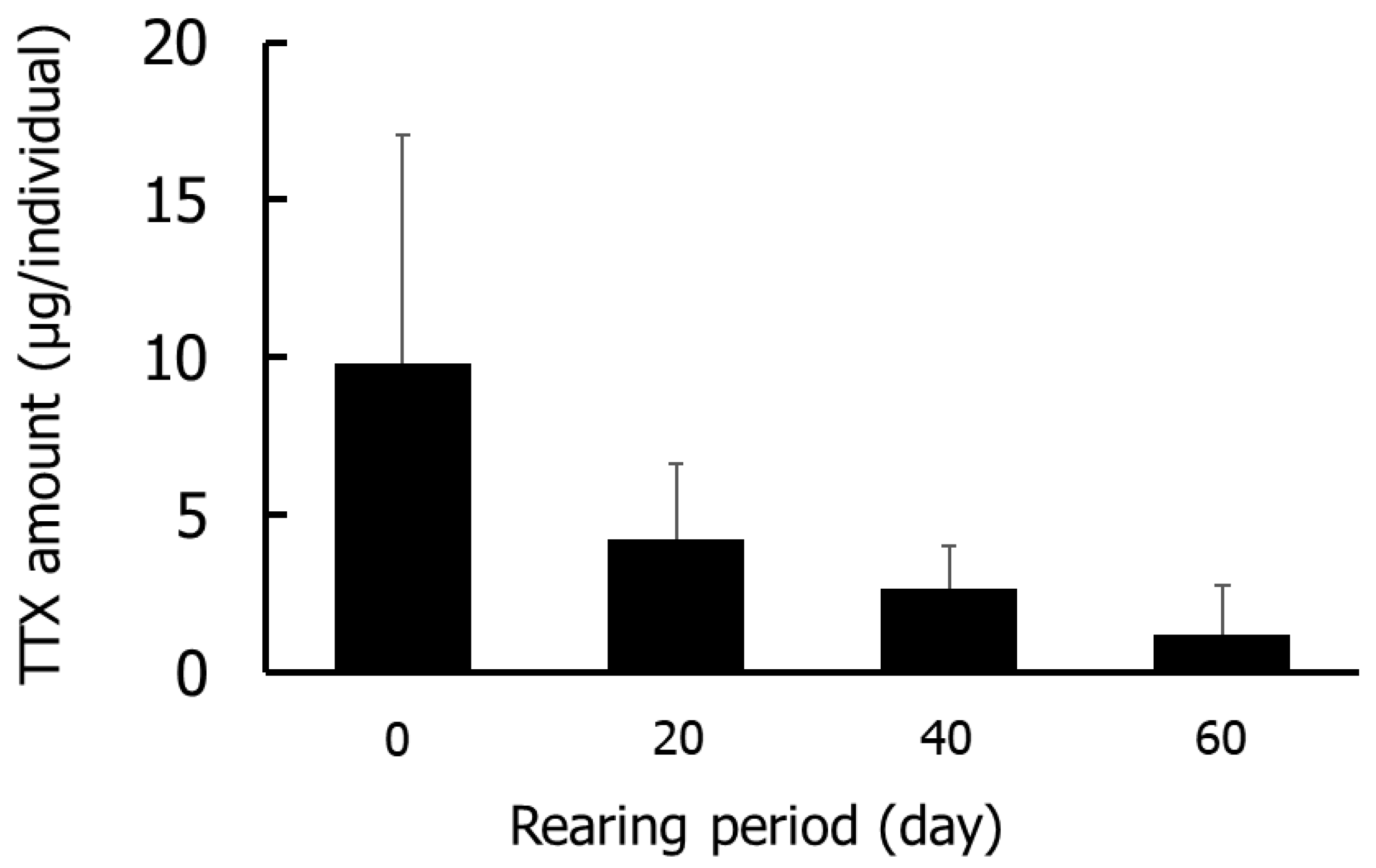
Figure 1 and Figure 2 show the results for the whole-body Group I specimens. The TTX concentrations were highest on day 0 (5.7–21.1 µg/g), followed by days 20 (3.0–6.2 µg/g), 40 (1.2–4.1 µg/g), and 60 (0.4–2.0 µg/g). The amounts of TTX were highest on day 0 (4.2–18.0 µg/individual) and decreased thereafter. No significant differences in TTX concentrations or amounts were detected in any rearing period.
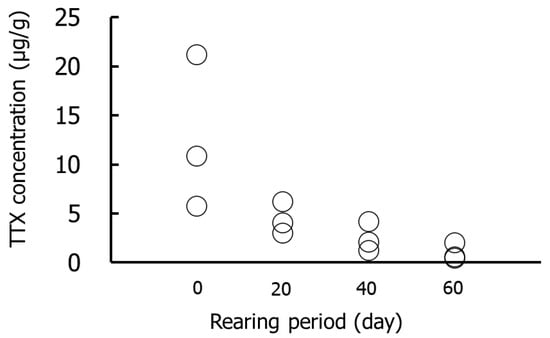
Figure 1.
TTX concentrations in the whole-body during rearing in Group I. Data are individual values (circles).
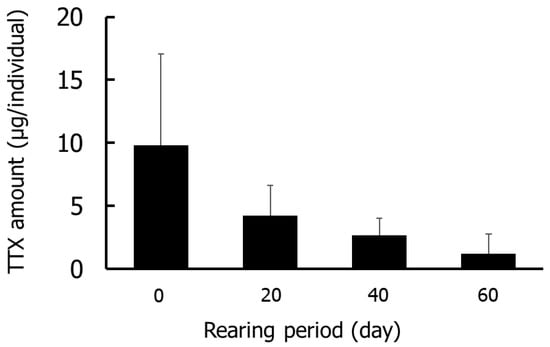
Figure 2.
Amounts of TTX in the whole-body during rearing in Group I. Data are means (column) and standard deviations (error bar).
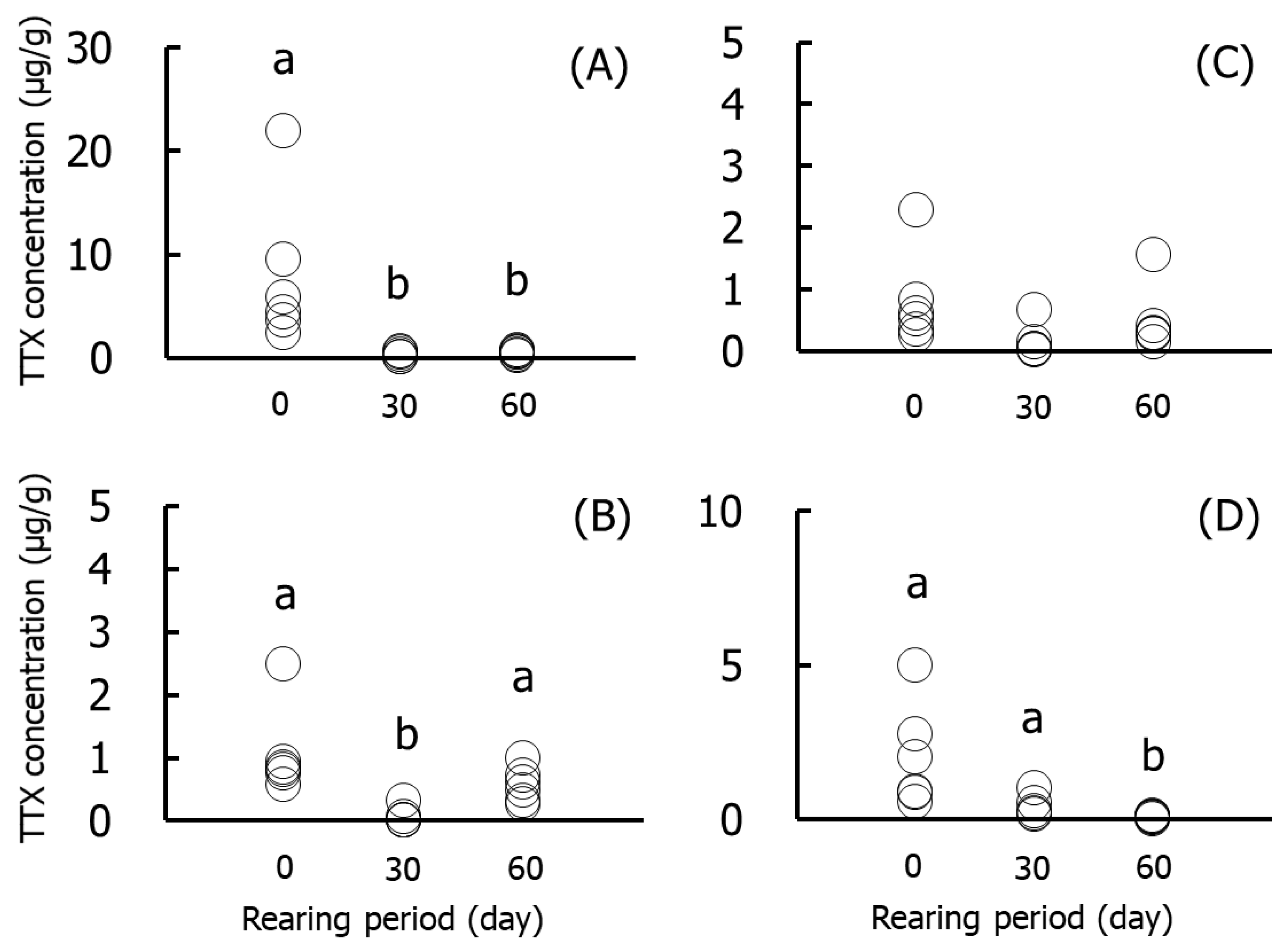
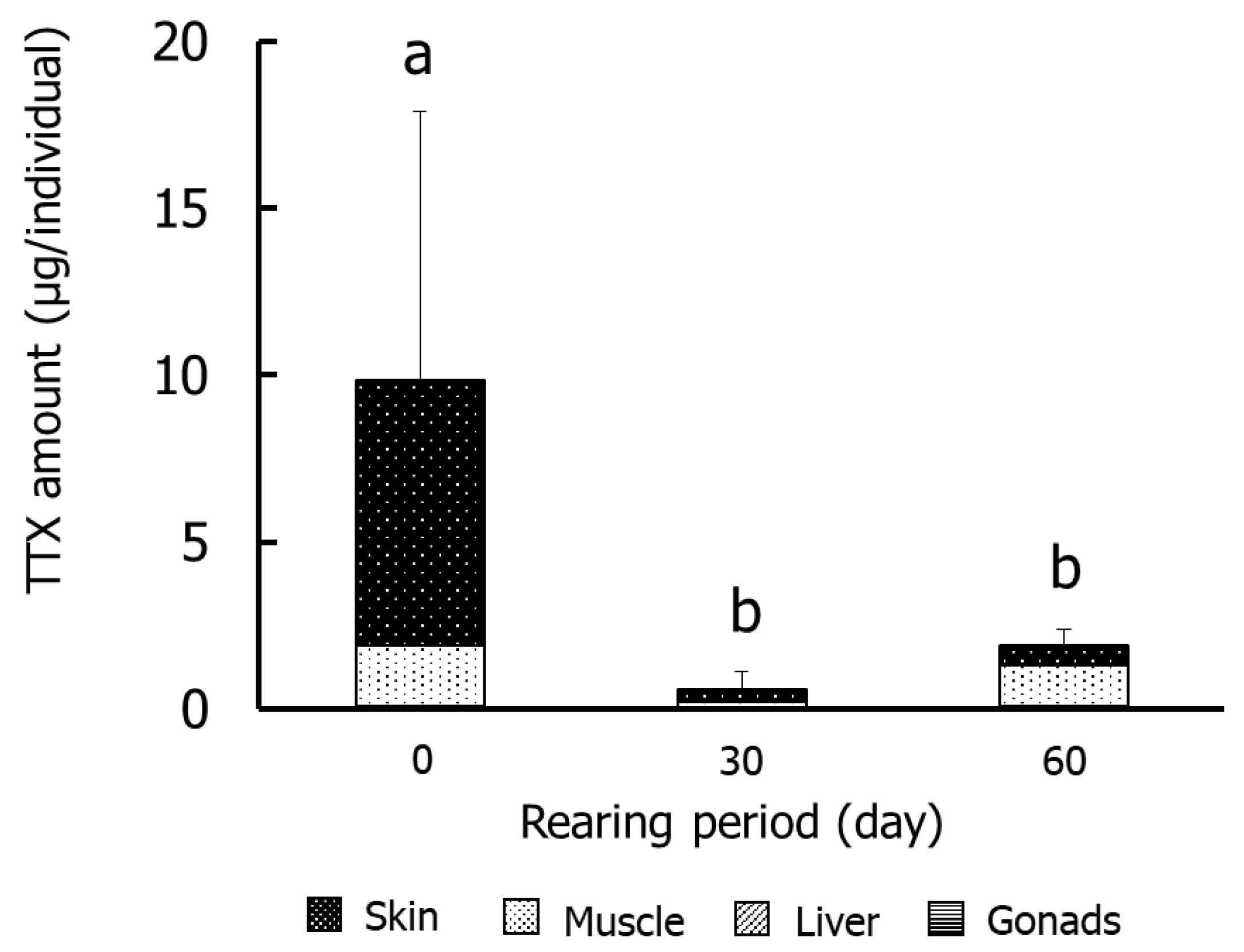
Figure 3 and Figure 4 show the results for the specific organs in Group II. The TTX concentrations in skin were significantly (p < 0.05) higher on day 0 (2.4–21.9 µg/g) than on days 30 and 60. The concentrations in muscle and gonads were significantly lower on days 30 and 60, respectively, than at other rearing times. The concentrations in the liver did not decrease significantly during rearing. The amounts of TTX were significantly higher on day 0 (9.8 µg/individual) than in the other rearing periods, and skin and muscle accounted for 80% and 18% of the levels, respectively. The amount in skin decreased over time and was ~30% on day 60.
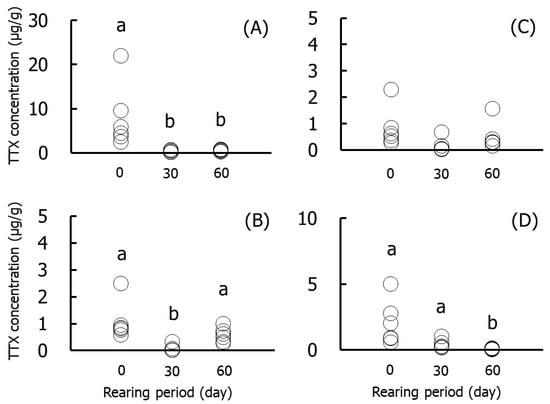
Figure 3.
TTX concentrations in the skin (A), muscle (B), liver (C), and gonads (D) during rearing in Group II. Data are individual values (circles). a > b, p < 0.05.
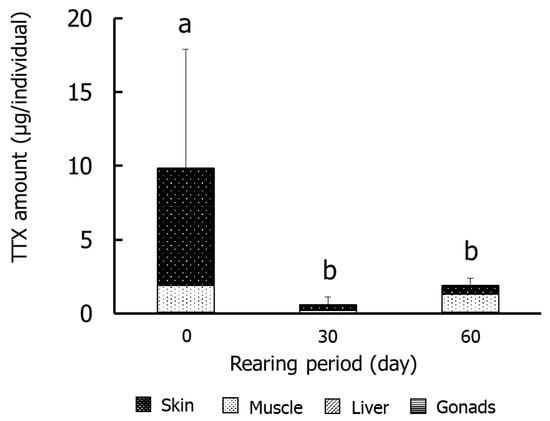
Figure 4.
Amounts of TTX in tissues during rearing in Group II. Data are means (column) and standard deviations (error bar). a > b, p < 0.05.
4. Discussion
In Group I, the amounts and concentrations of TTX decreased over time, albeit nonsignificantly. The mean and maximum concentrations were highest on day 0, at 12.6 and 21.1 µg/g, respectively. The concentrations in specimens reared on a nontoxic diet decreased with time, and the mean and maximum on day 60 were 1.0 and 2.0 µg/g, respectively. The amounts of TTX also decreased with time, and the average on day 60 was ~10% of that on day 0. In previous studies, after feeding nontoxic specimens of T. alboplumbeus a toxic diet for 30 days and then a nontoxic diet until the end of the experiment (170 or 210 days after rearing started), 50–80% of the administered TTX (equivalent to the TTX accumulated during the first 30 days) was retained until 60 or 70 days, and 30–60% (equivalent to 60–80% of the accumulated TTX on day 30) remained at the end of the experiment [18,20]. Therefore, Y. criniger has lower TTX retention compared to T. alboplumbeus.
In Group II, the TTX concentrations in skin were significantly lower on days 30 and 60 than on day 0. Y. criniger accumulates high concentrations of TTX in skin and eliminates it from the body on external stimulation [8,9,12]. In this study, Y. criniger was not exposed to external stimuli during rearing, so the decrease in TTX concentrations is unlikely to have been caused by external stimulation. Therefore, the skin of Y. criniger accumulates high concentrations of TTX, which is discharged (exuded) rapidly as a result of its low retention ability. In previous studies, T. rubripes and T. alboplumbeus retained identical or higher levels of TTX as that at the time of cessation of TTX feeding after 45 to 210 days of rearing on a nontoxic diet [18,19,20], indicating that TTX retention is lower in the skin of Y. criniger than in that of marine pufferfish of the genus Takifugu.
In our study, TTX was detected in the muscle of Y. criniger not only on day 0 but also on days 30 and 60. Therefore, Y. criniger muscle retains TTX. TTX is rarely detected in the muscle of Takifugu. In previous studies on nontoxic T. rubripes and T. alboplumbeus fed a toxic diet, TTX was almost undetectable in muscle [18,19,20]. TTX is present in the muscle of C. patoca [11], so Y. criniger muscle may have a TTX retention mechanism similar to that of C. patoca.
TTX concentrations in the liver on day 0 did not differ significantly from those after rearing. In previous studies on T. alboplumbeus, the liver accumulated the largest quantity of TTX at initiation of a nontoxic diet, which decreased with increased feeding duration [18,20]. However, the amounts of TTX in the skin and gonads increased in time, implying that TTX was transferred from the liver to the skin and gonads. In our study, the TTX concentrations in the gonads of Y. criniger were significantly lower on day 60 than on days 0 and 30 and were lower than those in the other three tissues on day 60. Therefore, TTX retention in the gonads was lower in Y. criniger than in T. alboplumbeus, and the toxin was not transferred from the liver to the gonads.
In Group II, the amounts of TTX were significantly lower in reared specimens (days 30 and 60) than in non-reared specimens (day 0), implying that TTX is not retained in Y. criniger. TTX-bearing fish consume TTX through the food chain, which begins with TTX-producing bacteria [1]. Such bacteria have been detected in Y. criniger and may supply TTX [24]. However, our findings indicate that TTX-producing bacteria did not supply enough TTX to render Y. criniger toxic. TTX in Y. criniger likely originates from TTX-bearing prey. Genetic analysis of the contents of the goby digestive tract revealed a highly toxic flatworm gene [25]. The Y. criniger used in that study were collected from the same river as the fish in our study, so our specimens likely ingested TTX from TTX-bearing flatworms.
Y. criniger retained TTX, albeit to a markedly lesser degree than Takifugu. Takifugu species possess pufferfish saxitoxin and TTX-binding protein (PSTBP), which is implicated in TTX absorption, transportation, and accumulation [26,27,28,29]. In a previous study, Western blotting using an antibody to PSTBP detected a protein homologous to PSTBP in C. patoca (in which TTX is present in muscle). However, the protein had a molecular weight of 50 kDa, less than half the PSTBP isoforms of Takifugu [30]. We plan to investigate this Y. criniger protein, with the aim of clarifying the molecular mechanism of TTX retention in goby and pufferfish.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.T., T.T. and O.A.; methodology, R.T.; validation, M.S. and Y.K.; formal analysis, M.S. and Y.Y.; investigation, R.T. and O.A.; resources, R.T., T.T. and O.A.; data curation, R.T., M.S., Y.Y. and Y.K.; writing—original draft preparation, R.T.; writing—review and editing, R.T., T.T. and O.A.; visualization, R.T., M.S., Y.Y. and Y.K.; supervision, T.T. and O.A.; project administration, R.T.; funding acquisition, R.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express sincere thanks to Former Captain Hisao Kanehara and the crew of the training ship Nagasaki-Maru, Nagasaki University, for their cooperation in the collection of Y. criniger specimens.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Noguchi, T.; Arakawa, O. Tetrodotoxin-distribution and accumulation in aquatic organisms, and cases of human intoxication. Mar. Drugs 2008, 6, 220–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shibuno, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Horinouchi, M.; Sano, M. Habitat use patterns of fishes across the mangrove-seagrass-coral reef seascape at Ishigaki Island, southern Japan. Ichthyol. Res. 2008, 55, 218–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekikawa, H.; Nanjo, K.; Mizutani, A.; Kohno, H. Ecological distribution of the toxic goby Yongeichthys criniger (Perciformes, Gobiidae) in the Urauchi river, Iriomote Island, southern Japan. Bull. Biogeogr. Soc. Jpn. 2017, 71, 109–120. [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto, Y.; Noguchi, T. Occurrence of a tetrodotoxin-like substance in a goby Gobius criniger. Toxicon 1971, 9, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, T.; Hashimoto, Y. Isolation of tetrodotoxin from a goby Gobius criniger. Toxicon 1973, 11, 305–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, T.; Kao, H.; Hashimoto, Y. Toxicity of the goby, Gobius criniger. Bull. Japan Soc. Sci. Fish. 1971, 37, 642–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tatsuno, R.; Shikina, M.; Soyano, K.; Ikeda, K.; Takatani, T.; Arakawa, O. Maturation-associated changes in the internal distribution of tetrodotoxin in the female goby Yongeichthys criniger. Toxicon 2013, 63, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibi, Y.; Tetsu, T.; Ochiai, Y.; Saito, T. Unexpected occurrence of fish toxification and proposed safety net. Refrigeration 2017, 92, 196–201. [Google Scholar]
- Nohara, K.; Tetsu, T.; Kohno, H.; Saito, T. Genetic population structure and tetrodotoxin content of yellowfin toxic goby Yongeichthys criniger in the Japanese coastal area. Aquat. Anim. 2019, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, T.; Sugiura, T. Studies on toxicity a goby, Yongeichthys criniger, from Iriomote Island. Bull. Inst. Ocean. Res. Develop. Tokai Univ. 1997, 18, 35–41. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmud, Y.; Tanu, M.B.; Takatani, T.; Asayama, E.; Arakawa, O.; Noguchi, T. Chelonodon patoca, a highly toxic marine puffer in Japan. J. Nat. Toxins 2001, 10, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nanjo, K.; Sekikawa, H.; Mizutani, A.; Kohno, H. Role of tetrodotoxin as a protection mechanism against predatory fish in the toxic goby Yongeichthys criniger: Results of laboratory experiments. Study Rev. Iriomote Is. 2017 ORRC Tokai Univ. 2018, 46–54. [Google Scholar]
- Kodama, M.; Ogata, T.; Sato, S. External secretion of tetrodotoxin from puffer fishes stimulated by electric shock. Mar. Biol. 1985, 87, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Noguchi, T.; Harada, T.; Murata, O.; Hashimoto, K. Tetrodotoxin as a biological defense agent for puffers. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1985, 51, 1175–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Imakiire, M.; Kishimoto, H. Toxicity of the fertilized eggs and the parent fishes in the shadow-goby, Yongeichthys criniger, from the Iriomote Island, southern Ryukyu. Sci. Rep. Mus. Tokai Univ. 2002, 4, 79–85. [Google Scholar]
- Itoi, S.; Yoshikawa, S.; Asahina, K.; Suzuki, M.; Ishizuka, K.; Takimoto, N.; Mitsuoka, R.; Yokoyama, N.; Detake, A.; Takayanagi, C.; et al. Larval pufferfish protected by maternal tetrodotoxin. Toxicon 2014, 78, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Itoi, S.; Suzuki, M.; Asahina, K.; Sawayama, E.; Nishikubo, J.; Oyama, H.; Takei, M.; Shiibashi, N.; Takatani, T.; Arakawa, O.; et al. Role of maternal tetrodotoxin in survival of larval pufferfish. Toxicon 2018, 148, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamori, K.; Kono, M.; Furukawa, K.; Matsui, T. The toxification of juvenile cultured kusafugu Takifugu niphobles by oral administration of crystalline tetrodotoxin. J. Food Hyg. Soc. Jpn. 2004, 45, 73–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Honda, S.; Arakawa, O.; Takatani, T.; Tachibana, K.; Yagi, M.; Tanigawa, A.; Noguchi, T. Toxification of cultured puffer fish Takifugu rubripes by feeding on tetrodotoxin-containing diet. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 2005, 71, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kono, M.; Matsui, T.; Furukawa, K.; Yotsu-Yamashita, M.; Yamamori, K. Accumulation of tetrodotoxin and 4,9-anhydrotetrodotoxin in cultured juvenile kusafugu Fugu niphobles by dietary administration of natural toxic komonfugu Fugu poecilonotus liver. Toxicon 2008, 51, 1269–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Kodama, M. Puffer fish toxin. In Standard Method of Analysis in Food Safety Regulation, 2015, Physical and Chemical Methods; Association, J.F.H., Ed.; Japan Food Hygiene Association: Tokyo, Japan, 2015; pp. 813–820. [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima, K.; Arakawa, O.; Taniyama, S.; Nonaka, M.; Takatani, T.; Yamamori, K.; Fuchi, Y.; Noguchi, T. Occurrence of saxitoxins as a major toxin in the ovary of a marine puffer Arothron firmamentum. Toxicon 2004, 43, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Kanahara, Y.; Tatsuno, R.; Soyano, K.; Nishihara, G.N.; Urata, C.; Takatani, T.; Arakawa, O. Maturation-associated changes in internal distribution and intra-ovarian microdistribution of tetrodotoxin in the pufferfish Takifugu pardalis. Fish. Sci. 2018, 84, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Ma, T.; Gong, X.; Zhang, N.; Bao, B. Identification of tetrodotoxin-producing bacteria from goby Yongeichthys criniger. Toxicon 2015, 104, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoi, S.; Sato, T.; Takei, M.; Yamada, R.; Ogata, R.; Oyama, H.; Teranishi, S.; Kishiki, A.; Wada, T.; Noguchi, K.; et al. The planocerid flatworm is a main supplier of toxin to tetrodotoxin-bearing fish juveniles. Chemosphere 2020, 249, 126217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yotsu-Yamashita, M.; Sugimoto, A.; Terakawa, T.; Shoji, Y.; Miyazawa, T.; Yasumoto, T. Purification, characterization, and cDNA cloning of a novel soluble saxitoxin and tetrodotoxin binding protein from plasma of the puffer fish, Fugu pardalis. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 5937–5946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yotsu-Yamashita, M.; Yamaki, H.; Okoshi, N.; Araki, N. Distribution of homologous proteins to puffer fish saxitoxin and tetrodotoxin binding protein in the plasma of puffer fish and among the tissues of Fugu pardalis examined by Western blot analysis. Toxicon 2010, 55, 1119–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yotsu-Yamashita, M.; Okoshi, N.; Watanabe, K.; Araki, N.; Yamaki, H.; Shoji, Y.; Terakawa, T. Localization of pufferfish saxitoxin and tetrodotoxin binding protein (PSTBP) in the tissues of the pufferfish, Takifugu pardalis, analyzed by immunohistochemical staining. Toxicon 2013, 72, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsuno, R.; Yamaguchi, K.; Takatani, T.; Arakawa, O. RT-PCR- and MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry-based identification and discrimination of isoforms homologous to pufferfish saxitoxin- and tetrodotoxin-binding protein in the plasma of non-toxic cultured pufferfish (Takifugu rubripes). Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2013, 77, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yotsu-Yamashita, M.; Nagaoka, Y.; Muramoto, K.; Cho, Y.; Konoki, K. Pufferfish saxitoxin and tetrodotoxin binding protein (PSTBP) analogues in the blood plasma of the pufferfish Arothron nigropunctatus, A. hispidus, A. manilensis, and Chelonodon patoca. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).