A Review of the Role of the Oceanic Rossby Waves in Climate Variability
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Ocean–Atmosphere Exchanges
1.1.1. The Tropics
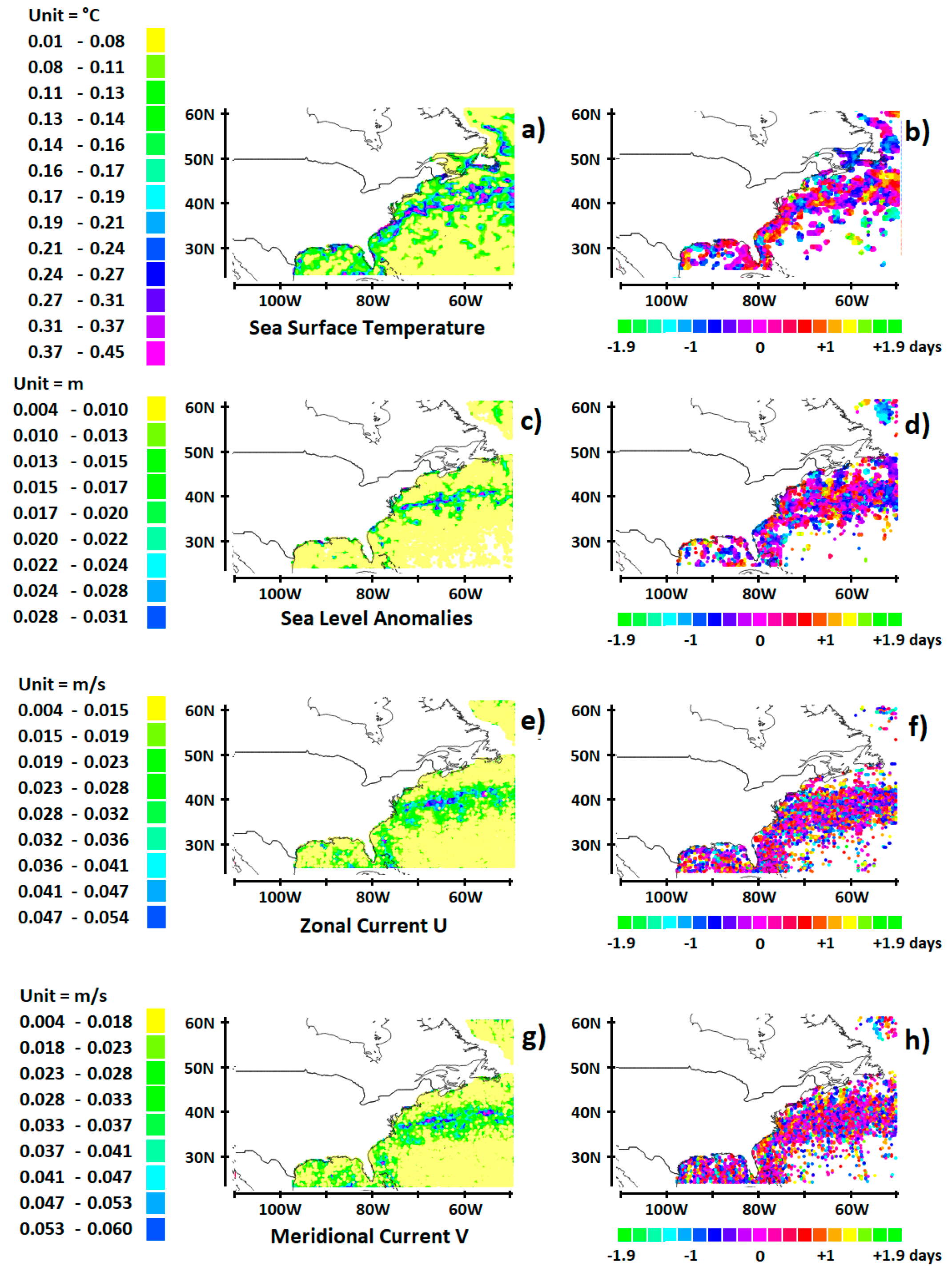
1.1.2. Mid-Latitudes
1.2. Resonance of Baroclinic Waves
1.3. Prospective Research
1.3.1. Subharmonic Modes of Rossby Waves
1.3.2. Very-Long-Period Rossby Waves Winding around the Subtropical Gyres
1.4. Solar Rossby Waves and Similar Implications in Space Weather
2. Tropical Oceans
2.1. The Atlantic Ocean
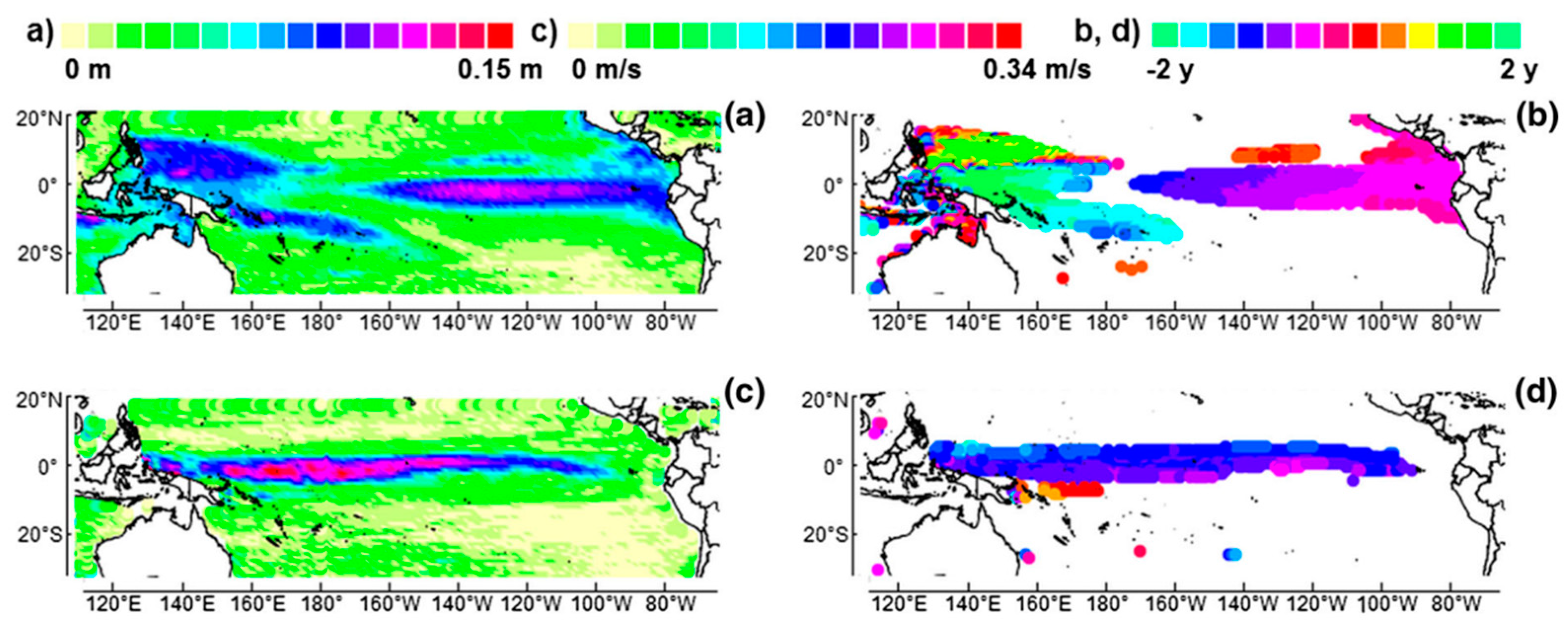
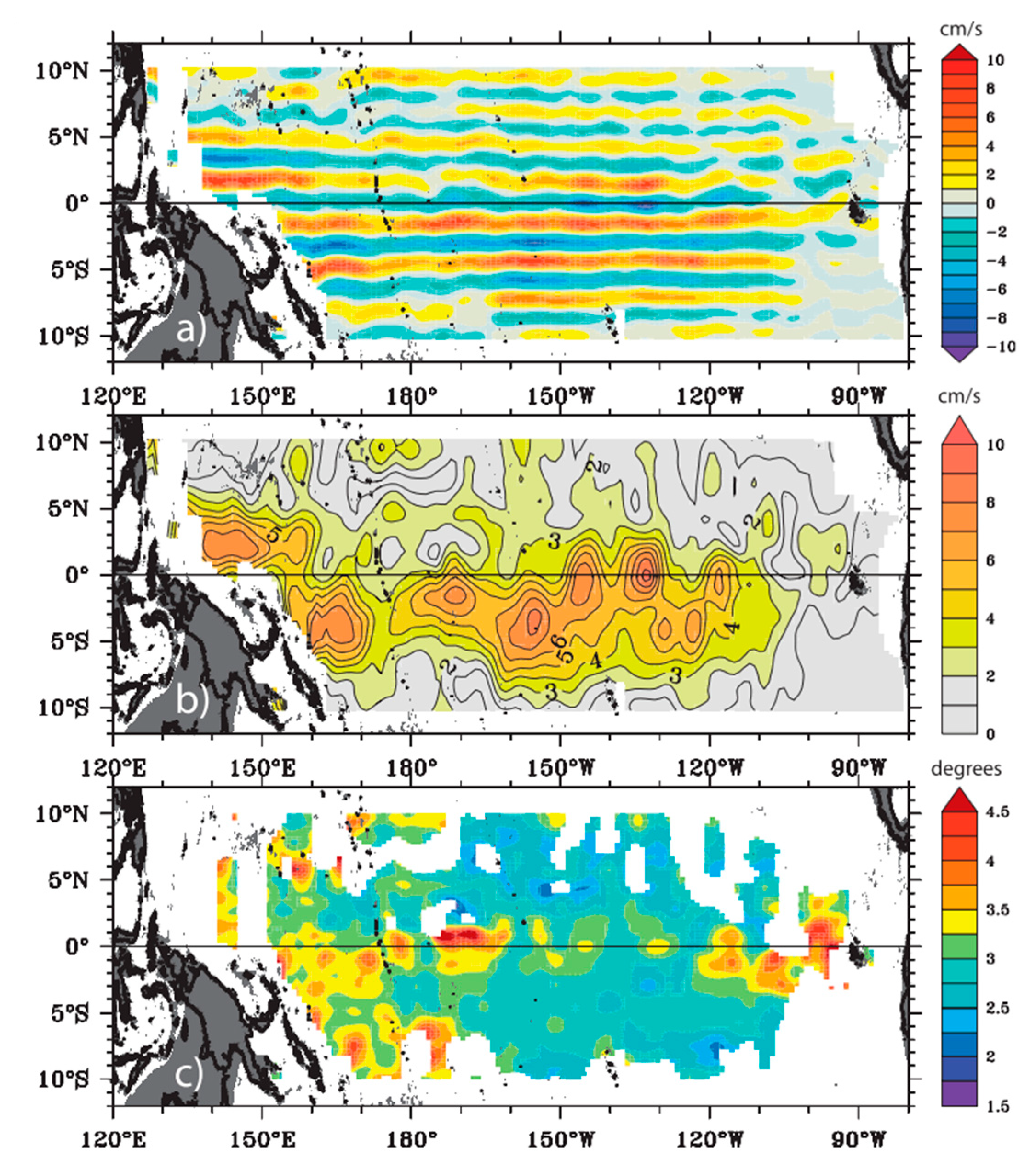
2.2. The Pacific Ocean
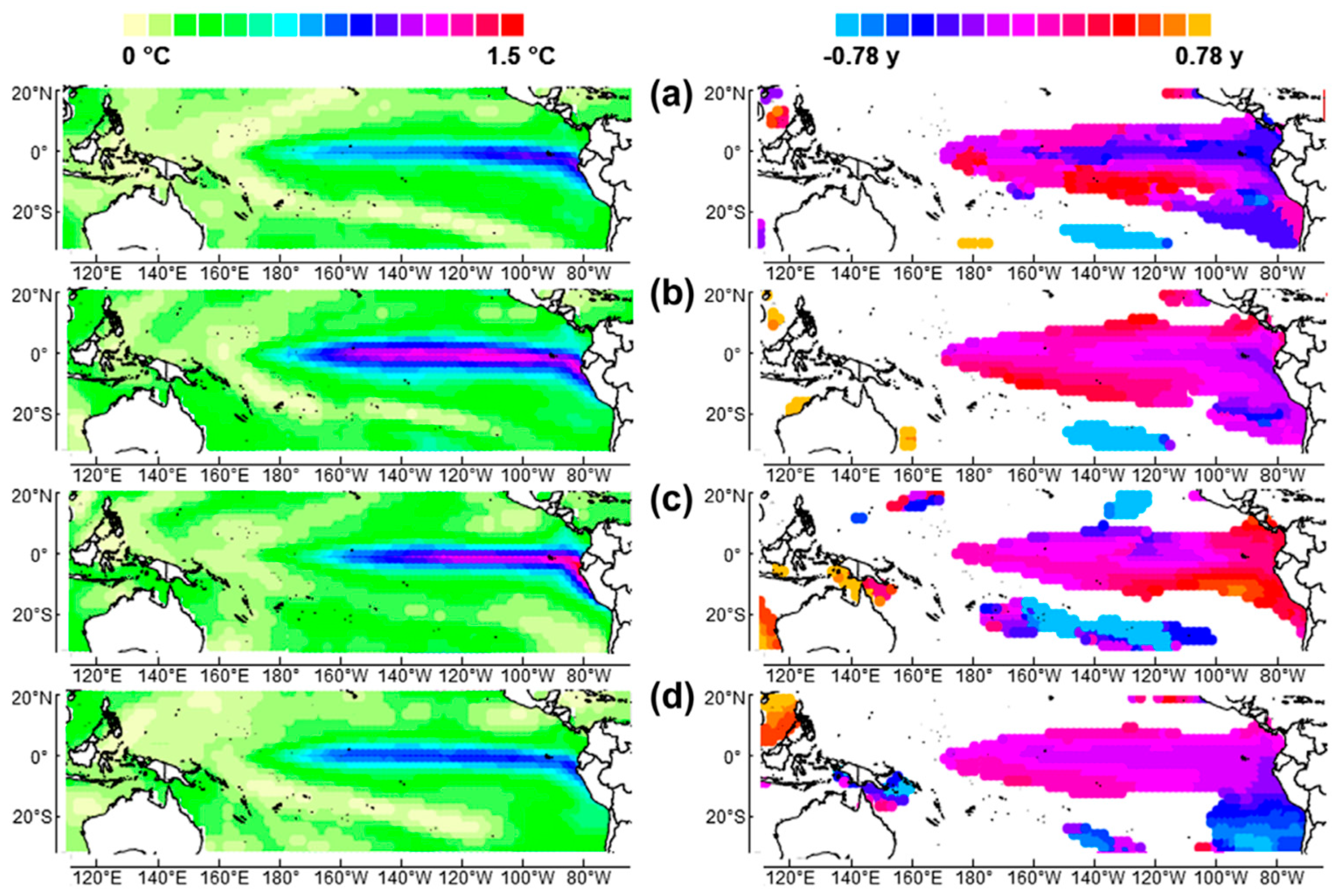
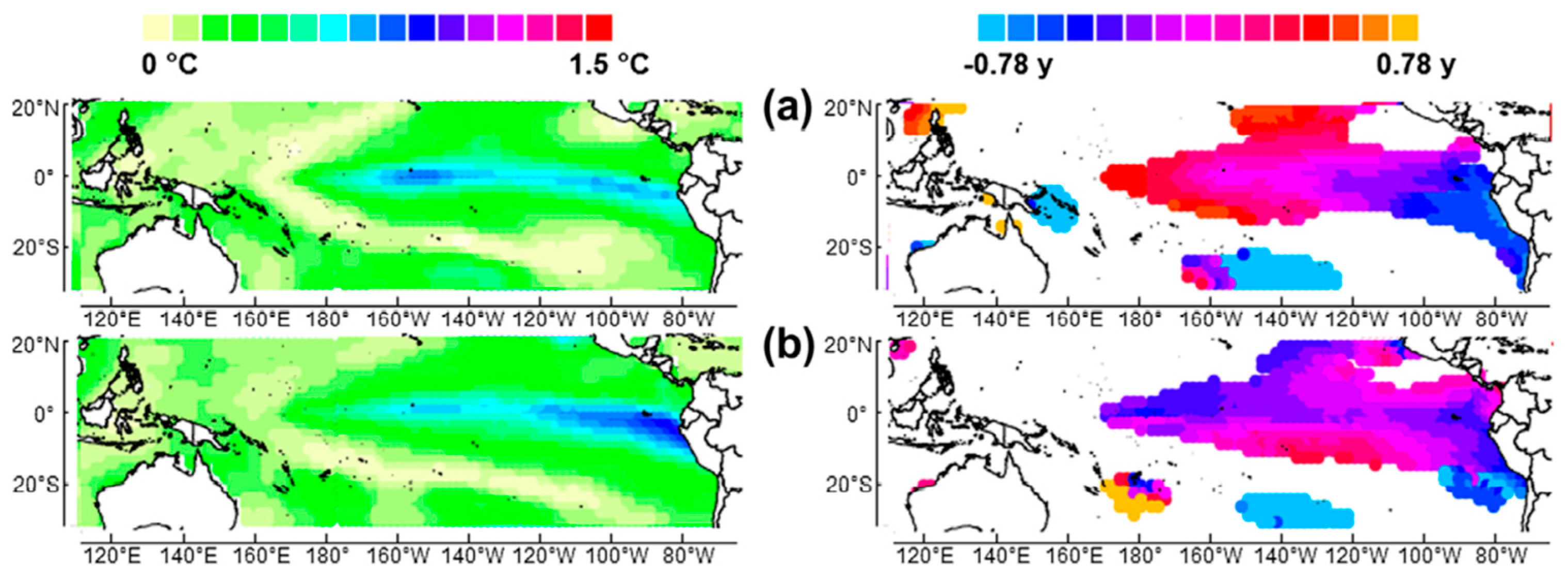
2.2.1. The El Niño–Southern Oscillation
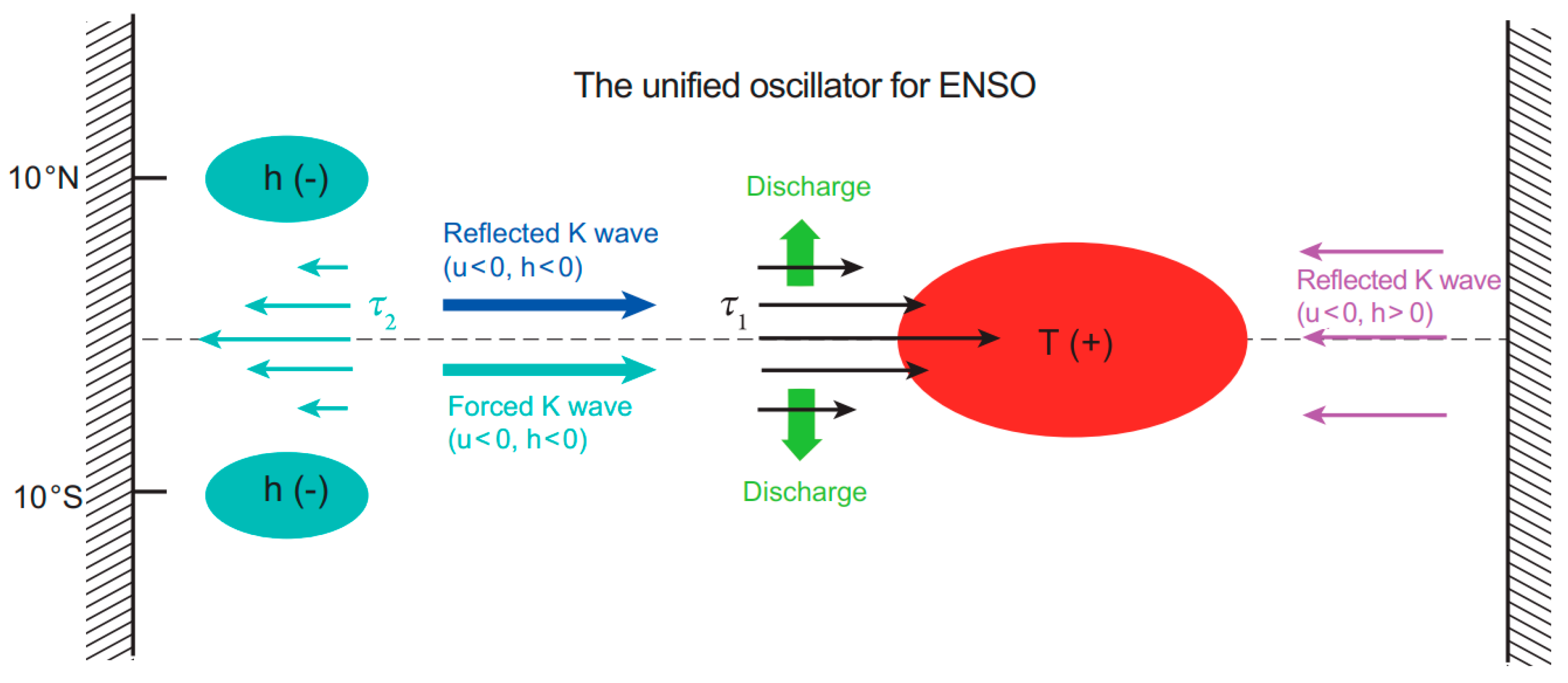
2.2.2. The Role of Coupled Baroclinic Waves in the Genesis of ENSO
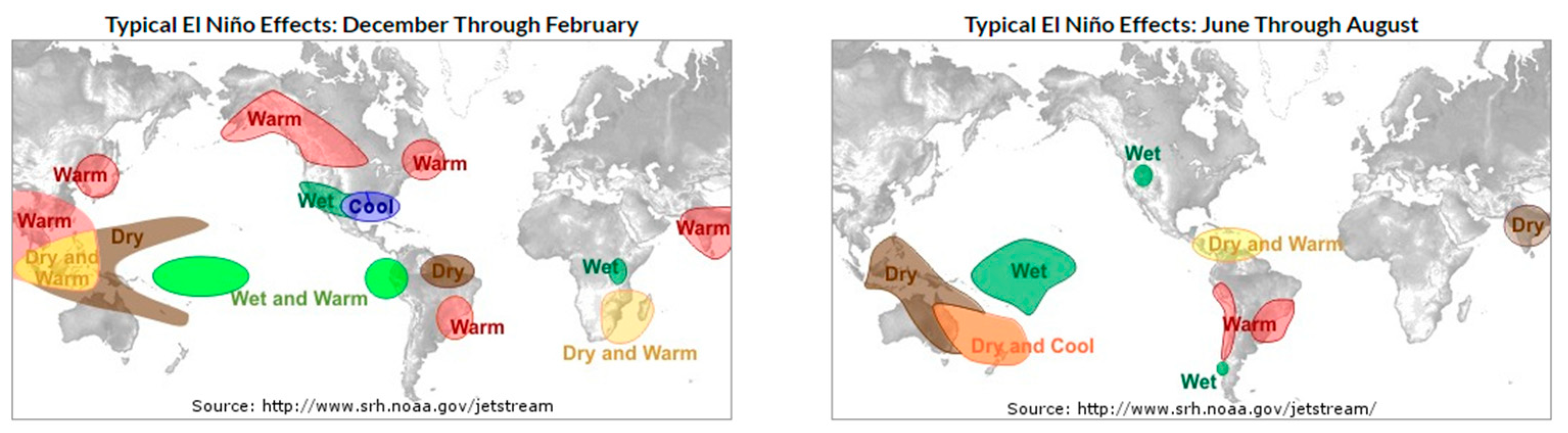
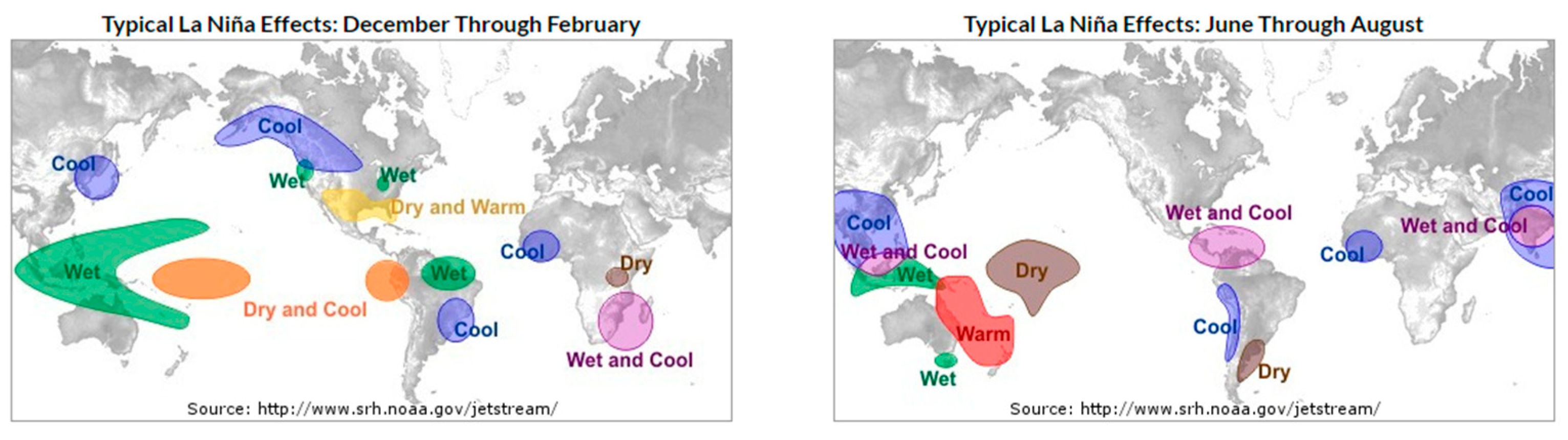
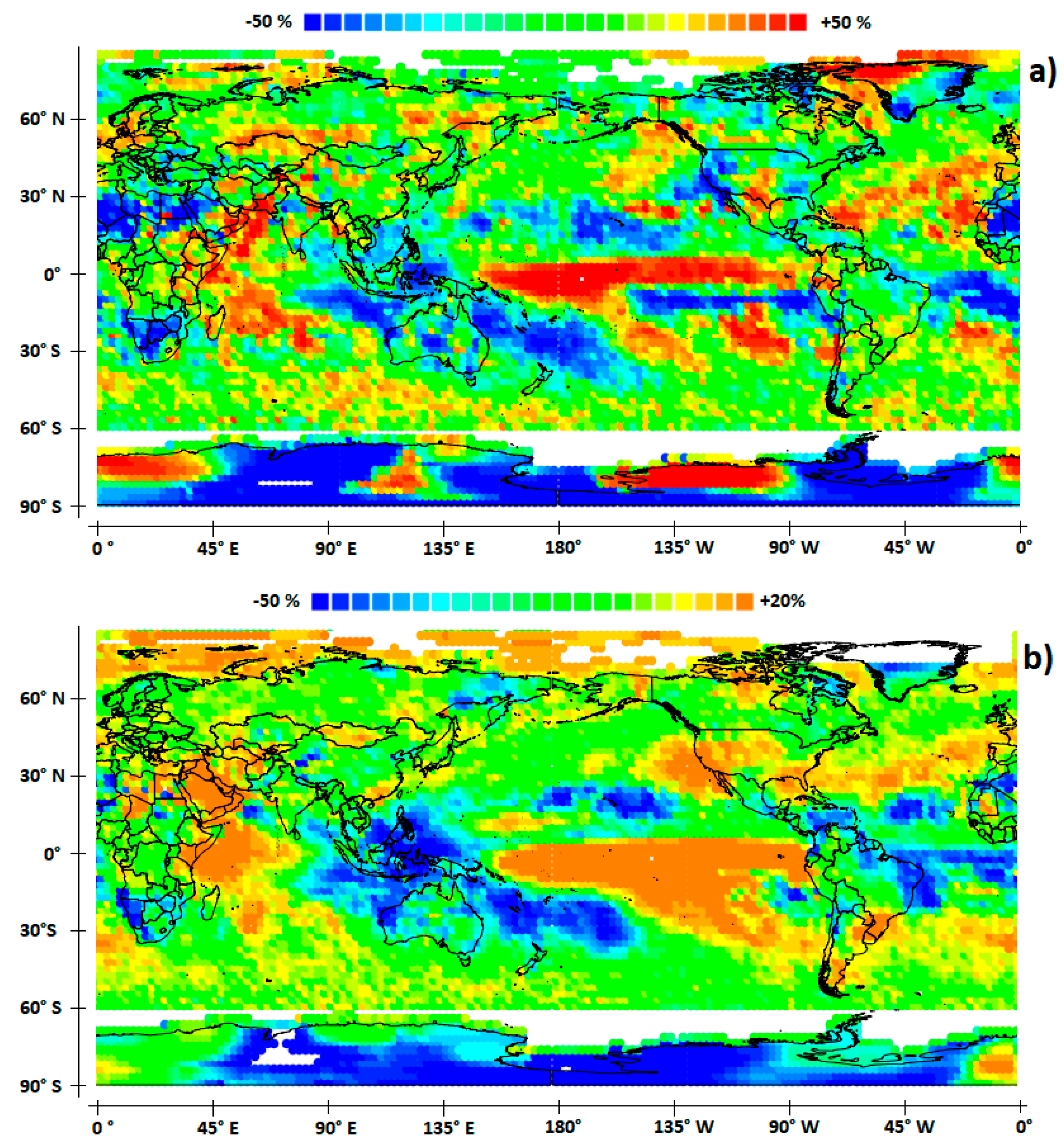
2.2.3. The Climate Impact of ENSO
2.3. The Indian Ocean
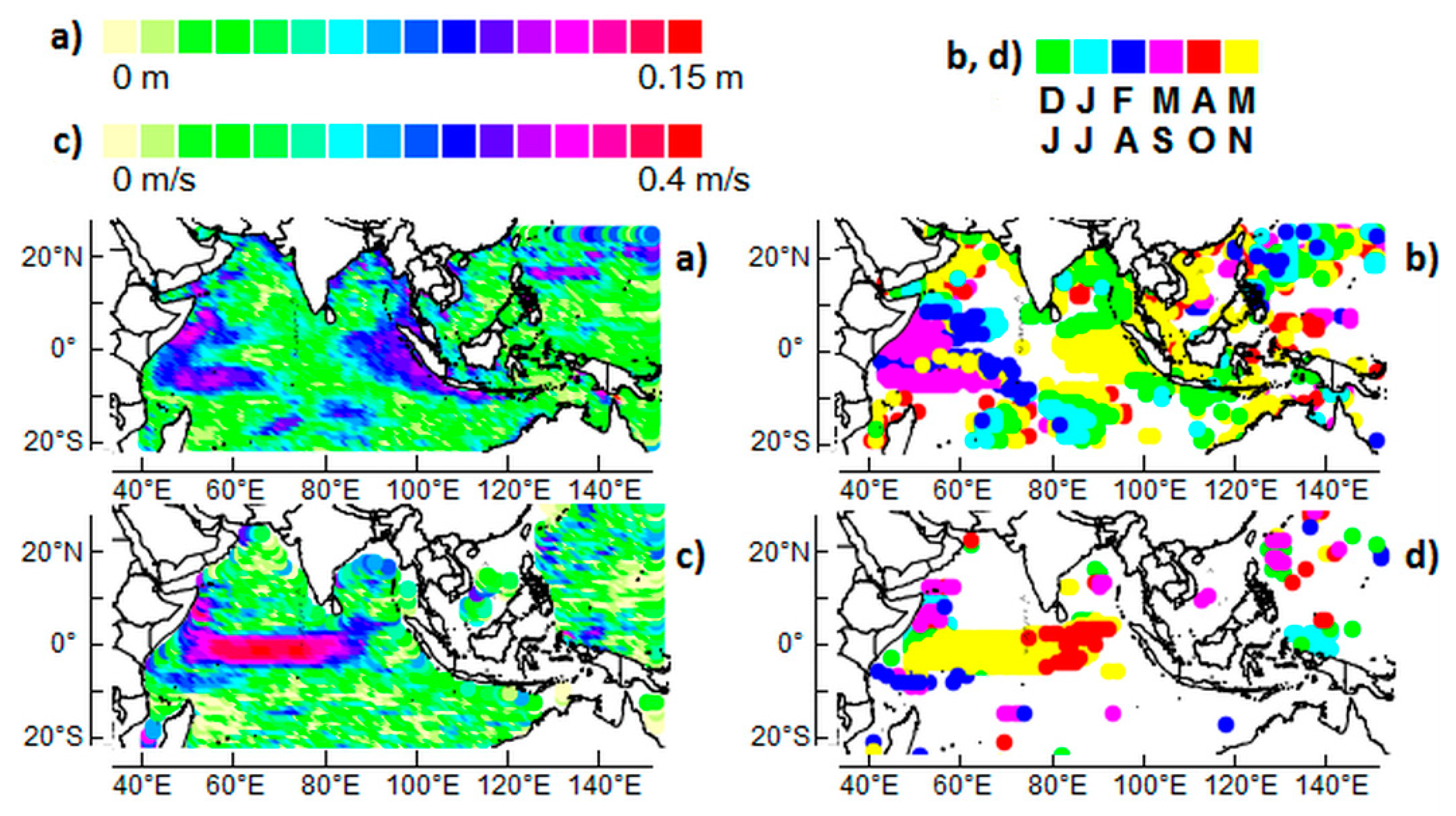
2.3.1. Tropical Rossby Waves
2.3.2. The Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD)
2.3.3. The Madden–Julian Oscillation (MJO)
3. Mid-Latitudes
3.1. The Band of Periods from a Few Days to a Year
3.1.1. Annual and Semiannual Rossby Waves
3.1.2. Resonant Forcing
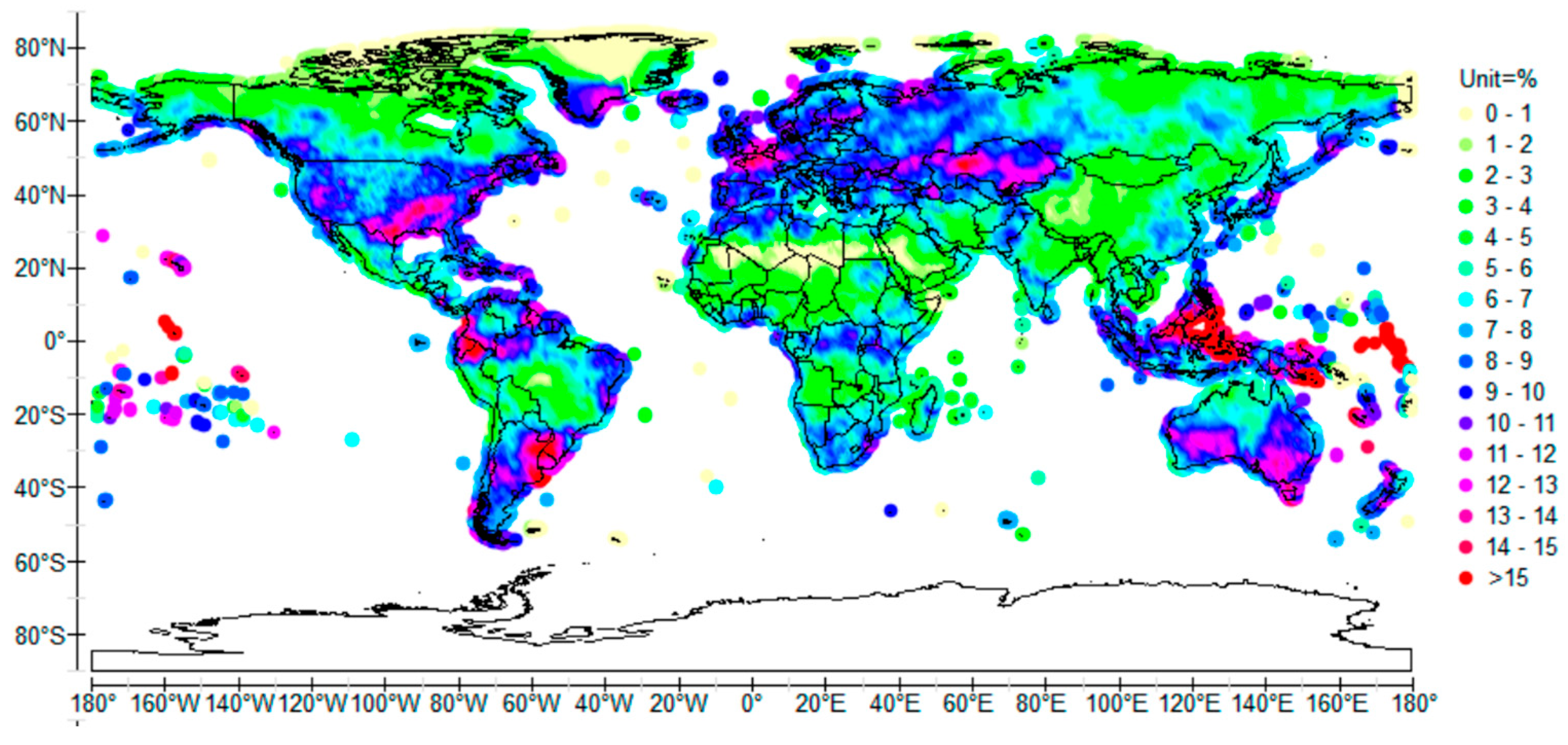
3.2. Decadal Variability
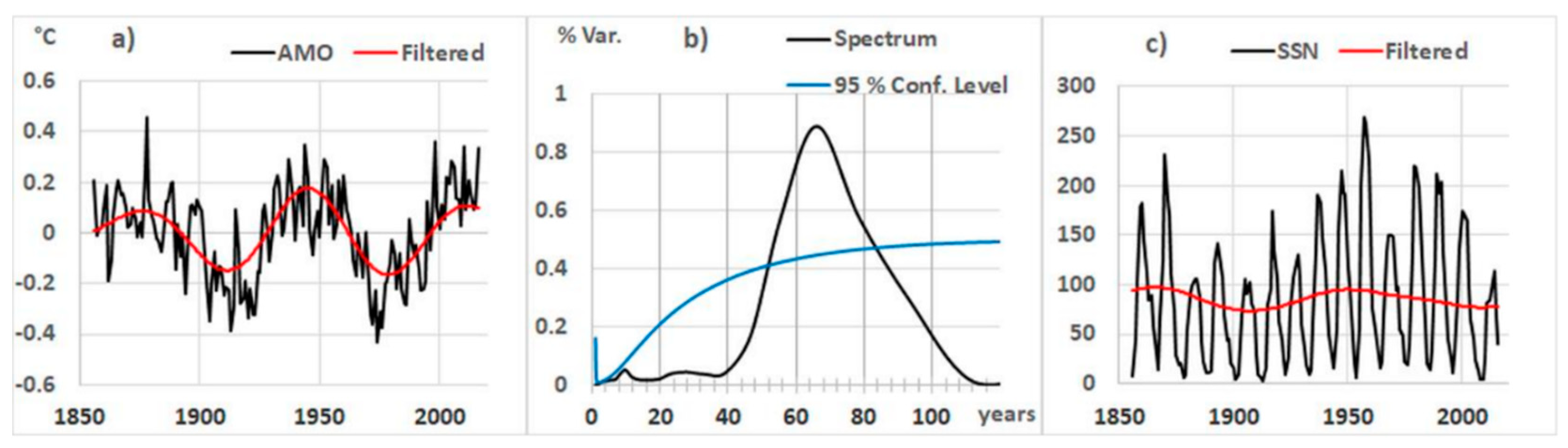
3.3. Multidecadal Variability
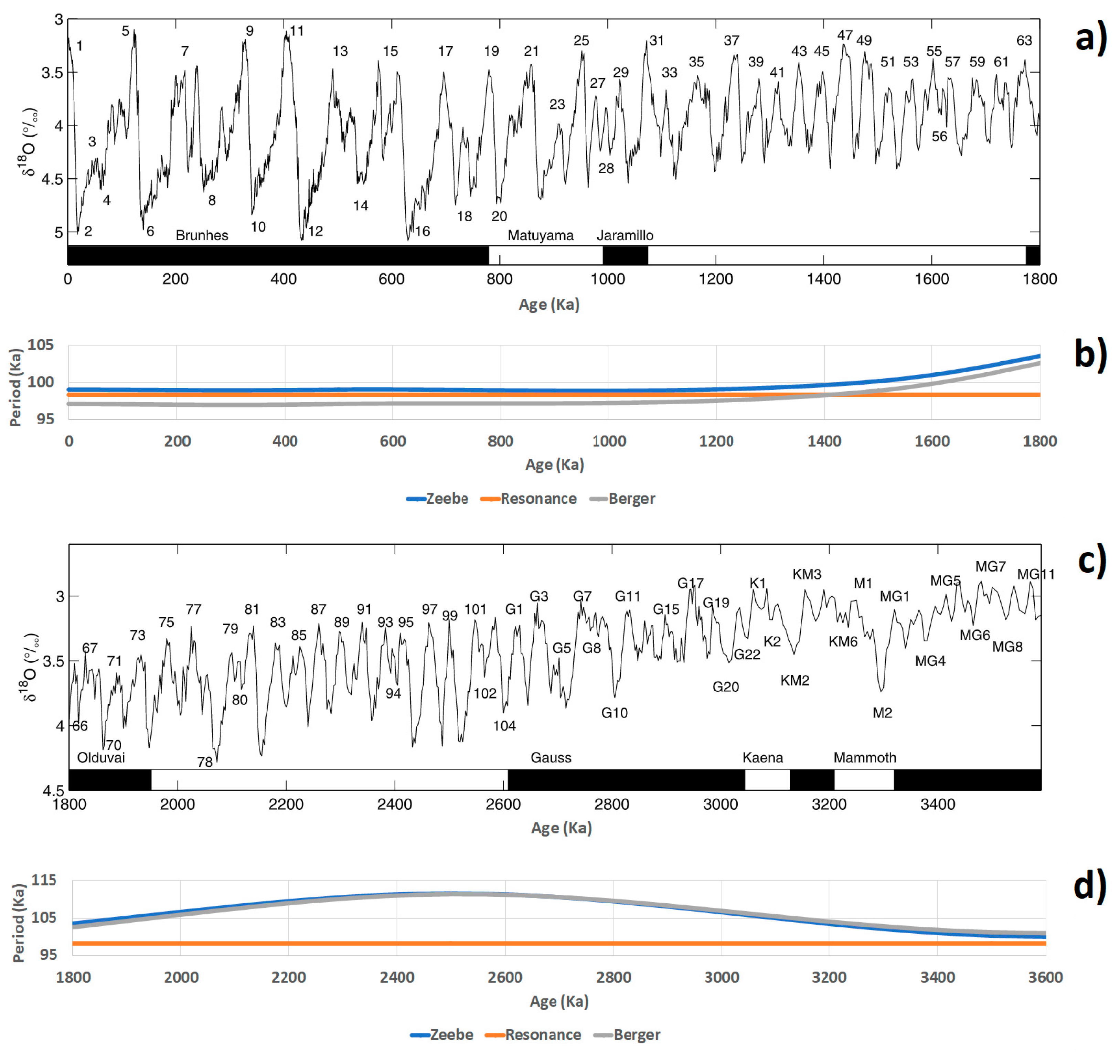
3.4. Orbital Forcing
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMO | Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation |
| CP | Central Pacific El Niño |
| ENSO | El Niño–Southern Oscillation |
| EP | Eastern Pacific El Niño |
| IOD | Indian Ocean Dipole |
| ITCZ | Inter Tropical Convergence Zone |
| MAR | Mid-Atlantic Ridge |
| MJO | Madden–Julian oscillation |
| MPT | Mid-Pleistocene Transition |
| NEC | North Equatorial Current |
| NECC | North Equatorial Counter Current |
| QSW | Quasi-Stationary Wave |
| SEC | South Equatorial Current |
| SLA | Sea Level Anomalies |
| SOI | Southern Oscillation Index |
| SSH | Sea Surface Height |
| SSN | Sunspot Number |
| SST | Sea Surface Temperature |
Appendix A. Prototype of Coupled Oscillator Systems
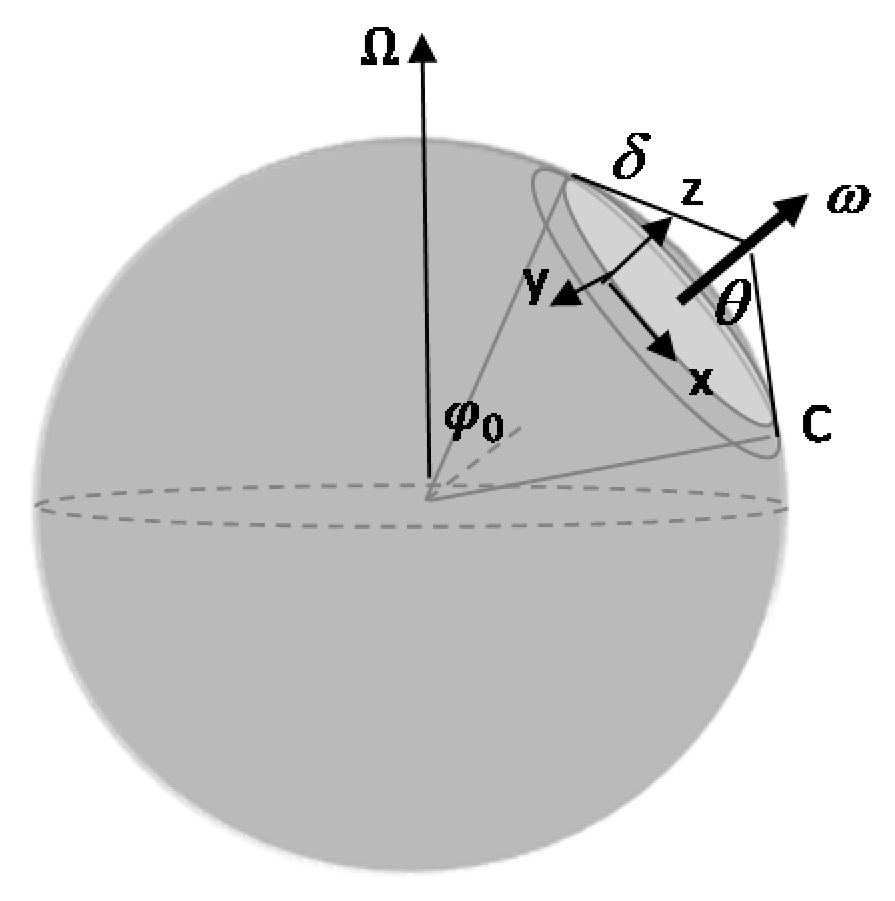
Appendix B. The β-Cone Approximation
References
- Farneti, R. Coupled Interannual Rossby Waves in a Quasi-geostrophic Ocean–Atmosphere Model. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2007, 37, 1192–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Alexander, M. Atmospheric bridge, oceanic tunnel, and global climatic teleconnections. Rev. Geophys. 2007, 45, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cessi, P.; Louazel, S. Decadal Oceanic Response to Stochastic Wind Forcing. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2001, 31, 3020–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z. How long is the memory of tropical ocean dynamics? J. Clim. 2002, 15, 3518–3522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z. Tropical Ocean Decadal Variability and Resonance of Planetary Wave Basin Modes. Part I: Theory. J. Clim. 2003, 16, 1539–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chelton, D.B.; Schlax, M.G. Global Observations of Oceanic Rossby Waves. Science 1996, 272, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sverdrup, H.U. Wind-Driven Currents in a Baroclinic Ocean; with Application to the Equatorial Currents of the Eastern Pacific. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1947, 33, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stommel, H.; Arons, A.B. On the abyssal circulation of the world ocean—I. Stationary planetary flow patterns on a sphere. Deep Sea Res. 1960, 6, 140–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stommel, H.; Yoshida, K. Kuroshio: Its Physical Aspects; University of Tokyo Press: Tokyo, Japan, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, M.M.; Bryden, H.L. Direct estimates and mechanisms of ocean heat transport. Deep Sea Res. Part. A Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 1982, 29, 339–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryden, H.L.; Roemmich, D.H.; Church, J.A. Ocean heat transport across 24° N in the Pacific. Deep Sea Res. Part. A Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 1991, 38, 297–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinault, J.-L. Long Wave Resonance in Tropical Oceans and Implications on Climate: The Atlantic Ocean. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2013, 170, 1913–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinault, J.-L. Long Wave Resonance in Tropical Oceans and Implications on Climate: The Pacific Ocean. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2015, 173, 2119–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinault, J.-L. Resonance of baroclinic waves in the tropical oceans: The Indian Ocean and the far western Pacific. Dyn. Atmos. Oceans 2020, 89, 101119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCreary, J.P.; Lukas, R. The response of the equatorial ocean to a moving wind field. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 1986, 91, 11691–11705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, A.E. Atmosphere-Ocean Dynamics; International Geophysics Series; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1982; 662p. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, M.Y.; Thouless, D.J. Topological interpretation of subharmonic mode locking in coupled oscillators with inertia. Phys. Rev. B 2001, 64, 014305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinault, J.-L. Resonantly Forced Baroclinic Waves in the Oceans: Subharmonic Modes. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2018, 6, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinault, J.-L. Resonantly Forced Baroclinic Waves in the Oceans: A New Approach to Climate Variability. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaqarashvili, T.V.; Albekioni, M.; Ballester, J.L.; Bekki, Y.; Biancofiore, L.; Birch, A.C.; Dikpati, M.; Gizon, L.; Gurgenashvili, E.; Heifetz, E.; et al. Rossby Waves in Astrophysics. Space Sci. Rev. 2021, 217, 1–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikpati, M.; McIntosh, S.W. Space Weather Challenge and Forecasting Implications of Rossby Waves. Space Weather 2020, 18, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raphaldini, B.; Teruya, A.S.; Raupp, C.; Bustamante, M. Nonlinear Rossby Wave–Wave and Wave–Mean Flow Theory for Long-term Solar Cycle Modulations. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2019, 887, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raphaldini, B.; Medeiros, E.; Raupp, C.; Teruya, A.S. A New Mechanism for Maunder-like Solar Minima: Phase Synchronization Dynamics in a Simple Nonlinear Oscillator of Magnetohydrodynamic Rossby Waves. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2020, 890, L13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Explain with Realism Climate Variability. Available online: http://climatorealist.neowordpress.fr (accessed on 5 March 2022).
- Ding, H.; Keenlyside, N.; Latif, M. Seasonal cycle in the upper equatorial Atlantic Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2009, 114, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brandt, P.; Claus, M.; Greatbatch, R.J.; Kopte, R.; Toole, J.M.; Johns, W.E.; Böning, C.W. Annual and Semiannual Cycle of Equatorial Atlantic Circulation Associated with Basin-Mode Resonance. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2016, 46, 3011–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Illig, S.; Dewitte, B.; Ayoub, N.; Du Penhoat, Y.; Reverdin, G.; De Mey, P.; Bonjean, F.; Lagerloef, G.S.E. Interannual long equatorial waves in the tropical Atlantic from a high-resolution ocean general circulation model experiment in 1981–2000. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Döös, K. Influence of the Rossby waves on the seasonal cycle in the tropical Atlantic. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 1999, 104, 29591–29598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foltz, G.R.; McPhaden, M.J. Interaction between the Atlantic meridional and Niño modes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zebiak, S.E. Air-Sea interaction in the equatorial Atlantic region. J. Clim. 1993, 6, 1567–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Aiki, H. The Climatological Horizontal Pattern of Energy Flux in the Tropical Atlantic as Identified by a Unified Diagnosis for Rossby and Kelvin Waves. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2020, 125, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hormann, V.; Lumpkin, R.; Foltz, G. Interannual North Equatorial Countercurrent variability and its relation to tropical Atlantic climate modes. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2012, 117, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, P.; Ji, L.; Li, H. A decadal climate variation in the tropical Atlantic Ocean from thermodynamic air-sea interactions. Nature 1997, 385, 516–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.; Yamagata, T.; Schopf, P.; Behera, S.; Carton, J.; Kessler, W.S.; Meyers, G.; Qu, T.; Schott, F.; Shetye, S.; et al. Climate Fluctuations of Tropical Coupled Systems—The Role of Ocean Dynamics. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 5122–5174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, A.; Shukla, J. On the dynamics of droughts in northeast Brazil: Observations, theory, and numerical exper-iments with a general circulation model. J. Atmos. Sci. 1981, 38, 2653–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lamb, P.; Peppler, R.A.; Hastenrath, S. Interannual variability in the tropical Atlantic. Nature 1986, 322, 238–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lough, J.M. Tropical Atlantic sea surface temperature and rainfall variations in Sub-Saharan Africa. Mon. Wea. Rev. 1986, 114, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palmer, T.N. Influence of the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans on Sahel rainfall. Nature 1986, 322, 251–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolter, K. Modes of tropical circulation, Southern Oscillation and Sahel rainfall anomalies. J. Clim. 1989, 8, 149–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gill, A.E. Some simple solutions for heat-induced tropical circulation. Q. J. Royal Met. Soc. 1980, 106, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindzen, R.S.; Nigam, S. On the role of sea surface temperature gradients in forcing low-level winds and convergence in the Tropics. J. Atmos. Sci. 1987, 44, 2418–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bjerknes, J. Atmospheric teleconnections from the equatorial Pacific. Mon. Wea. Rev. 1969, 97, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C. A review of ENSO theories. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2018, 5, 813–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCreary, J.P. A Model of Tropical Ocean-Atmosphere Interaction. Mon. Weather Rev. 1983, 111, 370–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Weisberg, R.H. The 1997–98 El Nino evolution relative to previous El Niño events. J. Clim. 2000, 13, 488–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.B.; Fletcher, J. Two types of warming over equator during El Niño. Chin. Sci. Bull. 1985, 8, 596–599. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Trenberth, K.E.; Stepaniak, D.P. Indices of El Nino evolution. J. Clim. 2001, 14, 1697–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larkin, N.K.; Harrison, D.E. Global seasonal temperature and precipitation anomalies during El Nino autumn and winter. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L16705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.-Y.; Kao, H.-Y. Decadal changes of ENSO persistence barrier in SST and ocean heat content indices: 1958–2001. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McPhaden, M.J.; Zebiak, S.E.; Glantz, M.H. ENSO as an Integrating Concept in Earth Science. Science 2006, 314, 1740–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clarke, A.J. An Introduction to the Dynamics of El Nino and the Southern Oscillation; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2008; p. 324. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, T.; McPhaden, M.J. Increasing intensity of El Niño in the central-equatorial Pacific. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, H.-Y.; Yu, J.-Y. Contrasting Eastern-Pacific and Central-Pacific Types of ENSO. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 615–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C. A unified oscillator model for the El Nino-Southern Oscillation. J. Clim. 2001, 14, 98–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashok, K.; Behera, S.K.; Rao, S.A.; Weng, H.; Yamagata, T. El Niño Modoki and its possible teleconnection. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2007, 112, C11007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kug, J.-S.; Jin, F.-F.; An, S.-I. Two Types of El Niño Events: Cold Tongue El Niño and Warm Pool El Niño. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 1499–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, N.K. On the definition of El Niño and associated seasonal average U.S. weather anomalies. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilyardi, E. El Niño–mean state–seasonal cycle interactions in a multi-model ensemble. Clim. Dyn. 2005, 26, 329–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirtman, B.P. Oceanic Rossby Wave Dynamics and the ENSO Period in a Coupled Model. J. Clim. 1997, 10, 1690–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyman, J.M.; Chelton, D.B.; Deszoeke, R.A.; Samelson, R.M. Tropical Instability Waves as a Resonance between Equatorial Rossby Waves. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2005, 35, 232–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cravatte, S.; Kessler, W.S.; Marin, F. Intermediate Zonal Jets in the Tropical Pacific Ocean Observed by Argo Floats. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2012, 42, 1475–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinault, J.-L. Anticipation of ENSO: What teach us the resonantly forced baroclinic waves. Geophys. Astrophys. Fluid Dyn. 2016, 110, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinault, J.-L. The Anticipation of the ENSO: What Resonantly Forced Baroclinic Waves Can Teach Us (Part II). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2018, 6, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, M.C.; Chang, W.L.; Leung, W.M. Impacts of El Niño–Southern Oscillation Events on Tropical Cyclone Landfalling Activity in the Western North Pacific. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 1419–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turner, J. The El Niño–Southern Oscillation and Antarctica. Int. J. Climatol. 2004, 24, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, X. ENSO-related impacts on Antarctic sea ice: A synthesis of phenomenon and mechanisms. Antarct. Sci. 2004, 16, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Majda, A.J.; Thual, S. Observations and Mechanisms of a Simple Stochastic Dynamical Model Capturing El Niño Diversity. J. Clim. 2017, 31, 449–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, H.; Behera, S.K.; Yamagata, T. Anomalous winter climate conditions in the Pacific rim during recent El Niño Modoki and El Niño events. Clim. Dyn. 2008, 32, 663–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capotondi, A.; Wittenberg, A.; Newman, M.; Di Lorenzo, E.; Yu, J.-Y.; Braconnot, P.; Cole, J.; Dewitte, B.; Giese, B.S.; Guilyardi, E.; et al. Understanding ENSO Diversity. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 921–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, P.-H.; Li, T. Characteristics of tropical cyclone genesis in the western north pacific during the developing and decaying phases of two types of El Niño. J. Trop. Meteor. 2015, 21, 14–22. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, J.-J.; Yamagata, T. Long-term El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO)-like variation with special emphasis on the South Pacific. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2001, 106, 22211–22227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.-J.; Masson, S.; Behera, S.; Delecluse, P.; Gualdi, S.; Navarra, A.; Yamagata, T. South Pacific origin of the decadal ENSO-like variation as simulated by a coupled GCM. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gent, O.; O’Neil, K.; Cane, M.A. A model of the semiannual oscillation in the equatorial Indian Ocean. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1983, 13, 2148–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, W.; McCreary, J.P.; Anderson, D.L.T.; Mariano, A.J. On the dynamics of the eastward surface jets in the equatorial Indian Ocean. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1999, 29, 2191–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hase, H.; Masumoto, Y.; Kuroda, Y.; Mizuno, K. Semiannual variability in temperature and salinity observed by Triangle Trans-Ocean Buoy Network (TRITON) buoys in the eastern tropical Indian Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2008, 113, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, T.G. Equatorial variability and resonance in a wind-driven Indian Ocean model. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 1993, 98, 22533–22552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luyten, J.R.; Roemmich, D.H. Equatorial Currents at Semi-Annual Period in the Indian Ocean. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1982, 12, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagura, M.; McPhaden, M.J. Dynamics of zonal current variations associated with the Indian Ocean dipole. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2010, 115, C11026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Li, L.; Yu, W. Behavior of the Wyrtki Jet observed with surface drifting buoys and satellite altimeter. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L18607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cane, M.A.; Moore, D.W. A Note on Low-Frequency Equatorial Basin Modes. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1981, 11, 1578–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.F. Low-frequency modes of tropical ocean dynamics. J. Clim. 2001, 14, 3874–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; McCreary, J.P.; Masumoto, Y.; Vialard, J.; Duncan, B. Basin Resonances in the Equatorial Indian Ocean. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2011, 41, 1252–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCreary, K.; Molinari, R. A numerical investigation on dynamics, thermodynamics and mixed-layer processes in the Indian Ocean. Prog. Oceanogr. 1993, 31, 181–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masumoto, M. Forced Rossby waves in the southern tropical Indian Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 27589–27602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermes, J.C.; Reason, C.J.C. Annual cycle of the South Indian Ocean (Seychelles-Chagos) thermocline ridge in a regional ocean model. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saji, N.H.; Goswami, B.N.; Vinayachandran, P.N.; Yamagata, T. A dipole mode in the tropical Indian Ocean. Nature 1999, 401, 360–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, P.J.; Moore, A.M.; Loschnigg, J.P.; Leben, R.P. Coupled ocean–atmosphere dynamics in the Indian Ocean during 1997–98. Lett. Nat. 1999, 401, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Xiang, B.; Liu, L.; Liu, N. Understanding the origins of interannual thermocline variations in the tropical Indian Ocean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saji, N.H.; Xie, S.-P.; Yamagata, T. Tropical Indian Ocean Variability in the IPCC Twentieth-Century Climate Sim-ulations. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 4397–4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Li, G.; Jiang, W.; Long, S.-M.; Lu, B. Asymmetric relationship between ENSO and the tropical Indian Ocean summer SST anomalies. J. Clim. 2021, 34, 5955–5969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Du, Y.; Wen, Z.; Wu, R.; Xie, S.-P. Evolution of South Tropical Indian Ocean Warming and the Climatic Impacts Following Strong El Niño Events. J. Clim. 2019, 32, 7329–7347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Liu, Q.; Sun, S.; Yang, J. Three Types of Indian Ocean Dipoles. J. Clim. 2015, 28, 3073–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Tozuka, T.; Ng, B.; Cai, W. Thermocline Warming Induced Extreme Indian Ocean Dipole in 2019. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL090079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaya, Y.; Ishikawa, I.; Kobayashi, C.; Endo, H.; Ose, T. Enhanced Meiyu-Baiu Rainfall in Early Summer 2020: Aftermath of the 2019 Super IOD Event. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL090671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C. Madden-Julian Oscillation. Rev. Geophys. 2005, 43, RG2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rui, H.; Wang, B. Development Characteristics and Dynamic Structure of Tropical Intraseasonal Convection Anomalies. J. Atmospheric Sci. 1990, 47, 357–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, A.; Gnanaseelan, C. Anomalous intraseasonal events in the thermocline ridge region of Southern Tropical Indian Ocean and their regional impacts. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2012, 117, C03021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- West, B.J.; Han, W.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y. The Role of Oceanic Processes in the Initiation of Boreal Winter Intraseasonal Oscillations Over the Indian Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2020, 125, e2019JC015426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMott, C.A.; Klingaman, N.P.; Woolnough, S.J. Atmosphere-ocean coupled processes in the Madden-Julian oscillation. Rev. Geophys. 2015, 53, 1099–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madden, R.A. Large-scale, free Rossby waves in the atmosphere—An update. Tellus 2007, 59A, 571–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiki, A.; Katsumata, M.; Horii, T.; Hasegawa, T.; Richards, K.J.; Yoneyama, K.; Shirooka, R. Abrupt cooling associated with the oceanic Rossby wave and lateral advection during CINDY2011. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2013, 118, 5523–5535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinoda, T.; Han, W.; Zamudio, L.; Lien, R.-C.; Katsumata, M. Remote Ocean Response to the Madden–Julian Oscillation during the DYNAMO Field Campaign: Impact on Somali Current System and the Seychelles–Chagos Thermocline Ridge. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez, A.O. Reconsidering the Role of Rossby Waves in the Madden-Julian Oscillation, Colorado State University SOARS Summer 2009. Available online: https://opensky.ucar.edu/islandora/object/manuscripts%3A580/datastream/PDF/view (accessed on 24 February 2022).
- Chowdhury, R.R.; Prasanna Kumar, S.; Narvekar, J.; Chakraborty, A. Back-to-back occurrence of tropical cyclones in the Arabian Sea during October–November 2015: Causes and responses. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2020, 125, e2019JC015836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinault, J.-L. Modulated Response of Subtropical Gyres: Positive Feedback Loop, Subharmonic Modes, Resonant Solar and Orbital Forcing. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2018, 6, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Traon, P.-Y.; Minster, J.-F. Sea level variability and semiannual Rossby waves in the South Atlantic subtropical gyre. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 1993, 98, 12315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Koblinsky, C.J.; Howden, S. Annual Rossby Wave in the Southern Indian Ocean: Why Does It “Appear” to Break Down in the Middle Ocean? J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2001, 31, 54–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, W.S.; Gourdeau, L. The Annual Cycle of Circulation of the Southwest Subtropical Pacific, Analyzed in an Ocean GCM. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2007, 37, 1610–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, M.M.; Sutton, P.J.H.; Roemmich, D. Wind-driven and steric fluctuations of sea surface height in the southwest Pacific. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, P.C.; Ivanov, L.M.; Melnichenko, O.V.; Wells, N.C. On long baroclinic Rossby waves in the tropical North Atlantic observed from profiling floats. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2007, 112, C05032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinault, J.-L. How extreme extratropical cyclones interact with the oceans: Two case studies, Kentucky, February 2020, and Germany. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022; submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Pinault, J.-L. Global warming and rainfall oscillation in the 5–10 yr band in Western Europe and Eastern North America. Clim. Chang. 2012, 114, 621–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinault, J.-L. Regions Subject to Rainfall Oscillation in the 5–10 Year Band. Climate 2018, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skákala, J.; Bruun, J.T. A Mechanism for Pacific Interdecadal Resonances. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2018, 123, 6549–6561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olascoaga, M.J. Deep ocean influence on upper ocean baroclinic instability. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2001, 106, 26863–26877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisiecki, L.E.; Raymo, M.E. A Pliocene-Pleistocene stack of 57 globally distributed benthic δ18O records. Paleoceanography 2005, 20, PA1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berger, A.; Loutre, M.-F. Insolation values for the climate of the last 10 million years. Quat. Sci. Rev. 1991, 10, 297–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeebe, R.E.; Lourens, L.J. Solar System chaos and the Paleocene–Eocene boundary age constrained by geology and astronomy. Science 2019, 365, 926–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



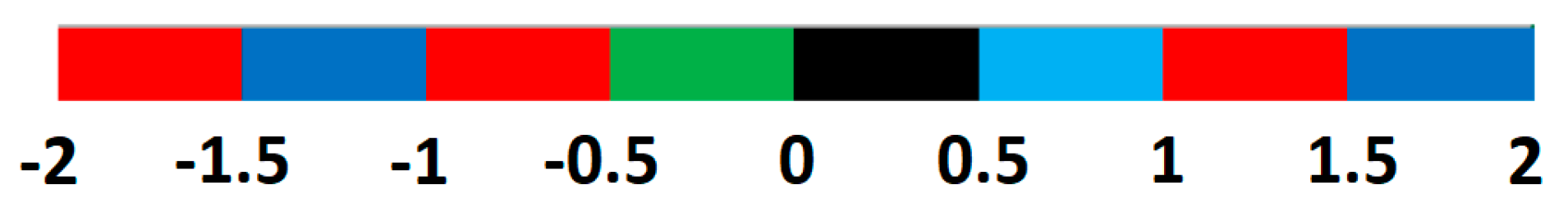


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pinault, J.-L. A Review of the Role of the Oceanic Rossby Waves in Climate Variability. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 493. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10040493
Pinault J-L. A Review of the Role of the Oceanic Rossby Waves in Climate Variability. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2022; 10(4):493. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10040493
Chicago/Turabian StylePinault, Jean-Louis. 2022. "A Review of the Role of the Oceanic Rossby Waves in Climate Variability" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 10, no. 4: 493. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10040493
APA StylePinault, J.-L. (2022). A Review of the Role of the Oceanic Rossby Waves in Climate Variability. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 10(4), 493. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10040493





