A Cooperative Hunting Method for Multi-AUV Swarm in Underwater Weak Information Environment with Obstacles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- In order to apply the proposed method in a real underwater environment, the actual constraints of underwater cooperative hunting tasks are considered. An underwater cooperative hunting task model including underwater static and dynamic obstacles, AUV sensing interaction distance limitation, AUV speed variation, target confrontation strategy, and other influencing factors is established.
- (2)
- In order to achieve the stability of the final formation of AUVs, the formation control function of the encirclement process is proposed, which realizes the effective usage of all the AUVs and improves the stability of the final formation. To solve the local oscillation problem during obstacle avoidance, based on the APF-based method, an obstacle avoidance preference motion control function is proposed to realize the smoothing path of the obstacle avoidance and shorten the path length.
- (3)
- To adapt to the requirements of different stages in the cooperative hunting process, an adaptive weight control unit is designed to adjust the collision-free and hunting strategy weights.
2. Problem Statement
2.1. Assumption for Hunter AUV
2.2. Strategy for Intelligent Target
3. Methods
3.1. APF-Based Method
3.2. Strategy of Hunting Preference
3.3. Strategy of Obstacle Avoidance Preference
3.4. Adaptive Weight Control Unit
4. Simulation Results
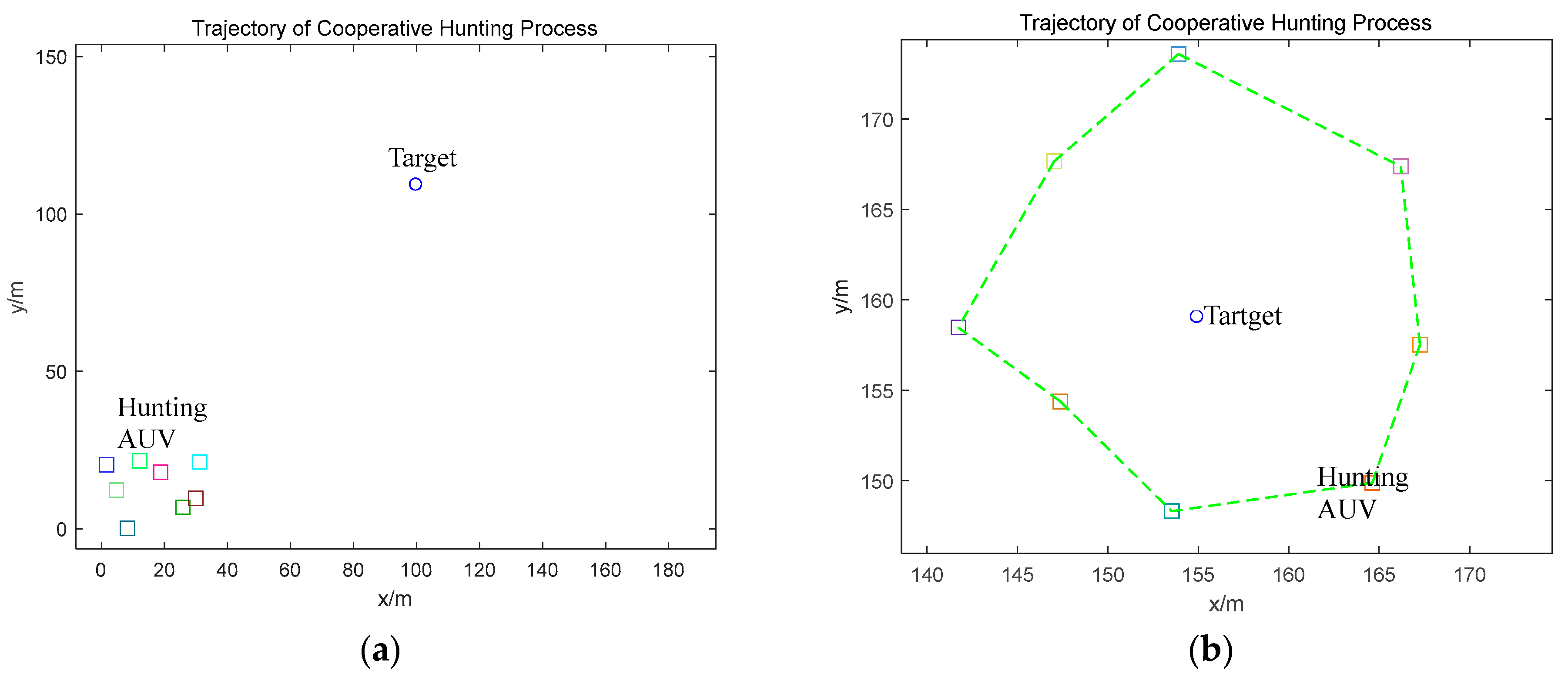
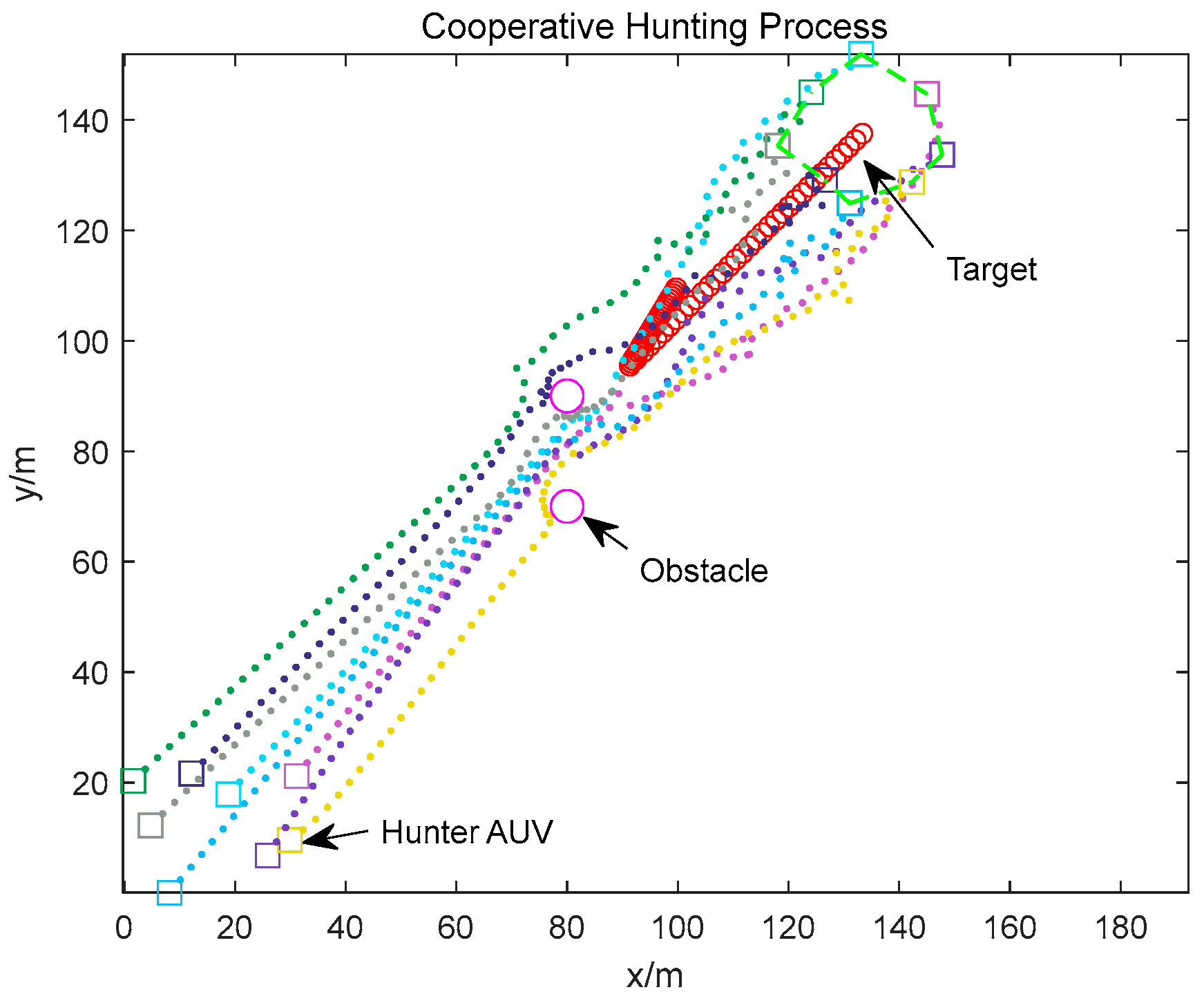
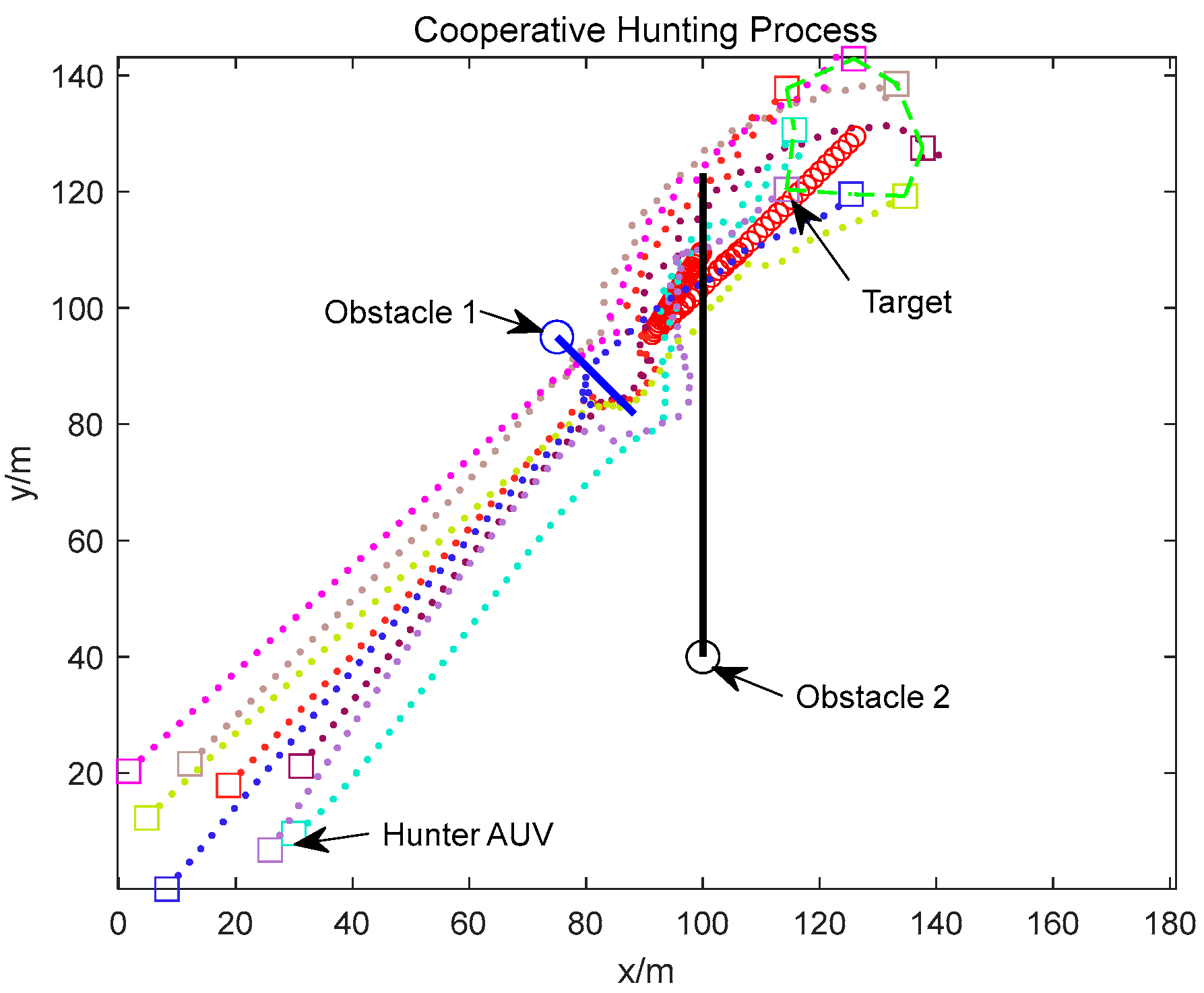
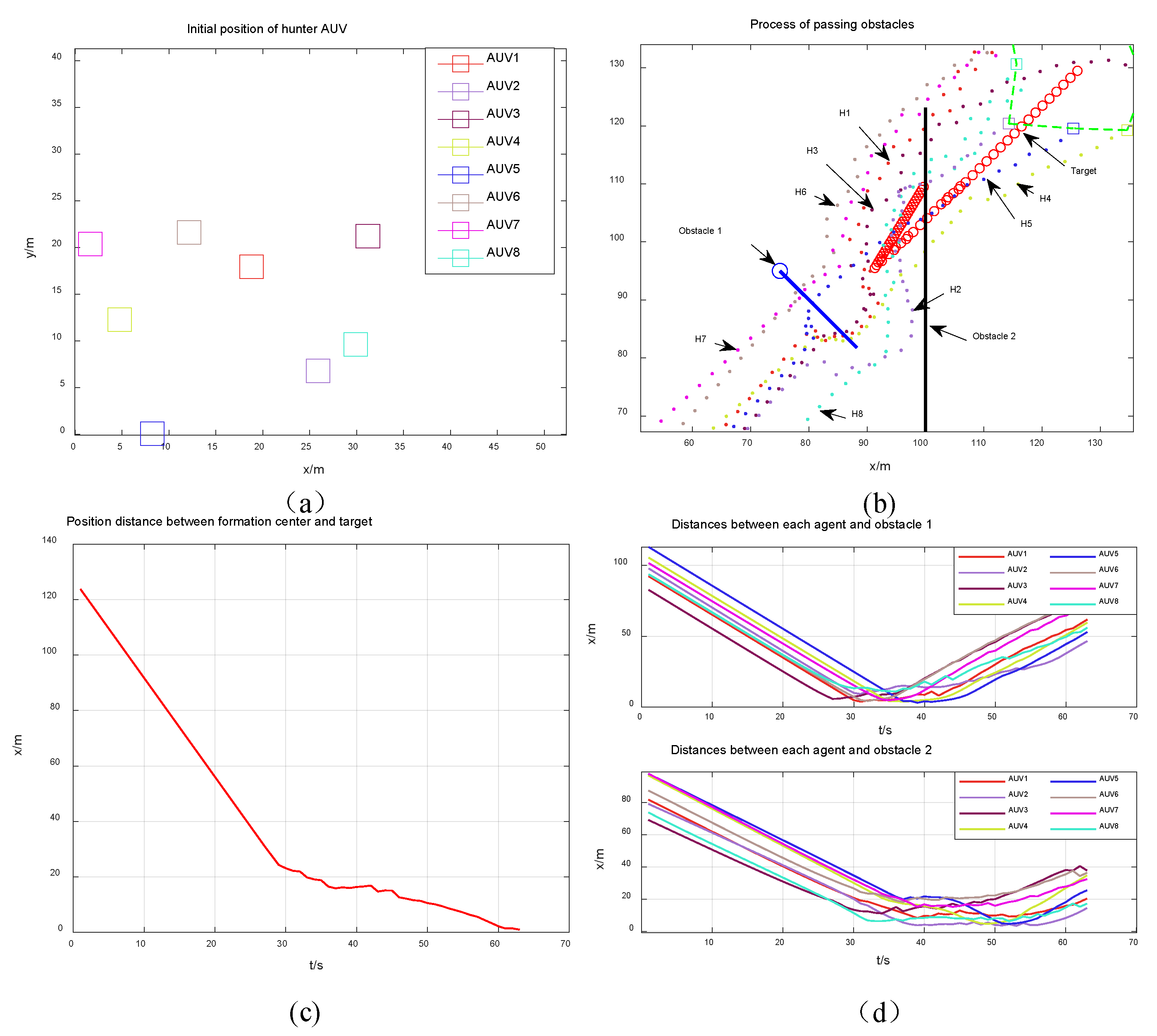
4.1. Static Obstacle Environment Simulation
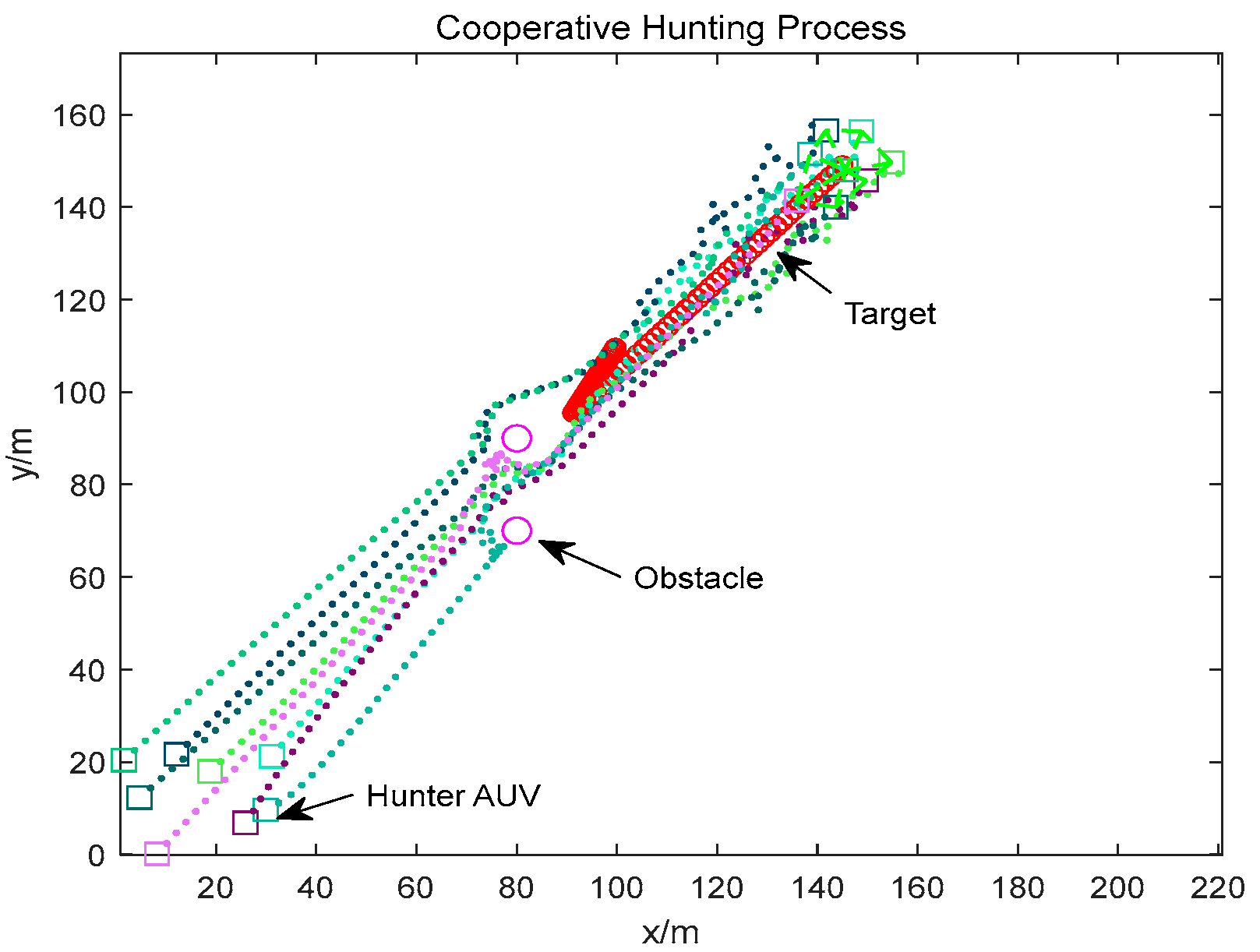
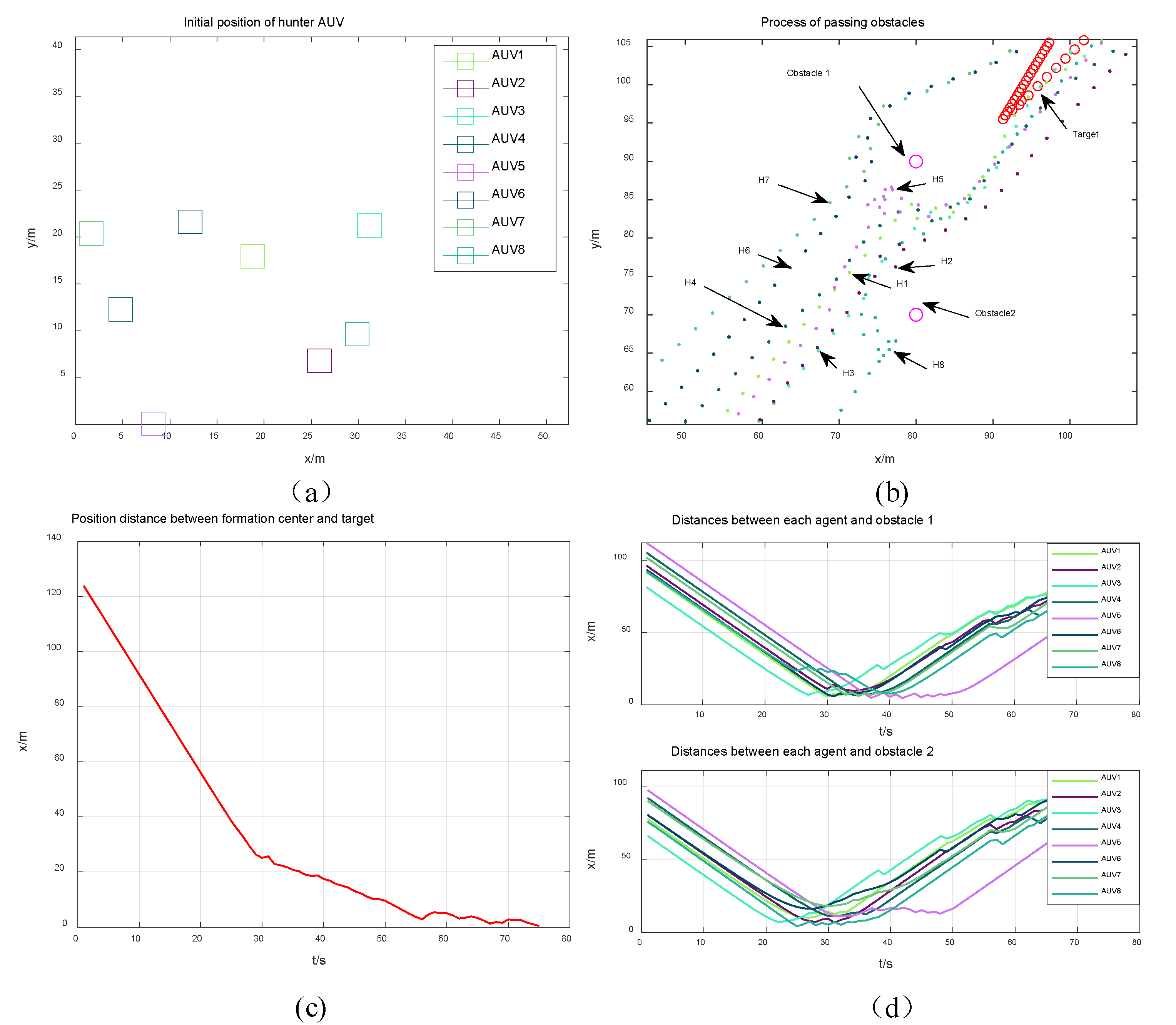
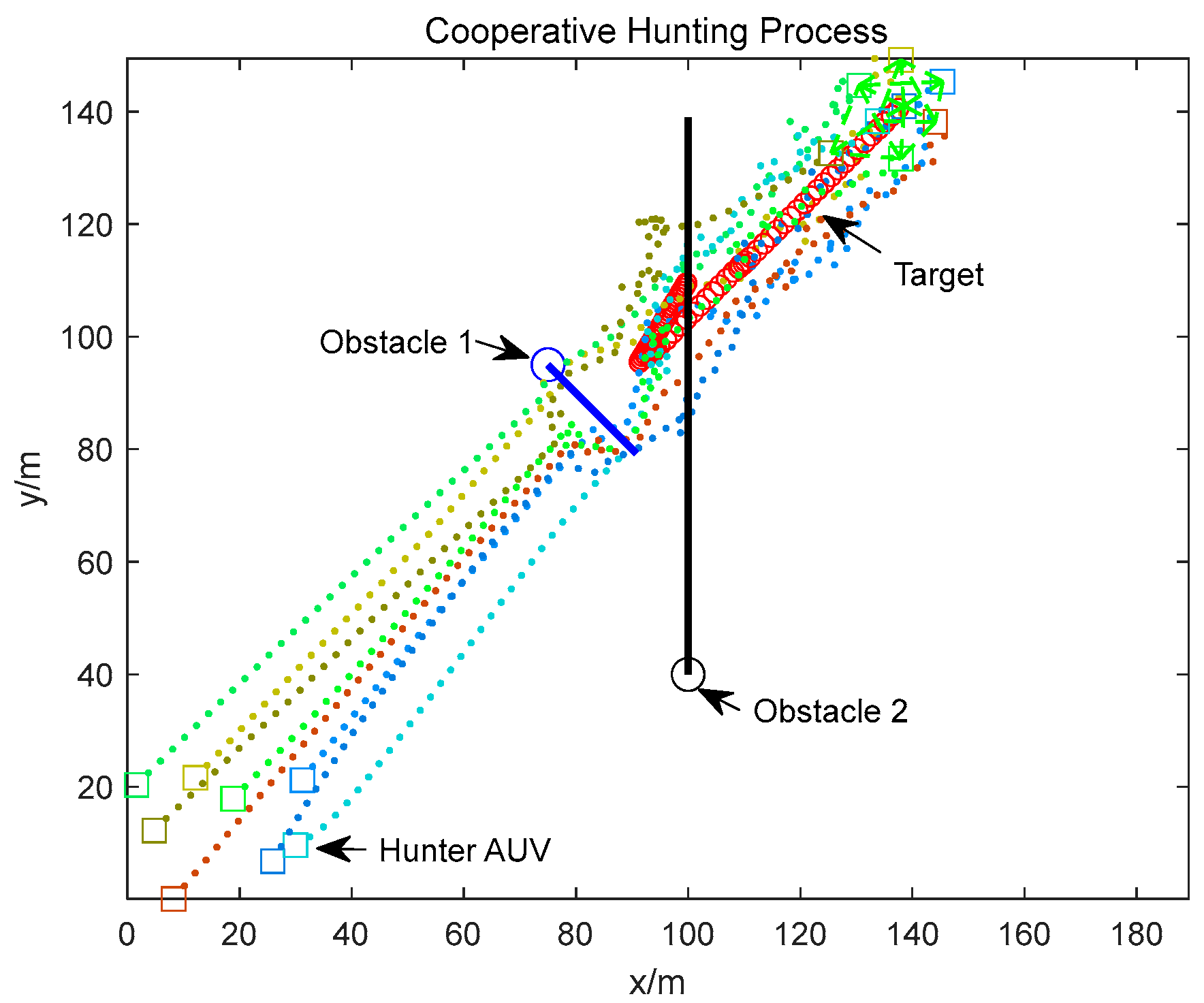
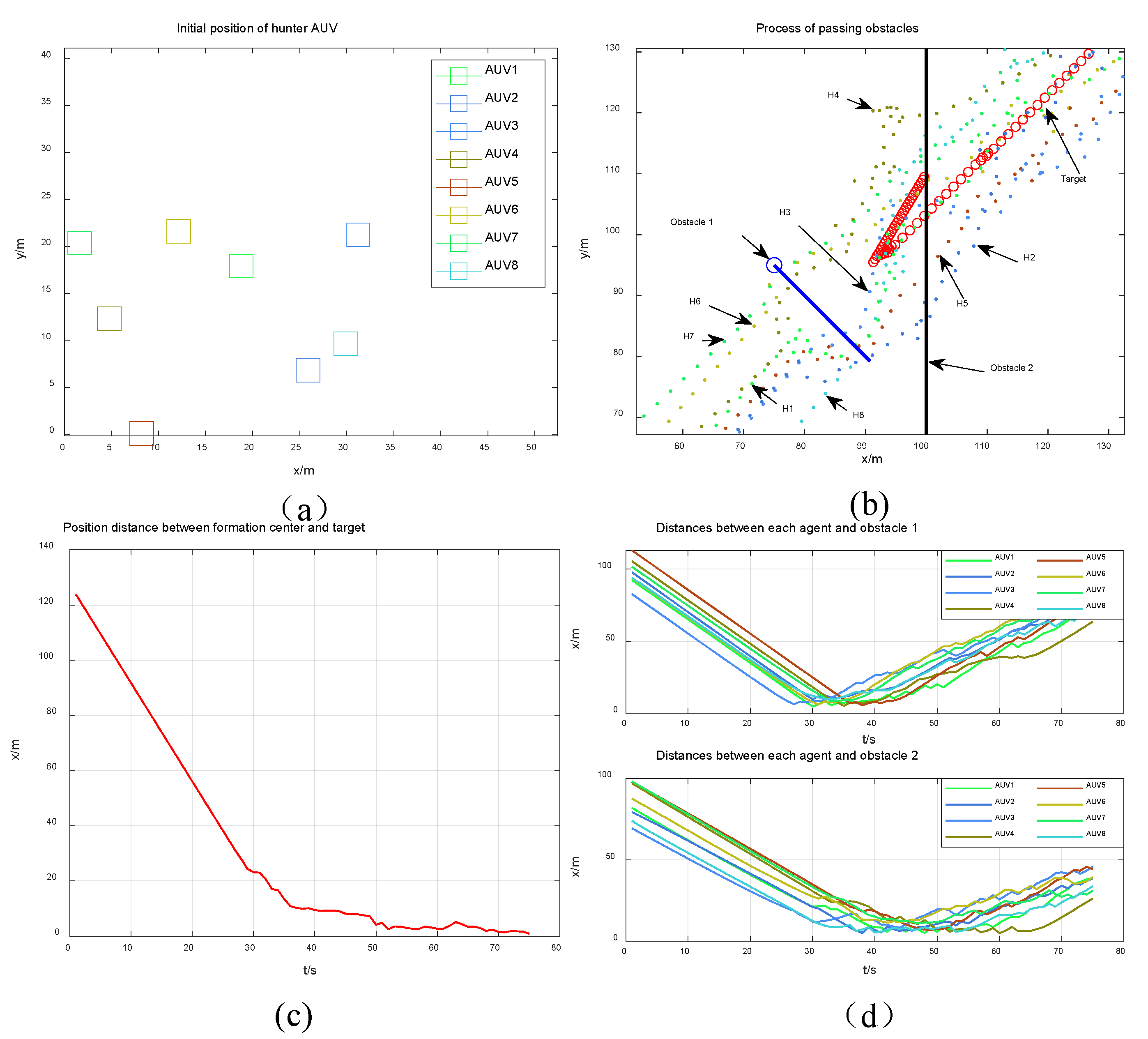
4.2. Dynamic Obstacle Environment Simulation
4.3. Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- An, R.; Guo, S.; Zheng, L.; Hirata, H.; Gu, S. Uncertain moving obstacles avoiding method in 3D arbitrary path planning for a spherical underwater robot. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2022, 151, 104011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Deng, Y.; Duan, H. Edge-based target detection for unmanned aerial vehicles using competitive Bird Swarm Algorithm. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2018, 78, 708–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, T.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, F.; Cen, N.; Li, T.; Xie, G. Global Vision-Based Formation Control of Soft Robotic Fish Swarm. Soft Robot. 2020, 8, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreychuk, A.; Yakovlev, K.; Surynek, P.; Atzmon, D.; Stern, R. Multi-agent pathfinding with continuous time. Artif. Intell. 2022, 305, 103662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Yang, L.; Shi, P.; Luo, C. An improved DSA-based approach for multi-AUV cooperative search. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2018, 2018, 2186574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Chen, P.C. Smooth Transition in Communication for Swarm Control With Formation Change. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 16, 6962–6971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebel, H.; Luo, W.; Yu, F.; Tang, Q.; Eberhard, P. Design and Experimental Validation of a Distributed Cooperative Transportation Scheme. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2020, 18, 1157–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Dong, X.; Li, Q.; Ren, Z. Distributed cooperative encirclement hunting guidance for multiple flight vehicles system. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2019, 95, 105475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelazo, D.; Franchi, A.; Buelthoff, H.H.; Giordano, P.R. Decentralized rigidity maintenance control with range measurements for multi-robot systems. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2015, 34, 105–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zelazo, D. Bearing Rigidity and Almost Global Bearing-Only Formation Stabilization. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2015, 61, 1255–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, M.; Xie, G. Simple agents, smart swarms: A cooperative search algorithm for swarms of autonomous underwater vehicles. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2022, 53, 1995–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarahari, M.; Khanmirza, E.; Doostie, S. Multi-objective multi-robot path planning in continuous environment using an enhanced Genetic Algorithm. Expert Syst. Appl. 2018, 115, 106–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Lv, R.; Cao, X.; Yang, S.X. Multi-AUV Hunting Algorithm Based on Bio-inspired Neural Network in Unknown Environments. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2015, 12, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, T.; Morere, P.; Ramos, F.; Francis, G. Bayesian Local Sampling-based Planning. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 1954–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, H.; Jimenez, M.; Goddard, Z.; Sparapany, M.; Boots, B.; Mazumdar, A. Adversarial Sampling-Based Motion Planning. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 4267–4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Dong, L.; Sun, C.; Wang, J. Asynchronous Multithreading Reinforcement-Learning-Based Path Planning and Tracking for Unmanned Underwater Vehicle. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2021, 52, 2757–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Z. Cooperative control for swarming systems based on reinforcement learning in unknown dynamic environment. Neurocomputing 2020, 410, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; He, H.; Yu, H.; Wang, H.; Li, G.; Shi, M.; Cao, D. Hybrid Path Planning Combining Potential Field with Sigmoid Curve for Autonomous Driving. Sensors 2020, 20, 7197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Ding, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Cao, D.; Xu, N.; Hu, C. A Motion Planning and Tracking Framework for Autonomous Vehicles Based on Artificial Potential Field-Elaborated Resistance Network (APFE-RN) Approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 1376–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Zhou, C.; Cheng, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Tan, M. A Distributed Hunting Approach for Multiple Autonomous Robots. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2013, 10, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.; Tang, J.; Lao, S. Collision Avoidance for Cooperative UAVs With Optimized Artificial Potential Field Algorithm. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 18382–18390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinostroza, M.A.; Xu, H.; Guedes Soares, C. Cooperative operation of autonomous surface vehicles for maintaining formation in complex marine environment. Ocean Eng. 2019, 183, 132–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Bucknall, R. The angle guidance path planning algorithms for unmanned surface vehicle formations by using the fast marching method. Appl. Ocean Res. 2016, 59, 327–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanes Luis, S.; Peralta, F.; Tapia Córdoba, A.; Rodríguez del Nozal, Á.; Toral Marín, S.; Gutiérrez Reina, D. An evolutionary multi-objective path planning of a fleet of ASVs for patrolling water resources. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2022, 112, 104852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Qu, X.; Wang, N.; Li, Y. Swarm velocity guidance based distributed finite-time coordinated path-following for uncertain under-actuated autonomous surface vehicles. ISA Trans. 2021, 112, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Zhu, D.; Sun, B. A multi-AUV cooperative hunting method in 3-D underwater environment with obstacle. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2016, 50, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Sun, H.; Jan, G.E. Multi-AUV cooperative target search and tracking in unknown underwater environment. Ocean Eng. 2018, 150, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhu, D. A Novel Cooperative Hunting Algorithm for Inhomogeneous Multiple Autonomous Underwater Vehicles. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 7818–7828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Yang, L.; Wu, L.; Fan, X. An Improved Spinal Neural System-Based Approach for Heterogeneous AUVs Cooperative Hunting. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2017, 20, 672–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Xu, X. Hunting Algorithm for Multi-AUV Based on Dynamic Prediction of Target Trajectory in 3D Underwater Environment. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 138529–138538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Sun, Q. Multiautonomous underwater vehicle consistent collaborative hunting method based on generative adversarial network. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2020, 17, 663–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Fu, Y.; Kang, F.; Gao, J.; Qiang, N. A Behavior-Driven Coordination Control Framework for Target Hunting by UUV Intelligent Swarm. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 4838–4859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Symbol | Description | Value | Units |
|---|---|---|---|
| t | Steps of time | 1 | s |
| n | Number of hunter AUVs | 8 | - |
| T | Maximum steps of simulation | 100 | s |
| L | AUV sensing range radius | 10 | m |
| VT1 | Target cruising speed | [−0.3, −0.5] | m/s |
| VT2 | Target escaping speed | 1.697 | m/s |
| Vmax | Maximum speed of hunter AUVs | 3 | m/s |
| Vmin | Minimum speed of hunter AUVs | 0.1 | m/s |
| Xt | Target initial coordinates | [100, 110] | m |
| rT | Target sensing range radius | 20 | m |
| R | Obstacle influence range | 8 | m |
| RT | Hunting convergence parameters | 10 | m |
| h0 | Friendly neighbor repulsion constant | 1 | - |
| ω | Perturbation | 0.1 | - |
| AUV Number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HAP-IAPF | 56.4 | 62.8 | 60.8 | 52.0 | 62.5 | 50.8 | 62.9 | 50.7 | 57.4 |
| APF based | 61.1 | 62.2 | 62.0 | 61.6 | 59.7 | 61.1 | 61.2 | 54.5 | 60.4 |
| AUV Number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HAP-IAPF | 111.8 | 98.2 | 119.6 | 107.0 | 107.2 | 117.7 | 118.8 | 113.6 | 111.7 |
| APF-based | 115.4 | 121.0 | 121.5 | 113.6 | 120.0 | 122.2 | 123.0 | 110.4 | 118.4 |
| Simulation Environment | Algorithm | Calculation Time (s) | Path Length (m) | Heading Deflections (Times) | Completion Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Static Environment | HAP-IAPF | 119.78 | 57.4 | 4.12 | 64 |
| APF-based | 112.25 | 60.4 | 5.38 | 75 | |
| OAPF | 162.63 | 59.4 | 4.50 | 67 | |
| Dynamic environment | HAP-IAPF | 126.00 | 111.7 | 4.50 | 63 |
| APF-based | 117.71 | 118.4 | 7.75 | 75 | |
| OAPF | 177.33 | 108.1 | 5.50 | 83 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Z.; Hu, Q.; Feng, H.; Feng, X.; Su, W. A Cooperative Hunting Method for Multi-AUV Swarm in Underwater Weak Information Environment with Obstacles. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1266. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10091266
Zhao Z, Hu Q, Feng H, Feng X, Su W. A Cooperative Hunting Method for Multi-AUV Swarm in Underwater Weak Information Environment with Obstacles. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2022; 10(9):1266. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10091266
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Zhenyi, Qiao Hu, Haobo Feng, Xinglong Feng, and Wenbin Su. 2022. "A Cooperative Hunting Method for Multi-AUV Swarm in Underwater Weak Information Environment with Obstacles" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 10, no. 9: 1266. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10091266
APA StyleZhao, Z., Hu, Q., Feng, H., Feng, X., & Su, W. (2022). A Cooperative Hunting Method for Multi-AUV Swarm in Underwater Weak Information Environment with Obstacles. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 10(9), 1266. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10091266






