Survey on Low-Cost Underwater Sensor Networks: From Niche Applications to Everyday Use
Abstract
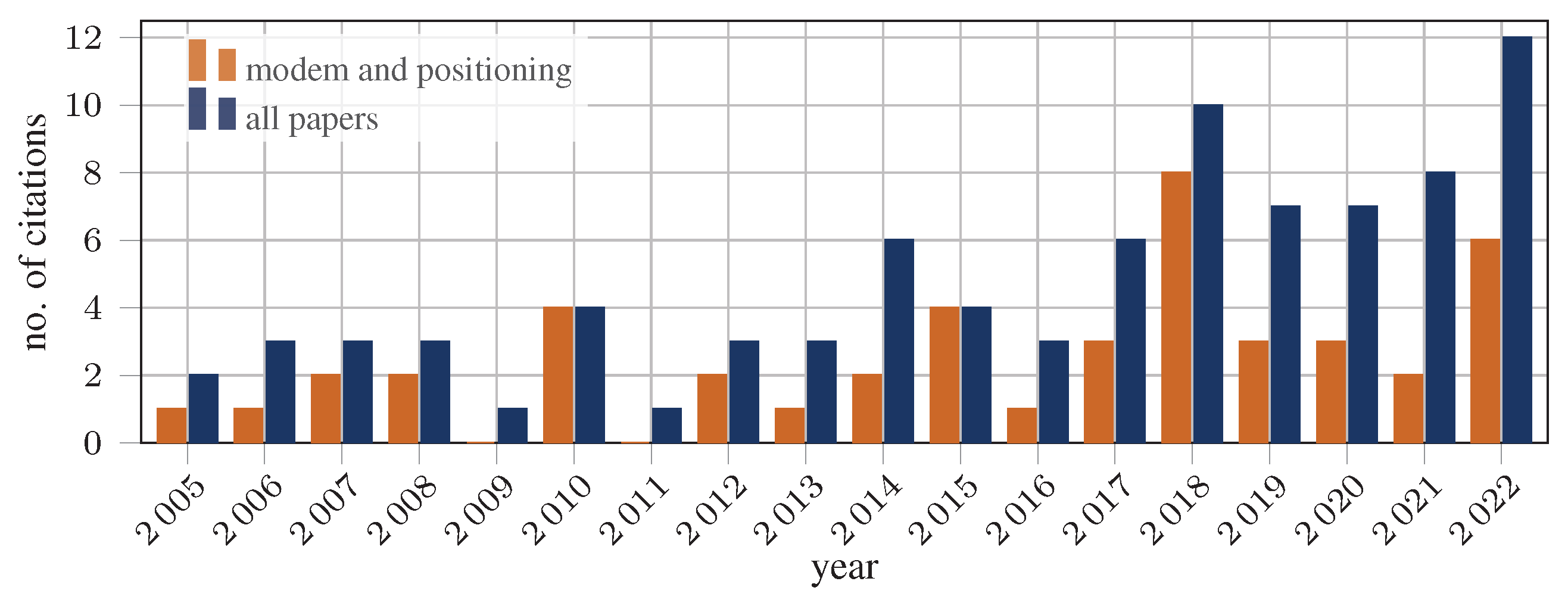
:1. Introduction
2. Underwater Acoustic Modems
2.1. Introduction to Underwater Wireless Communication
2.2. Acoustic Modems for Offshore Applications
2.3. Low-Cost Acoustic Modems
3. Underwater Acoustic Positioning Systems
3.1. Introduction to Underwater Positioning Systems
3.2. Acoustic Positioning for Offshore Applications
3.3. Low-Cost Acoustic Positioning Systems
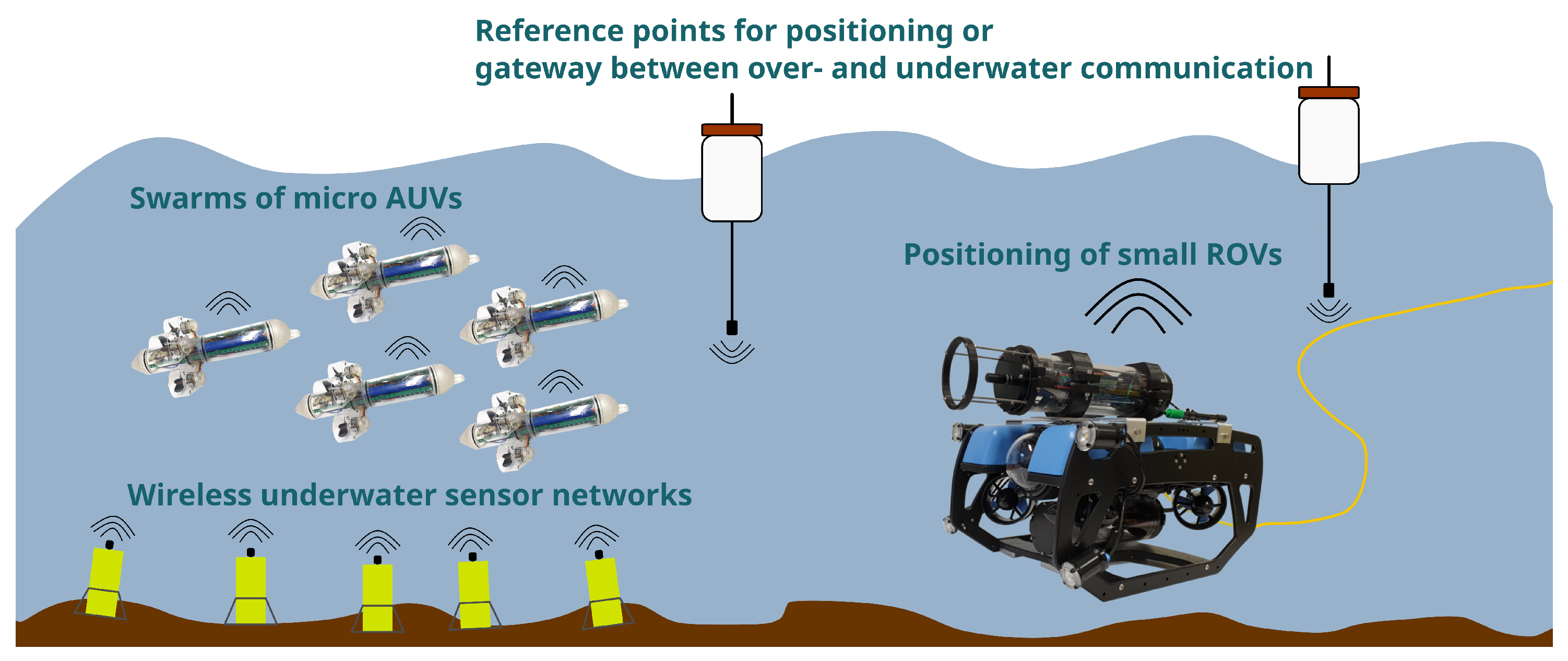
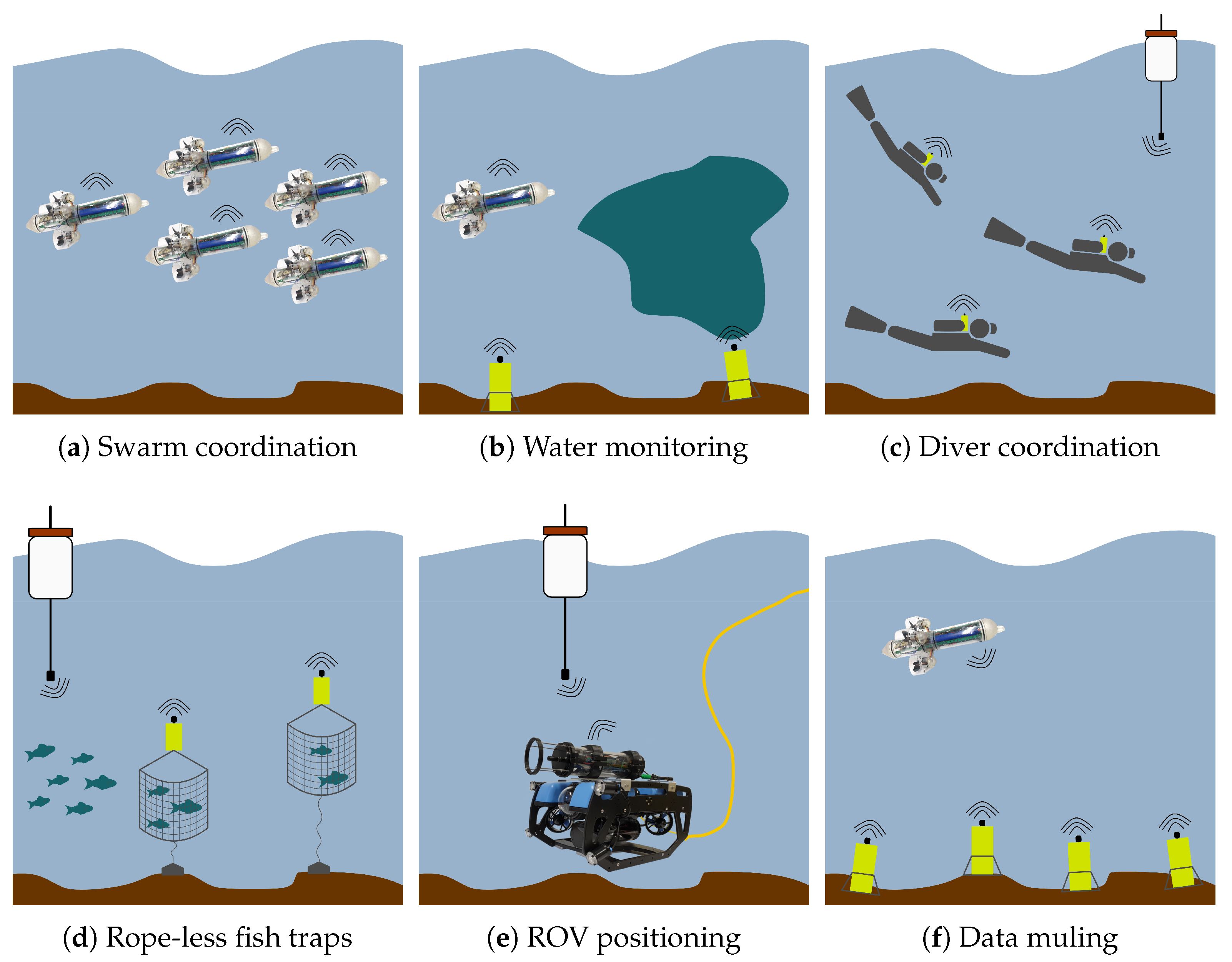
4. Applications
4.1. New Applications Enabled by Low-Cost Acoustic Modems and Positioning Systems
4.2. Current Challenges and Future Trends
5. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Underwater Acoustic Modems. Available online: https://evologics.de/acoustic-modems (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Develogic Subsea Systems. Available online: http://www.develogic.de/ (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Teledyne-Benthos Acoustic Modems. Available online: http://www.teledynemarine.com/acoustic-modems/ (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Sonardyne International Ltd. Micro-Ranger 2 USBL. Available online: http://www.sonardyne.com/products/micro-ranger-2-shallow-water-usbl-system/ (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- iXblue SAS. Gaps M7. Available online: http://www.ixblue.com/store/gaps-m7/ (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Blueprint Design Engineering Ltd. Seatrac Lightweigth. Available online: http://www.blueprintsubsea.com/seatrac/seatrac-lightweight (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Cario, G.; Casavola, A.; Gjanci, P.; Lupia, M.; Petrioli, C.; Spaccini, D. Long lasting underwater wireless sensors network for water quality monitoring in fish farms. In Proceedings of the MTS/IEEE OCEANS 2017, Aberdeen, UK, 19–22 June 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Signori, A.; Campagnaro, F.; Steinmetz, F.; Renner, B.C.; Zorzi, M. Data Gathering from a Multimodal Dense Underwater Acoustic Sensor Network Deployed in Shallow Fresh Water Scenarios. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2019, 8, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BlueROV2. Available online: https://bluerobotics.com/store/rov/bluerov2/ (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Hydromea Exray. Available online: http://www.hydromea.com/exray-wireless-underwater-drone/ (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Water Linked Modem M64. Available online: http://www.waterlinked.com/modem/m-64 (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Renner, B.C.; Heitmann, J.; Steinmetz, F. ahoi: Inexpensive, Low-power Communication and Localization for Underwater Sensor Networks and AUVs. ACM Trans. Sens. Netw. 2020, 16, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tritech Micron Modem—Acoustic Modem. Available online: http://www.tritech.co.uk/product/micron-data-modem (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Desert Star Systems. SAM-1 Technical Reference Manual. 2011. Available online: https://desertstarsystems.nyc3.digitaloceanspaces.com/Manuals/SAM-1TechnicalReferenceManual.pdf (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Low Cost Underwater Acoustic Modem for Makers of Underwater Things and OEMs! Available online: https://dspcommgen2.com/news-flash-low-cost-acoustic-modems-and-transducers-available-for-sale-now/ (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Sanchez, A.; Blanc, S.; Yuste, P.; Perles, A.; Serrano, J.J. An Ultra-Low Power and Flexible Acoustic Modem Design to Develop Energy-Efficient Underwater Sensor Networks. Sensors 2012, 12, 6837–6856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akyildiz, I.F.; Pompili, D.; Melodia, T. Underwater acoustic sensor networks: Research challenges. Ad Hoc Netw. 2005, 3, 257–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidemann, J.; Ye, W.; Wills, J.; Syed, A.; Li, Y. Research challenges and applications for underwater sensor networking. In Proceedings of the IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 3–6 April 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidemann, J.; Stojanovic, M.; Zorzi, M. Underwater Sensor Networks: Applications, Advances, and Challenges. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2012, 370, 158–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sendra, S.; Lloret, J.; Jimenez, J.M.; Parra, L. Underwater Acoustic Modems. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 4063–4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia, M.Y.I.; Poncela, J.; Otero, P. State-of-the-Art Underwater Acoustic Communication Modems: Classifications, Analyses and Design Challenges. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2021, 116, 1325–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, S.; Duecker, D.A.; Groves, K. Localisation of Unmanned Underwater Vehicles (UUVs) in Complex and Confined Environments: A Review. Sensors 2020, 20, 6203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-García, J.; Gómez-Espinosa, A.; Cuan-Urquizo, E.; García-Valdovinos, L.G.; Salgado-Jiménez, T.; Cabello, J.A.E. Autonomous Underwater Vehicles: Localization, Navigation, and Communication for Collaborative Missions. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paull, L.; Saeedi, S.; Seto, M.; Li, H. AUV Navigation and Localization: A Review. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2014, 39, 131–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, A.; Campagnaro, F.; Ashraf, K.; Rahman, M.R.; Ashok, A.; Guo, H. Communication for Underwater Sensor Networks: A Comprehensive Summary. ACM Trans. Sens. Netw. 2022, 19, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latypov, D. Compact quantum VLF/ELF sources for submarine to air communication. In Proceedings of the 2022 Sixth Underwater Communications and Networking Conference (UComms), Lerici, Italy, 30 August–1 September 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campagnaro, F.; Signori, A.; Zorzi, M. Wireless remote control for underwater vehicles. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 8, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Optical Communications. Available online: http://www.caci.com/optical-and-photonic-solutions (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Tapparello, C.; Casari, P.; Toso, G.; Calabrese, I.; Otnes, R.; van Walree, P.; Goetz, M.; Nissen, I.; Zorzi, M. Performance Evaluation of Forwarding Protocols for the RACUN Network. In Proceedings of the WUWNet ’13: Eighth ACM International Conference on Underwater Networks and Systems, Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 11–13 November 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Potter, J.; Alves, J.; Green, D.; Zappa, G.; Nissen, I.; McCoy, K. The JANUS underwater communications standard. In Proceedings of the 2014 Underwater Communications and Networking (UComms), Sestri Levante, Italy, 3–5 September 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ELAC UT 3000. Available online: http://www.elac-sonar.de/sphere-by-elac/ut-3000 (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Popoto Modem. Available online: http://popotomodem.com/ (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Cario, G.; Casavola, A.; Lupia, M.; Rosace, C. SeaModem: A Low-Cost Underwater Acoustic Modem for Shallow Water Communication. In Proceedings of the MTS/IEEE OCEANS 2015, Genova, Italy, 18–21 May 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonardyne. Underwater Acoustic Modem 6. Available online: http://www.sonardyne.com/product/underwater-acoustic-modems/ (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Subnero. Available online: https://subnero.com/ (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- SeaTrac Technology. Available online: http://www.blueprintsubsea.com/seatrac (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Coccolo, E.; Campagnaro, F.; Signori, A.; Favaro, F.; Zorzi, M. Implementation of AUV and Ship Noise for Link Quality Evaluation in the DESERT Underwater Framework. In Proceedings of the WUWNet ’18: Thirteenth ACM International Conference on Underwater Networks & Systems, Shenzhen, China, 3–5 December 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Walree, P.; Colin, M. In Situ Performance Prediction of a Coherent Acoustic Modem in a Reverberant Environment. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2021, 47, 236–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dol, H. EDA-SALSA: Towards smart adaptive underwater acoustic networking. In Proceedings of the MTS/IEEE OCEANS 2019, Marseille, France, 17–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modems for Underwater Communication. Available online: http://www.kongsberg.com/maritime/products/Acoustics-Positioning-and-Communication/modems/ (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Dol, H.; Colin, M.; van Walree, P.; Otnes, R. Field experiments with a dual-frequency-band underwater acoustic network. In Proceedings of the 2018 Fourth Underwater Communications and Networking Conference (UComms), Lerici, Italy, 28–30 August 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patria—Naval Solutions. Available online: http://www.patriagroup.com/products/naval-solutions (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Campagnaro, F.; Francescon, R.; Tronchin, D.; Zorzi, M. On the Feasibility of Video Streaming through Underwater Acoustic Links. In Proceedings of the 2018 Fourth Underwater Communications and Networking Conference (UComms), Lerici, Italy, 28–30 August 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, M.; Gurney, A.; Pompili, D. Adaptive Underwater Video Transmission via Software-Defined MIMO Acoustic Modems. In Proceedings of the MTS/IEEE OCEANS 2018, Charleston, SC, USA, 22–25 October 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LinkQuest Underwater Acoustic Modems. Available online: http://www.link-quest.com/html/models1.htm (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Demirors, E.; Shankar, B.G.; Santagati, G.E.; Melodia, T. SEANet: A Software-Defined Acoustic Networking Framework for Reconfigurable Underwater Networking. In Proceedings of the ACM WUWNET ’15: 10th International Conference on Underwater Networks & Systems, Washington, DC, USA, 22–24 October 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaujean, P.P.; Spruance, J.; Carlson, E.A.; Kriel, D. HERMES—A high-speed acoustic modem for real-time transmission of uncompressed image and status transmission in port environment and very shallow water. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2008, Québec City, QC, Canada, 15–18 September 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurdak, R.; Aguiar, P.; Baldi, P.; Lopes, C.V. Software Modems for Underwater Sensor Networks. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2007, Aberdeen, UK, 18–21 June 2007; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; bin Abbas, W.; Syed, A.A. A Low-cost and Flexible Underwater Platform to Promote Experiments in UWSN Research. In Proceedings of the WUWNet ’12: Seventh ACM International Conference on Underwater Networks and Systems, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 5–6 November 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherlock, B.; Neasham, J.A.; Tsimenidis, C.C. Implementation of a spread-spectrum acoustic modem on an android mobile device. In Proceedings of the MTS/IEEE OCEANS 2017, Aberdeen, UK, 19–22 June 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, B.; Li, Y.; Faunce, B.; Domond, K.; Kimball, D.; Schurgers, C.; Kastner, R. Design of a Low-Cost Underwater Acoustic Modem. IEEE Embed. Syst. Lett. 2010, 2, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morozs, N.; Mitchell, P.D.; Zakharov, Y.; Mourya, R.; Petillot, Y.R.; Gibney, T.; Dragone, M.; Sherlock, B.; Neasham, J.A.; Tsimenidis, C.C.; et al. Robust TDA-MAC for practical underwater sensor network deployment: Lessons from USMART sea trials. In Proceedings of the WUWNet ’18: Thirteenth ACM International Conference on Underwater Networks & Systems, Shenzhen, China, 3–5 December 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Tong, F.; Song, A.; Zhang, F. Evaluating Acoustic Communication Performance of Micro AUV in Confined Space. In Proceedings of the MTS/IEEE 2018 OCEANS, Kobe, Japan, 28–31 May 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherlock, B.; Morozs, N.; Neasham, J.; Mitchell, P. Ultra-Low-Cost and Ultra-Low-Power, Miniature Acoustic Modems Using Multipath Tolerant Spread-Spectrum Techniques. Electronics 2022, 11, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neasham, J.A.; Goodfellow, G.; Sharphouse, R. Development of the “Seatrac” miniature acoustic modem and USBL positioning units for subsea robotics and diver applications. In Proceedings of the MTS/IEEE OCEANS 2015, Genova, Italy, 18–21 May 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Succorfish SC4X Data Sheet. Available online: https://succorfish.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/SC4X-Data-Sheet_V5.pdf (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Su, Y.; Dong, L.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, X.; Wei, X. A General Embedded Underwater Acoustic Communication System Based on Advance STM32. IEEE Embed. Syst. Lett. 2021, 13, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiveNET: Sealink. Available online: http://www.divenetgps.com/sealink (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Indriyanto, S.; Edward, I.Y.M. Ultrasonic Underwater Acoustic Modem Using Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) Modulation. In Proceedings of the 2018 4th International Conference on Wireless and Telematics (ICWT), Nusa Dua, Indonesia, 12–13 July 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coccolo, E.; Campagnaro, F.; Tronchin, D.; Montanari, A.; Francescon, R.; Vangelista, L.; Zorzi, M. Underwater Acoustic Modem for a MOrphing Distributed Autonomous Underwater Vehicle (MODA). In Proceedings of the MTS/IEEE OCEANS 2022, Chennai, India, 21–24 February 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wu, K.; Yuan, F. Underwater Acoustic Micromodem for Underwater Internet of Things. Hindawi Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2022, 2022, 9148756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Jeon, J.H.; Park, S.J. Micro-modem for short-range underwater communication systems. In Proceedings of the MTS/IEEE OCEANS 2014, St. John’s, NL, Canada, 14–19 September 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermans, J.; Sklivanitis, G.; Pados, D.A. A First-of-its-kind Low Size, Weight and Power Run-Time Reconfigurable Underwater Modem. In Proceedings of the Sixt Underwater Communications and Networking Conference (UComms), Lerici, Italy, 30 August–1 September 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodman, O.J. An Introduction to Inertial Navigation; Technical report; University of Cambridge, Computer Laboratory: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Duecker, D.A.; Bauschmann, N.; Hansen, T.; Kreuzer, E.; Seifried, R. Towards Micro Robot Hydrobatics: Vision-based Guidance, Navigation, and Control for Agile Underwater Vehicles in Confined Environments. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 24 October 2020–24 January 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guth, F.; Silveira, L.; Botelho, S.; Drews, P.; Ballester, P. Underwater SLAM: Challenges, state of the art, algorithms and a new biologically-inspired approach. In Proceedings of the 5th IEEE RAS/EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics, Sao Paulo, Brazil, 12–15 August 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallios, A.; Ridao, P.; Ribas, D.; Hernández, E. Scan matching SLAM in underwater environments. Auton. Robot. 2014, 36, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.P.; Diamant, R.; Seah, W.K.; Waldmeyer, M. A survey of techniques and challenges in underwater localization. Ocean. Eng. 2011, 38, 1663–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chandrasekhar, V.; Seah, W.K.; Choo, Y.S.; Ee, H.V. Localization in Underwater Sensor Networks: Survey and Challenges. In Proceedings of the 1st ACM International Workshop on Underwater Networks (WUWNet), Los Angeles, CA, USA, 25 September 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eustice, R.M.; Whitcomb, L.L.; Singh, H.; Grund, M. Experimental Results in Synchronous-Clock One-Way-Travel-Time Acoustic Navigation for Autonomous Underwater Vehicles. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Rome, Italy, 10–14 April 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, G.; Zetik, R.; Thoma, R.S. Performance comparison of TOA and TDOA based location estimation algorithms in LOS environment. In Proceedings of the 5th Workshop on Positioning, Navigation and Communication, Hannover, Germany, 27 March 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmetz, F.; Duecker, D.A.; Sichert, N.; Busse, C.; Kreuzer, E.; Renner, B.C. UWRange: An Open ROS Framework for Simulating Acoustic Ranging and Localization for Underwater Robots under Realistic Conditions. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Kyoto, Japan, 23–27 October 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Dosso, S.E.; Sun, D. Motion-Compensated Acoustic Localization for Underwater Vehicles. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2016, 41, 840–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, J.; Champion, B.; Joordens, M.A. Current Algorithms, Communication Methods and Designs for Underwater Swarm Robotics: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 153–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Shu, H.; Liang, Q.; Du, D.H.C. Silent Positioning in Underwater Acoustic Sensor Networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2008, 57, 1756–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrje, U.; Isokeit, C.; Meyer, B.; Maehle, E. A Robust Acoustic-Based Communication Principle for the Navigation of an Underwater Robot Swarm. In Proceedings of the MTS/IEEE 2018 OCEANS, Kobe, Japan, 28–31 May 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djapic, V.; Dong, W.; Spaccini, D.; Cario, G.; Casavola, A.; Gjanci, P.; Lupia, M.; Petrioli, C. Cooperation of coordinated teams of Autonomous Underwater Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 9th IFAC Symposium on Intelligent Autonomous Vehicles (IAV), Leipzig, Germany, 29 June–1 July 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebkal, K.G.; Kebkal, A.G.; Glushko, E.V.; Kebkal, V.K.; Sebastião, L.; Pascoal, A.; Ribeiro, J.; Silva, H.; Ribeiro, M.; Indiveri, G. Underwater Acoustic Modems with Synchronous Chip-Scale Atomic Clocks for Scalable Tasks of AUV Underwater Positioning. Gyroscopy Navig. 2019, 10, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcocer, A.; Oliveira, P.J.R.; Pascoal, A.M.S. Underwater acoustic positioning systems based on buoys with gps. In Proceedings of the Eighth European Conferenceon Underwater Acoustics (ECUA), Carvoeiro, Portugal, 12–15 June 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, R.; Cruz, N.; Matos, A. Synchronized intelligent buoy network for underwater positioning. In Proceedings of the MTS/IEEE OCEANS 2010, Seattle, WA, USA, 20–23 September 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahr, A.; Leonard, J.J.; Fallon, M.F. Cooperative Localization for Autonomous Underwater Vehicles. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2009, 28, 174–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitag, L.; Grund, M.; Singh, S.; Partan, J.; Koski, P.; Ball, K. The WHOI micro-modem: An acoustic communications and navigation system for multiple platforms. In Proceedings of the MTS/IEEE OCEANS 2005, Washington, DC, USA, 17–23 September 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgado, M.; Oliveira, P.; Silvestre, C. Design and experimental evaluation of an integrated USBL/INS system for AUVs. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Anchorage, AK, USA, 3–7 May 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgado, M.; Oliveira, P.; Silvestre, C. Tightly coupled ultrashort baseline and inertial navigation system for underwater vehicles: An experimental validation. J. Field Robot. 2013, 30, 142–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caiti, A.; Di Corato, F.; Fenucci, D.; Allotta, B.; Costanzi, R.; Monni, N.; Pugi, L.; Ridolfi, A. Experimental results with a mixed USBL/LBL system for AUV navigation. In Proceedings of the Underwater Communications and Networking (UComms), Sestri Levante, Italy, 3–5 September 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EvoLogics GmbH. Underwater USBL Positioning Systems. Available online: https://evologics.de/usbl (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Tritech International Limited. MicronNav 200. Available online: http://www.tritech.co.uk/product/micronnav-200 (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Teledyne Instruments, Inc. Teledyne Benthos Trackit USBL System. Available online: http://www.teledynemarine.com/trackit?ProductLineID=59 (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Sonardyne International Ltd. Ranger 2 USBL. Available online: http://www.sonardyne.com/products/ranger-2-subsea-positioning-usbl/ (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Fenucci, D.; Munafò, A.; Phillips, A.B.; Neasham, J.; Gold, N.; Sitbon, J.; Vincent, I.; Sloane, T. Development of smart networks for navigation in dynamic underwater environments. In Proceedings of the IEEE/OES Autonomous Underwater Vehicle Workshop (AUV), Porto, Portugal, 6–9 November 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munafò, A.; Śliwka, J.; Petroccia, R. Localisation Using Undersea Wireless Networks. In Proceedings of the MTS/IEEE OCEANS 2018, Kobe, Japan, 28–31 May 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quraishi, A.; Bahr, A.; Schill, F.; Martinoli, A. A Flexible Navigation Support System for a Team of Underwater Robots. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Multi-Robot and Multi-Agent Systems (MRS), New Brunswick, NJ, USA, 22–23 August 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duecker, D.A.; Steinmetz, F.; Kreuzer, E.; Renner, C. Micro AUV Localization for Agile Navigation with Low-cost Acoustic Modems. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/OES Autonomous Underwater Vehicles Symposium (AUV), St. John’s, NL, Canada, 30 September–2 October 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busse, C.; Renner, B.C. Towards Accurate Positioning of Underwater Vehicles Using Low-cost Acoustic Modems. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 23–27 May 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iscar Ruland, E.A.; Shree, A.; Goumas, N.; Johnson-Roberson, M. Low cost underwater acoustic localization. Proc. Meet. Acoust. 2017, 30, 070006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghaffarivardavagh, R.; Afzal, S.S.; Rodriguez, O.; Adib, F. Underwater Backscatter Localization: Toward a Battery-Free Underwater GPS. In Proceedings of the 19th ACM Workshop on Hot Topics in Networks (HotNets), Virtual, 4–6 November 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.; Adib, F. Underwater Backscatter Networking. In Proceedings of the SIGCOMM ’19: ACM Special Interest Group on Data Communication, Beijing, China, 19–23 August 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WaterLinked. Underwater GPS (UGPS). Available online: https://www.waterlinked.com/underwater-gps (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Rypkema, N.R.; Fischell, E.M.; Schmidt, H. One-way travel-time inverted ultra-short baseline localization for low-cost autonomous underwater vehicles. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Singapore, 29 May–3 June 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerulean Sonar. ROV Locator Bundle Mark II. Available online: https://ceruleansonar.com/products/rovl-mkii (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Cerulean Sonar. ROV Locator Bundle Mark III. Available online: https://ceruleansonar.com/products/rov-locator-mark-iii (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Diamant, R.; Campagnaro, F.; Dahan, S.; Francescon, R.; Zorzi, M. Development Of A Submerged Hub For Monitoring The Deep Sea. In Proceedings of the UACE2017—4th Underwater Acoustics Conference and Exhibition, Skiathos, Greece, 3–8 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Safe Passage. Available online: https://bluecology.org/shop/safe-passage/ (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Iacoponi, S.; Jansenvanvuure, G.; Santaera, G.; Mankovskii, N.; Zhilin, I.; Renda, F.; Stefanini, C.; De Masi, G. H-SURF: Heterogeneous Swarm of Underwater Robotic Fish. In Proceedings of the MTS/IEEE OCEANS 2022, Hampton Roads, VA, USA, 17–20 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Toffolo, N.; Campagnaro, F.; Zorzi, M. A Network Infrastructure for Monitoring Coastal Environments and Study Climate Changes in Marine Systems. In Proceedings of the MTS/IEEE OCEANS 2022, Hampton Roads, VA, USA, 17–20 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Courtene-Jones, W.; Quinn, B.; Gary, S.F.; Mogg, A.O.; Narayanaswamy, B.E. Microplastic pollution identified in deep-sea water and ingested by benthic invertebrates in the Rockall Trough, North Atlantic Ocean. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zainab, T.; Karstens, J.; Landsiedel, O. Cross-domain fusion in smart seafloor sensor networks. Inform. Spektrum 2022, 45, 290–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innovative and Cutting-Edge Marine Systems and Technologies. Available online: https://h2o-robotics.com/ (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Advanced, Small, Low Cost AUV Technology. Available online: http://www.ecosub.uk/ (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Manzanilla, A.; Reyes, S.; Garcia, M.; Mercado, D.; Lozano, R. Autonomous Navigation for Unmanned Underwater Vehicles: Real-Time Experiments Using Computer Vision. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2019, 4, 1351–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- subcCULTron. Available online: https://labust.fer.hr/labust/research/projects/subcultron (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- microFloat—A Simple Underwater Robot for Distributed Sensing in Coastal Waters. Available online: http://www.pmec.us/research-projects/microfloat (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Francescon, R.; Campagnaro, F.; Coccolo, E.; Signori, A.; Guerra, F.; Favaro, F.; Zorzi, M. An Event-Based Stack For Data Transmission Through Underwater Multimodal Networks. In Proceedings of the Fifth Underwater Communications and Networking Conference (UComms), Lerici, Italy, 31 August–2 September 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, V.E.; Delea, C.; Oeffner, J.; Sarpong, B.; Burmeister, H.-C.; Jahn, C. Robotic service concepts for the port of tomorrow: Developed via a small-scale demonstration testbed. In Proceedings of the 2020 European Navigation Conference (ENC), Virtual, 23–24 November 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zach, J.; Busse, C.; Funk, S.; Möllmann, C.; Renner, B.C.; Tiedemann, T. Towards Non-invasive Fish Monitoring in Hard-to-Access Habitats Using Autonomous Underwater Vehicles and Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the MTS/IEEE OCEANS 2021, San Diego, CA, USA, 20–23 September 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Walree, P.A. Propagation and Scattering Effects in Underwater Acoustic Communication Channels. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2013, 38, 614–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmetz, F.; Renner, B.C. From the Long-Range Channel in the Ocean to the Short-Range and Very Shallow-Water Acoustic Channel in Ports and Harbors. In Proceedings of the Underwater Communications and Networking Conference (UComms), Lerici, Italy, 31 August–2 September 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitre, M.; Koay, T.B.; Deane, G.; Chua, G. Variability in Shallow Water Communication Performance Near a Busy Shipping Lane. In Proceedings of the 2021 Fifth Underwater Communications and Networking Conference (UComms), Lerici, Italy, 31 August–2 September 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fondriest Data Buoys. Available online: http://www.fondriest.com/products/wireless-data/data-buoys.htm?product_list_order=price (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Blue Trail Engineering, LLC. Cobalt Connectors and Cables. Available online: http://www.bluetrailengineering.com/cobalt (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Steinmetz, F.; Renner, B.C. Taking LoRa for a Dive: CSS for Low-Power Acoustic Underwater Communication. In Proceedings of the Underwater Communications and Networking Conference (UComms), Lerici, Italy, 30 August–1 September 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

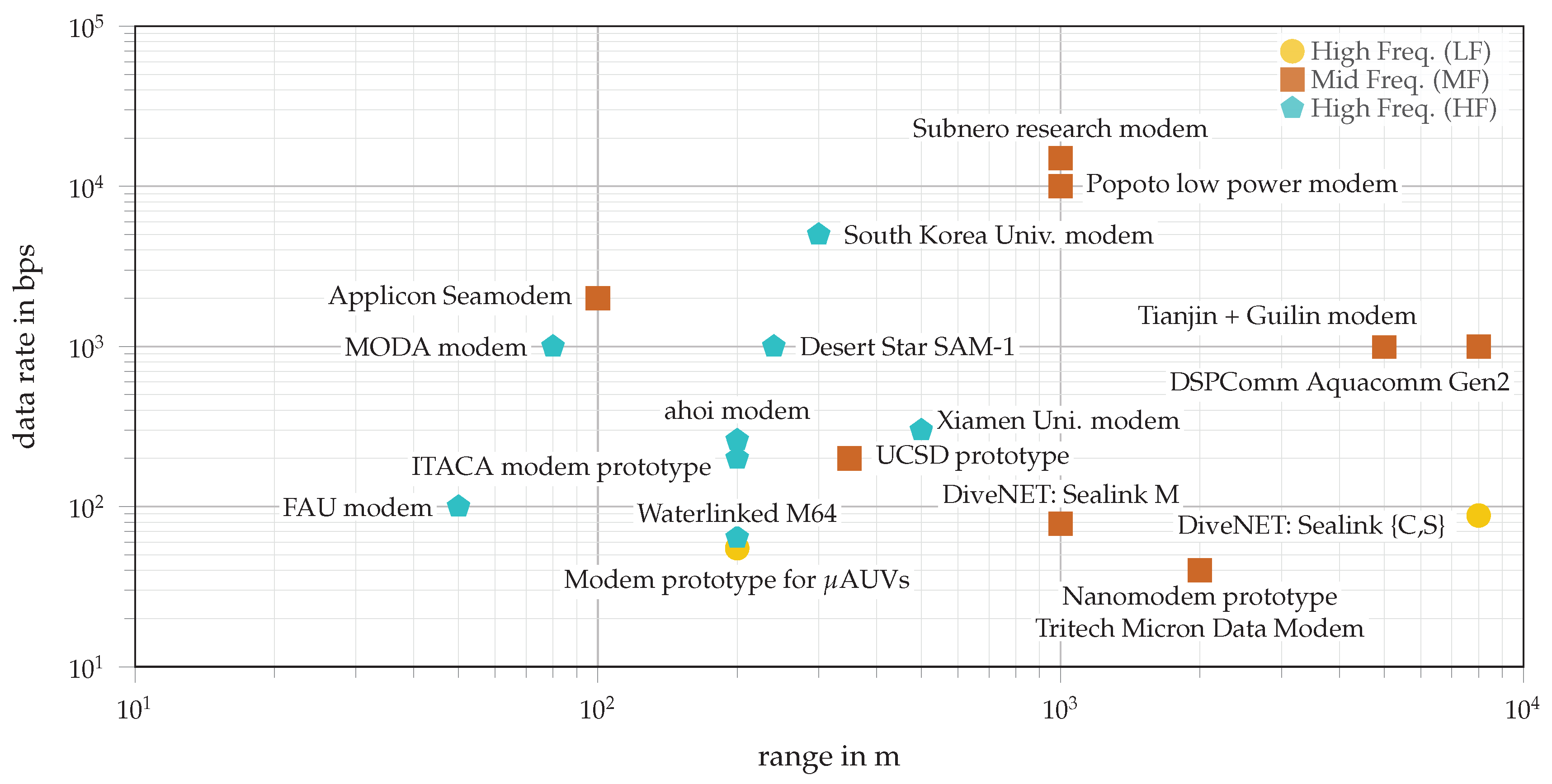



| Manufacturer and Model | Developer | Max Range | Bit Rate | Freq. Range | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LF | DiveNET: Sealink {C,S} [58] | commercial | 8 km | 80 bps | 5–15 kHz |
| Modem prototype for μAUVs [53] | research | 200 m | 55 bps | 11–14 kHz | |
| MF | UCSD prototype [51] | research | 350 m | 200 bps | 32–38 kHz |
| Nanomodem prototype [52,54] | research | 2 km | 40 bps | 24–28 kHz | |
| Tritech Micron Data Modem [13] | commercial | 2 km | 40 bps | 24–28 kHz | |
| Tianjin + Guilin modem [57] | research | {2.5–5} km | {0.125–1} kbps | 20–30 kHz | |
| Applicon Seamodem [33] | commercial | 100s of m | {0.75, 2} kbps | 25–35 kHz | |
| DSPComm Aquacomm Gen2 [15] | commercial | 8 km | {0.1, 1} kbps | 16–30 kHz | |
| DiveNET: Sealink M [58] | commercial | 1 km | 78 bps | 15–30 kHz | |
| Subnero research modem [35] | commercial | 1 km | 15 kbps | 20–32 kHz | |
| Popoto low power modem [32] | commercial | 1 km | 10 kbps | 20–40 kHz | |
| HF | ahoi modem [12] | research | 200 m | 260 bps | 50–75 kHz |
| ITACA modem prototype [16] | research | 200 m | 200 bps | 85–200 kHz | |
| Waterlinked M64 [11] | commercial | 200 m | 64 bps | 31–250 kHz | |
| Desert Star SAM-1 [14] | commercial | 240 m | 1 kbps | 34–48 kHz or 65–75 kHz | |
| MODA modem [60] | research | 80 m | 1 kbps | 50–70 kHz | |
| Xiamen Uni. modem [61] | research | 500 m | 200–300 bps | 35–45 kHz | |
| South Korea Univ. modem [62] | research | {100–300} m | {0.2–5} kbps | 70 kHz | |
| FAU modem [63] | research | 50 m | 100 bps | 100–150 kHz |
| System Possibilities | System Requirements | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Agent | Anchors | Self-Localization | Silent Positioning | High Update Rate | Simple Scalability | Resilience Clock Drifts | No Sync. Anchors | No Sync. Agent Anchors | Simplex Transmission |
| OWR, TOA | TX | RX | - | - | ✓ | - | - | (✓) | ✓ | ✓ |
| OWR, TDOA | TX | RX | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | ✓ |
| OWR, TOA | RX | TX | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | - | (✓) | ✓ | ✓ |
| OWR, TDOA | RX | TX | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | - | - | - | ✓ |
| TWR, TOA | TX/RX | RX/TX | ✓ | - | - | - | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | - |
| Device/Author | Algo. | Developer | Setup | Method | Area | Accuracy | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nanomodem [52] | [90,91] | research | LBL/SBL | TWR | 50 m × 50 m | lack of ground truth | TWR on network layer |
| Quraishi et al. [92] | [92] | research | SBL | OWR | 30 m × 15 m | 1.66 m RMS error | anchors transmit periodic (GNSS sync.) acoustic beacons |
| ahoi modem [12] | [93] | research | LBL | TWR | 70 m × 70 m | 1.36 m RMS error, 1.2 m CEP (GPS with 2.5 m CEP for ground truth) | BlueROV2 self-localization |
| ahoi modem [12] | [94] | research | SBL | TWR | 25 m × 25 m | positioning error below 0.4 m (RTK-GPS) | two anchors in small buoys |
| Ruland et al. [95] | [95] | research | LBL | OWR | — | — | simulation, self-build transducers |
| Jang et al. [97] | [96] | research | — | TWR | — | — | backscatter communication feasibility study |
| WaterLinked Underwater GPS [98] | — | commercial | SBL | OWR | 300 m × 300 m | 0.2% horizontal, 1% vertical | synchronization via cable or GPS at the beginning of a mission (0.17 m/h drift). |
| Rypkema et al. [99] | [99] | research | USBL | TWR | 140 m × 100 m | 6.4 m mean error to GPS, when the AUV surfaces | anchors transmit periodic (GPS sync.) acoustic beacons. AUV is synchronized with a CSAC |
| Blueprint Subsea Seatrac [6] | [55] | research/ commercial | USBL | TWR | 1000 m range | 0.1 m range resolution | integrated IMU and depth sensor |
| Cerulean Sonar Mark II [100] | — | commercial | USBL | OWR | 500 m range | 0.1 m slant range resolution | 0.5 m/h slant range error accumulation due to clock drifts |
| Cerulean Sonar Mark III [101] | — | commercial | USBL | TWR | 500 m range | 0.1 m slant range resolution | TWR to eliminate clock drifts |
| Sonardyne Micro-Ranger 2 USBL [4] | — | commercial | USBL | — | 995 m range | 5% slant range | typically no self-localization |
| Legacy Acoustic Modems and Positioning | Low-Cost Acoustic Modems and Positioning |
|---|---|
| Oil and Gas pipes inspection with AUVs | Micro AUV swarm coordination |
| Ship to submarine communication and positioning | Internal water quality assessment |
| Tsunami prevention systems | Divers mission coordination |
| Coastal surveillance and monitoring | Rope-less crab and fish traps |
| Military applications (MCM, ASW, REA, ISR) | Low-cost ROV positioning |
| Data muling in open sea with large AUVs | Data muling in internal waters with low-cost AUVs |
| Work class ROV USBL and positioning | and ASVs |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Campagnaro, F.; Steinmetz, F.; Renner, B.-C. Survey on Low-Cost Underwater Sensor Networks: From Niche Applications to Everyday Use. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11010125
Campagnaro F, Steinmetz F, Renner B-C. Survey on Low-Cost Underwater Sensor Networks: From Niche Applications to Everyday Use. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2023; 11(1):125. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11010125
Chicago/Turabian StyleCampagnaro, Filippo, Fabian Steinmetz, and Bernd-Christian Renner. 2023. "Survey on Low-Cost Underwater Sensor Networks: From Niche Applications to Everyday Use" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 11, no. 1: 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11010125
APA StyleCampagnaro, F., Steinmetz, F., & Renner, B.-C. (2023). Survey on Low-Cost Underwater Sensor Networks: From Niche Applications to Everyday Use. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 11(1), 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11010125






