J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11(2), 341; https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11020341 - 3 Feb 2023
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 2095
Abstract
Underwater wireless communication technology plays an important role in marine environment monitoring and ecological protection. Underwater optical wireless communications (UWOCs) can currently achieve a transmission distance of hundreds of meters, and the rate can reach hundreds of Mbps or even Gbps, with low
[...] Read more.
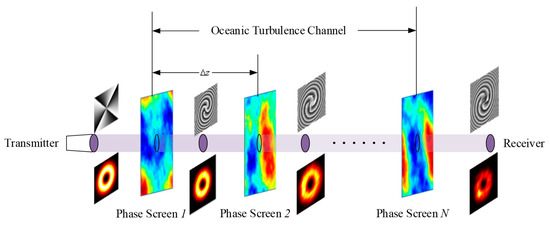
Underwater wireless communication technology plays an important role in marine environment monitoring and ecological protection. Underwater optical wireless communications (UWOCs) can currently achieve a transmission distance of hundreds of meters, and the rate can reach hundreds of Mbps or even Gbps, with low power consumption and high-speed features. In addition, UWOC also has the advantages of a small transceiver size and strong anti-electromagnetic interference ability, which is especially suitable for scenarios where underwater volume and power consumption are relatively limited. However, UWOC systems face problems such as unstable transceiver ends, ocean turbulence, and so on, resulting in reduced communication reliability and limited transmission distance. Establishing a stable and reliable communication link is critical to extending the communication distance of the UWOC system. In this paper, a model of ocean turbulence channels is established based on the power spectrum inversion method. The transmission characteristics of orbital angular momentum (OAM) light in an ocean turbulence channel are studied, then the mode selection of OAM light is determined. At the same time, the polarization coding technique is applied to the underwater OAM communication system for the first time. The simulation results show that this scheme can effectively extend the communication distance and reduce the system bit error rate.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Underwater Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks Technology)
►
Show Figures