Does the Elemental Composition of Rock Surfaces Affect Marine Benthic Communities of Diatoms and Cyanobacteria?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
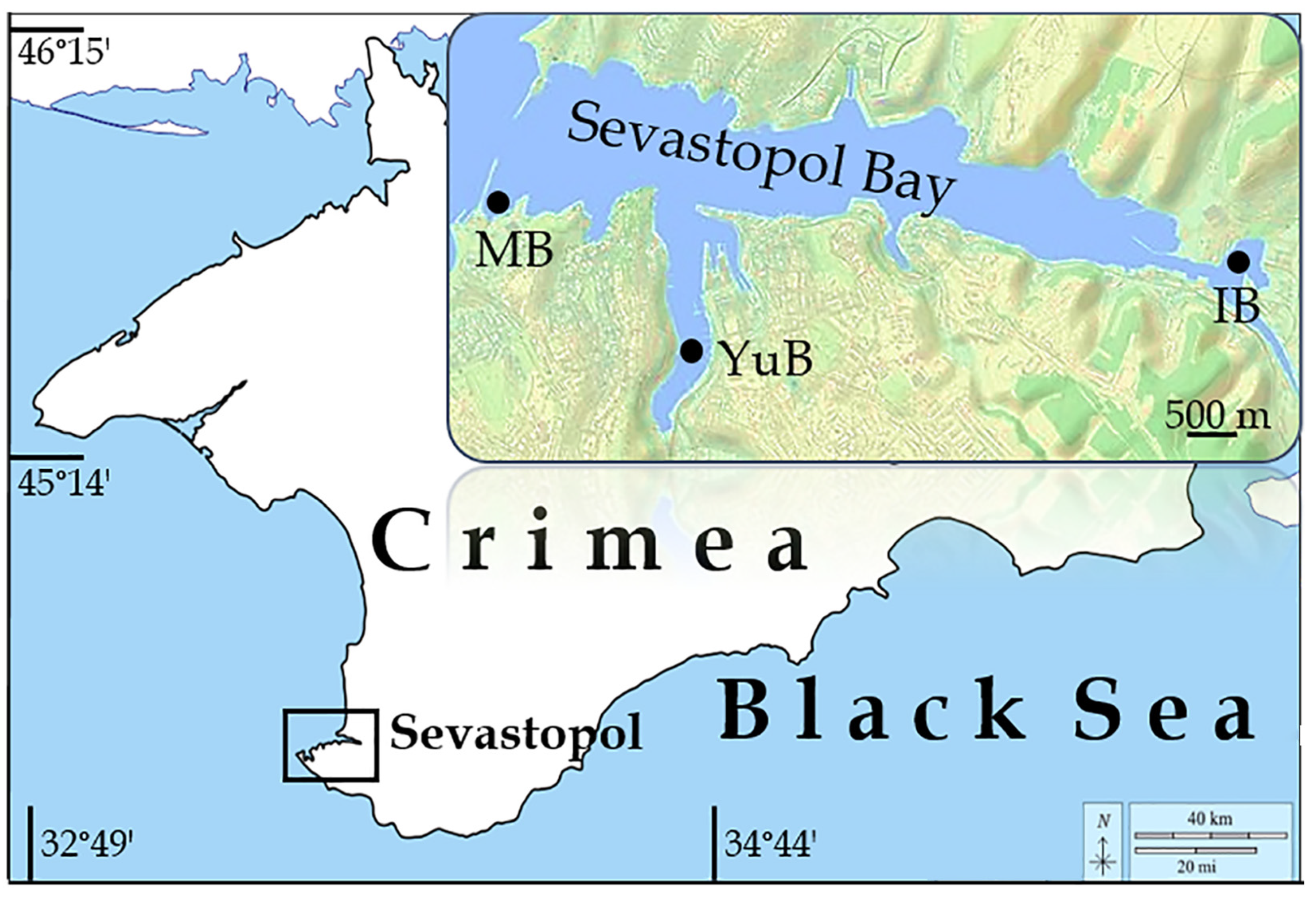
2.1. Sampling Area
2.2. Geological Samples
2.3. Microphytobenthos Sampling
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Abiotic Data Analysis
3.1.1. Elemental Composition of Rock Surfaces
3.1.2. Cluster Analysis of the Rocks Similarity in Terms of Composition and Content of Chemical Elements on Their Surface
3.2. Biotic Data Analysis
3.2.1. Composition of the Diatom and Cyanobacterial Communities on the Rock Surface
3.2.2. Correlations between the Abundance of Diatoms and Cyanobacteria in Epilithon Communities
3.3. Biotic Factors in Relation to the Abiotic Variables
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vernadsky, V.I. Living Matter; Nauka: Moskow, Russia, 1978; 358p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Cattaneo, A. Periphyton. In Bitton, Encyclopedia of Environmental Microbiology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002; pp. 2357–2367. [Google Scholar]
- Durr, S.; Thomason, J.C. Biofouling, 1st ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Singapore, 2010; 429p. [Google Scholar]
- Ryabushko, L.I. Microphytobenthos of the Black Sea; Gaevskaya, A.V., Ed.; EKOSI-Gidrofizica: Sevastopol, Ukraine, 2013; 416p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Ryabushko, L.I.; Begun, A.A. Diatoms of Microphytobenthos of the Sea of Japan; N. Orianda: Simferopol, Ukraine, 2015; Volume 1, 288p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, O.R. Marine and estuarine natural microbial biofilms: Ecological and biogeochemical dimensions. AIMS Microbiol. 2016, 2, 304–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epple, M. Biomineralization: From Biology to Biotechnology and Medical Application; Baeuerlein, E., Ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2001; 337p. [Google Scholar]
- Groussman, R.D.; Parker, M.S.; Armbrust, E.V. Diversity and evolutionary history of iron metabolism genes in diatoms. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sigler, W.; Bachofen, R.; Zeyer, J. Molecular characterization of endolithic cyanobacteria inhabiting exposed dolomite in central Switzerland. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 5, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tréguer, P.J.; De La Rocha, C.L. The world ocean silica cycle. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2013, 5, 477–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebeshuber, I.C. Biomineralization in marine organisms. Chapter 58, Part XI (Marinebiotechnological products in industrial application). In Springer Handbook of Marine Biotechnology; Kim, S.-K., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 1279–1300. ISBN 978-3-642-53970-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, H.; Lovell, C.R. Microbial surface colonization and biofilm development in marine environments. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 91–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryabushko, L.; Miroshnichenko, E.; Blaginina, A.; Shiroyan, A. Diatom and cyanobacteria communities on artificial polymer substrates in the Crimean coastal waters of the Black Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 169, 112521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benzerara, K.; Skouri-Panet, F.; Li, J.; Férard, C.; Gugger, M.; Laurent, T.; Couradeau, E.; Ragon, M.; Cosmidis, J.; Menguy, N.; et al. Intracellular Ca-carbonate biomineralization is widespread in cyanobacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 10933–10938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terekhov, E.P.; Mozherovsky, A.V.; Barinov, N.N. Patent. 2665152 Russian Federation, IPC G01N 33/24 Method for Determining the Genesis of Marine Sedimentary Deposits. Available online: https://i.moscow/patents/ru2665152c1_20180828 (accessed on 21 June 2021). (In Russian).
- Agarkova-Lyakh, I.V.; Lyakh, A.M. Coast state and the exogenous geological processes from Cape Konstantinovkiy to Cape Vinogradny on the south-western coast of Crimea. Sci. Notes V.I. Vernadsky Crime. Fed. Univ. 2019, 5, 118–133. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Romanyuk, O.S. Compile a Cadastre of the Surface part of the Crimean Coast in Relation to a Scale of 1:200,000: Report. Crimean Hydrogeological Expedition; Institute of Mineral Resources: Simferopol, Ukraine, 1988. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kovalsky, V.V. Geochemical Ecology; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1974; 300p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Gorbushina, A.A. Life on the rocks. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 1613–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, W. Experimental studies on the ecology of intertidal environments at Heron Island. II. The effect of substratum. Aust. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1961, 12, 132–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledger, M.E.; Hildrew, A.G. Temporal and spatial variation in the epilithic biofilm of an acid stream. Freshw. Biol. 1998, 40, 655–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, N.; Nagarkar, S.; Aitchison, J.C.; Williams, G.A. Microspatial variation in marine biofilm abundance on intertidal rock surfaces. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2006, 42, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rozhanskaya, L.I. The metals and its radionuklids composition in the hydrobionts of pelagial. In Hemoradioecologia of Pelagial and Bental; Naukova Dumka: Kiev, Ukraine, 1974; pp. 40–55. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Volcani, B.E. Role of Silicon in Diatom Metabolism and Silicification. In Biochemistry of Silicon and Related Problems, Nobel Foundation Symposia, Lidingo, 1977; Bendz, G., Lindqvist, I., Runnström-Reio, V., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1978; Volume 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ktitorova, E.N.; Lukyanov, Y.S.; Ivanova, K.K. Mass Concentration of Silicon in Sea Water Photometric Measurement Technique in the form of a Blue Form of Molybdosilicic Acid; Federal Service for Hydrometeorology and Environmental Monitoring: Moscow, Russia, 2010; 14p. (In Russian)
- Paasche, E.; Kristiansen, S. Silicon and ecology of marine plankton diatoms. II. Silicate-uptake kinetics in five diatom species. Mar. Biol. 1973, 19, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordova, V.S.; Sapozhnikov, S.P.; Sergeeva, V.E.; Karyshev, P.B. The basics of biosilicification (literature review). Bull. Chuvash Univ. 2013, 3, 401–409. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Dyakov, Y.T. (Ed.) Botany: Algology and Mycology Course; Moscow State University Press: Moscow, Russia, 2007; 559p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Alekin, O.A.; Lyahin, Y.I. Himiya Okeana; Gidrometeoizdat: Leningrad, Russia, 1984; 344p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Falciatore, A.; Jaubert, M.; Bouly, J.-P.; Bailleul, B.; Mockc, T. Diatom molecular research comes of age: Model species for studying phytoplankton biology and diversity. Plant Cell 2020, 32, 547–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohgai, M.; Matsui, T.; Okuda, T.; Tsukahara, H. Fine structure of adhesive parts of diatoms (Bacillariaceae) and adhesive mechanism. J. Shimonoseki Univ. Fish. 1984, 33, 27–35. [Google Scholar]
- Kala, R.; Pandey, V.D. Variable growth patterns of epilithic cyanobacteria on different rocks. In Recent Advancements in Sciences with Special Reference to Himalaya; Gautam, A.S., Ed.; Ancient Publishing House: Delhi, India, 2020; pp. 117–121. [Google Scholar]
- Zaets, I.; Burlak, O.; Rogutskyy, I.; Vasilenko, A.; Mytrokhyn, O.; Lukashov, D.; Foing, B.; Kozyrovska, N. Bioaugmentation in growing plants for lunar bases. Adv. Space Res. 2011, 47, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, V.A.; Ovsyany, E.I.; Repetin, L.N. Hydrological and Hydrochemical Regime of the Sevastopol Bay and Its Changes under the Influence of Climatic and Anthropogenic Factors; MGI NAS of Ukraine: Sevastopol, Ukraine, 2006; 90p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Moiseev, A.S. Hydrogeological sketch of the city of Sevastopol and its environs. In All-Union Geological Exploration Association of People’s Commissariat for Heavy Industry of the USSR; State Scientific and Technical Geological Exploration Publishing House: Moscow, Russia, 1932; Volume 137, 48p. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, A.A.; McCaughan, D.J.; McKee, F.S. Measurement of surface area of stones. Hydrobiologia 1988, 157, 85–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srebrodolsky, B.I. Secrets of Seasonal Minerals; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1989; 144p. [Google Scholar]
- Simonsen, R. Untersuchungen zur Systematik und Okologie der Bodendiatomeen der Westlichcn Ostsee. Int. Rev. Ges. Hydrobiol. Beih. 1962, 1, 9–144. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, W. A Synopsis of the British Diatomaceae; Smith and Beck, Pub.: London, UK, 1853; Volume 1, 89p. [Google Scholar]
- Proschkina-Lavrenko, A.I. (Ed.) Diatom Analysis. Guide to Fossil and Modern Diatoms; Book. 3; Gosgelioizdat: Leningrad, Russia, 1950; 398p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Proschkina-Lavrenko, A.I. Diatoms of the Black Sea Benthos; USSR Academy of Sciences Publishing House: Leningrad, Russia, 1963; 243p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Hendey, N.I. An Introductory Account of the Smaller Algae of British Coastal Waters, Part V: Bacillariophyceae (Diatoms); Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food, Fishery Investigations: London, UK, 1964; 317p. [Google Scholar]
- Guslyakov, N.E.; Zakordonets, O.A.; Gerasimyuk, V.P. Atlas of Diatoms of the Benthos of the Northwestern Part of the Black Sea and Adjacent Water Bodies; Naukova Dumka: Kyiv, Ukraine, 1992; 112p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Ryabushko, L.I.; Begun, A.A. Diatoms of Microphytobenthos of the Sea of Japan (Synopsis and Atlas); PK “KIA”: Sevastopol, Ukraine, 2016; Volume 2, 324p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Komárek, J.; Anagnostidis, K. Cyanoprokaryota. 1 Teil: Chroococcales. Süßwasserflora von Mitteleuropa; Bd 19/1; Spektrum Akademischer Verlag: Heidelberg, Germany; Berlin, Germany, 1999; 523p. [Google Scholar]
- Witkowski, A.; Lange-Bertalot, H.; Metzeltin, D. Diatom Flora of Marine Coasts I. Iconographia Diatomologica, Vol. 7: Diversity—Taxonomy—Identification; Lange-Bertalot, H., Ed.; A. R. G. Gantner Verlag K. G.: Koningstein, Germany, 2000; 925p. [Google Scholar]
- Komárek, J.; Anagnostidis, K. Cyanoprokaryota. 2 Teil: Oscillatoriales. Süßwasserflora von Mitteleuropa; Bd 19/2; Elsevier GmbH: München, Germany, 2005; 759p. [Google Scholar]
- Komárek, J. Cyanoprokaryota. 3 Teil: Heterocytous genera. Süßwasserflora von Mitteleuropa; 19/3; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; 1132p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiry, M.D.; Guiry, G.M. AlgaeBase; World-Wide Electronic Publication, National University of Ireland: Galway, Ireland, 2021; Available online: http://www.algaebase.org (accessed on 21 June 2021).
- Whitton, B.A.; Roth, E.; Friedrich, G. Use of Algae for Monitoring Rivers; Institut für Botanik Univ. Press: Innsbruck, Austria, 1991; 196p. [Google Scholar]
- Sörensen, T. A new method of establishing group of equal amplitude in plant sociology based on similarity of a species content and its application to analysis of the vegetation on Dannish commons. K. Dan. Vidensk. Selsk. Biol. Meddelelser 1948, 85, 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Vinogradova, O.; Bryantseva, Y. Taxonomic revision of the species composition of Cyanobacteria/Cyanoprokaryota of the Ukrainian coast of the Black Sea. Algologia 2017, 27, 436–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whitton, B.A. Ecology of Cyanobacteria II: Their Diversity in Space and Time; Springer Science+Business Media, B.V.: Berlin, Germany, 2012; 760p. [Google Scholar]
- Strzepek, R.F.; Hunter, K.A.; Frew, R.D.; Harrison, P.J.; Boyd, P.W. Iron-Light Interactions Differ in Southern Ocean Phyto-plankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2012, 57, 1182–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strzepek, R.F.; Boyd, P.W.; Sunda, W.G. Photosynthetic Adaptation to Low Iron, Light, and Temperature in Southern Ocean Phytoplankton. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 4388–4393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreno, C.M.; Lin, Y.; Davies, S.; Monbureau, E.; Cassar, N.; Marchetti, A. Examination of Gene Repertoires and Physiological Responses to Iron and Light Limitation in Southern Ocean Diatoms. Polar Biol. 2018, 41, 679–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderkamp, A.-C.; van Dijken, G.L.; Lowry, K.E.; Lewis, K.M.; Joy-Warren, H.L.; van de Poll, W.; Laan, P.; Gerringa, L.; Delmont, T.O.; Jenkins, B.D.; et al. Effects of Iron and Light Availability on Phytoplankton Photosynthetic Properties in the Ross Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2019, 621, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coale, T.H.; Bertrand, E.M.; Lampe, R.H.; Allen, A.E. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Micronutrient Utilization in Marine Diatoms. In The Molecular Life of Diatoms; Falciatore, A., Mock, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 567–604. [Google Scholar]
- Peers, G.; Price, N.M. Copper-containing plastocyanin used for electron transport by an oceanic diatom. Nature 2006, 441, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazzani, E.; Lauritano, C.; Saggiomo, M. Southern Ocean Iron Limitation of Primary Production between Past Knowledge and Future Projections. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Street, J.H.; Paytan, A. Iron, Phytoplankton Growth, and the Carbon Cycle. In Metal Ions in Biological Systems, Vol. 43—Biogeochemical Cycles of Elements; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; pp. 153–193. [Google Scholar]
- Kaushik, M.S.; Singh, P.; Tiwari, B.; Mishra, A.K. Ferric uptake regulator (FUR) protein: Properties and implications in cyanobacteria. Ann. Microbiol. 2015, 66, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; He, Q. PfsR is a key regulator of iron homeostasis in Synechocystis PCC 6803. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chakraborty, S.; Verma, E.; Singh, S.S. Cyanobacterial siderophores: Ecological and biotechnological significance. Ch. 19. In Cyanobacteria. From Basic Science to Applications; Mishra, A.K., Tiwari, D.N., Rai, A.N., Eds.; Academic Press, Elsevier Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 383–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, W.W.; Grizot, S.; Buchanan, S.K. Structural evidence for iron-free citrate and ferric citrate binding to the TonB-dependent outer membrane transporter FecA. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 332, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keren, N.; Aurora, R.; Pakrasi, H.B. Critical roles of bacterioferritins in iron storage and proliferation of cyanobacteria. Plant Physiol. 2004, 135, 1666–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, W.; Wang, T.; Perez-Fernandez, C.; DiRuggiero, J.; Kisailus, D. Iron acquisition and mineral transformation by cyanobacteria living in extreme environments. Mater. Today Bio 2022, 17, 100493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergey, E.A. Does rock chemistry affect periphyton accrual in streams? Hydrobiologia 2008, 614, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amber, A.; Lapi, S.; Ruth, T.; Maldonado, M. The Effects of Cu and Fe Availability on the Growth and Cu:C Ratios of Marine Diatoms. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2008, 53, 2451–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mora, K.; Echeveste, P. Physiological responses of Humboldt current system diatoms to Fe and Cu co-limitation. Mar. Environ. Res. 2023, 187, 105937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, V.N.R.; Kannan, V.; Duraisamy, A. Relative concentrations of Na, Ca and Mg for growth of some diatoms. Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. 1981, 90, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, M. Marine epibiosis. I. Fouling and antifouling: Some basic aspects. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1989, 58, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- López-Mejía, D.; Gutiérrez-Mendieta, F.J.; Zavala-Hurtado, J.A.; Siqueiros-Beltrones, D.A.; Varona-Cordero, F.; Herrera-Moro Chao, I.R. Physicochemical gradients in a coastal lagoon from the southern Gulf of Mexico; a multivariate approach. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2022, 52, 102284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntire, C.D.; Overton, W.S. Distributional patterns in assemblages of attached diatoms from Yaquina Estuary, Oregon. Ecology 1971, 52, 758–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cibic, T.; Blasutto, O.; Falconi, C.; Umani, F. Microphytobenthic biomass, species composition and nutrient availability in sublittoral sediments of the Gulf of Trieste (northern Adriatic Sea). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 75, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadian, O.; Pouladi, M.; Vazirizadeh, A.; Sedaghat, R. A Study of Diatoms Seasonal Distribution and Biodiversity in Helleh River Estuary, Persian Gulf. Environ. Stud. Persian Gulf 2015, 2, 32–44. [Google Scholar]
- Maraşlıoğlu, F.; Donmez, M. Seasonal Distribution of Epipelic Diatom Assemblages and Relations to Environmental Variables in a Mesotrophic Pond. Oxid. Commun. 2016, 39, 2466–2475. [Google Scholar]
- Balycheva, D.S. Species Composition, Structure and Function Characteristics of Microalgae of Antropogenic Substrates Periphyton in the Crimean Coastal Waters of the Black Sea. Ph.D. Thesis, Kovalevsky Institute of Biology of Southern Seas of Russian Academy of Sciences, Sevastopol, Ukraine, 2014; 193p. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Ryabushko, L.I.; Lishaev, D.N.; Kovrigina, N.P. Species Diversity of Epilithon Diatoms and the Quality of the Waters of the Donuzlav Gulf Ecosystem (Crimea, the Black Sea). Diversity 2019, 11, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryabushko, L.I.; Pospelova, N.V.; Balycheva, D.S.; Kovrigina, N.P.; Troshchenko, O.A.; Kapranov, S.V. Epizoon microalgae of the cultivated mollusk Mytilus galloprovincialis Lam. 1819, phytoplankton, hydrological and hydrochemical characteristic in the mussel-and-oyster farm area (Sevastopol, the Black Sea). Mar. Biol. J. 2017, 2, 67–83. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Shadrin, N.; Balycheva, D.; Anufriieva, E. Microphytobenthos in the Hypersaline Water Bodies, the Case of Bay Sivash (Crimea): Is Salinity the Main Determinant of Species Composition? Water 2021, 13, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobles, D.R.; Brown, R.M. The pivotal role of cyanobacteria in the evolution of cellulose synthases and cellulose synthase-like proteins. Cellulose 2004, 11, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaets, I.; Podolich, O.; Kukharenko, O.; Reshetnyak, G.; Shpylova, S.; Sosnin, M.; Khirunenko, L.; Kozyrovska, N.; de Vera, J.-P. Bacterial cellulose may provide the microbial-life biosignature in the rock records. Adv. Space Res. 2014, 53, 828–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokovikova, E.G. Cyanobacteria of Thermal Sources of the Baical Rift Zone and Their Role in the Deposition of Silica as Vodel Objects for the Study of Microfossils. Ph.D. Thesis, Paleontological Institute of RAS, Moscow, Russia, 2008; 17p. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]









| Rock Sample | Si | Fe | Na | Mg | Ca | C | Cl | Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inkerman Bay (IB) | ||||||||
| IB-1 | 8.9 ± 0.05 | 36.4 ± 0.1 | – | 1.1 ± 0.01 | 11.1 ± 0.05 | 21.8 ± 0.1 | 0.4 ± 0.001 | C |
| IB-2 | 5.8 ± 0.05 | 6.4 ± 0.05 | 3.3 ± 0.01 | 2.5 ± 0.01 | 6.6 ± 0.01 | 33.3 ± 0.1 | 3.8 ± 0.01 | C |
| IB-3 | 7.3 ± 0.01 | 16.3 ± 0.1 | 0.6 ± 0.001 | 1.3 ± 0.01 | 14.6 ± 0.1 | 22.1 ± 1.2 | 0.4 ± 0.001 | C |
| IB-4 | 3.2 ± 0.1 | 18.1 ± 0.05 | 0.7 ± 0.01 | 0.9 ± 0.05 | 26.5 ± 0.1 | 23.8 ± 0.1 | 0.5 ± 0.001 | C |
| IB-5 | 4.8 ± 0.1 | 8.2 ± 0.1 | – | 2.1 ± 0.01 | 25.2 ± 0.05 | 18.4 ± 0.05 | – | C |
| Martynova Bay (MB) | ||||||||
| MB-1 | 0.4 ± 0.001 | – | 2.6 ± 0.01 | 0.8 ± 0.001 | 19.5 ± 0.1 | 29.9 ± 0.05 | 3.0 ± 0.03 | C |
| MB-2 | 1.87 ± 0.1 | 0.9 ± 0.01 | 0.7 ± 0.01 | 0.8 ± 0.001 | 28.3 ± 0.1 | 25.7 ± 0.1 | 0.9 ± 0.01 | C |
| MB-3 | 6.33 ± 0.1 | – | 1.9 ± 0.01 | 0.7 ± 0.03 | 0.3 ± 0.03 | 46.8 ± 0.1 | 2.2 ± 0.1 | M |
| Yuzhnaya Bay (YuB) | ||||||||
| YuB-1 | 7.4 ± 0.1 | 2.3 ± 0.1 | – | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 10.5 ± 0.1 | 36.2 ± 0.2 | 0.5 | C |
| YuB-2 | 4.2 ± 0.1 | 0.7 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 0.6 ± 0.1 | 4.3 ± 0.1 | 48.8 ± 1.2 | – | C |
| YuB-3 | 7.5 ± 0.1 | 2.1 ± 0.1 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 0.6 ± 0.1 | 6.7 ± 0.1 | 42.2 ± 0.01 | – | C |
| Taxa | MB | IB | YuB | Ecol | Phyt | Abbreviated Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phylum Bacillariophyta | ||||||
| Achnanthes brevipes C.A. Agardh 1824 var. brevipes | 0.598 | – | – | BM | C | AchBr |
| Achnanthes brevipes var. intermedia (Kützing) P.T. Cleve 1895 | 0.924 | 3.654 | – | BM | C | AchBrI |
| Amphora bigibba Grunow ex A. Schmidt 1875 | 2.643 | – | 2.311 | M/F | BT not | AmBig |
| Amphora helenensis Giffen 1973 | – | + | – | M | B not | |
| Amphora ovalis (Kützing) Kützing 1844 | 0.990 | – | – | FB | C | AmOv |
| Amphora pediculus (Kützing) Grunow 1875 | – | + | – | F | ABT not | |
| Aulacoseira granulata (Ehrenberg) Simonsen 1979 | 2.815 | – | – | FB | C | AuGr |
| Bacillaria paxillifer (O.F. Müller) N. Hendey 1954 | – | 5.845 | 0.916 | BM | C | |
| Berkeleya rutilans (Trentepohl ex Roth) Grunow 1880 | 12.352 | 14.875 | 2.093 | BM | C | BerRu |
| Caloneis liber (W. Smith) P.T. Cleve 1894 | 0.881 | 0.335 | – | M | C | CaLib |
| Carinasigma rectum (Donkin) G. Reid 2012 | + | – | – | M | BT not | |
| Cocconeis peltoides Hustedt 1939 | – | + | – | M | B not | |
| Cocconeis placentula var. euglypta (Ehrenberg) P.T. Cleve 1895 | – | + | – | M | C | |
| Cocconeis scutellum Ehrenberg 1838 | + | 6.594 | – | BM | C | CoScu |
| Cocconeis neodiminuta Krammer 1990 | – | + | – | F | BT not | |
| Cocconeis neothumensis Krammer 1990 | – | + | – | M/F | B not | |
| Coscinodiscus jonesianus (Greville) Ostenfeld 1915 | 5.793 | 0.491 | – | M | B | CosJo |
| Cylindrotheca closterium (Ehrenberg) Reimer et Lewin 1964 | 18.380 | 1.021 | 4.449 | M | C | CyClo |
| Cymbella helvetica Kützing 1844 | + | – | – | F | BT not | |
| Diploneis smithii (Brébisson) P.T. Cleve 1894 | – | 2.746 | 0.916 | BM | C | |
| Fallacia tenera (Hustedt) D.G. Mann 1990 | – | + | – | F | B not | |
| Gomphonemopsis pseudexigua (Kützing) L.K. Medlin 1986 | 1.262 | + | – | M | ABT not | |
| Grammatophora marina (Lyngbye) Kützing 1844 | 1.728 | – | – | M | C | GrMa |
| Gyrosigma tenuissimum (W. Smith) J.W. Griffith et Henfrey 1856 | – | + | – | M | BT not | |
| Halamphora coffeiformis (C. Agardh) Levkov 2009 | 3.263 | 7.116 | 0.131 | BM | C | HaCof |
| Halamphora hyalina (Kützing) Rimet et R. Jahn 2018 | + | – | + | BM | ABT not | |
| Haslea ostrearia (Gaillon) Simonsen 1974 | – | 7.616 | 0.654 | M | BT | HOst |
| Haslea subagnita (Proschkina-Lavrenko) I.V. Makarova et N.I. Karajeva 1985 | 4.275 | + | 0.218 | B | C | HSub |
| Licmophora abbreviata C. Agardh 1831 | 1.332 | – | – | M | C | LiAb |
| Licmophora communis (Heiberg) Grunow 1880 | – | 2.910 | – | M | AB not | LicCom |
| Licmophora paradoxa (Lyngbye) C. Agardh 1828 | – | + | – | M | C | |
| Nanofrustulum shiloi (J.J. Lee, Reimer et McEnery) Round, Hallsteinsen et Paasche 1999 | – | + | – | M | B not | |
| Navicula cancellata Donkin 1873 | – | 3.047 | – | B | C | |
| Navicula directa (W. Smith) Ralfs ex Pritch. 1861 | – | 2.862 | 0.436 | BM | C | NavDir |
| Navicula palpebralis Brébisson ex W. Smith 1853 | 0.990 + 0.374 | 2.991 | – | M | ABT not | NavPal |
| Navicula pennata A.W.F. Schmidt 1876 | 3.167 | + | – | BM | BT not | NavPen |
| Navicula perminuta Grunow 1880 | – | + | – | M/F | C | |
| Navicula ramosissima (C. Agardh) P.T. Cleve 1895 | 3.291 | 3.815 | 1.047 | BM | ABT not | NavRam |
| Navicula salinicola Hustedt 1939 | – | + | – | F/BM | BT not | |
| Nitzschia aequorea Hustedt 1939 | – | + | – | M | BT not | |
| Nitzschia dissipata (Kützing) Rabenhorst 1860 | – | + | – | F | ABT not | |
| Nitzschia frustulum (Kützing) Grunow 1880 | – | + | – | M/F | C | |
| Nitzschia hybrida f. hyalina Proschkina-Lavrenko1963 | + | – | – | BM | B | |
| Nitzschia inconspicua Grunow 1862 | – | + | – | F | C | |
| Nitzschia sigma (Kützing) W. Smith 1853 | 0.761 | 0.363 | 0.523 | B | C | NitSigm |
| Nitzschia sigmoidea (Nitzsch) W. Smith 1853 | – | – | 0.218 | FB | BT not | NitSigd |
| Parlibellus delognei (Van Heurck) E.J. Cox 1988 | 13.889 | + | – | M | C | ParDel |
| Plagiogramma staurophorum (W. Gregory) Heiberg 1863 | – | 0.452 | – | M | BT not | PlSta |
| Plagiotropis lepidoptera (W. Gregory) Kuntze 1898 | + | + | – | M | ABT not | |
| Pleurosigma elongatum W. Smith 1852 | – | + | – | BM | C | |
| Psammodictyon panduriforme var. minor (Grunow) L.I. Ryabushko 2006 | 0.163 | + | 1.221 | M | BT not | PsPM |
| Rhopalodia gibba (Ehrenberg) O.F. Müller 1895 | 1.782 | – | – | F | ABT not | |
| Rhopalodia gibberula (Ehrenberg) O.F. Müller 1895 | 0.259 | – | 1.919 | M/F | BT not | RapGib |
| Rhoicosphenia marina (Kützing) M. Schmidt 1899 | – | 0.335 | – | M | B not | RhMar |
| Seminavis ventricosa (Gregory) M. Garcia-Baptista 1993 | 0.114 | 0.920 | – | M | C | SemVen |
| Striatella unipunctata (Lyngbya) C.A. Agardh 1832 | – | 2.174 | – | M | BT not | StUni |
| Tabularia fasciculata (C.A. Agardh) D.M. Williams et Round 1986 | – | 0.648 | 0.393 | BM | C | TabFa |
| Tabularia parva (Kützing) D.M. Williams et Round 1986 | – | + | – | BM | ABT not | |
| Tabularia tabulata (C.A. Agardh) Snoeijs 1990 | – | – | 0.480 | BM | C | TabTa |
| Tetramphora decussata (Grunow) Stepanek et Kociolek 2016 | – | + | – | M | BT not | |
| Trachyneis aspera (Ehrenberg) P.T. Cleve 1894 | 9.967 | 14.341 | – | M | C | TrAsp |
| Tryblionella coarctata (Grunow) D.G. Mann 1990 | – | 5.675 | 0.436 | BM | BT | TryCoar |
| Undatella lineolata (Ehrenberg) L.I. Ryabushko 2006 | 5.189 | 21.615 | 0.305 | BM | ABT not | UnLi |
| Average number of species | 31 | 48 | 19 | |||
| Average abundance of species, 103 cells/cm2 | 97 | 112 | 19 | |||
| Phylum Cyanobacteria | ||||||
| Calothrix parva Ercegovic 1925 | – | 1 | – | M | AB | Cp |
| Chroococcus minutus (Kützing) Nägeli 1849 | 2 | – | – | F | C | Cm |
| Gloeocapsopsis crepidinum (Thuret) Geitler ex Komárek 1993 | – | 1 | – | M/F | C | Gc |
| Kamptonema laetevirens (H.M. Crouan et P.L. Crouan ex Gomont) Strunecký, Komárek et J. Smarda 2014 | 3 | 4 | – | M/F | BT not | Kl |
| Komvophoron breve (N. Carter) Anagnostidis 2001 | 3 | – | – | B | BT | Kb |
| Leptolyngbya fragilis (Gomont) Anagnostidis et Komárek 1988 | 2 | 1 | 1 | M | C | Lpf |
| Leptolyngbya subtilis (West) Anagnostidis 2001 | 2 | – | 2 | F | BT not | Lps |
| Lyngbya confervoides C. Agardh ex Gomont 1892 | 4 | – | 1 | M | C | Lc |
| Lyngbya martensiana Meneghini ex Gomont 1892 | 3 | – | – | EuH | C | Lm |
| Lyngbya semiplena J. Agardh ex Gomont 1892 | 1 | – | – | M/F | BT not | Ls |
| Oscillatoria bonnemaisonii P. Crouan et H. Crouan ex Gomont 1892 | 1 | – | – | M | BT not | Ob |
| Oscillatoria corallinae Gomont ex Gomont 1890 | – | 1 | – | M | BT not | Oc |
| Phormidium breve (Kützing ex Gomont) Anagnostidis et Komárek 1988 | 1 | – | – | F | C | Phb |
| Phormidium holdenii (Forti) Branco, Sant’Anna, Azevedo et Sormus 1997 | – | 4 | – | M/F | ABT not | Phh |
| Phormidium nigroviride (Thwaites ex Gomont) Anagnostidis et Komárek 1988 | 3 | – | – | M | C | Phn |
| Phormidium retzii Kützing ex Gomont 1892 | – | 2 | – | F | C | Phr |
| Potamolinea aerugineacaeruleum (Gomont) M.D. Martins et L.H.Z. Branco 2016 | 4 | – | 1 | F | C | Pa |
| Pseudanabaena minima (G.S. An) Anagnostidis 2001 | 2 | – | – | F | ABT not | Psm |
| Spirulina subsalsa Oersted ex Gomont 1892 | 1 | – | – | M/F | C | Ss |
| Spirulina subtilissima Kützing ex Gomont 1892 | 2 | – | – | M/F | BT not | Ssm |
| Total number of species: 20, of which in bays: | 15 | 7 | 4 | |||
| Rock Sample | Rock Origin | Diatoms | Cyanobacteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| IB-1 | C | 104 | 588 |
| IB-2 | C | 149 | 899 |
| IB-3 | C | 140 | 1198 |
| IB-4 | C | 118 | 297 |
| IB-5 | C | 51 | 158 |
| MB-1 | C | 50 | 381 |
| MB-2 | C | 65 | 75 |
| MB-3 | M | 176 | 249 |
| YuB-1 | C | 28 | 42 |
| YuB-2 | C | 14 | 35 |
| YuB-3 | C | 18 | 12 |
| Elements | Diatom Communities | Cyanobacteria Communities |
|---|---|---|
| O | 0.67 | 0.21 |
| C | −0.45 | 0.04 |
| Ca | 0.48 | 0.04 |
| Fe | 0.11 | −0.23 |
| Si | −0.28 | −0.27 |
| Cl | 0.11 | 0.37 |
| Na | −0.01 | 0.32 |
| Mg | 0.19 | −0.23 |
| K | −0.46 | −0.47 |
| Al | −0.42 | −0.55 |
| S | −0.14 | −0.27 |
| Mn | −0.17 | −0.16 |
| Zn | 0.06 | −0.32 |
| Pb | 0.10 | −0.43 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blaginina, A.; Balycheva, D.; Miroshnichenko, E.; Ryabushko, L.; Kapranov, S.; Barinova, S.; Lishaev, D. Does the Elemental Composition of Rock Surfaces Affect Marine Benthic Communities of Diatoms and Cyanobacteria? J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11081569
Blaginina A, Balycheva D, Miroshnichenko E, Ryabushko L, Kapranov S, Barinova S, Lishaev D. Does the Elemental Composition of Rock Surfaces Affect Marine Benthic Communities of Diatoms and Cyanobacteria? Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2023; 11(8):1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11081569
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlaginina, Anastasiia, Daria Balycheva, Ekaterina Miroshnichenko, Larisa Ryabushko, Sergey Kapranov, Sophia Barinova, and Denis Lishaev. 2023. "Does the Elemental Composition of Rock Surfaces Affect Marine Benthic Communities of Diatoms and Cyanobacteria?" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 11, no. 8: 1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11081569
APA StyleBlaginina, A., Balycheva, D., Miroshnichenko, E., Ryabushko, L., Kapranov, S., Barinova, S., & Lishaev, D. (2023). Does the Elemental Composition of Rock Surfaces Affect Marine Benthic Communities of Diatoms and Cyanobacteria? Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 11(8), 1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11081569








