Bayesian Network Analysis for Shoreline Dynamics, Coastal Water Quality, and Their Related Risks in the Venice Littoral Zone, Italy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
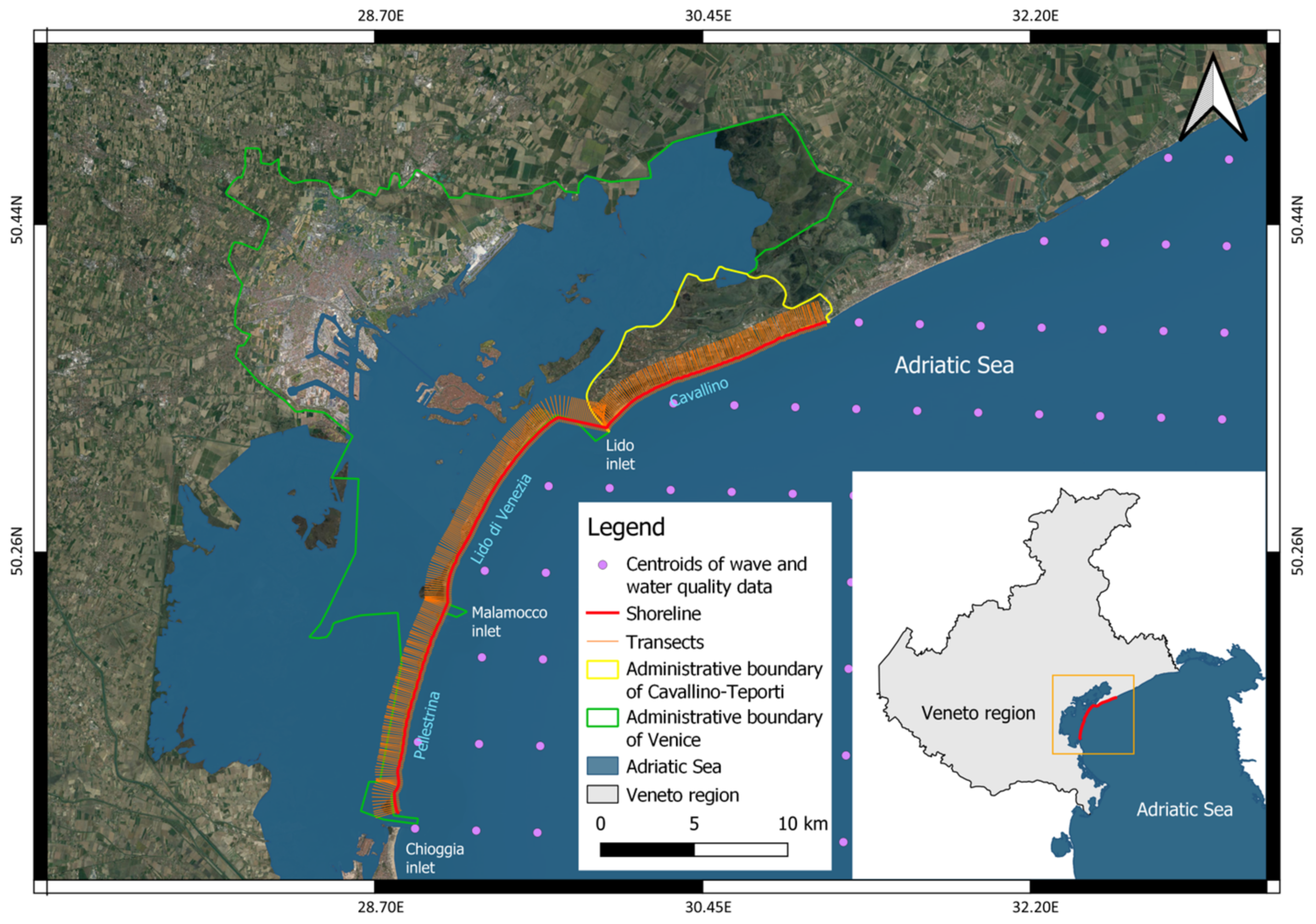
2.1. Case Study
2.2. Input Data
2.3. Methodological Approach
2.3.1. Phase 0: Data Collection and Pre-Processing
2.3.2. Phase 1: Correlation Analysis and Variable Selection
2.3.3. Phase 2: Bayesian Network Model
- Step 1: Model design and parametrization
- Step 2: Model validation
- Step 3: Sensitivity analysis
- Step 4: Baseline scenario analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Correlation Analysis
3.2. Bayesian Network Model
3.2.1. Model Design and Parametrization
3.2.2. Model Validation
3.2.3. Sensitivity Analysis
3.2.4. Baseline Scenario Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC. Chapter 6: Coastal Zones and Marine Ecosystems. In Climate Change 2001: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003; pp. 345–379. Available online: https://www.grida.no/publications/269 (accessed on 17 December 2022).
- IPCC. Climate Change 2014 Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 1–112. [Google Scholar]
- Poelhekke, L.; Jäger, W.S.; van Dongeren, A.; Plomaritis, T.A.; McCall, R.; Ferreira, Ó. Predicting coastal hazards for sandy coasts with a Bayesian Network. Coast. Eng. 2016, 118, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrela-Segrelles, C.; Gómez-Martinez, G.; Pérez-Martín, M.Á. Risk assessment of climate change impacts on Mediterranean coastal wetlands. Application in Júcar River Basin District (Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 790, 148032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastidas-Arteaga, E.; Creach, A. Climate change for coastal areas: Risks, adaptation and acceptability. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2020, 11, 295–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Bruno, J. The impact of climate change on the world’s marine ecosystems. Science 2010, 328, 1523–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpern, B.S.; Lbridge, S.; Selkoe, K.A.; Kappel, C.V.; Micheli, F.; D’Agrosa, C.; Bruno, J.F.; Casey, K.S.; Ebert, C.; Fox, H.E.; et al. A global map of human impact on marine ecosystems. Science 2008, 319, 948–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halpern, B.S.; Frazier, M.; Afflerbach, J.; Lowndes, J.S.; Micheli, F.; O’Hara, C.; Scarborough, C.; Selkoe, K.A. Recent pace of change in human impact on the world’s ocean. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Summary for Policymakers. In Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability; Field, C.B., Barros, V.R., Dokken, D.J., Mach, K.J., Mastrandrea, M.D., Bilir, T.E., Chatterjee, M., Ebi, K.L., Estrada, Y.O., Genova, R.C., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrarin, C.; Valentini, A.; Vodopivec, M.; Klaric, D.; Massaro, G.; Bajo, M.; Carraro, E. Integrated sea storm management strategy: The 29 October 2018 event in the Adriatic Sea. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 20, 73–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontolan, G.; Bezzi, A.; Martinucci, D.; Pillon, S.; Popesso, C.; Rizzetto, F. Sediment budget and management of the Veneto beaches, Italy: An application of the Littoral Cells Management System (SICELL). In Proceedings of the Conférence Méditerranéenne Côtière et Maritime, Ferrara, Italy, 25–27 November 2015; pp. 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morucci, S.; Coraci, E.; Crosato, F.; Ferla, M. Extreme events in Venice and in the North Adriatic Sea: 28–29 October 2018. Sci. Fis. Nat. 2020, 31, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosi, L.; Da Lio, C.; Donnici, S.; Strozzi, T.; Teatini, P. Vulnerability of Venice’s coastland to relative sea-level rise. Proc. Int. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. 2020, 382, 689–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rijn, L.C. Coastal erosion and control. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2011, 54, 867–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quartel, S.; Kroon, A.; Ruessink, B.G. Seasonal accretion and erosion patterns of a microtidal sandy beach. Mar. Geol. 2008, 250, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentaschi, L.; Vousdoukas, M.I.; Pekel, J.F.; Voukouvalas, E.; Feyen, L. Global long-term observations of coastal erosion and accretion. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorne, C.R.; Evans, E.P.; Penning-rowsell, E.C. Future Flooding and Coastal Erosion Risks; Thomas Telford Publishing: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchio, A.; Anzidei, M.; Serpelloni, E. Sea level rise projections up to 2150 in the northern Mediterranean coasts. Environ. Res. Lett. 2024, 19, 014050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppenheimer. The irreversible momentum of clean energy: Private-sector efforts help drive decoupling of emissions and economic growth. Science 2017, 355, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PNACC. Piano Nazionale di Adattamento ai Cambiamenti Climatici PNACC. 2017. Available online: https://politichecoesione.governo.it/media/2868/pnacc_luglio-2017.pdf (accessed on 17 December 2022).
- Loizidou, X.I.; Orthodoxou, D.L.; Loizides, M.I.; Petsa, D.; Anzidei, M. Adapting to sea level rise: Participatory, solution-oriented policy tools in vulnerable Mediterranean areas. Environ. Syst. Decis. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, D.H.; Kumar, N.D. Coastal Erosion Studies—A Review. Int. J. Geosci. 2014, 5, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, F.; Bayram, B.; Bakirman, T.; Bayrak, O.C.; Akpinar, B. An ensemble deep learning based shoreline segmentation approach (WaterNet) from Landsat 8 OLI images. Adv. Sp. Res. 2021, 67, 964–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toure, S.; Diop, O.; Kpalma, K.; Maiga, A.S. Shoreline detection using optical remote sensing: A review. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, K.; Splinter, K.D.; Harley, M.D.; Simmons, J.A.; Turner, I.L. CoastSat: A Google Earth Engine-enabled Python toolkit to extract shorelines from publicly available satellite imagery. Environ. Model. Softw. 2019, 122, 104528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitousek, S.; Vos, K.; Splinter, K.D.; Erikson, L.; Barnard, P.L. A Model Integrating Satellite-Derived Shoreline Observations for Predicting Fine-Scale Shoreline Response to Waves and Sea-Level Rise Across Large Coastal Regions. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2023, 128, e2022JF006936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelle, B.; Masselink, G.; Scott, T.; Stokes, C.; Konstantinou, A.; Marieu, V.; Bujan, S. Satellite-derived shoreline detection at a high-energy meso-macrotidal beach. Geomorphology 2021, 383, 107707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Asmar, H.M.; Hereher, M.E.; El Kafrawy, S.B. Surface area change detection of the Burullus Lagoon, North of the Nile Delta, Egypt, using water indices: A remote sensing approach. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Sp. Sci. 2013, 16, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zennaro, F.; Furlan, E.; Simeoni, C.; Torresan, S.; Aslan, S.; Critto, A.; Marcomini, A. Exploring machine learning potential for climate change risk assessment. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 220, 103752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlan, E.; Slanzi, D.; Torresan, S.; Critto, A.; Marcomini, A. Multi-scenario analysis in the Adriatic Sea: A GIS-based Bayesian network to support maritime spatial planning. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 134972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, H.V.; Sperotto, A.; Torresan, S.; Critto, A.; Marcomini, A. Integrating Bayesian Networks into ecosystem services assessment to support water management at the river basin scale. Ecosyst. Serv. 2021, 50, 101300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperotto, A.; Molina, J.-L.; Torresan, S.; Critto, A.; Marcomini, A. Reviewing Bayesian Networks potentials for climate change impacts assessment and management: A multi-risk perspective. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 202, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moe, S.J.; Carriger, J.F.; Glendell, M. Increased Use of Bayesian Network Models Has Improved Environmental Risk Assessments. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2021, 17, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaikkonen, L.; Parviainen, T.; Rahikainen, M.; Uusitalo, L.; Lehikoinen, A. Bayesian Networks in Environmental Risk Assessment: A Review. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2021, 17, 62–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäger, W.S.; Christie, E.K.; Hanea, A.M.; den Heijer, C.; Spencer, T. A Bayesian network approach for coastal risk analysis and decision making. Coast. Eng. 2018, 134, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, O.; Stewart, R.A.; Faivre, G.; Ware, D.; Tomlinson, R.; Mackey, B. Spatial Bayesian Network for predicting sea level rise induced coastal erosion in a small Pacific Island. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 238, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezzi, A.; Fontolan, G.; Nordstrom, K.F.; Carrer, D.; Jackson, N.L. Beach Nourishment and Foredune Restoration: Practices and Constraints along the Venetian Shoreline, Italy. J. Coast. Res. 2009, 1, 287–291. [Google Scholar]
- Rizzi, J.; Torresan, S.; Zabeo, A.; Critto, A.; Tosoni, A.; Tomasin, A.; Marcomini, A. Assessing storm surge risk under future sea-level rise scenarios: A case study in the North Adriatic coast. J. Coast. Conserv. 2017, 21, 453–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoccarato, C.; Da Lio, C. The Holocene influence on the future evolution of the Venice Lagoon tidal marshes. Commun. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, H.V.; Dal Barco, M.K.; Cadau, M.; Harris, R.; Furlan, E.; Torresan, S.; Rubinetti, S.; Zanchettin, D.; Rubino, A.; Kuznetsov, I.; et al. Multi-model chain for climate change scenario analysis to support coastal erosion and water quality risk management for the Metropolitan city of Venice. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberti, T.; Anzidei, M.; Faranda, D.; Vecchio, A.; Favaro, M.; Papa, A. Dynamical diagnostic of extreme events in Venice lagoon and their mitigation with the MoSE. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 10475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faranda, D.; Ginesta, M.; Alberti, T.; Coppola, E.; Anzidei, M. Attributing Venice Acqua Alta events to a changing climate and evaluating the efficacy of MoSE adaptation strategy. npj Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2023, 6, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solidoro, C.; Bandelj, V.; Bernardi, F.A.; Camatti, E.; Ciavatta, S.; Cossarini, G.; Facca, C.; Franzoi, P.; Libralato, S.; Canu, D.M.; et al. Response of the Venice Lagoon ecosystem to natural and anthropogenic pressures over the last 50 years. In Coastal Lagoons; Critical Habitats of Environmental Change; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; pp. 483–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogarin, S.; Madricardo, F.; Zaggia, L.; Sigovini, M.; Montereale-Gavazzi, G.; Kruss, A.; Lorenzetti, G.; Manfé, G.; Petrizzo, A.; Molinaroli, E.; et al. Tidal inlets in the Anthropocene: Geomorphology and benthic habitats of the Chioggia inlet, Venice Lagoon (Italy). Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2019, 44, 2297–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionello, P.; Barriopedro, D.; Ferrarin, C.; Nicholls, R.J.; Orlic, M.; Reale, M.; Umgiesser, G.; Vousdoukas, M.; Zanchettin, D. Extremes floods of Venice: Characteristics, dynamics, past and future evolution. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 21, 2705–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanchettin, D.; Bruni, S.; Raicich, F.; Lionello, P.; Adloff, F.; Androsov, A.; Antonioli, F.; Artale, V.; Carminati, E.; Ferrarin, C.; et al. Review article: Sea-level rise in Venice: Historic and future trends. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2020, 21, 2643–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchio, A.; Anzidei, M.; Serpelloni, E.; Florindo, F. Natural variability and vertical land motion contributions in the Mediterranean sea-level records over the last two centuries and projections for 2100. Water 2019, 11, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomaro, A.; Cavaleri, L.; Lionello, P. Climatology and trends of the Adriatic Sea wind waves: Analysis of a 37-year long instrumental data set. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 4237–4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Lio, C.; Tosi, L. Vulnerability to relative sea-level rise in the Po river delta (Italy). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 228, 106379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosi, L.; Da Lio, C.; Strozzi, T.; Teatini, P. Combining L- and X-Band SAR interferometry to assess ground displacements in heterogeneous coastal environments: The Po River Delta and Venice Lagoon, Italy. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbognin, L.; Teatini, P.; Tosi, L.; Strozzi, T.; Tomasin, A. Present Relative Sea Level Rise in the Northern Adriatic Coastal Area. Coast. Mar. Spat. Plan. 2010, 1147–1162. Available online: https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/33155996.pdf (accessed on 20 November 2023).
- Scardino, G.; Anzidei, M.; Petio, P.; Serpelloni, E.; De Santis, V.; Rizzo, A.; Liso, S.I.; Zingaro, M.; Capolongo, D.; Vecchio, A.; et al. The Impact of Future Sea-Level Rise on Low-Lying Subsiding Coasts: A Case Study of Tavoliere Delle Puglie (Southern Italy). Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinaroli, E.; Guerzoni, S.; Suman, D. Do the Adaptations of Venice and Miami to Sea Level Rise Offer Lessons for Other Vulnerable Coastal Cities? Environ. Manag. 2019, 64, 391–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramieri, E.; Hartley, A.; Office, M.; Barbanti, A.; National, I.; Santos, F.D. Methods for Assessing Coastal Vulnerability to Climate Change; ETC CCA Technical Paper 1/2011; ETC/CCA: Bologna, Italy, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruol, P.; Martinelli, L.; Favaretto, C.; Pinato, T.; Galiazzo, F.; Patti, S.; Anti, U.; Piazza, R.; Simonin, P.; Selvi, G. Gestione Integrata Della Zona Costiera Studio E Monitoraggio Per La Definizione Degli Interventi Di Difesa Dei Litorali Dall’erosione Nella Regione Veneto-Linee Guida; Edizioni Progetto Padova: Padova, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Facca, C.; Bonometto, A.; Boscolo, R.; Buosi, A.; Parravicini, M.; Siega, A.; Volpe, V.; Sfriso, A. Coastal lagoon recovery by seagrass restoration. A new strategic approach to meet HD & WFD objectives. In Proceedings of the 9th European Conference on Ecological Restoration, Oulu, Finland, 3–8 August 2014; pp. 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. EU Climate Adaptation Strategy. 2021. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:52021DC0082&from=EN (accessed on 20 November 2023).
- Scutari, M. Learning Bayesian Networks with the bnlearn R package. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 35, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogarin, S.; Zanetti, M.; Dal Barco, M.K.; Zennaro, F.; Furlan, E.; Torresan, S.; Pham, H.V.; Critto, A. Combining remote sensing analysis with machine learning to evaluate short-term coastal evolution trend in the shoreline of Venice. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 859, 160293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chataigner, T.; Yates, M.L.; Le Dantec, N.; Harley, M.D.; Splinter, K.D.; Goutal, N. Sensitivity of a one-line longshore shoreline change model to the mean wave direction. Coast. Eng. 2022, 172, 104025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharioudaki, A.; Reeve, D.E. Shoreline evolution under climate change wave scenarios. Clim. Chang. 2011, 108, 73–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, R.E. Logistic regression. In Reading and Understanding Multivariate Statistics; American Psychological Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Graupe, D. Principles of Artificial Neural Networks; World Scientific: Singapore, 2013; Volume 7, ISBN 9814522759. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L.E.O. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNDP. Egypt’s National Strategy for Adaptation to Climate Change and Disaster Risk Reduction; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Part B: Regional Aspects. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014; p. 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulzweida, U. Climate Data Operator (CDO) User Guide (Version 1.9.5). no. August, pp. 1–217. 2018. Available online: https://code.mpimet.mpg.de/projects/cdo/embedded/cdo.pdf (accessed on 17 December 2022).
- Gutierrez, B.T.; Plant, N.G.; Thieler, E.R. A Bayesian network to predict coastal vulnerability to sea level rise. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2011, 116, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scutari, M. Bayesian network constraint-based structure learning algorithms: Parallel and optimized implementations in the bnlearn R package. J. Stat. Softw. 2017, 77, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kragt, M.E. A Beginners Guide to Bayesian Network Modelling for Integrated Catchment. 2009. Available online: www.landscapelogic.org.au (accessed on 17 December 2022).
- Pollino, C.A.; Woodberry, O.; Nicholson, A.; Korb, K.; Hart, B.T. Parameterisation and evaluation of a Bayesian network for use in an ecological risk assessment. Environ. Model. Softw. 2007, 22, 1140–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelzenmüller, V.; Lee, J.; Garnacho, E.; Rogers, S.I. Assessment of a Bayesian Belief Network–GIS framework as a practical tool to support marine planning. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 1743–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coupé, V.M.H.; Peek, N.; Ottenkamp, J.; Habbema, J.D.F. Using sensitivity analysis for efficient quantification of a belief network. Artif. Intell. Med. 1999, 17, 223–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gačić, M.; Kovačević, V.; Cosoli, S.; Mazzoldi, A.; Paduan, J.D.; Mancero-Mosquera, I.; Yari, S. Surface current patterns in front of the Venice Lagoon. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 82, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benetazzo, A.; Fedele, F.; Carniel, S.; Ricchi, A.; Bucchignani, E.; Sclavo, M. Wave climate of the Adriatic Sea: A future scenario simulation. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 12, 2065–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benetazzo, A.; Carniel, S.; Sclavo, M.; Bergamasco, A. Wave–current interaction: Effect on the wave field in a semi-enclosed basin. Ocean Model. 2013, 70, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruol, P.; Martinelli, L.; Favaretto, C. Vulnerability analysis of the Venetian littoral and adopted mitigation strategy. Water 2018, 10, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plomaritis, T.A.; Costas, S.; Ferreira, Ó. Use of a Bayesian Network for coastal hazards, impact and disaster risk reduction assessment at a coastal barrier (Ria Formosa, Portugal). Coast. Eng. 2018, 134, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrìguez, J.D.; Aritz Pérez, A.; Lozano, J.A. Sensitivity Analysis of k-Fold Cross Validation in Prediction Error Estimation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2010, 32, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, M. Cross validatory choice and assessment of statistical predictions. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1974, 36, 111–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.; Furlan, E.; Pham, H.V.; Torresan, S.; Mysiak, J.; Critto, A. A Bayesian network approach for multi-sectoral flood damage assessment and multi-scenario analysis. Clim. Risk Manag. 2022, 35, 100410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulmer, R.H.; Stephenson, F.; Lohrer, A.M.; Lundquist, C.J.; Madarasz-Smith, A.; Pilditch, C.A.; Thrush, S.F.; Hewitt, J.E. Informing the management of multiple stressors on estuarine ecosystems using an expert-based Bayesian Network model. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 301, 113576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, C.; Silva, R.; Veloso-Gomes, F.; Taveira-Pinto, F. Potential effects of climate change on northwest portuguese coastal zones. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2009, 66, 1497–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco-Ochoa, C.; Zambrano-Medina, Y.; Plata-Rocha, W.; Monjardín-Armenta, S.; Rodríguez-Cueto, Y.; Escudero, M.; Mendoza, E. Long-term analysis of wave climate and shoreline change along the gulf of California. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasicchio, G.R.; Francone, A.; Simmonds, D.J.; D’Alessandro, F.; Frega, F. Prediction of shoreline evolution. Reliability of a general model for the mixed beach case. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondrat, V.; Šakurova, I.; Baltranaitė, E.; Kelpšaitė-Rimkienė, L. Natural and anthropogenic factors shaping the shoreline of klaipėda, Lithuania. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelpšaite, L.; Dailidiene, I. Influence of wind wave climate change on coastal processes in the eastern Baltic Sea. J. Coast. Res. 2011, 2011, 220–224. [Google Scholar]
- Susanti, I.; Nurlatifah, A.; Martono; Maryadi, E.; Slamet, S.L.; Siswanto, B.; Suhermat, M. Abrasion and accretion dynamics as impact of climate change in coastal area of Yogyakarta. AIP Conf. Proc. 2021, 2331, 030009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, M.E.; Walkden, M.J.A.; Hall, J.W. Systemic impacts of climate change on an eroding coastal region over the twenty-first century. Clim. Chang. 2007, 84, 141–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leatherman, S.P.; Zhang, K.; Douglas, B.C. Sea level rise shown to drive coastal erosion. Eos 2000, 81, 55–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scardino, G.; Sabatier, F.; Scicchitano, G.; Piscitelli, A.; Milella, M.; Vecchio, A.; Anzidei, M.; Mastronuzzi, G. Sea-level rise and shoreline changes along an open sandy coast: Case study of gulf of taranto, Italy. Water 2020, 12, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonioli, F.; Anzidei, M.; Amorosi, A.; Lo Presti, V.; Mastronuzzi, G.; Deiana, G.; De Falco, G.; Fontana, A.; Fontolan, G.; Lisco, S.; et al. Sea-level rise and potential drowning of the Italian coastal plains: Flooding risk scenarios for 2100. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2017, 158, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Variable | Abbreviation | Unit | Spatial Domain | Spatial Resolution | Timeframe Available | Data Format | Reference/Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sea surface height above the geoid | SSH | m | Mediterranean Sea | 0.0625 degrees | 1987–2023 | NetCDF | https://doi.org/10.25423/CMCC/MEDSEA_MULTIYEAR_PHY_006_004_E3R1 (accessed on 19 August 2022) |
| Eastward sea water velocity | ESV | m s−1 | Mediterranean Sea | 0.0625 degrees | 1987–2023 | NetCDF | |
| Northward sea water velocity | NSV | m s−1 | Mediterranean Sea | 0.0625 degrees | 1987–2023 | NetCDF | |
| Wave direction from | WAD | degree | Mediterranean Sea | 0.042 degrees | 1993–2023 | NetCDF | https://doi.org/10.25423/cmcc/medsea_multiyear_wav_006_012 (accessed on 19 August 2022) |
| Significant wave height | WAH | m | Mediterranean Sea | 0.042 degrees | 1993–2023 | NetCDF | |
| Sea surface wave mean period | WAP | s | Mediterranean Sea | 0.042 degrees | 1993–2023 | NetCDF | |
| Wind wave direction | WID | degree | Mediterranean Sea | 0.042 degrees | 1993–2023 | NetCDF | |
| Significant wind wave height | WIH | m | Mediterranean Sea | 0.042 degrees | 1993–2023 | NetCDF | |
| Sea-surface wind wave mean period | WIP | s | Mediterranean Sea | 0.042 degrees | 1993–2023 | NetCDF | |
| Absorption coefficient | CDM | m−1 | Global | 4 km | 1997–2023 | NetCDF | https://doi.org/10.48670/moi-00280 (accessed on 19 August 2022) |
| Diffuse attenuation | KD | m−1 | Global | 4 km | 1997–2023 | NetCDF | |
| Particulate backscattering | BBP | m−1 | Global | 4 km | 1997–2023 | NetCDF | |
| Reflectance | RRS | sr−1 | Global | 4 km | 1997–2023 | NetCDF | |
| Secchi transparency | ZSD | m | Global | 4 km | 1997–2023 | NetCDF | |
| Suspended particulate matter | SPM | g m−3 | Global | 4 km | 1997–2023 | NetCDF | |
| Shoreline evolution | SEV | m yr−1 | Venice case study | - | 2015–2019 | Shapefile | [59] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pham, H.V.; Dal Barco, M.K.; Pourmohammad Shahvar, M.; Furlan, E.; Critto, A.; Torresan, S. Bayesian Network Analysis for Shoreline Dynamics, Coastal Water Quality, and Their Related Risks in the Venice Littoral Zone, Italy. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12010139
Pham HV, Dal Barco MK, Pourmohammad Shahvar M, Furlan E, Critto A, Torresan S. Bayesian Network Analysis for Shoreline Dynamics, Coastal Water Quality, and Their Related Risks in the Venice Littoral Zone, Italy. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2024; 12(1):139. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12010139
Chicago/Turabian StylePham, Hung Vuong, Maria Katherina Dal Barco, Mohsen Pourmohammad Shahvar, Elisa Furlan, Andrea Critto, and Silvia Torresan. 2024. "Bayesian Network Analysis for Shoreline Dynamics, Coastal Water Quality, and Their Related Risks in the Venice Littoral Zone, Italy" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 12, no. 1: 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12010139
APA StylePham, H. V., Dal Barco, M. K., Pourmohammad Shahvar, M., Furlan, E., Critto, A., & Torresan, S. (2024). Bayesian Network Analysis for Shoreline Dynamics, Coastal Water Quality, and Their Related Risks in the Venice Littoral Zone, Italy. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 12(1), 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12010139







