Abstract
Coastal dunes, formed and shaped by aeolian sediment transport, play a crucial role in ecosystem services and act as natural flood and coastal erosion defenses. This paper delves into theoretical equations and numerical models predicting sediment transport. Numerical models like cellular automata, XBeach-DUNA, the coastal dune model, and others are analyzed for their ability to simulate dune morphology, erosion processes, and vegetation impacts accurately. Evaluated are field observation and measurement techniques, such as sand traps, impact sensors, and optical sensors, for their precision in quantifying aeolian dynamics. Further examined is the effectiveness of vegetation and fencing in dune stabilization, noting species-specific responses and the influence of fence design on sediment accumulation. These tools offer insights into optimizing aeolian sediment management for coastal protection. By conducting a systematic review and connecting theoretical, empirical, and modeling findings, this study highlights the complex challenge of measuring and managing aeolian sediment transport and proposes integrated strategies for enhancing coastal dune resilience against the backdrop of climate change and erosion. This study’s objectives to bridge gaps in current understanding are met, highlighting the need for a multidisciplinary approach to coastal dune management and conservation, especially combining wind- and wave-driven processes.
1. Introduction
The coastal environment, a dynamic interface between land and sea, is governed by a multitude of processes that shape and reshape its landscape. Sand dunes, very commonly present along coasts worldwide [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8], are highly dynamic marine environments affected by storm surges and water-level fluctuations as well as wind and wave processes. Sediment accumulation for dune formation depends mainly on a supply of sand to the beach [9,10,11]. Needed first is an active source of sediment supply to the beach, moving from the sea onto the beach profile through wave action [12] so that, secondly, through aeolian action, the sand can be blown inland into the adjacent dune. Additionally, an accommodative and supportive topography is needed that enables sediment transport over wide, dry beach area and onto spaces without anthropic disturbances [13,14]. Therefore, coastal dunes develop mainly on low-lying shores and on sandy barriers that have already been formed and shaped by the sea [15]. For dune development but also stabilization, this sediment supply must be continuous, as otherwise, the dune system will be forced into retreat. In the current climate context, the consensus of research suggests that even with sea-level rise, only nearshore erosion is caused, while the foredune systems will be able to maintain themselves through landward migration. And of course, this is only possible if the sediment budget of the littoral cell is at least neutral [1,16,17,18,19,20,21]. When the dune grows and establishes itself, vegetation can further stabilize that dune through sediment-trapping and root-related “anchoring” processes. These stabilization processes can be mimicked with the use of fences as a means of anthropogenic intervention against dune retreat. With a given sediment supply from the ocean to the beach, aeolian sediment transport, characterized by the movement of sand through wind action, not only is a critical factor in the formation, growth, and stabilization of coastal dunes but also plays a pivotal role in the geomorphological evolution of coastal dunes as well as their ecological functions and resilience against climate change and human impacts. If this sediment source is naturally unavailable, artificial nourishments may be the sole answer to supporting the existence of these dunes and their functionalities. This puts additional emphasis on the need for comprehensive modeling approaches used to evaluate optimal coastal management strategies.
Through a methodical review of the literature, this work delves into the evolution of theoretical approaches to sediment transport, assessing their applicability and the extent to which they capture the complex interactions at play in coastal environments. Furthermore, the current range of field measurement methodologies, from traditional sand traps to advanced optical sensors, is presented, with a discussion of their respective strengths and limitations in capturing the nuances of aeolian processes. The incorporation of vegetation and fencing as nature-based solutions for dune stabilization and coastal protection is also critically examined, highlighting species-specific responses and the design considerations that influence their effectiveness. Also central is the examination of numerical models, which have emerged as powerful tools in predicting and managing aeolian sediment processes. Models such as cellular automata [22,23,24], XBeach-DUNA [25], the coastal dune model [26], and more are discussed in detail, providing insights into their capabilities in simulating the interactions between wind, sand, and vegetation and the implications of their findings for coastal management strategies. By incorporating various theoretical perspectives, empirical evidence, and modeling approaches, a more comprehensive understanding of aeolian sediment transport and its importance in coastal dune dynamics is attained. Here, the complexity of measuring and managing these processes is highlighted, offering valuable insights into effective strategies for coastal dune stabilization and formation amid the challenges of coastal erosion and climate change.
This paper aims to dissect the intricacies of aeolian sediment transport by exploring theoretical frameworks, empirical models, and field measurement techniques, thereby offering a holistic and comprehensive view of the mechanisms driving sediment movement and dune morphology. The specific objectives of this study are as follows: (1) to gather and review published papers to understand the latest advancements in aeolian sediment transport; (2) to identify the evolution of established equations and evaluate their applicability for best predicting aeolian sediment transport in their respective use cases; (3) to assess the most effective validation techniques and field observation and measurement methods while giving an overview of possible methodologies; (4) to give insight into the role of vegetation on sediment behavior as well as the construction of fences on promoting sand accumulation in the context of nature-based solutions to coastal hazards; and (5) to discuss how the findings can be applied through models to better manage and predict aeolian sediment processes in coastal areas. Lastly, and as a main objective of this review paper, the sixth aim concerns the need for modeling approaches that simultaneously combine aeolian sediment processes with wave-driven ones. This aim is further investigated, as an all-encompassing model of both processes will allow the computational simulation to progress closer to the real-world scenarios that are modeled. By going through all six objectives, a comprehensive basis of the state of the art of the field of aeolian sediment transport as well as its progression is demonstrated to then help the field to progress further, highlight existing advancements and gaps with high potential for future research.
2. Materials and Methods
To identify and select the research relevant to the objectives, a methodical approach was employed, beginning with a systematic review that was further worked on with nonsystematic approaches. This involved conducting a comprehensive keyword search on the Web of Science database (https://www.webofscience.com/wos/woscc/basic-search, accessed on 5 March 2024) [27], ensuring a wide-ranging exploration of the literature without imposing any temporal restrictions to avoid bias (Table 1). For each keyword researched in the Web of Science’s database, three variables of the search results that were displayed were chosen. Firstly, we included results and the number of papers found when looking for the keyword in the Web of Science Core Collection while having “All Fields” selected. Secondly and thirdly, we further adjusted the quick filters after the initial results, and we included the number of highly cited papers and review papers in order to shine a light on the interest in the topics and to look for other previous review papers. The “highly cited papers” are determined by applying citation thresholds specific to each field and publication year. These thresholds identify the top 1% of papers in their respective fields based on citation frequency. These three variables were chosen to give insight into the field and the amount of research conducted across specific terms.

Table 1.
Results of the literature review about aeolian sediment transport on Web of Science database under Web of Science Core Collection in All Fields (state: 5 March 2024) [27].
After this keyword search was conducted, personal bias may have entered the methodology when meticulously assessing the relevance of each paper and prioritizing those that significantly contribute to the understanding of aeolian sediment transport, its prediction, and its management. Additionally, the references of the selected papers were evaluated to trace the evolution of research topics and identify key linkages between studies. This thorough methodology ensured the incorporation of a broad selection of research conducted within the last century. While personal biases may have affected this methodology, a robust foundation for the analysis was created by encompassing a diverse array of studies; this approach facilitated a comprehensive understanding of the complexities and advancements in the field of aeolian sediment transport.
The keyword search in the Web of Science database revealed that “aeolian sediment transport” as a standalone topic has the highest number of results (2130) and a substantial number of reviews (88) out of the 15 keyword combinations that were used, indicating it is an established area of research with significant secondary literature (Table 1). Specialized topics like “coastal aeolian sediment transport” and “aeolian sediment transport model” also have a considerable body of work (469 and 825 results, respectively), although only a small number of highly cited papers (0 and 4) are listed, suggesting that the field is in constant development while still being a highly specialized research topic. Hence, when “aeolian sediment transport” is combined with specific modifiers like “storm,” “fence,” or “vegetation,” the number of results and highly cited papers decreases further, indicating these are even more niche areas of study. Notably, “coastal aeolian sediment transport” and its further specified subtopics, while less researched than the general term, still show a focused interest in the coastal context of sediment transport. These overall data suggest a field with opportunities for further research in areas that intersect with ecological features and storm impacts. As the published research has been in constant development for over a century now, with the last review paper in this field being published in 2011 [28], the need for an up-to-date review arises as an aid to streamlining past research, enabling focused future developments.
Considering the identified literature, a review on formulas and field measurements, on dune reinforcement with vegetation and fences, and on modeling approaches is presented in the following sections. Finally, some conclusions are drawn.
3. Empirical Equations
Over the last century, the field has evolved through incremental advances, with research mainly focused on validating, elaborating, refining, and eventually adapting the work conducted by Bagnold [29,30]. Different formulations have evolved through modification and adjustment for specific cases, leading to a variety of applicable equations to calculate the sediment transport rate, or mass flux, Q [30,31,32,33,34,35]. An important, and controversial, parameter is the critical shear velocity (), which represents the capacity of an aeolian surface to resist wind erosion [36]. The relationship of this parameter to the sediments’ median grain size () was first described by Equation (1) [29]:
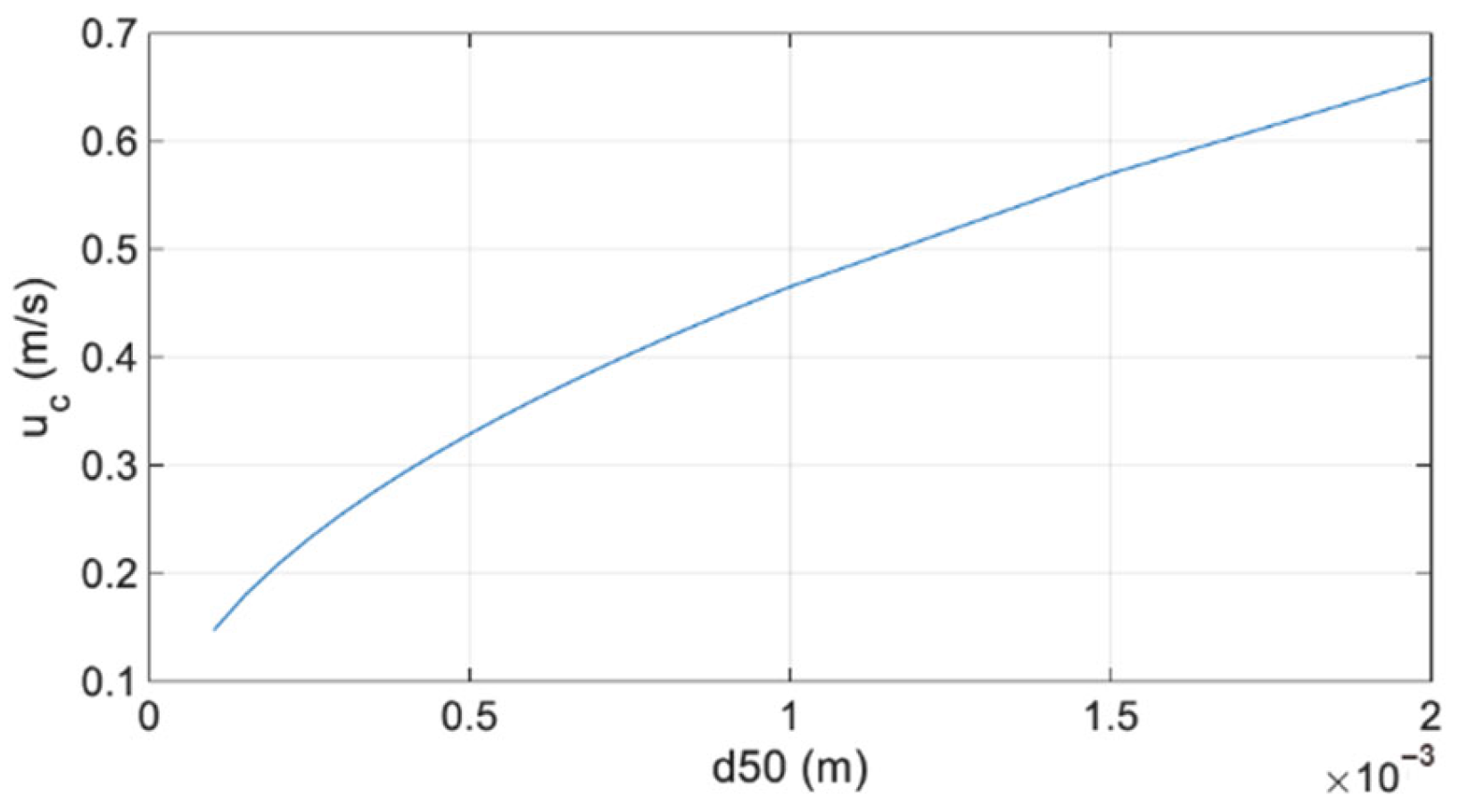
Here, and represent the density of sediments and density of air, respectively, with typical values of 2650 kg/m3 and 1.2 kg/m3. Parameter g represents the gravitational acceleration, considered to be 9.8 m/s2. is a constant, considered to be 0.1 according to Bagnold’s [29] experiments, in which a variation between 0.085 and 0.1, dependent on the stage of the movement, was defined. When sediment grain size increases, there is an increase in the critical velocity, responsible for initiating the movement of sediments (Figure 1).
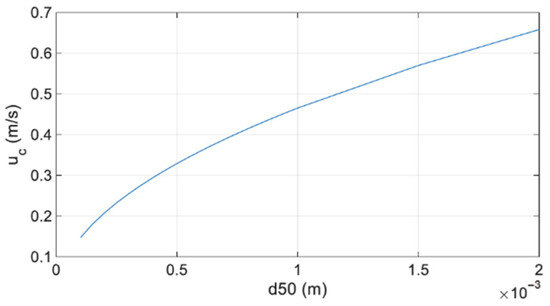
Figure 1.
Shear velocity of different sediment median grain sizes, according to Bagnold’s (1936) equation.
Aeolian sediment transport can be determined by the transport rate (Q), represented as a mass flow per unit of width (kg/s/m). Bagnold’s equations (Equations (1) and (2)) are foundational in aeolian transport studies, providing a basis for quantifying sediment transport by wind:
where represents the reference size of sand (considered 0.25 mm) and u represents the shear velocity (m/s). Here, is a constant that may present different values, depending on the formulations. In the case of Bagnold´s formulation [29,30], this value ranges between 1.5 and 3.5 depending on the grain size distribution. With minor differences, Kawamura [31], Owen [33], Hsu [37], and Lettau and Lettau [34] followed the assumption of Bagnold regarding the shear velocity (u) and threshold shear velocity (), with all of them showing similar patterns when u >> . To later compare this equation to the other formulations, a value of 1.8 is considered, which represents naturally graded dune sands [29]. The equation provides a physical basis for understanding aeolian sediment transport and is widely used for its simplicity and effectiveness in capturing the essential dynamics of sand movement. The downsides of this equation are that it assumes a uniform grain size and neglects the effects of sediment sorting and nonuniform grain distributions. Furthermore, it does not account for moisture content or other supply-limiting conditions, which can significantly affect sediment transport rates, and the assumption of a constant wind flow and neglect of turbulent fluctuations may limit its applicability in natural environments.
Kawamura’s equation (Equation (3)) focuses on the initiation of sediment movement, offering a method to calculate the threshold wind velocity necessary for sediment transport [31]. It builds on Bagnold’s work by introducing a more detailed analysis of grain lifting and saltation and includes the shear velocity (u) as well as the threshold shear velocity () as individual parameters:
Here, = 1.225 kg/m3, the constant = 2.78 is suggested, and the threshold shear velocity () is defined to include moisture influences. The equation provides insights into the conditions necessary for sediment transport to commence, but like Bagnold’s equation, it simplifies complex natural processes and may not fully capture the variability of natural wind conditions and surface properties. Additionally, a homogenous particle size distribution is assumed, imposing further deviations from the real-world processes.
In contrast, Zingg’s work (Equation (4)) contributed to the understanding of the grain size distribution’s effect on sediment transport [32]. His contributions are often cited in discussions of sediment sorting and the differential transport of grains of various sizes, and his equation modifies Bagnold’s equation as follows:
where = 0.83 was determined. This not only highlights the importance of grain size distribution in aeolian sediment transport but also is useful for studies focusing on sediment sorting mechanisms.
The Lettau and Lettau equation (Equation (5)) expanded the application of aeolian transport equations to different environmental settings, including vegetated surfaces and complex terrain [34]. It extends the work of Kawamura [31] as it also includes threshold shear velocity to estimate transport rate in the following way:
with a value of = 4.2. The equation incorporates considerations for surface roughness and obstacles and broadens the applicability of aeolian sediment transport models to a wider range of conditions. This, in turn, increases the complexity in application due to the need to accurately characterize surface conditions. But still, assumptions regarding uniformity and steadiness of wind may limit applicability in highly variable environments.
By increasing the threshold velocity, which entrains the sand grains at the surface, surface moisture plays a significant role as a transport limitation [38,39,40,41,42]. Authors like Hotta et al. [43], Belly [44], and Dong et al. [45] have demonstrated various methods to incorporate the moisture effect in the threshold shear velocity (), with the latter developing the following equation (Equation (6)), also derived from Bagnold [30]:
in which the threshold shear velocity depends on the mean grain diameter , the gravitational acceleration g, a constant C according to the mean grain diameter, and the moisture content M, in percentage and with the density of the sand grains (), the density of the air (), and the empirical coefficient of all being equal to Equation (1). The threshold shear velocity term is very relevant, especially regarding calculations considering moisture effects, because it determines the steady state of the sand transport [38]. But in contradiction to the steady-state hypothesis, in the wind channel, sand transport was observed to flux sporadically, suggesting that the dynamics of aeolian transport are similar to avalanches observed in a sand pile [46].
4. Numerical Models
Numerical models play a crucial role in advancing the understanding of aeolian sediment transport and its impact on coastal dune dynamics. This section introduces several contemporary modeling approaches that have been developed to simulate the complex interactions between wind, sand, vegetation, and coastal geomorphology. The discussion encompasses the foundational principles behind each model, their methodological advancements, and the implications of their findings for coastal management and erosion control. Through a detailed examination of the selected models, the contributions of computational simulations to the knowledge of coastal systems are highlighted, emphasizing their individual importance in predicting environmental changes and informing effective conservation strategies.
A powerful tool for simulating the dynamics of complex nonlinear systems that exhibit self-organizing behavior is called cellular automata modeling (CA). Werner´s CA model was developed to study aeolian dune formation [22], which was later extended in the DECAL model [47], including vegetation dynamics and interactions to reproduce the dune patterns that emerge in coastal landscapes. Following this, to simulate the behavior of coastal dunes in conjunction with the dynamics of the beach, the DuBeVeg (dune–beach–vegetation) model was developed by expanding DECAL to include the effects of waves, tides, and storm surges that bring sediments to the beach and can erode the beach profile [23]. The DuBeVeg model includes the effects of aeolian transport, hydrodynamic erosion and accretion, groundwater levels, and vegetation growth. The model considers the stochastic nature of the aeolian transport and wave erosion/accretion mechanisms, as well as the emergence of new vegetation in the beach–dune system and the limiting effect of groundwater on aeolian transport [24]. For recent usage, the original CA model presented in Werner [22] was adapted in Poppema et al. [48] to study the influence of buildings in aeolian transport, and the results were compared with field experiments. Different scenarios of buildings were tested, with different dimensions and groups of buildings. The results are comparable with field experiments, shown by the combination of scour and deposition beside the building and deposition downwind of the building.
Another study of aeolian transport involving buildings was conducted by Pourteimouri et al. [49] using the OpenFOAM model to simulate flow around a row of ten full-scale beach buildings (size of 6.00 × 2.50 × 2.50 m3). Results indicate that with small gap spacings, a row of ten buildings forms a singular bluff body against wind, minimally affecting jet flows through gaps while majorly altering airflows at the upwind face and forming vortices behind. Conversely, larger gaps render buildings virtually independent, reducing the funneling effect and less significantly altering streamwise velocity. The same model was used to study the influence of a row of ten beach buildings constructed on poles, focusing on understanding airflow, wind-induced erosion, and deposition patterns around the buildings [50]. The main finding is that by elevating buildings on poles, bed shear stress underneath and between them increases due to airflow compression and acceleration, which extends downstream farther than for buildings directly on the surface, potentially enhancing sediment transport towards the dune foot.
The coastal dune model (CDM) incorporates both ecological and physical processes, highlighting the critical role of vegetation in dune dynamics [26]. The model shows that the vertical growth of foredunes is eventually constrained by a negative feedback mechanism where wind flow and topography interact, leading to scale-invariant steady-state foredunes. It is said that this allows for the derivation of scaling relations that predict the maximum height and formation time of foredunes and that the position of the dune depends on the place where plants grow. But this has not yet been proven and has even been criticized [38]. By recognizing the need to implement the dynamic interplay between biological and geomorphological processes into this model, the active role of vegetation in modifying habitat and influencing coastal resilience is underscored, offering a more integrative perspective on dune formation and stabilization processes [51].
Developed by Bas Hoonhout and Sierd de Vries, the AEOLIS model focuses on simulating the spatio-temporal variations in aeolian sediment transport and availability, particularly in environments where sediment availability is limited [52]. By incorporating feedback mechanisms between sediment availability and transport, including the effects of self-grading and beach armoring, AEOLIS excels in replicating multiannual aeolian sediment transport rates, as evidenced in studies of the Sand Motor meganourishment in the Netherlands [53]. This model stands out for its ability to account for complex factors influencing sediment availability, such as soil moisture and sediment sorting, thereby providing critical insights into coastal sediment dynamics. Although AEOLIS faces challenges in capturing the full range of environmental influences on meganourishments, its versatile framework makes it valuable for understanding and predicting how sediment availability impacts aeolian processes in coastal zones. The model’s strengths lie in its detailed approach and predictive capabilities, making it a vital tool for designing nourishments that enhance coastal safety and resilience while promoting natural landscape development.
Another advancement in coastal dune modeling is the integration of the XBeach [54,55] and Duna models [25,56], referred to as XBeach-DUNA [25], which with its coupled model architecture provides a nuanced understanding of coastal dune evolution through a comprehensive treatment of nearshore and aeolian processes. By combining the hydrodynamic capabilities of XBeach with the aeolian transport mechanisms of Duna, the model adeptly captures the dual influences of wave action and wind transport on dune morphology. A distinguishing feature of XBeach-DUNA is its ability to simulate the temporal evolution of dune profiles over decadal timescales, encompassing the intricate balance between sediment deposition by storm-driven waves and aeolian transport facilitated by wind [25]. This holistic approach not only replicates observed behaviors, such as the reciprocal relationship between dune progradation rates and foredune heights, but also highlights the crucial role of vegetation in shaping dune morphology. The model is capable of capturing the interactions between physical and biological processes, marking a further step towards predicting coastal dune responses to environmental changes. Another integrative approach with XBeach can be mentioned, coupling it to CDM and AEOLIS into Windsurf to simulate the coevolution of the nearshore, beach, and dune [57].
Comparably, the cross-shore model (CS-Model), as described by Larson et al. [58], offers a comprehensive framework for simulating cross-shore material exchanges over decadal scales, essential for understanding regional coastal evolution. This model integrates multiple submodels, each dedicated to distinct processes such as dune erosion, overwash, wind-blown sand transport, and bar–berm material exchange, highlighted by a combination of empirical observations and relevant physical laws. Notably, the model employs a set of sand volume conservation equations for the dynamic representation of key morphological features, including dune height and shoreline changes. Validation against field and laboratory data shows the model’s capability to accurately simulate the midterm coastal profile changes driven by both natural processes and artificial nourishments [59,60]. This model’s novel approach to integrating detailed process-based submodels within a cohesive system provides another robust tool for predicting coastal evolution in response to changing environmental conditions and coastal management practices.
5. Field Observations
This section is divided into three subheadings to separate the main types of techniques used to measure sediment transport.
5.1. Sand Traps
Determining sediment transport using sand traps is, in principle, a very straightforward method. The sand trap is placed on a surface for a certain amount of time so that the sediments are blown into the trap. After installation, a period of adjustment may be considered before the trap should be opened for use to allow the disturbed surrounding area to return to its natural state, thus ensuring accurate measurements of aeolian transport. Next, the weight of the sand is measured, and the transport rates can be calculated. Additionally, the grain size distribution of the sample can be determined. But the problem with these kinds of traps is their efficiency. It has been shown that some traps catch too little sand [61], while others catch too much sand [62]. In addition, the small capacity of many vertical sand traps, they could be filled in a matter of minutes and would not be useful for massive sand transport rates from extremely high sand fluxes [63,64,65]. To shed light on the variations in grain size populations during transit, samples trapped at various heights can be compared in this context [66]. Additionally, every sand trap will influence the air current and, therefore, the sand transport [67]. In conclusion, it is an ongoing effort to design a sand trap that precisely catches all transported sand.
The first sand trap developed stems from Bagnold [68] and is a wooden horizontal sand trap that is 60 cm wide and 120 cm long (Figure 2a). After digging it into the ground, six linen bags are placed within to catch the sand. To prevent grains from bypassing the trap, it should be ensured that the trap is longer than the saltation length of the grains.
Following this idea, another trap was proposed by Leatherman [65] and developed as an adaptation of vertical sand traps (Figure 2b) [69]. This trap consists of a tube with a length of one meter and a diameter of 39 mm. On opposite sides of the tube, two slits are cut for 75 cm of the tube length. The rear slit (25 cm) is broader than the front slit (10 cm) to allow a greater through-flow of air and is covered with 50 μm nylon mesh. It is installed 25 cm into the ground, with the brim of the front slit connected with the sand to obtain optimal trapping efficiency. The trap’s “hard” efficiency of 139%, determined through comparison with the transport rates measured by the Bagnold trap [70], shows an improvement in efficiency.
To further improve these traps, a sand trap that is not influenced by changing wind directions was designed by De Ploey [71] and later developed by Van Dijk and Hollemans [72] and modified by Arens [61] at the University of Wageningen (Figure 2c). This pan trap is made up of round disks that allow the sand to be caught from all directions. Another advantage of this design is that it is possible to measure the transport rate at different heights above the surface. The pan trap´s efficiency varied between 7% and 27% in wind tunnel experiments [61] and was determined to be at about 15% at average wind velocities. The cause for this low efficiency is twofold. Firstly, due to the strong influence the trap has on the air currents, a scour hole at the base of the trap results in the brim of the lowest disk not being able connect to the surface, which hinders creeping sand grains from being trapped. Secondly, already entrapped sand can be easily blown out of the disks, which can be partially adjusted by putting beads or water into the disks.
Every trap described has the capability to collect creeping sand to some degree. However, the exact amount of creeping sand they capture, as well as their efficiency in doing so, remains undetermined. Thus, it is beneficial to employ a trap designed exclusively for capturing creep without interference from saltation. The creep trap must be completely dug in so that only a small slit 1 cm wide and 50 cm long is visible at the surface (Figure 2d). The creeping sand can then fall into this slit and will be collected by the buried metal box. Because of the small opening, it can be assumed that all the sand transported by saltation is not collected, leading to an efficiency close to 100% for creeping sand grains.
Opposite to this trap idea stands the swinging trap, the biggest disadvantage of which is the need for its elevation (Figure 2e) [73]. The trap’s characteristics resemble those of the mesh-style traps developed by Sherman et al. [74] and were modified so that it can be deployed faster and be less expensive than the Sherman design. This trap catches the sediment in a bag that can orient itself to the direction of the wind due to its mobility on the pole it is attached to. This is a big advantage for regions with fluctuating wind direction, but it comes at the cost of not being able to collect sand transported by creep or saltation close to the beach surface.

Figure 2.
Sand trap schematics of (a) the Bagnold trap [70], (b) the Sarre trap [70], (c) the pan trap [61], (d) the creep trap [70], and (e) the swinging trap installed in a wind tunnel [73].
Figure 2.
Sand trap schematics of (a) the Bagnold trap [70], (b) the Sarre trap [70], (c) the pan trap [61], (d) the creep trap [70], and (e) the swinging trap installed in a wind tunnel [73].

Enticingly, by using sand traps, it is possible to know not only the average flux of sediment transport over a specific period but also the grain particle size distribution of the transported sediments. The downside of these traps is that information on temporal variability of the transport during the sand collection period is unknown. Therefore, efforts have been made to develop continuously weighing sand traps [75,76,77], but as with all the sand traps discussed previously, their efficiency and precision are often lacking and/or inconsistent.
5.2. Impact Sensors
Even though sand traps are the most common method for measuring sediment transport in the field (e.g., [45,77,78,79]), there are several limitations to the measurement of small-scale aeolian processes due to poor temporal and spatial resolution. Attempts have been made to overcome these limitations of sand traps by decreasing wind-field disturbances [78] or by increasing the temporal resolution [76,77,79], with varying degrees of success. Therefore, alternative techniques have been explored to investigate saltation processes, using, for example, instruments that can capture this process at temporal scales of less than one second [80] and spatial scales of less than 0.2 m [81]. Consequently, instruments suited for measuring small-scale fluctuations in the saltation field like impact sensors and optical sensors were developed, which are often categorized in the at-a-point group.
Piezo-electric technology is used in most point-source measurements acquired from impact sensors to identify the effects of sand grains with a high time resolution [80,82,83,84,85]. A commercially produced example is the Sensit, an omnidirectional sensor with a piezo-electric crystal (Figure 3a) which has been used in various field deployments, having the ability to obtain grain impact counts [82,86,87]. But it has been shown that the output of the sensor has a positive linear dependence on temperature when using the kinetic energy channel, which is a disadvantage of the sensor, as with an increase in ambient temperature, the level of background noise also increases.
A second example of an omnidirectional, piezo-electric sensor is the Safire, manufactured by Saba and originally developed at the University of Amsterdam (Figure 3b). It is significantly less expensive than the Sensit and measures impact counts and voltage (with a maximum of 200 sand impacts/s) at a sample rate of 20 Hz while having minimal flow obstruction [14]. The main disadvantage of this sensor is the meticulous and careful calibration needed, as due to its high sensitivity, each sensor has a different momentum threshold [80].
As an alternative to piezo-electric crystal technology, microphones can be used to detect grain impacts, such as the Saltiphone, which was developed by Spaan and Van den Abeele [88]. Saltiphones are relatively large (0.19 m wide, 0.3 m long, and 0.2 m high), but they are also not expensive [14]. In field experiments, the microphone is anchored in a stainless steel tube at 0.1 m above the bed to protect the microphone against adverse environmental conditions [3,89,90]. The problem here is that 90% of all saltation occurs below that sensor height [61,88]. Enticingly, the Miniphone was developed, which uses a similar technology to the Saltiphone, and due to its smaller size, deployment at elevations lower than 0.01 m is made possible (Figure 3c) [91]. Additionally, relatively dense vertical and horizontal arrays are possible with little interference from the wind field.
To combat the Saltiphone’s lack of spatial resolution and the problem of sensitivity differences between multiple Sensit or Safire sensors, a system with multiple saltation sensors called the Saltation Detection System (SalDecS) was developed (Figure 3d) [92]. This system was developed to precisely fit this niche while also striving to be an even more low-cost tool. The SalDecS, developed at the Department of Physical Geography of Utrecht University, consists of one carrier bar that is equipped with 40 sensors. With this system, changes in morphological features (such as sand-strip migration or small-scale (centimeters) surface-moisture characteristics) can be recognized at large timescales (hours) while the characteristics of the saltation process related to wind turbulence can be studied at small timescales (seconds) [92].
Another major issue with a lot of the discussed sensors is that they are not meant to be used in remote locations with extreme weather conditions for extended periods of time. To keep their capacity to measure transport, they require either regular cleaning or a power source. Therefore, the SandFlow, a sensor aimed at long-scale and remote measurements, was developed by integrating principles from its precursor, the FlowCapt sensor, which was originally designed for snow transport (Figure 3e) [93]. Its acoustic detection mechanism, involving electroacoustic transducers within a durable thermopowder lacquered tube, enables the sensor to accurately capture the flux of sand particles by translating mechanical impacts into measurable acoustic signals. This allows for the quantification of sediment transport in real time across various particle sizes, with a noted high efficiency for particles coarser than 300 µm. The sensor’s design facilitates omnidirectional measurement, making it well suited for long-term monitoring in dynamic wind environments. The SandFlow’s application in field experiments demonstrates its potential to offer reliable sand transport data, provided the transport is intense enough, with a noted limitation in capturing very fine sand transport efficiently [93].

Figure 3.
Impact sensor depictions: (a) a schematic drawing of the Sensit saltation sensor and mounting stand [86]; (b) a picture of the saltation flux impact responder (Safire) [80]; (c) a picture of a field-ready Miniphone, shown next to a United States one-cent coin for scale [91]; (d) the physical design of a Saltation Detection sensor, with (from left to right) a photo, a schematic exterior view, and a schematic interior [92]; and (e) a schematic of the SF4 sensor used in the SandFlow [93].
Figure 3.
Impact sensor depictions: (a) a schematic drawing of the Sensit saltation sensor and mounting stand [86]; (b) a picture of the saltation flux impact responder (Safire) [80]; (c) a picture of a field-ready Miniphone, shown next to a United States one-cent coin for scale [91]; (d) the physical design of a Saltation Detection sensor, with (from left to right) a photo, a schematic exterior view, and a schematic interior [92]; and (e) a schematic of the SF4 sensor used in the SandFlow [93].
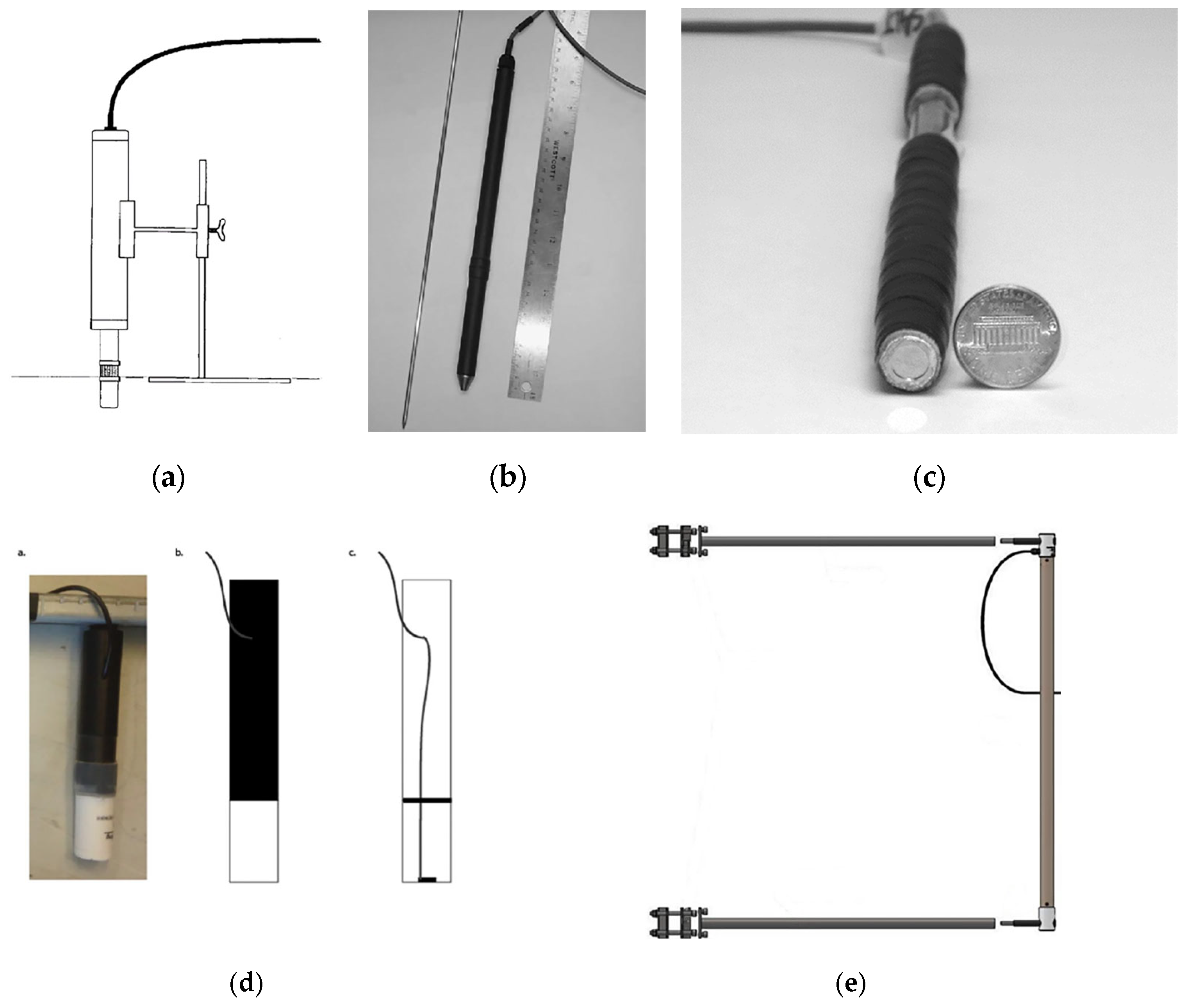
5.3. Optical Sensors
The first use of laser/CCD optical sensors to measure sand transport and record at-point measurements in a laboratory setting was documented by Butterfield [94] (Figure 4a). With movable distances between 10 and 100 mm, these sensors sample at a rate of 25 Hz. To quantify the mass flux concentration, Dong et al. [45] used particle image velocimetry (PIV) in the laboratory. In the field, various techniques have been used with differing degrees of success, including adhesive surfaces [95], tracers [96,97], and injections of colored sand [98], and have revealed limitations in the detection of small-scale spatio-temporal aeolian processes due to problems with temporal resolution or recovery of the sand.
Another commonly used optical sensor is the Wenglor [39,74,99,100,101], which can provide detailed information regarding transport variations over a period of seconds (Figure 4b). However, the information obtained from this optical sensor is limited to the number of sand grains that pass through its laser beam. Additionally, data on the grain size distribution of the sand that crosses the Wenglor beam area must be added to the Wenglor data if fluxes of aeolian sand transport are to be determined [102,103]. Wenglor sensors were used in fieldwork deployments to study sand transport dynamics in various experimental setups with different wind conditions, demonstrating their versatility. For example, Bauer and Davidson-Arnott [104] analyzed intense sand transport during a storm in Canada to determine vertical profiles of particle flux and the variations in this vertical distribution over time, while Hoonhout and de Vries [105] investigated sediment availability using spatial transects of vertically stacked Wenglor sensors to make inferences about spatial variations in aeolian sediment availability along the beach and dunes.
Lastly, the SANTRI optical sensor is a device that uses an optical gate mechanism to detect the movement, size, and, potentially, the speed of individual sand grains, offering high-resolution data (Figure 4c) [106]. Key benefits include its ability to provide particle counts and total signal responses well correlated with traditional sand-trap data, excellent repeatability among units, and the potential for extracting size distribution information from its linear response under certain conditions. However, its challenges involve managing noise levels in the signal and interference from extraneous light sources, which require careful operational parameter adjustments.

Figure 4.
Photographs of optical sensors, specifically (a) the laser/CCD optical sand transport with adjustable elevation and the separation of the periscopes [94], (b) the Wenglor YH03PCT8 fork sensor with its dimensions in millimeters [99], and (c) the SANTRI platform [107].
Figure 4.
Photographs of optical sensors, specifically (a) the laser/CCD optical sand transport with adjustable elevation and the separation of the periscopes [94], (b) the Wenglor YH03PCT8 fork sensor with its dimensions in millimeters [99], and (c) the SANTRI platform [107].

It has been shown that various field measurement techniques of aeolian sediment transport offer diverse perspectives into understanding the dynamic processes that shape coastal landscapes, highlighting the need for a correctly specified or multifaceted approach to accurately capture the complexity of sediment movement, as each method comes with its own strengths and weaknesses. Sand traps, with their straightforward design, have been fundamental in quantifying sediment transport rates. However, their efficiency varies, and their influence on airflow and sediment capture necessitates ongoing design improvements for precision. Impact sensors, utilizing piezo-electric technology, have enabled high-resolution detection of grain impacts, offering insights into the temporal dynamics of saltation. Optical sensors, on the other hand, provide detailed spatio-temporal data on sand transport but require complementary data to fully assess aeolian fluxes. With all this in mind, there still is more research and development happening and to be undertaken, for example, further refining optical electronic devices like the sand particle counter [108], calibration procedures of acoustic sensors [109], or the development of the TLS (terrestrial laser scanning) method to assess the variability of embryo dune formation [110], just to name a few.
6. Vegetation and Fences
The stabilization of coastal dunes is critical to preserving beach ecosystems and protecting coastal infrastructure from erosion and overwash. Vegetation has been extensively studied for its efficacy in sand stabilization and dune formation. Through biogeophysical interactions, vegetation enhances dune stability, with plant roots anchoring the sand, reducing erosion, and facilitating sediment accretion, thereby promoting dune growth and stability [111,112]. Moreover, recent studies have highlighted that vegetation not only contributes to dune stability but also influences dune morphology, biodiversity, and resilience against climatic variations and anthropogenic pressures.
6.1. Vegetation
Coastal dunes are dynamic landforms shaped by the biogeophysical interactions between sediment availability, aeolian transport, vegetation cover, and the beach state [12,38,100,113,114,115,116]. Large-scale processes like climate change can influence vegetation growth directly, leading to changes in dune morphologies and dynamics [117,118]. Additionally, the increase in extreme weather events and rising sea levels can harm and remove vegetation, promoting dune mobility [119,120,121]. The main process controlling dune type, morphology, and state of vegetation on a local scale is the regional sediment availability [12,113,122].
The process of dune formation begins with sand provided by the ocean being transported up the beach by wave and wind action, where the sediments slowly accumulate [12,13,14]. At some point, the rate of sediment accumulation and dune movement will slow down enough so that vegetation can try to establish itself, which further adds to the stabilization process that the dune is in by increasing the amount of aeolian transported sediments captured by vegetation or other barriers on the beach back shore [123]. The vegetation now functions as an “anchor” by utilizing roots to hold the dunes temporarily in place. Additionally, their shape reduces the velocity and forces sediment accumulation and trapping. In absence of vegetation, the dunes’ shape and location are constantly changing due to wind [123], making vegetation cover a main factor that determines dune mobility [124]. Driving forces for changes in the vegetation cover can be of both natural causes, e.g., due to the decline of the sediment supply rate to the coast [15,125], prolonged growing seasons caused by rising temperatures [126], decreasing frequency and intensity of tropical cyclones [127], increase in rainfall and decrease in windiness [128,129,130], and anthropogenic causes, e.g., land-use changes and dune stabilization programs through grass planting and afforestation [6,8,131,132,133,134] and the spread of invasive species and eutrophication due to atmospheric nitrogen deposition [8,124].
It is well-known that aeolian and hydrologically transported sediments accumulate around dune vegetation through interception by leaves and stems when there is an adequate supply of sediment. But more specifically, recent findings in flume studies point to below-ground biomass being a main determinant of lateral resistance in coastal dunes [135]. This was studied and proven in salt marsh systems [136,137,138]; therefore, possible transferability to coastal dunes can be proposed, even though there is a difference in sediment cohesion. According to Bryant et al. [139], above-ground biomass (wooden dowels) lessened erosion more than below-ground biomass, which was simulated by coir fibers. However, in naturally occurring dunes, below-ground biomass may comprise various plant organs (roots, rhizomes, and buried shoots) that have contrasting physical characteristics, indicating that, in particular, fine roots might be of higher importance than the total below-ground biomass [140]. Different dune grass species have different processes for biomass allocation and subsequent growth and expansion following burial events [141,142]. After such events, plant species like Ammophila breviligulata, Ammophila arenaria, and Uniola paniculata can effectively shift below-ground biomass back to above-ground biomass due to their outstanding ability of sediment accretion [141,142,143,144]. Depending on the root characteristics of each plant, anchoring and dune reinforcement may differ. For instance, Ammophila breviligulata and Spartina patens have similar average root diameters, with greater root surface area leading to high tensile strength values that have been shown to be two and three times greater, respectively, than Uniola paniculata and Panicum amarum, which may confer an advantage for sediment reinforcement and anchorage during disturbance events [145]. However, Ammophila and Uniola showed similar below-ground biomass despite clear differences in root traits, making erosional resistance dependent on the local context.
6.2. Fences
Fences are synthetic physical barriers that differentiate spaces with the purpose of constraining natural physical and biotic processes as well as human actions. Furthermore, as they mimic vegetation, the construction of fences can serve as a physical barrier to wind, reducing its velocity and thus enhancing sand deposition, which in turn supports the formation and stabilization of new and existing dunes [146,147]. Especially in the current context of coastal erosion and sea-level rise, many dunes worldwide have insufficient sediment supply, resulting in challenges to maintain their stability and size and, therefore, their functionality. This further emphasizes the high significance of vegetation and fences and their considerations of implementation into coastal management strategies. Fence construction can have many designs using many different construction materials, including concrete, iron, wood, wire, plastic, stone, sod, and vegetation [146]. Fences not only reduce wind velocity but also trap sand, which helps to create and stabilize dunes that provide protection against flooding and overwash [148]. As a soft engineering approach, fence construction can be easily integrated into the coastal ecosystem for dune reestablishment [149,150]. Furthermore, sand fences can control sand deposition as well as dune development [147,151,152], while also, in joint effort with newly built dune ridges, significantly reducing the onshore sand drift. This leads to the minimization of roads, buildings, and ecological features, like coastal forests and wetland, being buried by sand [43,153,154].
Experiments in a wind tunnel at Aachen University, Germany, were conducted to test the wind regime and sand-trapping efficiency of sand-trapping fences, with different fence porosities and fence heights (Figure 5) [155]. In these experiments, a total of 27 cases of different heights and porosities of sand fences were tested. It was shown that with higher wind velocity, the total amount of deposited sediments at the sand-trapping fence increased, caused by a higher aeolian sediment transport rate. With denser fence porosity, the deposited sediment on the windward side of the sand-trapping fence increased. The sediment accretion on the leeward side of the fence developed simultaneously but faster than the sediment accretion on the windward side of the fence [155].
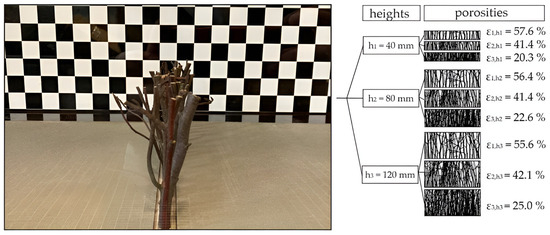
Figure 5.
Different fence heights and porosities considered in wind tunnel experiments (adapted from [155]).
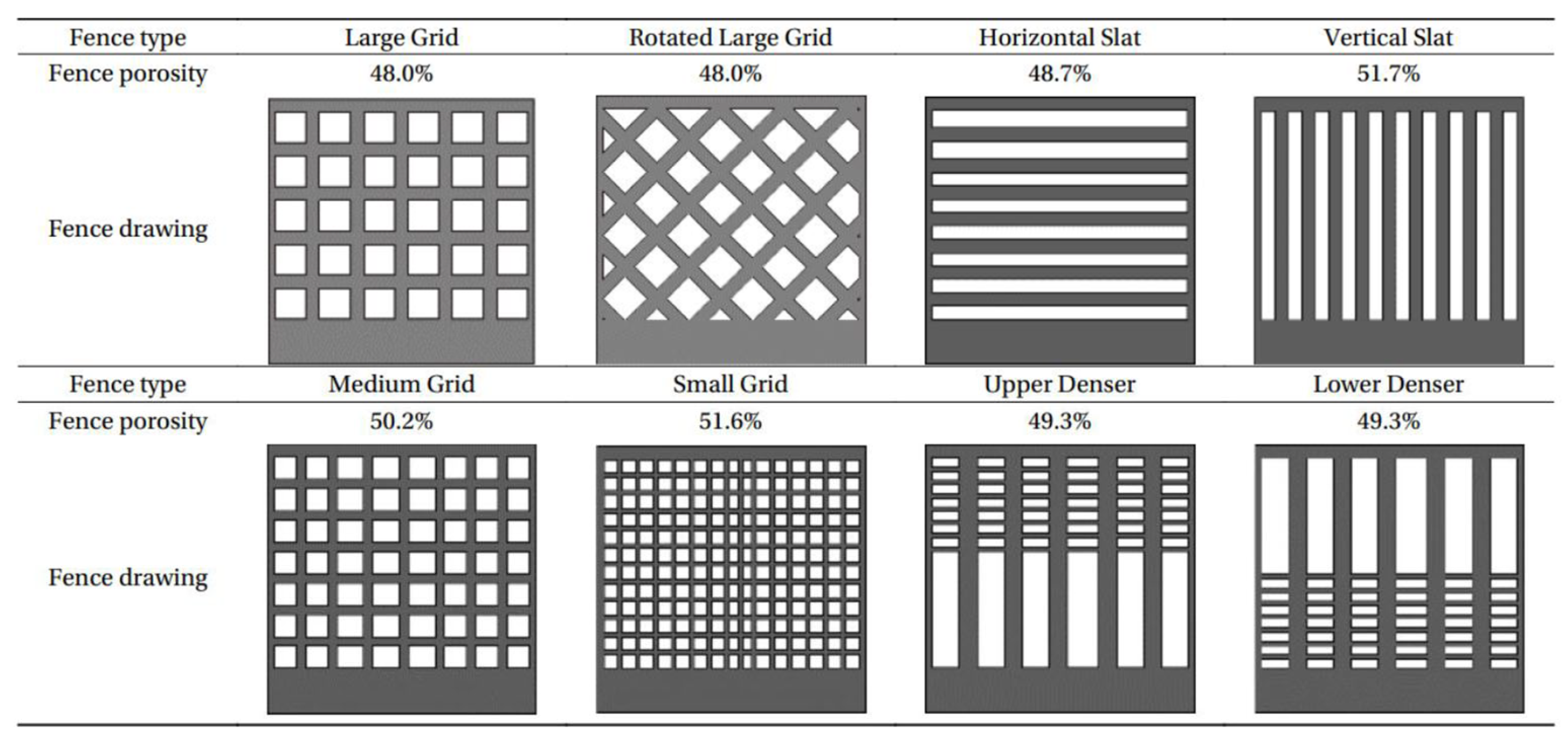
To better understand the optimal fence configuration of height and porosity, eight different configurations of fences were tested in field experiments by Ning et al. [150] (Figure 6). In all cases, after the fence construction perpendicular to the wind direction, as expected, with time, two sand deposits emerged on the windward and leeward sides of each fence. Again, all windward deposits were smaller than the leeward ones. The trapping efficiency of fence configurations ranked as follows: upper denser > lower denser > small grid > medium grid > vertical slat > large grid to rotated large grid. This shows that fences with small, nonuniform porosity have a higher trapping efficiency than fences with large, uniform porosity.
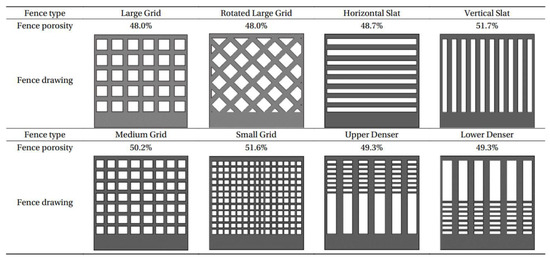
Figure 6.
Different fence configurations used in field experiments (adapted from [150]).
In general, 40–50% is the commonly considered optimal fence porosity for efficient sand trapping [43,156,157]. Further, it has been indicated that the relationship between fence height and trapping capacity is proportional [158]. Most of the research on fences focuses more on their ability to reduce wind than on their ability to trap sand [150], highlighting the need for further research on topics like the effect of opening size, geometry, and orientation, as well as porosity distribution, on sand trapping by fence structures.
Lastly, when looking into the relationship between wind velocities and fence effectiveness, the need for further research presents itself. Recent results from field experiments conducted at coastal dunes and on sand-trapping fences underline this need for knowledge on aeolian sediment transport rates and the interaction with coastal protection measures [155]. But their study showed that empirical transport models could not be applied between the sand-trapping fence due to the absence of a logarithmic wind profile, indicating a more complex interaction between the wind flow and the fence structure that impacts sediment transport rates. Further studies highlighted that even slight increases in wind speed could drive more intense saltation events, but these relationships are mediated by factors such as wind direction, precipitation intensity, and tide level [115]. Again, this shows the complex interactions between wind velocity and sediment transport in the presence of barriers like fences. Understanding these complex interactions between wind velocities and the effectiveness of fences in coastal areas is crucial for optimizing the use of fences in coastal dune management and erosion control efforts.
7. Conclusions
The presented detailed examination of aeolian sediment transport in coastal areas involved reviewing current knowledge to identify gaps and advancements in theoretical approaches to sediment transport. Continued evaluation included assessing the reliability and application of various empirical models designed to predict sediment movement while also acknowledging the necessity for further improvement of modeling aeolian processes, making them more complex and precise. Concerning the set objectives of this review study, we achieved the gathering and review of published papers to understand the latest advancements in aeolian sediment transport research. By scouting the field of aeolian sediment transport with a systematic keyword search and further diving into the most up-to-date research performed while looking at their origin, a broad yet precise summary was made.
Numerous model approaches were discussed, giving information on their application and specific use cases to better manage and predict aeolian sediment processes in coastal areas. This highlighted models like XBeach-DUNA [25], which merges the hydrodynamic capabilities of XBeach with the aeolian transport mechanisms of Duna, as well as the DuBeVeg model [23], which incorporates the dynamics of the beach alongside aeolian transport, hydrodynamic erosion and accretion, and vegetation growth, respectively. These advancements show the capability of holistic approaches but also highlight the need for further development, as the simplification of the processes, a limited temporal and spatial resolution, and a generalized or stochastic representation of the environmental conditions are still limiting factors.
The evolution of established equations was identified, and an evaluation of their applicability for best predicting aeolian sediment transport in their respective use cases was performed. The first equation set up by Bagnold [30] was the founding step within the field, which was further developed, validated, and modified by researchers throughout the last century. Even though some minor changes were made along the way and constant values were modified, they all display the same origin.
Next, the assessment of field measurement techniques revealed the strengths and limitations of methods such as sand traps, impact sensors, and optical sensors in capturing the dynamics of wind-driven sediment. While sand traps have been shown to have varying efficiency, they are the easiest to set up and use. More advanced measuring techniques like impact and optical sensors have been developed to increase the precision and scale of measurements made, even allowing specified research on small-scale processes such as saltation. This analysis underscores the necessity for methodological improvements to enhance measurement accuracy across different coastal contexts.
Further insight into the role of vegetation on sediment transport behavior, as well as the construction of fences, in the context of nature-based solutions to coastal hazards was given, highlighting its impact on dune mobility and recovery. Additionally, the importance of specific species in mitigating erosion and supporting dune formation, thereby contributing to coastal protection, was discussed. Also, fencing as a strategy for dune stabilization was evaluated, and the most effective design considerations were determined, creating an option for anthropogenic support of dunes. But whether human intervention is even a solution and whether its impacts should be generally minimized are controversial topics [159]. As all discussed topics in the field of aeolian sediment transport show big advancements and progression, this combination of processes and fields is deemed crucial for further development of the field, holding valuable insights and bringing us closer to a deeper understanding of the processes in action in coastal areas.
In sum, this review provided a clear overview of the key developments in aeolian sediment transport research over nearly a century, highlighting the current state of the art. While further detailed and systematic evaluation remains critical for a deeper understanding of this specialized field, the current overview reflects significant strides in current knowledge and sets the stage for future studies. Continued research is essential and promises to uncover new findings that will enhance management and preservation of coastal areas in the years ahead.
Author Contributions
In charge of conceptualization were C.C. and M.L. The methodology and the writing as well as original draft preparation was performed by P.H., with contributions also to the investigative parts made by P.H. and F.R. The formal analysis was conducted by S.C. and C.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the project AX-Coast: cross-shore features and internationalization of the COAST tool, funded by the EEA Grants, within the scope of the Blue Growth program, operated by the DGPM (Direção-Geral de Política do Mar). Also, the researcher Susana Costas is funded in the scope of the contract 2021.04286.CEECIND/CP1672/CT0001 with the DOI: 10.54499/2021.04286.CEECIND/CP1672/CT0001.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing is not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Pye, K. Coastal Dunes. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 1983, 7, 531–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesp, P.; Illenberger, W.; Rust, I.; McLachlan, A.; Hyde, R. Some Aspects of Transgressive Dunefield and Transverse Dune Geomorphology and Dynamics, South Coast, South Africa. Z. Geomorphol. Suppl. 1989, 73, 111–123. [Google Scholar]
- Arens, S.M. Rates of Aeolian Transport on a Beach in a Temperate Humid Climate. Geomorphology 1996, 17, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesp, P. Foredunes and Blowouts: Initiation, Geomorphology and Dynamics. Geomorphology 2002, 48, 245–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.D.; Bristow, C.S. Migration of Parabolic Dunes at Aberffraw, Anglesey, North Wales. Geomorphology 2004, 59, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, N.; Ben-Dor, E. Monitoring Sand Dune Stabilization along the Coastal Dunes of Ashdod-Nizanim, Israel, 1945–1999. J. Arid Environ. 2004, 58, 335–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesp, P.A.; Martinez, M.L.M. Transverse Dune Trailing Ridges and Vegetation Succession. Geomorphology 2008, 99, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provoost, S.; Jones, M.L.M.; Edmondson, S.E. Changes in Landscape and Vegetation of Coastal Dunes in Northwest Europe: A Review. J. Coast. Conserv. 2011, 15, 207–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einsele, G. Marine Depositional Events Controlled by Sediment Supply and Sea-Level Changes. Geol. Rundsch. 1993, 82, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauz, B.; Hijma, M.P.; Amorosi, A.; Porat, N.; Galili, E.; Bloemendal, J. Aeolian Beach Ridges and Their Significance for Climate and Sea Level: Concept and Insight from the Levant Coast (East Mediterranean). Earth Sci. Rev. 2013, 121, 31–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orford, J.D.; Wilson, P.; Wintle, A.G.; Knight, J.; Braley, S. Holocene Coastal Dune Initiation in Northumberland and Norfolk, Eastern UK: Climate and Sea-Level Changes as Possible Forcing Agents for Dune Initiation. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2000, 166, 197–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, A.D.; Hesp, P.A. Wave, Beach and Dune Interactions in Southeastern Australia. Mar. Geol. 1982, 48, 259–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson-Arnott, R.G.D.; Law, M.N. Measurement and Prediction of Long-Term Sediment Supply to Coastal Foredunes. J. Coast. Res. 1996, 12, 654–663. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, B.O.; Davidson-Arnott, R.G.D. A General Framework for Modeling Sediment Supply to Coastal Dunes Including Wind Angle, Beach Geometry, and Fetch Effects. Geomorphology 2003, 49, 89–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aagaard, T.; Orford, J.; Murray, A.S. Environmental Controls on Coastal Dune Formation; Skallingen Spit, Denmark. Geomorphology 2007, 83, 29–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, W.S. Coastal Sand Dunes of Oregon and Washington; Geological Society of America: New York, NY, USA, 1958; pp. 1–162. [Google Scholar]
- Ollerhead, J.; Davidson-Arnott, R.; Walker, I.J.; Mathew, S. Annual to Decadal Morphodynamics of the Foredune System at Greenwich Dunes, Prince Edward Island, Canada. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2013, 38, 284–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson-Arnott, R.G.D. Conceptual Model of the Effects of Sea Level Rise on Sandy Coasts. J. Coast. Res. 2005, 216, 1166–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson-Arnott, R.G.D.; Bauer, B.O. Controls on the Geomorphic Response of Beach-Dune Systems to Water Level Rise. J. Great Lakes Res. 2021, 47, 1594–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, J.C. Sea-Level Fluctuations Cause Periodic, Post-Glacial Progradation, South Kaipara Barrier, North Island, New Zealand. N. Z. J. Geol. Geophys. 1975, 18, 295–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lees, B. Timing and Formation of Coastal Dunes in Northern and Eastern Australia. J. Coast. Res. 2006, 22, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, B.T. Eolian Dunes: Computer Simulations and Attractor Interpretation. Geology 1995, 23, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keijsers, J.G.S.; De Groot, A.V.; Riksen, M.J.P.M. Modeling the Biogeomorphic Evolution of Coastal Dunes in Response to Climate Change. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2016, 121, 1161–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, M.; Horstman, E.M.; Wijnberg, K.M. Conceptualizing Aeolian Sediment Transport in a Cellular Automata Model to Simulate the Bio-Geomorphological Evolution of Beach–Dune Systems. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelvink, D.; Costas, S. Coupling Nearshore and Aeolian Processes: XBeach and Duna Process-Based Models. Environ. Model. Softw. 2019, 115, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, O.; Moore, L.J. Vegetation Controls on the Maximum Size of Coastal Dunes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 17217–17222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Web of Science Databse. Available online: https://www.webofscience.com/wos/woscc/basic-search (accessed on 5 March 2024).
- Jackson, N.L.; Nordstrom, K.F. Aeolian Sediment Transport and Landforms in Managed Coastal Systems: A Review. Aeolian Res. 2011, 3, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnold, R. The Movement of Desert Sand. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1936, 157, 594–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnold, R. The Physics of Blown Sand and Desert Dunes. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 1941, 18, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, R. Study on Sand Movement by Wind; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 1951.
- Zingg, A.W. Wind-Tunnel Studies of the Movement of Sedimentary Material. In Proceedings of the 5th Hydraulics Conference Bull; 1953; pp. 111–135. Available online: https://infosys.ars.usda.gov/WindErosion/publications/Andrew_pdf/470.pdf (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Owen, P.R. Saltation of Uniform Grains in Air. J. Fluid Mech. 1964, 20, 225–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lettau, K.; Lettau, H. Experimental and Micrometeorological Field Studies of Dune Migration. 1977. Available online: https://cir.nii.ac.jp/crid/1572824500750088064 (accessed on 5 March 2024).
- Durán, O.; Claudin, P.; Andreotti, B. On Aeolian Transport: Grain-Scale Interactions, Dynamical Mechanisms and Scaling Laws. Aeolian Res. 2011, 3, 243–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Lu, H. A Simple Expression for Wind Erosion Threshold Friction Velocity. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2000, 105, 22437–22443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.A. Computing Eolian Sand Transport from Routine Weather Data. Coast. Eng. Proc. 1974, 94, 1619–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson-Arnott, R.G.D.; Bauer, B.O. Aeolian Sediment Transport on a Beach: Thresholds, Intermittency, and High Frequency Variability. Geomorphology 2009, 105, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Fernandez, I.; Davidson-Arnott, R.; Bauer, B.O.; Walker, I.J.; Ollerhead, J.; Rhew, H. Assessing Aeolian Beach-Surface Dynamics Using a Remote Sensing Approach. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2012, 37, 1651–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nield, J.M. Surface Moisture-Induced Feedback in Aeolian Environments. Geology 2011, 39, 915–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, Y.; Ruessink, G.; Brakenhoff, L.B.; Donker, J.J.A. Measuring Spatial and Temporal Variation in Surface Moisture on a Coastal Beach with a Near-Infrared Terrestrial Laser Scanner. Aeolian Res. 2018, 31, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udo, K.; Kuriyama, Y.; Jackson, D.W.T. Observations of Wind-Blown Sand under Various Meteorological Conditions at a Beach. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotta, S.; Horikawa, K. CHAPTER 209: Function of Sand Fence Placed in Front of Embarkment. In Proceedings of the Coastal Engineering Proceedings, Seattle, WA, USA, 25–27 June 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Belly, P. Sand Movement by Wind; USACE: Washington, DC, USA, 1964.
- Dong, Z.; Sun, H.; Zhao, A. WITSEG Sampler: A Segmented Sand Sampler for Wind Tunnel Test. Geomorphology 2004, 59, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMenamin, R.; Cassidy, R.; McCloskey, J. Self-Organised Criticality at the Onset of Aeolian Sediment Transport. J. Coast. Res. 2002, 36, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nield, J.M.; Baas, A.C.W. The Influence of Different Environmental and Climatic Conditions on Vegetated Aeolian Dune Landscape Development and Response. Glob. Planet. Change 2008, 64, 76–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poppema, D.W.; Baas, A.C.W.; Hulscher, S.J.M.H.; Wijnberg, K.M. Cellular Automaton Modelling of the Effects of Buildings on Aeolian Bedform Dynamics. Aeolian Res. 2022, 59, 100840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourteimouri, P.; Campmans, G.H.P.; Wijnberg, K.M.; Hulscher, S.J.M.H. How Wind Direction and Building Spacing Influences Airflow Patterns and Sediment Transport Patterns around a Row of Beach Buildings: A Numerical Study. Aeolian Res. 2023, 61, 100867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourteimouri, P.; Campmans, G.H.P.; Wijnberg, K.M.; Hulscher, S.J.M.H. Modelling the Influence of Beach Building Pole Heights on Aeolian Morphology and Downwind Sediment Transport. Geomorphology 2023, 436, 108791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, O.; Herrmann, H.J. Vegetation against Dune Mobility. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 188001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoonhout, B.M.; Vries, S. de A Process-Based Model for Aeolian Sediment Transport and Spatiotemporal Varying Sediment Availability. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2016, 121, 1555–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoonhout, B.; de Vries, S. Simulating Spatiotemporal Aeolian Sediment Supply at a Mega Nourishment. Coast. Eng. 2019, 145, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelvink, D.; Reniers, A.; van Dongeren, A.; van Thiel de Vries, J.; McCall, R.; Lescinski, J. Modelling Storm Impacts on Beaches, Dunes and Barrier Islands. Coast. Eng. 2009, 56, 1133–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelvink, D.; McCall, R.; Mehvar, S.; Nederhoff, K.; Dastgheib, A. Improving Predictions of Swash Dynamics in XBeach: The Role of Groupiness and Incident-Band Runup. Coast. Eng. 2018, 134, 103–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kombiadou, K.; Costas, S.; Roelvink, D. Exploring Controls on Coastal Dune Growth Through a Simplified Model. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2023, 128, e2023JF007080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohn, N.; Hoonhout, B.M.; Goldstein, E.B.; de Vries, S.; Moore, L.J.; Vinent, O.D.; Ruggiero, P. Exploring Marine and Aeolian Controls on Coastal Foredune Growth Using a Coupled Numerical Model. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, M.; Palalane, J.; Fredriksson, C.; Hanson, H. Simulating Cross-Shore Material Exchange at Decadal Scale. Theory and Model Component Validation. Coast. Eng. 2016, 116, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palalane, J.; Fredriksson, C.; Marinho, B.; Larson, M.; Hanson, H.; Coelho, C. Simulating Cross-Shore Material Exchange at Decadal Scale. Model Application. Coast. Eng. 2016, 116, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallin, C. Long-Term Beach and Dune Evolution: Development and Application of the CS-Model. Ph.D. Thesis, Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Arens, S. Aeolian Processes in the Dutch Foredunes. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Khalaf, A.H. Specification and Calibration of Bagnold’s Model for Sand Transport: Urayq al Buldan Dune Field, Central Saudi Arabia. Ph.D. Thesis, Indiana University, Bloomington, IN, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Arens, S.M.; van der Lee, G.E.M. Saltation Sand Traps for the Measurement of Aeolian Transport into the Foredunes. Soil Technol. 1995, 8, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, L.L.; Alonso, I. Correlation of Aeolian Sediment Transport Measured by Sand Traps and Fluorescent Tracers. J. Mar. Syst. 2010, 80, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leatherman, S.P. A New Aeolian Sand Trap Design. Sedimentology 1978, 25, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, M.; Muñoz-Perez, J.J.; Román-Sierra, J.; Ruiz-Cañavate, A.; Gómez-Pina, G. Characterization of Wind-Blown Sediment Transport with Height in a Highly Mobile Dune (SW Spain). Geol. Acta 2015, 13, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnold, R.A. The Nature of Saltation and of “bed-Load” Transport in Water. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 1973, 332, 473–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnold, R. The Measurement of Sand Storms. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1938, 167, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarre, R.D. Evaluation of Aeolian Sand Transport Equations Using Intertidal Zone Measurements, Saunton Sands, England. Sedimentology 1988, 35, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijma, M.P.; Lodder, Q.J. An Evaluation of Aeolian Sand Transport Models Using Four Different Sand Traps at the Hors, Texel. Master’s Thesis, University Utrecht, Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- de Ploey, J. Some Field Measurements and Experimental Data on Wind-Blown Sands. Assess. Eros. 1980, 541–552. [Google Scholar]
- van Dijk, P.M.; Hollemans, W.A. Wind Erosion Measurements on the Island of Schiermonnikoog, Report. III. The Calibration of Wind. Erosion Measuring Devices by Means of Wind. Tunnel Research; Wageningen University: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Hilton, M.; Nickling, B.; Wakes, S.; Sherman, D.; Konlechner, T.; Jermy, M.; Geoghegan, P. An Efficient, Self-Orienting, Vertical-Array, Sand Trap. Aeolian Res. 2017, 25, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, D.J.; Li, B.; Farrell, E.J.; Ellis, J.T.; Cox, W.D.; Maia, L.P.; Sousa, P.H.G.O. Measuring Aeolian Saltation: A Comparison of Sensors. J. Coast. Res. 2011, 59, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.A. A Field Experiment on the Role of Small Scale Wind Gustiness in Aeolian Sand Transport. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1987, 12, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, D.W.T. A New, Instantaneous Aeolian Sand Trap Design for Field Use. Sedimentology 1996, 43, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, B.O.; Namikas, S.L. Design and Field Test of a Continuously Weighing, Tipping-Bucket Assembly for Aeolian Sand Traps. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1998, 23, 1171–1183. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Kraus, N.C. Horizontal Water Trap for Measurement of a Aeolian Sand Transport. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1999, 24, 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Namikas, S.L. Field Evaluation of Two Traps for High-Resolution Aeolian Transport Measurements. J. Coast. Res. 2002, 18, 136–148. [Google Scholar]
- Baas, A.C.W. Evaluation of Saltation Flux Impact Responders (Safires) for Measuring Instantaneous Aeolian Sand Transport Intensity. Geomorphology 2004, 59, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baas, A.C.W.; Sherman, D.J. Formation and Behavior of Aeolian Streamers. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2005, 110, F3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillette, D.A.; Stockton, P.H. The Effect of Nonerodible Particles on Wind Erosion of Erodible Surfaces. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1989, 94, 12885–12893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockton, P.H.; Gillette, D.A. Field Measurement of the Sheltering Effect of Vegetation on Erodible Land Surfaces. Land Degrad. Dev. 1990, 2, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillies, J.A.; Nickling, W.G.; King, J. Aeolian Sediment Transport through Large Patches of Roughness in the Atmospheric Inertial Sublayer. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2006, 111, F2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, N.; Nickling, W.G.; Gillies, J.A. Sand Transport by Wind on Complex Surfaces: Field Studies in the McMurdo Dry Valleys, Antarctica. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2010, 115, F03027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stout, J.E.; Zobeck, T.M. Intermittent Saltation. Sedimentology 1997, 44, 959–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiggs, G.F.S.; Atherton, R.J.; Baird, A.J. Thresholds of Aeolian Sand Transport: Establishing Suitable Values. Sedimentology 2004, 51, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaan, W.P.; van den Abeele, G.D. Wind Borne Particle Measurements with Acoustic Sensors. Soil Technol. 1991, 4, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dijk, P.M.; Stroosnijder, L.; de Lima, J.L.M.P. The Influence of Rainfall on Transport of Beach Sand by Wind. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1996, 21, 341–352. [Google Scholar]
- Sterk, G.; Jacobs, A.F.G.; Van Boxel, J.H. The Effect of Turbulent Flow Structures on Saltation Sand Transport in the Atmospheric Boundary Layer. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1998, 23, 877–887. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis, J.T.; Morrison, R.F.; Priest, B.H. Detecting Impacts of Sand Grains with a Microphone System in Field Conditions. Geomorphology 2009, 105, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Winter, W.; van Dam, D.B.; Delbecque, N.; Verdoodt, A.; Ruessink, B.G.; Sterk, G. Measuring High Spatiotemporal Variability in Saltation Intensity Using a Low-Cost Saltation Detection System: Wind Tunnel and Field Experiments. Aeolian Res. 2018, 31, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, M.; Goossens, D.; Riksen, M.J.P.M. Evaluating the SandFlow, an Acoustic Sediment Transport Sensor. Aeolian Res. 2020, 42, 100558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterfield, G.R. Transitional Behaviour of Saltation: Wind Tunnel Observations of Unsteady Winds. J. Arid Environ. 1998, 39, 377–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, R.; Stutz, M.L.; Sam Smith, A. A Field Investigation Study to Determine the Properties of Windblown Beach Sand. J. Coast. Res. 1998, 14, 444–450. [Google Scholar]
- Willetts, B.B.; Rice, M.A. Inter Saltation Collisions. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on the Physics of Blown Sand, Aarhus, Denmark, 28–31 May 1985; pp. 83–100. [Google Scholar]
- Willetts, B.B.; Rice, M.A. Wind Tunnel Tracer Experiments Using Dyed Sand. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on the Physics of Blown Sand, Aarhus, Denmark, 28–31 May 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Sherman, D.J. Evaluation of Aeolian Sand Transport Equations Using Intertidal-zone Measurements, Saunton Sands, England. Sedimentology 1990, 37, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugenholtz, C.H.; Barchyn, T.E. Laboratory and Field Performance of a Laser Particle Counter for Measuring Aeolian Sand Transport. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2011, 116, F1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, B.O.; Davidson-Arnott, R.G.D.; Hilton, M.J.; Fraser, D. On the Frequency Response of a Wenglor Particle-Counting System for Aeolian Transport Measurements. Aeolian Res. 2018, 32, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmutz, P.; Briggs, T.; Tereszkiewicz, P. The Utility of an Omni-Directional Photoelectronic Sensor Device to Measure Meso-Scale Variability in Aeolian Sediment Transport Activity. Aeolian Res. 2019, 36, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barchyn, T.E.; Hugenholtz, C.H.; Li, B.; Neuman, C.M.K.; Steven Sanderson, R. From Particle Counts to Flux: Wind Tunnel Testing and Calibration of the “Wenglor” Aeolian Sediment Transport Sensor. Aeolian Res. 2014, 15, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte-Campos, L.; Wijnberg, K.M.; Oyarte-Gálvez, L.; Hulscher, S.J.M.H. Laser Particle Counter Validation for Aeolian Sand Transport Measurements Using a Highspeed Camera. Aeolian Res. 2017, 25, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, B.O.; Davidson-Arnott, R.G.D. Aeolian Particle Flux Profiles and Transport Unsteadiness. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2014, 119, 1542–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoonhout, B.; de Vries, S. Field Measurements on Spatial Variations in Aeolian Sediment Availability at the Sand Motor Mega Nourishment. Aeolian Res. 2017, 24, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etyemezian, V.; Nikolich, G.; Nickling, W.; King, J.S.; Gillies, J.A. Analysis of an Optical Gate Device for Measuring Aeolian Sand Movement. Aeolian Res. 2017, 24, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens, D.; Nolet, C.; Etyemezian, V.; Duarte-Campos, L.; Bakker, G.; Riksen, M. Field Testing, Comparison, and Discussion of Five Aeolian Sand Transport Measuring Devices Operating on Different Measuring Principles. Aeolian Res. 2018, 32, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikami, M.; Yamada, Y.; Ishizuka, M.; Ishimaru, T.; Gao, W.; Zeng, F. Measurement of Saltation Process over Gobi and Sand Dunes in the Taklimakan Desert, China, with Newly Developed Sand Particle Counter. J. Geophys. Res. D Atmos. 2005, 110, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poortinga, A.; van Rheenen, H.; Ellis, J.T.; Sherman, D.J. Measuring Aeolian Sand Transport Using Acoustic Sensors. Aeolian Res. 2015, 16, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danchenkov, A.; Belov, N.; Stont, Z. Using the Terrestrial Laser Scanning Technique for Aeolian Sediment Transport Assessment in the Coastal Zone in Seasonal Scale. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 223, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charbonneau, B.R.; Wnek, J.P.; Langley, J.A.; Lee, G.; Balsamo, R.A. Above vs. Belowground Plant Biomass along a Barrier Island: Implications for Dune Stabilization. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 182, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chu, L.; Daryanto, S.; Lü, L.; Ala, M.; Wang, L. Sand Dune Stabilization Changes the Vegetation Characteristics and Soil Seed Bank and Their Correlations with Environmental Factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesp, P. Surfzone, Beach, and Foredune Interactions on the Australian South East Coast. J. Coast. Res. 1988, 3, 15–25. [Google Scholar]
- Sherman, D.J.; Lyons, W. Beach-State Controls on Aeolian Sand Delivery to Coastal Dunes. Phys. Geogr. 1994, 15, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, B.O.; Davidson-Arnott, R.G.D.; Hesp, P.A.; Namikas, S.L.; Ollerhead, J.; Walker, I.J. Aeolian Sediment Transport on a Beach: Surface Moisture, Wind Fetch, and Mean Transport. Geomorphology 2009, 105, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, T.S.N.; Kennedy, D.M.; Tamura, T.; Murray-Wallace, C.V.; Konlechner, T.M.; Augustinus, P.C.; Woodroffe, C.D. Interglacial-Glacial Climatic Signatures Preserved in a Regressive Coastal Barrier, Southeastern Australia. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2018, 501, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, R.W.G. Near-Future Sea Level Impacts on Coastal Dune Landscapes. Landsc. Ecol. 1991, 6, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, D.W.T.; Costas, S.; González-Villanueva, R.; Cooper, A. A Global ‘Greening’ of Coastal Dunes: An Integrated Consequence of Climate Change? Glob. Planet. Change 2019, 182, 103026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feagin, R.A.; Sherman, D.J.; Grant, W.E. Coastal Erosion, Global Sea-Level Rise, and the Loss of Sand Dune Plant Habitats. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2005, 3, 351–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houser, C.; Hapke, C.; Hamilton, S. Controls on Coastal Dune Morphology, Shoreline Erosion and Barrier Island Response to Extreme Storms. Geomorphology 2008, 100, 223–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psuty, N.P.; Silveira, T.M. Global Climate Change: An Opportunity for Coastal Dunes?? J. Coast. Conserv. 2010, 14, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesp, P.A. Conceptual Models of the Evolution of Transgressive Dune Field Systems. Geomorphology 2013, 199, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel-Buitrago, N.; Gracia, C.A.; Neal, W.J. Dune Ecosystems along the Central Caribbean Coast of Colombia: Evolution, Human Influences, and Conservation Challenges. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2023, 243, 106767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Kennedy, D.M.; McSweeney, S. Decadal Changes in Vegetation Cover within Coastal Dunes at the Regional Scale in Victoria, SE Australia. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 351, 119622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhs, D.R.; Roskin, J.; Tsoar, H.; Skipp, G.; Budahn, J.R.; Sneh, A.; Porat, N.; Stanley, J.D.; Katra, I.; Blumberg, D.G. Origin of the Sinai-Negev Erg, Egypt and Israel: Mineralogical and Geochemical Evidence for the Importance of the Nile and Sea Level History. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2013, 69, 28–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, D.W.T.; Cooper, J.A.G. Coastal Dune Fields in Ireland: Rapid Regional Response to Climatic. J. Coast. Res. 2011, 293–297. [Google Scholar]
- Levin, N. Climate-Driven Changes in Tropical Cyclone Intensity Shape Dune Activity on Earth’s Largest Sand Island. Geomorphology 2011, 125, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pye, K.; Blott, S.J. Decadal-Scale Variation in Dune Erosion and Accretion Rates: An Investigation of the Significance of Changing Storm Tide Frequency and Magnitude on the Sefton Coast, UK. Geomorphology 2008, 102, 652–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, G.M.; Hesp, P.A. Increasing Rainfall, Decreasing Winds, and Historical Changes in Santa Catarina Dunefields, Southern Brazil. Earth Surf. Process Landf. 2013, 38, 1036–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemmensen, L.B.; Hansen, K.W.T.; Kroon, A. Storminess Variation at Skagen, Northern Denmark since AD 1860: Relations to Climate Change and Implications for Coastal Dunes. Aeolian Res. 2014, 15, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilton, M.J. The Loss of New Zealand’s Active Dunes and the Spread of Marram Grass (Ammophila Arenaria). N. Z. Geogr. 2006, 62, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tribe, H.M.; Kennedy, D.M. The Geomorphology and Evolution of a Large Barrier Spit: Farewell Spit, New Zealand. Earth Surf. Process Landf. 2010, 35, 1751–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pye, K.; Blott, S.J.; Howe, M.A. Coastal Dune Stabilization in Wales and Requirements for Rejuvenation. J. Coast. Conserv. 2014, 18, 27–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Kennedy, D.M.; Konlechner, T.M.; McSweeney, S.; Chiaradia, A.; McGuirk, M. Changes in the Vegetation Cover of Transgressive Dune Fields: A Case Study in Cape Woolamai, Victoria. Earth Surf. Process Landf. 2022, 47, 778–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feagin, R.A.; Furman, M.; Salgado, K.; Martinez, M.L.; Innocenti, R.A.; Eubanks, K.; Figlus, J.; Huff, T.P.; Sigren, J.; Silva, R. The Role of Beach and Sand Dune Vegetation in Mediating Wave Run up Erosion. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 219, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, H.; Garbutt, A.; Ladd, C.; Malarkey, J.; Skov, M.W. Soil Stabilization Linked to Plant Diversity and Environmental Context in Coastal Wetlands. J. Veg. Sci. 2016, 27, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Battisti, D.; Fowler, M.S.; Jenkins, S.R.; Skov, M.W.; Rossi, M.; Bouma, T.J.; Neyland, P.J.; Griffin, J.N. Intraspecific Root Trait Variability along Environmental Gradients Affects Salt Marsh Resistance to Lateral Erosion. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 7, 00150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silliman, B.R.; He, Q.; Angelini, C.; Smith, C.S.; Kirwan, M.L.; Daleo, P.; Renzi, J.J.; Butler, J.; Osborne, T.Z.; Nifong, J.C.; et al. Field Experiments and Meta-Analysis Reveal Wetland Vegetation as a Crucial Element in the Coastal Protection Paradigm. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, 1800–1806.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, D.B.; Anderson Bryant, M.; Sharp, J.A.; Bell, G.L.; Moore, C. The Response of Vegetated Dunes to Wave Attack. Coast. Eng. 2019, 152, 103506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Battisti, D.; Griffin, J.N. Below-Ground Biomass of Plants, with a Key Contribution of Buried Shoots, Increases Foredune Resistance to Wave Swash. Ann. Bot. 2020, 125, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.K.; Zinnert, J.C. Mechanisms of Surviving Burial: Dune Grass Interspecific Differences Drive Resource Allocation after Sand Deposition. Ecosphere 2018, 9, e02162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reijers, V.C.; Hoeks, S.; van Belzen, J.; Siteur, K.; de Rond, A.J.A.; van de Ven, C.N.; Lammers, C.; van de Koppel, J.; van der Heide, T. Sediment Availability Provokes a Shift from Brownian to Lévy-like Clonal Expansion in a Dune Building Grass. Ecol. Lett. 2021, 24, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hacker, S.D.; Jay, K.R.; Cohn, N.; Goldstein, E.B.; Hovenga, P.A.; Itzkin, M.; Moore, L.J.; Mostow, R.S.; Mullins, E.V.; Ruggiero, P. Species-Specific Functional Morphology of Four US Atlantic Coast Dune Grasses: Biogeographic Implications for Dune Shape and Coastal Protection. Diversity 2019, 11, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarnetske, P.L.; Ruggiero, P.; Seabloom, E.W.; Hacker, S.D. Coastal Foredune Evolution: The Relative Influence of Vegetation and Sand Supply in the US Pacific Northwest. J. R. Soc. Interface 2015, 12, 20150017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, S.L.; Zinnert, J. Whole Plant Traits of Coastal Dune Vegetation and Implications for Interactions with Dune Dynamics. Ecosphere 2022, 13, e4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grafals-Soto, R.; Nordstrom, K. Sand Fences in the Coastal Zone: Intended and Unintended Effects. Environ. Manag. 2009, 44, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itzkin, M.; Moore, L.J.; Ruggiero, P.; Hacker, S.D. The Effect of Sand Fencing on the Morphology of Natural Dune Systems. Geomorphology 2020, 352, 106995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Laan, D.; van Tongeren, O.F.R.; van der Putten, W.H.; Veenbaas, G. Vegetation Development in Coastal Foredunes in Relation to Methods of Establishing Marram Grass (Ammophila Arenaria). J. Coast. Conserv. 1997, 3, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.L.; Thetford, M.; Yager, L. Evaluation of Sand Fence and Vegetation for Dune Building Following Overwash by Hurricane Opal on Santa Rosa Island, Florida. Artic. J. Coast. Res. 2001, 17, 936–948. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, Q.; Li, B.; Zhou, C.; He, Y.; Liu, J. Effect of Fence Opening Configurations on Dune Development. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2023, 42, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordstrom, K.F.; Jackson, N.L. Offshore Aeolian Sediment Transport across a Human-Modified Foredune. Earth Surf. Process Landf. 2018, 43, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, N.L.; Nordstrom, K.F. Aeolian Sediment Transport on a Recovering Storm-Eroded Foredune with Sand Fences. Earth Surf. Process Landf. 2018, 43, 1310–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsje, B.W.; van Wesenbeeck, B.K.; Dekker, F.; Paalvast, P.; Bouma, T.J.; van Katwijk, M.M.; de Vries, M.B. How Ecological Engineering Can Serve in Coastal Protection. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, D.J.; Nordstrom, K.F. Hazards of Wind-Blown Sand and Coastal Sand Drifts: A Review. J. Coast. Res. 1994, 263–275. [Google Scholar]
- Eichmanns, C.; Schüttrumpf, H. A Nature-Based Solution for Coastal Protection: Wind Tunnel Investigations on the Influence of Sand-Trapping Fences on Sediment Accretion. Front. Built Environ. 2022, 8, 878197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bofah, K.K.; Al-Hinai, K.G. Field Tests of Porous Fences in the Regime of Sand-Laden Wind. J. Wind. Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 1986, 23, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelssohn, I.A.; Hester, M.W.; Monteferrante, F.J.; Talbot, F. Experimental Dune Building and Vegetative Stabilization in a Sand-Deficient Barrier Island Setting on the Louisiana Coast, USA. J. Coast. Res. 1991, 7, 137–149. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, Q.; Li, B.; Ellis, J.T. Fence Height Control on Sand Trapping. Aeolian Res. 2020, 46, 100617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Fernandez, I.; Davidson-Arnott, R.G.D.; Hesp, P.A. Is ‘Re-Mobilisation’ Nature Restoration or Nature Destruction? A Commentary. J. Coast. Conserv. 2019, 23, 1093–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).