Free and Forced Vibration Characteristics of a Composite Stiffened Plate Based on Energy Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
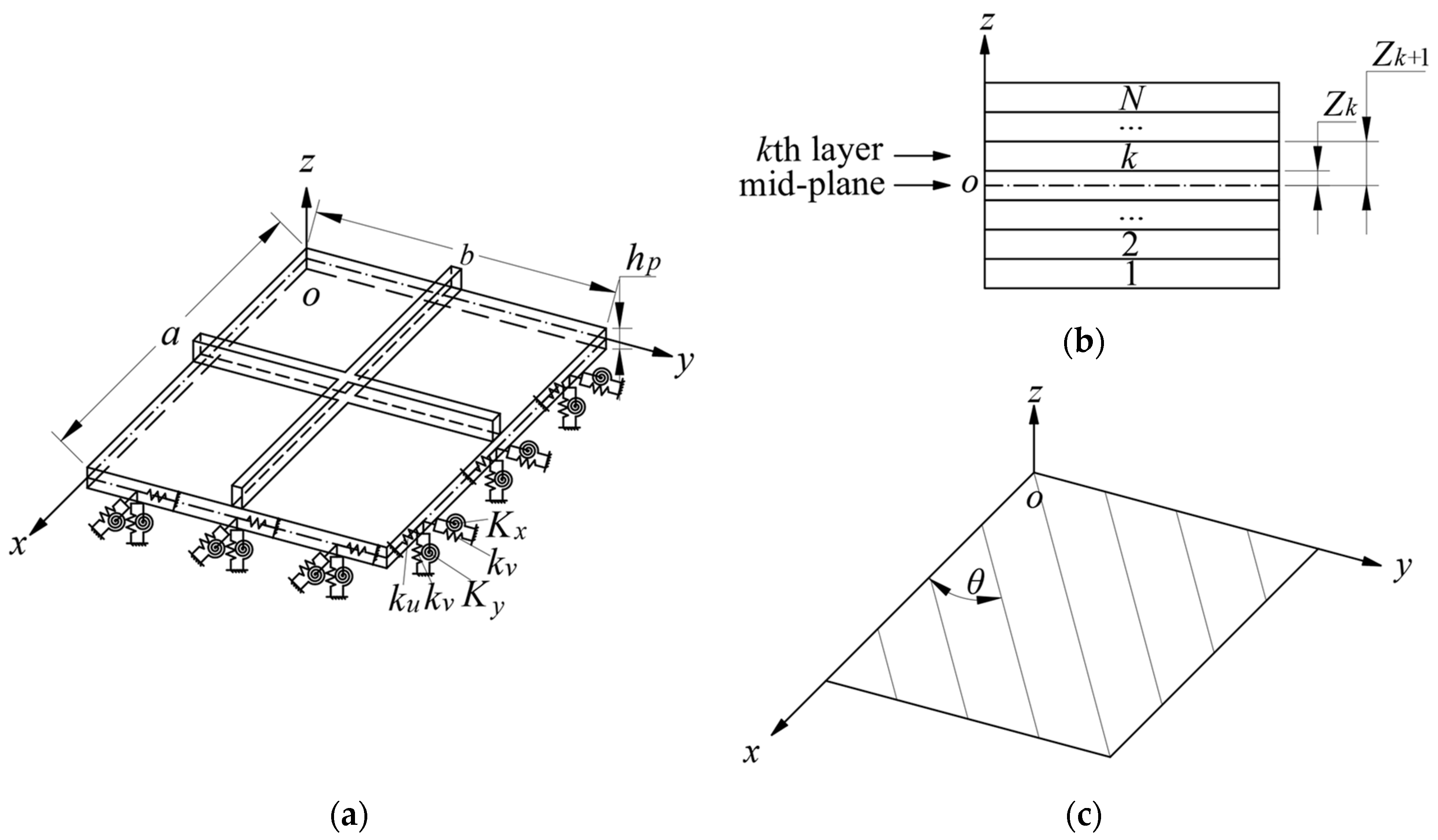
2. Theoretical Formulations
2.1. Kinematics and Stress–Strain Relations
2.1.1. Kinematics and Stress–Strain Relations of Laminate Panel
2.1.2. Kinematics and Stress–Strain Relations of Laminate Stiffener
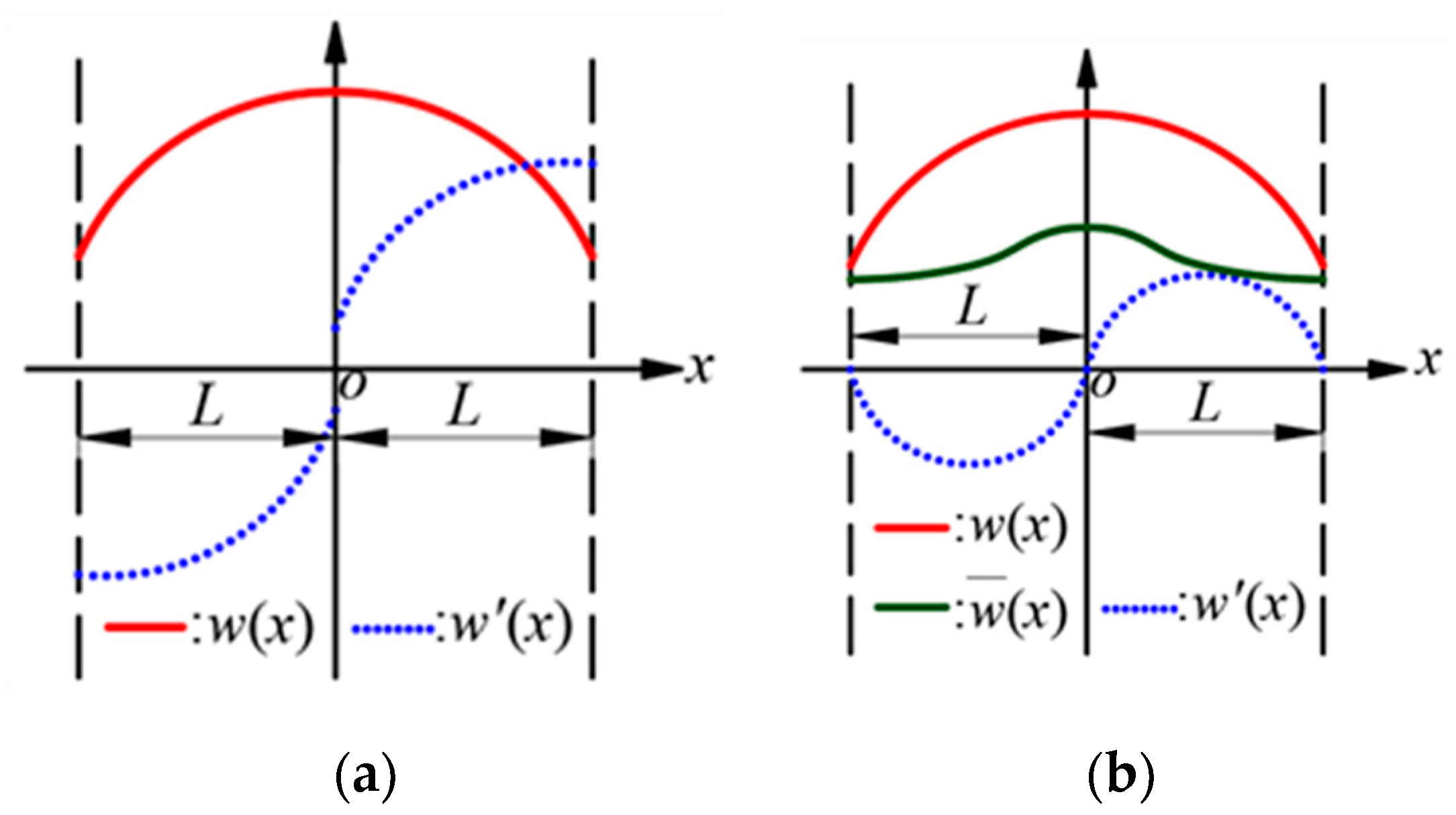
2.2. Admissible Displacement Functions
2.3. Governing Equation and Solution
3. Numerical Results and Discussions
3.1. Convergency Analysis
3.2. Method Verification
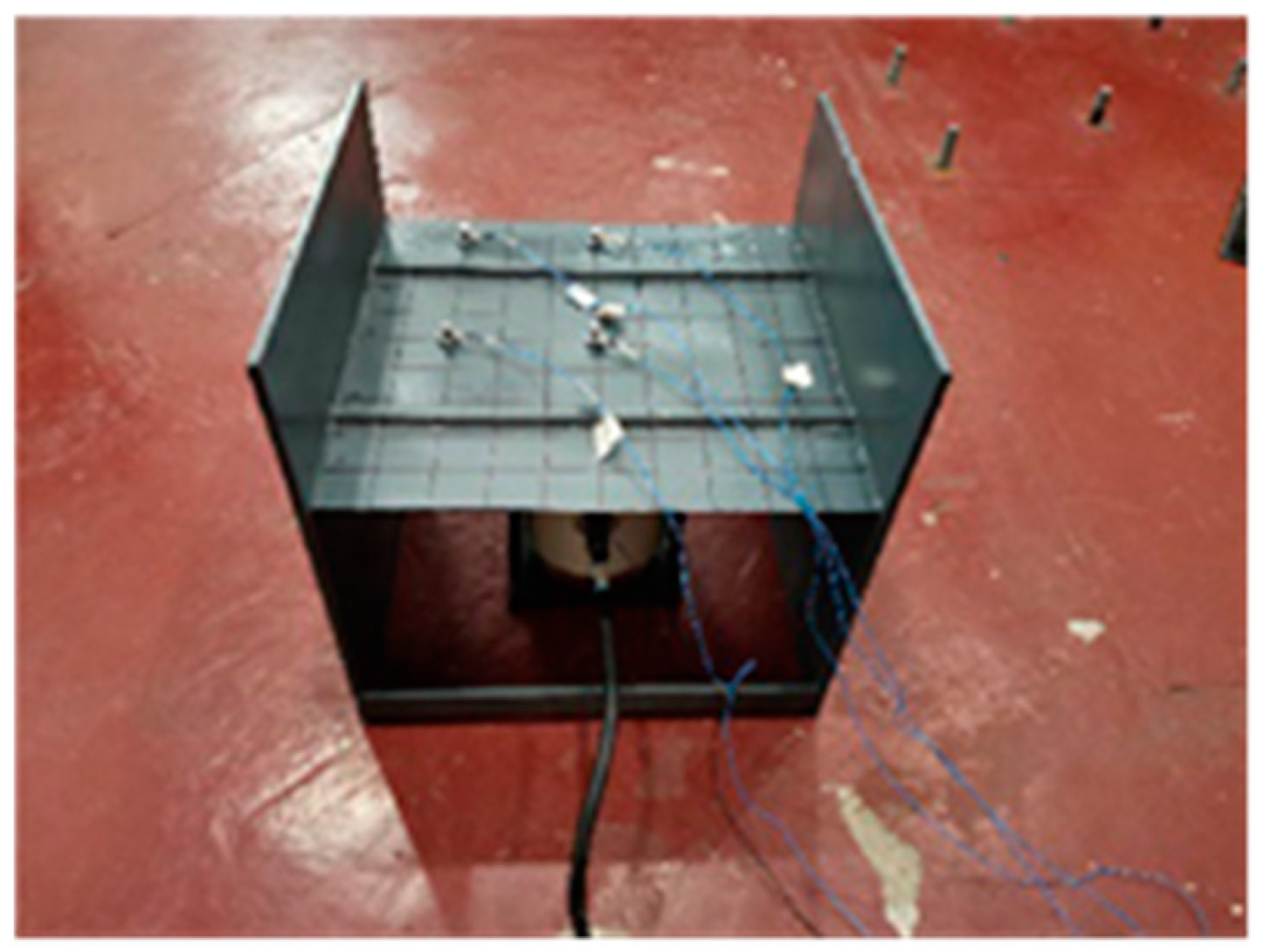
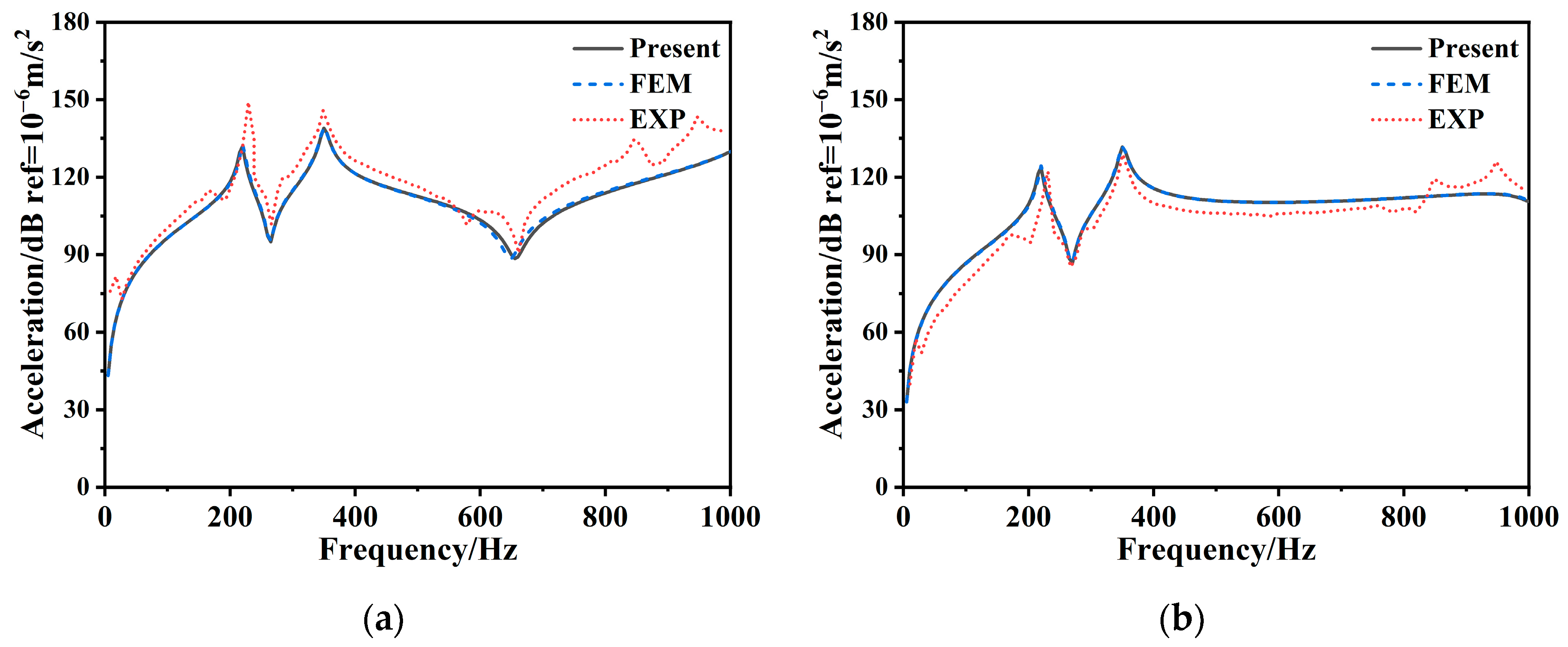
3.2.1. Composite Stiffened Plate Vibration Characteristics Verification
3.2.2. Steel Stiffened Plate Vibration Characteristics Verification
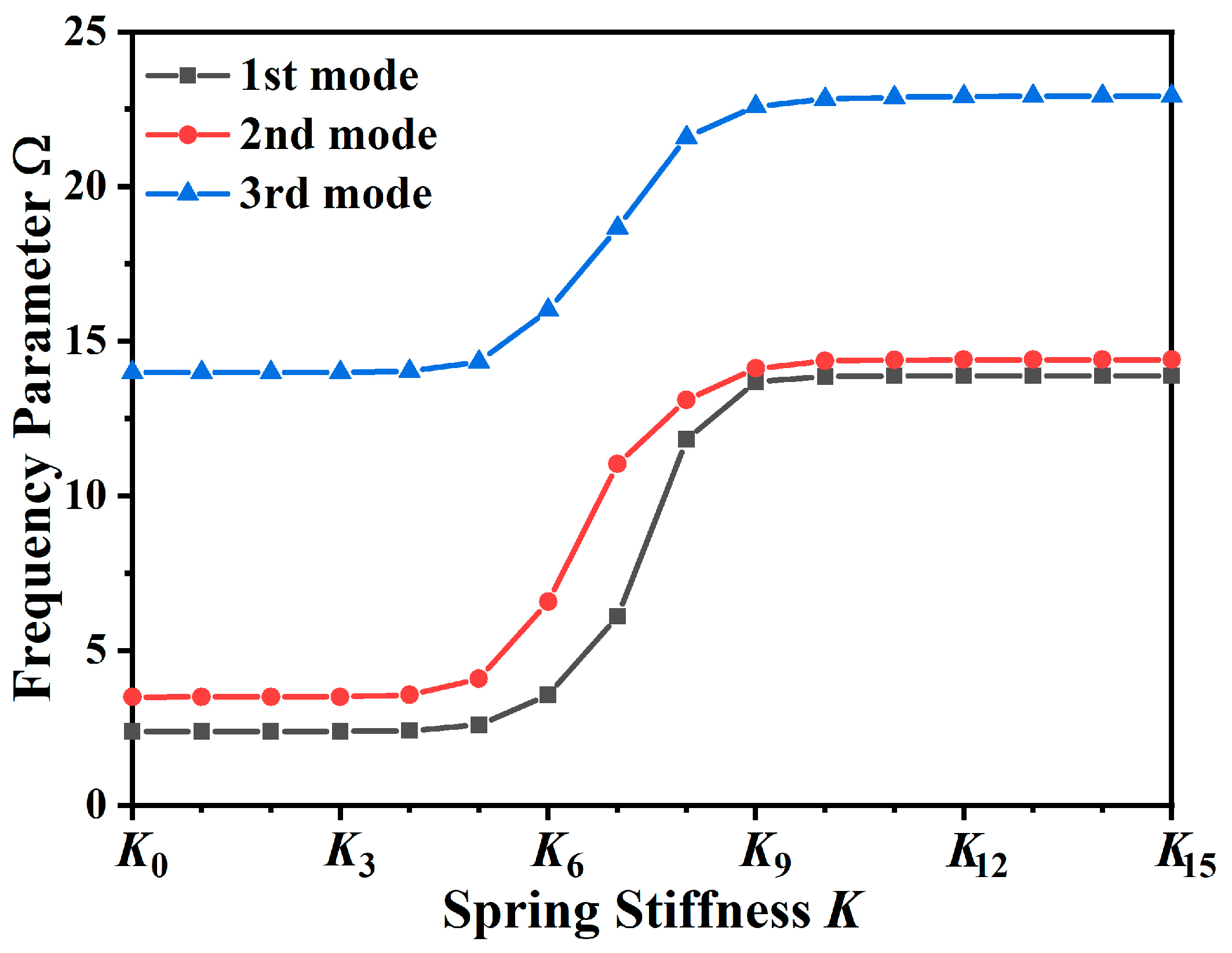
3.3. Parameter Analysis
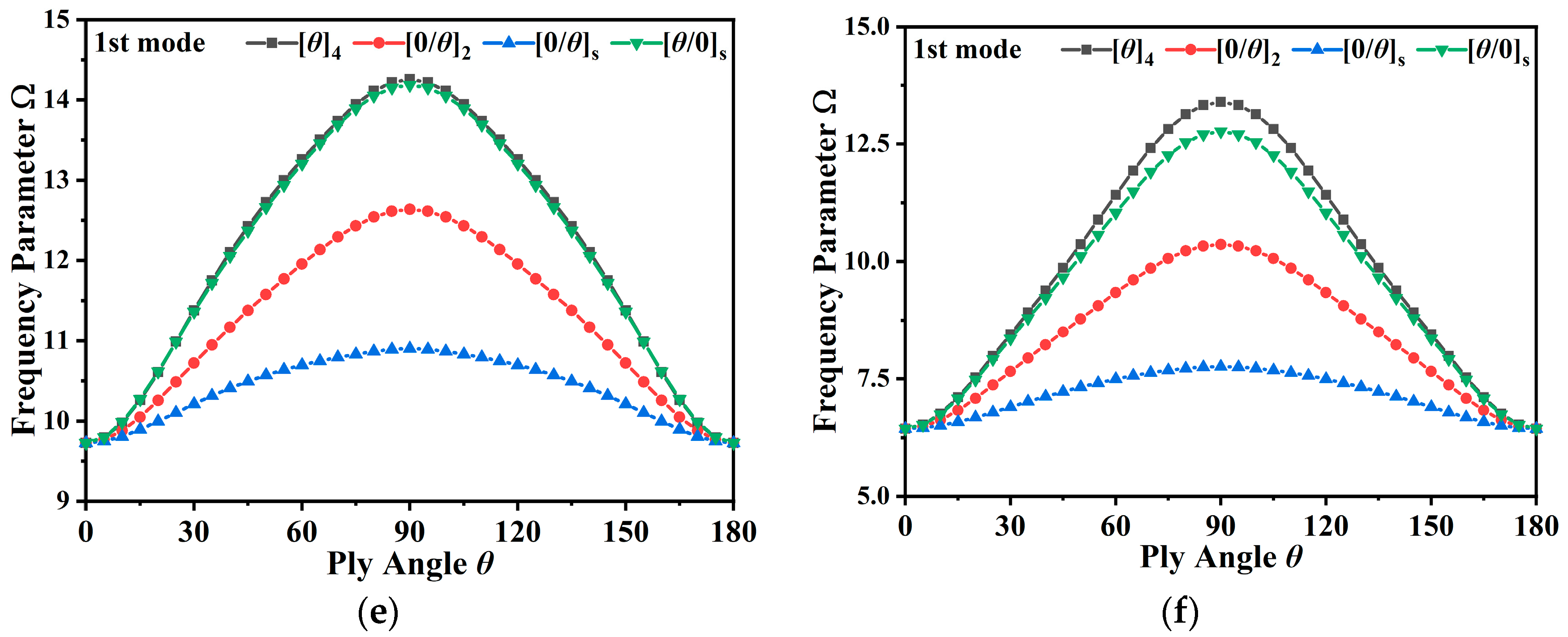
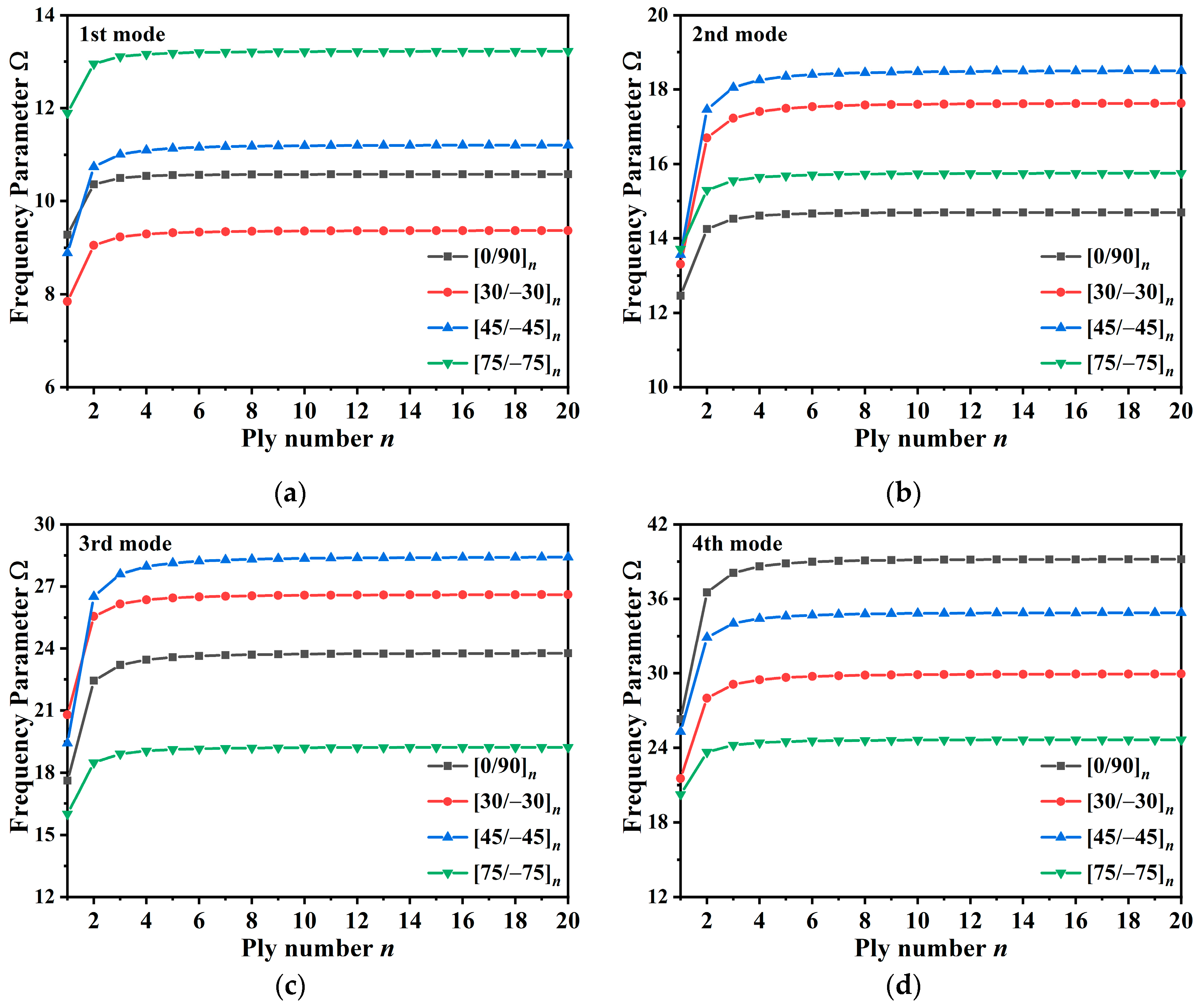
3.3.1. Free Vibration of Composite Stiffened Plate
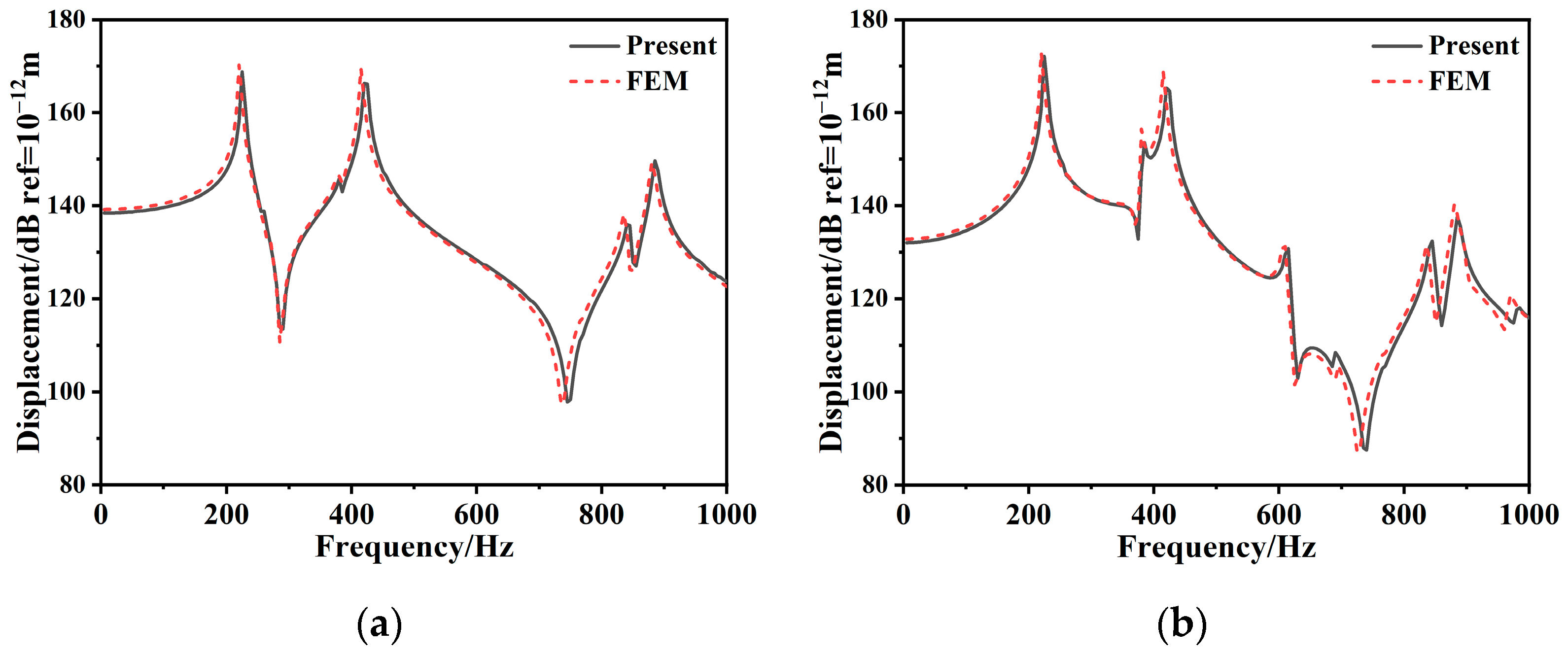
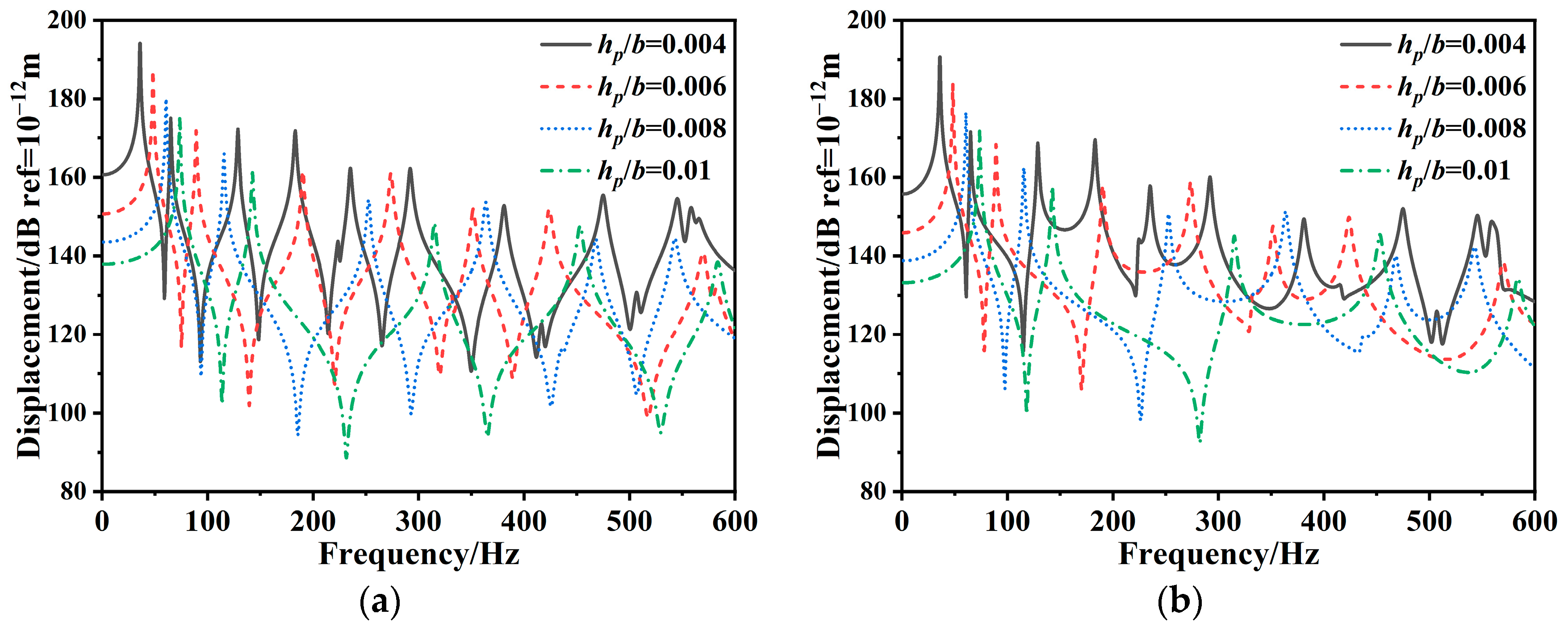
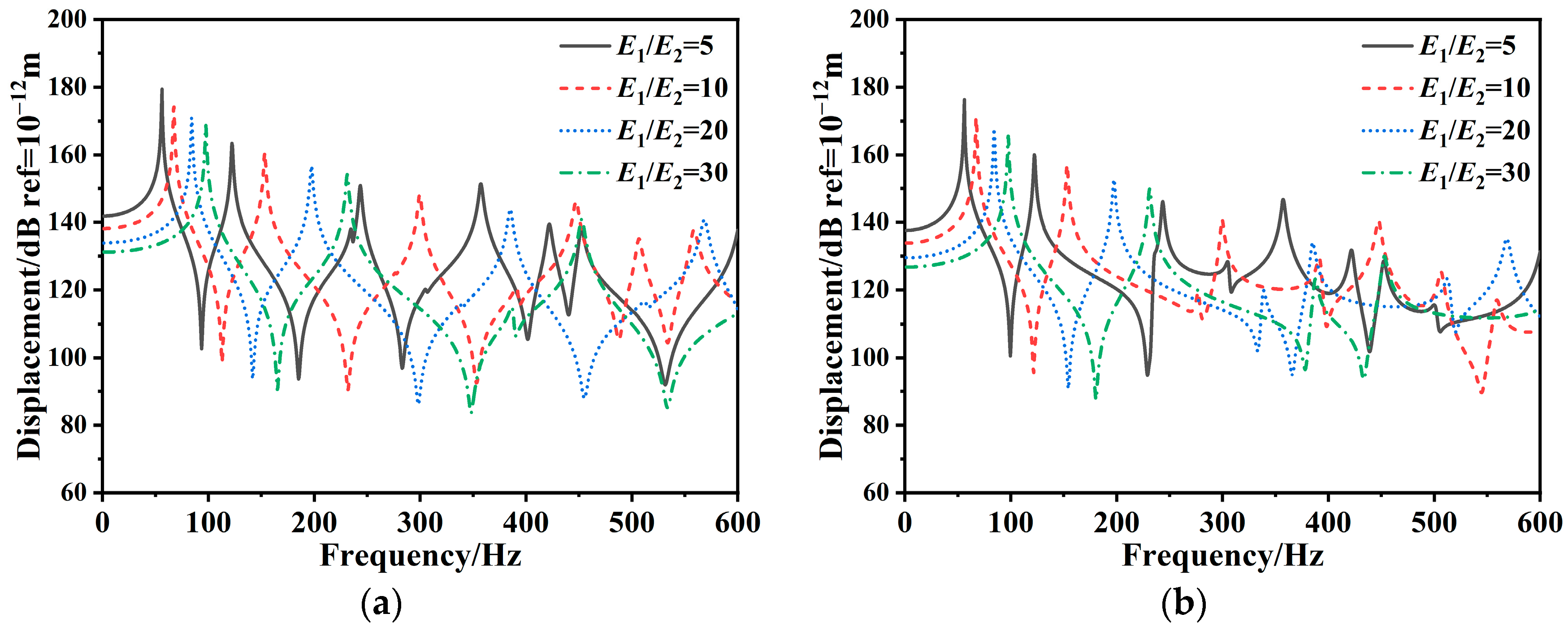
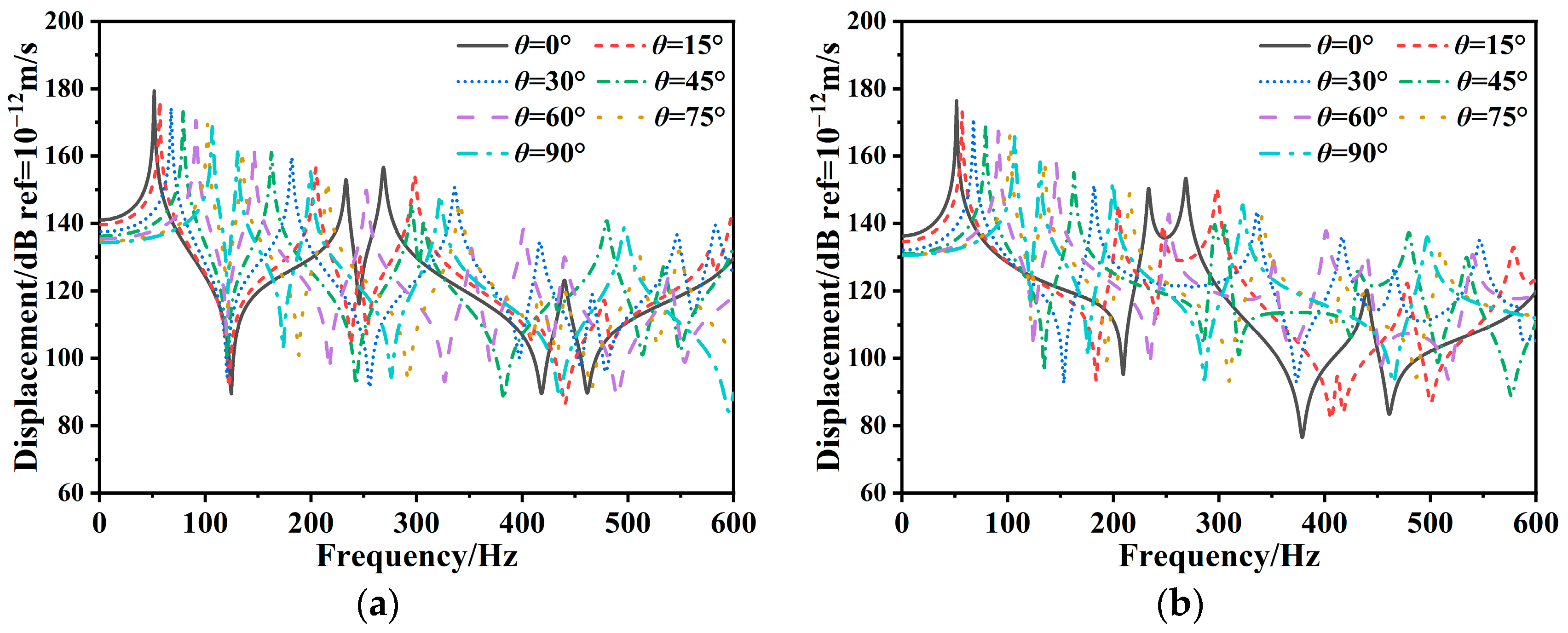
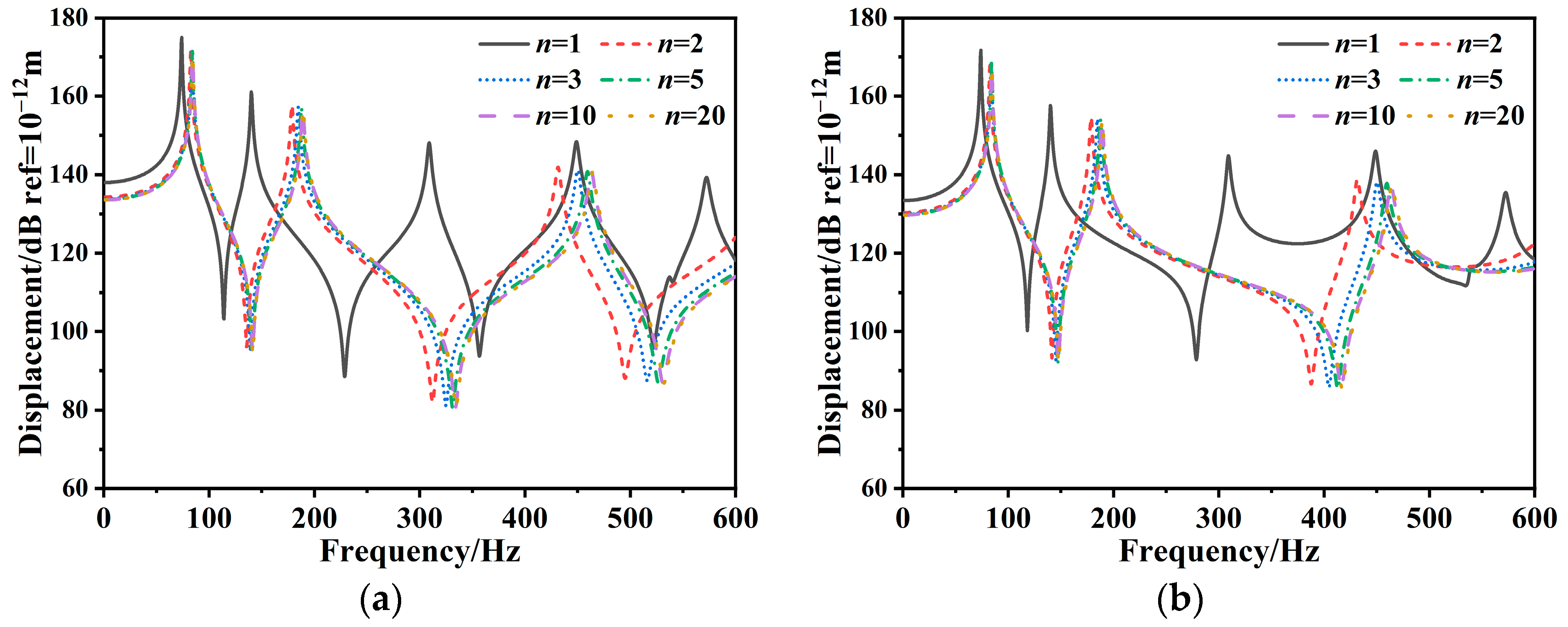
3.3.2. Forced Vibration of Composite Stiffened Plate
4. Conclusions
- The theoretical model developed in this paper is suitable for studying the free and forced vibration characteristics of isotropic and composite stiffened plates with good convergence efficiency and calculation accuracy.
- Increasing both the thickness and material stiffness of the laminate panel enhances the overall stiffness and natural frequency of the composite stiffened plate, subsequently reducing the vibration response.
- In designing the laminate ply scheme, increasing the ply angle can reduce the first-order resonance peak and enhance the low-order vibration response of a rectangular composite stiffened plate. Additionally, the vibration response of the composite stiffened plate can be minimized by increasing the ply number. However, as the ply number increases to a certain level, the vibration behavior of the composite stiffened plate remains unchanged.
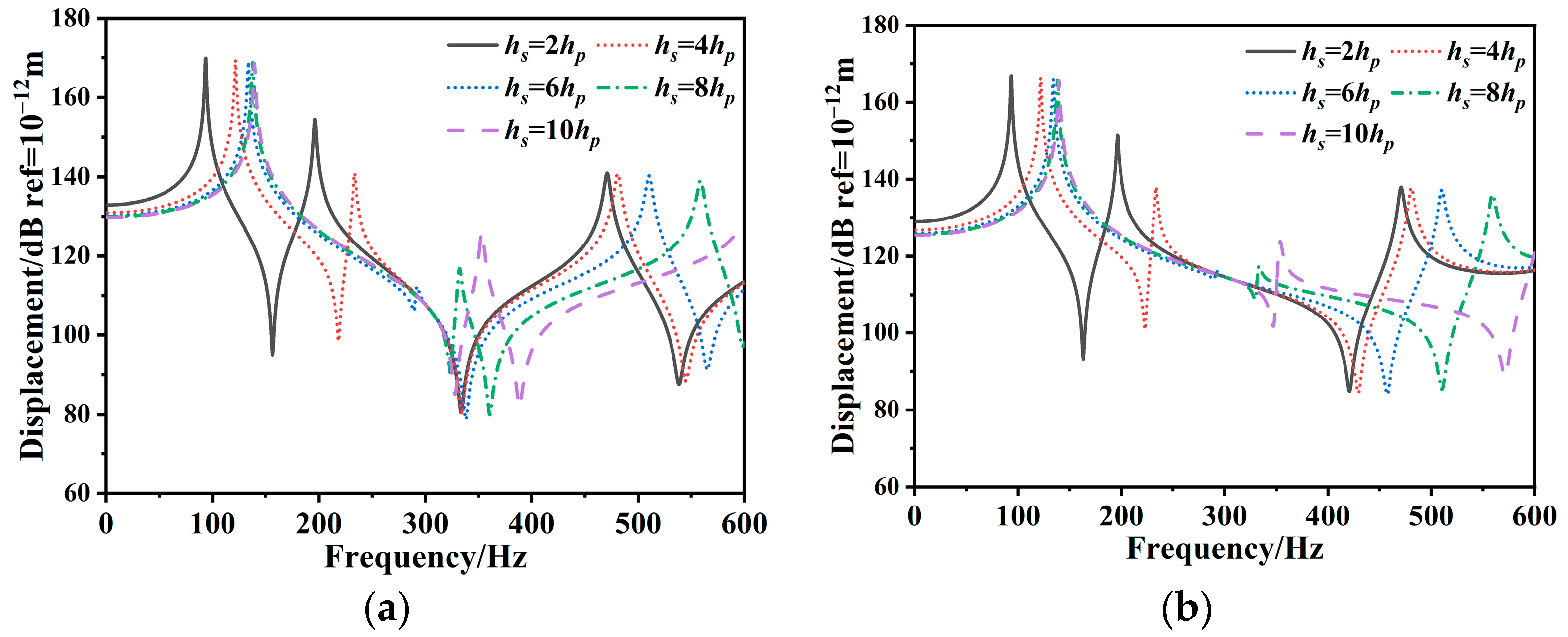
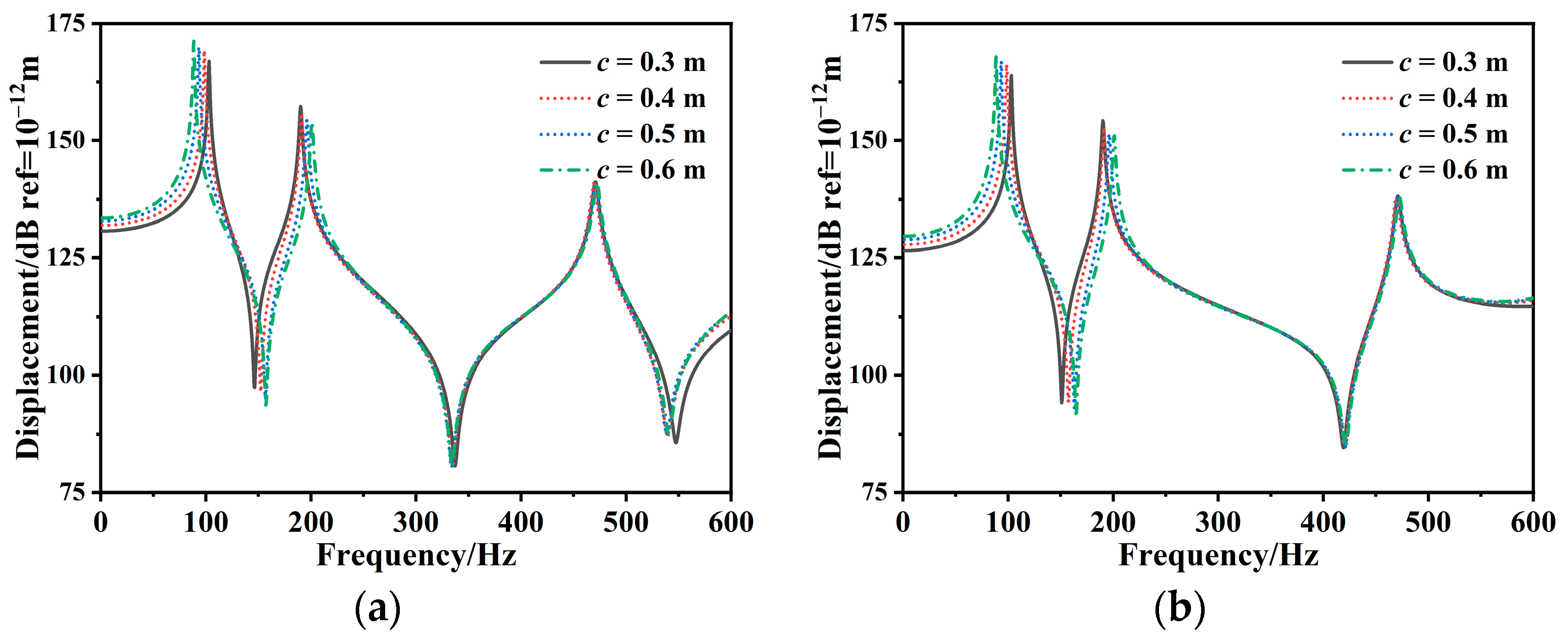
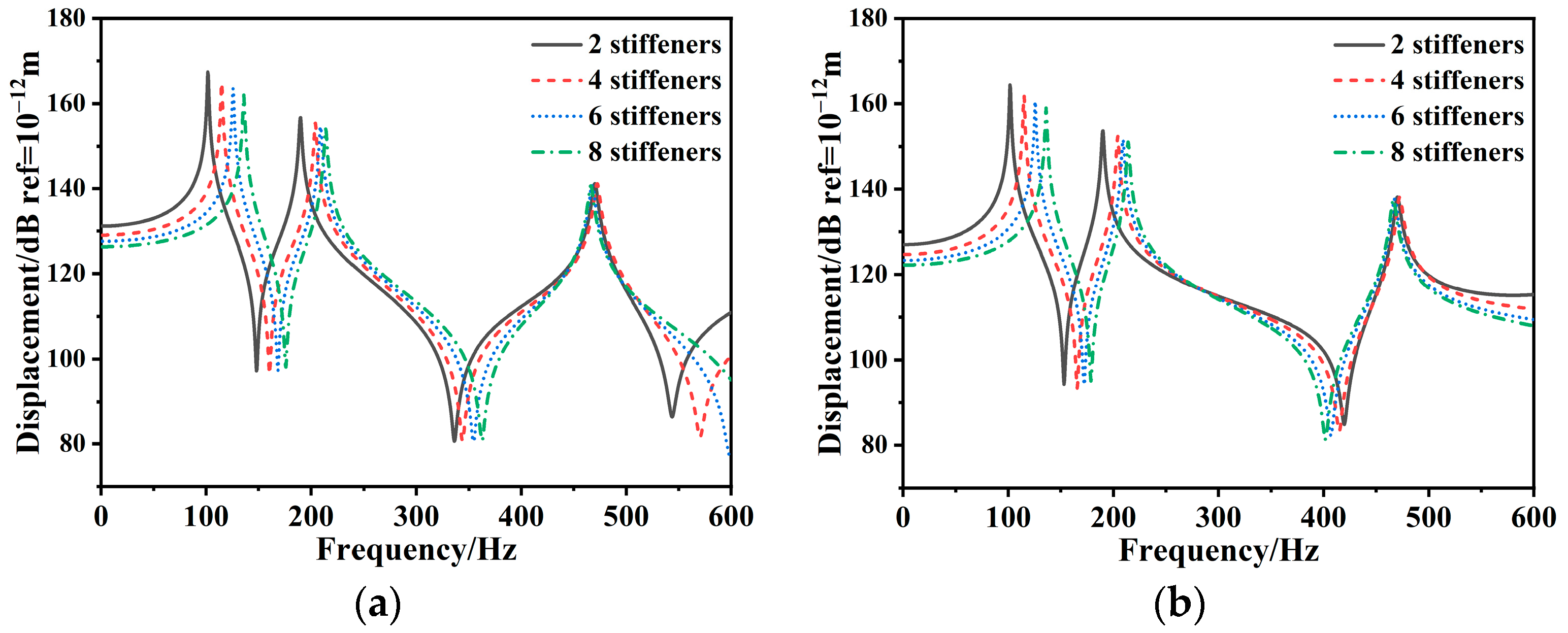
- The natural frequency of the composite stiffened plate increases, and the vibration response peak shifts to a higher frequency region as the stiffener height increases. Conversely, with an increase in the stiffener space, the fundamental frequency of the composite stiffened plate decreases, while the amplitude of the first-order resonance peak increases. Additionally, as the number of stiffeners increases, the composite stiffened plate natural frequency increases, and the vibration response decreases.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hertzberg, T. LASS, Lightweight Construction Applications at Sea; SP Technical Research Institute of Sweden: Växjö, Sweden, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Evegren, F.; Hertzberg, T.; Rahm, M. LASS-C, Lightweight Construction of a Cruise Vessel; SP Technical Research Institute of Sweden: Växjö, Sweden, 2011; p. 44. [Google Scholar]
- Aksu, G.; Ali, R. Free Vibration Analysis of Stiffened Plates Using Finite Difference Method. J. Sound Vib. 1976, 48, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.J.; Liu, W.; Chern, S.M. Vibration Analysis of Stiffened Plates. Comput. Struct. 1994, 50, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-M.; Lee, I. Vibration Analysis of Anisotropic Plates with Eccentric Stiffeners. Comput. Struct. 1995, 57, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, K.M.; Xiang, Y.; Kitipornchai, S.; Lim, M.K. Vibration of Rectangular Mindlin Plates with Intermediate Stiffeners. J. Vib. Acoust. 1994, 116, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.X.; Liew, K.M.; Kitipornchai, S. Buckling and Free Vibration Analyses of Stiffened Plates Using the FSDT Mesh-Free Method. J. Sound Vib. 2006, 289, 421–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, D.S.; Vladimir, N.; Choi, T.M. Simplified Procedure for The Free Vibration Analysis of Rectangular Plate Structures with Holes and Stiffeners. Pol. Marit. Res. 2015, 22, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, D.; Vladimir, N.; Choi, T. Natural Vibration Analysis of Stiffened Panels with Arbitrary Edge Constraints Using the Assumed Mode Method. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part M J. Eng. Marit. Environ. 2015, 229, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, D.S.; Kim, B.H.; Kim, J.-H.; Choi, T.M.; Vladimir, N. Free Vibration Analysis of Stiffened Panels with Lumped Mass and Stiffness Attachments. Ocean Eng. 2016, 124, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, D.S.; Kim, J.-H.; Choi, T.M.; Kim, B.H.; Vladimir, N. Free and Forced Vibration Analysis of Arbitrarily Supported Rectangular Plate Systems with Attachments and Openings. Eng. Struct. 2018, 171, 1036–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, D.S.; Kim, B.H.; Kim, J.-H.; Vladimir, N.; Choi, T.M. Forced Vibration Analysis of Arbitrarily Constrained Rectangular Plates and Stiffened Panels Using the Assumed Mode Method. Thin-Walled Struct. 2015, 90, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.C.; Dong, C.Y.; Wang, F.; Qu, X.Y. Static and Dynamic Analyses of Isogeometric Curvilinearly Stiffened Plates. Appl. Math. Model. 2017, 45, 336–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Lin, T.R. An Analytical Study of Vibration Response of a Beam Stiffened Mindlin Plate. Appl. Acoust. 2019, 155, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, P.R. Free Vibration Analysis of Stiffened Plates. J. Vib. Eng. Technol. 2020, 8, 869–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, P.R.; Barik, M. A Numerical Investigation on the Dynamic Response of Stiffened Plated Structures under Moving Loads. Structures 2020, 28, 1675–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Lin, Y.; Banerjee, J.R. Spectral Dynamic Stiffness Theory for Free Vibration Analysis of Plate Structures Stiffened by Beams with Arbitrary Cross-Sections. Thin-Walled Struct. 2021, 160, 107391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Shen, Y.; Chen, W.; Yang, J.; Peng, L.X. Bending and Free Vibration Analyses of Circular Stiffened Plates Using the FSDT Mesh-Free Method. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2021, 202–203, 106498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Pan, J.; Lin, T.R. Vibration of Rectangular Plates Stiffened by Orthogonal Beams. J. Sound Vib. 2021, 513, 116424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Niu, J.; Jia, R. Dynamic Analysis of Arbitrarily Restrained Stiffened Plate under Moving Loads. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2021, 200, 106414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, D.-H.; Boo, S.-H. Efficient Structural Dynamic Analysis Using Condensed Finite Element Matrices and Its Application to a Stiffened Plate. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Liu, T.; Wang, Q.; Qin, B.; Wang, A.; Shi, X. Free Vibration Characteristics of Concentric Stiffened Rectangular Plates Determined Based on Spectral Tchebyshev Technique. Appl. Acoust. 2022, 191, 108670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; He, X.; Chen, W.; Liang, N.; Peng, L.X. Meshless Simulation and Experimental Study on Forced Vibration of Rectangular Stiffened Plate. J. Sound Vib. 2022, 518, 116602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fan, J.; Shen, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Ren, N. Free Vibration Analysis of Stiffened Rectangular Plate with Cutouts Using Nitsche Based IGA Method. Thin-Walled Struct. 2022, 181, 109975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Pang, F.; Li, H.; Jia, D. A Semi-Analytical Method for the Dynamic Characteristics of Stiffened Plate with General Boundary Conditions. Thin-Walled Struct. 2022, 178, 109513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Jia, X.; Lin, Y.; Liu, H.; Wu, W. Experimental Investigation on Vibro-Acoustic Characteristics of Stiffened Plate Structures with Different Welding Parameters. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rikards, R.; Chate, A.; Ozolinsh, O. Analysis for Buckling and Vibrations of Composite Stiffened Shells and Plates. Compos. Struct. 2001, 51, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadian, M.T.; Zangeneh, M.S. Application of Super Elements to Free Vibration Analysis of Laminated Stiffened Plates. J. Sound Vib. 2003, 259, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, G.; Qiu, J.; Liu, Y. Free Vibration Analysis of Stiffened Laminated Plates. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2006, 43, 1357–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, A.N.; Bandyopadhyay, J.N. Free Vibration Analysis of Laminated Stiffened Shells. J. Eng. Mech. 2005, 131, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prusty, B.G.; Ray, C. Free Vibration Analysis of Composite Hat-Stiffened Panels by Method of Finite Elements. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2004, 23, 533–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prusty, B.G. Free Vibration and Buckling Response of Hat-Stiffened Composite Panels under General Loading. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2008, 50, 1326–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thinh, T.I.; Quoc, T.H. Finite Element Modeling and Experimental Study on Bending and Vibration of Laminated Stiffened Glass Fiber/Polyester Composite Plates. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2010, 49, S383–S389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhar, A.; Phoenix, S.S.; Satsangi, S.K. Finite Element Analysis of Laminated Composite Stiffened Plates Using FSDT and HSDT: A Comparative Perspective. Compos. Struct. 2010, 92, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damnjanović, E.; Marjanović, M.; Nefovska-Danilović, M. Free Vibration Analysis of Stiffened and Cracked Laminated Composite Plate Assemblies Using Shear-Deformable Dynamic Stiffness Elements. Compos. Struct. 2017, 180, 723–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damnjanović, E.; Nefovska-Danilović, M.; Petronijević, M.; Marjanović, M. Application of the Dynamic Stiffness Method in the Vibration Analysis of Stiffened Composite Plates. Procedia Eng. 2017, 199, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Kapania, R.K. Vibration Analysis of Curvilinearly Stiffened Composite Panel Subjected to In-Plane Loads. AIAA J. 2017, 55, 981–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, L.; Mishra, S.S.; Nayak, A.N.; Sahu, S.K. Free Vibration Characteristics of Laminated Composite Stiffened Plates: Experimental and Numerical Investigation. Compos. Struct. 2020, 233, 111557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, L.; Tripathy, A.; Nayak, A.N.; Sahu, S.K. Free Vibration Behavior of Angle-Ply Laminated Composite Stiffened Plates. Int. J. Struct. Stab. Dyn. 2021, 21, 2150187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, L.; Jena, T.; Nayak, A.N. Forced Vibration Analysis of Laminated Composite Stiffened Plates. Int. J. Struct. Eng. 2021, 11, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Maeder, M.; Sepahvand, K.; Matsagar, V.A.; Marburg, S. Damping Analysis of Stiffened Laminated Composite Plates in Thermal Environment. Compos. Struct. 2022, 300, 116163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Sepahvand, K.; Matsagar, V.A.; Marburg, S. Dynamic Response of Stiffened Laminated Composite Plate in Thermal Environment. Compos. Struct. 2022, 300, 116049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Guo, A.; Liang, S.; Qu, P.; Hu, Y.; Liu, C. Structural Dynamic Properties of Stiffened Composite Plates with Embedded Multi-Layered Viscoelastic Damping Membranes. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2022, 30, 4536–4549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.X.; Huang, Z.M.; Wei, D.Y.; He, X.C. Static and Dynamic Analysis of the Composite Laminated Stiffened Plates via the MLS Meshless Method. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2023, 151, 309–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.L. Vibration Analysis of Rectangular Plates with General Elastic Boundary Supports. J. Sound Vib. 2004, 273, 619–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.L. Free Vibrations of Beams with General Boundary Conditions. J. Sound Vib. 2000, 237, 709–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.L. Comparison of Fourier Sine and Cosine Series Expansions for Beams with Arbitrary Boundary Conditions. J. Sound Vib. 2002, 255, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, W.L.; Zhang, X.; Li, W. Free In-Plane Vibration Analysis of Rectangular Plates with Elastically Point-Supported Edges. J. Vib. Acoust. 2010, 132, 031002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Li, W.L.; Jin, G.; Yang, T.; Liu, Z. An Analytical Method for the In-Plane Vibration Analysis of Rectangular Plates with Elastically Restrained Edges. J. Sound Vib. 2007, 306, 908–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.; Jin, G.; Chen, Y.; Ma, X.; Su, Z. Free Vibration Analysis of Laminated Composite Shallow Shells with General Elastic Boundaries. Compos. Struct. 2013, 106, 470–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.; Jin, G.; Su, Z.; Chen, Y. A Modified Fourier Solution for Vibration Analysis of Moderately Thick Laminated Plates with General Boundary Restraints and Internal Line Supports. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2014, 80, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. A Series Solution for the In-Plane Vibration Analysis of Orthotropic Rectangular Plates with Elastically Restrained Edges. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2014, 79, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Shi, D.; Liang, Q.; Ahad, F. An Improved Fourier Series Solution for the Dynamic Analysis of Laminated Composite Annular, Circular, and Sector Plate with General Boundary Conditions. J. Compos. Mater. 2016, 50, 4199–4233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Shi, D.; Shi, X. A Modified Solution for the Free Vibration Analysis of Moderately Thick Orthotropic Rectangular Plates with General Boundary Conditions, Internal Line Supports and Resting on Elastic Foundation. Meccanica 2016, 51, 1985–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, E.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, C.; Fang, Y. A Semi-Analytical Solution for Free Vibration of Thick Orthotropic Annular Sector Plates with General Boundary Conditions, Internal Radial Line and Circumferential Arc Supports. Ocean Eng. 2018, 163, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Xie, F.; Liu, T.; Qin, B.; Yu, H. Free Vibration Analysis of Moderately Thick Composite Materials Arbitrary Triangular Plates under Multi-Points Support Boundary Conditions. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2020, 184, 105789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Q.; Zha, S. Free and Forced Vibration of the Moderately Thick Laminated Composite Rectangular Plate on Various Elastic Winkler and Pasternak Foundations. Shock. Vib. 2017, 2017, 7820130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Shi, D.; Wang, Q. An Improved Fourier Series Solution for Free Vibration Analysis of the Moderately Thick Laminated Composite Rectangular Plate with Non-Uniform Boundary Conditions. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2017, 121, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhong, R.; Shao, D.; Wang, Q.; Guan, X. Dynamic Analysis of Rectangular Plate Stiffened by Any Number of Beams with Different Lengths and Orientations. Shock. Vib. 2019, 2019, 2364515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Jia, D.; Li, H.; Gao, C.; Wang, H. A Unified Method to Analyze Free and Forced Vibration of Stiffened Plates under Various Edge Conditions. Eur. J. Mech. A Solids 2022, 94, 104573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| M × N | Mode | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | |
| 8 × 8 | 4.797 | 12.910 | 14.782 | 16.028 | 16.139 | 28.417 | 35.808 | 38.122 |
| 10 × 10 | 4.776 | 12.909 | 14.769 | 16.015 | 16.127 | 28.369 | 35.793 | 38.100 |
| 12 × 12 | 4.767 | 12.908 | 14.762 | 16.009 | 16.121 | 28.334 | 35.786 | 38.090 |
| 14 × 14 | 4.763 | 12.908 | 14.755 | 16.005 | 16.117 | 28.318 | 35.782 | 38.084 |
| 16 × 16 | 4.760 | 12.908 | 14.751 | 16.002 | 16.115 | 28.299 | 35.781 | 38.079 |
| 18 × 18 | 4.758 | 12.908 | 14.746 | 16.000 | 16.112 | 28.291 | 35.780 | 38.076 |
| 20 × 20 | 4.756 | 12.908 | 14.743 | 15.998 | 16.111 | 28.277 | 35.779 | 38.074 |
| FEM | 4.753 | 12.901 | 14.571 | 15.982 | 16.102 | 28.028 | 35.767 | 38.052 |
| Boundary Condition | ku | kv | kw | Kx | Ky |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| C | 1013 | 1013 | 1013 | 1013 | 1013 |
| S | 1013 | 1013 | 1013 | 0 | 0 |
| Mode | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Present | 209.24 | 221.38 | 258.63 | 311.01 | 341.27 |
| FEM | 212.83 | 221.25 | 269.40 | 309.71 | 352.99 |
| Rikards [27] | 215.00 | 235.50 | 274.50 | 315.40 | 361.40 |
| Mode | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Present | 220.17 Hz | 240.23 Hz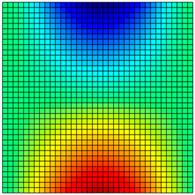 | 349.71 Hz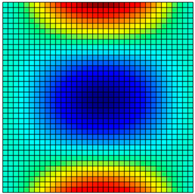 |
| FEM | 220.12 Hz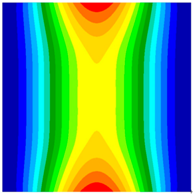 | 240.11 Hz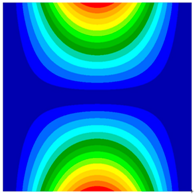 | 350.14 Hz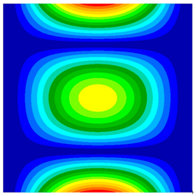 |
| Exp [22] | 230.40 Hz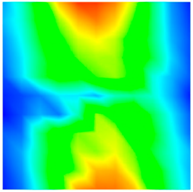 | 247.70 Hz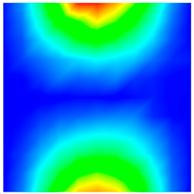 | 353.30 Hz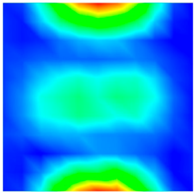 |
| a/b | hp/b | Mode | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | ||
| 1 | 0.004 | 17.296 | 31.251 | 42.998 | 57.475 | 71.400 | 78.258 | 88.508 | 94.805 |
| 0.006 | 14.577 | 28.325 | 38.064 | 56.861 | 60.123 | 69.609 | 75.925 | 94.564 | |
| 0.008 | 13.615 | 27.424 | 34.629 | 52.222 | 56.719 | 67.693 | 71.524 | 94.325 | |
| 0.01 | 13.175 | 27.040 | 32.466 | 48.139 | 56.638 | 65.901 | 69.545 | 89.673 | |
| 1.5 | 0.004 | 13.223 | 20.751 | 29.578 | 30.920 | 44.150 | 54.949 | 58.010 | 58.462 |
| 0.006 | 11.280 | 17.429 | 28.178 | 29.853 | 44.048 | 46.452 | 50.476 | 55.188 | |
| 0.008 | 10.503 | 16.289 | 27.788 | 28.777 | 40.523 | 43.978 | 45.990 | 55.001 | |
| 0.01 | 10.130 | 15.773 | 27.621 | 27.876 | 37.190 | 43.657 | 43.907 | 54.865 | |
| 2 | 0.004 | 11.232 | 16.889 | 20.444 | 26.700 | 26.852 | 39.138 | 40.386 | 42.911 |
| 0.006 | 10.079 | 13.843 | 18.637 | 26.527 | 26.632 | 38.294 | 39.700 | 39.830 | |
| 0.008 | 9.526 | 12.740 | 18.112 | 26.159 | 26.595 | 34.993 | 37.099 | 39.110 | |
| 0.01 | 9.244 | 12.228 | 17.891 | 25.795 | 26.562 | 32.619 | 35.246 | 38.991 | |
| a/b | E1/E2 | Mode | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | ||
| 1 | 5 | 11.005 | 21.798 | 30.566 | 40.533 | 46.054 | 57.599 | 59.312 | 74.392 |
| 10 | 13.444 | 26.549 | 36.823 | 47.556 | 57.003 | 70.504 | 71.136 | 89.122 | |
| 20 | 17.052 | 33.525 | 45.820 | 57.779 | 73.389 | 87.699 | 88.245 | 109.186 | |
| 30 | 19.890 | 38.964 | 52.879 | 65.977 | 85.950 | 100.363 | 101.743 | 125.247 | |
| 1.5 | 5 | 8.270 | 13.830 | 22.373 | 24.690 | 34.583 | 35.041 | 42.004 | 45.955 |
| 10 | 9.977 | 16.818 | 27.771 | 30.030 | 40.716 | 42.419 | 52.952 | 56.415 | |
| 20 | 12.520 | 21.295 | 35.374 | 37.495 | 50.173 | 53.201 | 68.495 | 72.111 | |
| 30 | 14.532 | 24.845 | 41.186 | 43.210 | 57.842 | 61.758 | 80.176 | 84.535 | |
| 2 | 5 | 7.032 | 10.745 | 15.353 | 21.279 | 23.259 | 29.550 | 30.584 | 32.940 |
| 10 | 8.454 | 12.948 | 19.239 | 26.428 | 28.708 | 34.794 | 37.643 | 40.713 | |
| 20 | 10.575 | 16.277 | 24.778 | 33.885 | 36.167 | 42.497 | 48.374 | 52.104 | |
| 30 | 12.258 | 18.936 | 29.035 | 39.443 | 42.127 | 48.664 | 56.875 | 60.918 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gu, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, W.; Sun, J.; Lin, Y.; Fang, Y. Free and Forced Vibration Characteristics of a Composite Stiffened Plate Based on Energy Method. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 875. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12060875
Gu X, Wang X, Wu W, Sun J, Lin Y, Fang Y. Free and Forced Vibration Characteristics of a Composite Stiffened Plate Based on Energy Method. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2024; 12(6):875. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12060875
Chicago/Turabian StyleGu, Xin, Xianzhong Wang, Weiguo Wu, Jie Sun, Yongshui Lin, and Yueming Fang. 2024. "Free and Forced Vibration Characteristics of a Composite Stiffened Plate Based on Energy Method" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 12, no. 6: 875. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12060875
APA StyleGu, X., Wang, X., Wu, W., Sun, J., Lin, Y., & Fang, Y. (2024). Free and Forced Vibration Characteristics of a Composite Stiffened Plate Based on Energy Method. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 12(6), 875. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12060875





