Accumulation and Phytoremediation Potentiality of Trace and Heavy Metals in Some Selected Aquatic Plants from a Highly Urbanized Subtropical Estuary
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
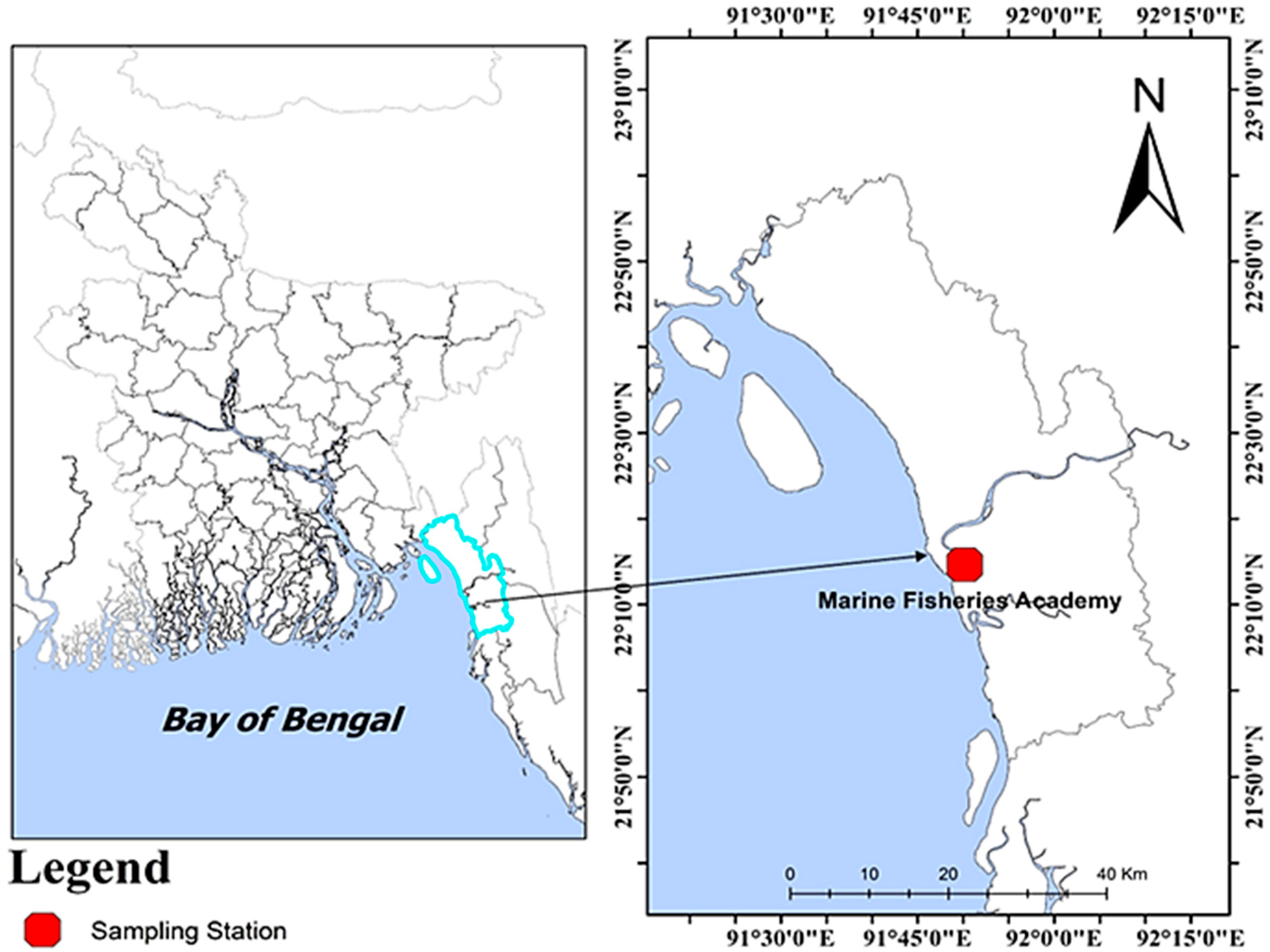
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection, Preparation and Analysis
2.3. Ecological Risk Assessments of Heavy Metals
2.3.1. Contamination Factor (CF)
2.3.2. Pollution Load Index (PLI)
2.3.3. Geo-Accumulation Index (Igeo)
2.3.4. Enrichment Factor (EF)
2.3.5. Assessment of Potential Ecological Risk Index
2.3.6. Bioconcentration Factor (BCF)
2.3.7. Translocation Factor (TF)
2.3.8. Assessment of Phytoremediation Potential
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Metal Concentration in Sediment
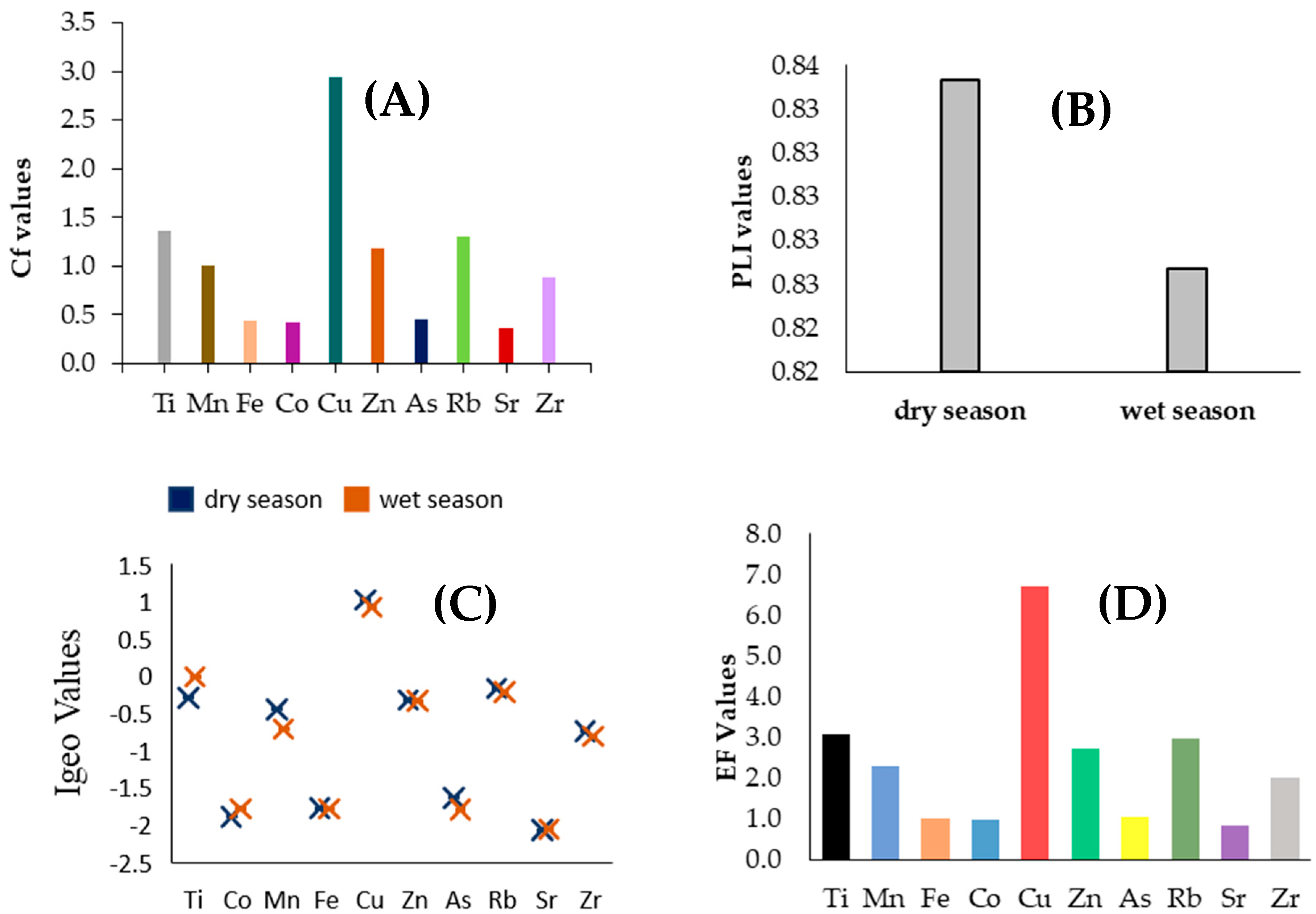
3.2. Assessment of Metal Pollution in Sediment
3.2.1. Enrichment Factor (EF)
3.2.2. Ecological Risk Index
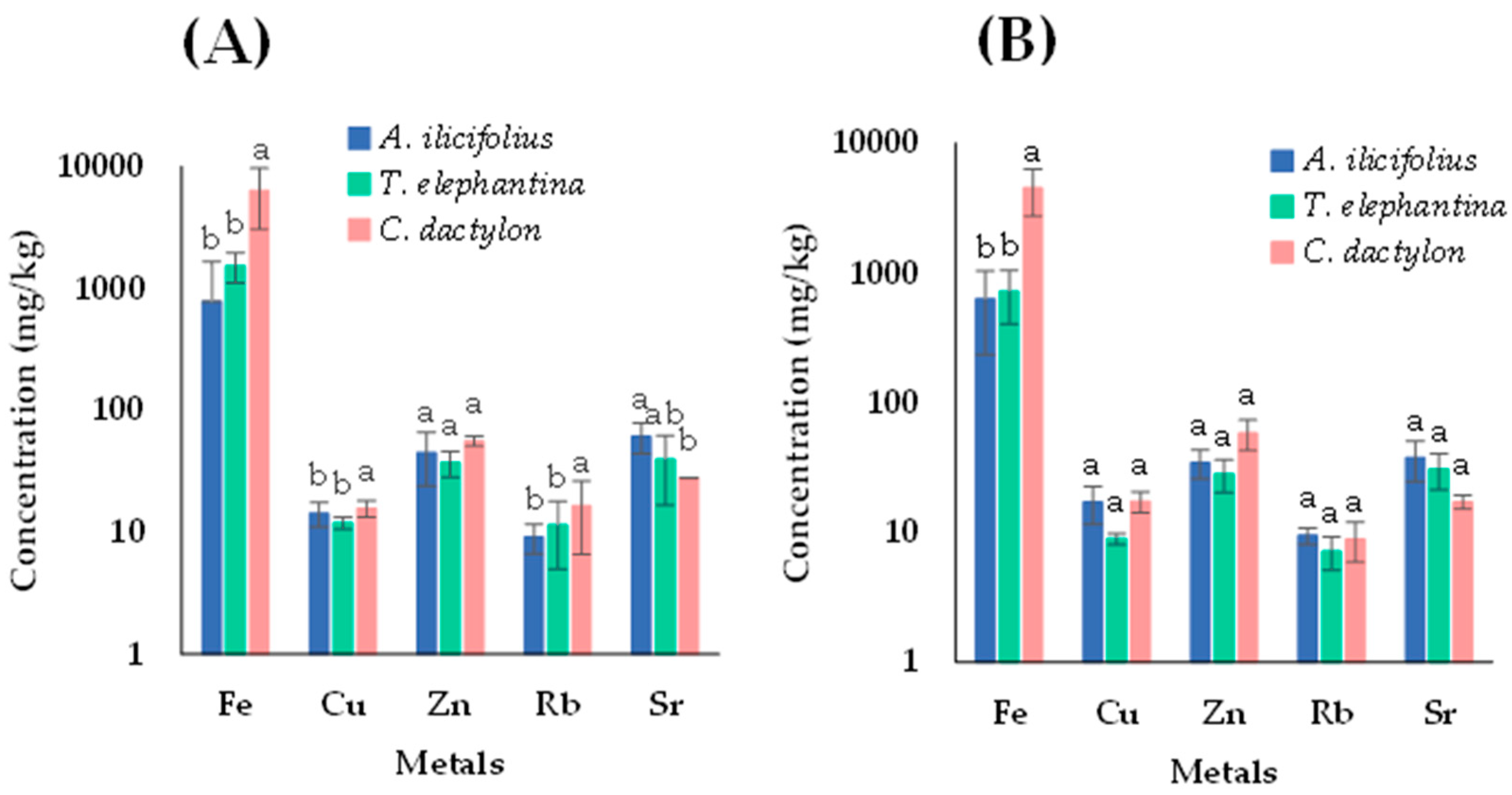
3.3. Concentration of Metals in Aquatic Plants
3.4. Phytoremediation Potential
3.5. Relationship of Metal Concentrations in Sediment with Plant Tissue
3.6. Pollution Source Identification
Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Cluster Analysis for Source identification
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Charvalas, G.; Solomou, A.D.; Giannoulis, K.D.; Skoufogianni, E.; Bartzialis, D.; Emmanouil, C.; Danalatos, N.G. Determination of heavy metals in the territory of contaminated areas of Greece and their restoration through hyperaccumulators. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 3858–3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, R.; Varun, M.; Paul, M.S. Phytoremediation: Uptake and role of metal transporters in some members of Brassicaceae. In Phytoremediation: Management of Environmental Contaminants, Volume 3; Ansari, A.A., Gill, S.S., Gill, R., Lanza, G.R., Newman, L., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 453–468. [Google Scholar]
- Corral-Bobadilla, M.; Lostado-Lorza, R.; Somovilla-Gómez, F.; Escribano-García, R. Biosorption of Cu(II) ions as a method for the effective use of activated carbon from grape stalk waste: RMS optimization and kinetic studies. Energy Sources Part A 2022, 44, 4706–4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekabira, K.; Oryem–Origa, H.; Mutumba, G.B.; Basamba, T.A. Heavy Metal Phytoremediation by Commelina benghalensis (L.) and Cynodon dactylon (L.) Growing in Urban Stream Sediments. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/20.500.12306/375 (accessed on 2 February 2024).
- Malik, R.N.; Husain, S.Z.; Nazir, I. Heavy metal contamination and accumulation in soil and wild plant species from industrial area of Islamabad, Pakistan. Pak. J. Bot. 2010, 42, 291–301. [Google Scholar]
- Duman, F.; Cicek, M.; Sezen, G. Seasonal changes of metal accumulation and distribution in common club rush (Schoenoplectus lacustris) and common reed (Phragmites australis). Ecotoxicology 2007, 16, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.S.; Hossain, M.B.; Babu, S.O.F.; Rahman, M.; Ahmed, A.S.; Jolly, Y.N.; Akter, S. Source of metal contamination in sediment, their ecological risk, and phytoremediation ability of the studied mangrove plants in ship breaking area, Bangladesh. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 141, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, U.; Zaman, S.; Mitra, A. Enrichment Factor and Translocation Factor of selective Heavy Metals in Saccharum spontaneum and Typha elephantina species growing in the fly ash ponds of Mejia Thermal Power Station. J. Sci. Eng. Health Manag. 2017; unpublished work. [Google Scholar]
- National Parks. Species of Acanthus ilicifolius. Available online: https://www.nparks.gov.sg/florafaunaweb/flora/3/4/3487 (accessed on 15 January 2023).
- Saleh Muneera, A.; AL-Sodany Yassin, M.; Abdel Khalik Kadry, N.; Eid Ebrahim, M. Heavy metals accumulation and translocation by Typha elephantina Roxb. and Typha domingensis Pers. in an arid habitat: Perspectives for phytoremediation. World WJARR 2019, 4, 044–053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harlan, J.R.; De Wet, J.M.J.; Rawal, K.M. Origin and distribution of the seleucidus race of Cynodon dactylon (L.) pers. var. Dactylon (gramineae). Euphytica 1970, 19, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, M.A.M.; Aktar, M. Heavy metals in salt marsh sediments of porteresia bed along the Karnafully River coast, Chittagong. Soil Water Res. 2012, 7, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, M.A.K. Study on the Trace Metals in Water, Sediment and Jew Fish (Otolithoides microdon) of the Karnafully River Estuary. Master’s Thesis, Institute of Marine Science and Fisheries, University of Chittagong, Chittagong, Bangladesh, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Forkan, M. Terminal Operation of Jamuna Oil Company Ltd. and Impacts of Waste Oil on the Karnafully River Estuary. Master’s Thesis, Institute of Marine Science and Fisheries, University of Chittagong, Chittagong, Bangladesh, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, T. Study on the Environment Impact Assessment (EIA) of the Effluent Discharged by the Chittagong Urea Fertilizer Limited (CUFL) on the Karnafully River Estuary. Master’s Thesis, Institute of Marine Sciences, University of Chittagong, Chittagong, Bangladesh, 1992; p. 55. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.M.; Ali, M.L.; Islam, M.S.; Rahman, M.Z. Preliminary assessment of heavy metals in water and sediment of Karnaphuli River, Bangladesh. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2016, 5, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.P.; Mohan, D.; Sinha, S.; Dalwani, R. Impact assessment of treated/untreated wastewater toxicants discharged by sewage treatment plants on health, agricultural and environmental quality in the wastewater disposal area. Chemosphere 2004, 55, 227–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhouyain, A.M. Fresh and brackish water pollution in Bangladesh. Fish. Inf. Bull. 1983, 1, 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Tyler, P.A.; Buckey, R.T. Pollution of a Tasmanian river by mine effluents I. Chemical evidence. Int. Rev. Gesamten Hydrobiol. Hydrogr. 1973, 58, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Bhuyan, M.S.; Monwar, M.M.; Akhtar, A. Some health hazard metals in commercially important coastal Molluscan species in Bangladesh. Bangladesh J. Zool. 2016, 44, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kord, B.; Mataji, A.; Babaie, S. Pine (Pinus eldarica Medw.) needles as indicator for heavy metals pollution. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 7, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addo, M.A.; Darko, E.O.; Gordon, C.; Nyarko, B.J.B.; Gbadago, J.K.; Nyarko, E.; Botwe, B.O. Evaluation of heavy metals contamination of soil and vegetation in the vicinity of a cement factory in the Volta Region, Ghana. Int. J. Sci. Technol. 2012, 2, 40–50. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Teng, A.; Xu, W.; Liu, X. Distribution and pollution assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments in the Yellow Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 83, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almiqrhi, A.A. Determination of heavy metals (Pb, Zn, Cd, Cu) in coastal sediments and fish urban area of Semarang, Indonesia. J. Environ. Anal. Toxicol. 2018, 8, 568. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, K.R.; Amaya-Santos, G.; Yargicoglu, E.; Cooper, D.E.; Negri, M.C. Phytoremediation of heavy metals and PAHs at slag fill site: Three-year field-scale investigation. Int. J. Geotech. Eng. 2019, 13, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.B.; Masum, Z.; Rahman, M.S.; Yu, J.; Noman, M.A.; Jolly, Y.N.; Arai, T. Heavy Metal Accumulation and Phytoremediation Potentiality of Some Selected Mangrove Species from the World’s Largest Mangrove Forest. Biology 2022, 11, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Idris, A.M.; Islam, A.R.M.T.; Ali, M.M.; Rakib, M.R.J. Hydrological distribution of physicochemical parameters and heavy metals in surface water and their ecotoxicological implications in the Bay of Bengal coast of Bangladesh. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 68585–68599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.; Alam, S.; Hasan, M.S. Modeling climate change impact on hydrology of Karnafuli River basin using soil water assessment tool (SWAT). In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Water and Flood Management (ICWFM 2013), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 9–11 March 2013; pp. 529–536. [Google Scholar]
- Rizbi, S.N.H. Bangladesh District Gazetteers, Chittagong; Govt. of Bangladesh, Service and General Administration Department, Bangladesh Govt. Press: Dacca, Bangladesh, 1971; p. 64.
- Alam, M.W.; Zafar, M. Occurrences of Salmonella spp. in water and soil sample of the Karnafuli river estuary. Microbes Health 2012, 1, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, R.J.; Neogi, S.B.; Islam, M.S.; Mahmud, Z.H.; Yamasaki, S.; Nair, G.B. Influence of catastrophic climatic events and human waste on Vibrio distribution in the Karnaphuli estuary, Bangladesh. EcoHealth 2009, 6, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolly, Y.N.; Rakib, M.R.J.; Kumar, R.; Islam, A.R.M.T.; Rabby, A.; Mamun, K.M.; Akter, S.; Kabir, J.; Bhuiyan, T.J.; Chowdhury, A.M.S.; et al. Deciphering the source of heavy metals in industrially affected river sediment of Shitalakshya river, Bangladesh, and potential ecological and health implications. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2023, 10, 100268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.R.; McLennan, S.M. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution; Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson, D.L.; Wilson, J.G.; Harris, C.R.; Jeffrey, D.W. Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgoländer Meeresunters. 1980, 33, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, G. Index of geo-accumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. GeoJournal 1969, 2, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Ergin, M.; Saydam, C.; Baştürk, Ö.; Erdem, E.; Yörük, R. Heavy metal concentrations in surface sediments from the two coastal inlets (Golden Horn Estuary and Izmit Bay) of the northeastern Sea of Marmara. Chem. Geol. 1991, 91, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, G.F.; Olmos, M.A. Sediment-bound heavy metals as indicators of human influence and biological risk in coastal water bodies. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2008, 65, 1407–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yongming, H.; Peixuan, D.; Junji, C.; Posmentier, E.S. Multivariate analysis of heavy metal contamination in urban dusts of Xi’an, Central China. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 355, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phaenark, C.; Pokethitiyook, P.; Kruatrachue, M.; Ngernsansaruay, C. Cd and Zn accumulation in plants from the Padaeng zinc-mine area. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2009, 11, 479–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, A.R.A.; Mohamed, H.M. Effect of microbial inoculation and EDTA on the uptake and translocation of heavy metal by corn and sunflower. Chemosphere 2009, 76, 893–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.; Cao, X.; Zhou, Q.; Ma, L.Q. Accumulation of Pb, Cu, and Zn in native plants growing on a contaminated Florida site. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 368, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, R.; Yadav, S.; Yadav, S. Phytoextraction potential of heavy metals by native wetland plants growing on chlorolignin containing sludge of pulp and paper industry. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 98, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Liao, Y.; Shou, L. Concentration and potential health risk of heavy metals in seafoods collected from Sanmen Bay and its adjacent areas, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 131, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merciai, R.; Guasch, H.; Kumar, A.; Sabater, S.; García-Berthou, E. Trace metal concentration and fish size: Variation among fish species in a Mediterranean river. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 107, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varol, M.; Kaya, G.K.; Alp, A. Heavy metal and arsenic concentrations in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) farmed in a dam reservoir on the Firat (Euphrates) River: Risk-based consumption advisories. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599, 1288–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaray, S.K.; Nayak, B.B.; Lin, S.; Bhatta, D. Geochemical speciation and risk assessment of heavy metals in the river estuarine sediments—A case study: Mahanadi basin, India. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 1837–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Hossain, M.B.; Matin, A.; Sarker, M.S.I. Assessment of heavy metal pollution, distribution and source apportionment in the sediment from Feni River estuary, Bangladesh. Chemosphere 2018, 202, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliman, N.F.; Nasr, S.M.; Okbah, M.A. Potential ecological risk of heavy metals in sediments from the Mediterranean coast, Egypt. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2015, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatramanan, S.; Ramkumar, T.; Anithamary, I.; Vasudevan, S. Heavy metal distribution in surface sediments of the Tirumalairajan river estuary and the surrounding coastal area, east coast of India. Arab. J. Geosci. 2014, 7, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, M.A.M.; Rahman, M.; Rahman, S.M.A.; Hassan, M.R.; Fardous, Z.; Chowdhury, M.A.Z.; Hossain, M.B. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in the surficial sediments from the lower Meghna River estuary, Noakhali coast, Bangladesh. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2021, 36, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, B.; Ismail, A.; Arshad, A.; Yap, C.K.; Kamarudin, M.S. Anthropogenic impacts on heavy metal concentrations in the coastal sediments of Dumai, Indonesia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 148, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achary, M.S.; Satpathy, K.K.; Panigrahi, S.; Mohanty, A.K.; Padhi, R.K.; Biswas, S.; Panigrahy, R.C. Concentration of heavy metals in the food chain components of the nearshore coastal waters of Kalpakkam, southeast coast of India. Food Control 2017, 72, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Narwal, S.; Agnihotri, S. Typha elephantina Roxb.: A review on ethanomedicinal, morphological, phyto-chemical and pharmacological perspectives. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2020, 13, 5546–5550. [Google Scholar]
- IAEA. Guidebook on Applications of Radiotracers in Industry; Technical Report Series No. 316; International Atomic Energy Agency: Vienna, Austria, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Kamaruzzaman, B.Y.; Shuhada, N.T.; Akbar, B.; Shahbudin, S.; Jalal, K.C.A.; Ong, M.C.; Goddard, J.S. Spatial concentrations of lead and copper in bottom sediments of Langkawi Coastal Area, Malaysia. Res. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 5, 179. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yu, L.; Feng, H. Metal pollution in coastal sediments. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2015, 1, 203–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, T.; Hoque, S.; Akter, S. Pollution in the Bay of Bengal: Impact on marine ecosystem. Open J. Mar. Sci. 2014, 5, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusuma Wardhani, W.; Dwi Ariesyady, H.; Andarani, P.; Ngoc Nguyen, M.; Yokota, K.; Inoue, T. Assessment of zinc concentrations in surface sediment from urban and industrial sites of Umeda River, Japan. Water Supply 2022, 22, 3941–3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Lu, Y.; Wang, T.; Hu, W.; Jiao, W.; Naile, J.E.; Giesy, J.P. Ecological risk assessment of arsenic and metals in sediments of coastal areas of northern Bohai and Yellow Seas, China. Ambio 2010, 39, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.F.; Wang, L.J.; Huo, C.L.; Guan, D.M. Assessment on heavy metals pollution in surface sediments in Jinzhou Bay. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2008, 2, 178–181. [Google Scholar]
- GESAMP. The Review of the Health of the Oceans. Rep. Stud. 1982, 15, 108. [Google Scholar]
- Mirlean, N.; Baisch, P.; Diniz, D. Arsenic in groundwater of the Paraiba do Sul delta, Brazil: An atmospheric source? Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 482, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ra, K.; Kim, J.-K.; Hong, S.H.; Yim, U.H.; Shim, W.J.; Lee, S.-Y.; Kim, Y.-O.; Lim, J.; Kim, E.-S.; Kim, K.-T. Assessment of pollution and ecological risk of heavy metals in the surface sediments of Ulsan Bay, Korea. Ocean Sci. J. 2014, 49, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sany, S.B.T.; Salleh, A.; Sulaiman, A.H.; Sasekumar, A.; Rezayi, M.; Tehrani, G.M. Heavy metal contamination in water and sediment of the Port Klang coastal area, Selangor, Malaysia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 69, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, B. Principles of Geochemistry; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Yang, S.L.; Milliman, J.D.; Xu, K.H.; Qin, W.H.; Wu, C.S.; Shi, B.W. Spatial, temporal, and human-induced variations in suspended sediment concentration in the surface waters of the Yangtze Estuary and adjacent coastal areas. Estuaries Coasts 2012, 35, 1316–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priju, C.P.; Narayana, A.C. Spatial and temporal variability of trace element concentrations in a tropical lagoon, Southwest Coast of India: Environmental Implications. J. Coast. Res. 2006, 22, 1053–1057. [Google Scholar]
- Loska, K.; Cebula, J.; Pelczar, J.; Wiechuła, D.; Kwapuliński, J. Use of enrichment, and contamination factors together with geo-accumulation indexes to evaluate the content of Cd, Cu, and Ni in the Rybnik water reservoir in Poland. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1997, 93, 347–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OSPAR Commission. Metals in Sediment and Biota: Status and Trend of Copper Burden; OSPAR Commission: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Eid, E.M.; Galal, T.M.; Shaltout, K.H.; El-Sheikh, M.A.; Asaeda, T.; Alatar, A.A.; Barcelo, D. Biomonitoring potential of the native aquatic plant Typha domingensis by predicting trace metals accumulation in the Egyptian Lake Burullus. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 714, 136603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kfle, G.; Asgedom, G.; Goje, T.; Abbebe, F.; Habtom, L.; Hanes, H. The level of heavy metal contamination in selected vegetables and animal feed grasses grown in wastewater irrigated area, around Asmara, Eritrea. J. Chem. 2020, 2020, 1359710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaranyika, M.F.; Nyati, W. Uptake of heavy metals by Typha capensis from wetland sites polluted by effluent from mineral processing plants: Implications of metal–metal interactions. 3 Biotech 2017, 7, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shackira, A.M.; Puthur, J.T. An assessment of heavy metal contamination in soil sediments, leaves and roots of Acanthus ilicifolius L. In Proceedings of the 23rd Swadeshi Science Congress, Kottayam, India, 6–8 November 2013; pp. 689–692. [Google Scholar]
- Muthusaravanan, S.; Sivarajasekar, N.; Vivek, J.S.; Paramasivan, T.; Naushad, M.; Prakashmaran, J.; Al-Duaij, O.K. Phytoremediation of heavy metals: Mechanisms, methods and enhancements. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2018, 16, 1339–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, M.J.; Acevedo, S.O.A.; Prieto, G.F.; González, N.T. Phytoremediation of soils contaminated with heavy metals. Int. J. Biodivers. 2018, 2, 362–376. [Google Scholar]
- Fitz, W.J.; Wenzel, W.W. Arsenic transformations in the soil–rhizosphere–plant system: Fundamentals and potential application to phytoremediation. J. Biotechnol. 2002, 99, 259–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosselli, W.; Keller, C.; Boschi, K. Phytoextraction capacity of trees growing on a metal contaminated soil. Plant Soil 2003, 256, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisha, P.; Athira, P.S.; Anagha, B.; Charles, P.E.; Prabakaran, K.; Rajaram, R. First report on occurrence of heavy metals in dried fishes from major fishing villages in Kerala coast, Southwest India. Hyg. Environ. Health Adv. 2023, 6, 100051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereswill, R.; Streloke, M.; Schulz, R. Current-use pesticides in stream water and suspended particles following runoff: Exposure, effects, and mitigation requirements. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2013, 32, 1254–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.V., III; Piatak, N.M.; Bedinger, G.M. Zirconium and Hafnium; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2017; No. 1802-V.
- Thomsen, E.; Andreasen, R. Agricultural lime disturbs natural strontium isotope variations: Implications for provenance and migration studies. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaav8083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.Y.; Chen, J.J.; Lee, C.G.; Chiu, C.Y.; Lai, W.L.; Liao, S.W. Integrated estuary management for diffused sediment pollution in Dapeng Bay and neighboring rivers (Taiwan). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 173, 499–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, P.; Panda, U.C.; Bhatta, D.; Sahu, K.C. Use of sequential leaching, mineralogy, morphology and multivariate statistical technique for quantifying metal pollution in highly polluted aquatic sediments—A case study: Brahmani and Nandira Rivers, India. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 163, 632–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Khan, Y.S.A.; Sarker, M.A.K. Trace Metal Concentration in Water of the Karnaphuli River Estuary of the Bay of Bengal; Asian Network for Scientific Information: Punjab, Pakistan, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Bhuiyan, M.A.; Parvez, L.; Islam, M.A.; Dampare, S.B.; Suzuki, S. Heavy metal pollution of coal mine-affected agricultural soils in the northern part of Bangladesh. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 173, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
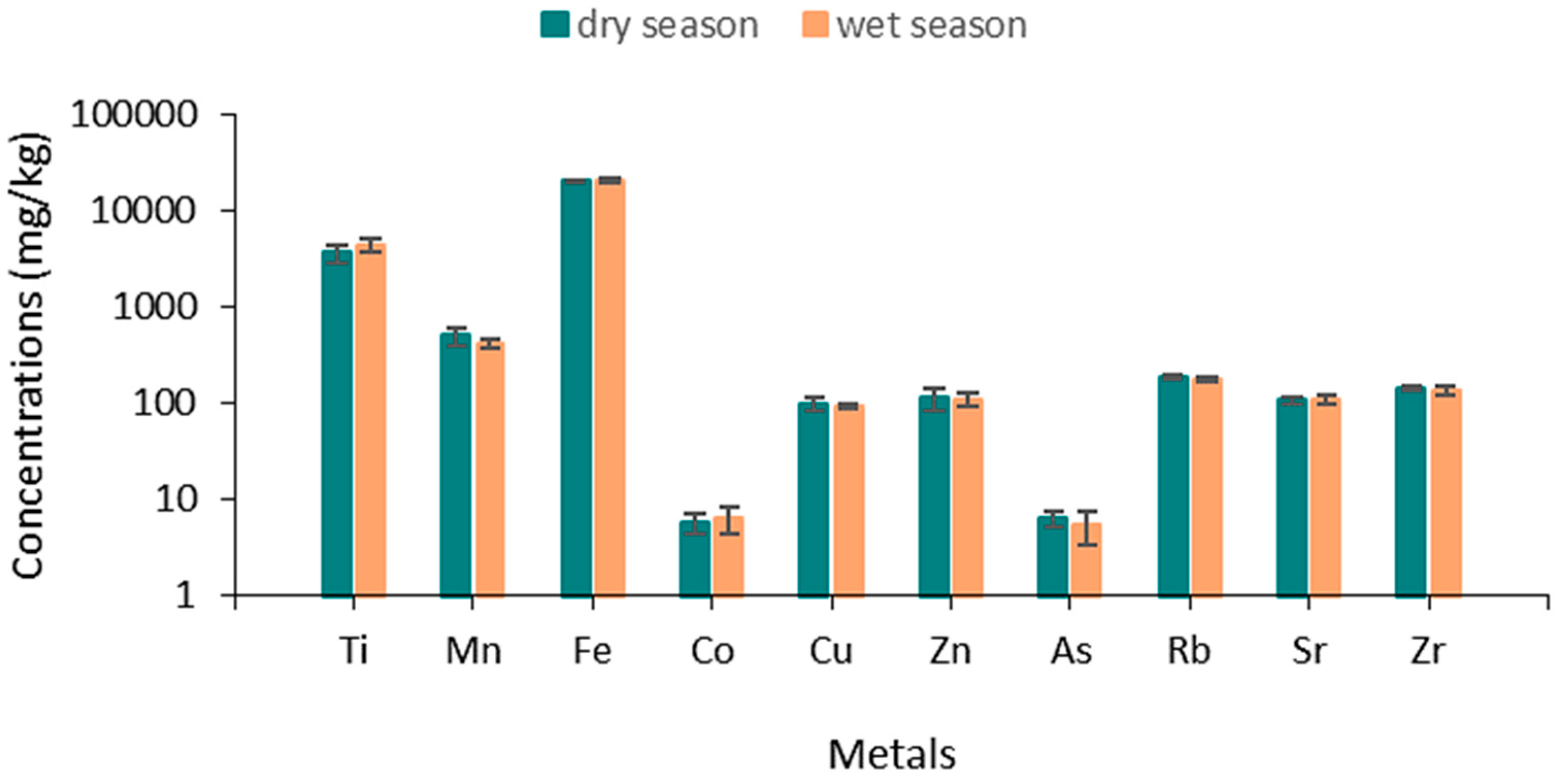
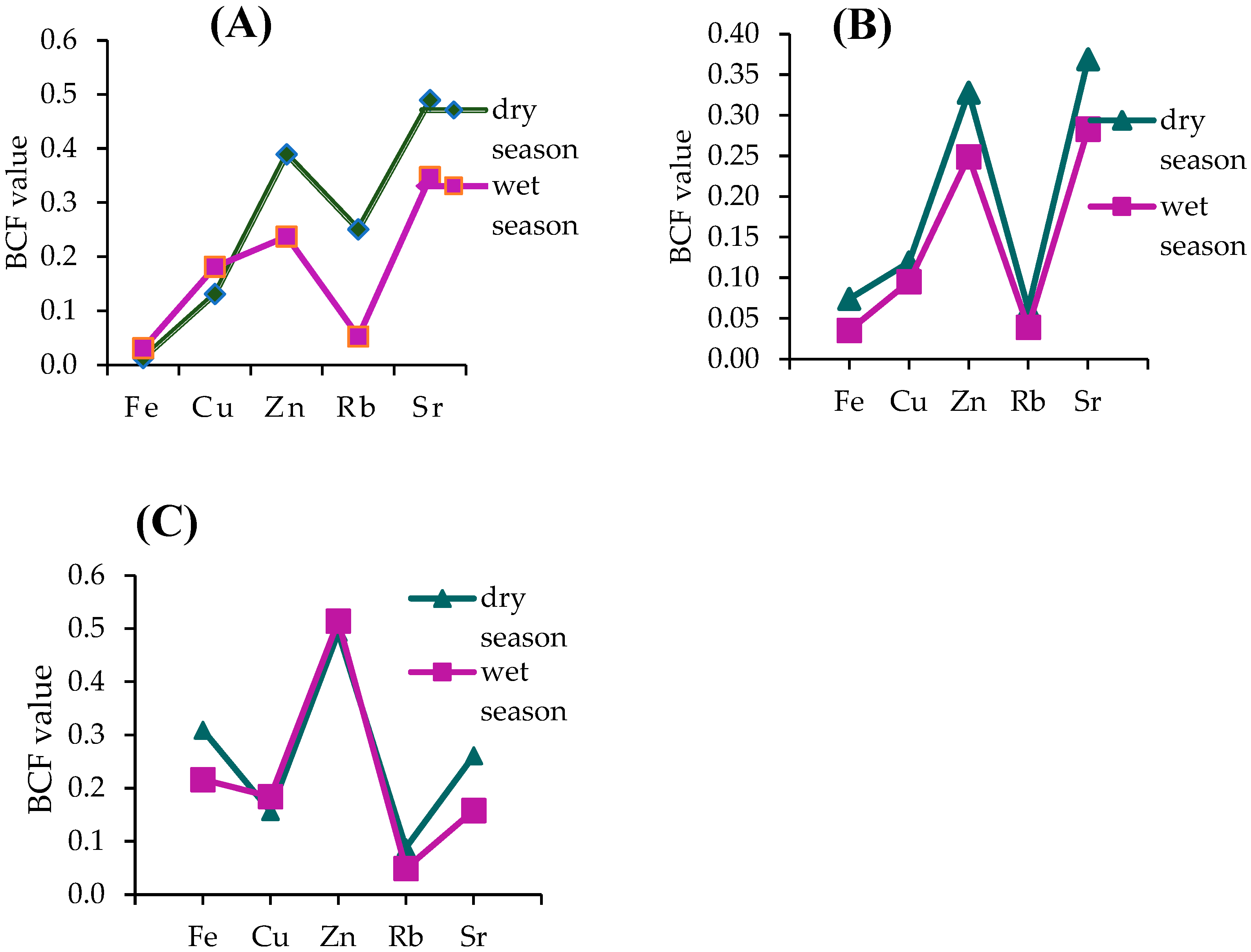
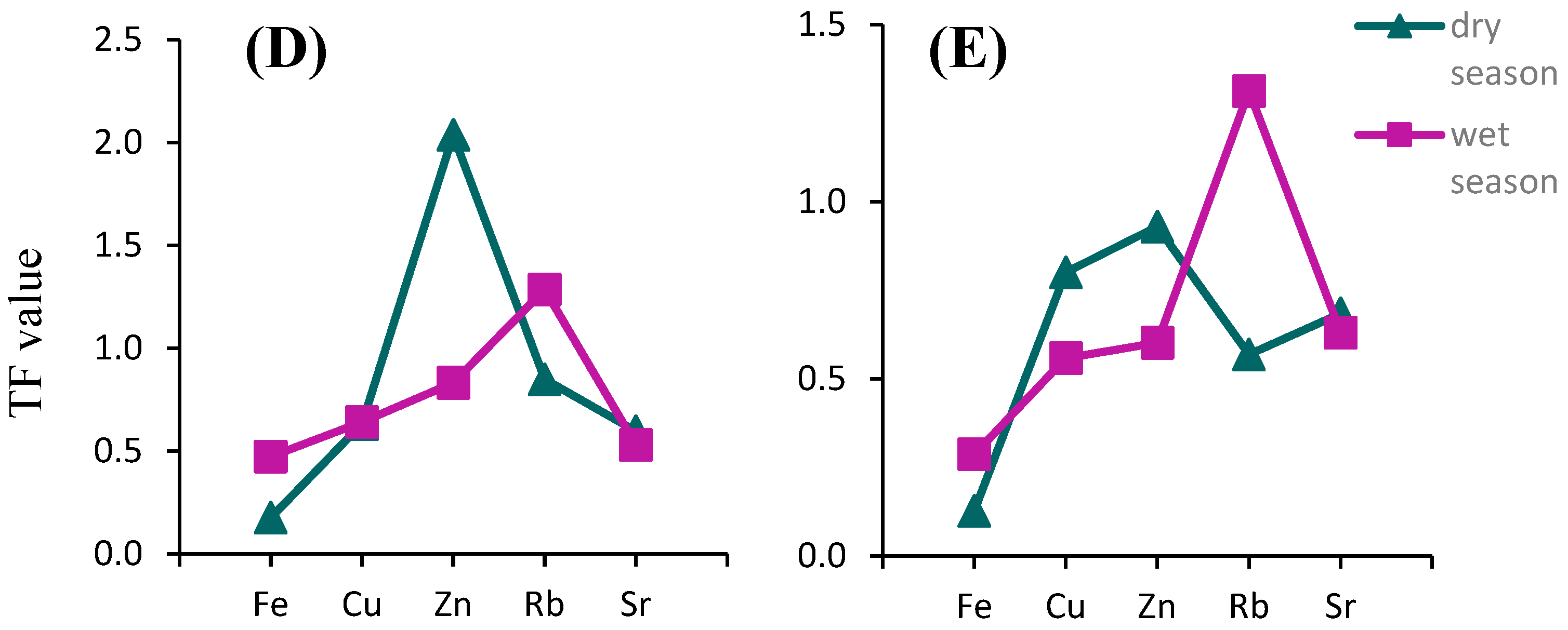
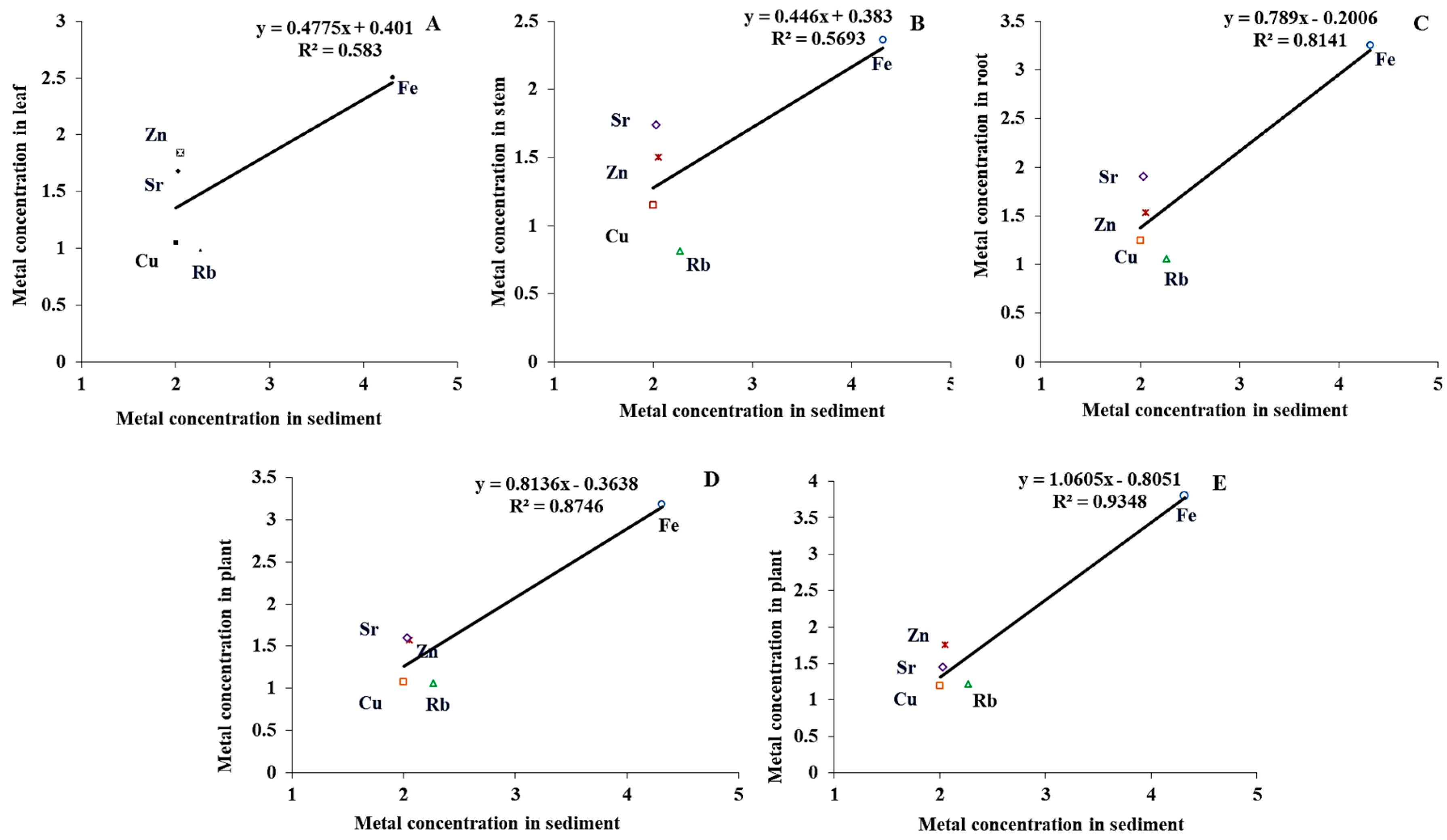

| Location | Fe | Cu | Zn | Sr | As | Rb | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ship-break area, Sitakunda, Chittagong | 68,260 | 18.7 | 151.5 | 142 | 10.55 | 226.4 | [7] |
| Tirumalairajn river, India | 2342 | 20.7 | 35.8 | - | - | - | [50] |
| Mediterranean coast, Egypt | 13,256 | 8.46 | 22.19 | - | - | - | [49] |
| Coastal sediment of Dumai, Indonesia | 30,100 | 6.08 | 53.89 | - | - | - | [52] |
| Yangtze estuary, China | - | 29 | 93 | - | 10.1 | - | [67] |
| Meghna river estuary, Bangladesh | 1290 | 6.22 | 42.41 | - | - | - | [51] |
| Karnaphuli River estuary, Bangladesh (dry season) | 20,600 | 100.39 | 113.53 | 107.33 | 6.29 | 185.86 | Present study |
| Certified values | 47,200 a | 33 b | 95 c | 300 d | 13 d | 140 d | - |
| Sampling Season | RI | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn | Cu | Zn | As | Co | ||
| Dry season | 1.10 | 15.21 | 1.20 | 4.84 | 2.023 | 24.37 |
| Wet season | 0.91 | 14.22 | 1.18 | 4.28 | 2.18 | 22.77 |
| Mean | 1.00 | 14.71 | 1.19 | 4.56 | 2.10 | |
| Site | Species | Fe | Cu | Zn | Rb | Sr | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mangrove forest of KVCR, India | Acanthus ilicifolius | 1163.67 | 144.8 | 22.7 | - | - | [74] |
| Mongla Sundarban, Bangladesh | Avicennia officinalis | 619.39 | 19.79 | 12.54 | - | 19.88 | [26] |
| Karnaphuli River estuary, Bangladesh | Acanthus ilicifolius | 784.64 | 14.29 | 45 | 9.19 | 60.98 | Current study |
| Egyptian lake Burullus | Typha domingensis | 29.9 | 8.9 | 7.7 | - | - | [71] |
| Wetland, Kwekwe, Zimbabwe | Typha capensis | 9413 | 35 | 162 | - | - | [73] |
| Karnaphuli River estuary, Bangladesh | Typha elephantina | 1531.52 | 11.96 | 37.19 | 11.46 | 39.6 | Current study |
| Nakivubo channelized stream, Uganda | Cynodon dactylon | 4018.77 | 73.75 | 148.38 | - | - | [12] |
| Karnaphuli River estuary, Bangladesh | Cynodon dactylon | 6376.89 | 15.71 | 55.97 | 16.44 | 28.02 | Current study |
| Wastewater irrigated area, Asmara, Eritrea | Cynodon dactylon | 1138.82 | 14.26 | 45.55 | - | - | [72] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tanjin, F.; Rahman, M.M.; Jolly, Y.N.; Riya, K.K.; Akter, S.; Albeshr, M.F.; Arai, T.; Yu, J.; Hossain, M.B. Accumulation and Phytoremediation Potentiality of Trace and Heavy Metals in Some Selected Aquatic Plants from a Highly Urbanized Subtropical Estuary. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12071131
Tanjin F, Rahman MM, Jolly YN, Riya KK, Akter S, Albeshr MF, Arai T, Yu J, Hossain MB. Accumulation and Phytoremediation Potentiality of Trace and Heavy Metals in Some Selected Aquatic Plants from a Highly Urbanized Subtropical Estuary. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2024; 12(7):1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12071131
Chicago/Turabian StyleTanjin, Fatema, Md. Mofizur Rahman, Yeasmin Nahar Jolly, Khadijatul Kubra Riya, Shirin Akter, Mohammed Fahad Albeshr, Takaomi Arai, Jimmy Yu, and Mohammad Belal Hossain. 2024. "Accumulation and Phytoremediation Potentiality of Trace and Heavy Metals in Some Selected Aquatic Plants from a Highly Urbanized Subtropical Estuary" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 12, no. 7: 1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12071131
APA StyleTanjin, F., Rahman, M. M., Jolly, Y. N., Riya, K. K., Akter, S., Albeshr, M. F., Arai, T., Yu, J., & Hossain, M. B. (2024). Accumulation and Phytoremediation Potentiality of Trace and Heavy Metals in Some Selected Aquatic Plants from a Highly Urbanized Subtropical Estuary. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 12(7), 1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12071131











