The Formation and Modification of the Arcuate Tectonic Belt in the Northeastern Tibetan Plateau: Insight from Three-Dimensional Finite Element Numerical Simulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
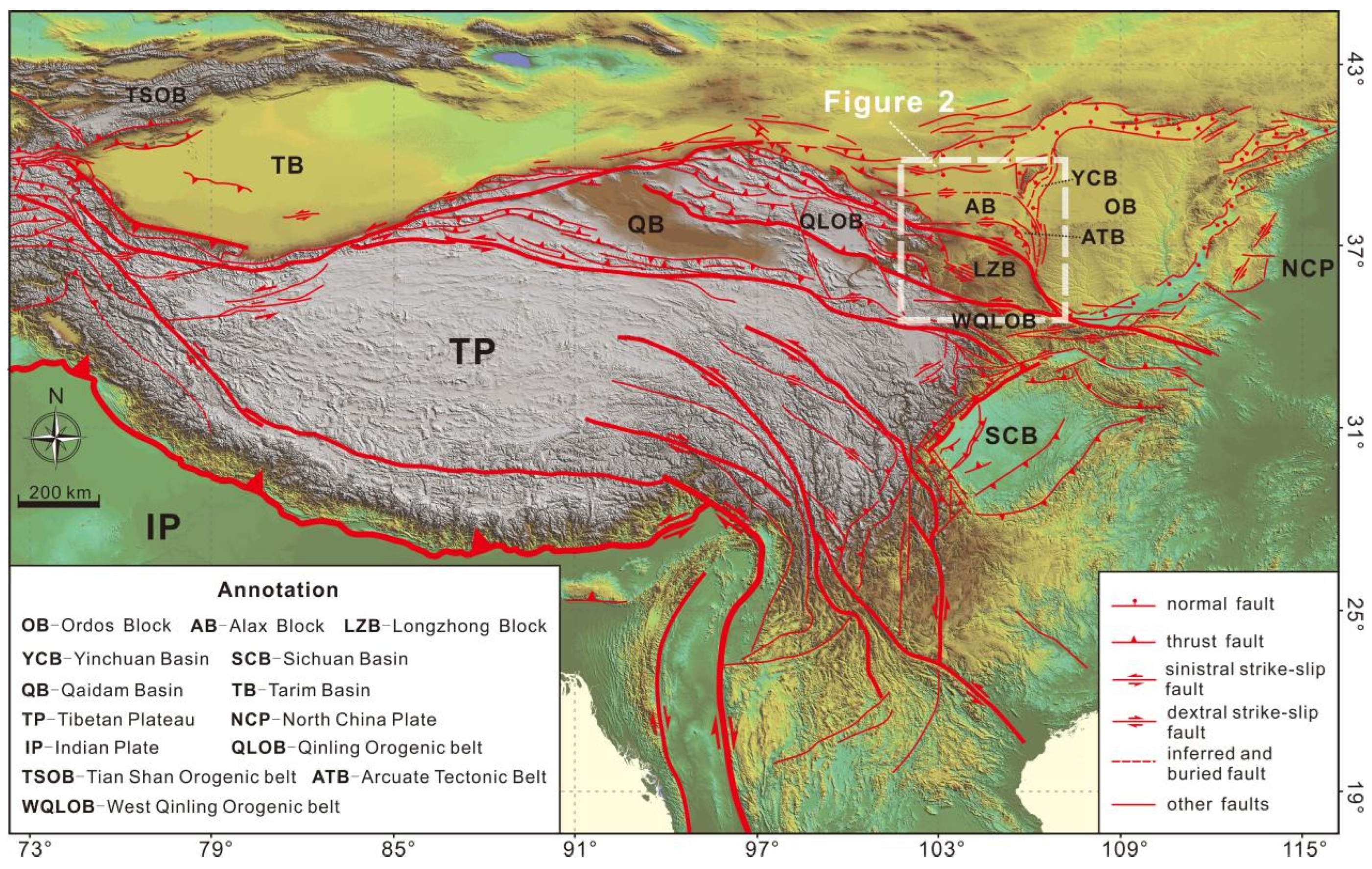
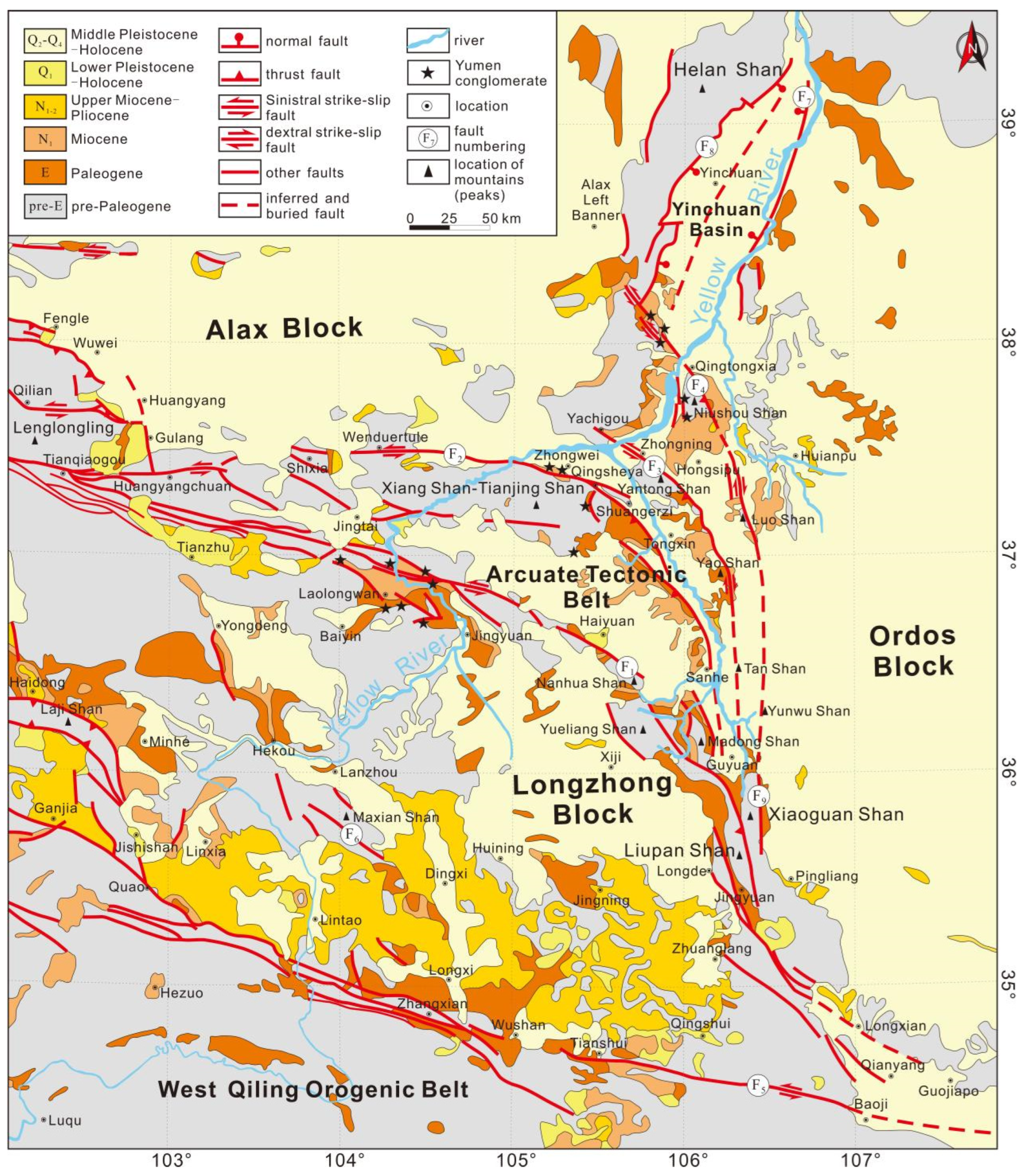
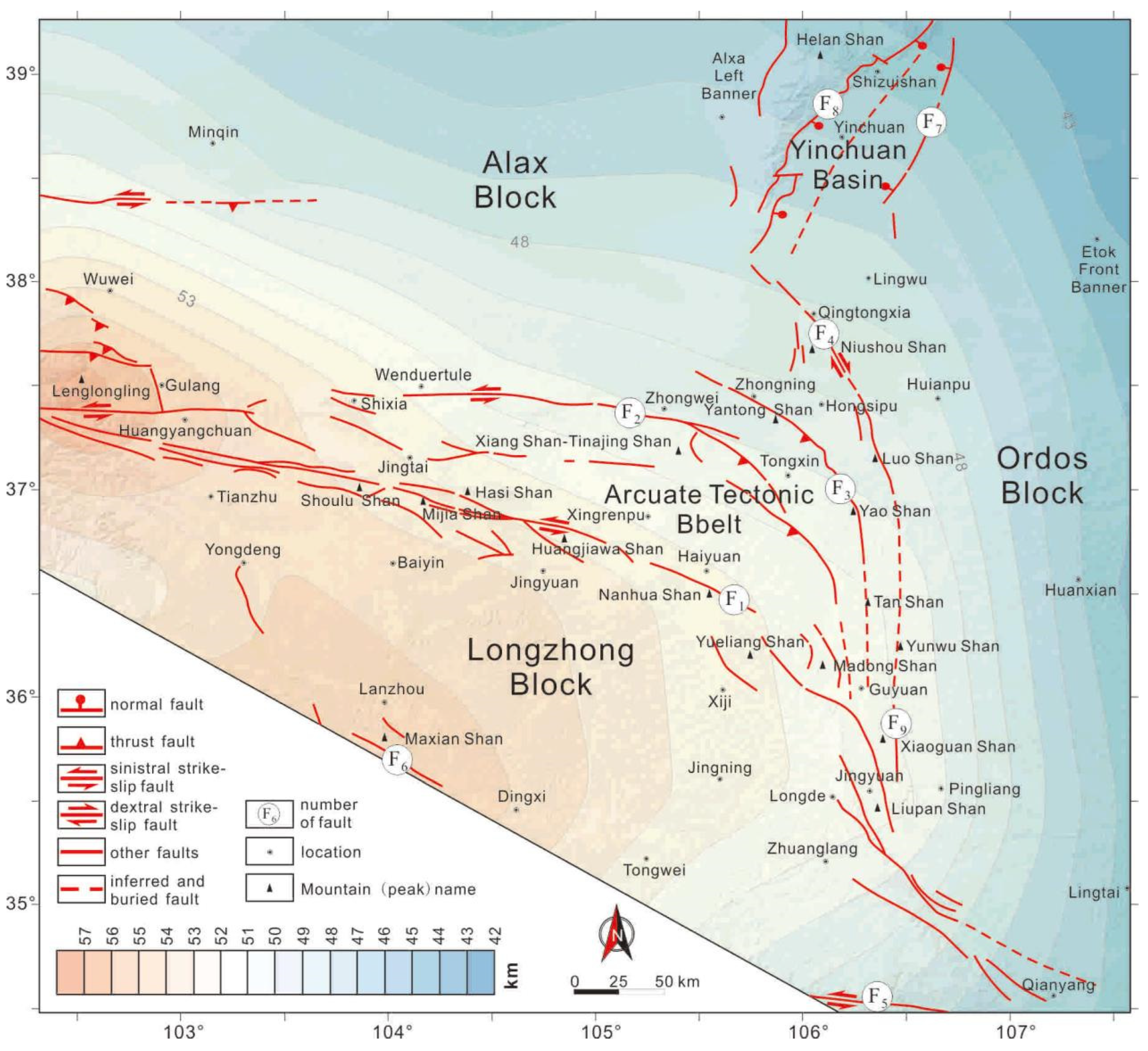
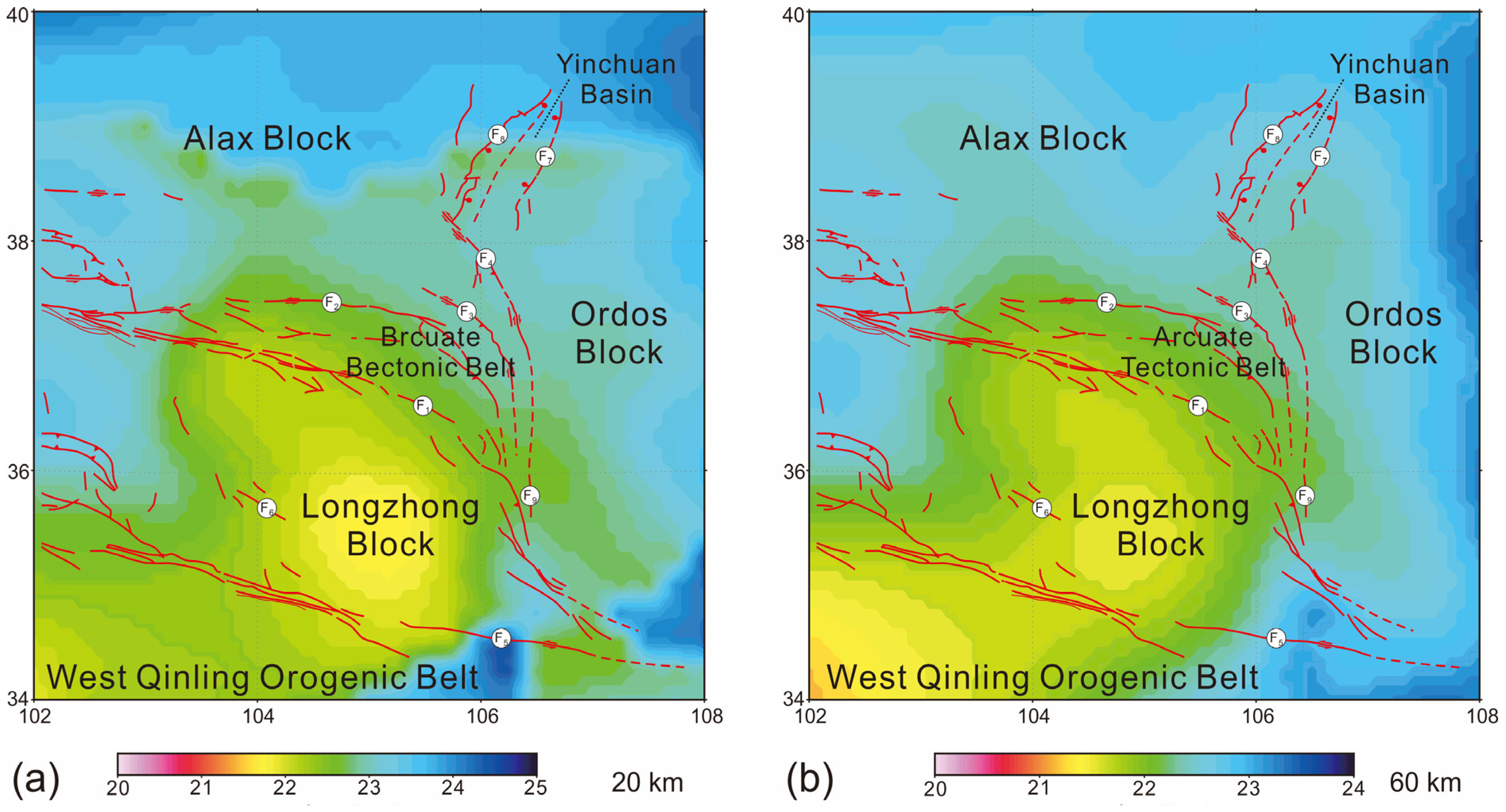
2. Geological and Geophysical Background
2.1. Tectonic Setting
2.2. Distribution Characteristics of Crustal Thickness and Rheological Strength
3. Numerical Model
3.1. Governing Equation
3.2. Finite Element Model and Boundary Conditions
3.3. Model Parameters
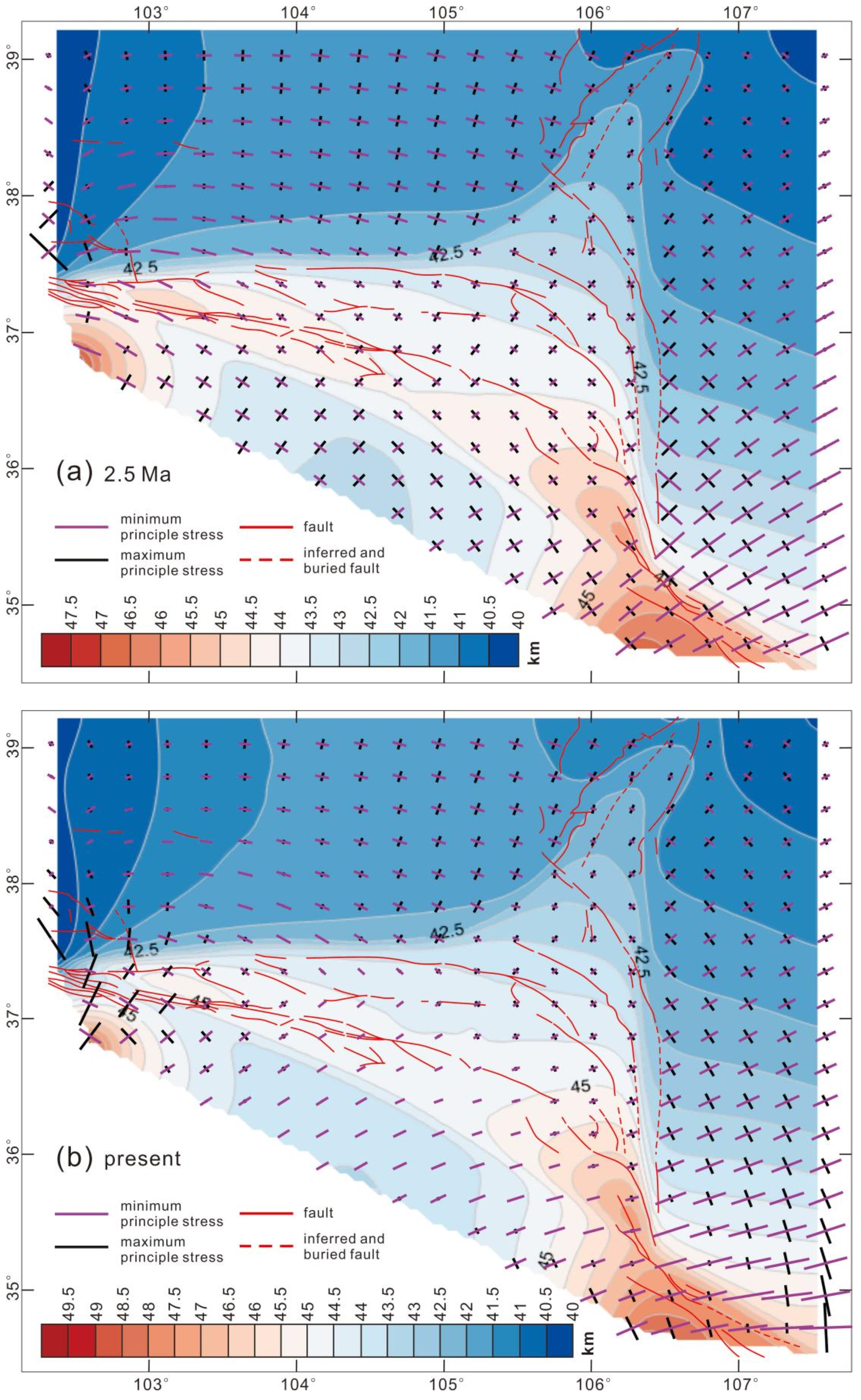
4. Results
4.1. Impact of Horizontal Strength Variation on Arcuate Tectonic Belt Formation
4.2. Effect of the Directional Change in Block Convergence Velocity on Crustal Thickness and Stress Field
4.3. Impact of Vertical Strength Variation on Arcuate Tectonic Belt Formation
5. Discussion
5.1. Formation of the Arcuate Tectonic Belt and the Horizontal Heterogeneity of Lithospheric Strength
5.2. Formation of the Arcuate Tectonic Belt and the Vertical Heterogeneity in Lithospheric Strength
5.3. Model Limitation
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- The lateral heterogeneity of lithospheric strength in the northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau governs the formation of the arcuate tectonic belt. When the lithospheric strength of the Meso-Cenozoic basins is 0.25 times or less than that of the Alax and Ordos blocks, it is more favorable for the formation of the arcuate tectonic belt and the northeastward expansion of the Tibetan Plateau. During the formation of the arcuate tectonic belt, intense shearing deformation occurs along the southern boundary of the Alax block and the western boundary of the Ordos block.
- (2)
- The simulation results show that when the viscosity of the middle crust is 10 times that of the lower crust and 0.1 times that of the upper crust, the crust is more conducive to shortening and thickening. The weak middle-lower crust of the Tibetan Plateau is beneficial for the formation of the arcuate tectonic belt and crustal thickening. However, it does not alter the deformation and geomorphology resulting from the horizontal heterogeneity of the lithospheric strength.
- (3)
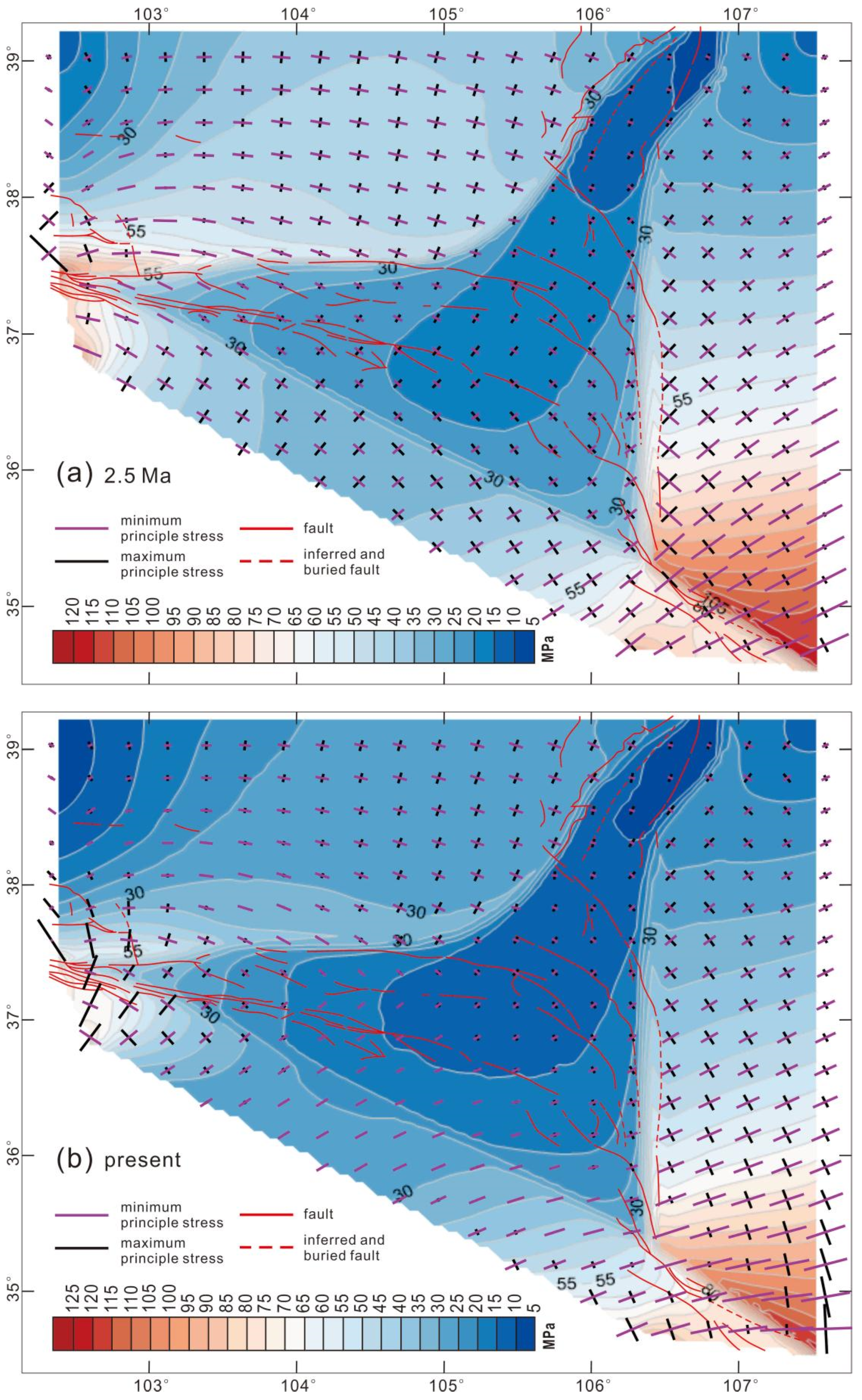
- In combination with geological surveys, our results indicate that the arcuate tectonic belt was formed during the NE-SW compression stage from 9.5 to 2.5 Ma. The crustal shortening and thickening propagated from the Haiyuan fault zone to the northeast. Since 2.5 Ma, the faults within the arcuate tectonic belt mainly exhibited strike-slip behavior under the ENE-WSW compression. In the Liupan Shan region, however, the faults showed a nearly E-W orientation with thrust faulting characteristics. Throughout this process, crustal shortening and surface uplift were relatively slight, and the process was primarily characterized by the modification of the geomorphological pattern.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Molnar, P.; Tapponnier, P. Cenozoic Tectonics of Asia: Effects of a continental collision. Science 1975, 189, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Replumaz, A.; Tapponnier, P. Reconstruction of the Deformed Collision Zone between India and Asia by Backward Motion of Lithospheric Blocks. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2003, 108, 2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapponnier, P.; Peltzer, G.; Armijo, R.; Le Dain, A.-Y.; Cobbold, P. Propagating Extrusion Tectonics in Asia: New Insights from Simple Experiments with Plasticine. Geology 1982, 10, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapponnier, P.; Xu, Z.-Q.; Roger, F.; Meyer, B.; Arnaud, B.N.; Wittlinger, G.; Yang, J.-S. Oblique stepwise rise and growth of the Tibet Plateau. Science 2001, 294, 1671–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Z.; Li, Q.S.; Gao, R.; Zhang, H.S.; Shen, X.Z.; Liu, X.Z.; Gong, C. Anisotropic Regime across Northeastern Tibet and Its Geodynamic Implications. Tectonophysics 2016, 671, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.-L.; Zhu, C.-Y.; Wang, G.-C.; Zhang, P. Demarcation of the Geomorphological Boundaries of Southeastern Tibet: Implications for Expansion Mechanisms of the Plateau Edge. Seismol. Geol. 2019, 41, 281–299, (In Chinese with an English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Molnar, P.; Tapponnier, P. Active Tectonics of Tibet. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1978, 83, 5361–5375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapponnier, P.; Molnar, P. Active Faulting and Tectonics in China. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1977, 82, 2905–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Pei, S.-P.; Cui, Z.-X.; Chen, Y.J.; Liu, Y.-B.; Xue, X.-T.; Li, J.-W.; Li, L.; Zuo, H. A New Growth Model of the Northeastern Tibetan Plateau from High-Resolution Seismic Imaging by Improved Double-Difference Tomography. Tectonophysics 2021, 798, 228699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.-Y.; Luo, A.-X.; Wang, C.-Y.; Ouyang, Z.-J.; Feng, J.-P. Formation and Evolution Characteristics of Arcuate Tectonic Belt. J. Xi’an Univ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 42, 752–759, (In Chinese with an English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, C.-P.; Li, W.; Xu, S.-Z.; Zhang, J.; Gao, S.-N.; Jia, C. The characteristics and formation mechanism of the curved structural belt. Chin. J. Geol. 2018, 53, 1171–1185, (In Chinese with an English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Dong, S.-W.; Liu, Y.; Hu, J.-M.; Chen, X.-H.; Chen, P. Cenozoic Tectonic Evolution of the South Ningxia Region, Northeastern Tibetan Plateau Inferred from New Structural Investigations and Fault Kinematic Analyses. Tectonophysics 2015, 649, 139–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.-P.; Li, Z.-H.; Huang, T.; Jiang, B.-Y.; Cui, J.-W. Origin of the Latent Palaeohigh in Hongsibu Basin of Ningxia, China and Its Effect on the Regional Desertification. J. Earth Sci. Environ. 2020, 42, 688–700, (In Chinese with an English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Q.-Y.; Zhang, P.-Z.; Zheng, W.-J.; Chai, C.-Z.; Wang, W.-T.; Du, P.; Yu, J.-X. Dextral Strike-slip of Sanguankou-Niushoushan Fault Zone and Extension of Arc Tectonic Belt in the Northeastern Margin of the Tibet Plateau. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2016, 46, 691–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.-B.; Shi, W.; Chen, H.; Qiu, S.-D.; Yin, Y.-G.; Zhao, Y. Quaternary Active Characteristics of the Liumugao Fault in the Northern Segment of the Niushoushan-Luoshan Fault. Geol. J. 2016, 22, 1004–1014. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Qin, X.; Shi, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Z.-X. Segmentation of the Active Liumugao Fault, NE Tibetan Plateau as Revealed by DEM-derived Geomorphic Indices. GeoSyst. GeoEnviron. 2022, 1, 100056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Hu, J.-M.; Gong, W.-B.; Kang, R.; Li, L.-B. Characteristics and Transition Mechanism of Late Cenozoic Structural Deformation within the Niushoushan–Luoshan Fault Zone at the Northeastern Margin of the Tibetan Plateau. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 114, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-C.; Shan, X.-J.; Qu, C.-Y.; Wang, Z.-J. Fault Locking and Slip Rate Deficit of the Haiyuan-Liupanshan Fault Zone in the Northeastern Margin of the Tibetan Plateau. J. Geodyn. 2016, 102, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-N.; Li, C.-Y.; Pierce, I.K.D.; Zhang, P.-Z.; Zheng, W.-J.; Dong, J.-Y.; Chen, G.; Ai, M.; Ren, G.-X.; Luo, Q.-X. New Slip Rates for the Tianjingshan Fault Using Optically Stimulated Luminescence, GPS, and Paleoseismic Data, NE Tibet, China. Tectonophysics 2019, 755, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.-J.; Ding, G.-Y. The Tectonic Feature of a Quasi-trijunction in the Northeastern Corner of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Earthq. Res. China 1998, 14, 27–35, (In Chinese with an English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.-T.; Zhang, P.-Z.; Lei, Q.-Y. Deformational Characteristics of the Niushoushan-Luoshan Fault Zone and Its Tectonic Implications. Seismol. Geol. 2013, 35, 195–207, (In Chinese with an English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.-Z.; Hu, C.-B.; Orellana-Rovirosa, F.; Zhang, K.-J.; Zhou, L.-S.; Zhang, H.; Shi, Y.-L. Geodynamics of Progressive Growth of Arcuate Fold-and-Thrust Belts: Insights from Numerical Modeling of the NE Margin of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. J. Struct. Geol. 2023, 175, 104939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.-Y.; Shi, W.; Hou, G.-T.; Wang, J.-Q.; Li, Z.-C.; Zhao, Y.-L. Neogene Paleomagnetic Chronology of the Laolongwan Basin, NW China: New Insight for the Northeastward Expansion of the Tibetan Plateau. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2024, 265, 106115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.-X.; Shi, W.; Yang, Y. Late Cenozoic Geomorphic Evolution in the Northeastern Tibetan Plateau: Constraints on U-Pb Age Spectra of Detrital Zircons in the Wuwei Basin, NW China. Geomorphology 2024, 449, 109044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Hu, J.-M.; Chen, P.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.-C.; Qin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y. Yumen Conglomerate Ages in the South Ningxia Basin, North-eastern Tibetan Plateau, as Constrained by Cosmogenic Dating. Geol. J. 2020, 55, 7138–7147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burov, E.B. Rheology and Strength of the Lithosphere. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2011, 28, 1402–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Yang, Y.-Q. Extensional Collapse of the Tibetan Plateau: Results of Three-dimensional Finite Element Modeling. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2003, 108, 2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, R.; Mooney, W. Weakness of the Lower Continental Crust: A Condition for Delamination, Uplift, and Escape. Tectonophysics 1998, 296, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, S.X.; Wei, R.Q.; Liu, Y.G. Three-dimensional rheological structure of the lithosphere in the Ordos and its adjacent area. Geophys. J. Int. 2005, 163, 339–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, S.X.; Wei, R.-Q.; Ning, J.-Y. Effect of the Brittle Fracture on the Rheological Structure of the Lithosphere and Its Applications in the Ordos. Tectonophysics 2007, 429, 267–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.-L.; Morgan, W.J. Injection of Indian Crust into Tibetan Lower Crust. Tectonics 1987, 6, 489–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Dong, S.-W.; Hu, J.-M. Neotectonics around the Ordos Block, North China: A Review and New Insights. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020, 200, 102969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-C.; Shan, X.-J.; Qu, C.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Song, X.-G.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, G.-H.; Nocquet, J.-M.; Gong, W.-Y.; Gan, W.-J.; et al. Elastic Block and Strain Modeling of GPS Data around the HaiyuanLiupanshan Fault, Northeastern Tibetan Plateau. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2017, 150, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; He, H.-L.; Gao, W.; Sun, H.-Y.; Wei, Z.-Y.; Hao, H.-J.; Zou, J.-J.; Sun, W.; Su, P. Holocene Paleoearthquakes on the Tianqiaogou-Huangyangchuan Fault in the Northeastern Boundary Fault System of the Tibetan Plateau. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2019, 186, 104049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.-F.; Chen, H.-L.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.-Z. Activities and Geomorphic Deformation of the Fault Belt on the Southern Margin of Wuwei Basin, Gansu Province during the Late Quaternary. Geol. Bull. China 2022, 41, 327–346, (In Chinese with an English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, Y.; Zhao, G.-Z.; Wang, J.-J.; Tang, J.; Chen, X.-B.; Deng, Q.-H.; Xuan, F.; Zhao, J.-M. Crustal Electric Structure of Haiyuan Arcuate Tectonic Region in the Northeastern Margin of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau, China. Acta Seismol. Sin. 2005, 27, 431–440, (In Chinese with an English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.-Z.; Lin, Y.-Q.; Xu, X.; Li, H.-L.; Guo, X.-Y.; Li, C.-S.; Tong, X.-F. Crustal-scale Architecture and Origin of the Haiyuan Arcuate Tectonic Belt, NE Tibet. Tectonophysics 2024, 890, 230485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.-H.; Pan, S.-Z.; Wang, F.-Y.; Tian, X.-F.; Liu, B.-F.; Song, J.-J. Deep Crustal Structure and Deformation Features of the Northeastern Margin of the Tibetan Plateau, as Revealed by Controlled-source Seismic Profiling along the Aba-Guyuan-Wuqi Transect. Tectonophysics 2024, 885, 230418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Hu, J.-M.; Gong, W.-B.; Li, L.-B. Cenozoic Deformation and Evolution of the Niushou Shan-Luo Shan Fault Zone in the Northeast Margin of the Tibet Plateau. Earth Sci. Front. 2013, 20, 18–35, (In Chinese with an English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Laske, G.; Masters, G.; Ma, Z.-T.; Pasyanos, M.E. Update on CRUST1.0: A 1-degree Global Model of Earth’s Crust. Geophys. Res. Abstr. 2013, 15, 2658. [Google Scholar]
- Walter, D.M.; Carol, B.-L.; María, G.S.; Miguel, A.C. Earth Crustal Model 1(ECM1): A 1° × 1° Global Seismic and Density Model. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2023, 243, 104493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-F.; Chen, J.-H.; Guo, B.; Li, S.-C.; Li, Y.; Qi, S.-H.; Zhao, P.-P. Seismic Structure and Deformation Features beneath the Yinchuan-Hetao Graben, NW China. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 2022, 329–330, 106911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.-J.; Feng, S.-Y.; Ji, J.-F.; Wang, S.-J.; Zhang, J.-S.; Yuan, H.-K.; Yang, G.-J. Lithospheric Structure and Faulting Characteristics of the Helan Mountains and Yinchuan Basin: Results of Deep Seismic Reflection Profiling. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2017, 60, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-J.; Liu, B.-J.; Jia, S.-X.; Deng, X.-G.; Song, X.-H.; Li, Y.-Q. Study on S-wave Velocity Structure Difference of Yinchuan Basin and Blocks on Both Sides Using Artificial Seismic Sounding Profiles. Prog. Geophys. 2017, 32, 1936–1943, (In Chinese with an English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.-B.; Bai, Z.-M.; Klemperer, S.L.; Liang, X.-F.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Yang, X.-S.; Wei, Y.-H.; Zhu, G.-H. Crustal-Scale Wedge Tectonics at the Narrow Boundary between the Tibetan Plateau and Ordos Block. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2021, 554, 116700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-J.; Liu, B.-J.; Tian, X.-F.; Liu, B.-F.; Song, X.-H.; Deng, X.-G.; Sun, Y.-N.; Ma, C.-J.; Yang, Y.-D. Crustal P-wave Velocity Structure in the Northeastern Margin of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau and Insights into Crustal Deformation. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2019, 61, 1221–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-J.; Bai, Z.-M.; Klemperer, S.L.; Tian, X.-B.; Xu, T.; Chen, Y.; Teng, J.-W. Crustal Structure across Northeastern Tibet from Wide-Angle Seismic Profiling: Constraints on the Caledonian Qilian Orogeny and Its Reactivation. Tectonophysics 2013, 606, 140–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coblentz, D.D.; Richardson, R.M. Analysis of the South American Intraplate Stress Field. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1996, 101, 8643–8657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, R.M. Finite Element Modeling of Stress in the Nazca Plate: Driving Forces and Plate Boundary Earthquakes. Tectonophysics 1978, 50, 223–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.K.; Bush, J.W.M.; Royden, L.H. Dynamic Topography Produced by Lower Crustal Flow against Rheological Strength Heterogeneities Bordering the Tibetan Plateau. Geophys. J. Int. 2005, 162, 575–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, K.L.; Royden, L.H. The Role of Crustal Strength Variations in Shaping Orogenic Plateaus, with Application to Tibet. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2008, 113, B08407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- England, P.; Houseman, G. Finite Strain Calculations of Continental Deformation 2. Comparison with the India–Asia Collision Zone. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1986, 91, 3664–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- England, P.; McKenzie, D. A Thin Viscous Sheet Model for Continental Deformation. Geophys. J. R. Astron. Soc. 1986, 70, 295–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houseman, G.; England, P. Finite Strain Calculations of Continental Deformation 1. Method and General Results for Convergent Zones. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1986, 91, 3651–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royden, L.H.; Burchfie, B.C.; King, R.W.; Wang, E.; Chen, Z.-L.; Shen, F.; Liu, Y.-P. Surface Deformation and Lower Crustal Flow in Eastern Tibet. Science 1997, 276, 788–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.-J.; Dong, S.-W.; Zhang, H.; Shi, Y.-L. Numerical Investigation of the Geodynamic Mechanism for the Late Jurassic Deformation of the Ordos Block and Surrounding Orogenic Belts. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 114, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buiter, S.J.H.; Babeyko, A.Y.; Ellis, S.; Gerya, T.V.; Kaus, B.J.P.; Kellner, A.; Schreurs, G.; Yamada, Y. The Numerical Sandbox: Comparison of Model Results for a Shortening and an Extension Experiment. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2006, 253, 29–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerya, T.V.; Yuen, D.A. Characteristics-Based Marker-in-Cell Method with Conservative Finite-Differences Schemes for Modeling Geological Flows with Strongly Variable Transport Properties. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 2003, 140, 293–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.-J.; Liu, M. Edge-Driven Asthenospheric Convection beneath the North China Craton: A Numerical Study. Tectonophysics 2023, 849, 229726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.-M.; Niu, F.-L.; Ding, Z.-F.; Chen, Q.-F. Complicated Crustal Deformation beneath the NE Margin of the Tibetan Plateau and Its Adjacent Areas Revealed by Multi-station Receiver-function Gathering. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2018, 497, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royden, L.H.; Burchfie, B.C.; Robert, D.V.D.H. The Geological Evolution of the Tibetan Plateau. Science 2008, 321, 1054–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.-J.; Liu, M. Rheological control of lateral growth of the Tibetan Plateau: Numerical results. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2018, 123, 10124–10141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.-J.; Dong, S.-W.; Liu, M.; Zhang, H.; Shi, Y.-L. The Rheological Structure of East Asian Continental Lithosphere. Tectonophysics 2025, 895, 230575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucazeau, F. Analysis and mapping of an updated terrestrial heat flow data set. Geochem. Geophys. Geo Syst. 2019, 20, 4001–4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-L.; Ye, Z.; Gao, R.; Huang, X.-F. A Distinct Contrast in the Lithospheric Structure and Limited Crustal Flow across the Northeastern Tibetan Plateau: Evidence from Vs and Vp/Vs Imaging. Tectonophysics 2022, 836, 229413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-N.; Li, C.-Y.; Zhang, P.-Z.; Wang, X.-G.; Zhang, L.-S. Changes in Fault Movement Property and Genetic Mechanism on the Western Segment of the Xiangshan-Tianjingshan Fault Zone. Seismol. Geol. 2016, 38, 732–746, (In Chinese with an English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.K.; Royden, L.H. Topographic Ooze: Building the Eastern Margin of Tibet by Lower Crustal Flow. Geology 2000, 28, 703–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.-J.; Hu, D.-G.; Zhang, H.; Fan, T.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Li, B.; Shi, Y.-L. Numerical Study on the Dynamics of Lithospheric Deformation Pattern in the Northeastern Tibetan plateau. Prog. Geophys. 2017, 32, 2383–2393, (In Chinese with an English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.-J.; Mooney, W.D.; Li, S.-L.; Okaya, N.; Detweiler, S. Crustal Structure of the Northeastern Margin of the Tibetan Plateau from the Songpan-Ganzi Terrane to the Ordos Basin. Tectonophysics 2006, 420, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Fault | Initial Age Ma | Maximum Horizontal Compression | Tectonic Event | Fault Mechanism | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | ~9.5 | NE-SW | thrust | thrust | [12,14,21] |
| 5.4 | ENE-WSW | thrust and strike-slip | thrust and sinistral strike-slip | ||
| 2.6 | strike-slip | sinistral strike-slip (west); thrust and sinistral strike-slip (east) | |||
| F2 | 5.4 | NE-SW | thrust | thrust and sinistral strike-slip | [14,21] |
| ~2.7 | ENE-WSW | strike-slip | normal-sinistral strike-slip (west); thrust and sinistral strike-slip (east) | ||
| F3 | 5.4 or ~2.7 | NE-SW or ENE-WSW | thrust | thrust and dextral strike-slip | [13,14,21] |
| F4 | ~2.5 | NW-SE | thrust and strike-slip | thrust and sinistral strike-slip | [14,17,39] |
| 0.15 | NNE-SSW | strike-slip | dextral strike-slip |
| Block | Case–1 (Pa·s) | Case–2 (Pa·s) | Case–3 (Pa·s) | Case–4 (Pa·s) | Case–5 (Pa·s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OB and AB | 1 × 1023 | 1 × 1023 | 1 × 1023 | 1 × 1023 | 1 × 1023 |
| M-CB | 1 × 1023 | 5 × 1022 | 2.5 × 1022 | 1 × 1022 | 2.5 × 1022 |
| LZB | 1 × 1023 | 5 × 1022 | 2.5 × 1022 | 1 × 1022 | 5 × 1022 |
| Block | Layer | Case–6 (Pa·s) | Case–7 (Pa·s) | Case–8 (Pa·s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OB and AB | UC | 1 × 1023 | 1 × 1023 | 1 × 1023 |
| MC | 1 × 1023 | 1 × 1023 | 1 × 1023 | |
| LC | 1 × 1023 | 1 × 1023 | 1 × 1023 | |
| LM | 1 × 1023 | 1 × 1023 | 1 × 1023 | |
| M-CB | UC | 2.5 × 1022 | 2.5 × 1022 | 2.5 × 1022 |
| MC | 2.5 × 1022 | 2.5 × 1022 | 7.5 × 1021 | |
| LC | 7.5 × 1021 | 7.5 × 1020 | 7.5 × 1020 | |
| LM | 2.5 × 1022 | 2.5 × 1022 | 2.5 × 1022 | |
| LZB | UC | 5 × 1022 | 5 × 1022 | 5 × 1022 |
| MC | 5 × 1022 | 5 × 1022 | 5 × 1021 | |
| LC | 5 × 1021 | 5 × 1020 | 5 × 1020 | |
| LM | 5 × 1022 | 5 × 1022 | 5 × 1022 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Shi, W.; Sun, Y.; Hou, G. The Formation and Modification of the Arcuate Tectonic Belt in the Northeastern Tibetan Plateau: Insight from Three-Dimensional Finite Element Numerical Simulation. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13010170
Zhao Y, Shi W, Sun Y, Hou G. The Formation and Modification of the Arcuate Tectonic Belt in the Northeastern Tibetan Plateau: Insight from Three-Dimensional Finite Element Numerical Simulation. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(1):170. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13010170
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yilin, Wei Shi, Yujun Sun, and Guiting Hou. 2025. "The Formation and Modification of the Arcuate Tectonic Belt in the Northeastern Tibetan Plateau: Insight from Three-Dimensional Finite Element Numerical Simulation" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 1: 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13010170
APA StyleZhao, Y., Shi, W., Sun, Y., & Hou, G. (2025). The Formation and Modification of the Arcuate Tectonic Belt in the Northeastern Tibetan Plateau: Insight from Three-Dimensional Finite Element Numerical Simulation. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(1), 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13010170





