Abstract
This study analyzes the mineralogical and geochemical composition of 38 surface sediment samples from the northwest African continental shelf between Cap Boujdour (26.5° N) and Cap Blanc (20.5° N). Using a multiproxy approach, sediment characteristics were assessed through grain size, calcium carbonate (CaCO3), and organic carbon (Corg) measurements, along with X-ray diffraction (XRD) and X-ray fluorescence (XRF) for geochemical analysis. Bottom water properties, including temperature, salinity, and dissolved oxygen, were measured at various stations using a Conductivity, Temperature, and Depth (CTD) sensor. The results reveal that the inner shelf sediments are primarily mud, with high concentrations of terrigenous elements such as iron (Fe), silicon (Si), rubidium (Rb), and potassium (K), with Fe and Si concentrations ranging from 2.1 to 4.3 wt%. The middle and outer shelf sediments are dominated by biogenic carbonates, with CaCO3 levels approaching 65%, and elevated calcium (Ca) and strontium (Sr) content. These areas also exhibit the highest bottom water temperatures (up to 16 °C), salinity (36%), and moderate oxygen levels (2–4 mL/L). Slope sediments are enriched with mud and montmorillonite, and aeolian contributions are more pronounced south of Dakhla, as indicated by elevated quartz levels (up to 20%) and the presence of illite, aluminum oxide (Al2O3), and iron oxide (Fe2O3). This study provides valuable new insights into sedimentary processes on the northwest African shelf, offering implications for regional environmental management and resource exploration.
1. Introduction
Continental shelf ecosystems are the interfaces between the oceanic domain and the human-occupied terrestrial realm, which make them an important component of the marine environment [1]. The study of continental shelf surface sediments provides valuable insight into how materials are sorted and deposited in deep-sea environments through various processes such as current drift, turbidity, and submarine landslides, revealing ocean dynamics [2,3,4,5,6,7]. The spatial and temporal characterization of these sediments aids in interpreting sedimentary archives collected from the same region, enabling the reconstruction of climatic and oceanographic changes, such as variations in temperature, salinity, and ocean currents over millennia [8]. These sediments also serve as a substrate for diverse life forms. For instance, the analysis of organic matter and carbonates in the sediments can offer clues about biological productivity and the health of deep-sea ecosystems. Certain marine species, including cold-water corals and sponges, rely on these sediment conditions to thrive. Understanding these habitats has important implications for the conservation of deep-sea ecosystems [2,3,4,9]. Additionally, there is an economic interest in studying these sediments, as they can help identify potential reservoirs of gas and oil, or organic-rich source rocks crucial for the formation of these resources. Some deep-sea sediments may also contain polymetallic nodules, ferromanganese crusts, or other valuable mineral resources of interest for the submarine mining industry [10,11,12].
Numerous studies have explored the characteristics of modern sedimentation along the southern part of the NW African Atlantic continental shelf, located in the Canary Current System, providing valuable data on sediment dynamics and depositional patterns [13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22]. However, despite these advances, the southern part of the NW African continental shelf remains critically understudied, with significant gaps in our understanding of key aspects such as the spatial distribution of surface sediments, sediment composition, and their controlling factors. Most of the existing studies were conducted during the 1970s and 1980s, leaving a notable temporal gap in our knowledge of more recent sedimentary processes.
The objective of the present study is to address this gap by providing updated insights into the temporal changes in sediment composition, particularly in response to environmental shifts and increasing human activities. Using advanced analytical techniques like X-ray fluorescence (XRF) and X-ray diffraction (XRD), along with hydrological assessments of bottom water, this research aims to generate more accurate and comprehensive data compared to earlier works. Furthermore, by collecting new samples from the northern part of the NW African continental shelf, this study seeks to enhance the spatial resolution of sedimentological and geochemical maps, capturing localized variations in sediment composition that may have been overlooked in previous studies due to lower sampling densities or less precise methodologies.
2. Study Area
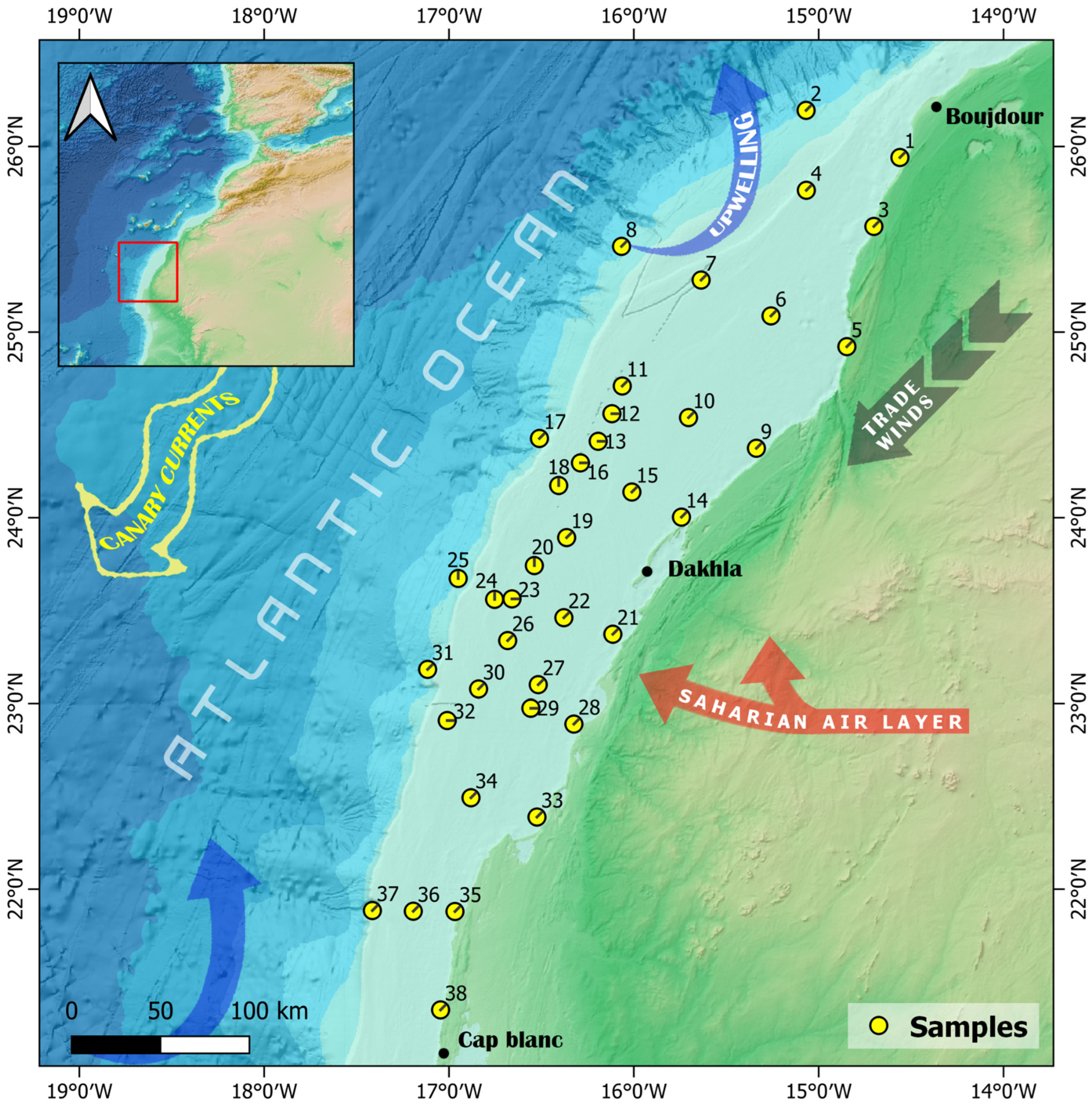
The study area is located in the NW African Atlantic continental shelf, between 26.5° N and 20.5° N (Figure 1). The shelf in this area extends around 120 km wide, with a depth shallower than 100 m [20,23,24]. Approximately 10 m of unconsolidated sediment cover most of the shelf, gradually thinning toward the shelf edge [25]. The slopes are dissected by canyon systems and channels revealed by several seismic studies [20,23,24]. As far as climatic parameters are concerned, the study area is influenced by the climate of the adjacent lands, which are characterized by an arid desert climate, with average annual rainfall of between 25 and 50 mm [15,26]. The precipitation pattern is highly irregular, typical of hyper-arid regions. Rainfall occurs only on a few days each year, often in brief, intense, and stormy bursts that significantly exceed the inter-annual average [27]. The arid climate and the presence of coastal dunes prevent the development of permanent rivers or streams [24]. Two dominant wind systems are present in the area: the northeast trade winds (indicated by the dark arrow in Figure 1) and the Saharan Air Layer (SAL) (indicated by the red arrow Figure 1). The northeast trade winds, driven by the Azores High, blow consistently from the northeast towards the southwest, particularly during the boreal winter. These winds play a crucial role in coastal dynamics, driving the nutrient-rich upwelling system along the coast (illustrated by the blue arrow in Figure 1), referred to as the Canary Current Upwelling system, which is key to the region’s high marine productivity [28]. In addition to upwelling, these surface winds contribute to the transport of Saharan dust, particularly during the dry season. The SAL, on the other hand, is a hot, dry air mass that forms over the Sahara Desert and travels at higher altitudes (1.5–6 km) across the Atlantic Ocean [29,30]. While the SAL’s influence peaks in summer, it significantly contributes to long-range dust transport, elevating dust particles, which contain iron (Fe), aluminum (Al), and other constituents that influence the ocean’s environment and biogeochemistry [31], to higher atmospheric levels and carrying them over the shelf and beyond. This combination of surface trade winds and elevated SAL dust transport shapes both the atmospheric and oceanographic conditions of the southern Moroccan continental shelf, affecting sediment deposition and marine ecosystems.
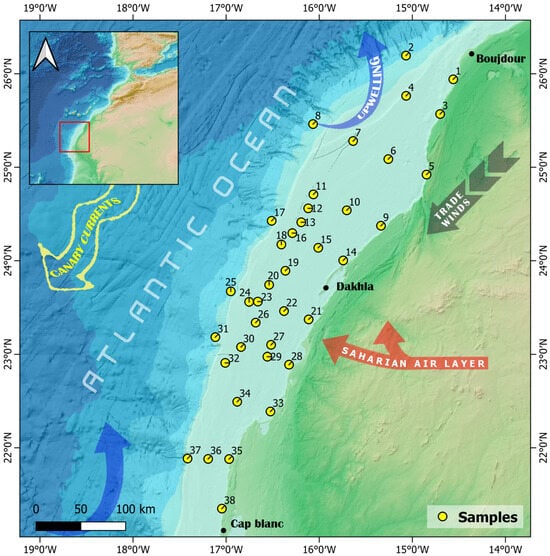
Figure 1.
Geographic position of the study area and spatial distribution of the collected samples (General Bathymetric Chart of the Oceans).
The major surface current in this area is the Canary Current (indicated by the large yellow arrow in Figure 1), which is part of the Eastern Boundary Current System and is characterized by a south-westward flow toward Cape Verde, where it joins the North Equatorial Current [32,33,34,35]. The interaction of the Canary Current, trade winds parallel to the coast, and the rotation of the Earth (Ekman transport) generates upwelling currents, which are very abundant along this part of the NW African continental shelf [32,36,37]. They bring to the surface cold, nutrient-rich waters (15–16 °C) with salinities around 36% and oxygen levels as low as 2 mL/L [36,38]. In addition, the upwelling brings low oxygenated water to the shelf that is rich in carbon dioxide (low pH) and, in the southern part (Cap Blanc), has relatively low calcium carbonate (CaCO3) saturation states [4]. This may have implications for the preservation of carbonate minerals in the sediment. The annual duration of upwelling is longest near Cape Blanc and decreases progressively both to the north and south [14,39,40,41,42]. It stimulates high primary productivity and leads to elevated concentrations of suspended organic matter [16,24,34,36,43,44].
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sampling of Sediment and Water Column Environment
Thirty-eight surface sediment samples were collected from the South Atlantic margin of NW Africa (26.5° N–20.5° N) using a Van Veen grab sampler aboard various research vessels, including Amir Moulay Abdellah (AMA), Al Hassan Al Marrakchi (AHAM), and R/V Dr. Fridtjof Nansen (DFN) (see Table 1), as part of multiple oceanographic programs: the oceanographic and environmental monitoring program (INRH) and the Ecosystem Assessment for Fisheries (EAF)-Nansen program. The sampling network is distributed along transects perpendicular and parallel to the coast, at depths ranging from 17 to 602 m (Figure 1). The grab collects surface sediment over a small area (approximately 0.1 m2), sampling the top 5–10 cm of mixed sediment. To avoid post-sampling contaminations, samples were freeze-dried in plastic bags for further analysis.

Table 1.
Location, sampling date, vessel, and collected variables.
To assess water column properties at the sediment sampling stations, vertical profiles of temperature (T, °C), salinity (Sal, psu), and dissolved oxygen (DO, mL/L) were conducted at each station. These data were obtained using a Conductivity–Temperature–Depth (CTD) sensor (Sea-Bird 911 plus) for temperature and salinity, and a dissolved oxygen sensor (SBE-43) for DO (Table 1).
For DFN data, water sampling was conducted at the offshore station to analyze salinity and DO for the validation and calibration of the DO and conductivity sensors. Salinity was measured using a Guildline Portasal 8410A salinometer, while DO was determined through Winkler titrations performed with a Metrohm 916 Ti-Touch potentiometric titrator.
3.2. Sedimentological Analysis
Particle size analysis was performed using a Mastersizer 3000 laser diffraction analyzer (Technology platform, Chouaib Doukkali University, El Jadida, Morocco), which measures particles between 0.375 and 3500 μm, with a particle refractive index of 1.555. Each measurement lasts approximately 30 s and is repeated twice to ensure good reproducibility of the results. Before measurements, samples rich in mud were suspended in distilled water for 24 h. Ultrasound is used during the measurement to ensure the good dispersion of fine particles. The grain size results were processed by the software GRADISTAT (version 4.0) [45], with the mud, sand, and gravel boundaries after Udden (1914) [46] and Wentworth (1932) [47]: clay and silt (mud) < 63 μm) and sand (63–2000 μm) and gravel (2–64 mm). The mean and sorting index was calculated according to Folk and Ward (1957) [48]:
where Φx represents the particle diameter (in phi units) corresponding to the xth percentile of the distribution.
Similarly, the sorting index (σ) is determined using the equation:
3.3. Geochemical Analysis
Non-destructive analysis (X-ray fluorescence) measurements were conducted using a Bruker S2 Puma 2 Energy Dispersive X-Ray Fluorescence device (Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA), which features a direct excitation beam path that fully utilizes its high-power 50-watt X-ray tube, set at 50 kV with a silver (Ag) anode.
X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis was performed using a Bruker D8 ADVANCE ECO X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) scanner, which use Kα radiation from copper with wavelength λ = 1.5406 A. The range of 2θ explored is between 10 and 70 degrees with a step size of 0.067°. The mineralogical phases of the obtained powders and salts are identified by comparison with those of the ICDD database (International Center for Diffraction Data). Organic matter was determined using the Loss on Ignition (LOI) protocol of Nelson and Sommers (1996) [49]. Each sample is dried, weighed, and heated to 550 °C for 4 h to burn the organic matter. The weight loss after this step is attributed to organic content. The calcium carbonate (CaCO3) was determined through Calcimetry (Gasometric Method) following the protocol of Fournier et al. (2012) [50].
3.4. Statistical Analysis
The statistical description, including the mean, standard deviation, and max and min, for the selected major and trace elements is summarized in Table 2, calculated using PAST software 4.03 [51]. The standard scree plot technique determined the number of components plotted.

Table 2.
Chemical composition of surface sediments.
4. Results
4.1. Hydrological Characteristics of the Bottom Water
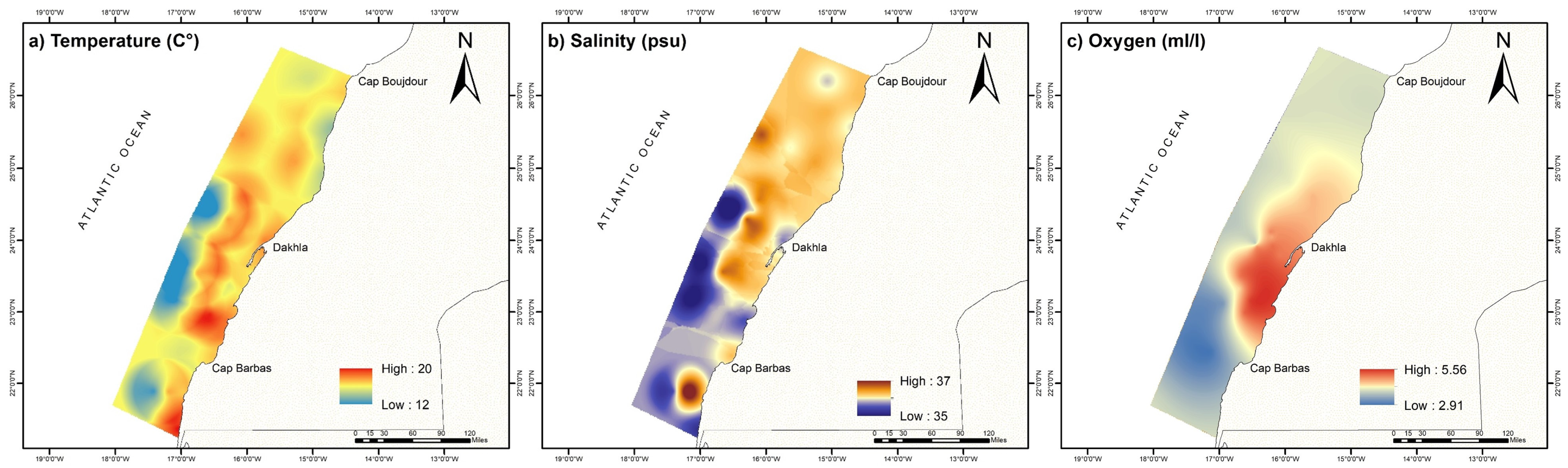
The bottom water environment shows large spatial variability and a temperature range of between 12 and 20 C°, with the lowest temperature found further offshore (Figure 2a), coinciding with the lowest salinity, around 35 psu (Figure 2b), and moderate oxygen levels (Figure 2c). Notably, less saline waters, around 36 psu, are located in the vicinity south of Cape Boujdour, in the coastal zone. Additionally, temperatures of around 12 °C and salinity levels of approximately 35.32 psu are observed between Dakhla and Cap Blanc offshore. The continental shelf in the coastal area of Dakhla exhibits relatively high levels of dissolved oxygen, at around 5 mL/L, whereas the lowest oxygen levels (<3 mL/L) are found in the south, both on the shelf and offshore (Figure 2c).
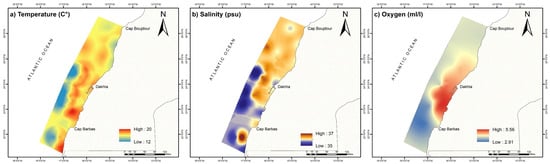
Figure 2.
Distribution of hydrological parameters in the bottom water: (a) temperature (°C), (b) salinity (psu), and (c) dissolved oxygen (mL/L).
This distribution highlights the activity of upwelling in these regions and agrees with previously described upwelling zones, which start from Cap Boujdour and derive southward offshore from Dakhla [52].
4.2. Grain Size, Carbonates, and Organic Carbon
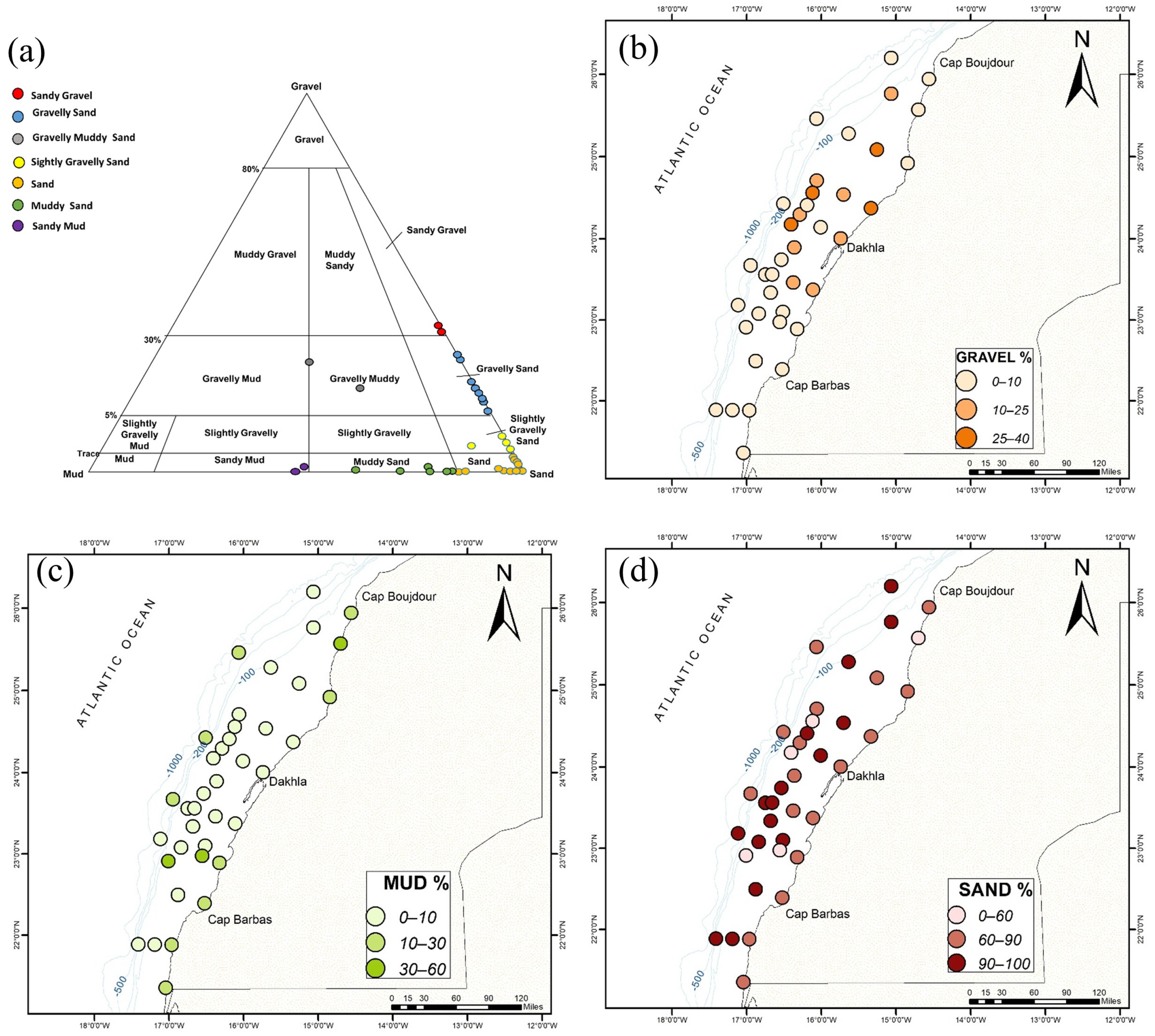
The grain-size distribution in the study area is shown in Figure 3 and Table 2. Most of the collected samples are dominated by sand, with percentages ranging between 46 and 99%. The highest values, between 85 and 99%, are recorded in the middle and outer shelf. The mean grain-size fraction ranges between 46.33 and 1482.62 µm. The collected samples are moderately to poorly sorted (1.62–4.00) and can be classified as sand, silty gravely sand, and gravely sand (Figure 3a). The percentage of mud ranges between 0 and 53%, with the highest values recorded in the inner shelf, near Cap Boujdour and south of Dakhla. Mud levels also increase in samples collected along the slope, with % mud above 15%. The sediment of these samples is poorly sorted to very poorly sorted (2–4) muddy sand/muddy sand facies. The gravel fraction does not surpass 35%. High percentages (5–35%) are found within sandy samples, located between 23.5° N and 25° N, from the inner to the outer shelf.
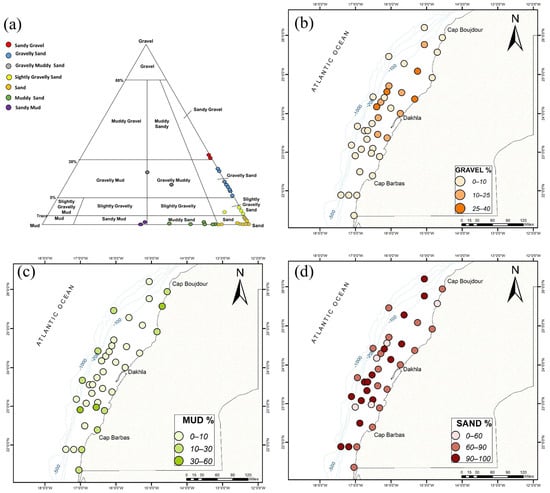
Figure 3.
Facies (a) and grain-size spatial distribution ((b): gravel%; (c): sand%; and (d): mud%) of collected samples.
The general trend shown by the grain-size maps is an increase in coarse sediment (sand) along the continental shelf and then a decrease when reaching the continental slope (Figure 3d). For example, samples from the middle shelf reached 99% sand, compared to the inner and continental slope, where it decreased by 10–20%. However, the grain-size data do not show significant latitudinal variation.
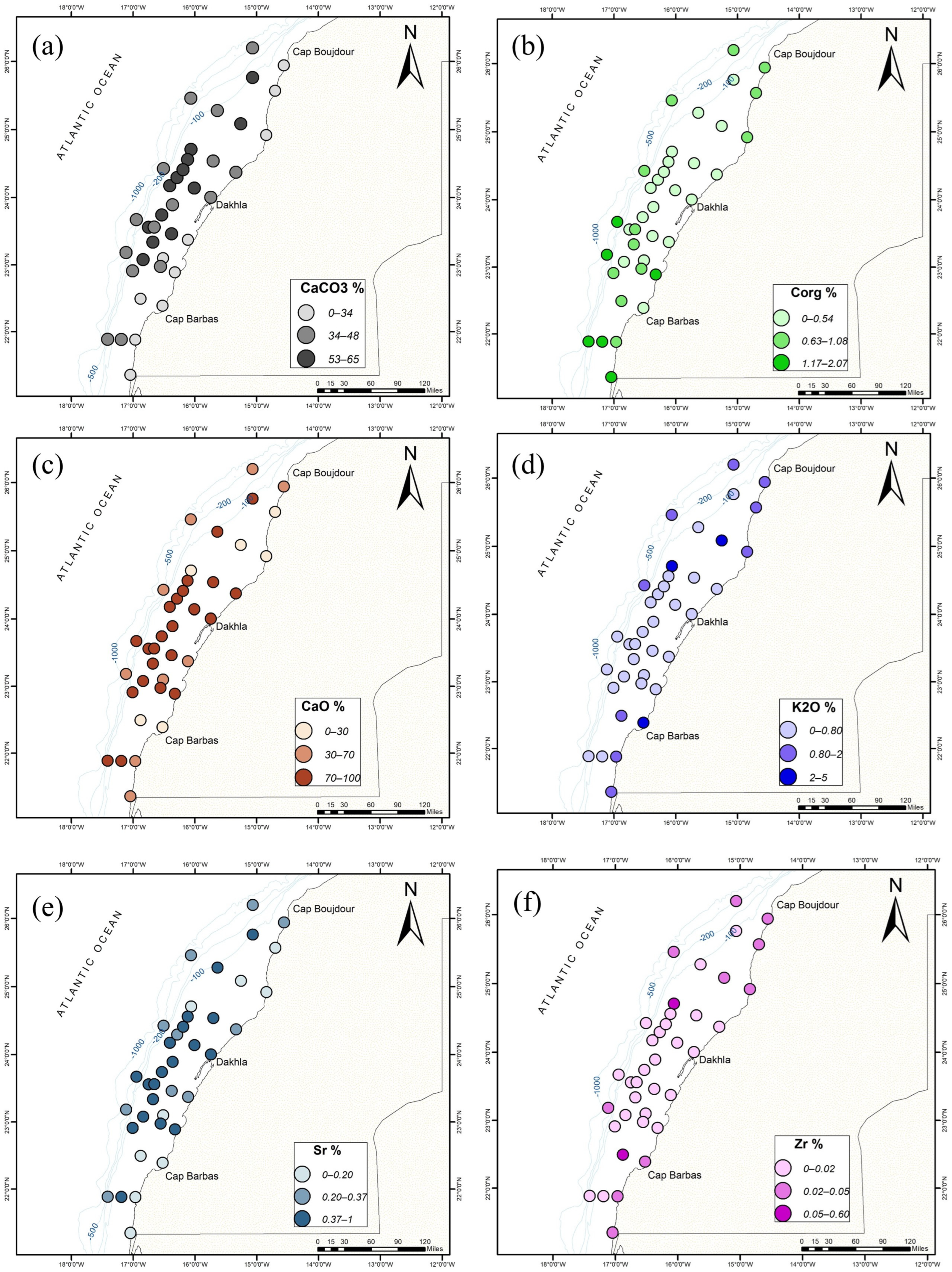
The values of organic carbon (Corg) range between 0.08 and 2.06% (SD: 0.44) and are associated with mud-rich samples. The percentage also increases latitudinally from north to south, especially below 23° N. The calcium carbonate (CaCO3) concentration has a different trend and shows a high percentage in coarse samples (16.84–64.91%; SD: 13). Directed observations of the samples suggest that the high calcium carbonate (CaCO3) concentration is related to the presence of biogenic bioclasts (Table 2).
4.3. Geochemical Composition of the Bulk Sediment Fraction (<2 mm)
4.3.1. Non-Destructive Analysis (X-Ray Fluorescence)
The X-ray fluorescence indicates the presence of 28 chemical elements in the collected sediments. Some elements were excluded from the subsequent evaluation due to their low detection levels. Statistical descriptions of selected major and trace elements are summarized in Table 2.
The major elements are presented as percentages of oxides and include silicon dioxide (SiO2: 1.43–70.40%), titanium dioxide (TiO2: 0.00–1.15%), aluminum oxide (Al2O3: 0.17–25.01%), iron oxide (Fe2O3: 0.59–6.09%), manganese oxide (MnO: 0.00–0.05%), magnesium oxide (MgO: 0.65–2.86%), calcium oxide (CaO: 0.19–92.40%), sodium oxide (Na2O: 0.66–11.10%), potassium oxide (K2O: 0.08–4.51%), and phosphorus pentoxide (P2O5: 0.00–1.19%). The trace elements are given in ppm and include chromium (Cr: 48–629 ppm), nickel (Ni: 0–94 ppm), zinc (Zn: 0–88 ppm), rubidium (Rb: 0–201 ppm), strontium (Sr: 101–5598 ppm), zirconium (Zr: 7–600 ppm), chlorine (Cl: 270–69,000 ppm), sulfur (S: 120–7493 ppm), and bromine (Br: 0–280 ppm).
In terms of spatial distribution of the measured chemical elements, some of them show a clear grain-size dependency (Figure 4). For instance, the concentrations of calcium (Ca) and strontium (Sr) are important in coarse samples (Figure 4c,e). They are very visible in those samples located in the middle and outer shelf between 25° N and 22.5° N. SiO2, TiO2, AL2O3, Fe2O3, K2O, and Rb are enriched in samples with high percentages of mud. The rest of the elements show more complex spatial variation and require further statistical analysis (e.g., PCA) to uncover the relationship between elements and samples (following section).
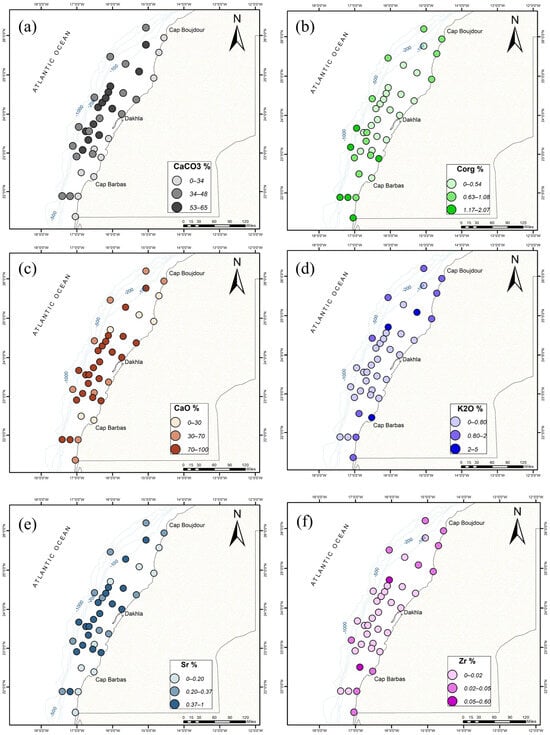
Figure 4.
Spatial distribution of (a) calcium carbonate (CaCO3%), (b) organic carbon (Corg%), (c) calcium oxide (CaO%), (d) potassium oxide (K2O%), (e) strontium (Sr%), and (f) zirconium (Zr%) in the study area.
4.3.2. Abundance of Quartz and Carbonate Minerals
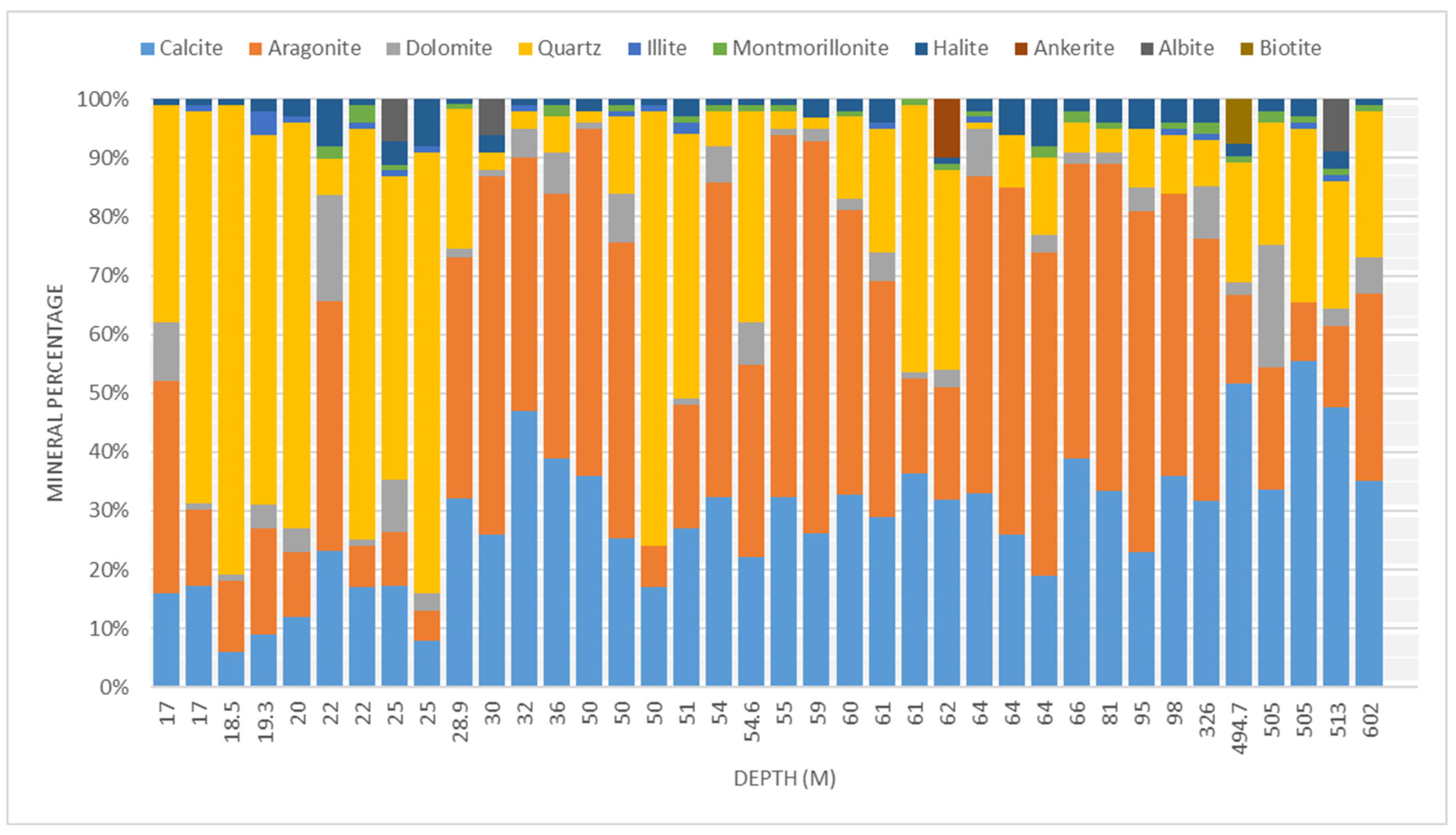
The X-ray diffraction (XRD) results show an abundance of quartz (SiO2) in coastal areas and decreases offshore, while the opposite is true for carbonate minerals such as aragonite (Ca4C4O12) and calcite (Ca6C6O18), as illustrated in Figure 5 and Figure 6. In the inner shelf (0–30 m depth), quartz (SiO2) dominates the mineral composition, with percentages between 37% and 79%. Aragonite (Ca4C4O12) ranges from 5 to 42.4% and calcite (Ca6C6O18) ranges from 6 to 40.5%. The middle and outer shelf (30–100 m depth) shows a gradual shift toward increased carbonate content. In many intervals, the percentage of calcite (Ca6C6O18) and aragonite (Ca4C4O12) reaches 90%. The percentage of quartz minerals is between 1% and 45.5% and the content is highly variable (Figure 5). The outer shelf (>100 m) is dominated by carbonate minerals, particularly calcite (32–56%) and variable aragonite (10–45%).
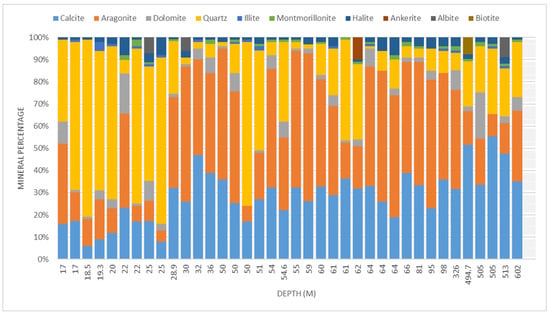
Figure 5.
Mineral composition percentage of collected samples organized according to depth (m).
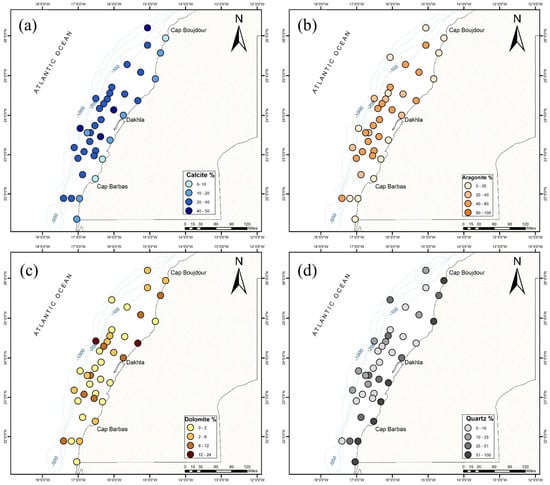
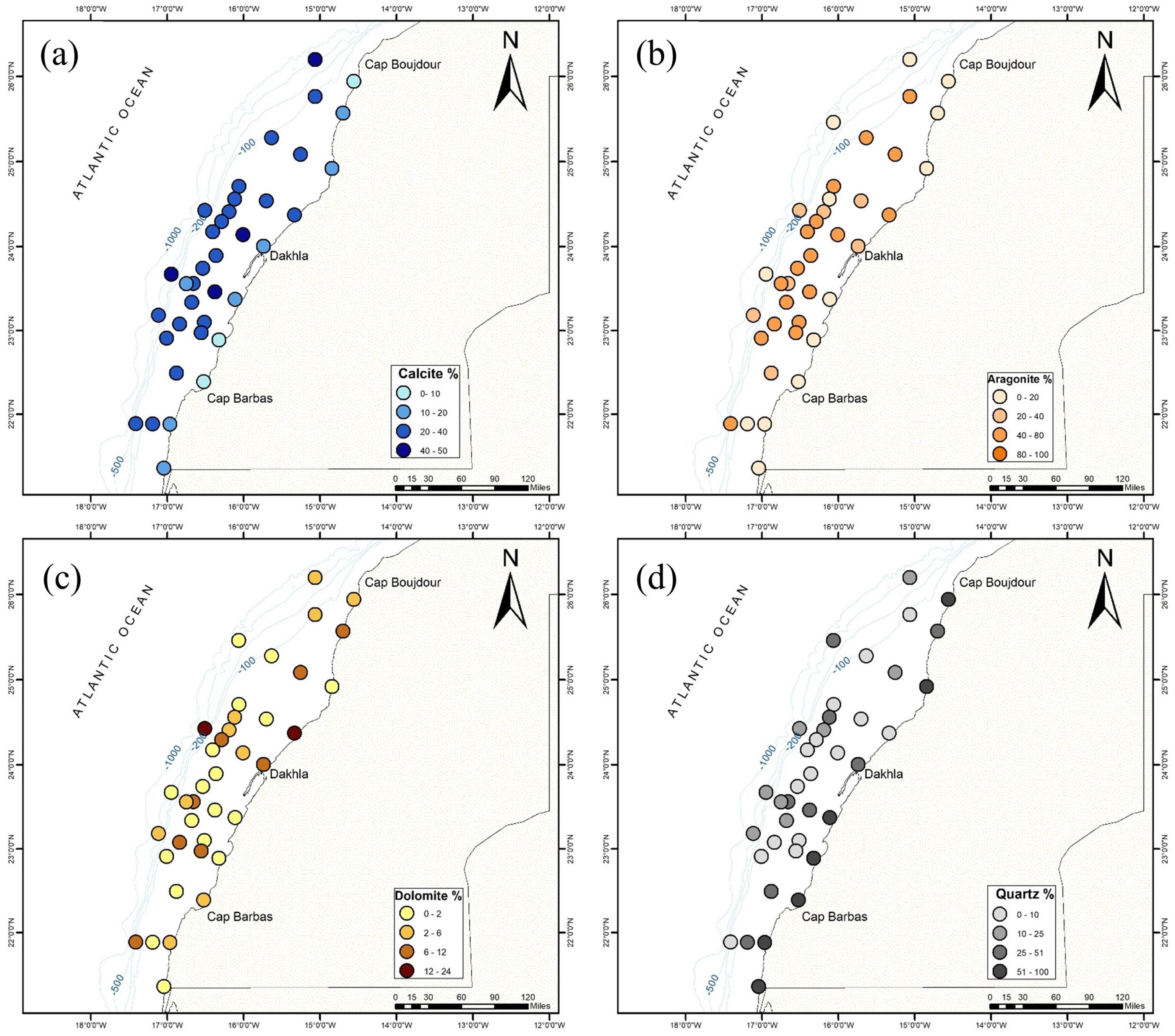
Figure 6.
Spatial distribution of the main mineral phases in the study area with respect to (a) calcite%, (b) aragonite%, (c) dolomite%, and (d) quartz%.
In terms of accessory minerals, the DRX data show the presence of montmorillonites (Si7.80Al1.72Li0.16Fe0.20Mg0.28O20), which are more present in samples collected along the outer shelf and slope, with an estimated percentage between 1% and 3%. Dolomite (Ca4Mg3C6O18) and halite (Na4Cl4) are present in almost all samples and do not show a preferential occurrence for a particular depth. The presence of ankerite (Ca2.99Mg0.82Fe2.03Mn0.16C6.00O18.00) (1–10%) and albite (NaAlSi3O8) (6–9%) in some samples may suggest unique local conditions or sources.
5. Discussion
5.1. Correlations Between Variables and Between Surface Samples Using Normalized Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
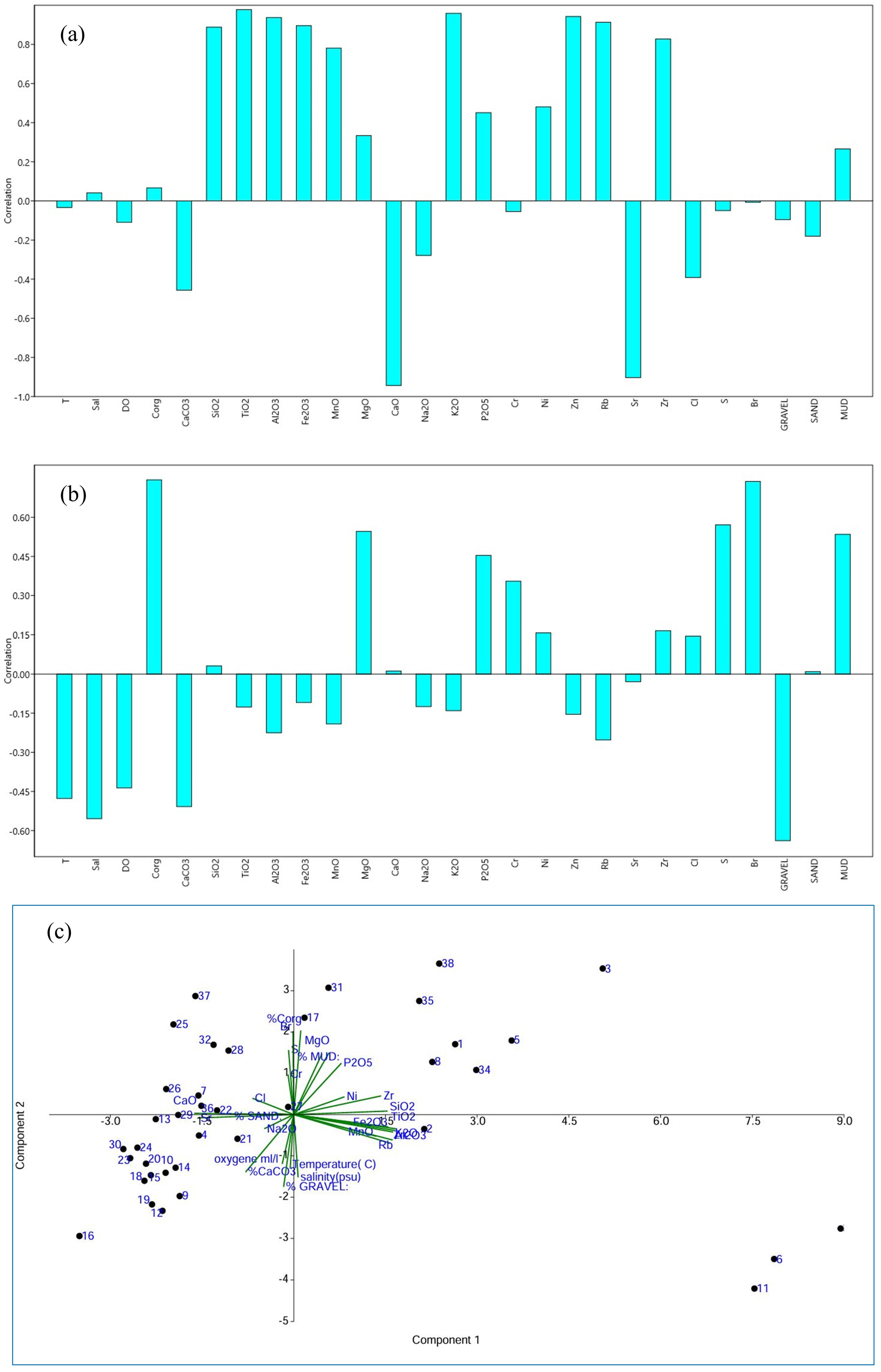
The obtained two components, F1 and F2, explain, respectively, 42.40% and 14.94% of the total variance with respect to the initial dataset (Figure 7a,b). F1 shows high and positive loading of mud associated with Corg, SiO2, Al2O3, K2O, TiO2, MnO, Fe2O3, MgO, P2O5, Ni, Zn, Rb, and Zr. These chemical elements are usually used to construct a combination of clay minerals, oxides, and heavy minerals, commonly found in fine-grained sediments, reflecting the interplay of terrigenous input, organic matter accumulation, and hydrodynamic sorting in low-energy environments [8]. SiO2 and Al2O3 are indicative of silicate minerals, particularly clay minerals like kaolinite, illite, and smectite, which are abundant in fine fractions and derived from coastal weathering and aeolian dust [6,53,54]. K2O suggests the presence of potassium-bearing minerals such as illite, muscovite, and K-feldspar. TiO2 and Fe2O3 are typically associated with heavy minerals like ilmenite, rutile, and magnetite, while MgO may be linked to chlorite or other magnesium-rich clays [55]. P2O5 is closely linked to organic matter and can be present in fine sediments due to adsorption onto clays or binding with iron oxides. It can also form phosphate minerals in mud-rich environments, which might point to phosphate minerals like apatite, often associated with organic material or biogenic activity [56].
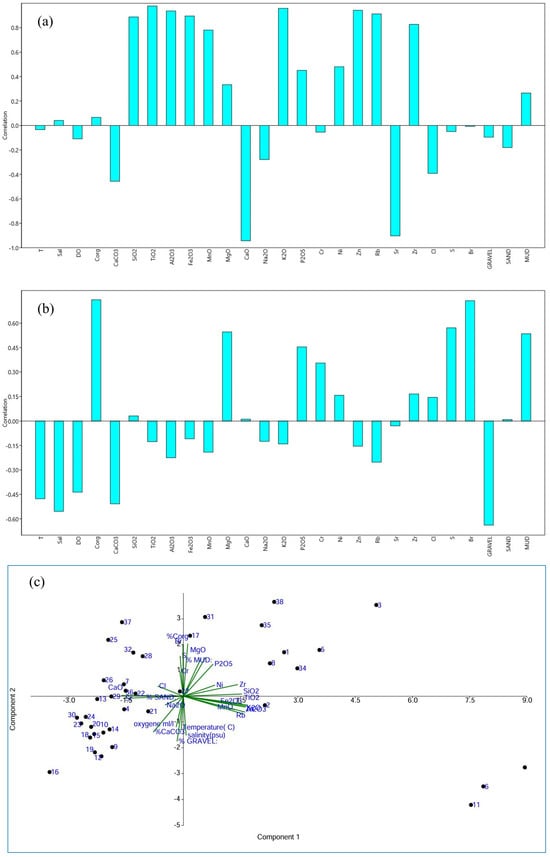
Figure 7.
PCA results illustrating the main compositional trends in collected continental surface sediments. (a): Factor 1; (b): Factor 2; (c): PCA.
The trace elements Ni, Zn, and Rb are often found in fine-grained sediments due to their tendency to adsorb onto clay minerals or organic matter. Zn, in particular, can be tied to sulfides in anoxic environments or adsorbed to clays and oxides [53]. Rb is commonly found in association with K-bearing minerals, such as biotite, muscovite, feldspar, and illite, due to its substitution in K-bearing minerals [53,57]. Zr is primarily found in zircon, which tends to be concentrated in coarser sediment fractions, signifying the presence of detrital grains. In the present study, it is concentrated in fine-grained sediments, probably due to sorting during transport and deposition processes in low-energy settings. Together, these elements reflect a complex mix of detrital input, weathering products, and possible diagenetic changes in the fine-grained matrix of the sediments.
The negative loadings of CaCO3, CaO, Sr, Cl, % gravel, and % sand in Factor F1 suggest their association with coarser-grained sediments (Figure 7a). The correlation between CaO and CaCO3 is expected and is related to the presence of biogenic material (like shells, corals, and plankton) in the coarse fraction of the sediment. Sr tends to substitute for calcium in calcium carbonate minerals. Therefore, in environments where calcium carbonate (CaCO3) is abundant (such as in biogenic sediments), often Sr is found at elevated levels [53]. Associations with respect to these elements are typically abundant in higher-energy depositional environments, where coarser particles dominate, and calcium carbonates, often related to biogenic processes, are more prevalent.
Factor 2 explains 14.94% of the total variance and seems to separate the samples in terms of organic matter richness (Figure 7b). MgO, P2O5, S, and Br show high positive loadings with % gravel and organic matter. Bromine (Br) is used to quantify marine organic matter and related productivity [58,59,60]. S could be related to reducing seafloor conditions/bottom-water anoxia [61,62]. MgO can be linked to organic matter in muddy shelf sediments through adsorption or complexation. The presence of clays and organic material can enhance MgO retention in these sediments, particularly in low-energy, anoxic environments where organic matter is abundant [63]. In mud-rich, organic-rich environments, phosphorus is more likely to be trapped and preserved due to its strong association with organic particles and the reducing conditions that limit its release back into the water column. Also, P can be immobilized in sediments through the formation of mineral phases like apatite, particularly in the presence of calcium and organic material [63].
On the negative side of F2, high loading is observed between hydrological parameters (T (temperature), Sal (salinity), DO (dissolved oxygen)) and CaCO3 as well as gravel (Figure 7b). This suggests that the correlation arises from interacting mechanisms that promote carbonate preservation, bioconstruction, and precipitation. A significant portion of the gravel-sized material in the samples consists of biogenic carbonates, such as shell fragments or coral debris, rather than terrigenous (land-derived) rocks. Warm, saline environments, which are vital sites for marine carbonate production and the deposition of coarser sediments, play a crucial role in this process [64]. Furthermore, well-oxygenated offshore waters facilitate the growth of carbonate-producing mollusks and support the recycling of organic matter [4]. They also facilitate the degradation of organic matter produced during upwelling periods throughout the year, except during the fall season when activity intensifies south of Dakhla. Consequently, the concentration of organic carbon (Corg) in the sediment remains low [52].
The distribution of the samples in the biplot shows a homogeneous group on the left side of the PCA axis (Figure 7c), indicating they share a similar lithological and chemical composition and hydrological characteristic. Their correlation with variables such as CaCO3, Ca, % gravel, and % sand suggests they are likely carbonate-rich with coarser sediments. In contrast, the samples on the right side of PC1 are more dispersed, suggesting that the finer sediments in the study area have a more varied lithological composition.
5.2. Provenance of the Sediments
Sedimentation on the continental shelf is influenced by multiple factors, including climatic conditions such as hinterland humidity (affecting runoff and drainage), wind system patterns, and hydrodynamic forces like bottom currents, wave action, and upwelling. Tectonic factors, including shelf width and slope, along with the geology and relief of source rocks, also play a role [65]. The results obtained in this study support these influences for the northwest African continental margin and further contribute to a comprehensive understanding of the lithological and geochemical characteristics of surface sediments in this region.
The inner shelf can be separated into two main areas. Samples located north of 25° N and south of 23° N show a relatively high percentage of terrigenous sediments (mud % between 15 and 60%). The fine fraction in these samples is likely due to the erosion of sandy beaches located along the coast. The second area of the inner shelf is between 25° N and 23° N. The three samples located in this area show a high content of coarse sediments, with a total percentage of sand and gravel almost equal to 100%. The coastline near these samples consists of rocky cliffs, which probably do not supply sufficient fine-grained sediments to this area. This sedimentological contrast between the two areas proves that coastal erosion influences more the sedimentation process compared to aeolian transport in the inner shelf.
The middle shelf and outer shelf are dominated by biogenic carbonate sands. Visual inspection of the samples revealed the presence of a high quantity of biogenic bioclasts. The XRF analysis revealed a strong positive correlation between calcium (Ca) and strontium (Sr), which is a known indicator of biogenic carbonate sources [53,66]. The DRX analysis supported these observations and showed the presence of calcite and aragonite as the main mineralogical phases. It is worth mentioning that aragonite is a very metastable mineral that remains in that chemical state for only a short time before transforming into calcite, which is more stable. Samples collected in the same area during previous studies have also mentioned that 70% of the carbonate content fraction consists of relatively fresh bivalve shells and shell fragments [19,24,67]. The species Pinna ramulosa is very common in the sediment composition, with local concentrations of scaphopod and gastropod shells [67]. Several factors have been mentioned as reasons for prevention of terrigenous sediment deposition in this part of the NW African shelf. The wind system, which is parallel to the coast, prevents aeolian dust from reaching the continental shelf. In terms of river discharge, the nearest major river is the Seguia el Hamra, located 200 km north, which is no longer active because of the arid climate of the hinterland. Additionally, coastal sand dunes play the role of a barrier that stops inland streams from reaching the ocean [24]. Other factors mentioned are the important vertical turbulence which slows the settling rates and nutrient regeneration within the water column. Only a small fraction of organic detritus produced in the water column reaches the bottom [7,13]. Studies suggest that most of the sediment in the middle and outer shelf is a relict [68]. The stability of the shelf during the rapid Holocene transgression contributed to the development of a widespread sand cover [15]. In this continental shelf area, non-carbonate grains consist of notable amounts of glauconite, while terrigenous components increase substantially south of 21°30′ N. The rounded and polished condition of the glauconite grains implies that they are not formed in place (authigenic) but rather sourced from nearby Mid-Tertiary rock exposures, resembling patterns observed off northern NW Africa [22].
On the continental slope, the carbonate fraction is mostly from planktonic foraminifera [19,24,67]. However, the percentage of mud increases by 15–20% compared to the middle and outer shelf and is suspected to be deposited in these locations through the activation of rivers during glacial epochs and low sea-level stand. The DRX data show the presence of montmorillonite as the main clay mineral found in the slope samples. According to [24], this mineral requires an important degree of chemical weathering at the source throughout the area to form, which can only happen during glacio-pluvial periods. The climate in northwest Africa was more humid than it is at present [69]. With its winter rains, the Mediterranean climatic zone shifted south into the south part of the study area, extending as far south as Cap Blanc. By default, the Sahara Desert also shifted southward into Mauritania, along the northwest African coast [19]. This movement of rain to the south probably intensified chemical weathering in the southern part of Morocco, which produced more montmorillonite and kaolinitic clay, compared to what is produce nowadays under the arid climate of that area. During the rise in sea level, the climate became more arid and the montmorillonite was eroded, leading to the formation of illite, thus explaining the shoreward increase in illitic clay [24].
The contribution of Saharan dust to the sedimentation process on the continental shelf is considered “normal” north of Dakhla since the prevailing winds are either onshore (N) or along the shore (NE), preventing aeolian dust from reaching deep waters [68]. On the contrary, this contribution is more pronounced south of Dakhla because of the Saharan Air Layer (or SAL), which forms when dry air and dust rise from Africa’s west coast and ride the trade winds above the Atlantic Ocean. Sediments transported by this wind have the capacity to bypass the coast and be transported beyond the continental shelf into the deep sea, even reaching the western Atlantic [17,70,71]. The quantity of atmospheric dust has been estimated to be between 20 and 70 µg·m−3, with an increased concentration to the south, reaching more than 500 µg·m−3 south of 18° N [17]. Lepple [72] estimated the amount of aeolian dust transported offshore of northern Mauritania to be between 1.5 and 6.5 × 105 metric tons km−1 of coastline annually. D’Almeida [73] estimated the Saharan dust flux amounts to be around 0.6–0.7 Pg (1015 g) per year−1, with approximately one-third of this dust being deposited in the North Atlantic Ocean [74].
Several studies have mentioned the presence of geochemical and mineralogical similarities between the terrigenous sediments collected on the northwest African shelf and the Saharan dust [75]. The same minerals have been described by Johnson [76] in the Saharan dust, which is 30% quartz, 10% plagioclase, and 0.7% dolomite. However, the same author indicates that this composition could be affected by some changes related to the source areas [43,77] and sorting effects during transport. Other studies confirm the presence of several aluminosilicate phases in the Sahara dust—containing variable amounts of silicon (Si), aluminum (Al), iron (Fe), and potassium (K) [54]—and indicate that it is rich in titanium (Ti) [78]. The obtained XRF results confirmed the presence of the same elements in the samples collected near the coast, especially those south of Dakhla, which highlight the contribution of Saharan dust to sedimentation in this part of the study area. Quartz and dolomite have also been found in the same samples using XRD, confirming previous observations. In terms of possible sources for the dust reaching the west African continental shelf, the literature suggests the Bodele depression in Chad [79] and a low relief area extending over eastern Mauritania, western Mali, and southern Algeria [16,80].
In contrast to the aeolian inputs observed in the NW African shelf (quartz, clays) and carbonate-dominated outer shelf, the southern African coast is more fluvially driven (Orange River siliciclastics) and contains lower carbonates. These distinctions reflect different sediment sources (aeolian and fluvial) and environmental regimes (hyper-arid and semi-arid) [81].
The continental shelf south of Dakhla is also marked by a relatively high percentage of organic matter and is related to the upwelling currents, which are very dominant in this part of the NW African shore. Upwelling currents are known for bringing cold, nutrient-rich water (15–16 °C) to the surface, characterized by salinity levels of around 36%, low carbonate saturation, and low oxygen concentrations (approximately 2 mL/L). These conditions promote higher primary productivity by phytoplankton, leading to increased zooplankton production and, consequently, a greater deposition of organic matter on the seafloor [4,24].
This phenomenon also results in low carbonate content in sediments because calcifying organisms (such as shellfish, corals, and mollusks) rely on calcium carbonate (CaCO3) to build their structures [4].
This study indicates that the high concentrations of Ca and CaCO3, along with the low Corg observed at most stations (Figure 4), are associated with the presence of biogenic carbonates, likely of marine origin. Additionally, high temperatures and salinity can influence carbonate precipitation in marine sediments [82,83].
6. Conclusions
This study investigates the sedimentological and geochemical characteristics of surface sediments and bottom water hydrological properties along the NW African continental shelf. The results show significant spatial variability in sediment composition, where sand predominates in the middle and outer shelf areas, indicating high-energy hydrodynamic conditions. In contrast, finer mud and higher organic carbon content are found on the inner shelf and continental slope, reflecting lower-energy environments. Calcium carbonate content is notably higher in the middle and outer shelf zones, with biogenic materials such as shell fragments and foraminifera tests reflecting high biological productivity in these regions.
Geochemical analysis reveals clear relationships between sediment size, distribution, and elemental composition. Silicon, aluminum, potassium, and iron are concentrated in fine-grained sediments, while calcium and strontium are associated with coarser, sandy sediments. A shift in the mineralogical composition is observed across the shelf, from quartz in the nearshore to calcite and aragonite offshore, highlighting the transition from terrigenous to biogenic influences. These findings illustrate the complex interplay between sedimentary processes and underlying hydrodynamic conditions.
The sources of sediment in the region are diverse, with coastal erosion contributing significantly in the inner shelf, while relic sediments from past glacial periods dominate the middle and outer shelf. Additionally, upwelling and windborne dust, especially south of Dakhla, enhance sediment composition. This study provides new insights into sediment dynamics by incorporating new data from NW Africa which refine the spatial resolution of geochemical and sedimentological maps. The results of this study not only advance our understanding of sediment dynamics on the NW African continental shelf but also enable meaningful comparisons with other eastern boundary systems, such as the southern African shelf. These insights provide a strong framework for regional environmental management, resource exploration, and conservation strategies, while establishing a critical baseline for future studies on sedimentary responses to climatic and anthropogenic pressures.
Author Contributions
H.N.-H., writing—review and editing, methodology, and conceptualization; K.E.K., writing—review, project administration, and supervision; O.K., writing—review and editing and formal analysis; A.M., resources, investigation, review, and data curation; M.C., review, visualization, investigation, and data curation; C.J., validation and data curation; M.I., resources; B.Z., review, project administration, and supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the EAF-Nansen Program, supported by the Norwegian Ministry of Foreign Affairs (NORAD), the Institute of Marine Research (IMR), and the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data produced or analyzed in this study are contained within the published article. Should additional details be required, the corresponding authors can provide the datasets used and examined in this study upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their gratitude to the editors and reviewers for their valuable comments with respect to improving the quality of the manuscript. This paper/report uses data generated through the activities under the EAF-Nansen Programme as part of the collaboration between the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) on behalf of the EAF-Nansen Programme and Morocco. The EAF-Nansen Programme is a partnership between the FAO, the Norwegian Agency for Development Cooperation (Norad) and the Institute of Marine Research (IMR) in Norway for sustainable management of the fisheries in partner countries and regions. The authors thank the captains and crews of the R/V Fridtjof Nansen who assisted in the surveys as well as all the participants.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors confirm that there are no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| NW Africa | Northwest Africa |
| SAL | Saharan Air Layer |
| DO | Dissolved oxygen |
| Sal | Salinity |
| CaCO3 | Calcium carbonate |
| Corg | Organic carbon |
| CTD | Conductivity, Temperature, and Depth sensor |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| XRF | X-ray fluorescence |
References
- Buhl-Mortensen, L.; Buhl-Mortensen, P.; Dolan, M.F.J.; Dannheim, J.; Bellec, V.; Holte, B. Habitat Complexity and Bottom Fauna Composition at Different Scales on the Continental Shelf and Slope of Northern Norway. Hydrobiologia 2012, 685, 191–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowski, C. Physically Disturbed Deep-Sea Macrofauna in the Peru Basin, Southeast Pacific, Revisited 7 Years after the Experimental Impact. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2001, 48, 3809–3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, N.; VanBlaricom, G.R.; Dayton, P.K. Man-Made Structures on Marine Sediments: Effects on Adjacent Benthic Communities. Mar. Biol. 1982, 70, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhl-Mortensen, L.; Houssa, R.; M’bengue, B.; Nyadjro, E.S.; Cervantes, D.; Idrissi, M.; Mahu, E.; Dia, A.S.; Olsen, M.; Mas, C.; et al. Lophelia Reefs off North and West Africa–Comparing Environment and Health. Mar. Biol. 2024, 171, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robledo Ardila, P.A.; Álvarez-Alonso, R.; Árcega-Cabrera, F.; Durán Valsero, J.J.; Morales García, R.; Lamas-Cosío, E.; Oceguera-Vargas, I.; DelValls, A. Assessment and Review of Heavy Metals Pollution in Sediments of the Mediterranean Sea. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardila, P.A.R.; Alonso, R.Á.; Valsero, J.J.D.; García, R.M.; Cabrera, F.Á.; Cosío, E.L.; Laforet, S.D. Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution in Marine Sediments from Southwest of Mallorca Island, Spain. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 16852–16866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, D.J.P. Continental Shelf Sedimentation. In The Geology of Continental Margins; Burk, C.A., Drake, C.L., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1974; pp. 117–135. ISBN 978-3-662-01143-0. [Google Scholar]
- Lamarque, B.; Deflandre, B.; Schmidt, S.; Bernard, G.; Dubosq, N.; Diaz, M.; Lavesque, N.; Garabetian, F.; Grasso, F.; Sottolichio, A.; et al. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Surface Sediment Characteristics and Benthic Macrofauna Compositions in a Temperate High-Energy River-Dominated Ocean Margin. Cont. Shelf Res. 2022, 247, 104833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasemann, C.; Mokievsky, V.; Sablotny, B.; Tekman, M.B.; Soltwedel, T. Effects of Sediment Disturbance on Deep-Sea Nematode Communities: Results from an in-Situ Experiment at the Arctic LTER Observatory HAUSGARTEN. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2020, 533, 151471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hein, J.R.; Mizell, K.; Koschinsky, A.; Conrad, T.A. Deep-Ocean Mineral Deposits as a Source of Critical Metals for High- and Green-Technology Applications: Comparison with Land-Based Resources. Ore Geol. Rev. 2013, 51, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lèbre, É.; Kung, A.; Savinova, E.; Valenta, R.K. Mining on Land or in the Deep Sea? Overlooked Considerations of a Reshuffling in the Supply Source Mix. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 191, 106898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stow, D.A.V.; Mayall, M. Deep-Water Sedimentary Systems: New Models for the 21st Century. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2000, 17, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberwein, A.; Mackensen, A. Regional Primary Productivity Differences off Morocco (NW-Africa) Recorded by Modern Benthic Foraminifera and Their Stable Carbon Isotopic Composition. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2006, 53, 1379–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutze, G.F.; Coulbourn, W.T. Recent Benthic Foraminifera from the Continental Margin of Northwest Africa: Community Structure and Distribution. Mar. Micropaleontol. 1984, 8, 361–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMaster, R.L.; Lachance, T.P. Northwestern African Continental Shelf Sediments. Mar. Geol. 1969, 7, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhammdi, N.; Snoussi, M.; Medina, F.; Jaaïdi, E.B. Chapter 10 Recent Sedimentation in the NW African Shelf. Geol. Soc. Lond. Mem. 2014, 41, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milliman, J.D. Effects of Arid Climate and Upwelling upon the Sedimentary Regime off Southern Spanish Sahara. Deep Sea Res. 1977, 24, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarnthein, M.; Thiede, J.; Pflaumann, U.; Erlenkeuser, H.; Fütterer, D.; Koopmann, B.; Lange, H.; Seibold, E. Atmospheric and Oceanic Circulation Patterns off Northwest Africa During the Past 25 Million Years. In Geology of the Northwest African Continental Margin; von Rad, U., Hinz, K., Sarnthein, M., Seibold, E., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1982; pp. 545–604. ISBN 978-3-642-68411-1. [Google Scholar]
- Seibold, E.; Diester-Hass, L.; Fütterer, D.; Hartmann, M.; Kögler, F.; Lange, H.; Müller, P.; Pflaumann, U.; Schrader, H.; Suess, E. Late Quaternary Sedimentation off the Western Sahara. An. Acad. Bras. Ciências = Ann. Braz. Acad. Sci. 1976, 48, 287–296. [Google Scholar]
- Seibold, E. The Northwest African Continental Margin—An Introduction. In Geology of the Northwest African Continental Margin; von Rad, U., Hinz, K., Sarnthein, M., Seibold, E., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1982; pp. 3–20. [Google Scholar]
- Siedler, G.; Seibold, E. Currents Related to Sediment Transportat the Ibero-Moroccan Continental Shelf. Meteor. Forschungsergebnisse Reihe A Allg. Phys. Chem. Meeres 1974, 14, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Summerhayes, C.P.; Nutter, A.H.; Tooms, J.S. The Distribution and Origin of Phosphate in Sediments off Northwest Africa. Sediment. Geol. 1972, 8, 3–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refk, R. Synthèse Des Résultats Des Travaux Océanographiques Effectués Dans Les Eaux Atlantiques Marocaines Durant La Période 1947–1980; Technical Report; Institut National de Recherche Halieutique (INRH): Casablanca, Morocco, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Summerhayes, C.P.; Milliman, J.D.; Briggs, S.R.; Bee, A.G.; Hogan, C. Northwest African Shelf Sediments: Influence of Climate and Sedimentary Processes. J. Geol. 1976, 84, 277–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tooms, J.S.; Summerhayes, C.P.; McMaster, R.L. Marine Geological Studies on the North-West African Margin: Rabat-Dakar; H.M. Stationery Office (HMSO): London, UK, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths, J.F. Climates of Africa; World Survey of Climatology; Elsevier Publishing Company: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1972; Volume 10, ISBN 0-444-41526-2. [Google Scholar]
- Maoulainine, C.M. Monographie Régionale de La Région Eddakhla—Oued Eddahab: 2018. Available online: http://www.abhatoo.net.ma/maalama-textuelle/developpement-economique-et-social/developpement-economique/reperes-du-developpement-economique/indicateurs-socio-economiques/monographie-regionale-de-la-region-eddakhla-oued-eddahab-2018 (accessed on 2 February 2025).
- Benazzouz, A.; Mordane, S.; Orbi, A.; Chagdali, M.; Hilmi, K.; Atillah, A.; Lluís Pelegrí, J.; Hervé, D. An Improved Coastal Upwelling Index from Sea Surface Temperature Using Satellite-Based Approach—The Case of the Canary Current Upwelling System. Cont. Shelf Res. 2014, 81, 38–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, T.N.; Prospero, J.M. The Large-Scale Movement of Saharan Air Outbreaks over the Northern Equatorial Atlantic. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1972, 11, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunion, J.P.; Velden, C.S. The Impact of the Saharan Air Layer on Atlantic Tropical Cyclone Activity. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 2004, 85, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jickells, T.D.; An, Z.S.; Andersen, K.K.; Baker, A.R.; Bergametti, G.; Brooks, N.; Cao, J.J.; Boyd, P.W.; Duce, R.A.; Hunter, K.A.; et al. Global Iron Connections Between Desert Dust, Ocean Biogeochemistry, and Climate. Science 2005, 308, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allain, C. Les Conditions Hydrologiques Sur La Bordure Atlantique de l’Afrique Du Nord-Ouest. Rapports et Procès-Verbaux des Réunions de la Commission Internationale pour l’Exploration Scientifique de la Méditerranée. Rapp. P. -V. Réun. CIEM 1970, 159, 25–29. [Google Scholar]
- Carr, M.-E. Estimation of Potential Productivity in Eastern Boundary Currents Using Remote Sensing. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2001, 49, 59–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, E. Northwest African Upwelling Scenario. Oceanol. Acta 2001, 24, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittelstaedt, E. The Ocean Boundary along the Northwest African Coast: Circulation and Oceanographic Properties at the Sea Surface. Prog. Oceanogr. 1991, 26, 307–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.G.W. The Variability of Oceanographic Observations off the Coast of North-West Africa. Deep Sea Res. Oceanogr. Abstr. 1972, 19, 405–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Rad, U.; Wissmann, G. Cretaceous-Cenozoic History of the West Saharan Continental Margin (NW Africa): Development, Destruction and Gravitational Sedimentation. In Geology of the Northwest African Continental Margin; Von Rad, U., Hinz, K., Sarnthein, M., Seibold, E., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1982; pp. 106–131. ISBN 978-3-642-68411-1. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, P.G.W.; Folkard, A.R. Chemical Oceanographic Observations off the Coast of North-West Africa, with Special Reference to the Process of Upwelling. Available online: https://library.metoffice.gov.uk/portal/Default/en-GB/RecordView/Index/61929 (accessed on 2 February 2025).
- Groupe MEDIPROD, Résultats de la campagne cineca—Charcot II. 1971.
- Schemainda, R.; Nehring, D.; Schulz, S. Ozeanologische Untersuchungen zum Produktionspotential der nordwestafrikanischen Wasserauftriebsregion 1970–1973: Diese Arbeit wurde Prof. Dr. habil. Erich Bruns zum 75. Geburtstag gewidmet (Études océanologiques sur le potentiel de production de la région d’upwelling au nord-ouest de l’Afrique de 1970 à 1973). Geodätische und Geophysikalische Veröffentlichungen 1975, 88.
- Shaffer, G. Étude à Méso-Échelle de La Variabilité de l’upwelling Côtier Au Large Du Nord-Ouest de l’Afrique. Meteor. Forschungsergebnisse Reihe A 1976, 17, 21–72. [Google Scholar]
- Weichart, G. Meereschemische Untersuchungen im nordwestafrikanischen Auftriebsgebiet 1968. Meteor. Forschungsergebnisse Reihe A Allg. Phys. Chem. Meeres 1974, 14, 33–70. [Google Scholar]
- Emery, K.O.; Lepple, F.; Toner, L.; Uchupi, E.; Rioux, R.H.; Pople, W.; Hulburt, E.M. Suspended Matter and Other Properties of Surface Waters of the Northeastern Atlantic Ocean. J. Sediment. Res. 1974, 44, 1087–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Rocha, J.; Milliman, J.; Santana, C.; Vicalvi, M. Continental Margin Sedimentation off Brazil; E. Schweizerbart’sche Verlagsbuchhandlung (Nägele u. Obermiller): Stuttgart, Germany, 1975; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Blott, S.J.; Pye, K. GRADISTAT: A Grain Size Distribution and Statistics Package for the Analysis of Unconsolidated Sediments. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2001, 26, 1237–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udden, J.A. Mechanical Composition of Clastic Sediments. GSA Bull. 1914, 25, 655–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentworth, C.K. The Classification and Terminology of the Pyroclastic Rocks. Natl. Res. Counc. Bull. 1932, 89, 19–53. [Google Scholar]
- Folk, R.L.; Ward, W.C. Brazos River Bar [Texas]; A Study in the Significance of Grain Size Parameters. J. Sediment. Res. 1957, 27, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.W.; Sommers, L.E. Total Carbon, Organic Carbon, and Organic Matter. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 3 Chemical Methods; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1996; pp. 961–1010. ISBN 978-0-89118-866-7. [Google Scholar]
- Fournier-Sowinski, J.; Bonnot-Courtois, C.; Paris, R.; Vot, M. Analyses Granulométriques. Principes et Méthodes; BRGM (Bureau de Recherches Géologiques et Minières): Orléans, France, 2012; Available online: https://hal.science/hal-04648219 (accessed on 3 February 2023).
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.; Ryan, P. PAST: Paleontological Statistics Software Package for Education and Data Analysis (Version 2.09); Natural History Museum, University of Oslo: Oslo, Norway, 2001; Available online: https://www.nhm.uio.no/english/research/resources/past/ (accessed on 7 November 2023).
- MAKAOUI, A. Étude Hydrologique de l’upwelling Côtier Marocain et Sa Contribution à La Sédimentologie Du Plateau Continental. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculté des Sciences Ben M’Sik, Université Hassan II, Casablanca, Morocco, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Rothwell, R.G.; Croudace, I.W. Twenty Years of XRF Core Scanning Marine Sediments: What Do Geochemical Proxies Tell Us. In Micro-XRF Studies of Sediment Cores: Applications of a Non-Destructive Tool for the Environmental Sciences; Croudace, I.W., Rothwell, R.G., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 25–102. ISBN 978-94-017-9849-5. [Google Scholar]
- Caquineau, S.; Gaudichet, A.; Gomes, L.; Magonthier, M.; Chatenet, B. Saharan Dust: Clay Ratio as a Relevant Tracer to Assess the Origin of Soil-derived Aerosols. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1998, 25, 983–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govin, A.; Holzwarth, U.; Heslop, D.; Ford Keeling, L.; Zabel, M.; Mulitza, S.; Collins, J.A.; Chiessi, C.M. Distribution of Major Elements in Atlantic Surface Sediments (36°N–49°S): Imprint of Terrigenous Input and Continental Weathering. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2012, 13, 2011GC003785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, M.P.; Tostevin, R.; Tosca, N.J. Marine Phosphate Availability and the Chemical Origins of Life on Earth. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croudace, I.W.; Rindby, A.; Rothwell, R.G. ITRAX: Description and Evaluation of a New Multi-Function X-Ray Core Scanner. In New Techniques in Sediment Core Analysis; Geological Society of London: London, UK, 2006; Volume 267, pp. 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caley, T.; Malaizé, B.; Zaragosi, S.; Rossignol, L.; Bourget, J.; Eynaud, F.; Martinez, P.; Giraudeau, J.; Charlier, K.; Ellouz-Zimmermann, N. New Arabian Sea Records Help Decipher Orbital Timing of Indo-Asian Monsoon. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2011, 308, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, M.; Jilbert, T.; De Lange, G.J.; Lourens, L.J.; Reichart, G. Bromine Counts from XRF Scanning as an Estimate of the Marine Organic Carbon Content of Sediment Cores. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2008, 9, 2007GC001932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, M.; Lourens, L.J.; Tuenter, E.; Reichart, G.-J. Anomalously High Arabian Sea Productivity Conditions during MIS 13. Clim. Past Discuss. 2009, 5, 1989–2018. [Google Scholar]
- Harff, J.; Endler, R.; Emelyanov, E.; Kotov, S.; Leipe, T.; Moros, M.; Olea, R.; Tomczak, M.; Witkowski, A. Late Quaternary Climate Variations Reflected in Baltic Sea Sediments. In The Baltic Sea Basin; Harff, J., Björck, S., Hoth, P., Eds.; Central and Eastern European Development Studies (CEEDES); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 99–132. ISBN 978-3-642-17219-9. [Google Scholar]
- Sluijs, A.; Röhl, U.; Schouten, S.; Brumsack, H.; Sangiorgi, F.; Sinninghe Damsté, J.S.; Brinkhuis, H. Arctic Late Paleocene–Early Eocene Paleoenvironments with Special Emphasis on the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum (Lomonosov Ridge, Integrated Ocean Drilling Program Expedition 302). Paleoceanography 2008, 23, 2007PA001495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdige, D.J. Geochemistry of Marine Sediments; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2020; ISBN 978-0-691-21609-6. [Google Scholar]
- Pomar, L.; Hallock, P. Carbonate Factories: A Conundrum in Sedimentary Geology. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2008, 87, 134–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nittrouer, C.A.; Wright, L.D. Transport of Particles across Continental Shelves. Rev. Geophys. 1994, 32, 85–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaragosi, S.; Bourillet, J.-F.; Eynaud, F.; Toucanne, S.; Denhard, B.; Van Toer, A.; Lanfumey, V. The Impact of the Last European Deglaciation on the Deep-Sea Turbidite Systems of the Celtic-Armorican Margin (Bay of Biscay). Geo-Mar. Lett. 2006, 26, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, R.S.; Seibold, E.; Werner, F. Facies Distribution Patterns on the Spanish Sahara Continental Shelf, Mapped with Side Scan Sonar. Meteor Forschungsergebnisse Reihe C Geol. Geophys. 1973, 17, 55–77. [Google Scholar]
- Emery, K.O. Relict Sediments on Continental Shelves of World. AAPG Bull. 1968, 52, 445–464. [Google Scholar]
- Frenzel, B. Climatic Fluctuations of the Ice Age. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1975, 56, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Delany, A.C.; Claire Delany, A.; Parkin, D.W.; Griffin, J.J.; Goldberg, E.D.; Reimann, B.E.F. Airborne Dust Collected at Barbados. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1967, 31, 885–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radczewski, O.E. Eolian Deposits in Marine Sediments 1. In Recent Marine Sediments; American Association of Petroleum Geologists: Washington, DC, USA, 1939; ISBN 978-1-62981-251-9. [Google Scholar]
- Lepple, F.K. Eolian Dust over the North Atlantic Ocean. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Delaware, Newark, NJ, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- d’Almeida, G.A. Desert Aerosol: Characteristics and Effects on Climate. In Paleoclimatology and Paleometeorology: Modern and Past Patterns of Global Atmospheric Transport; Leinen, M., Sarnthein, M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1989; pp. 311–338. ISBN 978-94-010-6937-3. [Google Scholar]
- Duce, R.A.; Liss, P.S.; Merrill, J.T.; Atlas, E.L.; Buat-Menard, P.; Hicks, B.B.; Miller, J.M.; Prospero, J.M.; Arimoto, R.; Church, T.M.; et al. The Atmospheric Input of Trace Species to the World Ocean. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 1991, 5, 193–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzano, G.; Kuhlmann, H.; Alonso, B. Storminess Control over African Dust Input to the Moroccan Atlantic Margin (NW Africa) at the Time of Maxima Boreal Summer Insolation: A Record of the Last 220 Kyr. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2002, 183, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.R. Mineralogical Dispersal Patterns of North Atlantic Deep-Sea Sediments with Particular Reference to Eolian Dusts. Mar. Geol. 1979, 29, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarnthein, M. Neogene Sand Layers off Northwest Africa: Composition and Source Environment; Initial Reports of the Deep Sea Drilling Project; U.S. Government Printing Office: Washington, WA, USA, 1978; Volume 38–41. [Google Scholar]
- Schütz, L.; Rahn, K.A. Trace-Element Concentrations in Erodible Soils. Atmos. Environ. 1982, 16, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washington, R.; Todd, M.C.; Lizcano, G.; Tegen, I.; Flamant, C.; Koren, I.; Ginoux, P.; Engelstaedter, S.; Bristow, C.S.; Zender, C.S.; et al. Links between Topography, Wind, Deflation, Lakes and Dust: The Case of the Bodélé Depression, Chad. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, 2006GL025827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McTainsh, G.H.; Walker, P.H. Nature and Distribution of Harmattan Dust. Z. Geomorphol. 1982, 26, 417–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compton, J.; Maake, L. Source of the Suspended Load of the Upper Orange River, South Africa. S. Afr. J. Geol. 2007, 110, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spalding, C.; Finnegan, S.; Fischer, W.W. Energetic Costs of Calcification under Ocean Acidification. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2017, 31, 866–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerreiro, C.V.; Ferreira, A.; Cros, L.; Stuut, J.-B.; Baker, A.; Tracana, A.; Pinto, C.; Veloso, V.; Rees, A.P.; Cachão, M.A.P.; et al. Response of Coccolithophore Communities to Oceanographic and Atmospheric Processes across the North- and Equatorial Atlantic. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1119488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).