Review of Research Progress on the Influence of Groundwater Discharge on Seabed Stability
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Current Status of Research on SGD
3. Literature Review Methodology
- Planning the review: Determining the need for this review paper and identifying the research questions.
- Conducting the review: Selecting original research, data extraction, and reporting of results.
- R.Q.1 What does submarine groundwater discharge (SGD) imply?
- R.Q.2 How does SGD interact with the seabed?
- R.Q.3 What are the main seabed geological structures affected by SGD?
- R.Q.4 What are the future research directions and trends?
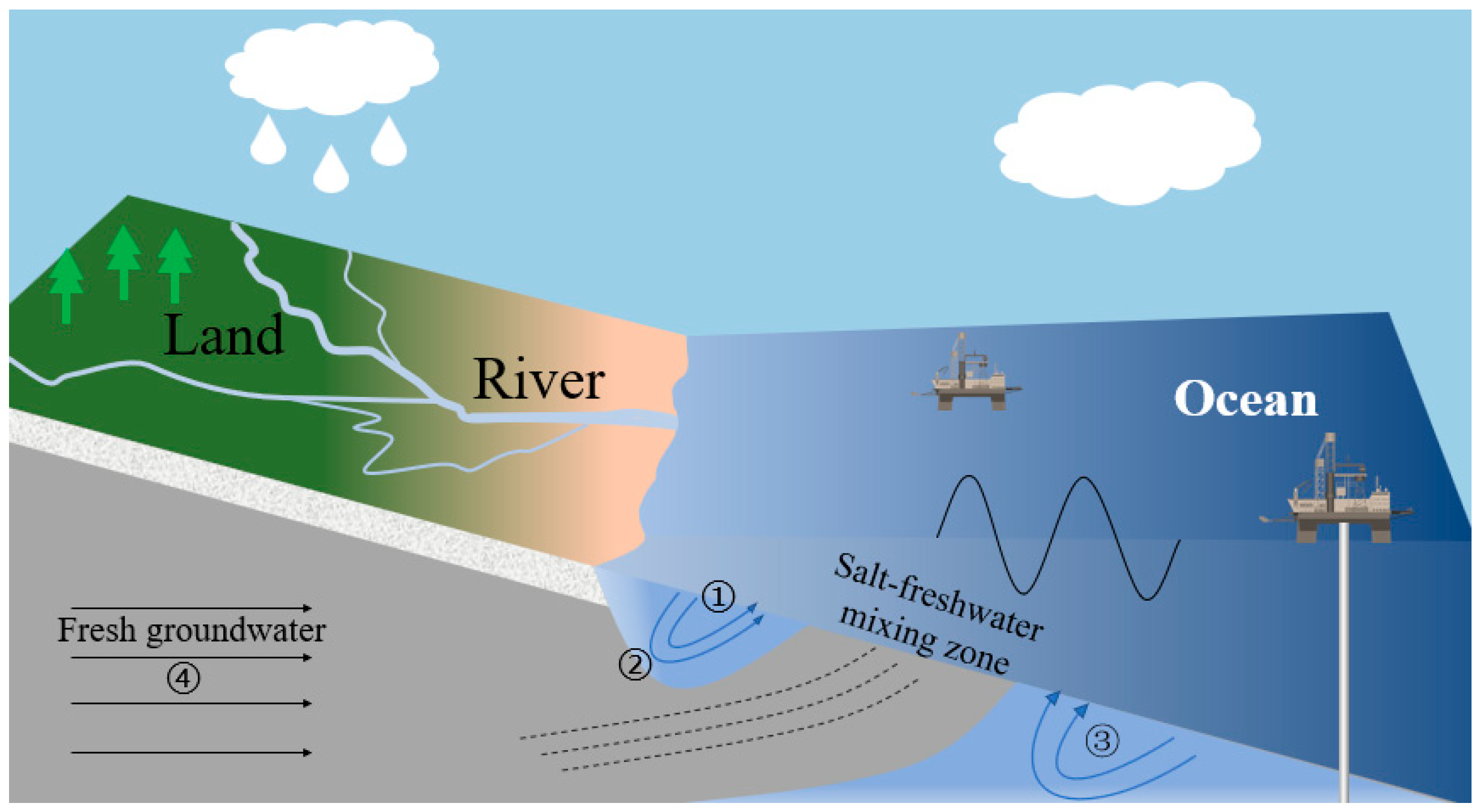
4. The Interaction Mechanism Between SGD and Seabed
4.1. Regional Geological Conditions Affect SGD
4.2. Hydrological Conditions Affect SGD
4.3. SGD Triggers the Submarine Instability Mechanism
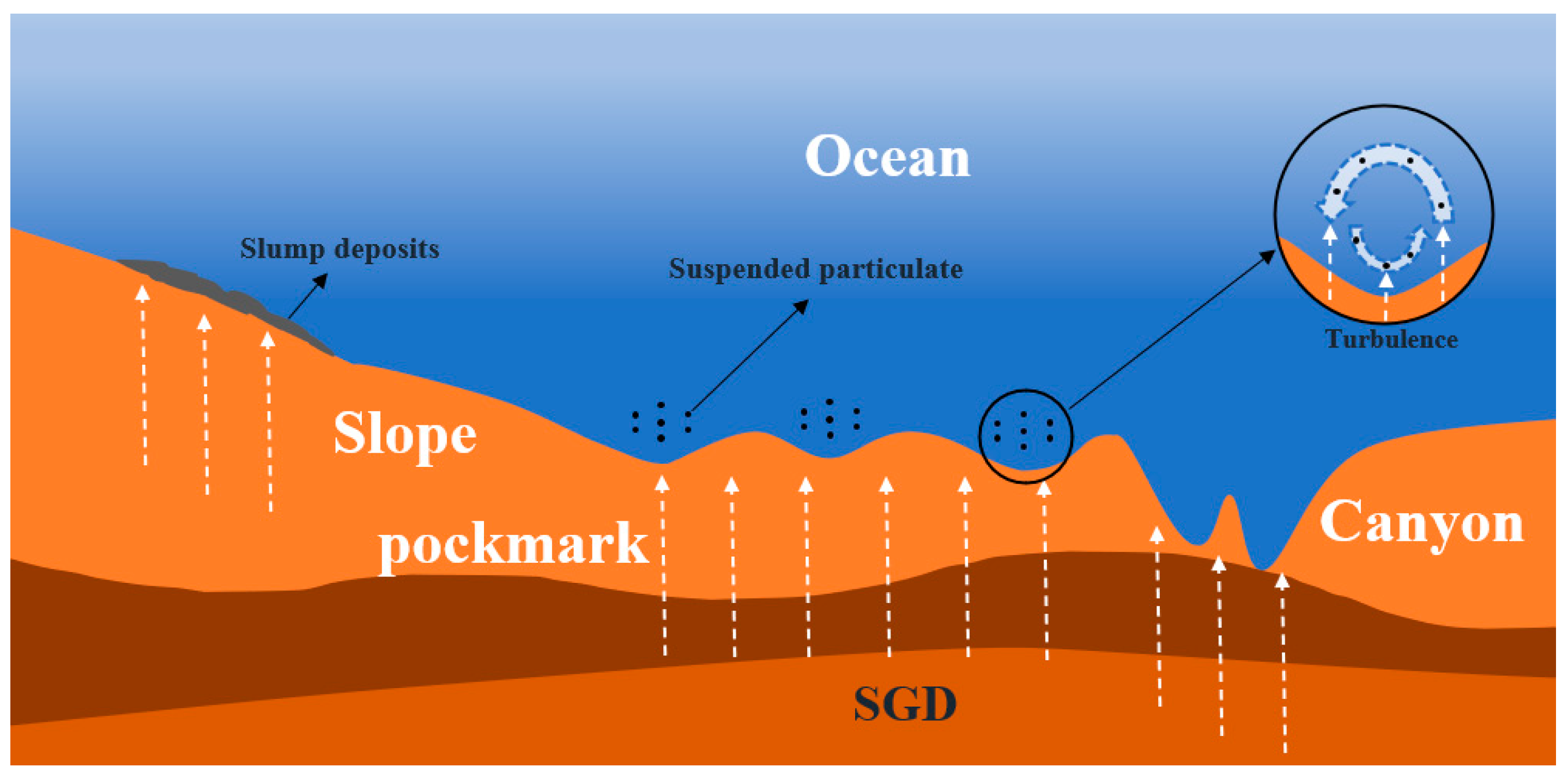
5. The Impact of SGD on the Stability of the Seabed
5.1. SGD-Induced Slope Instability and Failure
5.2. SGD Leads to the Formation of Pockmarks
5.3. SGD Triggers Seabed Erosion and Resuspension
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moore, W.S. The Effect of Submarine Groundwater Discharge on the Ocean. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2010, 2, 59–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.L.; Wang, X.J. Submarine groundwater discharge: A review. Adv. Earth Sci. 2015, 30, 636–646. [Google Scholar]
- Зекцер, И.С.; Liu, J.C. Marine hydrogeological problems. World Sci. 1986, 10, 36. [Google Scholar]
- Burnett, W.C.; Bokuniewicz, H.; Huettel, M.; Moore, W.S.; Taniguchi, M. Groundwater and Pore Water Inputs to the Coastal Zone. Biogeochemistry 2003, 66, 3–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harishidayat, D.; Al-Shuhail, A.; Randazzo, G.; Lanza, S.; Muzirafuti, A. Reconstruction of Land and Marine Features by Seismic and Surface Geomorphology Techniques. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Ye, Q.; Zhang, Y. Analysis of Characteristics and Main Controlling Factors of Shallow Geological Hazards in the Zhongsha Islands Region of the South China Sea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, E.Y.; Kim, G.; Primeau, F.; Moore, W.S.; Cho, H.; DeVries, T.; Sarmiento, J.L.; Charette, M.A.; Cho, Y. Global Estimate of Submarine Groundwater Discharge Based on an Observationally Constrained Radium Isotope Model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 8438–8444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tait, D.R.; Sippo, J.Z.; Jeffrey, L.C.; Maher, D.T.; Mukherjee, A.; Ralph, C.; Das, K. Groundwater Discharge and Bank Overtopping Drive Large Carbon Exports from Indian Sundarban Mangroves. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 955, 176463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, A.; Moore, W.S.; Pierce, T.; Shiller, A.M. The Effects of Submarine Groundwater Discharge and the Bonnet Carré Spillway on Nutrient Dynamics in the Western Mississippi Sound. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 953, 176080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Xiao, K.; Luo, M.; Li, H. Submarine Groundwater Discharge and Associated Metal Elements into an Urbanized Bay. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 192, 115092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, E.J.; Julian, M. The 1979 Var Delta Landslide on the French Riviera: A Retrospective Analysis. J. Coast. Res. 1997, 13, 27–35. [Google Scholar]
- Oehler, T.; Mogollón, J.M.; Moosdorf, N.; Winkler, A.; Kopf, A.; Pichler, T. Submarine Groundwater Discharge within a Landslide Scar at the French Mediterranean Coast. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 198, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, J.J.L.; Mountjoy, J.J.; Spain, E.; Gall, M.; Tait, L.W.; Ladroit, Y.; Micallef, A. Fresh Submarine Groundwater Discharge Offshore Wellington (New Zealand): Hydroacoustic Characteristics and Its Influence on Seafloor Geomorphology. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1204182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillman, J.I.T.; Gorman, A.R.; Pecher, I.A. Geostatistical Analysis of Seafloor Depressions on the Southeast Margin of New Zealand’s South Island—Investigating the Impact of Dynamic near Seafloor Processes on Geomorphology. Mar. Geol. 2015, 360, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micallef, A.; Averes, T.; Hoffmann, J.; Crutchley, G.; Mountjoy, J.J.; Person, M.; Cohen, D.; Woelz, S.; Bury, S.J.; Ahaneku, C.V.; et al. Multiple Drivers and Controls of Pockmark Formation across the Canterbury Margin, New Zealand. Basin Res. 2022, 34, 1374–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachelhaus, S.L.; Moran, S.B.; Kelly, R.P. An Evaluation of the Efficacy of Radium Isotopes as Tracers of Submarine Groundwater Discharge to Southern Rhode Island’s Coastal Ponds. Mar. Chem. 2012, 130–131, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Zhang, G.; Dong, D.; Zhao, M.; Wang, X. Widespread Fluid Seepage Related to Buried Submarine Landslide Deposits in the Northwestern South China Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2021GL096584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Li, Z.; Nai, H.; Liu, H.; Shan, H.; Jia, Y. Seabed Dynamic Responses Induced by Nonlinear Internal Waves: New Insights and Future Directions. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Li, Q.; Li, Z.; Duan, M.; Li, S.; Zhou, Q.; Geng, M.; Chen, J.; Jia, Y. Seabed Fluid Flow in the China Seas. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1158685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, W.S. Large Groundwater Inputs to Coastal Waters Revealed by 226Ra Enrichments. Nature 1996, 380, 612–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrison, G.H.; Glenn, C.R.; McMurtry, G.M. Measurement of Submarine Groundwater Discharge in Kahana Bay, O’ahu, Hawai’i. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2003, 48, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, T.J.; Moore, W.S.; Kloepfer, J.; Sochaski, M.A. The Flux of Barium to the Coastal Waters of the Southeastern USA: The Importance of Submarine Groundwater Discharge. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1998, 62, 3047–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, I.R.; Burnett, W.C.; Dittmar, T.; Suryaputra, I.G.N.A.; Chanton, J. Tidal Pumping Drives Nutrient and Dissolved Organic Matter Dynamics in a Gulf of Mexico Subterranean Estuary. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 1325–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwashote, B.M.; Murray, M.; Burnett, W.C.; Chanton, J.; Kruse, S.; Forde, A. Submarine Groundwater Discharge in the Sarasota Bay System: Its Assessment and Implications for the Nearshore Coastal Environment. Cont. Shelf Res. 2013, 53, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Kim, J.-S.; Hwang, D.-W. Submarine Groundwater Discharge from Oceanic Islands Standing in Oligotrophic Oceans: Implications for Global Biological Production and Organic Carbon Fluxes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2011, 56, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulaiova, H.; Gonneea, M.E.; Henderson, P.B.; Charette, M.A. Geochemical and Physical Sources of Radon Variation in a Subterranean Estuary—Implications for Groundwater Radon Activities in Submarine Groundwater Discharge Studies. Mar. Chem. 2008, 110, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodellas, V.; Garcia-Orellana, J.; Tovar-Sánchez, A.; Basterretxea, G.; López-Garcia, J.M.; Sánchez-Quiles, D.; Garcia-Solsona, E.; Masqué, P. Submarine Groundwater Discharge as a Source of Nutrients and Trace Metals in a Mediterranean Bay (Palma Beach, Balearic Islands). Mar. Chem. 2014, 160, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudron, P.; Cockenpot, S.; Lopez-Castejon, F.; Radakovitch, O.; Gilabert, J.; Mayer, A.; Garcia-Arostegui, J.L.; Martinez-Vicente, D.; Leduc, C.; Claude, C. Combining Radon, Short-Lived Radium Isotopes and Hydrodynamic Modeling to Assess Submarine Groundwater Discharge from an Anthropized Semiarid Watershed to a Mediterranean Lagoon (Mar Menor, SE Spain). J. Hydrol. 2015, 525, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trezzi, G.; Garcia-Orellana, J.; Rodellas, V.; Santos-Echeandia, J.; Tovar-Sánchez, A.; Garcia-Solsona, E.; Masqué, P. Submarine Groundwater Discharge: A Significant Source of Dissolved Trace Metals to the North Western Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Chem. 2016, 186, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodellas, V.; Garcia-Orellana, J.; Trezzi, G.; Masqué, P.; Stieglitz, T.C.; Bokuniewicz, H.; Cochran, J.K.; Berdalet, E. Using the Radium Quartet to Quantify Submarine Groundwater Discharge and Porewater Exchange. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2017, 196, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamborski, J.; Bejannin, S.; Garcia-Orellana, J.; Souhaut, M.; Charbonnier, C.; Anschutz, P.; Pujo-Pay, M.; Conan, P.; Crispi, O.; Monnin, C.; et al. A Comparison between Water Circulation and Terrestrially-Driven Dissolved Silica Fluxes to the Mediterranean Sea Traced Using Radium Isotopes. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2018, 238, 496–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Ryu, J.-W.; Yang, H.-S.; Yun, S.-T. Submarine Groundwater Discharge (SGD) into the Yellow Sea Revealed by 228Ra and 226Ra Isotopes: Implications for Global Silicate Fluxes. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2005, 237, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Mandal, A.K. Linkages between Submarine Groundwater Systems and the Environment. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2012, 4, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, W.S.; Sarmiento, J.L.; Key, R.M. Submarine Groundwater Discharge Revealed by 228Ra Distribution in the Upper Atlantic Ocean. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 309–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, H.A.; Charette, M.A.; Harvey, C.F. Patterns and Variability of Groundwater Flow and Radium Activity at the Coast: A Case Study from Waquoit Bay, Massachusetts. Mar. Chem. 2011, 127, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, M.; Burnett, W.C.; Smith, C.F.; Paulsen, R.J.; O’Rourke, D.; Krupa, S.L.; Christoff, J.L. Spatial and Temporal Distributions of Submarine Groundwater Discharge Rates Obtained from Various Types of Seepage Meters at a Site in the Northeastern Gulf of Mexico. Biogeochemistry 2003, 66, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.J.; Rapaglia, J.P.; Cochran, J.K.; Bokuniewicz, H.J.; Yang, S. Submarine Groundwater Discharge to Great South Bay, NY, Estimated Using Ra Isotopes. Mar. Chem. 2008, 109, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganju, N.K. A Novel Approach for Direct Estimation of Fresh Groundwater Discharge to an Estuary: Estimation of Groundwater Discharge. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L11402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Orellana, J.; Cochran, J.K.; Bokuniewicz, H.; Daniel, J.W.R.; Rodellas, V.; Heilbrun, C. Evaluation of 224Ra as a Tracer for Submarine Groundwater Discharge in Long Island Sound (NY). Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2014, 141, 314–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, A.C.; Watanabe, A.; Nadaoka, K.; Motooka, S.; Herrera, E.C.; Yamamoto, T. Estimation of Nearshore Groundwater Discharge and Its Potential Effects on a Fringing Coral Reef. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 770–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xue, Y.; Zou, C.; Luo, M.; Li, G.; Li, L.; Cui, L.; Li, H. Advances in the Study of Submarine Groundwater Discharge (SGD) in China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2022, 65, 1948–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Wan, L.; Wang, X.; Jiang, X. Estimation of Seawater–Groundwater Exchange Rate: Case Study in a Tidal Flat with a Large-Scale Seepage Face (Laizhou Bay, China). Hydrogeol. J. 2015, 23, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, H.; Jiao, J.J.; Barry, D.A.; Li, L.; Luo, X.; Wang, C.; Wan, L.; Wang, X.; Jiang, X.; et al. Submarine Fresh Groundwater Discharge into Laizhou Bay Comparable to the Yellow River Flux. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.R.; Ma, Z.Y.; Zhang, B.; Yuan, X.J.; Liu, H.T.; Liu, J. Tracing Submarine Groundwater Discharge and Associated Nutrient Fluxes into Jiaozhou Bay by Continuous 222Rn Measurements. Earth Sci. J. China Univ. Geosci. 2013, 38, 1073–1080+1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, M.; Ishitobi, T.; Chen, J.; Onodera, S.; Miyaoka, K.; Burnett, W.C.; Peterson, R.; Liu, G.; Fukushima, Y. Submarine Groundwater Discharge from the Yellow River Delta to the Bohai Sea, China. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2008, 113, 2007JC004498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, R.N.; Burnett, W.C.; Taniguchi, M.; Chen, J.; Santos, I.R.; Ishitobi, T. Radon and Radium Isotope Assessment of Submarine Groundwater Discharge in the Yellow River Delta, China. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2008, 113, 2008JC004776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Burnett, W.; Dimova, N.; Diao, S.; Mi, T.; Jiang, X.; Yu, Z. Hydrodynamics in the Yellow River Estuary via Radium Isotopes: Ecological Perspectives. Cont. Shelf Res. 2013, 66, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Xia, D.; Burnett, W.C.; Dimova, N.T.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Gao, M.; Jiang, X.; Yu, Z. Natural 222Rn and 220Rn Indicate the Impact of the Water–Sediment Regulation Scheme (WSRS) on Submarine Groundwater Discharge in the Yellow River Estuary, China. Appl. Geochem. 2014, 51, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.R.; Huang, L.; Yuan, X.J.; Liu, H.T.; Li, K.P. Estimating submarine groundwater discharge to the Jiulong River estuary using Ra isotopes. Adv. Water Sci. 2011, 22, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Moore, W.S.; Zhang, L.; Du, J.; Zhang, J. Using Radium Isotopes to Estimate the Residence Time and the Contribution of Submarine Groundwater Discharge (SGD) in the Changjiang Effluent Plume, East China Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2012, 35, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Du, J.; Yi, L. Ra Tracer-Based Study of Submarine Groundwater Discharge and Associated Nutrient Fluxes into the Bohai Sea, China: A Highly Human-Affected Marginal Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2017, 122, 8646–8660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Jiao, J.J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liang, W.; Tang, D. Evaluation of Water Residence Time, Submarine Groundwater Discharge, and Maximum New Production Supported by Groundwater Borne Nutrients in a Coastal Upwelling Shelf System. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2018, 123, 631–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Xiao, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Kuang, X.; Li, H. Quantification of the Water Age and Submarine Groundwater Discharge in a Typical Semi-Enclosed Bay Using Stable Oxygen (18O) and Radioactive Radium (228Ra) Isotopes. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 127088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Jing, W. Significance of Submarine Groundwater Discharge in Nutrient Budgets in Tropical Sanya Bay, China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Han, A.; Chen, L.; Tan, E.; Lin, H. Fluxes of Dissolved Organic Carbon and Nutrients via Submarine Groundwater Discharge into Subtropical Sansha Bay, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 207, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Xiao, K.; Qu, W. Evaluations of Submarine Groundwater Discharge and Associated Heavy Metal Fluxes in Bohai Bay, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 695, 133873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y. Using 222Rn to Estimate Submarine Groundwater Discharge (SGD) and the Associated Nutrient Fluxes into Xiangshan Bay, East China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 73, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Wang, Z.; Zhai, W.; Moore, W.S.; Li, Q.; Yan, X.; Qi, D.; Jiang, Y. Net Subterranean Estuarine Export Fluxes of Dissolved Inorganic C, N, P, Si, and Total Alkalinity into the Jiulong River Estuary, China. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2015, 149, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Du, J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, S. Nutrient Input through Submarine Groundwater Discharge in Two Major Chinese Estuaries: The Pearl River Estuary and the Changjiang River Estuary. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 203, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Jia, Y.; Zhu, C.; Lu, L.; Guo, X.; Feng, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; He, M.; Peng, J. Research Progress and Prospects of Geohazard Mechanism and Risk Prevention Related to Seabed Fluid Migration. Chin. J. Eng. Sci. 2023, 25, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, H. Literature Review as a Research Methodology: An Overview and Guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 2019, 104, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, I.R.; Erler, D.; Tait, D.; Eyre, B.D. Breathing of a Coral Cay: Tracing Tidally Driven Seawater Recirculation in Permeable Coral Reef Sediments. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2010, 115, 2010JC006510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, P.; Wang, S.S.J.; Robinson, C.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.-G.; Barry, D.A. Memory of Past Random Wave Conditions in Submarine Groundwater Discharge. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 2401–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, C.; Xin, P.; Li, L.; Barry, D.A. Groundwater Flow and Salt Transport in a Subterranean Estuary Driven by Intensified Wave Conditions: Wave-Driven Flow and Transport in a Subterranean Estuary. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 165–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, A.D.; Bakker, M.; Post, V.E.A.; Vandenbohede, A.; Lu, C.; Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Simmons, C.T.; Barry, D.A. Seawater Intrusion Processes, Investigation and Management: Recent Advances and Future Challenges. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 51, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, N.; Garziglia, S.; Bompais, X.; Woerther, P.; Witt, C.; Kopf, A.; Migeon, S. Transient Groundwater Flow Through a Coastal Confined Aquifer and Its Impact on Nearshore Submarine Slope Instability. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2020, 125, e2020JF005654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holz Boffo, C.; Bayer Da Silva, D.; Manica, R.; De Oliveira Borges, A.L.; Roessler Viana, A. Submarine Slope Destabilization and Gully Formation by Water Sapping: Physical Simulation of an Underestimated Trigger of Subaqueous Sediment Gravity Flows. Sedimentology 2022, 69, 1599–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadatkhah, N.; Kassim, A.; Siat, Q.A.; Micallef, A. Salt Leaching by Freshwater and Its Impact on Seafloor Stability: An Experimental Investigation. Mar. Geol. 2023, 455, 106959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micallef, A.; Person, M.; Gupta, S.; Saadatkhah, N.; Camille, A.; Gratacós, Ò. Can Offshore Meteoric Groundwater Generate Mechanical Instabilities in Passive Continental Margins? J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2023, 128, e2022JF006954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalai, C.; Dhar, A. Impact of Beach Face Slope Variation on Saltwater Intrusion Dynamics in Unconfined Aquifer under Tidal Boundary Condition. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2023, 89, 102298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegmann, S.; Sultan, N.; Kopf, A.; Apprioual, R.; Pelleau, P. Hydrogeology and Its Effect on Slope Stability along the Coastal Aquifer of Nice, France. Mar. Geol. 2011, 280, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.A.; Larsson, O.; Engdahl, M. Early Holocene Coastal Landslides Linked to Land Uplift in Western Sweden. Geogr. Ann. Ser. Phys. Geogr. 2017, 99, 288–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paull, C.K.; Dallimore, S.R.; Caress, D.W.; Gwiazda, R.; Lundsten, E.; Anderson, K.; Melling, H.; Jin, Y.K.; Duchesne, M.J.; Kang, S.-G.; et al. A 100-Km Wide Slump along the Upper Slope of the Canadian Arctic Was Likely Preconditioned for Failure by Brackish Pore Water Flushing. Mar. Geol. 2021, 435, 106453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Q.; Qian, Q.; Wang, G.; Fu, X.; Su, D. Analytical Solution for Slope Instability Assessment Considering Impact of Confined Aquifer. J. Cent. S. Univ. 2015, 22, 1502–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelascini, L.; Steer, P.; Mouyen, M.; Longuevergne, L. Finite-Hillslope Analysis of Landslides Triggered by Excess Pore Water Pressure: The Roles of Atmospheric Pressure and Rainfall Infiltration during Typhoons. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 22, 3125–3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boffo, C.H.; De Oliveira, T.A.; Da Silva, D.B.; Manica, R.; Borges, A.L.D.O. Continental-Slope Instability Triggered by Seepage: An Experimental Approach. J. Sediment. Res. 2020, 90, 921–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Guo, X.; Qiao, L.; Yu, L.; Xu, G.; Liu, T. Formation Mechanism of Large Pockmarks in the Subaqueous Yellow River Delta. Mar. Georesources Geotechnol. 2019, 37, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virtasalo, J.J.; Schröder, J.F.; Luoma, S.; Majaniemi, J.; Mursu, J.; Scholten, J. Submarine Groundwater Discharge Site in the First Salpausselkä Ice-Marginal Formation, South Finland. Solid Earth 2019, 10, 405–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loher, M.; Reusch, A.; Strasser, M. Long-term Pockmark Maintenance by Fluid Seepage and Subsurface Sediment Mobilization—Sedimentological Investigations in Lake Neuchâtel. Sedimentology 2016, 63, 1168–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idczak, J.; Brodecka-Goluch, A.; Łukawska-Matuszewska, K.; Graca, B.; Gorska, N.; Klusek, Z.; Pezacki, P.D.; Bolałek, J. A Geophysical, Geochemical and Microbiological Study of a Newly Discovered Pockmark with Active Gas Seepage and Submarine Groundwater Discharge (MET1-BH, Central Gulf of Gdańsk, Southern Baltic Sea). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 742, 140306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goff, J.A. Modern and Fossil Pockmarks in the New England Mud Patch: Implications for Submarine Groundwater Discharge on the Middle Shelf. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 12213–12220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buongiorno Nardelli, B.; Budillon, F.; Watteaux, R.; Ciccone, F.; Conforti, A.; De Falco, G.; Di Martino, G.; Innangi, S.; Tonielli, R.; Iudicone, D. Pockmark Morphology and Turbulent Buoyant Plumes at a Submarine Spring. Cont. Shelf Res. 2017, 148, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maa, P.-Y.; Mehta, A.J. Mud Erosion by Waves: A Laboratory Study. Cont. Shelf Res. 1987, 7, 1269–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, C.; Minier, J.-P. Progress in Particle Resuspension from Rough Surfaces by Turbulent Flows. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2014, 45, 1–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, J.; Liu, X.; Jeng, D.-S.; Shan, H. Effects of Wave-Induced Seabed Liquefaction on Sediment Re-Suspension in the Yellow River Delta. Ocean Eng. 2014, 89, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Jia, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wen, M.; Lu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Shan, H. Wave Flume Experiments on the Contribution of Seabed Fluidization to Sediment Resuspension. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2018, 37, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Jia, Y.; Lu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Peng, Z. Effects of Upward Seepage on the Resuspension of Consolidated Silty Sediments in the Yellow River Delta. J. Coast. Res. 2019, 36, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Arsdale, R.; Cox, R.; Lumsden, D.; Kwon, Y. The Past, Present, and Future Mississippi River. J. Geol. 2023, 131, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, P.; Shim, M.J.; Howden, S.D.; Shiller, A.M. Temporal and Spatial Distributions of Nutrients and Trace Elements (Ba, Cs, Cr, Fe, Mn, Mo, U, V and Re) in Mississippi Coastal Waters: Influence of Hypoxia, Submarine Groundwater Discharge, and Episodic Events. Cont. Shelf Res. 2019, 175, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, D.; Paul, J.; Cox, R. Geochemical and Isotopic Evidence for Upward Flow of Saline Fluid to the Mississippi River Valley Alluvial Aquifer, Southeastern Arkansas, USA. Hydrogeol. J. 2021, 29, 1421–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, M.R.; Binda, G.; Archer, C.; Pozzi, A.; Michetti, A.M.; Noble, P.J. Mechanisms of Earthquake-Induced Chemical and Fluid Transport to Carbonate Groundwater Springs After Earthquakes. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 5225–5244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Tsai, F.T.-C.; Yuill, B.T.; Wu, C. A Three-Dimensional Stratigraphic Model of the Mississippi River Delta, USA: Implications for River Deltaic Hydrogeology. Hydrogeol. J. 2020, 28, 2341–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Tsai, F.T.-C. Understanding Dynamics of Groundwater Flows in the Mississippi River Delta. J. Hydrol. 2020, 583, 124616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolker, A.S.; Cable, J.E.; Johannesson, K.H.; Allison, M.A.; Inniss, L.V. Pathways and Processes Associated with the Transport of Groundwater in Deltaic Systems. J. Hydrol. 2013, 498, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlain, E.L.; Törnqvist, T.E.; Shen, Z.; Mauz, B.; Wallinga, J. Anatomy of Mississippi Delta Growth and Its Implications for Coastal Restoration. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaar4740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locci-Lopez, D.; Lorenzo, J.M. Seepage-Induced Pore Pressure Variations Beneath an Earthen Levee Measured with a Novel Seismic Tool. Geosciences 2023, 13, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, C.R.; Georgiou, I.Y.; Kolker, A.S. Hydrodynamic and Geomorphic Controls on Mouth Bar Evolution. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 1540–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yu, G.; La Rovere, A.; Ranzi, R. Erodibility of Fluidized Cohesive Sediments in Unidirectional Open Flows. Ocean Eng. 2017, 130, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, G.A.; Wilson, G.V.; Periketi, R.K.; Cullum, R.F. Sediment Transport Model for Seepage Erosion of Streambank Sediment. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2006, 11, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, G.A.; Wilson, G.V.; Simon, A.; Langendoen, E.J.; Akay, O.; Fuchs, J.W. Measuring Streambank Erosion Due to Ground Water Seepage: Correlation to Bank Pore Water Pressure, Precipitation and Stream Stage. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2007, 32, 1558–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solórzano-Rivas, S.C.; Werner, A.D.; Irvine, D.J. Mixed-Convective Processes Within Seafloor Sediments Arising From Fresh Groundwater Discharge. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 600955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, C.; Liu, H. Impacts of Consolidation Time on the Critical Hydraulic Gradient of Newly Deposited Silty Seabed in the Yellow River Delta. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
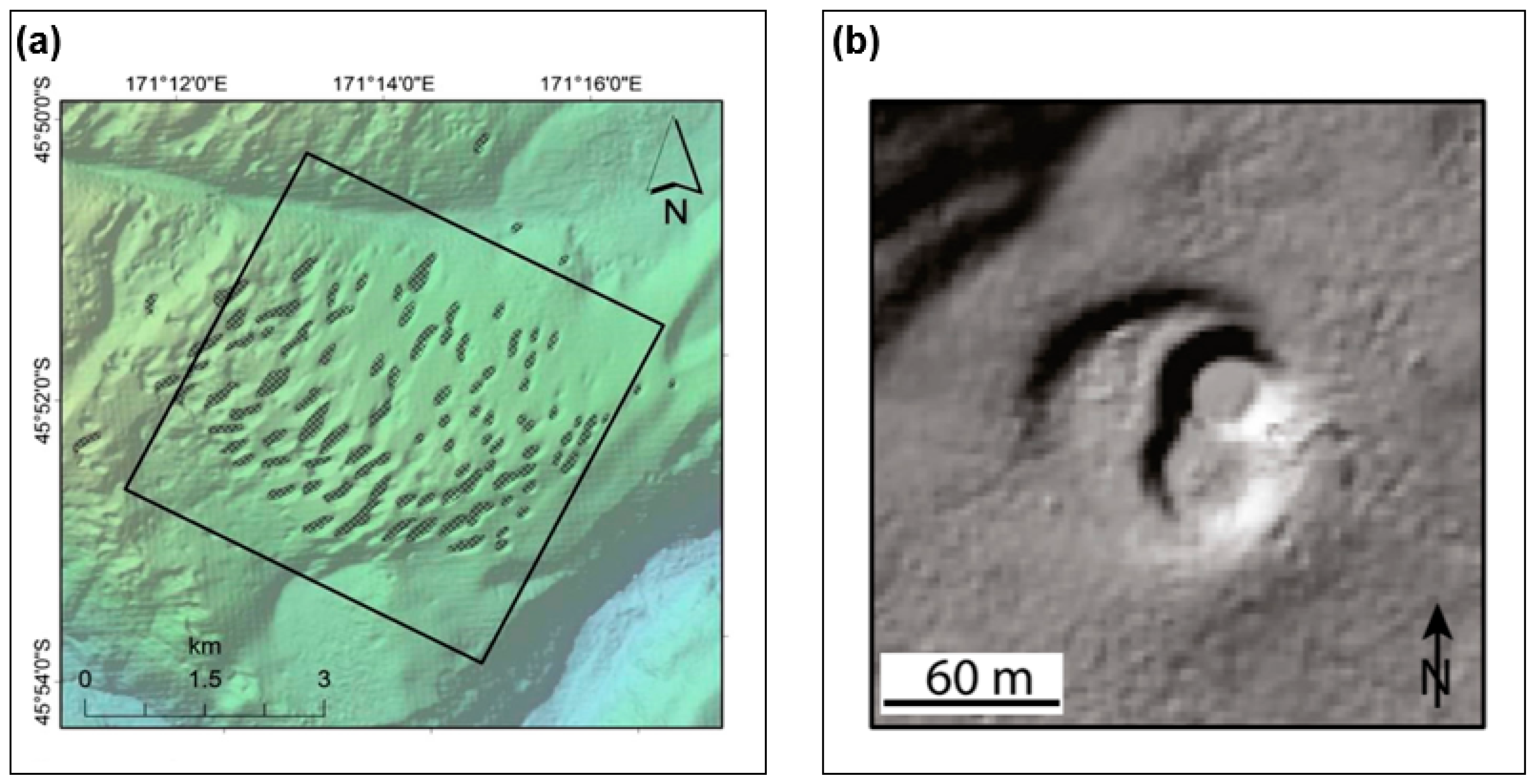


| Research Area | Scale | SGD Rate | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Atlantic | 9.867 × 107 km2 | (2–4) × 1013 m3/a | [34] |
| South Atlantic Bay | 3.84 × 104 km2 | 3 × 107 m3/d | [22] |
| Waquoit Bay | 3 km2 | 362–2550 m3/d | [35] |
| Northeast Gulf of Mexico | 2 × 104 m2 | 1.6–2.5 m3/min | [36] |
| Great South Bay | 235 km2 | 3.5–4.5 ×109 L/d | [37] |
| West Falmouth Bay | - | 0.85 m3/s | [38] |
| Long Island | 3162 km2 | (3.2–7.4) × 1013 L/a | [39] |
| Ishigaki Island | 10.82 km2 | 0.39–0.58 m3/s | [40] |
| Research Area | Scale (km2) | SGD Rate (cm d−1) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bohai Sea | 77,000 | 0.25–1.17 | [51] |
| HuangHai Sea | 333,333 | 0.08–0.47 | [32] |
| Eastern Hainan Shelf | 90,000 | 0.9–1.6 | [52] |
| Jiaozhou Bay | 367 | 6.38–8.29 | [44] |
| Laizhou Bay | 6870 | 2.2–4.7 | [53] |
| Sanya Bay | 6.5 | 4.3 ± 2.1–7.8 ± 4.1 | [54] |
| Sansha Bay | 244 | 2.00 | [55] |
| Bohai Bay | 16,000 | 2.0–4.8 | [56] |
| Xiangshan Bay | 6.28 | 0.23–0.69 | [57] |
| Jiulong River Estuary | 71.1 | 9.70–20.3 | [58] |
| Pearl River Estuary | 2000 | 6–14 | [59] |
| Yangtze River Estuary | 25,000 | 0.85–4 | [59] |
| Yellow River Estuary | 1800 | 15.6–166.7 | [48] |
| Method | Feature | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Geophysical exploration | Direct study through geophysical detection evidence | [13,66] |
| Simulation experiment | Control variable simulation of reduced-scale seepage observation phenomenon | [67,68] |
| Numerical model | Calculate the critical value of submarine sediment instability using boundary conditions | [69,70] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, Z.; Shan, H.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, L.; Wang, S.; Jia, Y.; Quan, Y. Review of Research Progress on the Influence of Groundwater Discharge on Seabed Stability. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13030560
Jia Z, Shan H, Liu H, Zhang Z, Jiang L, Wang S, Jia Y, Quan Y. Review of Research Progress on the Influence of Groundwater Discharge on Seabed Stability. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(3):560. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13030560
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Zhentian, Hongxian Shan, Hanlu Liu, Zhengrong Zhang, Long Jiang, Siming Wang, Yonggang Jia, and Yongzheng Quan. 2025. "Review of Research Progress on the Influence of Groundwater Discharge on Seabed Stability" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 3: 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13030560
APA StyleJia, Z., Shan, H., Liu, H., Zhang, Z., Jiang, L., Wang, S., Jia, Y., & Quan, Y. (2025). Review of Research Progress on the Influence of Groundwater Discharge on Seabed Stability. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(3), 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13030560







